Ch. 8: Labour Market Decisions of Households: The Supply of Labour
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Human Capital
Human resources considered in terms of their contrubtions to the economy
: Skills, education, etc
Supply of labour
Factors of Production: Land, capital and entrepreneurship
Opportunity Cost
Can do two things with time: Work for pay or enjoy leisure
What you give up to get the next best alt.
Trade off
Leisure Activities
Non-market work like househod chores
Consumpton time like enjoying purchases of food, entertainment made in the marketplace
Idleness: Rest and relaxation
Substitution Effect (Labour)
Leisure and work hours are subbed for each other as the wage rate changes, people work more
Positive effect on the supply
Income Effect (Supply)
The change in hours caused by changes in income
Negative effect on supply
Factors that Influence the Decision to Work
Age: Lifecycle issues
Reservation wage rate
Retirement
Fertility and family size
Investment in education
Non-employment income: Access to money other than work
Types of Non-employment Income
Inheritance
Demogrant: Lump sum payment based on membership in a particular demographic group
Welfare benefits
Employment insurance
Subsidized daycare
Labour Supply Curve
Graph showing the number of hours of work offered in relation to the wage rate
Typically not willing to work as many hours due to low wage
Wages increase= opportunity cost increases
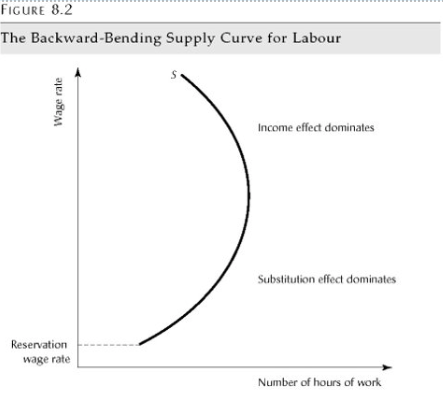
The Backward-Bending Supply Curve for Labour
May choose to purchase more labour
Slope becomes negative
Sub. effect dominates at low wage rates
Income effect dominates at high wages
Price of Leisure
Wage rate per hour for the hour not worked
Opportunity cost
Wage Rate Elasticity of Labour Supply
= Percentage change in Quanitity of Labour supplied / Percentage change in Wage Rate
Market Supply Curve for Labour
Sum the individual supply curves for labour in a given occupation
Generally the supply curve is upwards sloping
Can be a movement along a supply curve as well as shifts of the curve
Changes in Supply
An increase in the supply of labour can occur because
More people trained in that job
Lessening barriers to the occupation (no licensing)
Increased immigration with the same skills
Changes in the Qunaitity Supplied of Labour
Movement along the curve means quantity supplied
Wages are on vertical axis
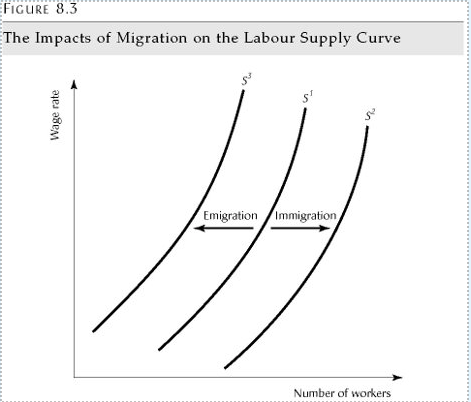
Immigration and Emigration
Immigration increase the supply of labour in the occupation
Emigration decreases
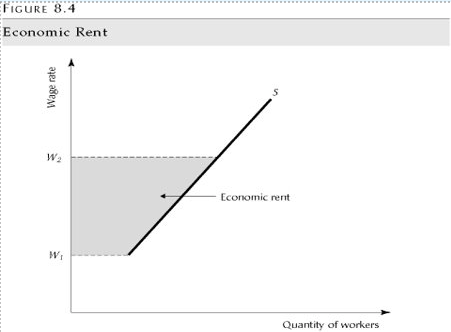
Economic Rent
Wage rate received in excess of the reseveration wage rate
Migration
Decision to migrate depends on many factors
Higher salaries
Lower tax rates
Exposure to leading edge technologies
Opportunities for personal growth
Family issues
Climate
Normal Good
Product or service for which demand increases as consumer income rises and decreases as income falls
Reservation wage rate
Lowest wage individual is willing to work for