HAN 456 Midterm
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
theory
set of interrelated concepts, definitions, and propositions that explains or predicts events or situations by specifying relations among variables
true
(T/F) Theories are made up of concepts (the bricks), constructs (the theories), and variables
concepts
the idea that have been developed or adapted for use in a theory
constructs
(building blocks) major components of a theory
variables
(operational tools) refers to the measurable factors, or attributes of an individual or system
target population
the intended recipient of services: individuals, families, social networks, etc.
health promoting behavior
the prescribed health __ behaviors which we want client or target population to begin/continue to engage in
health compromising behavior
the health compromising behavior that which we want client/patient or target population to stop engaging in
health behavior theory (HBT)
theory about health behavior, adapted from social and behavioral science drawing upon psychology, sociology, anthropology, consumer behavior and marketing
HBT’s goal
___: to maintain and improve health, reduce disease risk, manage chronic illness
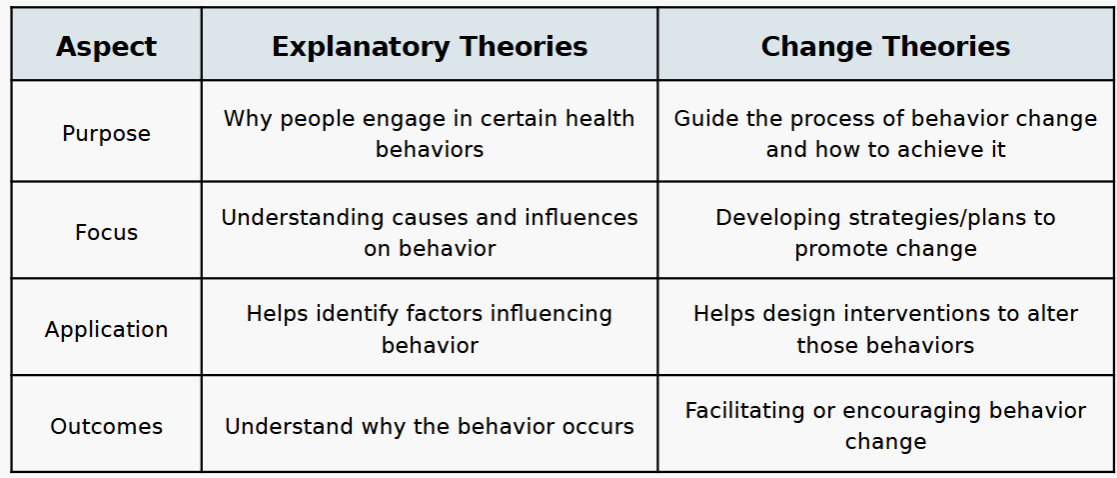
explanatory theory
describes the reasons why a problem exists. considers factors that contribute to a problem—which can be changed
- health belief model, theory of planned behavior, PAPM
change theory
guides the development of health interventions, Helps design interventions/program messages to alter behaviors, guides what you do about the problem and how a program should work
explanatory vs change
preventative health behaviors
any activity undertaken by individuals who believe themselves to be healthy for the purpose of preventing or detecting illness in an asymptomatic state
illness behavior
any activity undertaken by individuals who perceives himself to be ill, to define the state of health, and to discover a suitable remedy
sick role behavior
__ behavior occurs when ppl have consulted a healthcare professional, received a diagnosis, and begun a course of treatment
- leads to some degree of exemption from usual tasks
primary
actions to prevent contracting an illness or disease
- vaccination, masks
secondary
actions to detect and treat illness or disease early
- screenings, physicals
tertiary
actions to reduce impact of illness or disease
- medications, cessation of poor habits
SDOH
includes socioeconomic status, culture, geographic location, access to healthcare, education
socio-ecologic model (SEM)
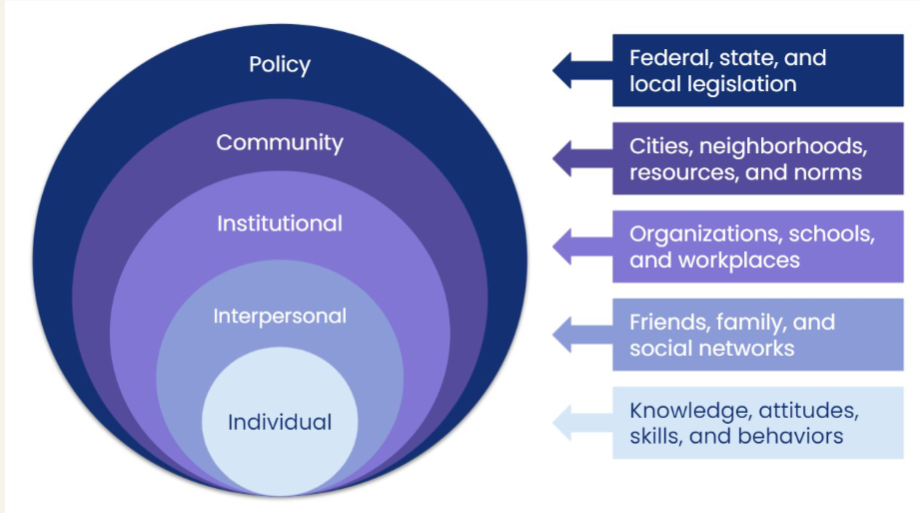
intrapersonal
focus is on individual characteristics that influence behavior.
- knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, motivation, perceptions, personal physical characteristics (gender, age, height)
interpersonal
assumes individuals exist within, and are influenced by a social environment
- opinions/thoughts/advice of surrounding ppl (family, coworkers, friends) influences the one.
institutional/organizational
provides direct services for ppl. sets standards for member. may collaborate w other organizations. (worksite, places of worship, schools)
community
made up of social networks and norms.
- can be defined by neighborhood, ethnicity, etc.
societal lvl/policy
local state, federal policies, and laws that regulate or support health actions and practices.
- how does sbu internalize and enforce the “no smoking on campus” rule
physical environment
man-made or natural environment. is a medium for transmitting disease. cause for stress, safety/danger.
culture
a shared system of learned norms, beliefs, values, and behaviors that differ across populations defined by region, nationality, or religion
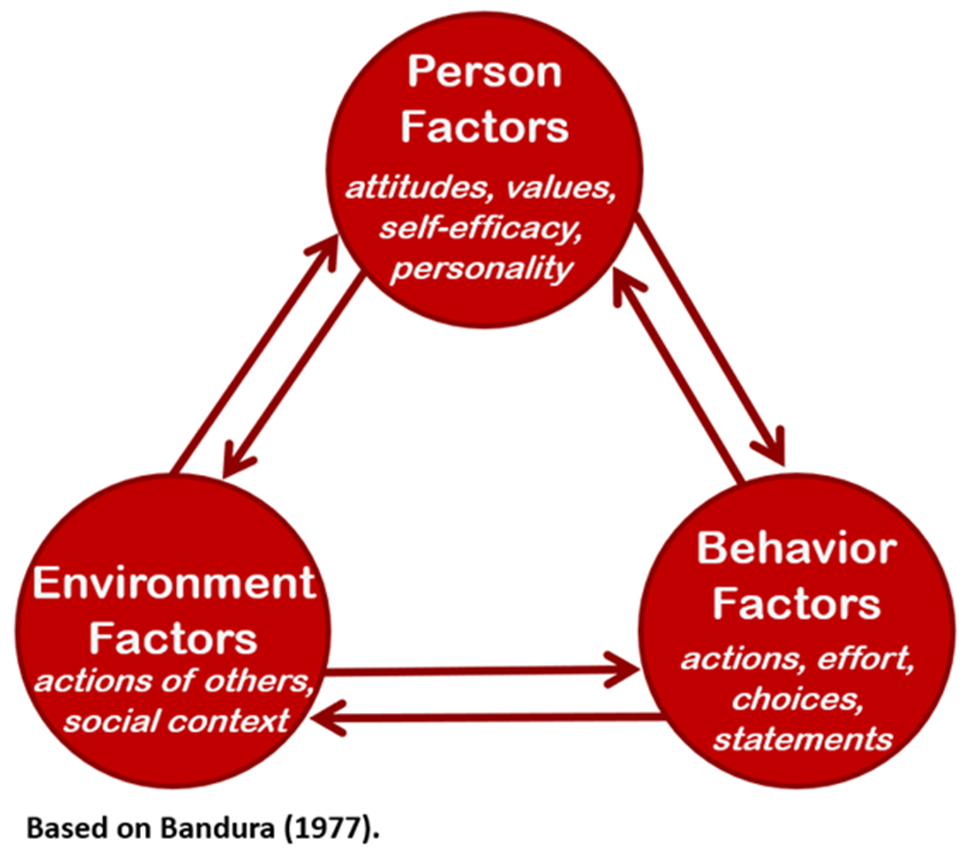
reciprocal causation
the notion that an individual’s behavior is influenced by the environment +
the notion that the environment is influenced by individual behavior.
value expectancy
HBM is a ___ model.
- the pt will take action if they feel it is effective/necessary
HBM
this model focuses on the individual (intrapersonal) and attempts to explain and predict behaviors
perceived susceptibility
ones subjective perception of the risk of contracting a health condition
- “it can/can’t happen to me”
perceived severity
feelings concerning the seriousness of a condition or of leaving it untreated
perceived benefits
the beliefs regarding the effectiveness of the various actions for reducing the disease threat and/or its efficacy
perceived barriers
the potential negative aspects of a particular health action. ones opinion of the tangible and psychological costs of the advised action
cues to action
strategies to activate “readiness”—bodily events or environmental events
self-efficacy
confidence in one’s ability to take action
pre-comtemplative
(TTM) the person has no intention of changing behavior, pt may be unaware of consequences of their behavior
- “i dont have a problem”
contemplative
(TTM) pt acknowledges need for change, may or may not have a plan, not ready to change but understands the consequences
- “maybe someday -or- im not ready to change”
preparation
(TTM) getting ready to take action soon, may have developed a plan, pt may have even attempted change
- “i started looking into __” OR “im looking for information/resources”
action
(TTM) pt has put plan into action. concrete steps toward change have occurred. change has occurred in less than 6 months and not yet consistent.
maintenance
(TTM) behavior is incorporated into daily life and has been consistent over a long period of time
- “i feel confidence managing triggers and preventing relapses”
relapse
(TTM) should be seen as an opportunity to learn from unsuccessful attempts to change behavior
termination
(TTM) behavior change is complete. characterized by 0 temptation and 100% self-efficacy
- ideal but not necessary and is rare
consciousness raising
becoming aware of the problem behavior
- “how change occurs”
environmental reevaluation
pt examines how the behavior impacts social/behavioral environments
- “how change occurs”
stimulus control
removal of cues/triggers of problem behavior
- “how change occurs”
counter conditioning
seeking substitutes for problem behavior
- “how change occurs”
reinforcement management
rewards for engaging in target behavior
relapse…
___ can occur at any of these stages: preparation, action, maintenance (PAPM)
PAPM
stage theory that identifies ppl who are unaware of risk or precaution OR ppl choosing not to engage in target behavior
true
(T/F) PAPM theory can be used for osteoporosis prevention, mammography, Hep B vaccination, colorectal cancer screening, or home testing 4 radon gas
1. unaware
an individual is completely unaware/never heard of a health hazard
- PAPM
2. unengaged
once ppl have heard about a hazard, they form opinions about it. consideration without personal engagement.
- PAPM
3. Deciding about action
the pt faces a decision about acting.
- PAPM
4. decided not to act
PAPM ends with this. pt has made a definitive decision not to act (for now).
- pt is more resistant to persuasion and may have confirmation bias
- PAPM
5. Decided to act
this stage represents the intention to act. pt may make a plan and the action may still fall bc of outside variables
- PAPM
6. action
pt actively engages in behavior change.
- contention w variables specific to early or one-time action
- PAPM
7. maintenance
continued behavior change! (not always applicable ex. screening)
- PAPM
do not
Once stages 1 and 2 are completed in PAPM, people __ __ return
stages of inaction
= stage 1.Unaware, 2.Unengaged, and 4.Decided not to act.
- these stages recognize the important differences among people who are not acting and not even thinking about acting
theory concept
Behavior is influenced by the intention to act or not act on a given health behavior
true
(T/F)
the theory of reasoned action (TRA) consists of 3 constructs, meanwhile the theory of planned behavior (TPB) consists of 2 TRA constructs and a new one
TRA/TPB
these theories are strictly for the purpose of predicting or explaining a behavior. Intention is the greatest prediction of behavior and behavior is equated with volitional control
- (an intrapersonal level theory.)
theory of reasoned action
(TRA) posits that Intention is the greatest predictor of behavior.
- Intention is mediated by Attitude, Subjective norm, Volition control
attitude
the degree to which a particular behavior is positively or negatively valued.
subjective norms
one’s perceived social pressure to engage in a behavior or not—normative beliefs and the motivation to comply
volitional control
behaviors that one can choose to engage in or not engage in (going to class, eating veggies/drinking water)
theory of planned behavior
(TPB) posits that Volitional control is replaced w behavioral control—attitude, subjective norms, and behavioral control
perceived behavioral control
one’s perception over the control they have to perform or not perform a behavior
- (personal beliefs, perceived power, skills/abilities, available time/resources)
social cognitive theory
theory assumes that ppl can learn by watching others, behavior eventually become self-regulated, and reinforcement/punishment have direct and indirect effect on behavior
reciprocal determinism
Environmental factors influence individuals and groups, but individuals and groups can also influence the environment and regular their own behavior
true
(T/F) social cognitive theory has 6 constructs categorized into Intrapersonal or cognitive factors, Environmental factors, and Behavioral factors
interpersonal/cognitive factors
(SCT Construct) contains self-efficacy and self-regulation (controlling our behaviors based on our personal standards, which is made possible through the development and maintenance of concrete skills)
environmental factor
(SCT Construct) contains Observational Learning, (learning to perform a behavior by exposure of displays of such behavior) Reinforcements, (system of rewards and punishments) and Observational Learning Complications (depends on attention, retention, production, and motivation— shaped by expectations, retention by intellect, and motivation by perceived costs and benefits.
behavioral factors
(SCT Construct) contains behavioral capability (knowledge and skill to perform a given behavior) and self-efficacy
moral disengagement
people rationalize unethical/harmful behaviors allowing them to act against their own standards
diffusion and displacement of responsibility
attributing decisions to the group as opposed to taking responsibility
dehumanization and attribution of blame
perception of inadequate difference and blaming the victim
euphemistic labeling
using milder language to describe harmful actions (harmless fling vs affair)
moral justification
reconstructing harmful actions as beneficial and necessary