anisci final
1/418
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
419 Terms
what are the 5 animal welfare freedoms?
freedom from hunger and thirst
freedom from discomfort
freedom from pain, injury, and disease
freedom to express most normal behaviors
freedom from fear and distress
(avian digestive system)
crop - proventriculus - gizzard - duodenum - small intestine - ceca - colon - cloaca
(ruminant digestive system)
esophagus - rumen - reticulum - omasum - abomasum - small intestine - cecum - colon - rectum
(hindgut fermenter digestive system)
esophagus - stomach - small intestine - cecum - large colon - small colon - rectum
functions of water:
temp regulation
joint lubrication
chemical reactions
waste excretion
functions of carbohydrates:
converted to fat
energy
heat
functions of protein:
lean tissue
enzymes
hormones
metabolites
excess for energy
functions of fats:
insulation
temp regulation
energy storage
functions of vitamins:
regulate body functions
growth
metabolism
functions of minerals:
enzymes
skeletal system
fluid balance
acid/base balance
oxygen and nerve function
protein synthesis
immune system
ranking of most important tissues:
1. Skeletal
2. Muscle
3. Fat
what can muscle fatigue be caused by
ATP depletion
conduction failure/ion imbalance
drop in pH
what is an endemic disease?
a disease constantly present in a population
What is habituation?
reduced response to repetitive stimuli
What is sensitization?
an increased behavioral response after exposure to stimuli
what is observational behavior?
behavior learned by observing others
what is associative behavior?
behavior responding to punishment/rewards
What is classical conditioning?
Learning by association
What is operant conditioning?
learning through consequences
what is animal welfare?
animals being treated humanely
what are animal rights?
animals having rights equal to humans
what strategies does PETA use
anthropomorphism, focus on high-profile issues, employing celebrities
What does the Humane Society of the United States focus on?
litigation and lobbying
What are Fraser's 3 conceptions
basic health and functioning
affective states
natural living
what are the inputs and outputs of assessing welfare
what's going in vs. how the animals respond
what is the single largest cost in animal production
nutrition
what is mechanical vs chemical digestion
physical breakdown of food vs changing chemical structure of food
what is absorption?
movement of nutrients into a cell
how do avians digest food?
with organ w/ stones to grind feed into smaller sizes
what do hindgut fermenters have?
large cecums that ferment feed
(monogastric digestive system)
esophagus - stomach - small intestine - cecum - colon - rectum
What are the 6 categories of nutrients
water, carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals
how is water lost?
milk, sweat, feces, urine, lungs
how much water should be consumed by BW %?
5-6% of BW
How do ruminants use carbs?
Microorganisms in rumen generate volatile fatty acids
examples of monosaccharides:
glucose, fructose, galactose
examples of disaccharides
lactose, sucrose, maltose
What cannot be digested by livestock?
lignin and cellulose
Who is non-protein nitrogen useful for
ruminants
essential vs nonessential amino acids
Essential: Must be taken in through diet
Non-Essential: Body manufactures
what % of lipids do most foods contain, and what % should they not exceed
5%, 10%
What vitamins are fat-soluble, and who are they essential for?
A, D, E, K, monogastrics and ruminants
What vitamins are water-soluble, and who are they essential for?
B, C, monogastric only
Describe roughages:
source of carbs, high fiber
pasture, hay, sileage
Describe concentrates:
carb source
grains, energy by-products
describe energy by-products
distillers grains
corn gluten
beet pulp
food waste
What are the 3 types proteins:
animal/plant by-products, non-protein nitrogen
list animal by-products
meat/bone meal
blood meal
fish meal
feather meal
dried skim milk
list plant by-products
wet/dry distiller grains
corn gluten
cottonseed meal
soybean meal
What is non-protein nitrogen?
urea
list 4 non-nutritive additives
color
flavor
antibiotics
health & digestion
what development occurs in prenatal growth?
tissue, skeletal, organ, etc
what is hyperplasia?
increase in fiber number
what is hypertrophy?
increase in fiber size
what is postnatal muscle growth primarily?
hypertrophy
what is accretion?
growth by gradual buildup
what type of growth curve is more profitable?
a steep curve
describe muscle tissue growth:
fastest early in life
describe bone growth:
decreasing rate, mostly complete by puberty
describe fat growth:
fastest near maturity
what is intra-abdominal fat?
fat deposited in abdominal cavity
what is subcutaneous fat?
fat deposited under skin; backfat
what is intermuscular fat?
fat between muscles
what is intramuscular fat?
fat within muscles; marbling
sex differences in fat:
Female > castrated > uncastrated
sex differences in weight:
Uncastrated > castrated > female
what is compensatory growth
A period of accelerated growth that follows a time of nutrient restrictions
what is nutrient partitioning?
Utilization of nutrients is partitioned among various tissues and organs according to their physiological importance
ranking of most important organ systems:
1. Nervous
2. Circulatory
3. Respiratory
4. Digestive
5. Reproductive
after partitioning, what do remaining nutrients go towards?
Growth
Finishing
Production
Work
Reproduction
what is a positive energy balance?
when an animal has enough nutrients to meet all its needs
what is a negative energy balance?
when nutrient intake does not meet needs
what is the goal of hormone modification of growth
to stimulate production of growth hormone through raising the levels of other hormones
Federal Gov disallows for hormones to be added into what animal products?
pork and poultry products
what are beta agonists?
Synthetic chemicals which shift nutrients away from fat production to the promotions of lean muscle growth
what are antimicrobial growth promotants
Antibiotics used in animal feed since 1950s
Describe anaerobic metabolism
Glucose
Lower ATP yield
Faster
Cytoplasm
Products: lactic acid
Describe aerobic metabolism
Glucose and oxygen
Greater ATP yield - more energy
Slower
Cytoplasm and mitochondria
Products: CO2 and water
what are acute adaptations
changes in physiology that occur during or soon after exercise
what are chronic adaptations
changes in physiology occurring in response to regular exercise
describe steady-state training:
Longer duration
Lower intensity
Aerobic metabolism
Slow-twitch muscle - increase muscle endurance
describe interval training:
Shorter duration
Higher intensity
Anaerobic metabolism
Fast-twitch muscle - increase muscle size
what happens when ATP is depleted and muscle can no longer contract?
muscle fatigue and cramps
describe the different types of diseases:
Clinical disease - signs of disease readily apparent
Subclinical disease - no overt signs of disease
Acute disease - sudden onset of clinical signs, short duration
Chronic disease - signs develop slowly, last for a long time
Zoonotic disease - passed between animals and humans
list the most common signs of diseases:
Appetite loss
Listlessness, depression
Droopy ears
Head held low, arched back
Isolate
Coughing, wheezing, labored breathing
Stiff, labored movement
Loose stools
What is pathogenicity?
ability of an organism to cause disease
What is virulence?
severity of disease and the ability to overcome the animal's immune system
what are endo vs ecto parasites?
inside body vs outside body
(acquired immunity chart)
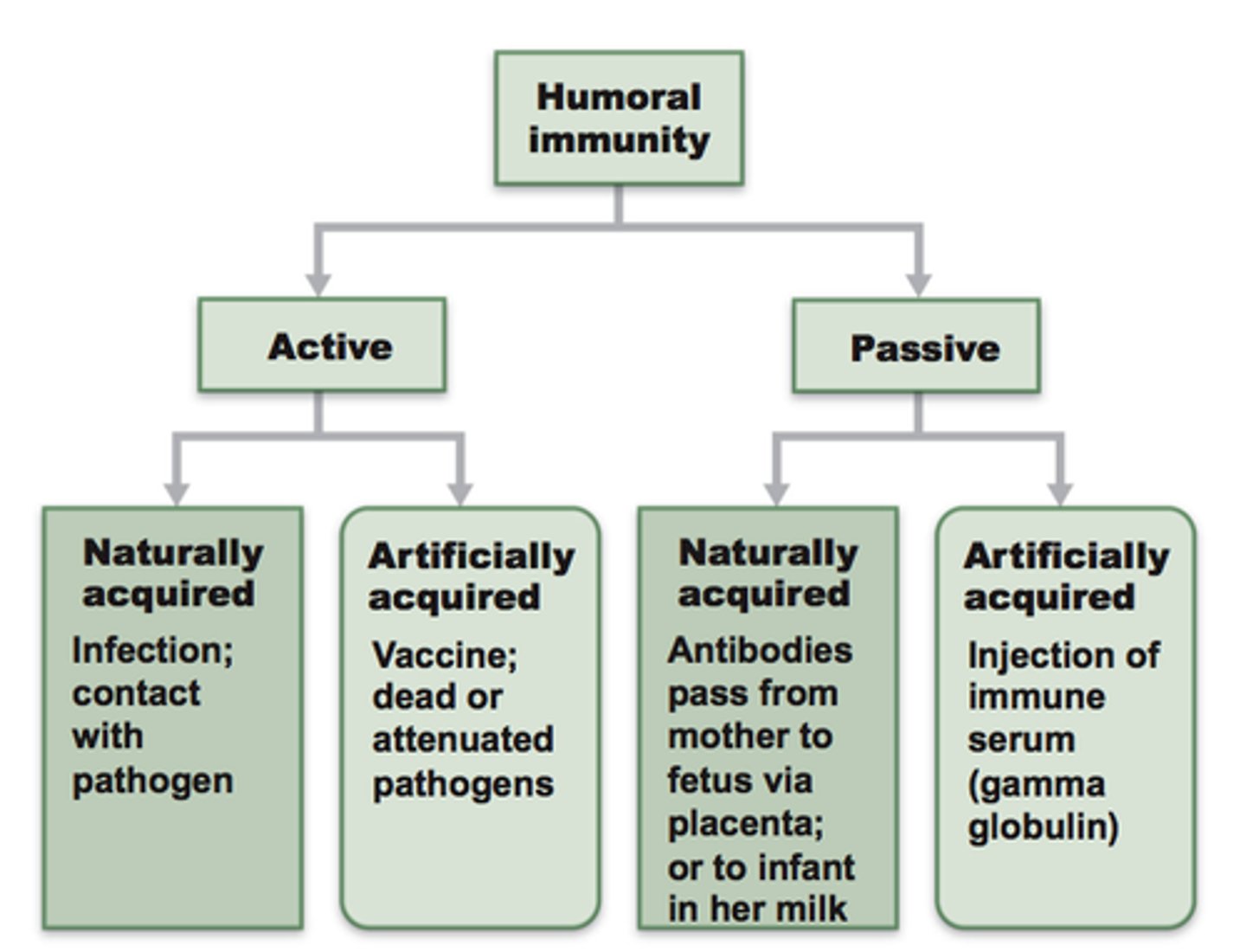
immune lines of defense:
innate barriers -> innate immune cells -> acquired immunity
what should be avoided when administering medication to livestock
high value meat cut areas
types of vaccines:
Live - weak or modified form that does not produce disease
Killed/inactivated - proteins or small pieces of pathogen
Toxoid - toxin produced by pathogen
Biosynthetic - artificial substance similar to pathogen of interest
mRNA - gives body the mRNA instructions to make viral antigens that the body then produces an immune response to
what is a companion animal?
an animal in which the owner has an emotional connection with the animal
what are the most common companion animals globally?
dogs and cats
What country ranks #1 for most dogs and cats
USA
How many dogs are there in the US?
83-88 million
How many cats are there in the US?
60-62 million
what percent of american households own dogs vs cats?
dogs: 45%
cats: 26%
describe domestication:
selection by humans for certain traits
what is neoteny?
retention of juvenile traits in adults