Cell Division - Biology 4Q
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Growth and development; Cell replacement; Asexual reproduction
List three (3) reasons why cells divide:
GCA
Sexual reproduction
Involves two specialized cells, called gametes, coming from the parents that will result to a unique offspring.
Asexual reproduction
Process by which a single parent reproduces by itself without the involvement of gametes.
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms wherein one cell divides into two cells of the same size. Happens in bacteria.
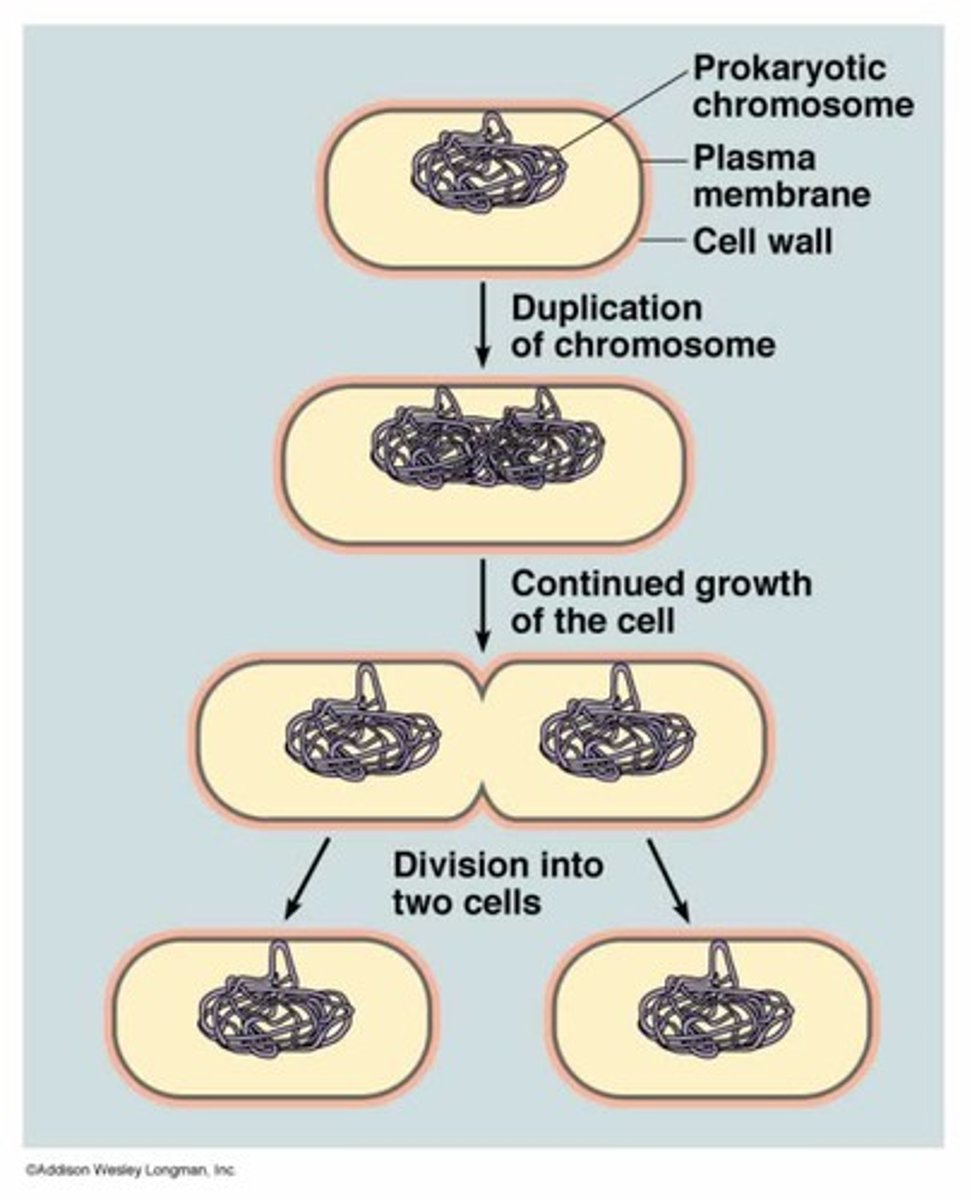
Cell structure lacks a nucleus; less DNA in the form of a single circular chromosome; no spindle fibers
What causes bacteria to produce faster?
CLN
Budding
A form of asexual reproduction in which a new cell grows out of the body of a parent.
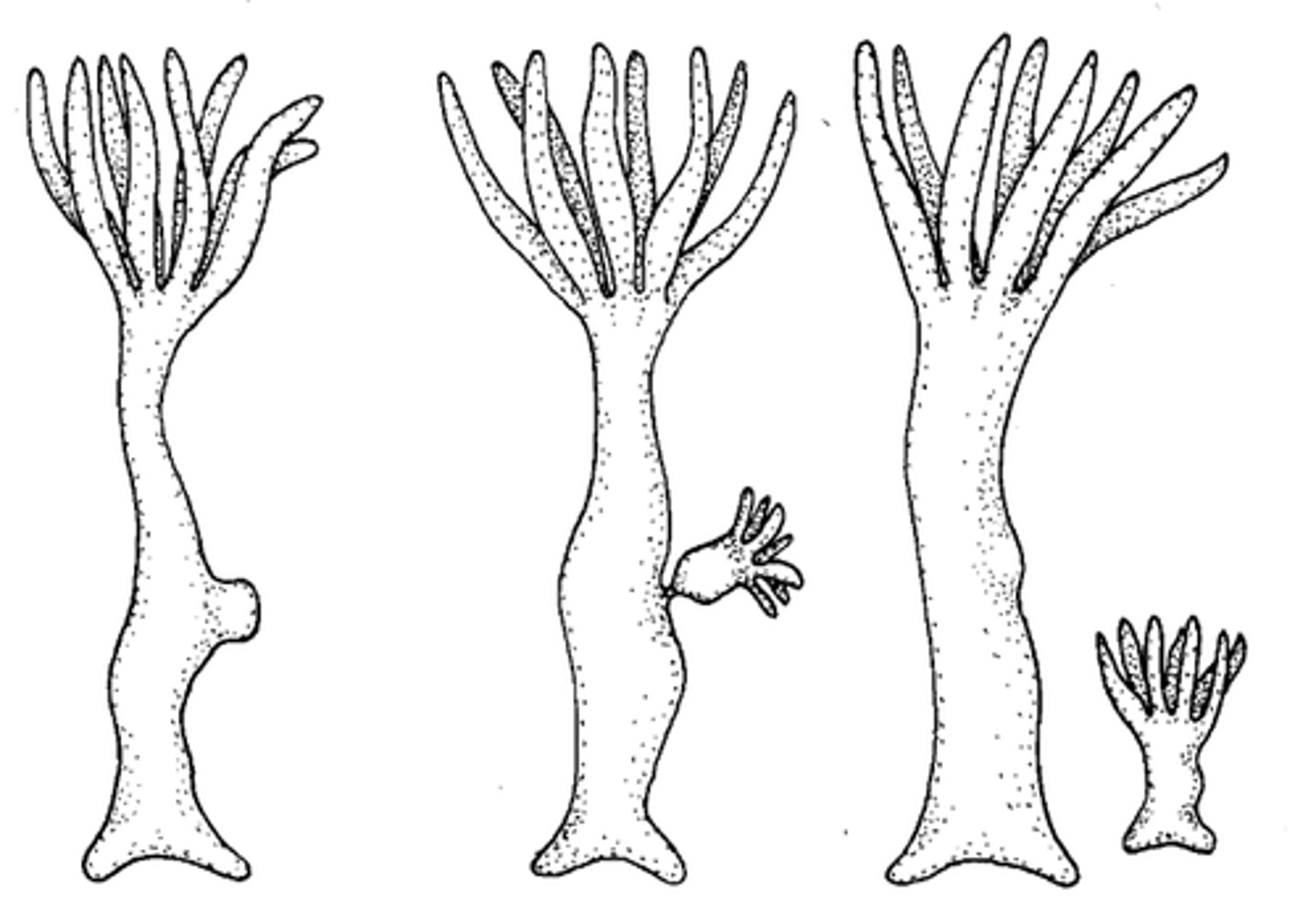
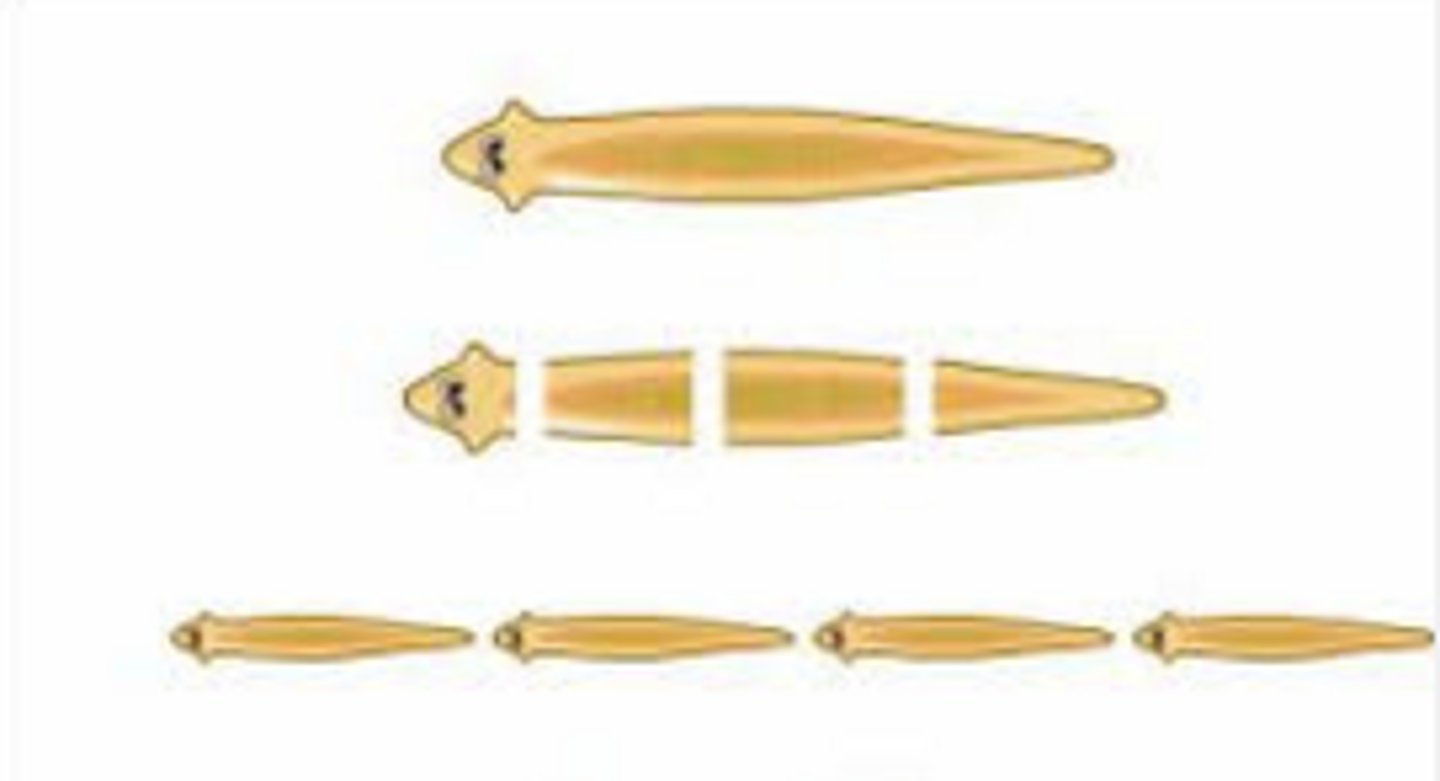
Fragmentation
A form of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.

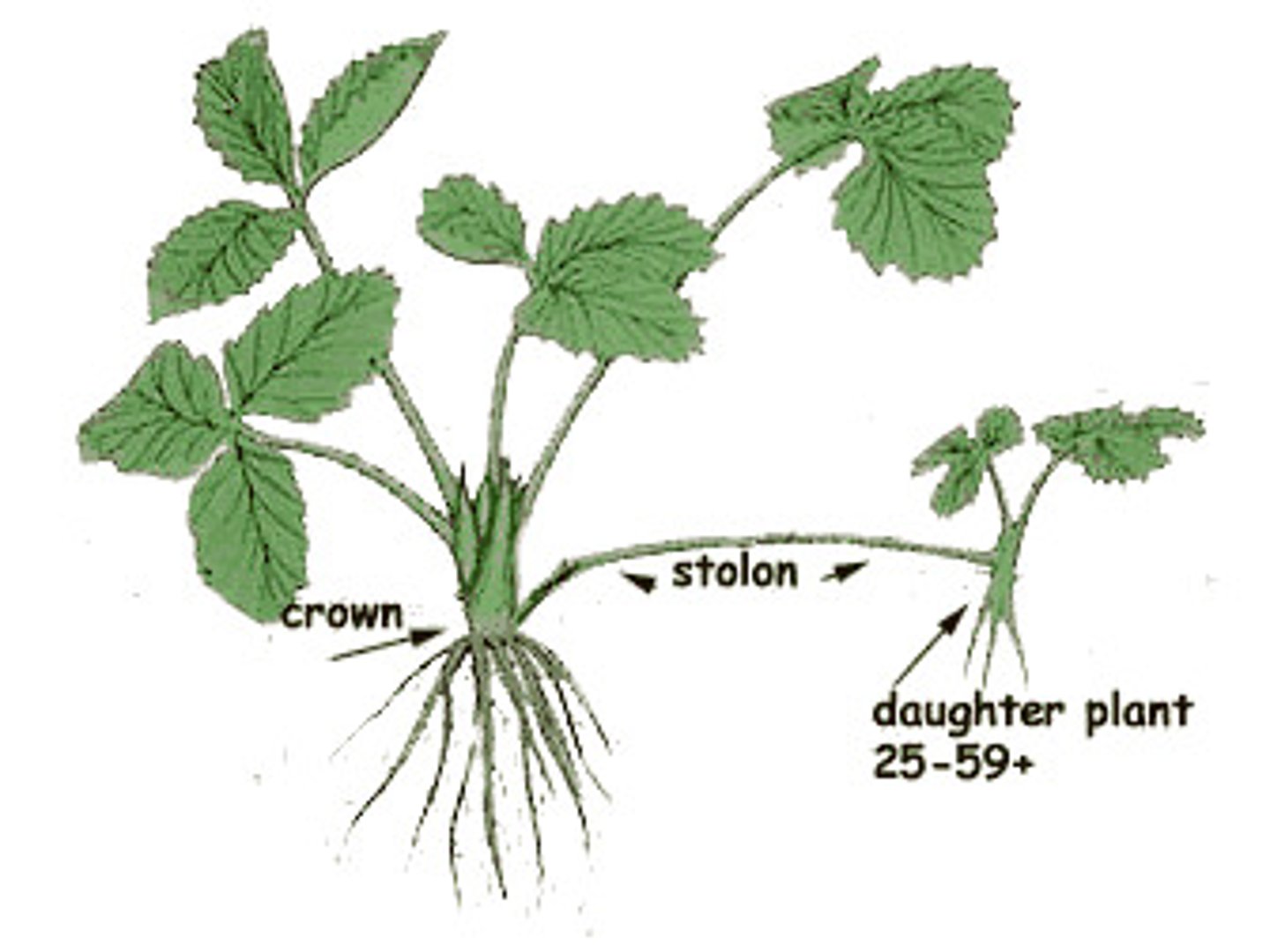
Vegetative reproduction
A form of asexual reproduction in which offspring grow from a part of a parent plant.
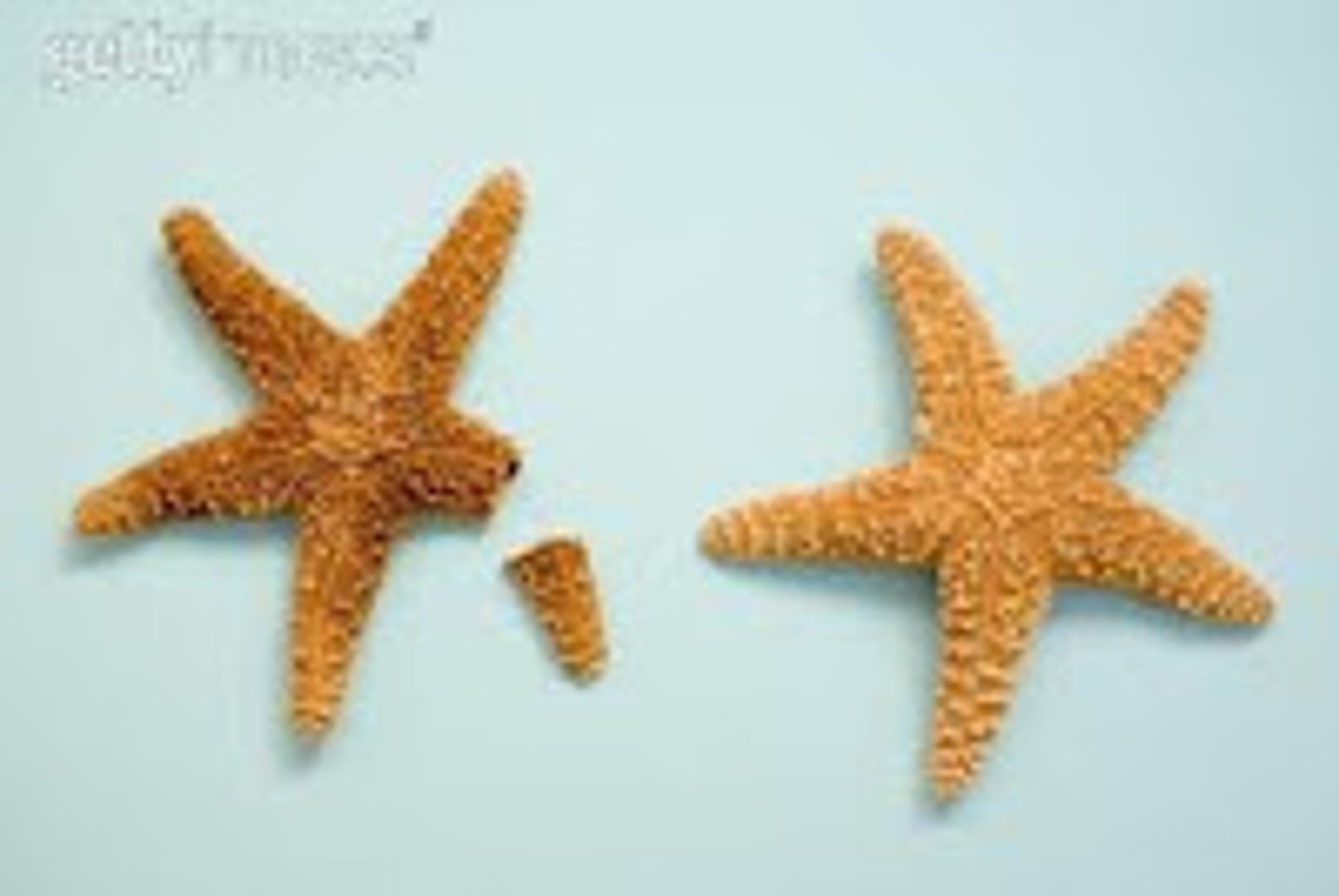
Regeneration
A form of asexual reproduction that replaces or restores damaged or missing cells, tissues, organs, and entire body parts to full function.

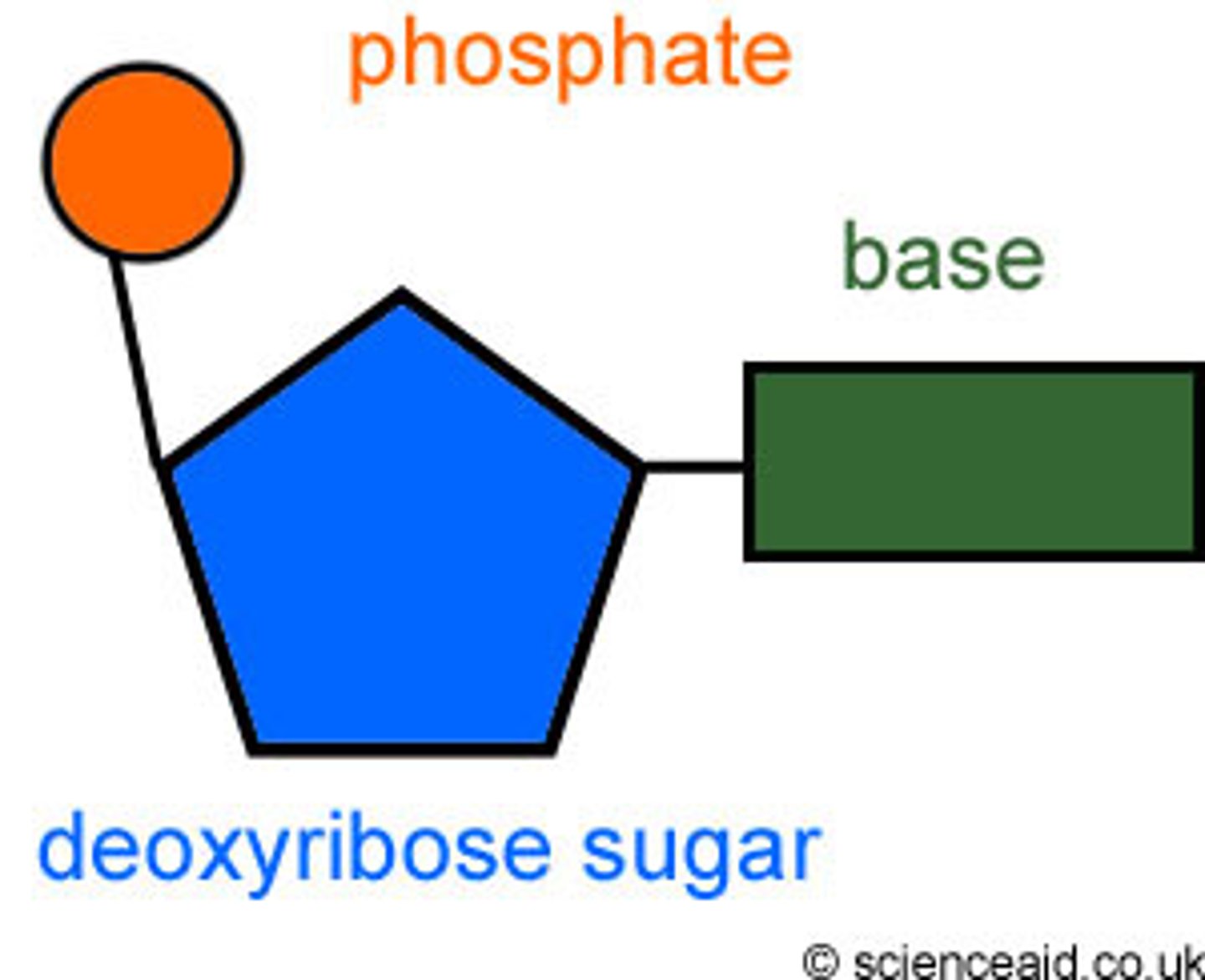
DNA/Deoxyribonucleic Acid
A double-stranded molecule that carries the genetic information inherited from parents and make the body function normally through life.
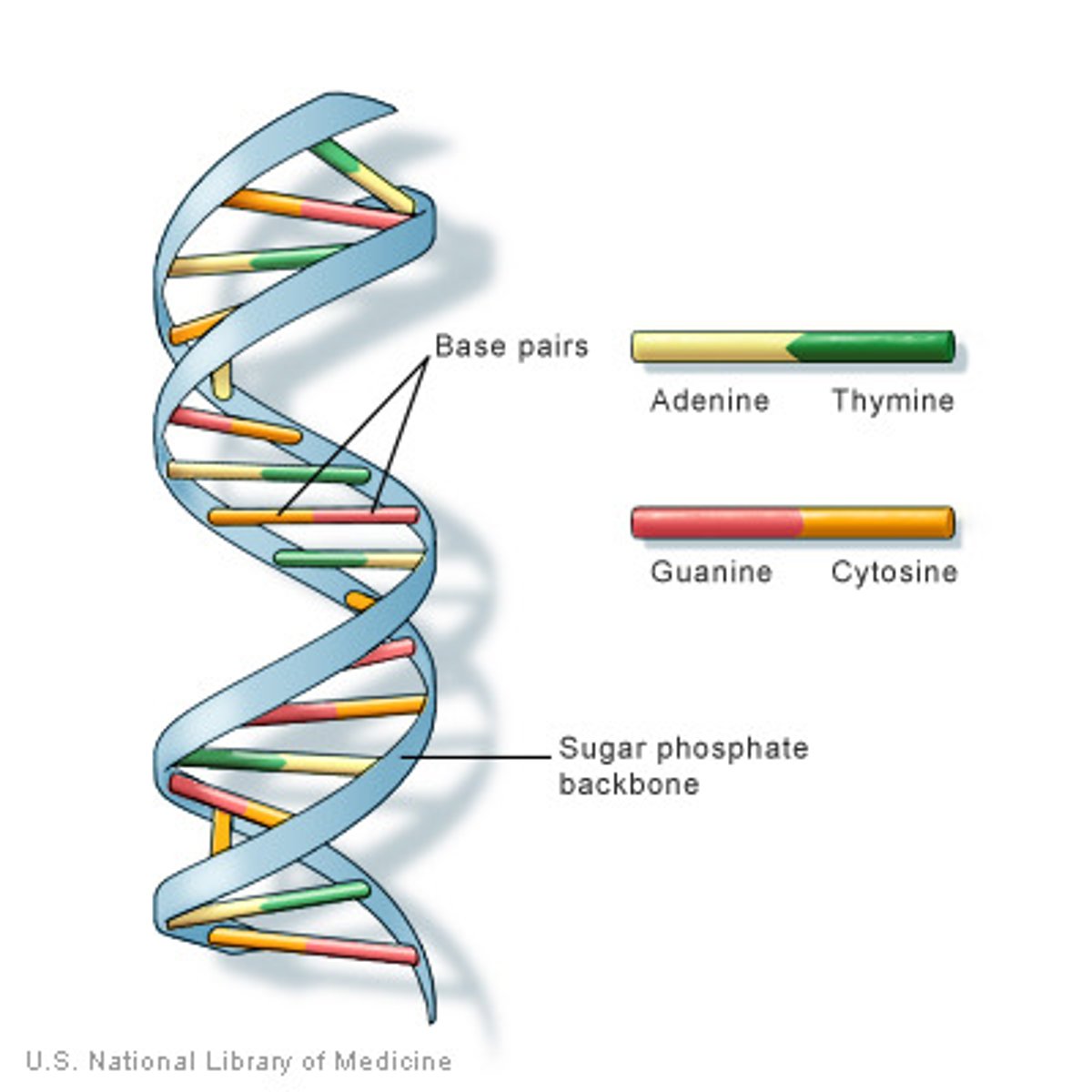
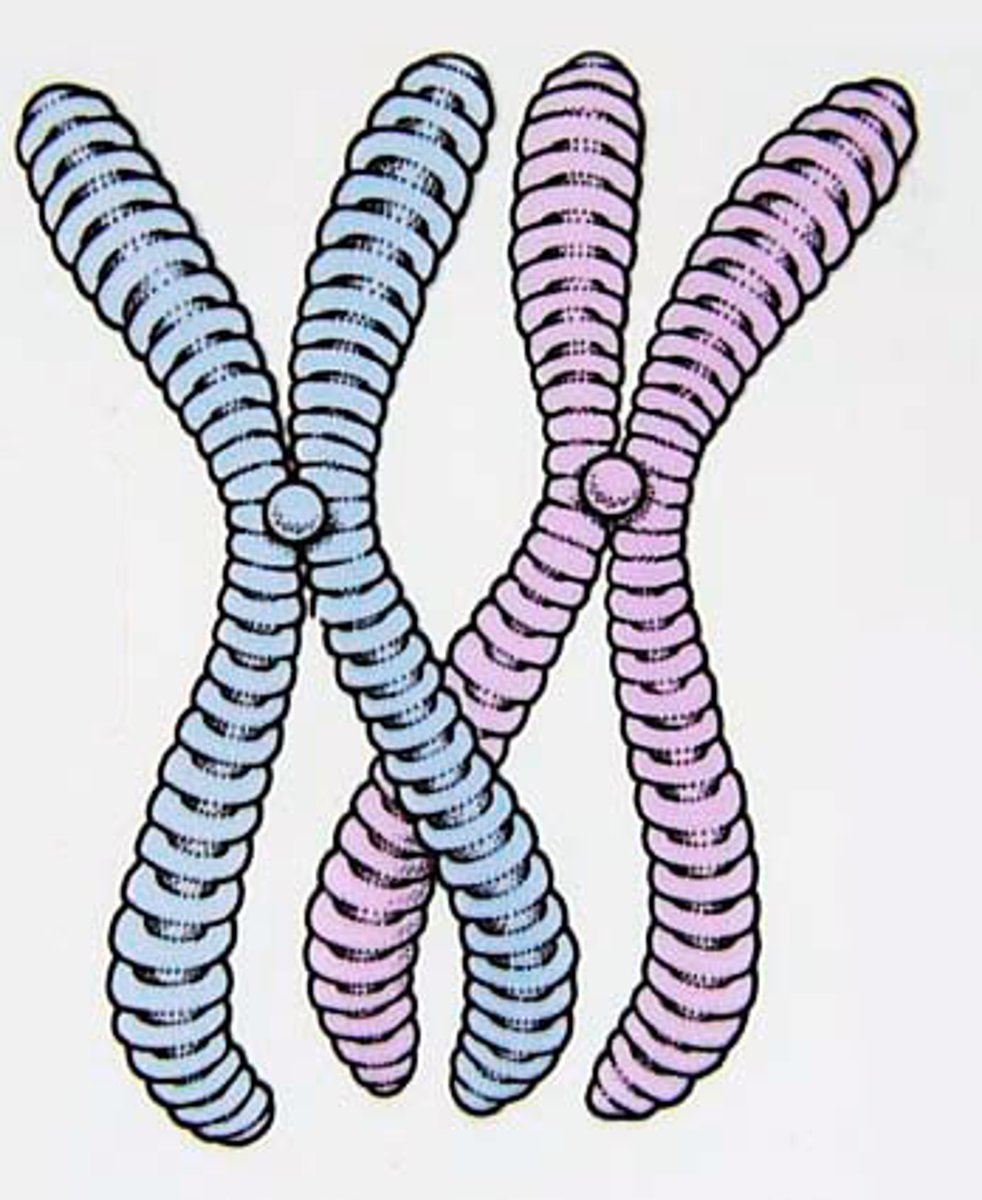
Chromosome
Tightly-coiled structures where the cell's genetic material is organized. It is a long, continuous thread of DNA wounded together by histones.
10 feet
How long in feet are chromosomes if stretched end to end?
46
How many chromosomes do humans have in their body cells?
23
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have in their body cells?
22
Referred to as autosomes and are inherited equally by males and females.
23rd pair
The chromosome pair that determines sex.
Loosely
Before cell division, the DNA is __________ organized.
Tightly condensed
During cell division, the DNA becomes __________ into chromosomes.
To avoid chromosomes getting entangled and to avoid cells getting only one or no copy of chromosome
What's the purpose of tightly condensing the DNA?
Histones
Protein found in the chromosome that gives chromosomes their shape, binding DNA, and helps control the activity of genes.
Chromatin
A complex set of macromolecules that contain loose DNA, proteins, and RNA. It is responsible for packaging the DNA efficiently into smaller volume so that it fits the nucleus of a cell. As the cell progresses in cell division, it further condenses, coiling more and more tightly around the proteins and eventually forming small, thick rods.
Protect; Prevent; Control; Reinforce
The chromatin has four primary purposes, these are...
To __________ the DNA structure and sequence.
To __________ DNA damage.
To __________ gene expression and DNA replication.
To __________ the DNA molecule to allow mitosis and meiosis.
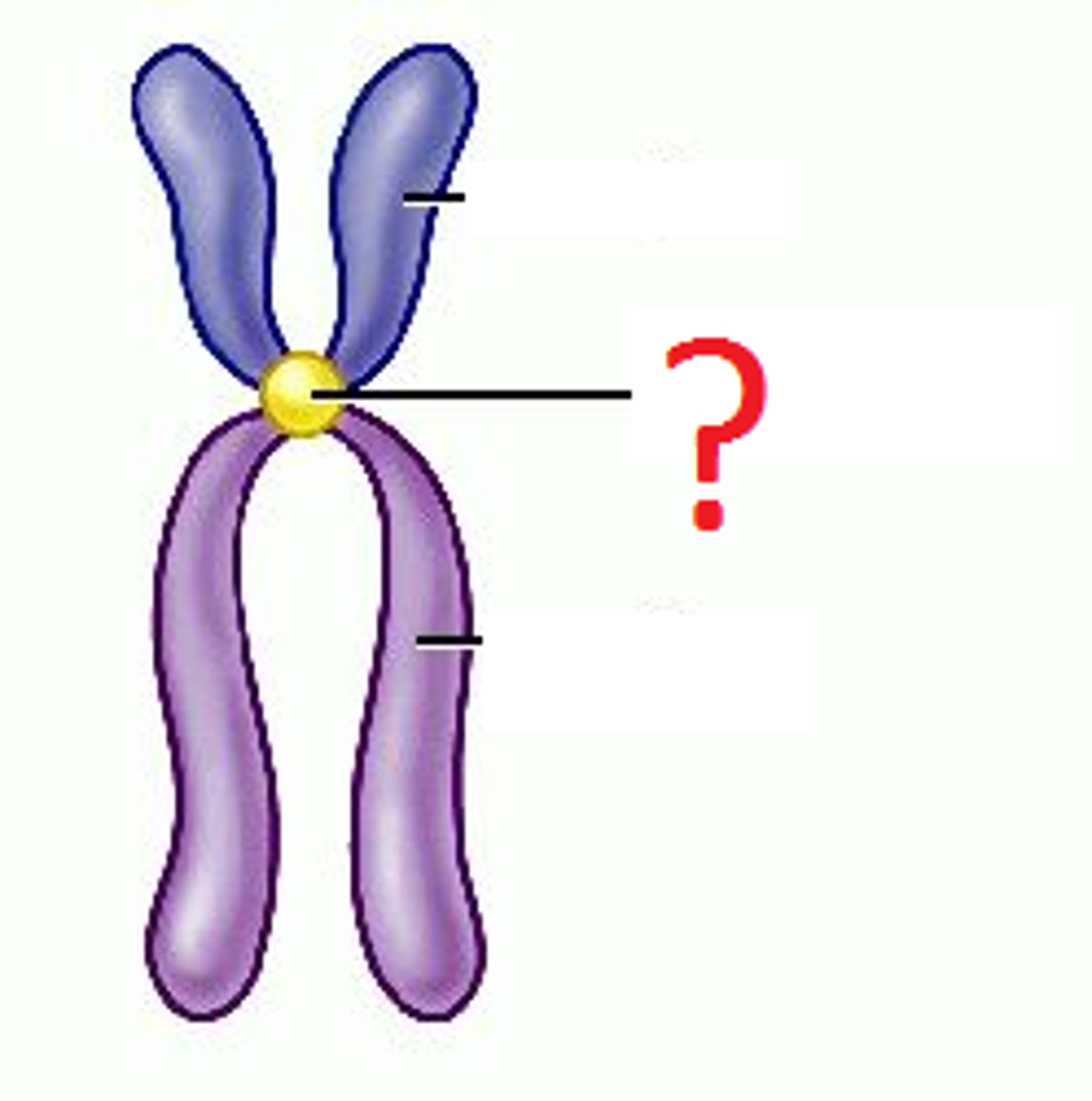
Chromatid
Refers to each strand of duplicated chromosomes.
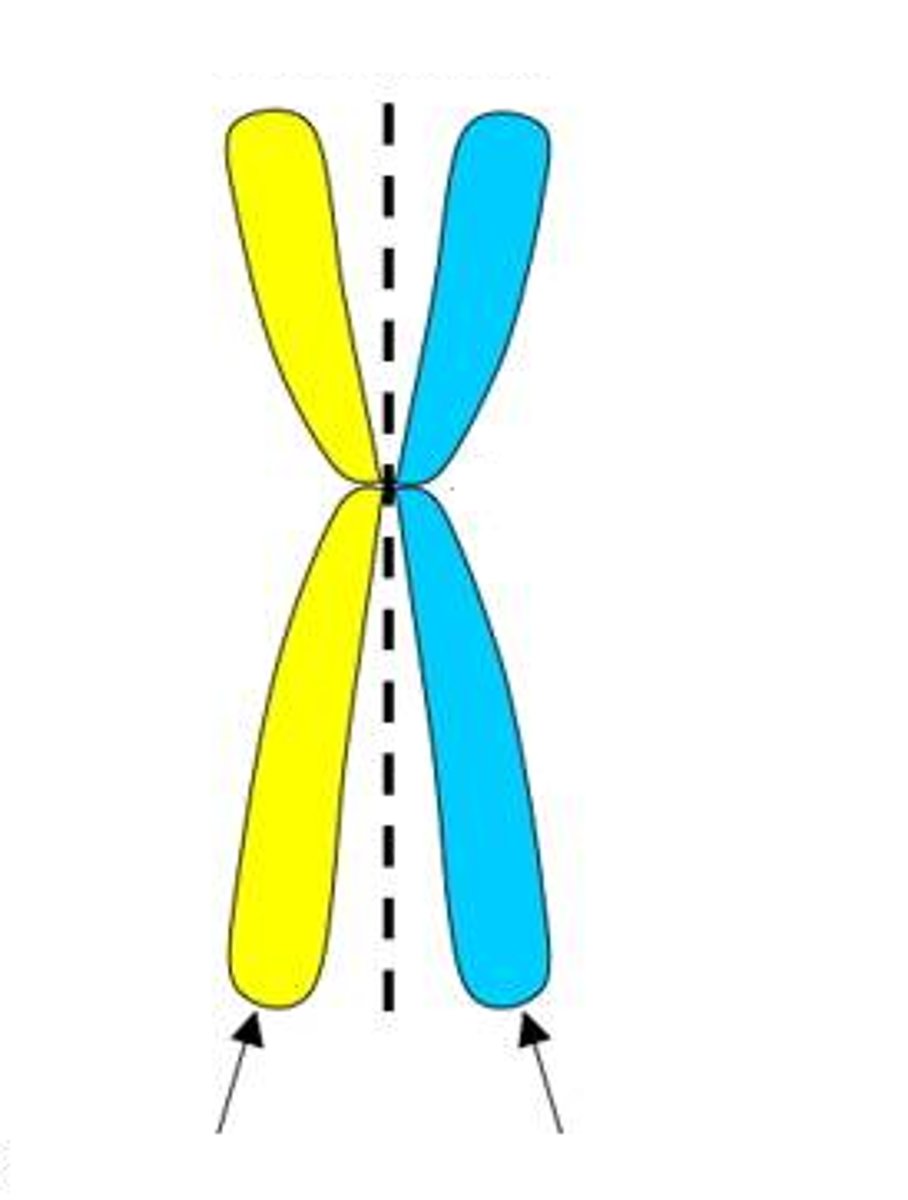
Sister chromatids (Chromosomes)
Two chromatids held together by a centromere.
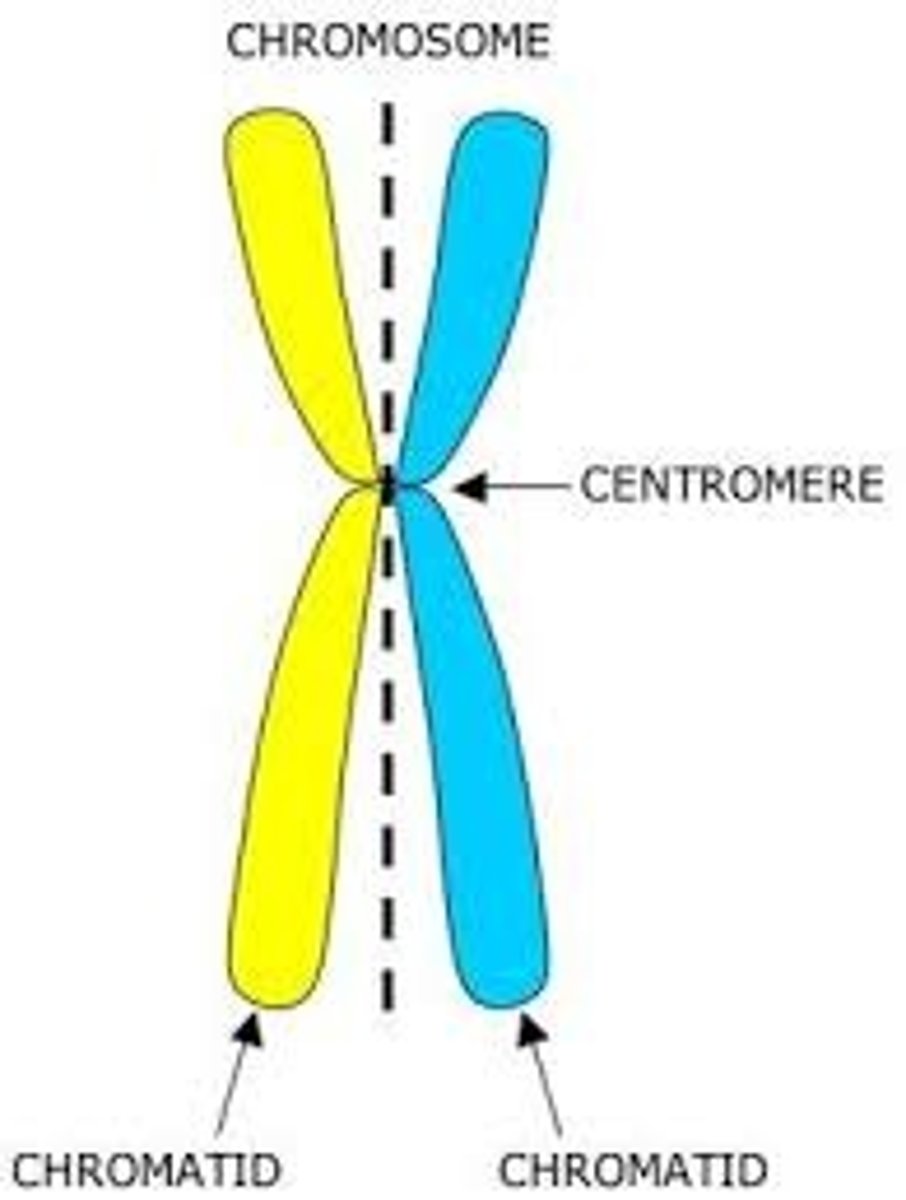
Centromere
A region of condensed pinched chromosomes.
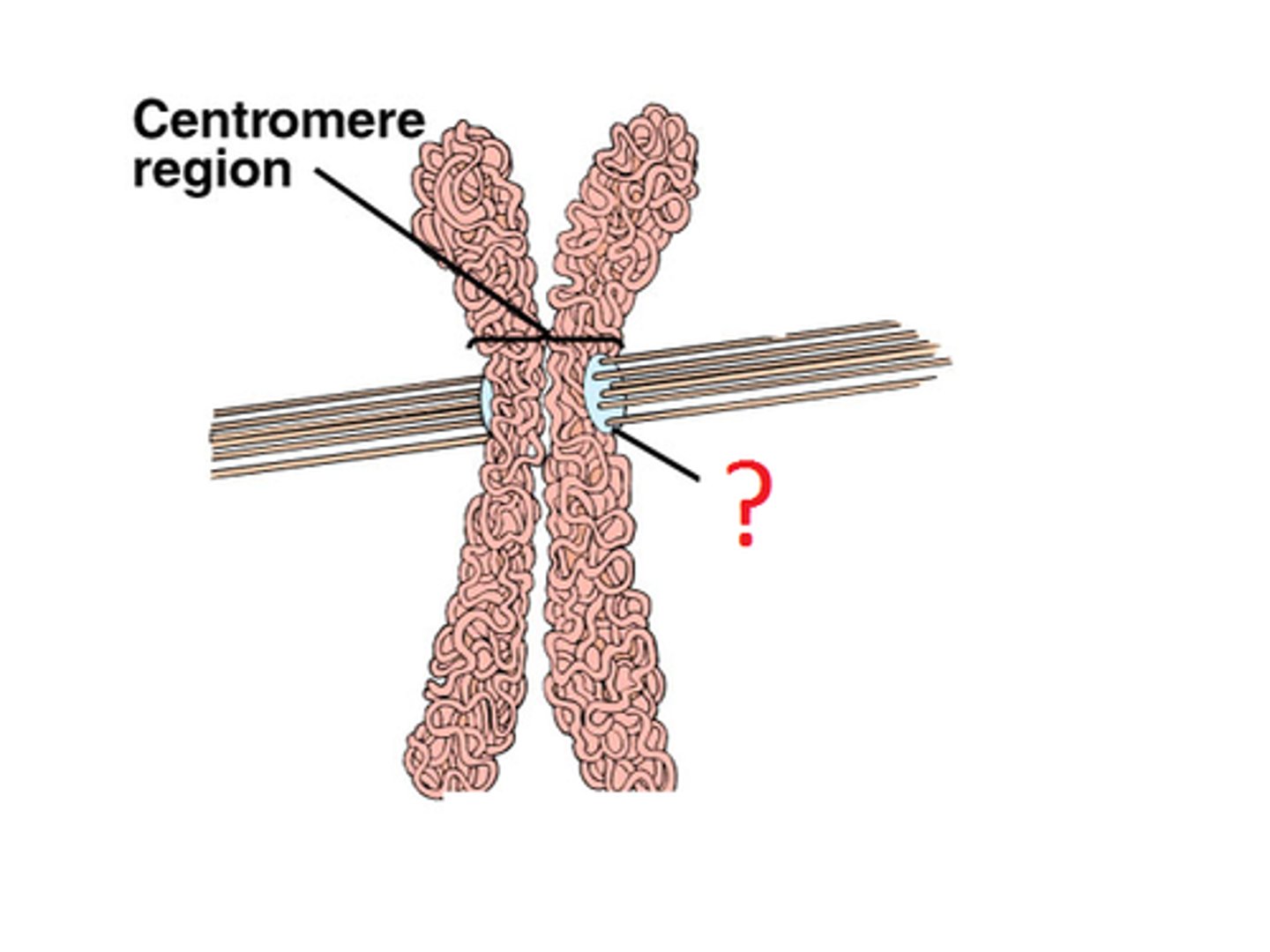
Kinetochore
A group of proteins located at the centromere. It is attached to the long spindle fibers during cell division.
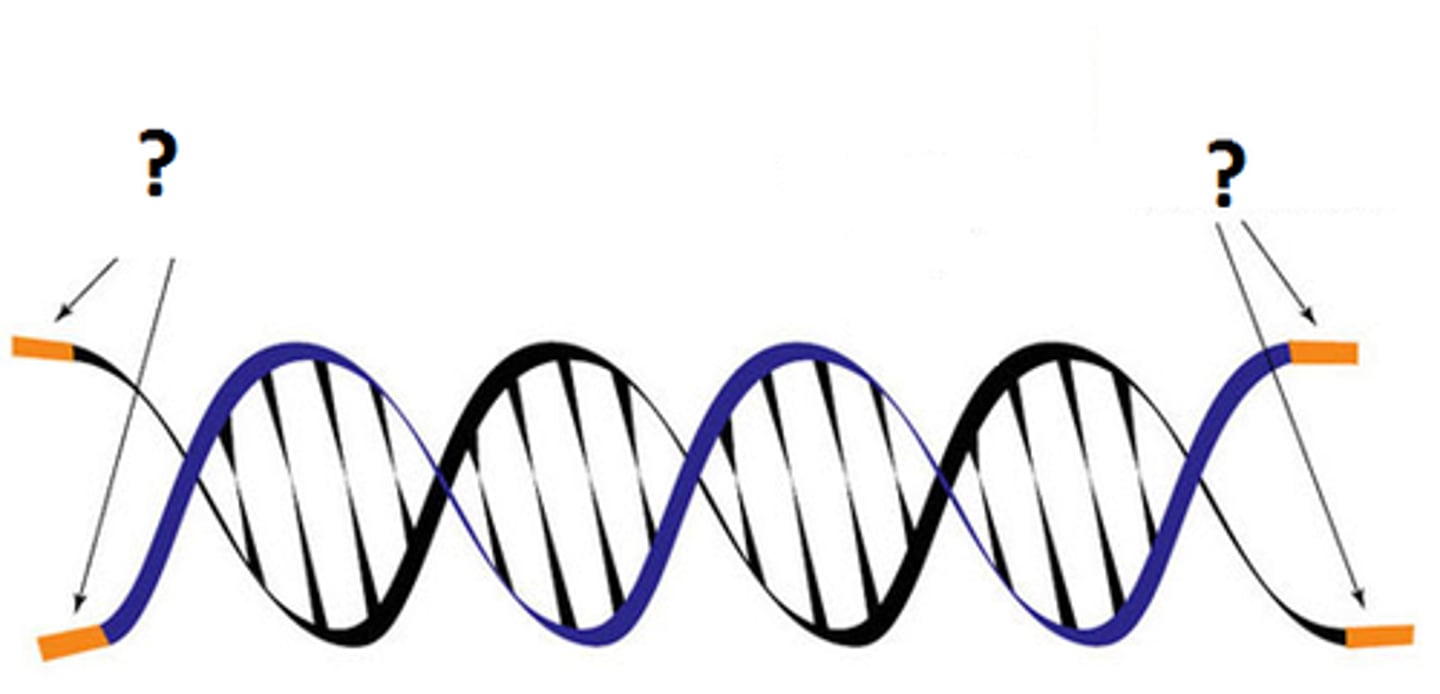
Telomere
Structures found at the end of the DNA molecule. It contains repeated nucleotides which contain genetic information that do not translate into traits.
Centrosome
A small dense region of cytoplasm that serves as the main microtubule organizing center where microtubules are organized and assembled.
Centrioles
Cylinder-shaped organelles made of short microtubules arranged in a circle. Found within the centrosome.
Microtubules
Strands that develop from each centrosome, forming spindle fibers.
Spindle fibers
Fibers that affix to the sister chromatids and help divide it between the two cells.
Prevents ends of chromosomes attaching to one another and prevents loss of genes
What's the purpose of telomeres?
Nucleotides
Since a small section of __________ is lost each time DNA is copied, it is preferable for these __________ to be lost from the telomeres rather than from the genes themselves.
Interphase
The first stage of the cell cycle considered as the growth period. It consists of G1, S, and G2.
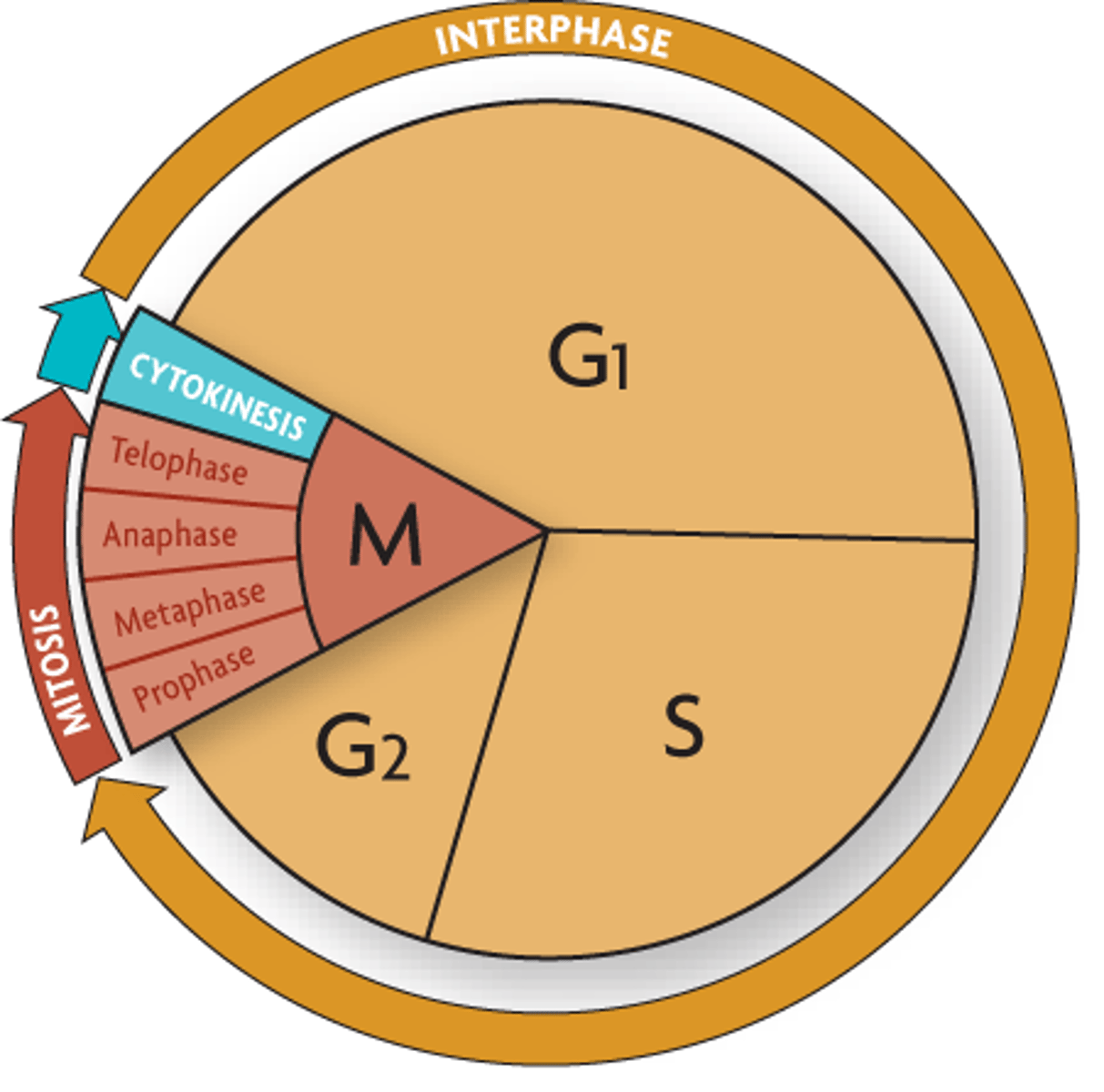
Gap 1 (G1)
The cells carry out its normal metabolic functions. Cells increase their size, as their organelles increase in number. Embryonic cells divide divide rapidly and exponentially. Cells spend most of their life cycle (though length differs among cell types).
Size limit
Cells have a required __________, therefore cannot grow bigger than their normal size.
Cell surface with volume
The cell's upper limit size is due to the ratio of __________.
Synthesis (S)
Refers to the time that the cell makes a copy of the genetic material in the form of nuclear DNA. DNA replication happens where each chromosome that contains one DNA molecule is copied with enough accuracy. This ensures that the daughter cell receives exact copies of the parents' genetic material during cell division. Once complete, the nucleus contains two complete and identical sets of DNA molecule. Microtubules are also produced, which are protein complex that will later help the cell organize its contents.
Gap 2 (G2)
Cells continue to carry out their normal functions and undergo further growth. Contains a critical checkpoint before transitioning to the next stage. Cells make sure that everything is in order, including growing to its correct size and duplicating DNA without damage.
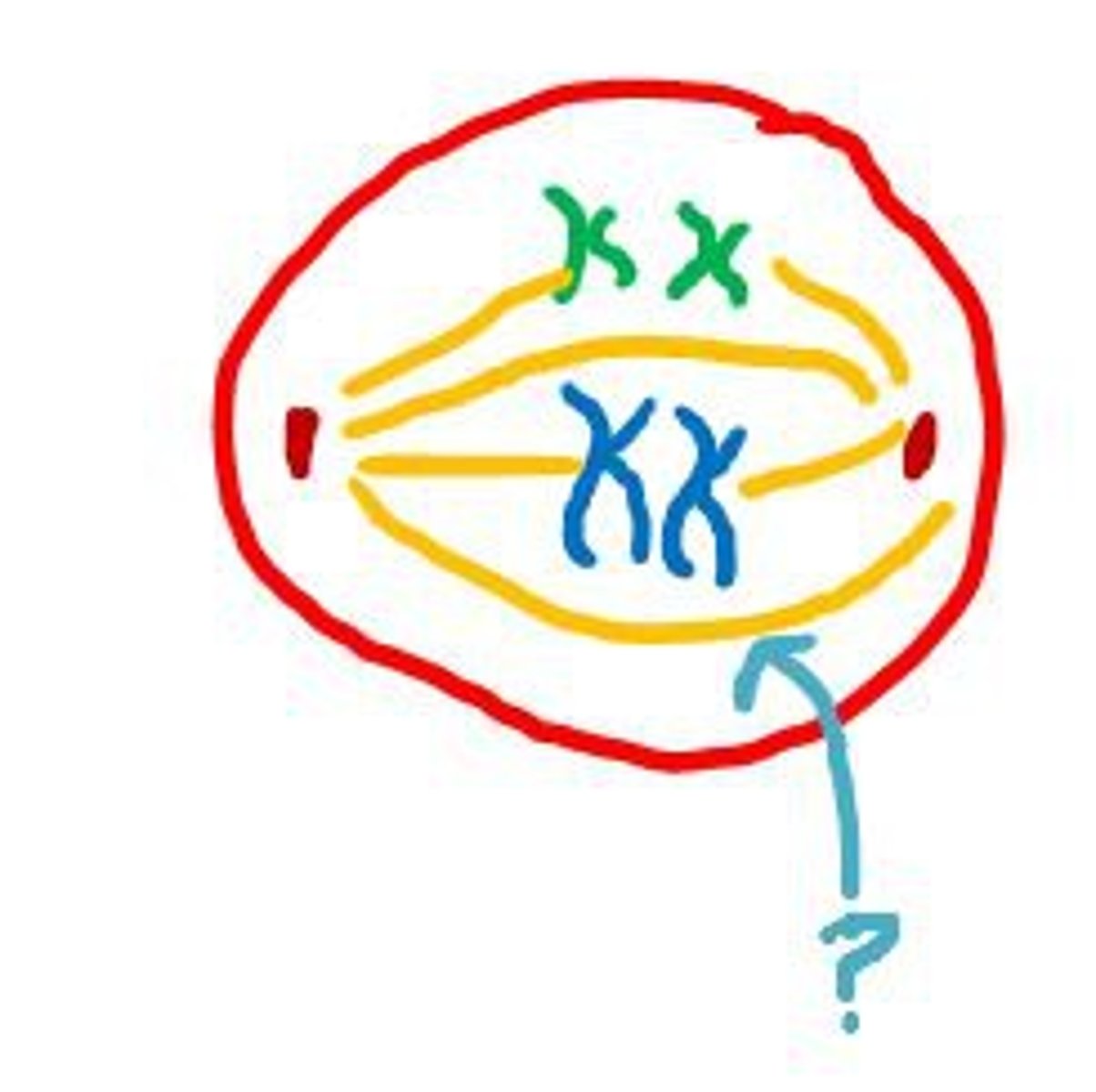
Mitosis
Involves the division of nucleus and the genetic material. The hereditary material of the parent cell is given to the daughter cells. Leads to the formation of two daughter cells containing identical genetic materials. The cell's nuclear membrane disintegrates, while the DNA condenses, forming two nuclei. Consists of four parts: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
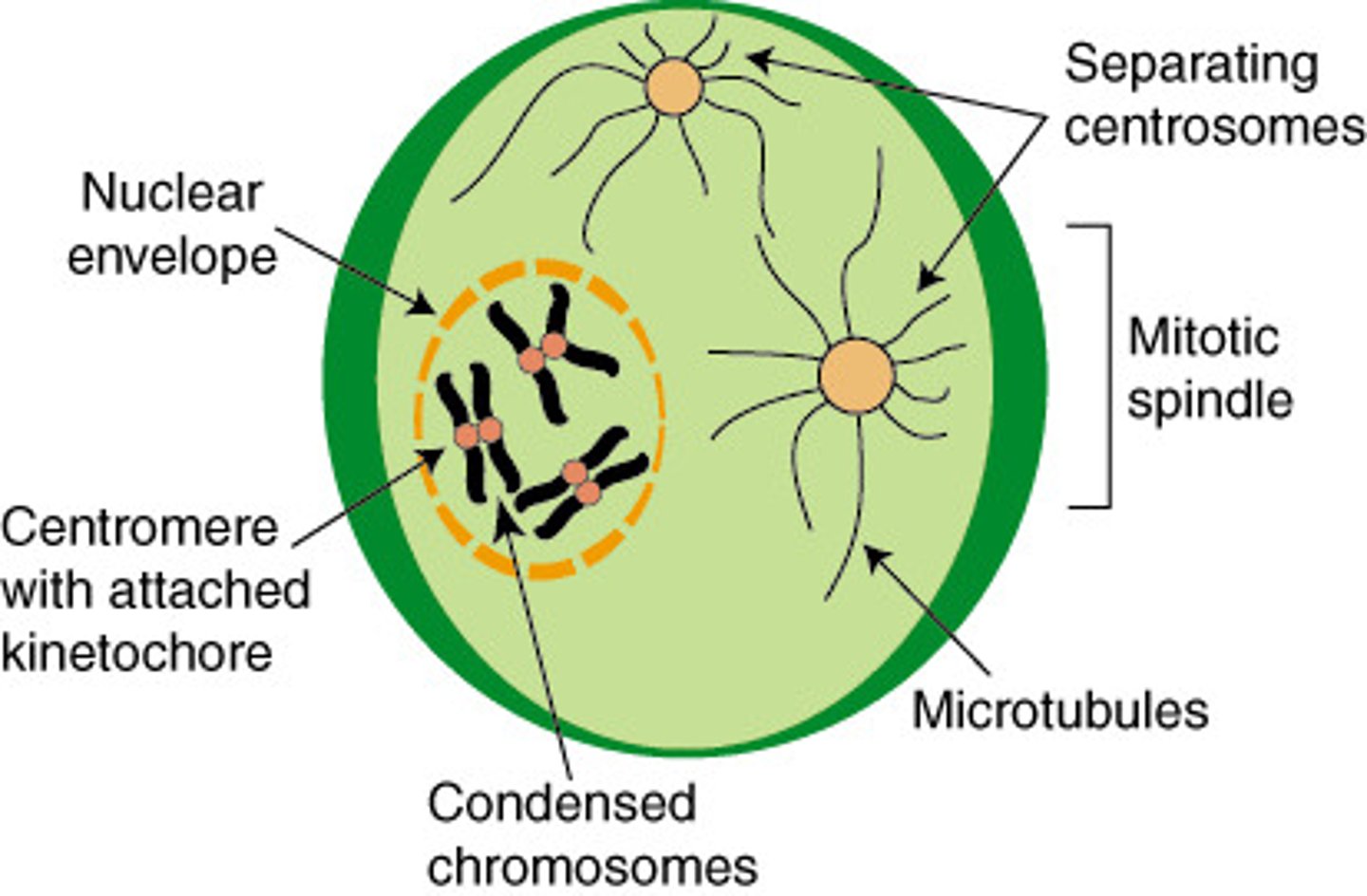
Prophase
Processes involved in the _____.
- Chromatin condenses into tightly coiled chromosomes
- Individual chromosomes become visible as threadlike structures
- Chromosomes package into neat bundles (easier for division and stops entanglement and breaking)
- Nuclear envelope breaks down
- Nucleolus disappears
- Two mitotic spindles starts assembling
- Microtubule-organizing center (centrosomes in animal cells) begin to migrate to opposite poles
- Organized microtubules which form spindle fibers grow from centrosome and extend toward center of cell toward opposite poles
- Microtubules attach with the chromosomes, one on each sister chromatid
- Some don't connect with the chromosomes, but grow and continue to extend from pole to pole
- By the end of this, the chromosome is being prepared to line up at the center of the cell
Before
Pro means "_____."
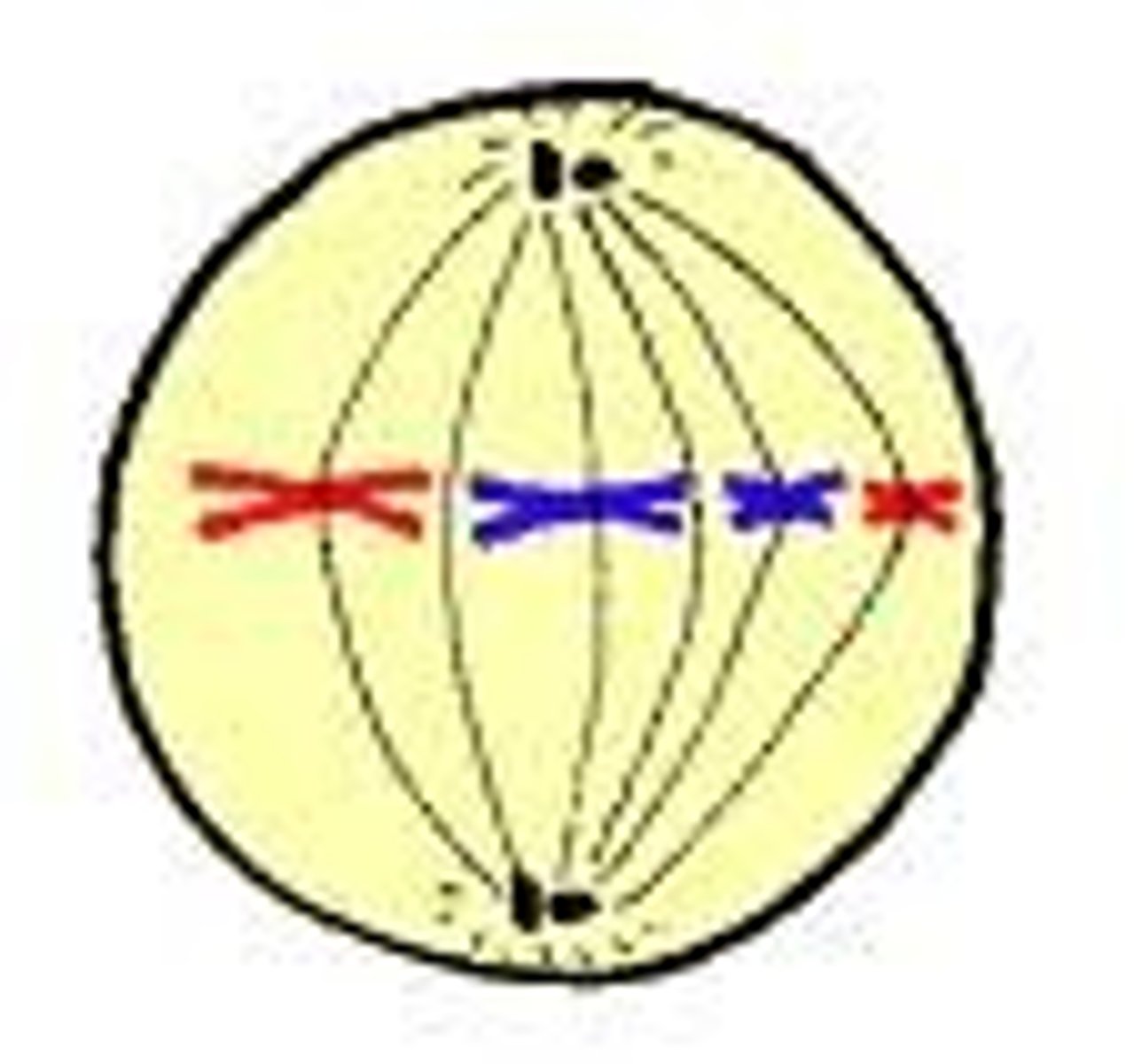
Metaphase
- Spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore of the sister chromatids facilitates movement of chromosomes toward middle of the cell
- Chromosomes line up along the __________ plate
- This phase happens fast
After
Meta means "_____."
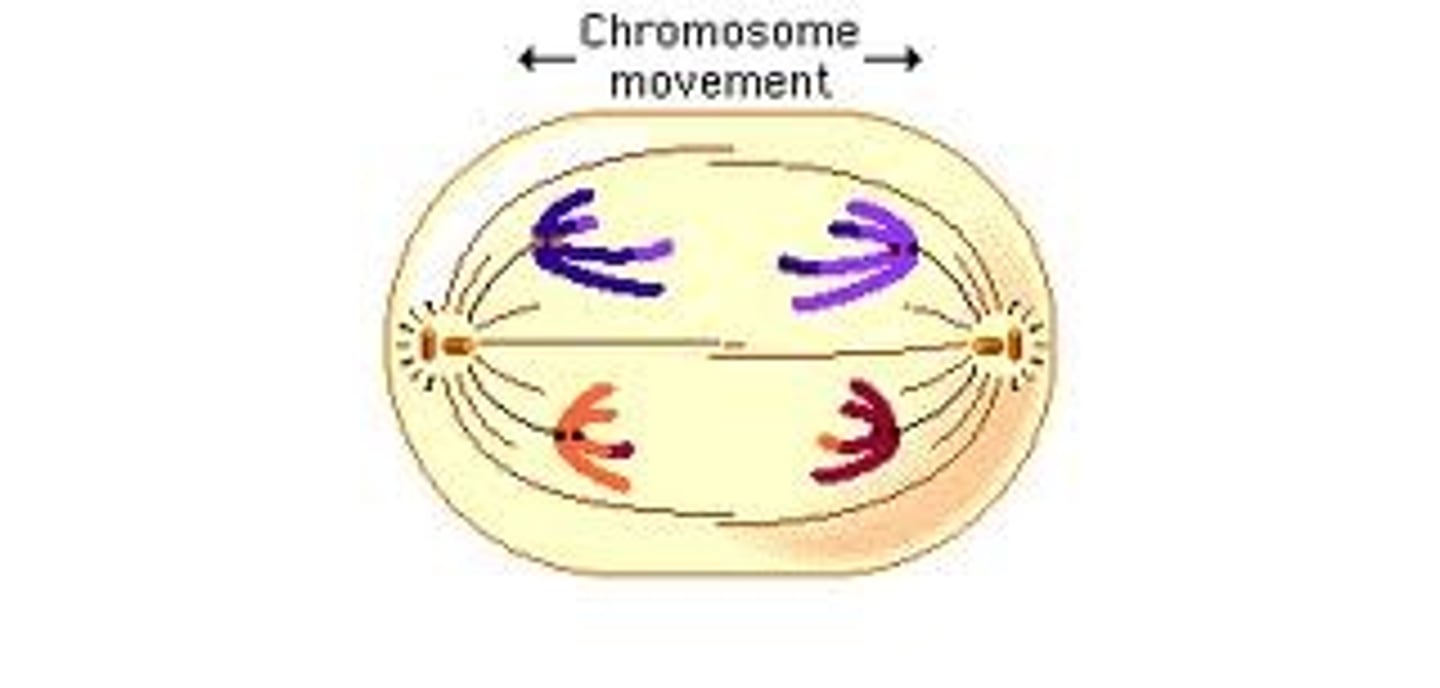
Anaphase
Processes involved in the _____.
- Sister chromatids are tightly paired due to the centromere and protein cohesin
- Cohesin breaks down and sister chromatids separate
- Spindle fibers shorten to pull sister chromatids away from each other toward the opposite ends of the cell
- In animal cells, some microtubules lengthen, making the cell elongated under the microscope
- In plant cells, there is no significant change in length due to the cell wall
Up or back
Ana means "_____."
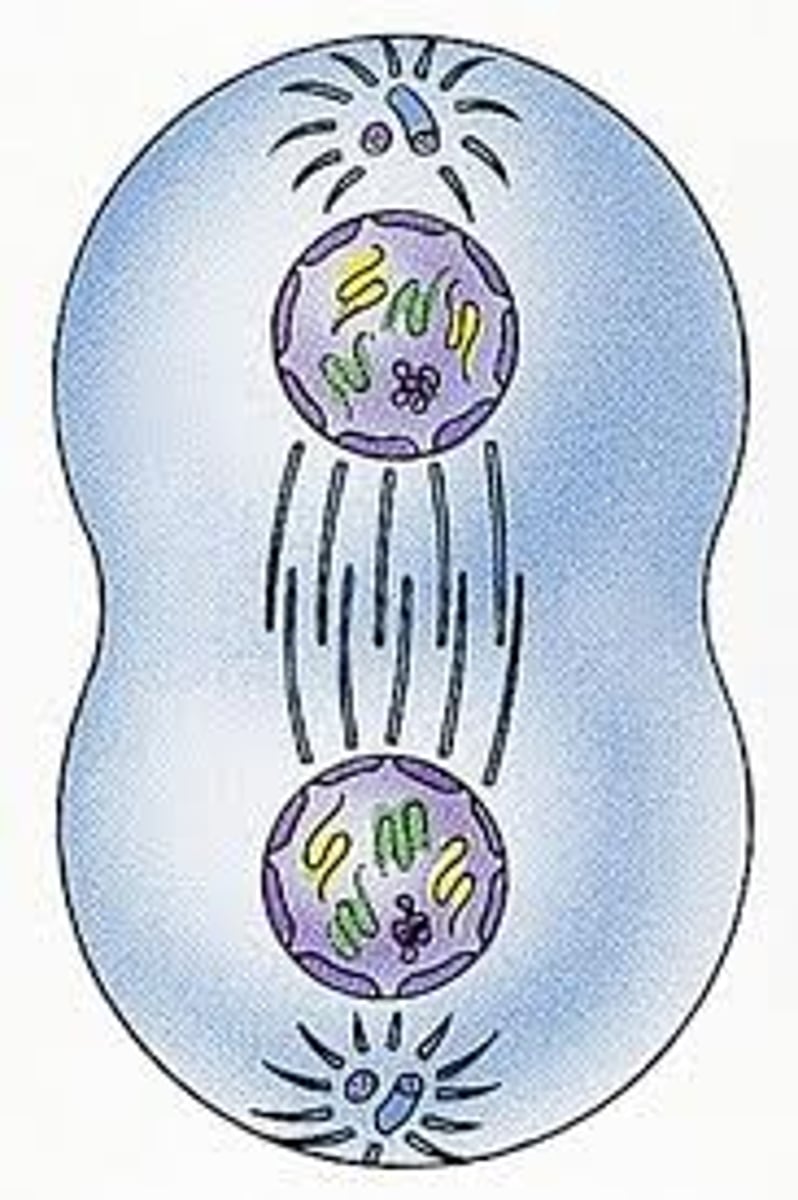
Telophase
Processes involved in the _____.
- Complete sets of identical chromosomes are positioned at the center of each pole
- Microtubules and spindle fibers all disintegrate
- Small fragments and protein molecules rebuild nuclear membrane around each set of chromosomes
- Nuclear membrane starts to form
- Chromosomes are no longer visible
End
Telo means "_____."
Cytokinesis
Basically divides the cytoplasm of the cell. It begins early during telophase and continues after the nuclei have formed into daughter cells.
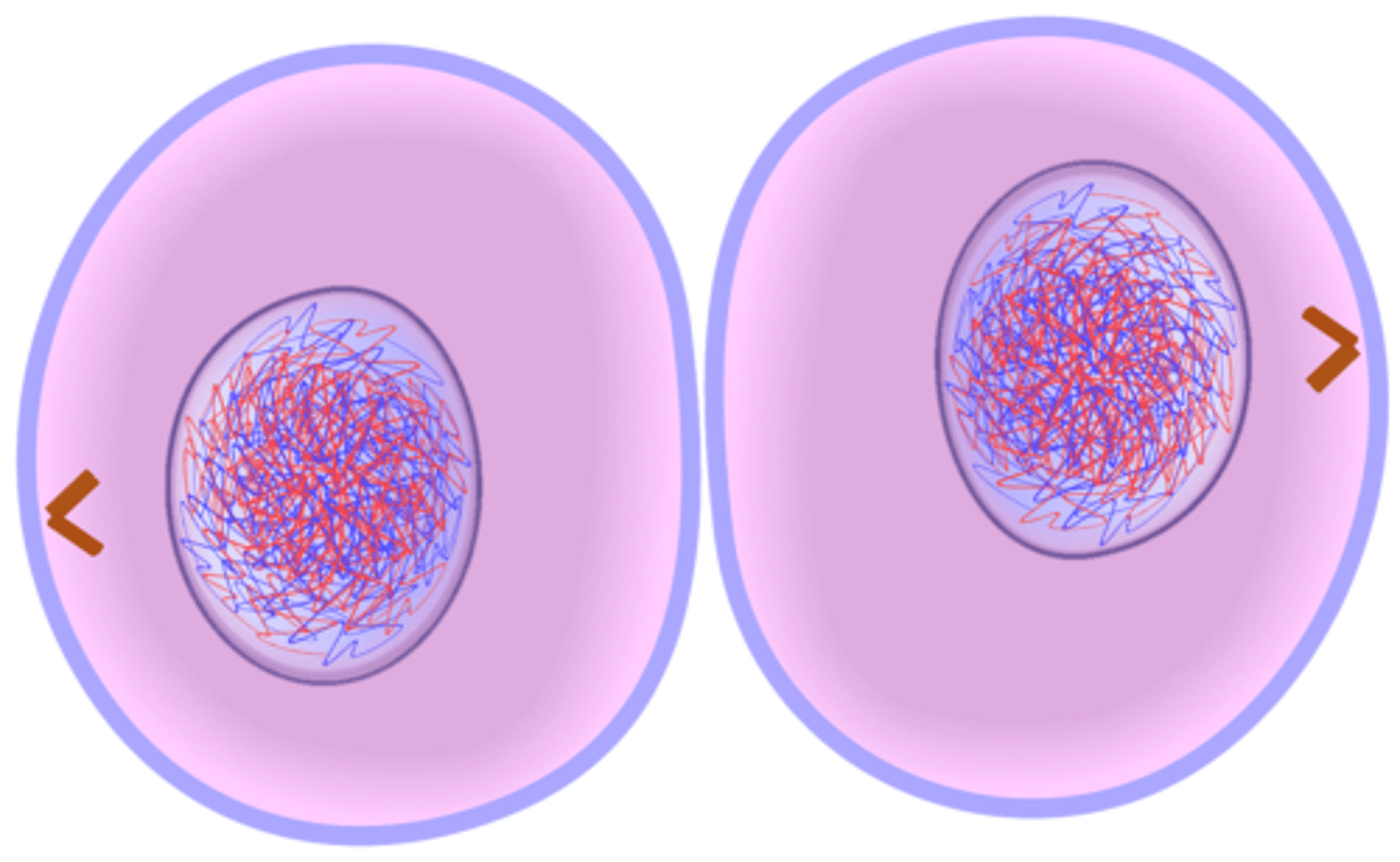
Cleavage furrow
Also known as trench. In animal cells, cytokinesis starts with the formation of _____. It is pulled inward by tiny strands of protein actin.
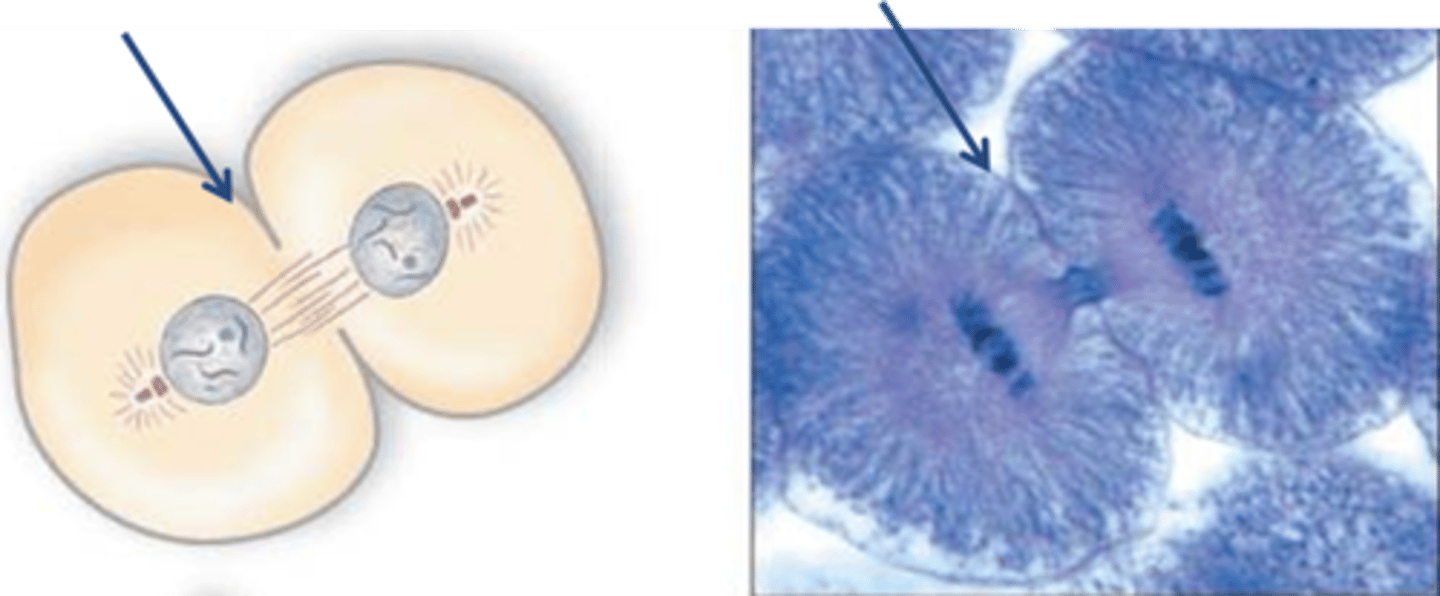
Microfilaments
Protein actin.
Golgi apparatus
Organelle responsible for the formation of the cell plate.
Vesicle
Organelle that supplies cell wall material and lipids to form a plasma membrane to the cell plate.
Embryonic stage and childhood years
The rate of cell division is faster during this time in terms of stage and years.
Skin cell
The rate of cell replacement is higher in areas subjected to a lot of wear and tear, such as __________.
Growth; DNA duplication; Cell division
Enumerate three (3) definite stages of the cell cycle:
GDC
Gap zero
Cells are unlikely to divide but still continue to perform normal functions. Such cells, like neuron and heart cells that are highly differentiated or specialized and that the body cannot easily replace, are said to be permanently in this gap.
About 100 trillion cells
How many cells are there in the body?
Cell cycle
This cycle allows for growth and repair of cells.
Abnormal cell growth
If the cell cycle grows out of control, what can occur and may manifest in the body of the organism?