BIOL 4101 concept quiz 3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
7 possible stress conditions
-osmotic stress
-oxidative stress
-metal toxicity
-ethanol treatment
-temp
-DNA damage
-alternative carbon source (glycerol or sucrose)
blank for spec
-deionized water
hemocytometer count to cells/µL
-divide average count by 0.004 µL
electrophoresis
-technique to separate components of a mixture of charged molecules (proteins, DNAs, RNAs) in an electric field
-electric force acts on charged particles to move them through gel
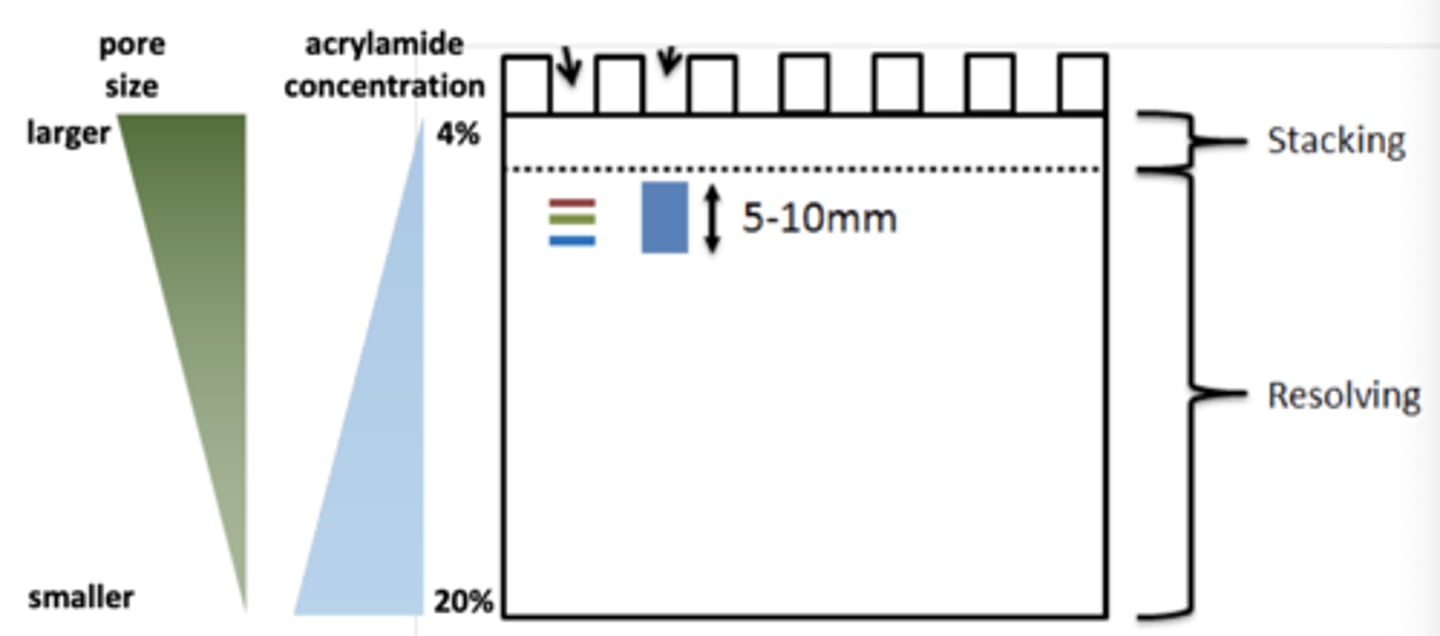
polyacrylamide gel, molecules, pores
-polymerized acrylamide; separating gel
-long molecules of acrylamide and shorter molecules of bis-acrylamide; ratio and concentration determines pore size (can be in a gradient)
-has pores filled with aqueous solution that catch proteins
making a separating gel: ammonium persulfate, TEMED
-ammonium persulfate in acrylamide mix initiates cross linking
-TEMED speeds up polymerization
stacking gel and running gel
-stacking gel: precast sample wells
-running gel: resolving gel
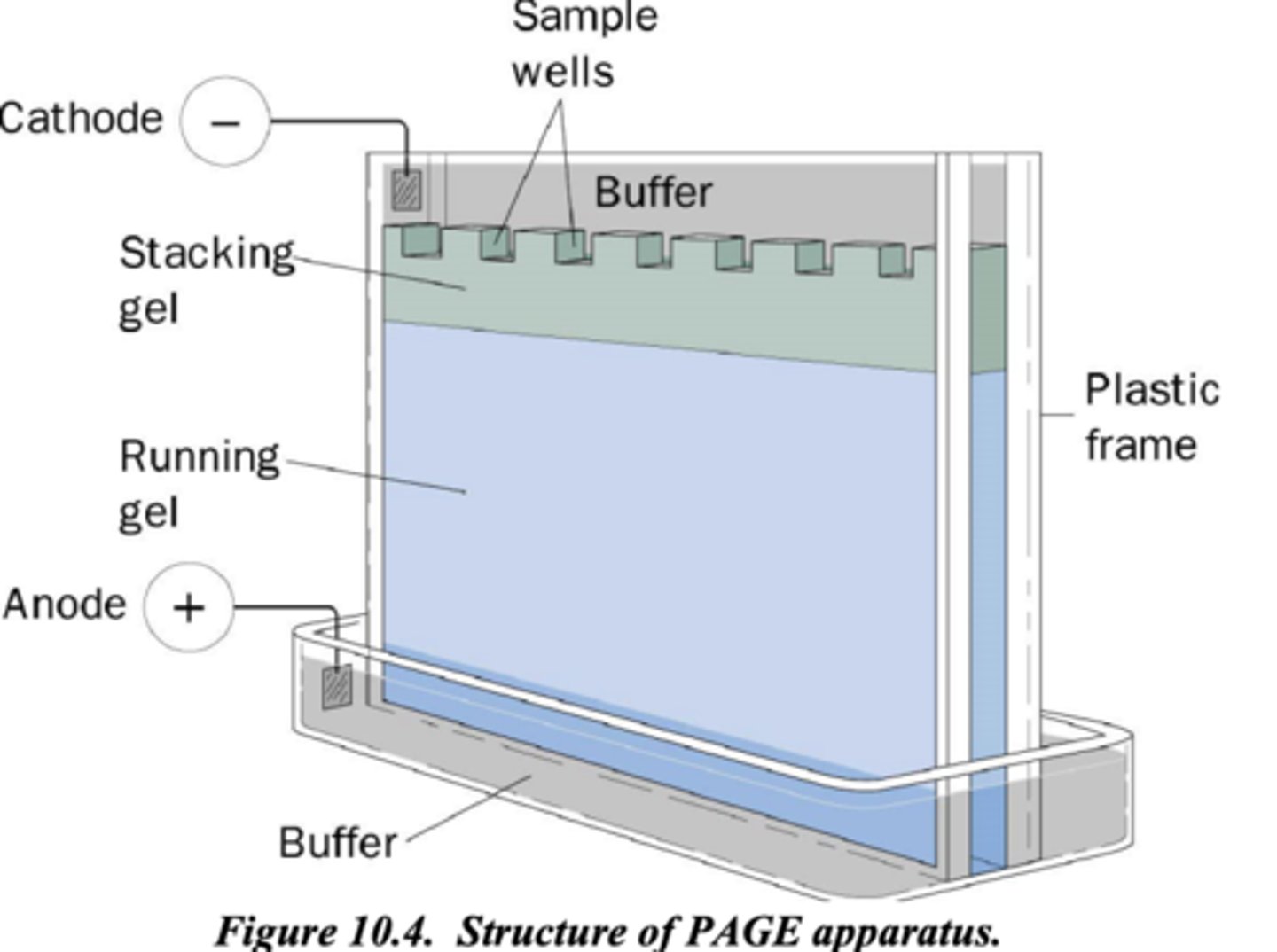
electrical current in gel electrophoresis: cathode, anode, buffer
-cathode (-) contacts aqueous buffer covering sample wells
-anode (+) contacts separate buffer at bottom
note both electrodes are capacitors with uniform E field btwn
-buffers are not connected, so is a single circuit
2 steps to extract proteins
1. weaken or break cell walls with physical or chemical procedures
2. lyse membranes with heat and SDS
SDS-PAGE, how it works, speed of separation depends on
-(sodium dodecyl sulfate PAGE)
-separates proteins extracted from live yeast
-speed of separation varies according to protein length (smaller go faster)
SDS
-ionic detergent that has strong negative charge at one end which forms electrostatic bonds with positive areas of protein being boiled (making it net negative), and has long linear hydrocarbon which straightens protein
-remains stably attached
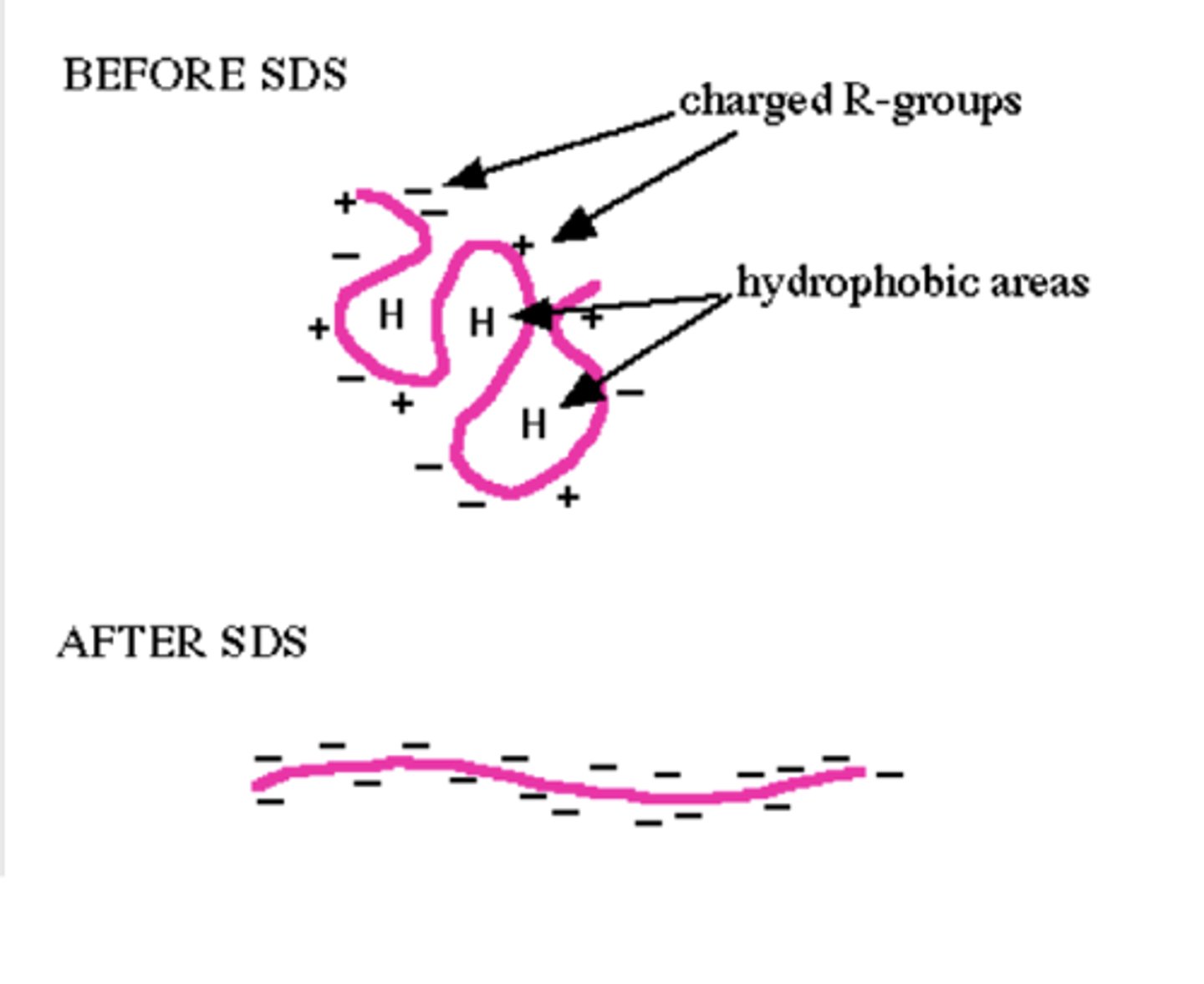
2-ME (2-mercaptoethanol)
-reduces disulfide bridges to get rid of 4º/3º structure
3 things that must happen to a protein for PAGE to work
-separate 4º structures into 3º
-break all disulfide bonds
-linearize proteins
Laemmli buffer, 5 things it contains
-what yeast lysate is boiled in
-tris buffer (pH 6.8)
-glycerol to increase density of sample for loading
-SDS, 2-ME (denaturing agents)
-bromophenol blue tracking dye
bromophenol blue tracking dye: size, dye front
-very small molecule (few AAs) so it moves ahead of all protein samples
-dye front can be seen moving down gel so you know when to stop running it
protein standard
-run in same gel as samples to allow for estimates of protein masses in kD
coomassie brilliant blue, why use it, acid and base color
-non-covalently binds proteins in gel since without stain proteins are invisible
-confirms presence of proteins in lysate run through SDS PAGE before doing blotting and Ab staining
-red if acidic (not bound to protein), blue if basic (bound to protein)
blotting, why do this, how it works, 2 membranes
-electrophoretically transferring molecules from gel to membrane
-makes proteins accessible for testing (Ab staining); inaccessible in gel
-molecules move through and out of gel to be trapped on membrane
-nitrocellulose paper (NCP) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
transfer buffer
-used in blotting chamber for protein transfer
-similar to SDS PAGE electrode buffer, with no SDS and has methanol added to help pros bind to mem
absorbance, standard curves
-absorbance (A): net amount of light that reaches spec sensor after passing through air, container, and sample
-standard curve: get a of series of BSA solutions with known conc to give relationship between A and pro conc for a particular spec
bradford assay, reagent
-assay: way to estimate conc of pros in solution, used to generate standard curve
-bradford reagent: has coomassie brilliant blue to bind proteins and change color for spec to measure at A595
formula for standard curve
A595 = m (pro conc) + b
immunostaining, indirect immunostaining
-antibodies used as detectors to identify molecules or proteins
-indirect immunostaining: bind 1º Ab to immobilized pros, 2º Ab binds to 1º
primary and secondary Ab
-1º: bind to antigen and stays through washing procedure (pro) (anti-TAP rabbit IgG)
-2º: bind to 1º Ab and stays through washing, have covalently attached molecule for visualization (radioactive, fluorescent, chemiluminescent, enz) (anti-rabbit goat IgG)
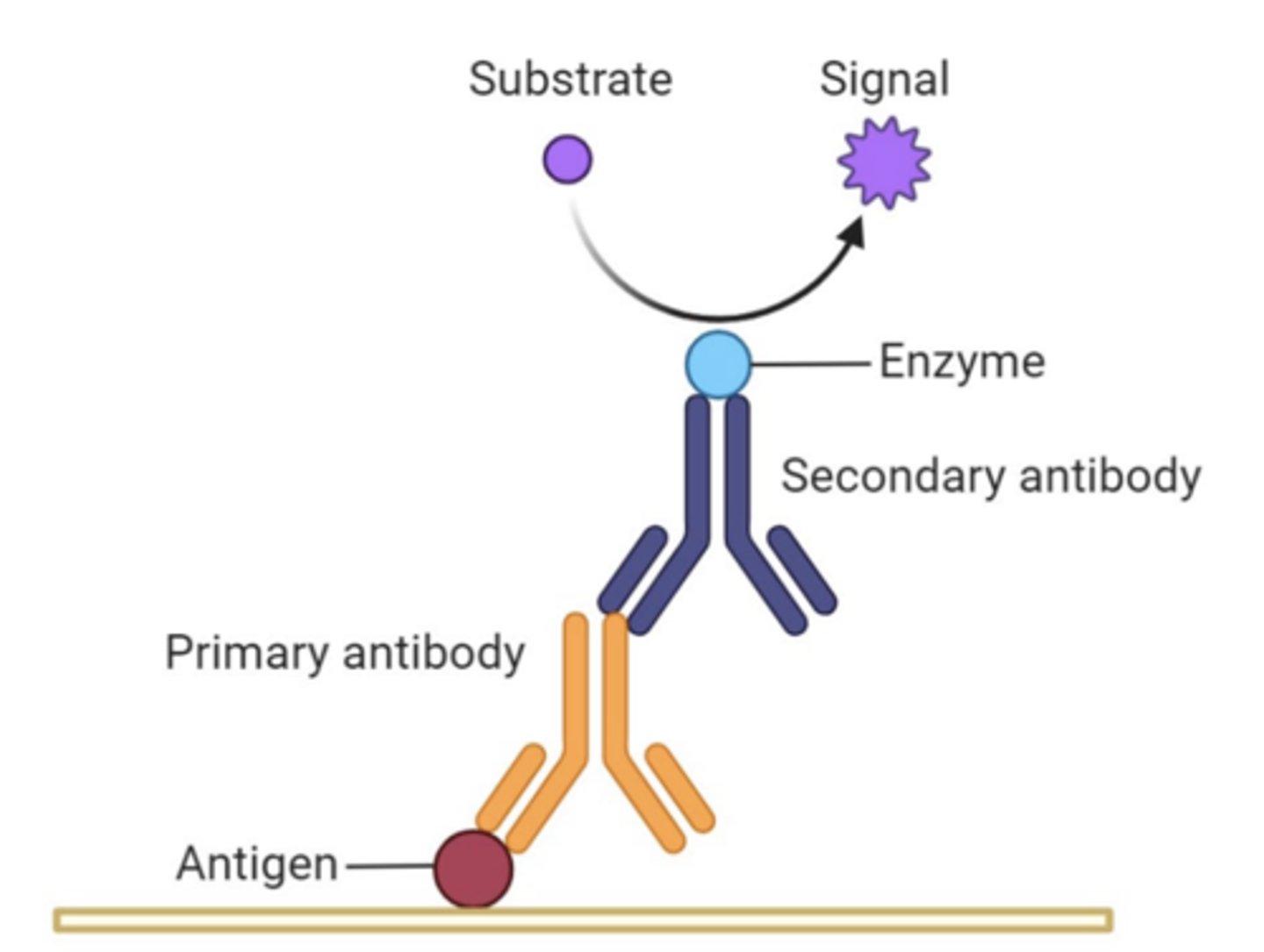
horseradish peroxidase (HRP), tetramethyl benzidine (TMB)
-HRP: enzyme attached to 2º Ab
-TMB: substrate for HRP, reaction results in blue precipitate that sinks into membrane to mark location of 2º Ab
blocking agent
-prevents Ab from binding to membrane so they bind to targets
-BSA used