neuroanat exam 1 review
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
old quiz questions, ta review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
How many pairs of spinal nerves do humans have?
31
Which format shows the soft tissue as relatively hypointense compared to cerebral spinal fluid?
MRI-T2
Which of the following provide myelin in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann cells
Which is the dividing groove between the primary motor gyrus and the primary somatosensory gyrus?
central sulcus
List the divisions of the spinal cord from caudal to rostral.
Coccygeal, sacral, lumbar, thoracic, cervical
Which imaging technique would best highlight a skull fracture?
CT-bone window
Which of the following terms is used to describe the location of gray matter in the brain?
Peripherally
Which lobe would be represented in the bottom left corner of an axial image of the brain?
The patient’s right occipital lobe
Temporal cortex is ___ to the lateral fissure
inferior
What neurodiagnostic procedure is used to examine the details of cerebral blood vessels with contrast dyes?
Angiography
In which of these images would CSF appear as bright white? CT, T1 MRI, T2 MRI, PET
T2 MRI
A surgeon removes the skull cap and notes that the arachnoid granulations are scarred and non-functioning. Which condition might the patient have been exhibiting?
Communicating hydrocephalus, epidural hematoma, noncommunicating hydrocephalus, multiple sclerosis
Communicating hydrocephalus
Which of these conditions would be caused by a tear in the middle meningeal artery?
subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, or epidural hematoma
epidural hematoma
A patient develops a tumor in the medial dorsal column. Which body part is most likely to be affected?
arms, face, legs, hearing
legs
A patient shows damage to his ventral horn of the spinal cord. What would he show?
inability to move, inability to sense light tough, inability to sense vibrations, inability to show emotion
inability to move
Which fossa contains the foramen magnum?
anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa, posterior cranial fossa, or lateral cranial fossa
posterior cranial fossa
Which sheet of matter separates the cerebellum from the rest of the brain?
falx cerebri, foramen magnum, tentorium cerebelli, tentorium cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
The ______ connects the lateral ventricle to the 3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct, central canal, interventricular foramen, lateral aperture
interventricular foramen
Which vessel is located midline in the spinal cord?
anterior, posterior, lateral, or central
anterior
Occlusion of the posterior spinal artery will not affect:
the dorsal column, the ventral corticospinal tract, the tectospinal tract, or the substantia gelatinosa
the ventral corticospinal tract
The ______ is responsible for pain/temperature sensation while _____ is responsible for vibration perception.
a) spinothalamic, dorsal columns
b) corticospinal, dorsal columns
c) spinothalamic, Clarke’s column
d) corticospinal, Clarke’s column
spinothalamic, dorsal column
The motor tract adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract is the
rubrospinal, tectospinal, reticulospinal, or vestibulospinal
rubrospinal
Which tract results in ipsilateral innervation after decussating twice?
dorsal spinocerebellar, ventral spinocerebellar, lateral spinothalamic, or ventral spinothalamic
ventral spinocerebellar
The spinothalamic tract is responsible for information regarding
movement of the shoulders and neck, movement of the trunk, mechanosensation, or pain and temperature
pain and temperature
What is responsible for providing unconscious proprioceptive information?
spinocerebellar, spinothalamic, cerebrospinal, or corticobulbar
spinocerebellar
Neurons carrying pain and temperature information decussate ______, while neurons carrying voluntary motor information decussate ________.
A. In the pyramid of the medulla / immediately in the spinal cord
B. This path does not decussate / in the pyramid of the medulla
C. Immediately in the spinal cord / in the pyramid of the medulla
D. In the pyramid of the medulla / this path does not decussate
C. Immediately in the spinal cord / in the pyramid of the medulla
17. The parietal lobe is located ______ to the occipital lobe
A. caudal
B. Rostral
C. Lateral
D. Inferior
B. Rostral
18. Which region does NOT develop from the diencephalon?
A. Thalamus
B. Hypothalamus
C. Cerebellum
D. Epithalamus
C. Cerebellum
19. In what order does somatic motor information travel?
A. Primary motor cortex -> ventral horn -> pyramidal decussation
B. Ventral horn -> pyramidal decussation -> primary motor cortex
C. Primary motor cortex -> pyramidal decussation -> ventral horn
D. Primary motor cortex -> thalamus -> ventral horn
C. Primary motor cortex -> pyramidal decussation -> ventral horn
20. The spinal cord’s _______ is lined with ependymal cells and filled with CSF; it opens upward into the inferior fourth ventricle.
A. Anterior median fissure
B. Central Canal
C. Posterior median sulcus
D. None of the above
B. Central Canal
21. The ______ is a thin connective tissue membrane that covers the brain surface and extends into sulci and fissures and around blood vessels throughout the brain
A. Dura
B. Pia
C. Subrarachnoid
D. Arachnoid
B. Pia
22. Which image technique is best to view brain tumors?
A. PET
B. MRI
C. CT
D. Angiography
B. MRI
23. An elderly man suffers a fall and hits his head on the pavement. His wife hurries him to the ER. Urgent, quick imaging is needed to see what damage may have been done to his brain. Which imaging modality would be best used in this situation?
A. MRI
B. CT
C.T2 MRI
D. PET
B. CT
24. The middle cranial fossa contains what lobe?
A. Parietal
B. Occipital
C. Temporal
D. Frontal
C. Temporal
25. Which means “toward the tailbone”?
A. Ventral
B. Rostral
C. Medial
D. Caudal
D. Caudal
26. The three small foramina in the 4th ventricle is where
A. CSF Exits
B. CSF is produced
C. Afferent fibers from the trigeminal nerve enter the brainstem
D. The arachnoid granulations are located
A. CSF Exits
27. A patient has a lesion of the right lateral spinothalamic tract at T9. What impairment would you expect this to result in?
A. Absence of vibration sensation on the left side of the body generalized below T9
B. Absence of pain and temperature sensation on the left side of the body generalized above T9
C. Absence of pain and temperature sensation on the right side of the body generalized below T9
D. Absence of pain and temperature sensation on the left side of the body generalized below T9
D. Absence of pain and temperature sensation on the left side of the body generalized below T9
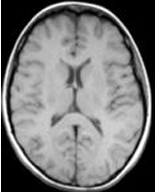
28. The white “ring” seen around the brain in MRI imaging is
A. Bone
B. CSF
C. Fat
D. Air
C. Fat
29. There is a tumor at the connection point between the lateral and third ventricles, the interventricular foramen. What could be expected?
A. Noncommunicating hydrocephalus
B. Subarachnoid obstruction
C. Dilation of ventricles
D. Communicating hydrocephalus
E. A & C
F. B & D
E. A & C
30. Damage to the right fasciculus gracilis at T7 will lead to:
A. Loss of position and vibration sensation in the right leg
B. Loss of position and vibration sensation in the left leg
C. Loss of position and vibration sensation in right arm
D. Loss of position and vibration sensation in left arm
A. Loss of position and vibration sensation in the right leg
31. Which of the following is NOT a negative manifestation?
A. Parkinson’s
B. Multiple Sclerosis
C. Seizures
D. Hemiparesis
C. Seizures
32. What produces CSF in the brain?
A.Arachnoid granulations
B.Choroid plexus
C.Fibroblasts
D.Leptomeningeal layer
B.Choroid plexus
33. Mary presents with a loss of motor control on the left side. She exhibits a babinski sign and has increased deep tendon reflexes in the left lower extremity. The lesioned spinal cord structure is the:
A. Left UMN lateral corticospinal tract
B. Right UMN lateral corticospinal tract
C. Right fasciculus gracilis
D. Right spinocerebellar tract
B. Right UMN lateral corticospinal tract
34. A 65 yo walks into the clinic to see his doctor for problems in his gait. After performing a basic neurological exam and performing a scan, the doctor confirms that the patient is suffering from a lesion to Clarke’s column. Which of the following best supports the doctor’s diagnosis?
A.Loss of unconscious proprioception
B.Loss of conscious proprioception
C.Bilateral loss of strength in the patent’s legs
D.None of these
A.Loss of unconscious proprioception
35. The rubrospinal tract originates in the
A. Medulla
B. Red nucleus
C. Raphe nuclei
D. Reticular formation
B. Red nucleus
36. Which disorder is most likely to have multifocal pathology?
A.Multiple sclerosis
B.Brain tumor
C.Head trauma
D. Optic neuritis
A.Multiple sclerosis
37. Where do the 2nd order neurons in the spinothalamic tract terminate?
A.Thalamus
B.Somatosensory Cortex
C.Immediately in the spinal cord
D.Pyramids
A.Thalamus
38. Which axon would transmit an action potential the fastest?
A. Skinny Unmyelinated Axon
B. Thick Unmyelinated Axon
C. Skinny Myelinated Axon
D. Thick Myelinated Axon
D. Thick Myelinated Axon
39. Which sheet of matter separates the two cerebral hemispheres?
A. Falx Cerebri
B. Falx Cerebelli
C. Tentorium Cerebelli
D. Tentorium Cerebri
A. Falx Cerebri
40. A white matter lesion will only produce negative signs and symptoms
A. True
B. False
A. True