Artifacts
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
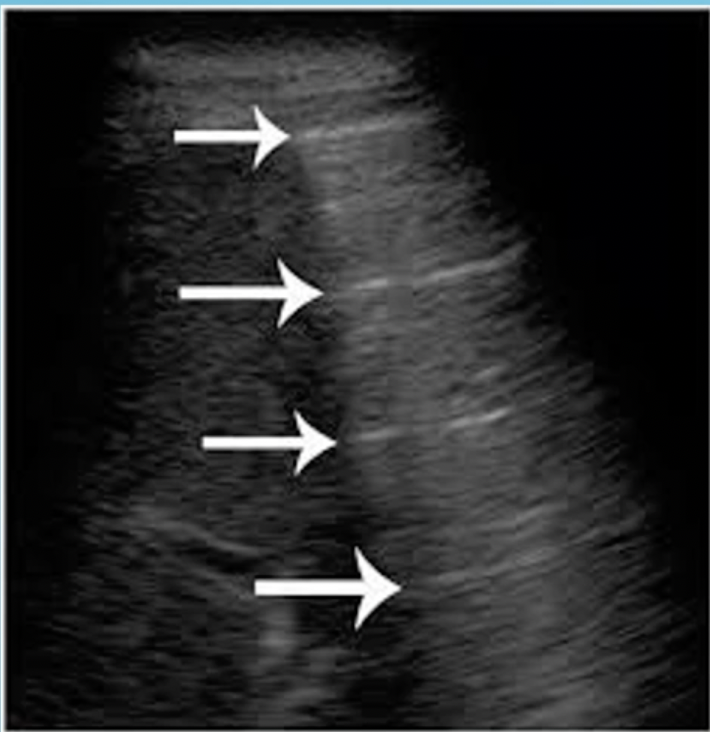
What artifact is this?
Reberferations
What assumption does reverberation violate?
sound travels directly from the reflector and back
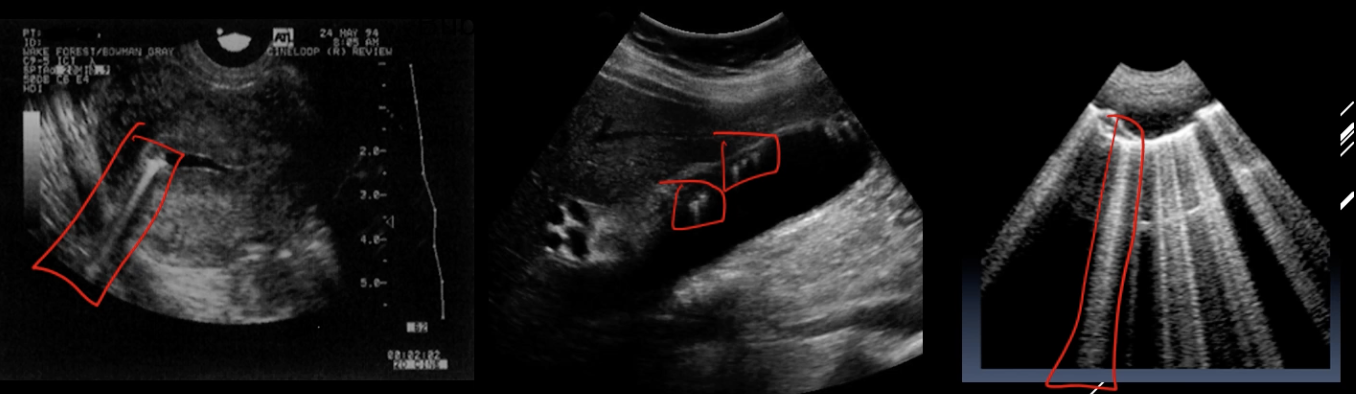
What artifact is this
comet tail/ring down
What is a comet tail/ring down
a merged from of reverberation and a solid hyperachoic line that appears behind a strong reflector in ultrasound imaging.
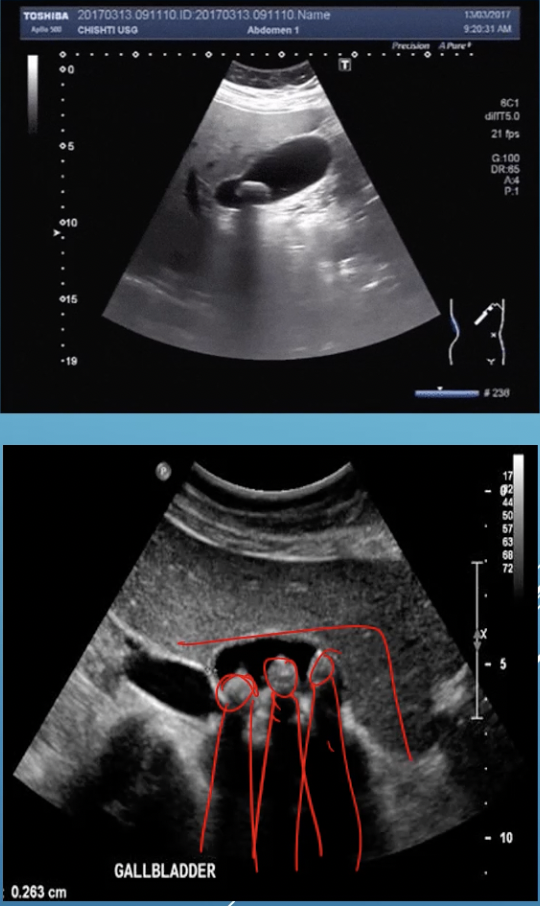
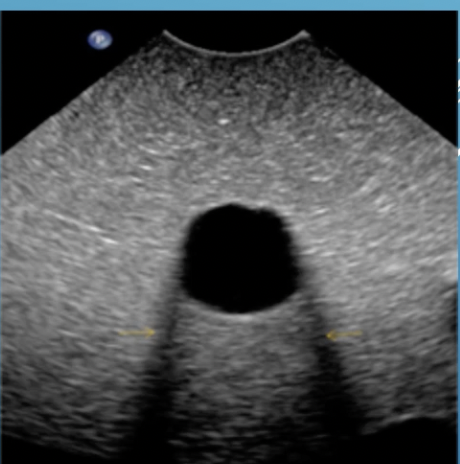
What artifact is this
shadow
What is shadow artifact
anechoic or hypoechoic. high attenuation or scatter, and obscures digital image
Shadowing violates the assumption that
the reflection intensity is related to the tissues property
Edge shadow is also called
shadow by refraction
What artifact is this
edge shadowing
Edge shadowing is
The refraction at the edge of a curved structure. The beam is diverging and loses intensity
Enhancement artifact appears
hyperachoic
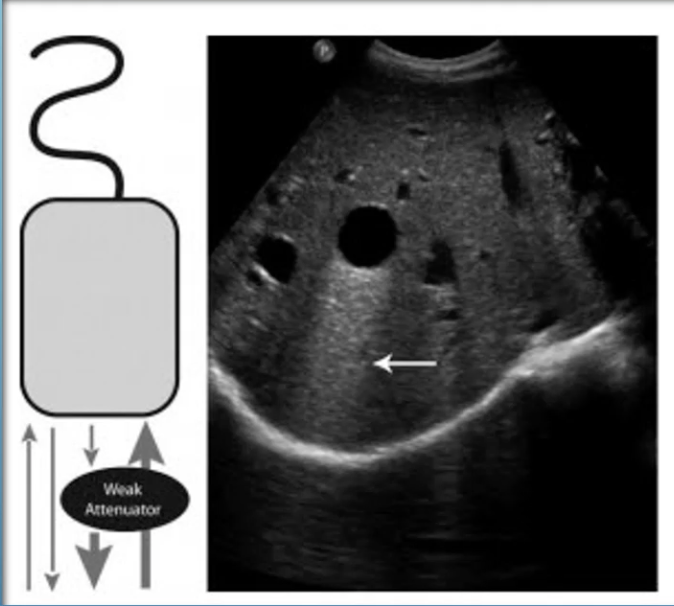
What artifact is this
enhancement
Enhancement artifact happens
Posterior to structures with low attentiations
Enhancement violates the assumption that
the intensity of the reflection is related to the tissue properties
focal enhancement looks like
a TGC error
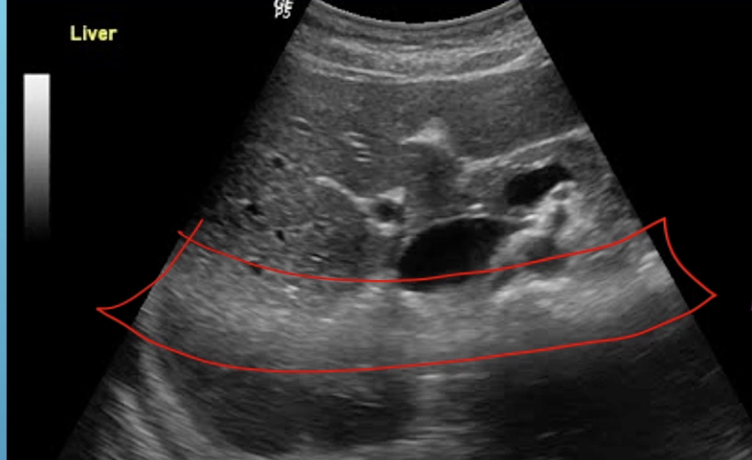
What artifact is this
focal enhancement
What assumption does focal enhancement violate
the intensity of the reflection is related to the tissue properties
Mirror artifact is
a duplicate of the real anatomy and will ALWAYS be deeper than the real structure
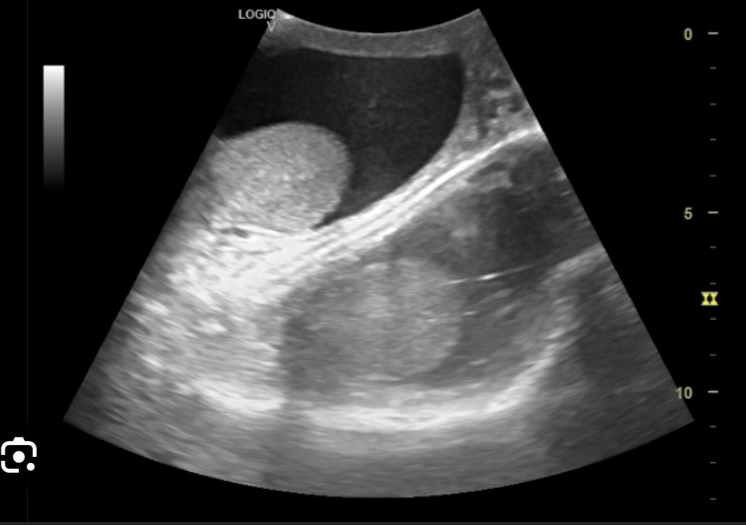
What artifact is this
mirror
Mirror artifacts are at an _________ distance from the reflector
equal
The mirror artifact violates the assumptions that
sound travels in a straight line AND sound travels directly to the reflector and back
mirror artifact can also appear in our
color and spectral doppler analysis
Mirror artifact on doppler is called
cross talk
Propagation speed artifact is when
the prop speed is greater than 1.54 km/sec and the go-return-time is invalid
When the PS is > 1.54 km/sec
it makes the reflector shallower
When the PS is < 1.54 km/sec
it makes the reflector deeper
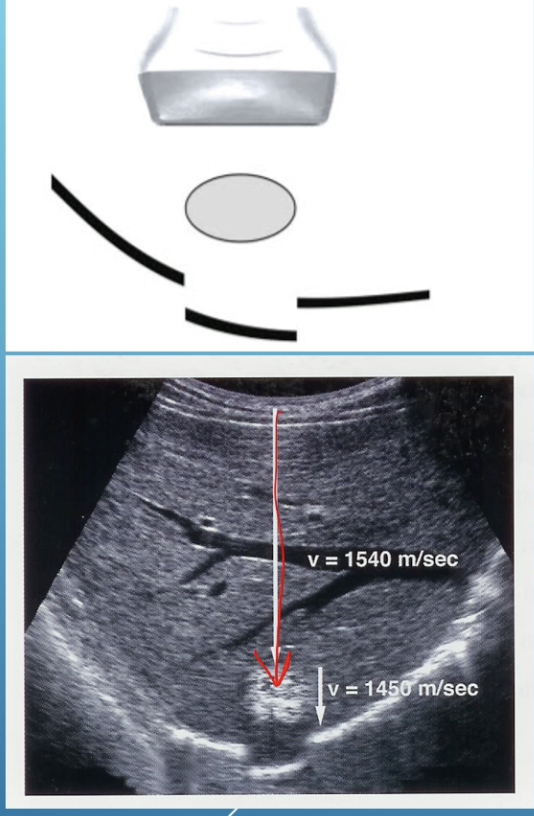
What artifact is this
Propagation speed
PS error is also referred to as
range error artifact
PS artifact violates the assumption that
sound travels at 1,540 m/sec
side lobe and grading lobe artifacts are
weak echos that are not in the main sound beam are put into the sound beam
Side lobe/ grading lobe artifacts violate the assumption that
Reflections arise only from structures in the main beam axis
subdicing will reduce
grating lobes by making it into smaller pieces
apodization will reduce
grating lobes by adjusting the voltages so the middle voltages are excited
Side lobes are created by _______ element transducers
single
Grating lobes are created by _________ element transducers
array
Refraction artifact
sound changes direction with oblique incidence and change in PS
like mirror is makes another copy but at he same depth
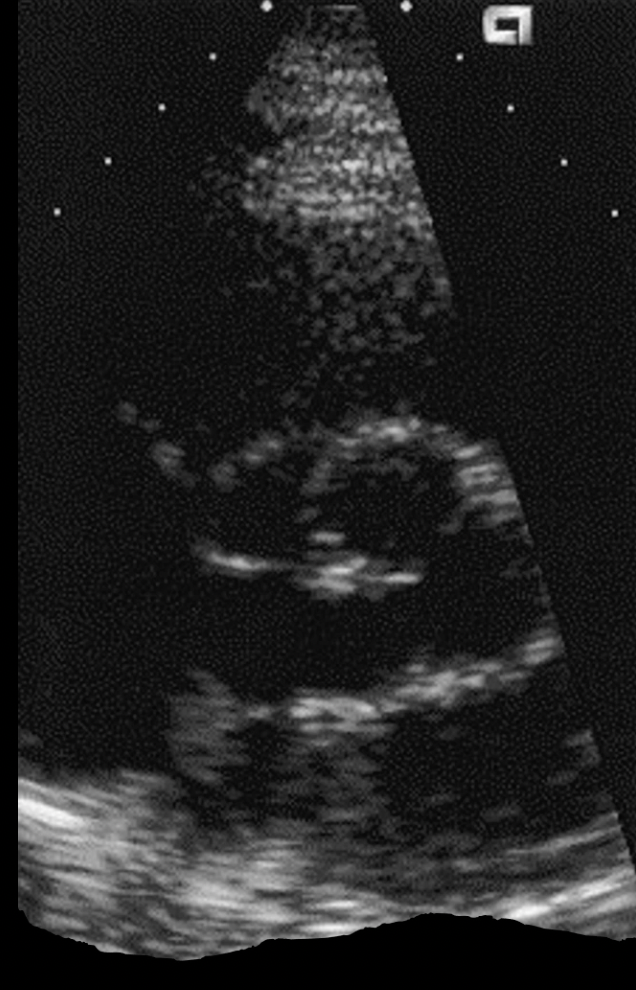
What artifact is this
refraction
Refraction degrades
lateral resolution
Refraction violates the assumption that
sound travels in a straight line
slice thickness artifact is the
height of the sound beam and the US pulls n reflections above and below sound beam and puts them in the beams main axis
happens in hallow structure like the bladder
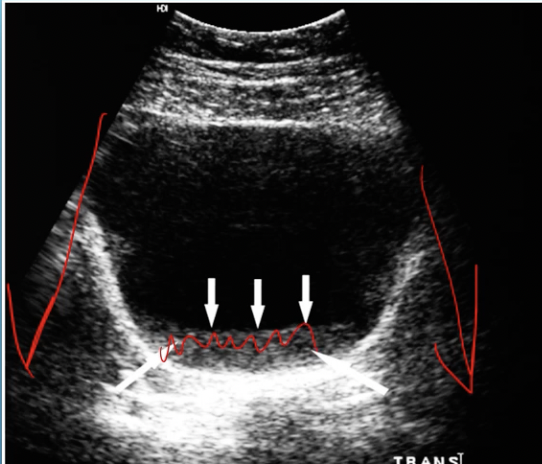
What artifact is this
slice thickness
Slice thickness violates the assumption that
the imaging plane is always extremely thin
Lateral Resolution artifacts
ability to identify two structures side by side
will lump together structures and make it look like one
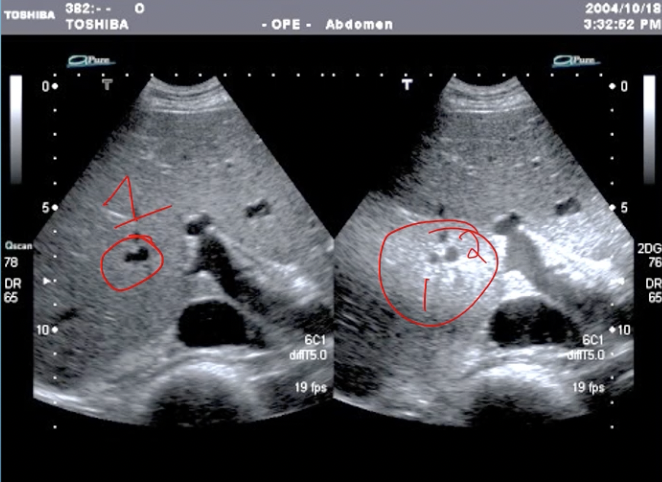
What artifact is this
lateral resolution
How to adjust lateral resolution
adjust focus to decrease beam width bc structures need ot be further apart than the beam width
axial resolutions is
the ability to identify structures that are parallel or on top of each other (front and back)
SPL/2
high freq transducers have better
axial resolution
Multi-path artifact
path reflects of 2nd structure
reflects off two structures
Multi-path artifact violates the assumption
that a pulse travels directly to a structure and back
Curved and oblique reflector artifacts is similar to the
multi path artifact
hits curved structure at oblique angle and bounces of so takes longer to get to transducer
Temporal Resolution artifact
slow shutter speed
cant accurately image structures in motions
low frame rate = low TR
Spatial resolution artifact
Overall detail
high line density = increased SR
greater pixel density = greater SR
Range ambiguity artifact
reflection by a very deep reflector that is beyond the depth of the image
The reflection from the first pulse reaches the reflector after the plus is emitted so the system assumes the reflection is from the second pulse so the echo is placed to close or shallow
Acoustic speckle artifact
low level echos that are not valuable to image
affect detial resolution
Electronic interference
disturbance from other electrical equipment
causes moving bands
degrades image quality
clutter or noise artifact
low level echos we don’t need
can be from side lobe or thickness artifact