Last A&P Unit Exam
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
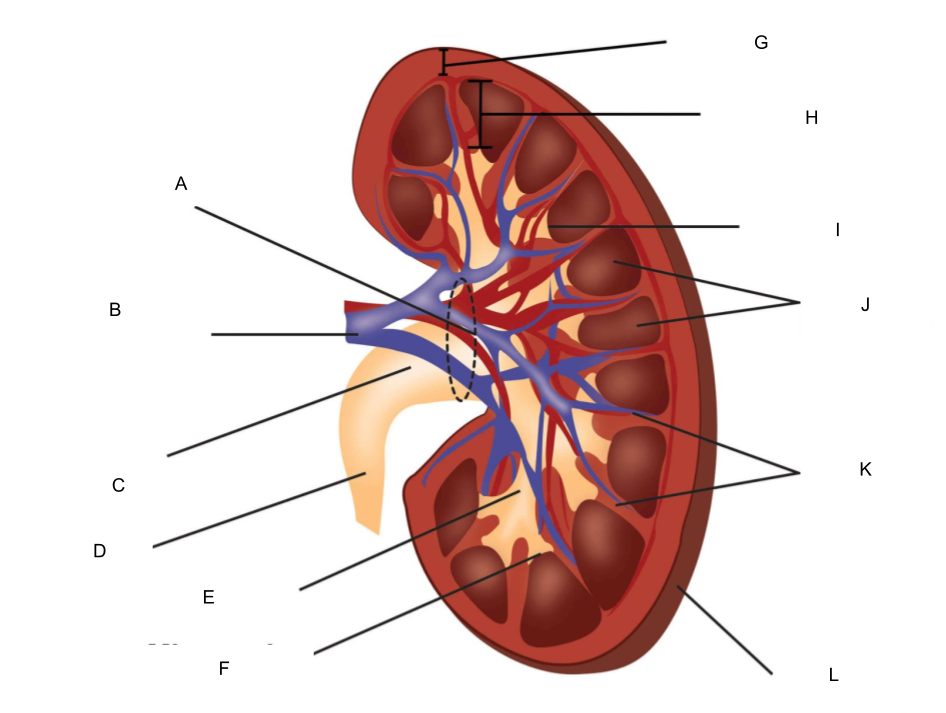
What is A?
hilum
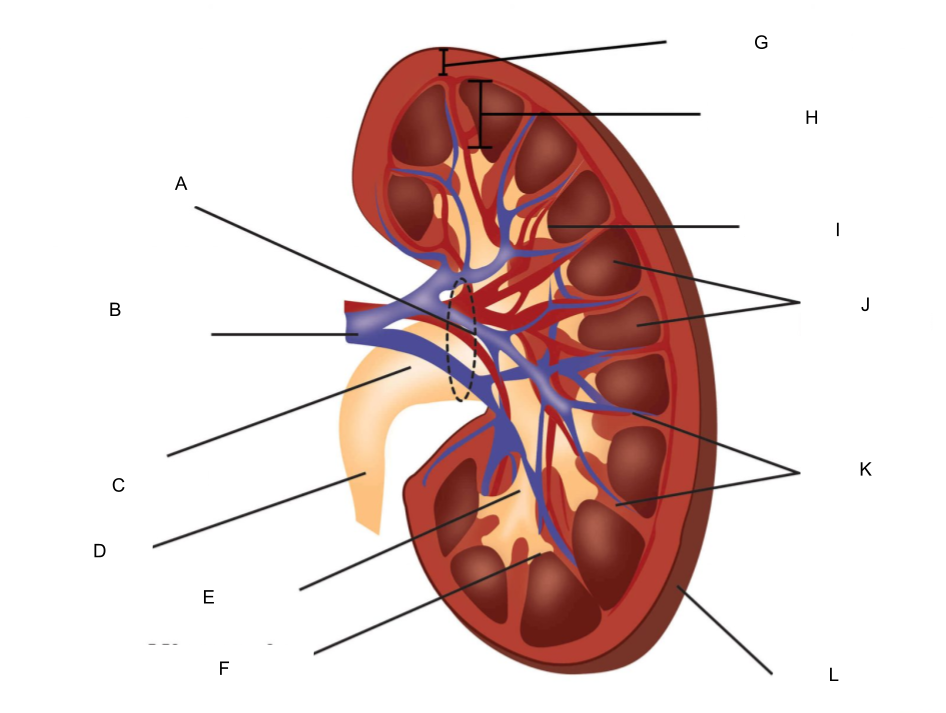
What is B?
renal artery and renal vein
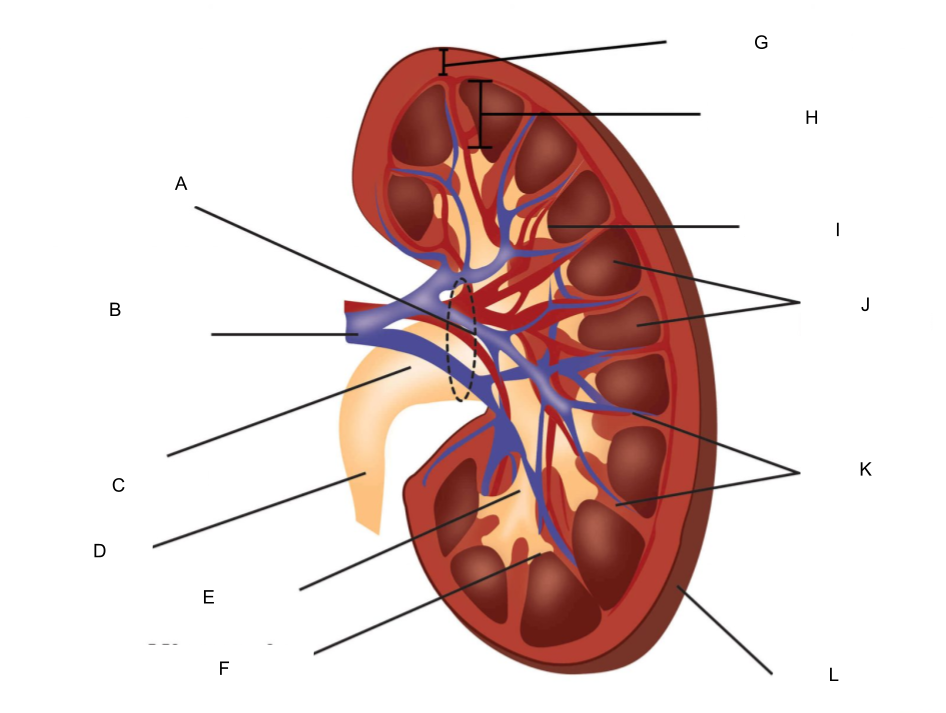
What is C?
renal pelvis
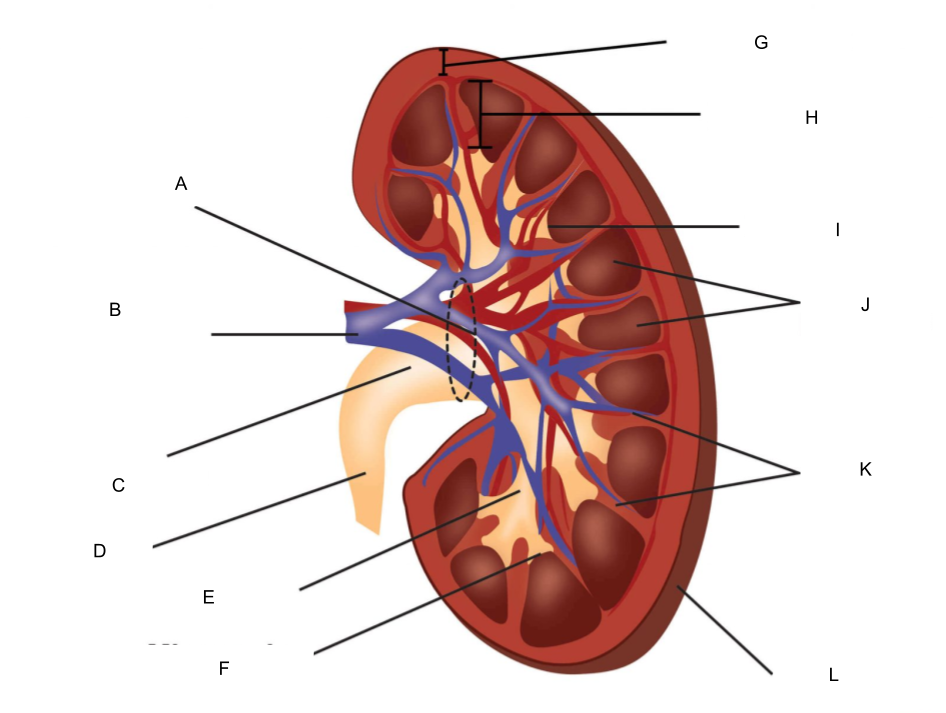
What is D?
ureter
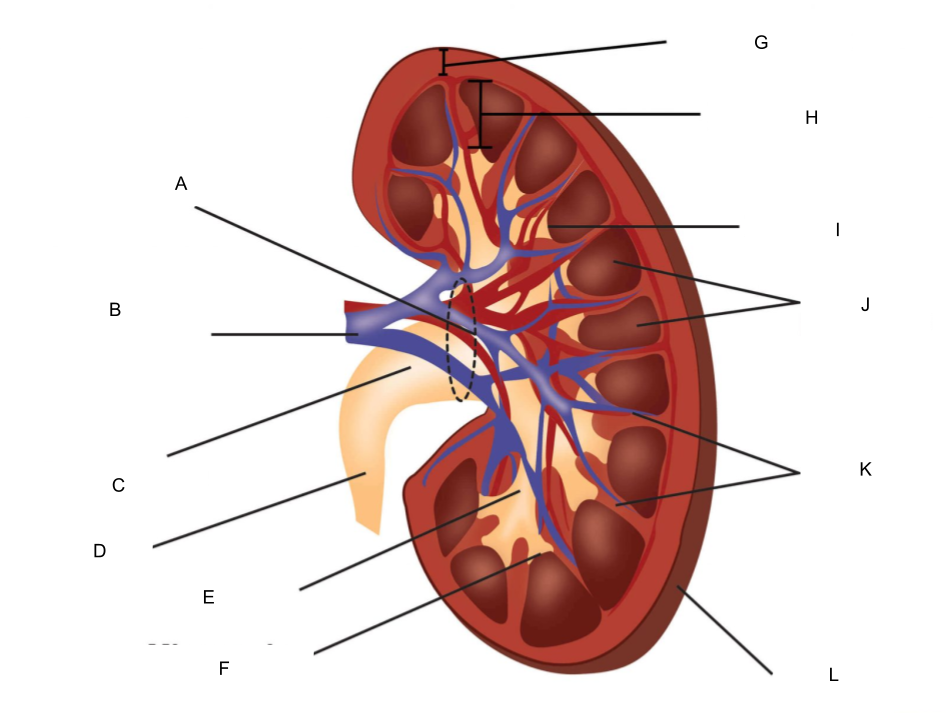
What is E?
major calyx
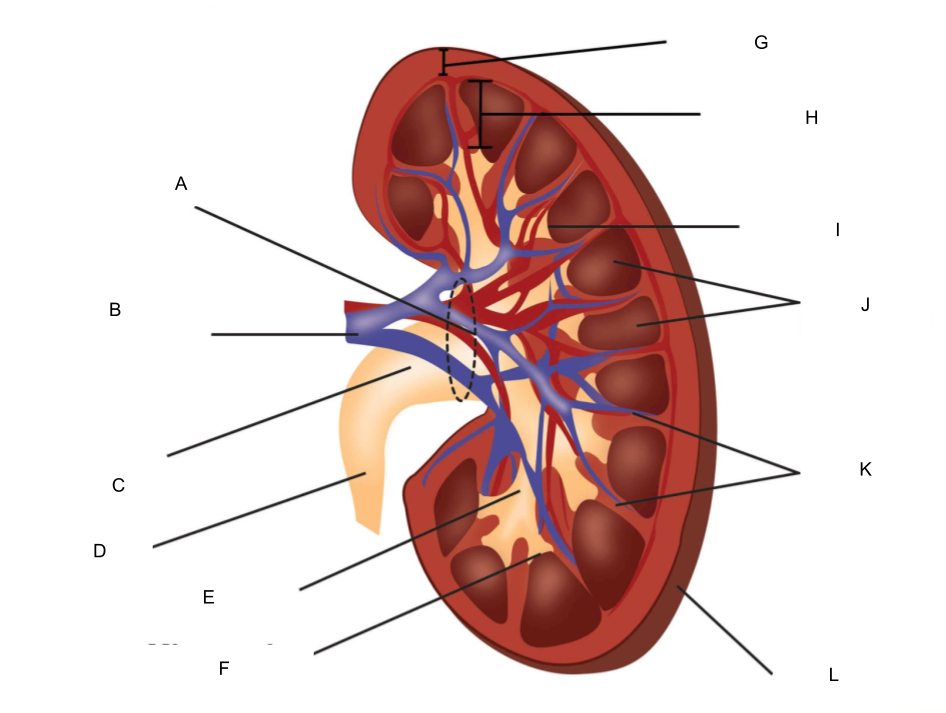
What is F?
minor calyx
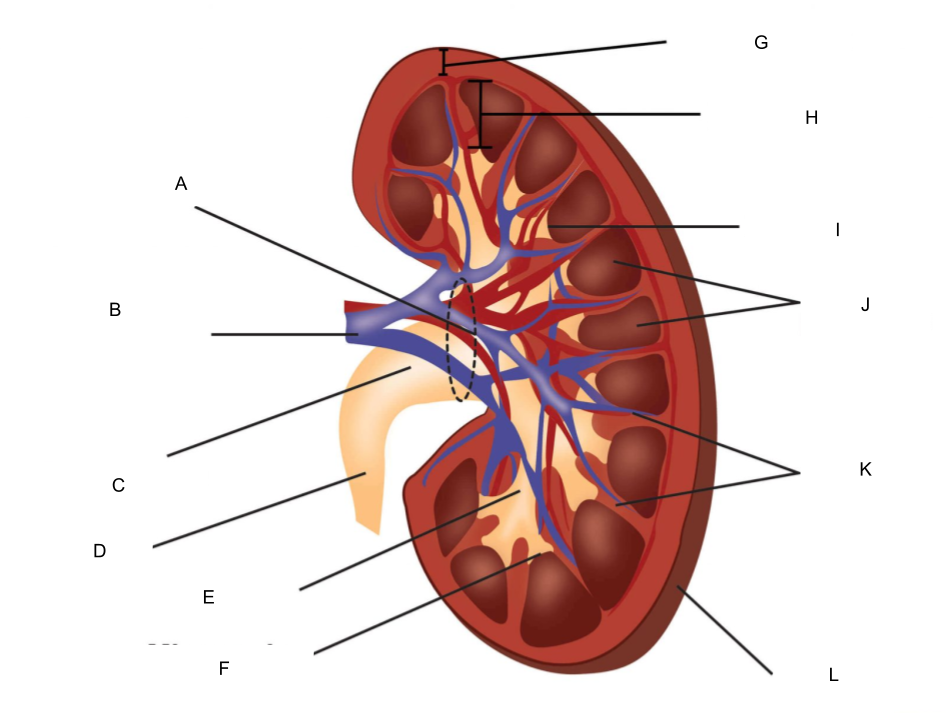
What is G?
renal cortex
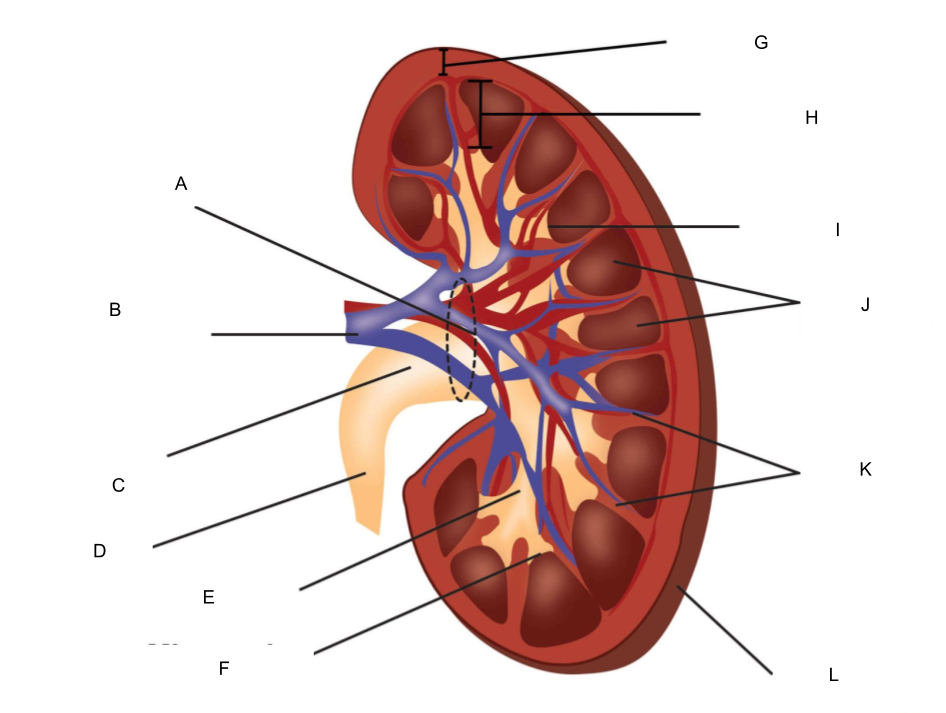
What is H?
renal medulla
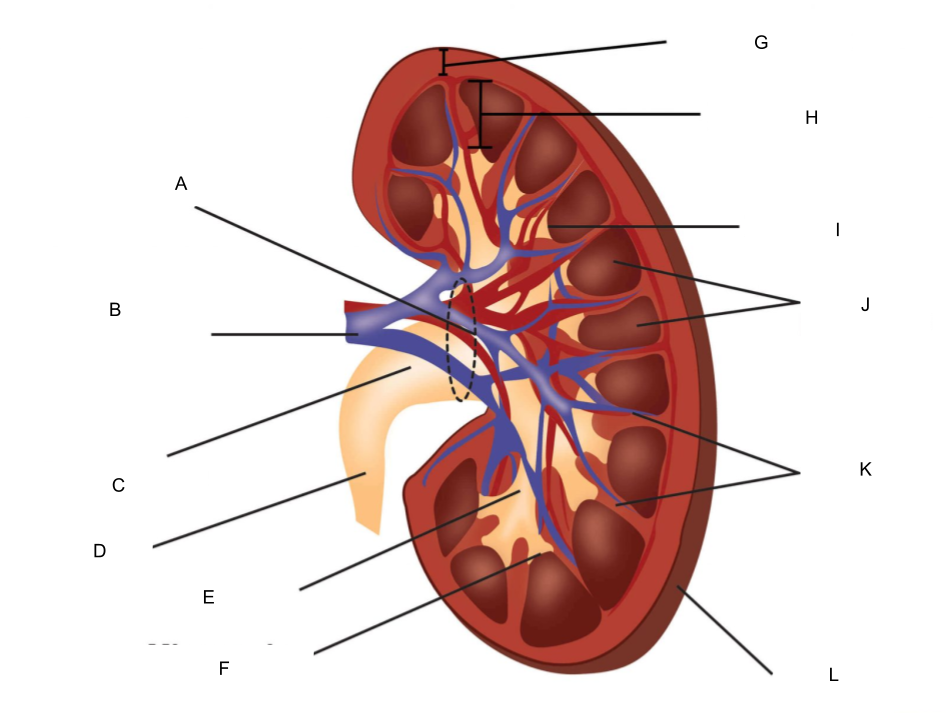
What is I?
renal papilla
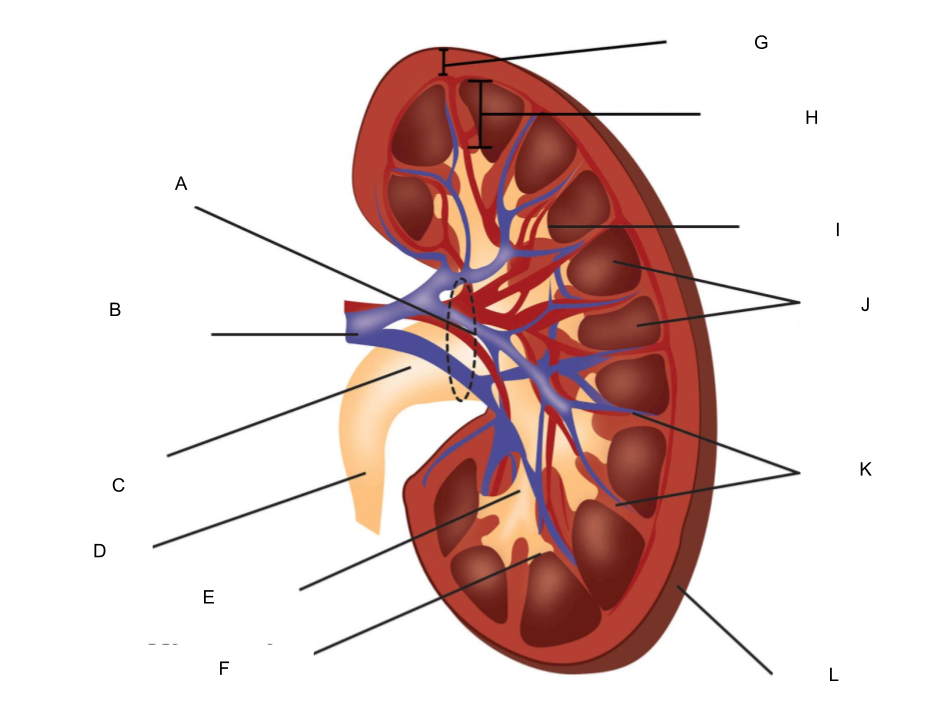
What is J?
renal pyramids
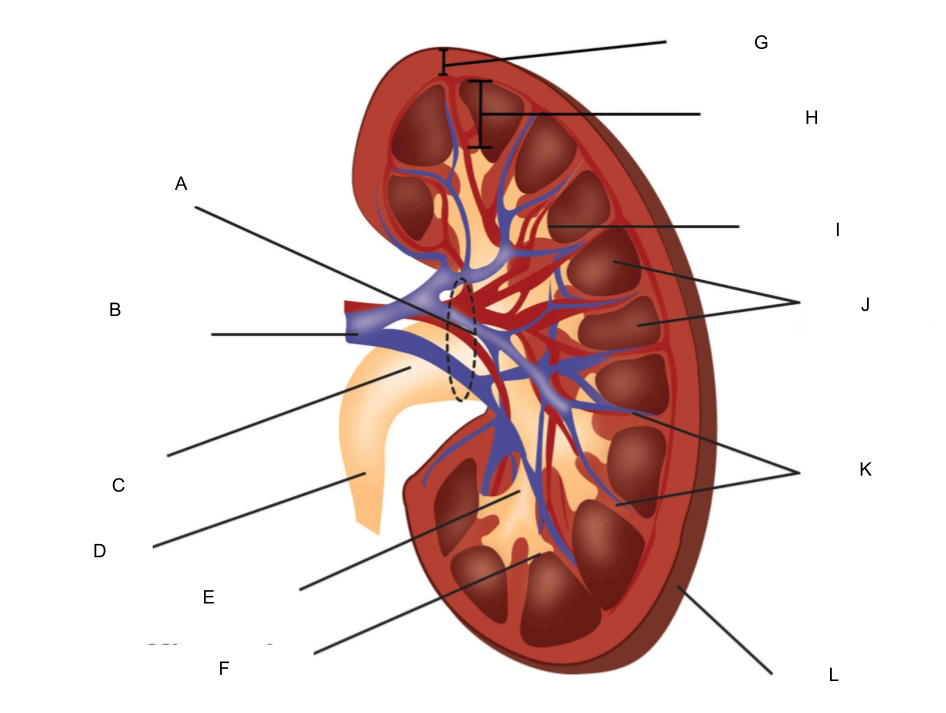
What is K?
renal columns
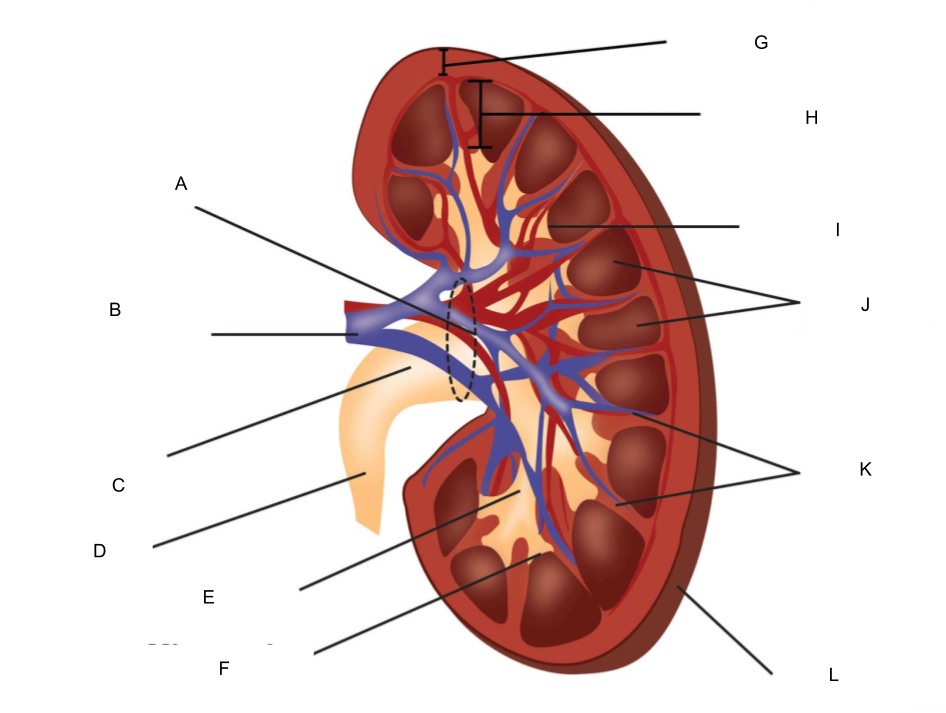
What is L?
fibrous capsule
What is glycolysis’ location?
cytoplasm
What is glycolysis’ reactant?
glucose (6C)
What is glycolysis product?
2x pyruvate + 2ATP (3C)
What is glycolysis’ function?
break glucose
What is bridge’s location?
cytoplasm/mitochondria
What is bridge’s reactant?
2 pyruvate
What is bridge’s product?
2x acetyl CoA (2C) + 2CO2 + NADH
What is bridge’s function?
removing a carbon, make a 2C (acetyl CoA), make a 3C (pyruvate)
What is Kreb’s cycle’s location?
matrix of mitochondria
What is Kreb’s cycle’s reactant?
2x Acetyl CoA (2C)
What is Kreb’s cycle’s product?
4 x CO2, NADH + FADH2
What is Kreb’s cycle’s function?
transfer high energy from C-H bonds to NAD+->NADH, FADH->FADH2
What is electron transport chain +oxidative phosphorylation’s location?
cristae of mitochondria
What is electron transport chain +oxidative phosphorylation’s function?
harness energy to pump H+ (protons) to generate a gradient, use the proton gradient to synthesize ADP+Pi->ATP
What side of the electron transport chain + oxidative phosphorylation are the hydrogen atoms on?
intermembane space
What side of the electron transport chain + oxidative phosphorylation is the ATP on?
matrix of mitochondria
What do all epithelial cells have?
basement membrane
How is surface area of intestines increase?
circular folds, villi, and microvilli
What are circular folds?
mucosa and submucosa
What are villi?
projections of mucosa with capillary and lymph networks
What are microvilli?
cytoplasmic extension of columnar cells
What is the main role of the small intestine?
digestion and absorption of nutrients
What is the main role of the large intestine?
absorb water and electrolytes from undigested food material to form feces for defecation
What are the parts of the small intestine?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
What are the parts of the large intestine?
cecum, colon, rectum, mucous producing crypts, teniae coli
What are the four names of the sphincters?
pyloric, esophageal, ileocecal, anal
What is the pyloric sphincter?
thick ring of smooth mucles
What does the esophageal sphincter do?
regulate movement of food
What does the ileocecal sphincter do?
ensures directionality to food movement
What does the anal sphincter do?
elimination of feces/defecation
What are gastric pits?
openings of gastric glands
What are the cells of gastric pits?
surface mucous, mucous neck, parietal, endocrine, chief
What do surface mucous cells secrete?
mucous
What do mucous neck cells secrete?
mucous
What do parietal cells secrete?
HCI
What do endocrine cells secrete?
regulatory hormones
What do chief cells secrete?
pepsinogen
What are the 2 main kinds of fermentation?
lactic acid and alcohol
Is lactic acid fermentation done by humans or yeast and most bacteria?
humans
Is alcohol fermentation done by humans or yeast and most bacteria?
yeast and most bacteria
What are the main points of the male reproductive system?
testicles, epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens, spermatic cord, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral gland, urethra, external genitalia, spermatogenesis
What are the main points of the female reproductive system?
ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, external genitalia, hymen, accessory glands, broad ligament, oogenesis
What do testicles do?
produce testosterone and sperm
What does the epididymis do?
matures, recycles, and transfers sperm
What does the ductus (vas) deferens do?
propels/stores sperm and fluid
What is the spermatic cord?
channel for blood vessels/nerves
What do the seminal vesicles do?
produce most of seminal fluid
What does the prostate do?
make prostatic fluid
What does the bulbourethral gland do?
neutralizes urinary acids
What is the urethra?
tube with prostatic, membranous, and spongy regions
What are a male’s external genitalia?
penis and scrotum
What is spermatogenesis, and does this happen to males or females?
testes->emission-ejaculation->semen, males
What do ovaries do?
produce immature female gametes, secrete estrogen and progesterone, and secrete inhibin
What do uterine tubes do?
connect ovaries and uterus
What does the uterus do?
protects, nourishes, removes wastes
What is the vagina?
a passageway
What are a female’s external genitalia?
clitoris, labia majora, labia minora
What does the hymen do and when is it broken?
blocks vagina, with first penetration
What are the accessory glands of the female reproductive system?
urethral glands, greater vestibular glands
What does the broad ligament do?
hold structures in place
What is oogenesis, and does this happen to males or females?
production of female gametes in ovaries, females
What are the processes of the digestive system?
mastication (chewing), deglutination (swallowing), food movement (peristalsis), secretions
What is mastication?
food broken does into smaller pieces by teeth when jaw moves
What are the phases of deglutination?
voluntary, pharyngeal, esophageal
What is the order of food movement in peristalsis?
esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, colon, defecation
What happens in the stomach during peristalsis?
chyme moves towards and through pyloric sphincter and bulkier food toward body of stomach
What happens in the small intestine during peristalsis?
chyme moves through ileocecal sphincter and is mixed
What happens in the large intestine during peristalsis?
produces feces and absorbs water
What happens in the colon during peristalsis?
conversion of the chyme to feces
What are the four areas of secretion?
oral cavity, stomach, intestines, emptied into duodenum
What is secreted in the oral cavity and why?
saliva to moisten and lubricate food
What is secreted in the stomach and why?
chyme to digest proteins and activate other enzymes
What is secreted in the intestines and where?
protease (mainly endo) and peptidase (endo or exo)
Glucose to ATP table: What happens to carbs?
polysaccharides->salivary amylase (mouth)->smaller polypeptides->pancreatic amylase->disaccharides (small intestine-lumen space)->disaccharidase->monosaccharides (small intestine-epithelial cells)
Glucose to ATP table: What happens to proteins?
polypeptides->pepsin (stomach)->smaller polypeptides->trypsin, chymotrypsin->carboxypeptidases->amino acids (small intestine-lumen space) or dipeptidases->amino acids (small intestine-epithelial cells)
Glucose to ATP table: What happens to nucleic acids?
DNA, RNA->nuclease->nucleotides (small intestine-lumen space)->neucleotidases->nucleotide->nucleosidases->nucleoside (small intestine-epithelial cells)
Glucose to ATP table: What happens to fats?
fat globules->bile salt (emulsifies)->lipase->glycerol, fatty acids (small intestine-lumen space)
On a 90’s food pyramid, what foods are considered best for you?
bread, cereal, rice and pasta at 6-11 servings
On a 90’s food pyramid, what foods are on the 2nd tier?
vegetables at 3-5 servings and fruit at 2-4 servings
On a 90’s food pyramid, what foods are on the 3rd tier?
milk, yogurt and cheese at 2-3 servings and meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs and nuts at 2-3 servings
On a 90’s food pyramid, what foods are considered the worst for you?
fats, oils and sweets used sparingly
On a scientific food pyramid, what is considered the best for you?
daily exercise and weight control
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are on the 2nd tier?
whole grain foods and plant oils (olive, canola, corn, sunflower, peanut and other vegetable oils) at most meals
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are on the 3rd tier?
vegetables in abundance and fruit at 2-3 servings
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are on the 4th tier?
nuts and legumes at 1-3 servings
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are on the 5th tier?
fish, poultry and eggs at 0-2 servings
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are on the 6th tier?
dairy or calcium supplement at 1-2 servings
On a scientific pyramid, what foods are considered the worst for you?
red meat and butter, and white rice, white bread, potatoes, pasta and sweets used sparingly