Unit 1 AP Biology Review
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review for AP Bio topics 1.1-1.8Q2A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
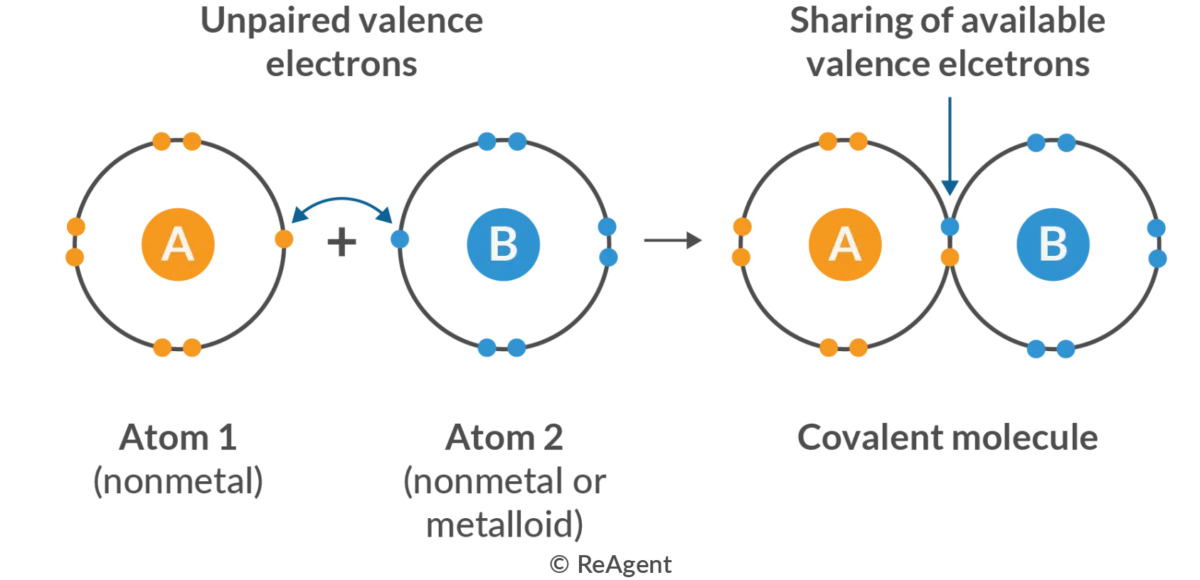
Ionic Bonds
Transfer Electrons (Charged Particles)
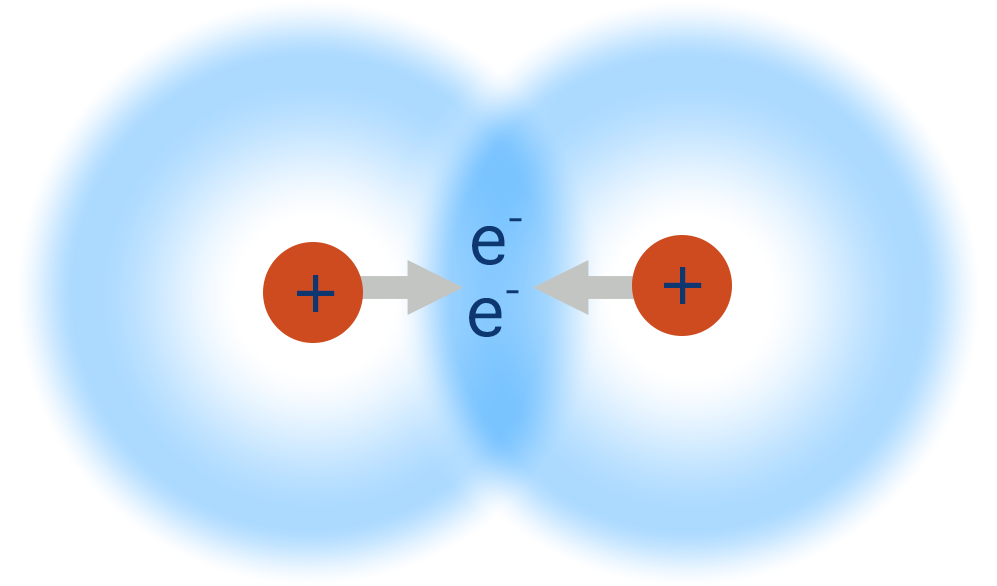
Covalent Bonds
Share Electrons (Non-Metals)
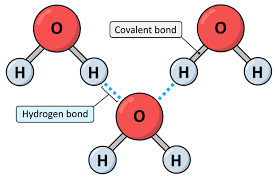
Hydrogen Bonds
An partially positive Hydrogen atom (H) attracts to the partially negative elements F,O,N of ANOTHER molecule
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to draw electrons to itself (More electrons? Generally, More electronegative)
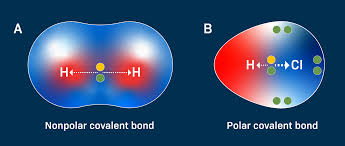
Non- Polar Covalent
Electrons are shared equally - Balanced distribution so no partial charges
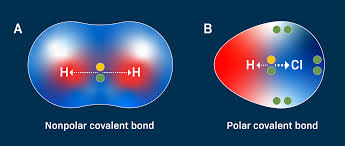
Polar Covalent
Unequally shared electrons - one atom has higher electronegativity which creates partial positive and negative charges
Out of C,H,O which element is the most electronegative?
Oxygen - pulls more electrons (Partially negative)
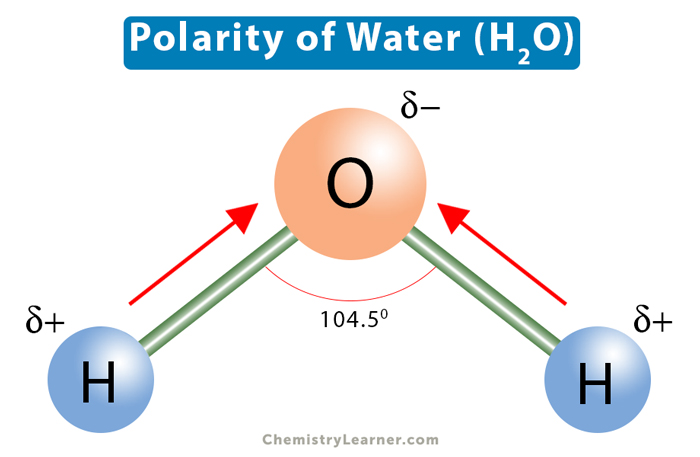
Water is a _____ Molecule?
Polar (has partial negatives and positives)
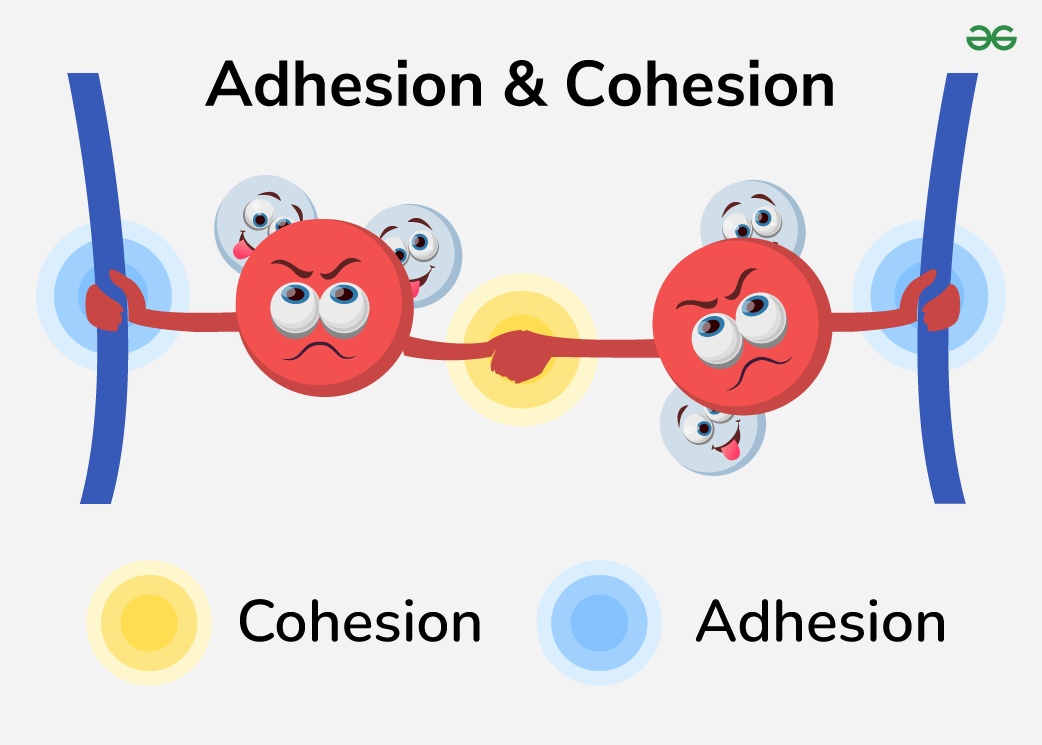
Cohesion
Tendency of water molecules to stick to each other (hydrogen bonding)
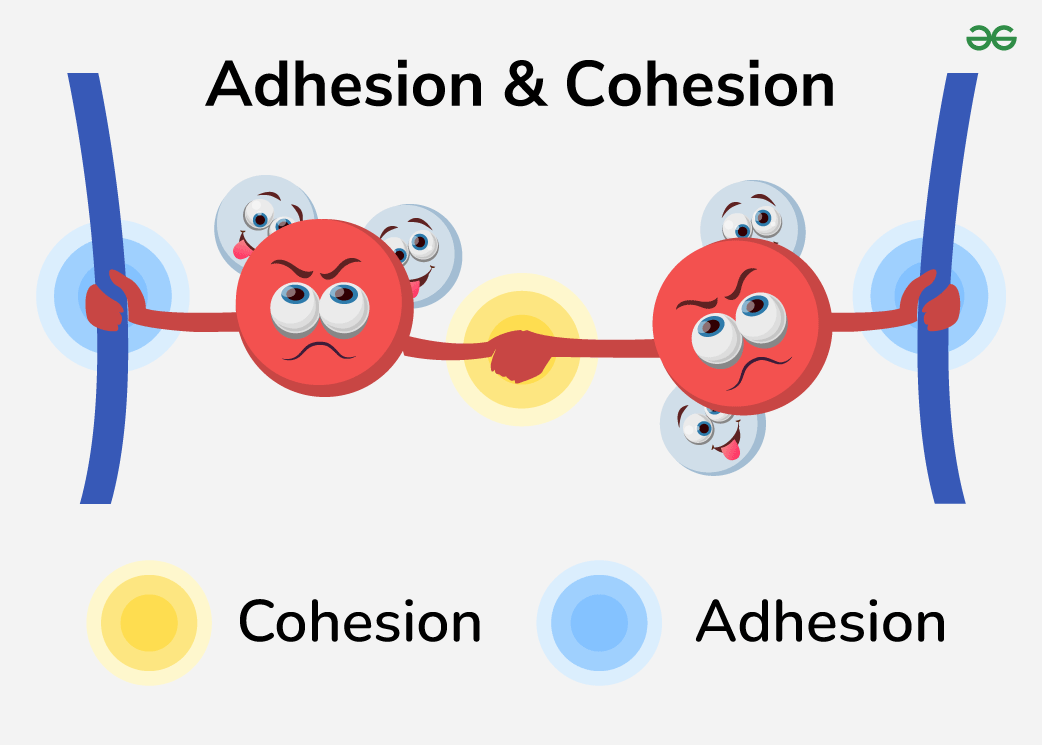
Adhesion
The ability of water to stick to other surfaces (surfaces must then be polar for a polar molecule to attract it!)

High Heat Capacity
When temperature increases more bonds will break however the overall temp remains stable
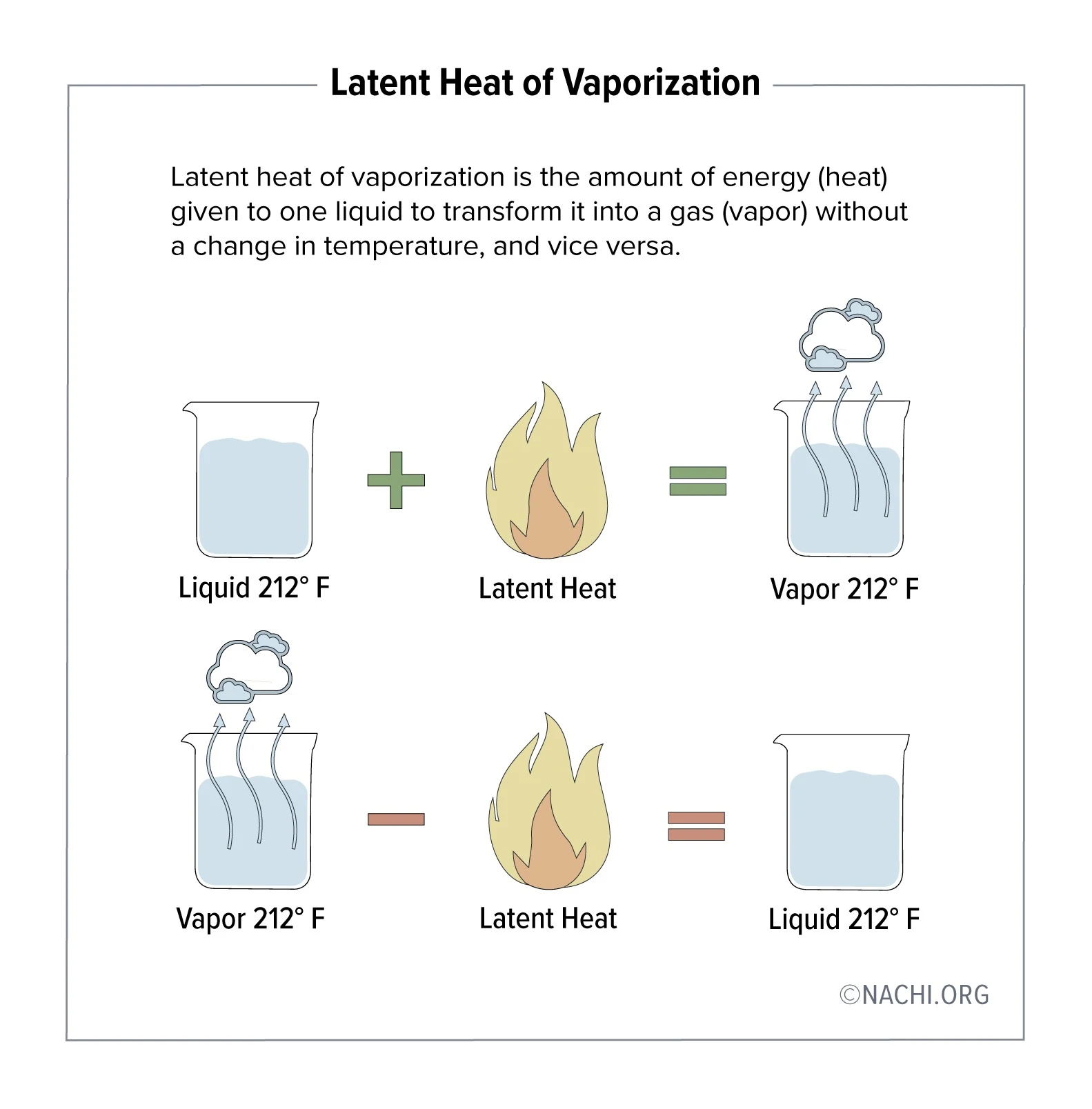
High heat vaporization
Cooling mechanism ex. evaporation of sweat (so theres no large temp fluctuations in animals)
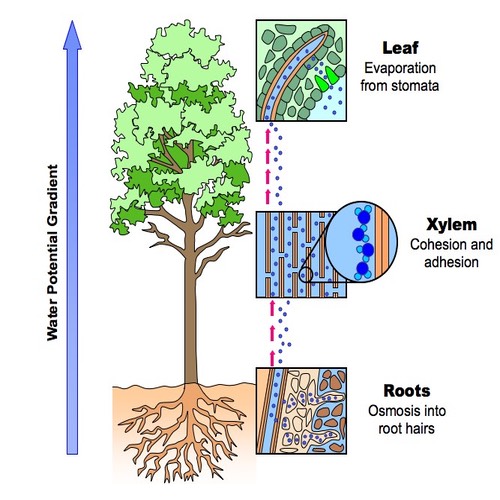
Transpiration
Water Molecules are attracted to each other through cohesion which allows water to move from the soil, up the xylem (the polar stem) to the leaves.
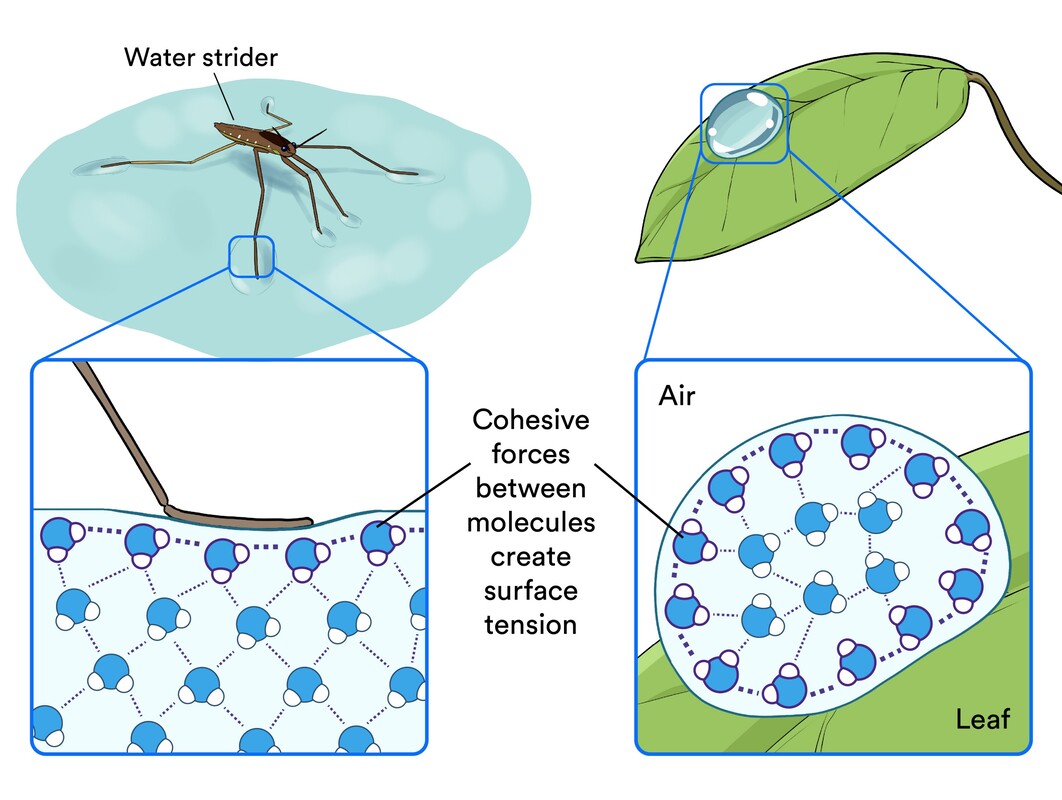
Surface Tension
An interaction between water and air - water is strongest on the top layer do to molecules on top attracting horizontally (inward)
What is Standard Error?
Shows you how good your data is “Measure of precision”
Small Deviation is better!
x̄ = Mean
n = # Data Points
S = How spread out data is
2x SEM 95% confident of the true mean
Autotroph
Produces its own food (Plants & Photosynthesis)
Heterothroph
Consumes other organisms for energy (yoo)
4 Major Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
What atoms do all 4 major molecules have?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
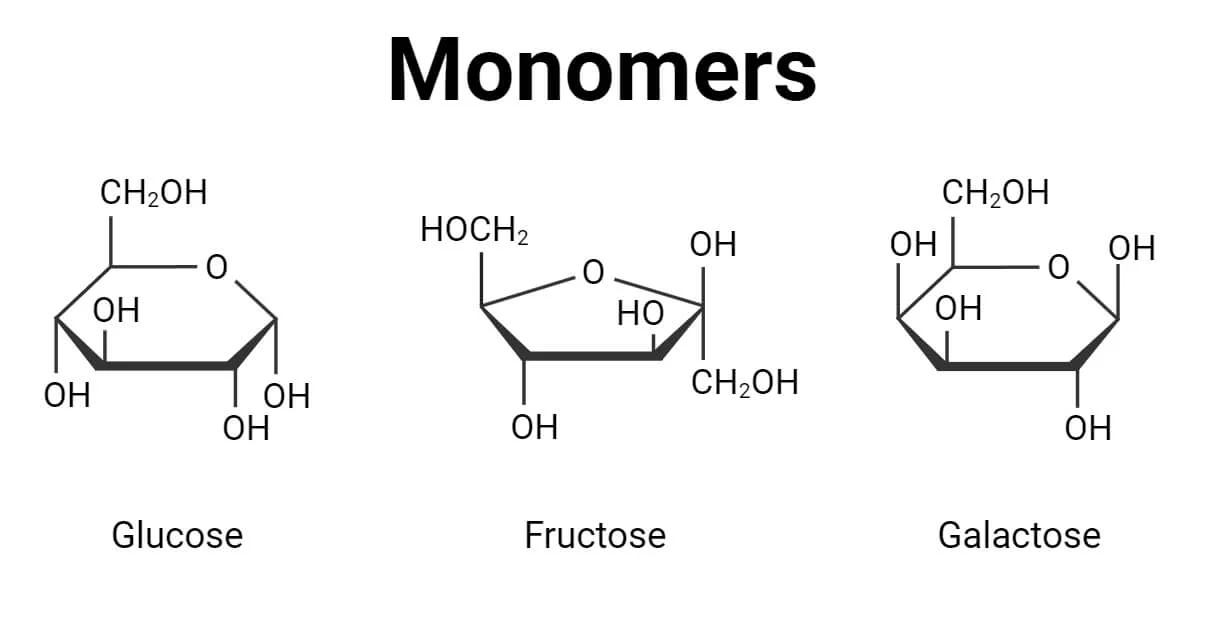
Multiple monomers create a…
Polymer
Elements in Carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Elements in Lipids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
How are phospholipids different from regular lipids?
They contain phosphorus.
Elements in Proteins
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Nucleic Acids
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
Polymer
A large molecule made of many monomers bonded together in a REPEATING chain-like fashion
Dehydration Synthesis
How monomers are bonded together
An H+ is removed from a monomer and OH- is removed from another, this results in H2O and a covalent bond between the two monomers.
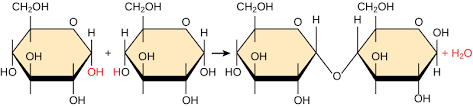
Monomer of Carbohydrates
Glucose - Energy for cell
Monomer of Lipids
Glycerol and Fatty Acids - Long term energy storage & primary structure for cell
Monomer of Proteins
Amino Acids - Give us phenotypes and facilitate chemical reactions
Monomer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides - RNA & DNA (store genetic info)
R- Groups from proteins might contain what element?
Sulfur (Disulfide bonds)
Hydrolosis
Water is added to the bond between monomers to break the bond and seperate them