AP Biology Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
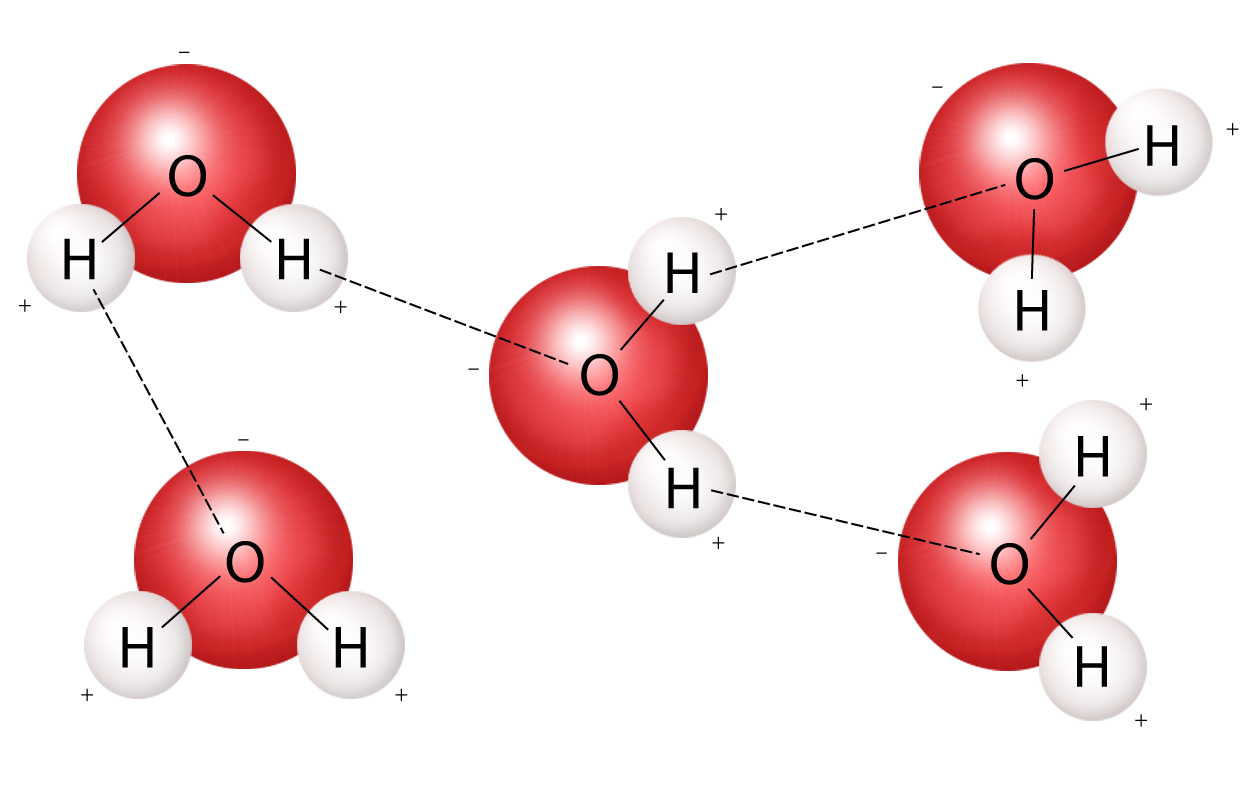
Cohesion
A hydrogen bond between the **same** molecules or two water molecules
2
New cards
Adhesion
A hydrogen bond between two **different** molecules, such as water and an amino acid
3
New cards
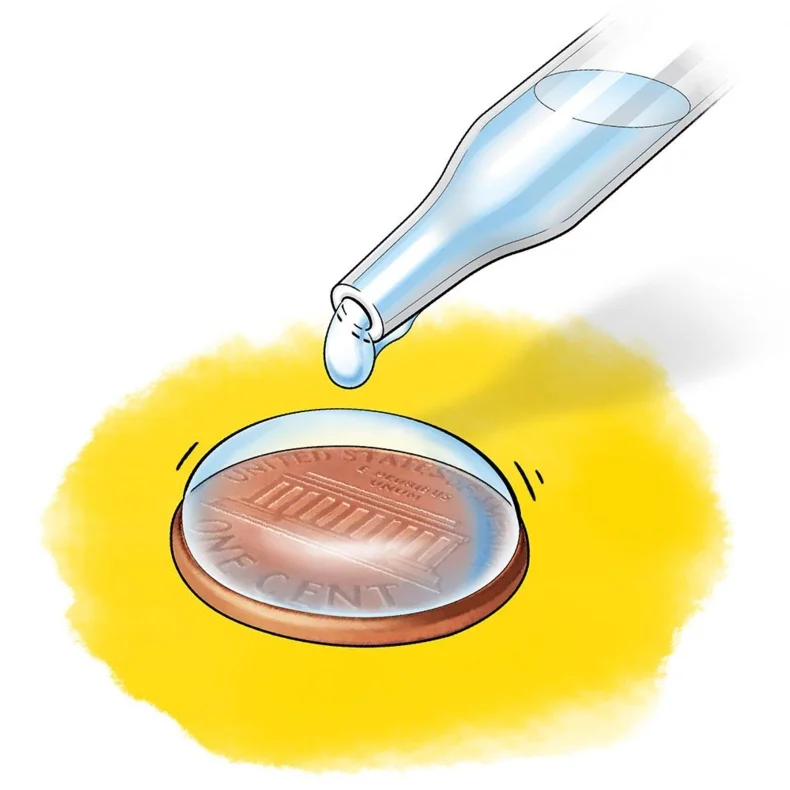

Surface Tension
A phenomenon, resulting from **cohesive** properties, when hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules at the surface (leaves of aquatic plants depend on it for better access to sunlight during photosynthesis)
4
New cards
High Solvency
Resulting from **adhesive** properties, water’s ability to dissolve other molecules (allows materials to dissolve and be easily accessed by cells so living systems can obtain nutrients from their environment)
5
New cards
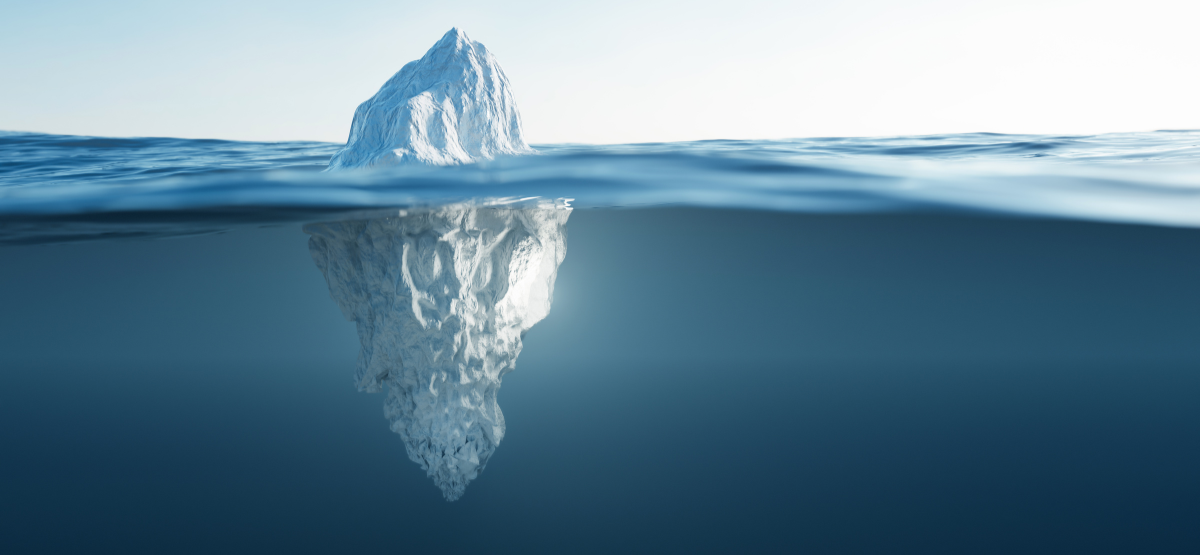

Ability of Ice to Float
Water’s **cohesive** property and **unique hydrogen bond** interaction make water as a solid more dense (allows aquatic organisms to thrive in cold conditions since only the surface of the water gets frozen over)
6
New cards
High Heat Capacity
Water’s **cohesive** ability to absorb an abundance of thermal energy and resist sudden temperature changes (sea animals depend on it to maintain their body temperature)
7
New cards
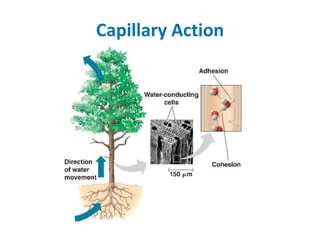
Capillary Action
The forces of **cohesion**, which causes water to stick together, and **adhesion**, which cause water droplets to stick to stem walls and be pulled upward during transpiration (so plants can access water)
8
New cards
Macromolecule
A molecule that is necessary to sustain life- **Nucleic Acids, Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Lipids**
9
New cards
Monomer
A molecule that makes up a polymer
10
New cards
Polymer
A macromolecule made up of monomers
11
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
**Forms covalent bonds** by joining monomers into polymers and releasing water as a byproduct (⬠ + ⬠ → ⬠⬠ + H20)
12
New cards
Hydrolysis
**Cleves covalent bonds** by breaking polymers into monomers and adding water subcomponents to each monomer (⬠⬠ + H20→ ⬠ + ⬠ )
13
New cards
Nucleic Acid
A polymer/macromolecule present in **DNA and RNA**, made out of **nucleotides**
14
New cards
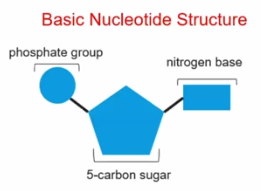
Nucleotides
Nucleic Acid’s **monomer**- contains a phosphate group, nitrogen base, and 5-carbon sugar
15
New cards
What elements does nucleic acid contain?
Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
16
New cards
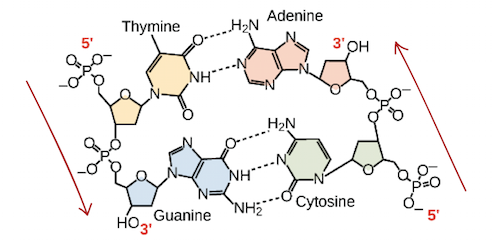
What is the directionality of nucleotides?
Characterized by its anti-parallel 3’ hydroxyl ends and 5’ phosphate ends, with __2 hydrogen bonds__ between Adenine and Thymine and __3 hydrogen bonds__ between Guanine and Cysostine. During synthesis, nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end.
17
New cards
Pyrimidines Family of Nitrogenous Bases
**Cytosine, thymine, and uracil**- have a single six-membered ring
18
New cards
Purines Family of Nitrogenous Bases
**Adenine and guanine**- have a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring
19
New cards
What influences the structure and function of nucleic acid polymers?
1. A change in nucleotides will lead to a change in its **function**, since biological information is stored in its sequence.
2. and in **stability**, since the amount of hydrogen bonds between nitrogen base pairs affects how stable the molecule’s structure is (the more hydrogen bonds, the more stable)
20
New cards
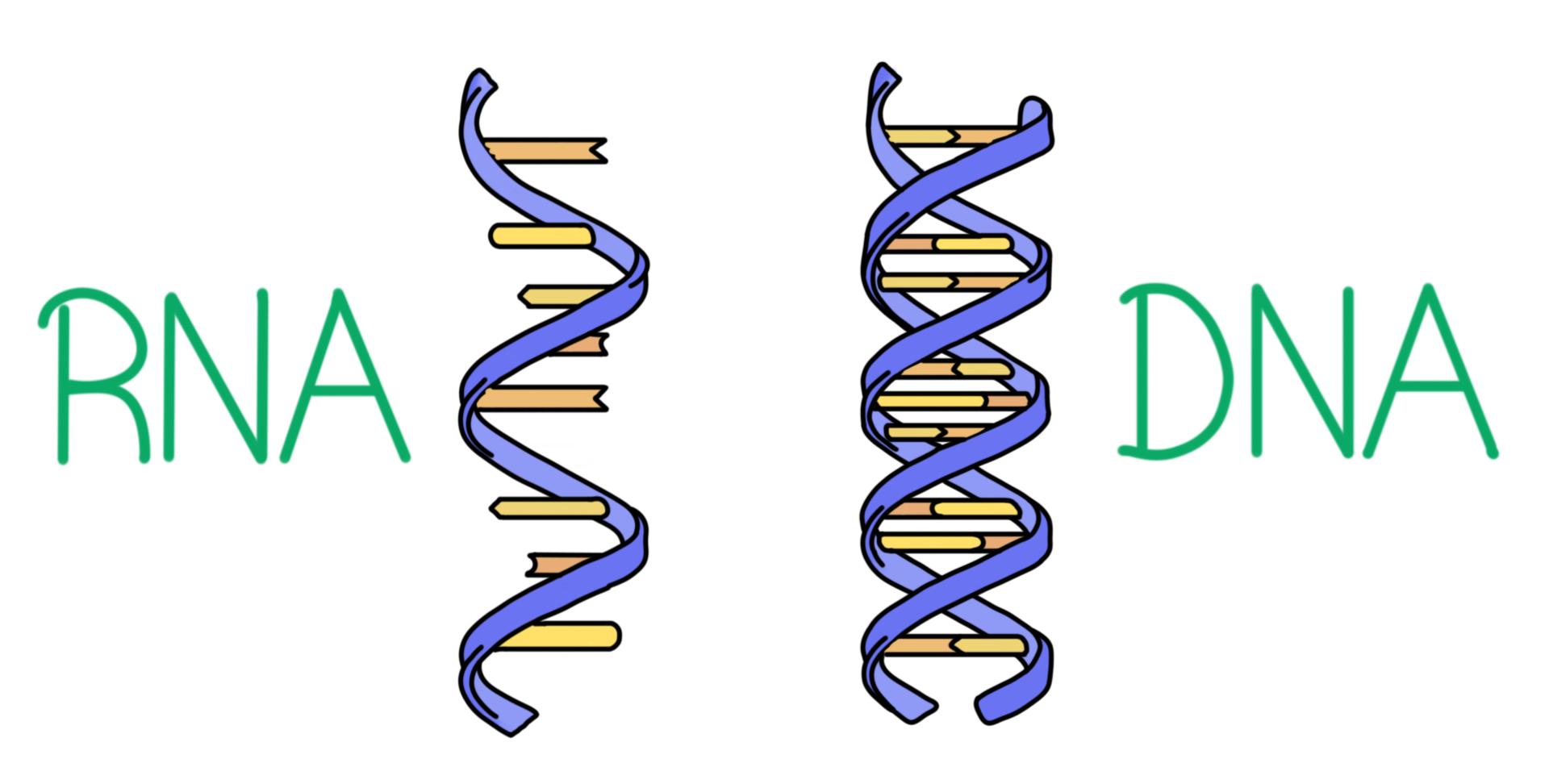
What are the similarities between DNA and RNA?
Both are comprised of a **5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base**, their nucleotides are connected with **covalent bonds**, and they have the same **directionality**
21
New cards
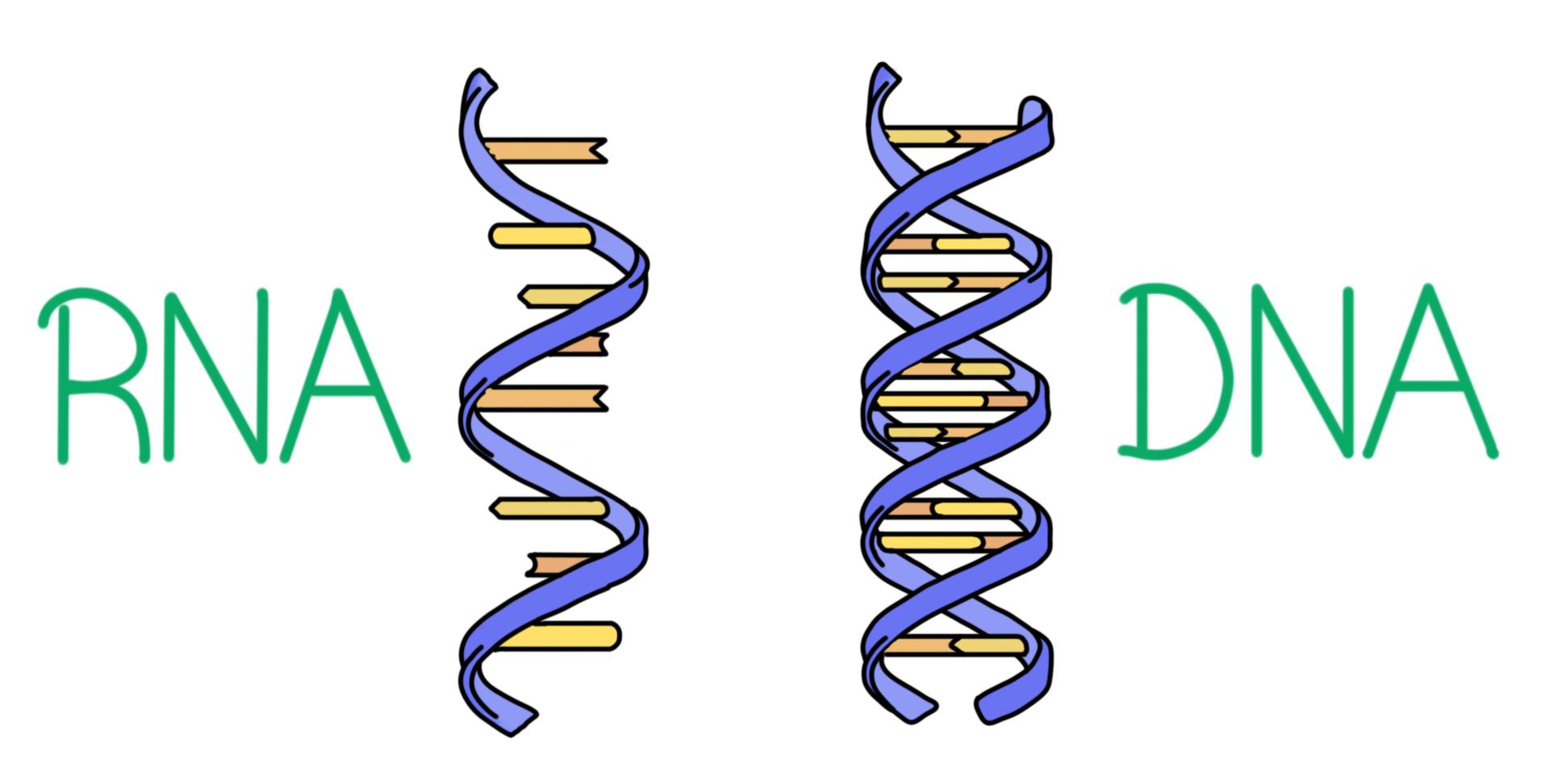
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
**Sugars** (DNA = deoxyribose, RNA = ribose), **4th Nitrogenous Base** (DNA = thymine, RNA = uracil), **Number of Strands** (DNA = double-stranded, RNA = single-stranded)
22
New cards
Proteins
A polymer/macromolecule made out of **amino acid**
23
New cards
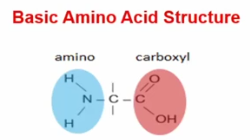
Amino Acids
Protein’s **monomer**- Comprised of a center carbon with an amino terminus on one end and carboxyl end on the other, and R group attached to the center carbon
24
New cards
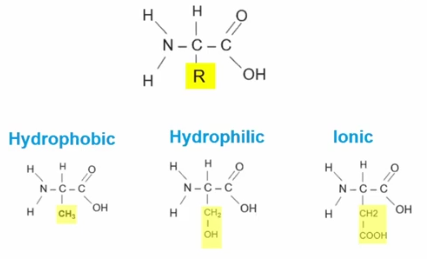
R Group
A group of atoms attached to the central carbon in an amino acid, that **can change the chemical property of proteins to hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or ionic**
25
New cards
What elements does protein contain?
Carbon and Nitrogen
26
New cards
Polypeptide
A primary structure of proteins and sequence of amino acids bonded together
27
New cards
Peptide Bond
A **covalent bond** formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid the amino group of another
28
New cards
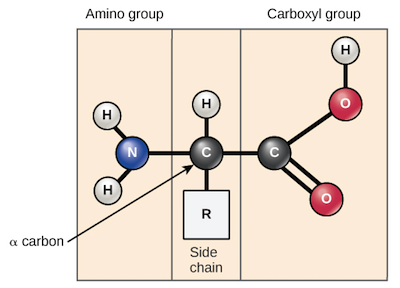
What is the directionality of amino acids?
The **linear chains of amino acids** gives directionality with an amino terminus and carboxyl terminus
29
New cards

Primary Structure
The first element of protein structure, characterized by a **non functional sequence of amino acids (polypeptides) held together with peptide bonds**
30
New cards
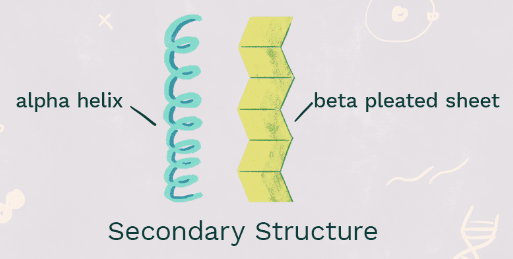
Secondary Structure
The second element of protein structure, when amino acid chains **fold/twist into alpha-helices and beta-shee**ts
31
New cards
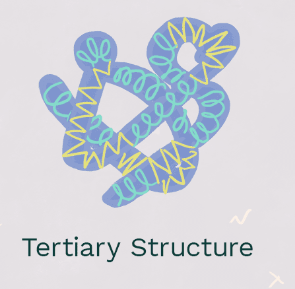
Tertiary Structure
The **3D functional form for most proteins**, who’s R Group is stabilized. **The protein bends** since nonpolar (hydrophobic) acids fold inwards and polar (hydrophilic acids fold outside
32
New cards
Quaternary Structure
The final element of protein structure for some proteins, that is comprised of **multiple polypetite units togethe**r and usually functions as hemoglobin
33
New cards
Chaperones
Protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins
34
New cards
What influences the structure and function of protein polymers?
**A change in polarity in the R Group** can affect the direction the protein bends in and change its function to receive different molecules
35
New cards
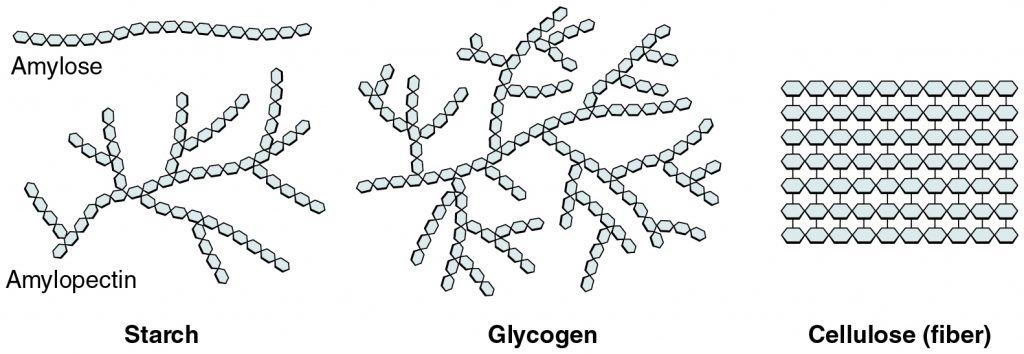
Carbohydrates
A polymer/macromolecule present in **starches and sugars**, made out of **monosaccharides** or “simple sugars”, with a **linear or branched structure**
36
New cards
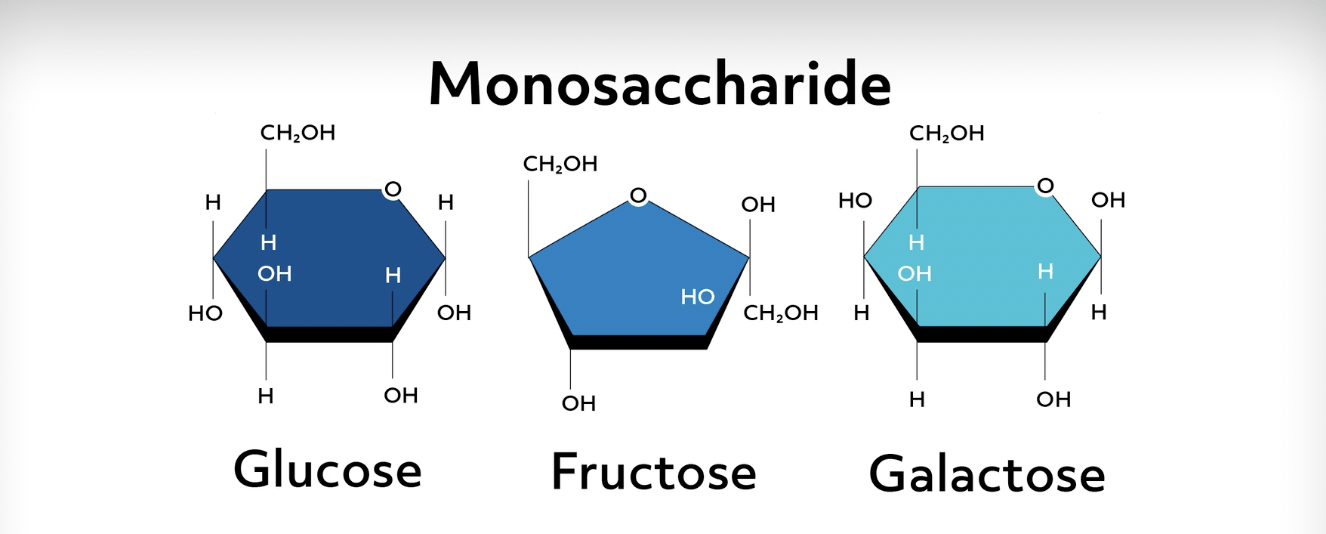
Monosaccharides or “Simple Sugars”
Carbohydrates’ **monomer**- (CH2O)n, a carbon chain bonded to two hydrogens and one oxygen
37
New cards
What element do carbohydrates contain?
Carbon
38
New cards
Polysaccharides
A carbohydrate polymer, formed of **monosaccharides**
39
New cards
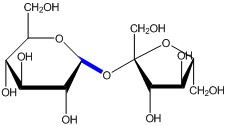
Glycosidic Bond
A **covalent bond** formed between carbohydrate or sugar molecules
40
New cards
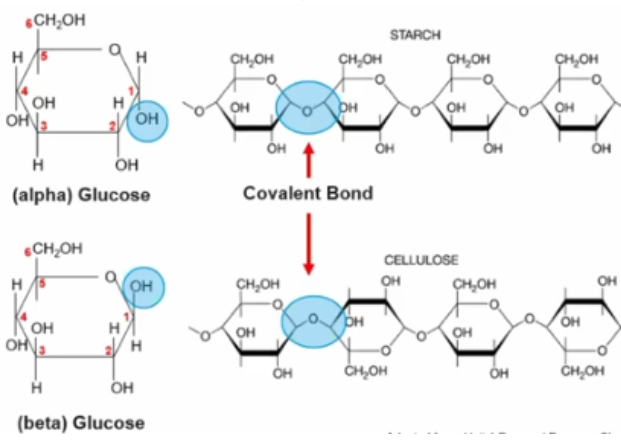
What is the directionality of monosaccharides?
The directionality is decided by **the assembly of polysaccharides, connected by glycosidic bonds**
41
New cards
What influences the structure and function of carbohydrate polymers?
The **orientation of monosaccharides** and **type of sugar monomer** determine their function
42
New cards
Lipids
A polymer/macromolecule present in **fats**, made out of **fatty acid and glucose**
43
New cards
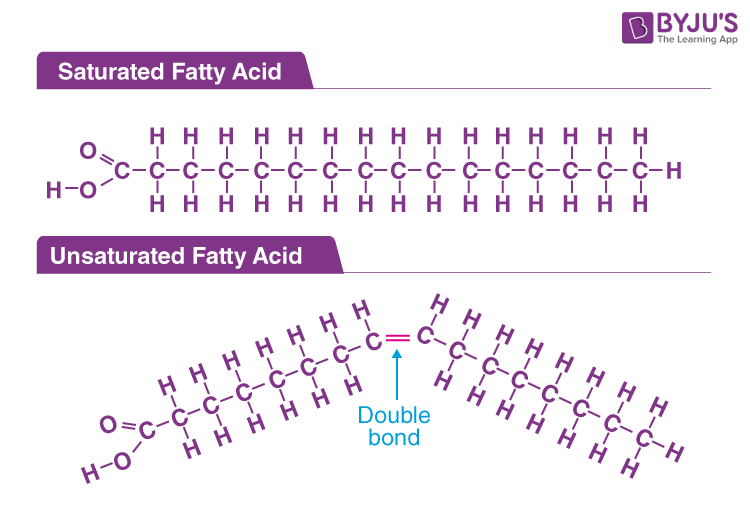
Fatty Acid & Glucose
Lipid’s non-polar **monomer** (does not have true monomer), comprised of a straight chain of carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and a carboxyl group
44
New cards
What element do lipids contain?
Carbon and Phosphorus
45
New cards
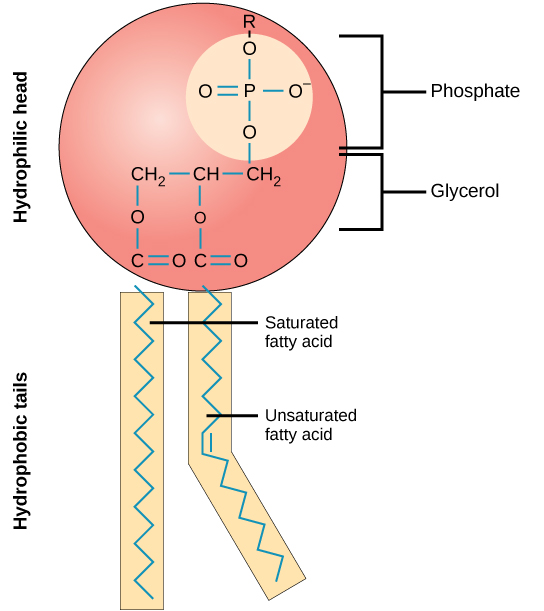
Phospholipids
Membrane lipids **with hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions** that decide their interactions with other molecules
46
New cards
What influences the structure and function of lipid polymers?
The **saturation** __(saturated= single bonds, unsaturated= double bonds)__ of fatty acids determines the structure and function of lipids