7. Corneal Light Transmission
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
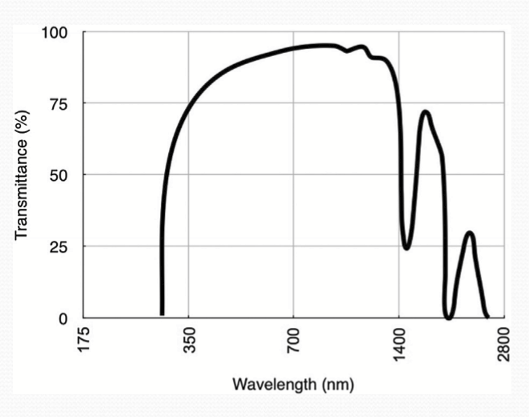
What percent does the visible spectrum transmit through the cornea?
85-99%, with visible range= 380-740 nm
Which wavelengths scatter more in the cornea?
Smaller wavelengths scatter more light than larger wavelengths; so violet scatters more and transmits less than red.
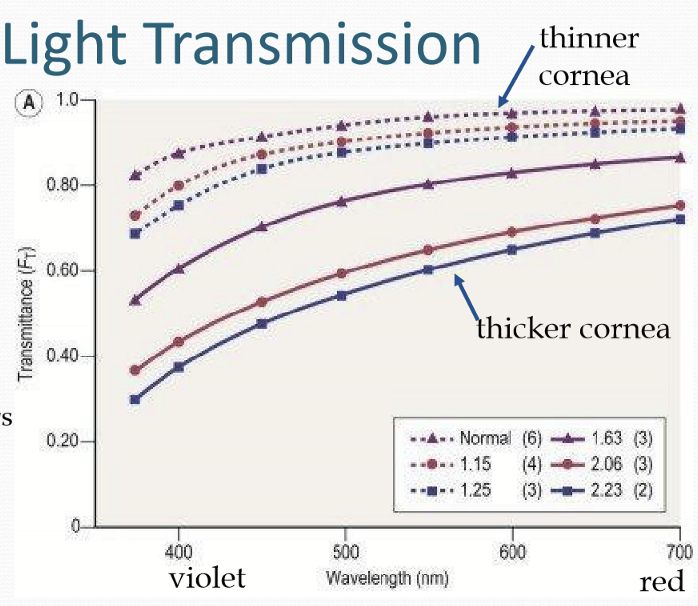
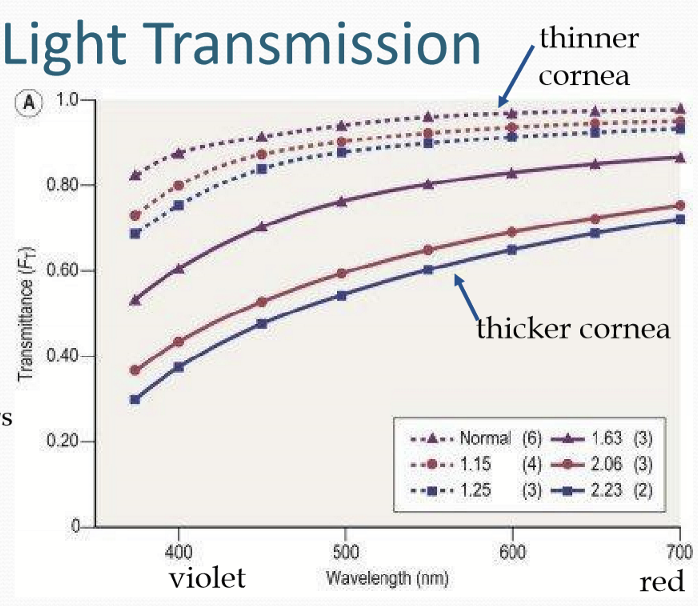
What happens to transmission if the cornea thickens?
Less transmission in thicker corneas
Where is light scattering the highest?
In the cellular tissue due to organelles and nuclei.
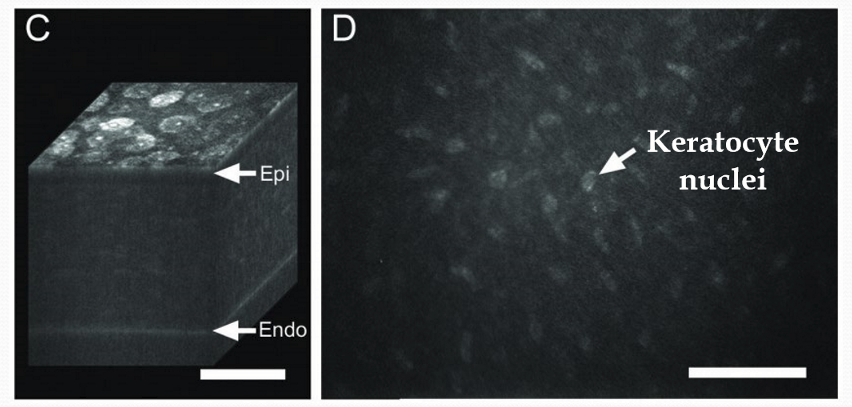
List the structures/cell that scatter light from greatest to least.
Endothelial cells > Epithelial cells > Nerve cells > Keratocytes > > Collagen fibrils or ECM
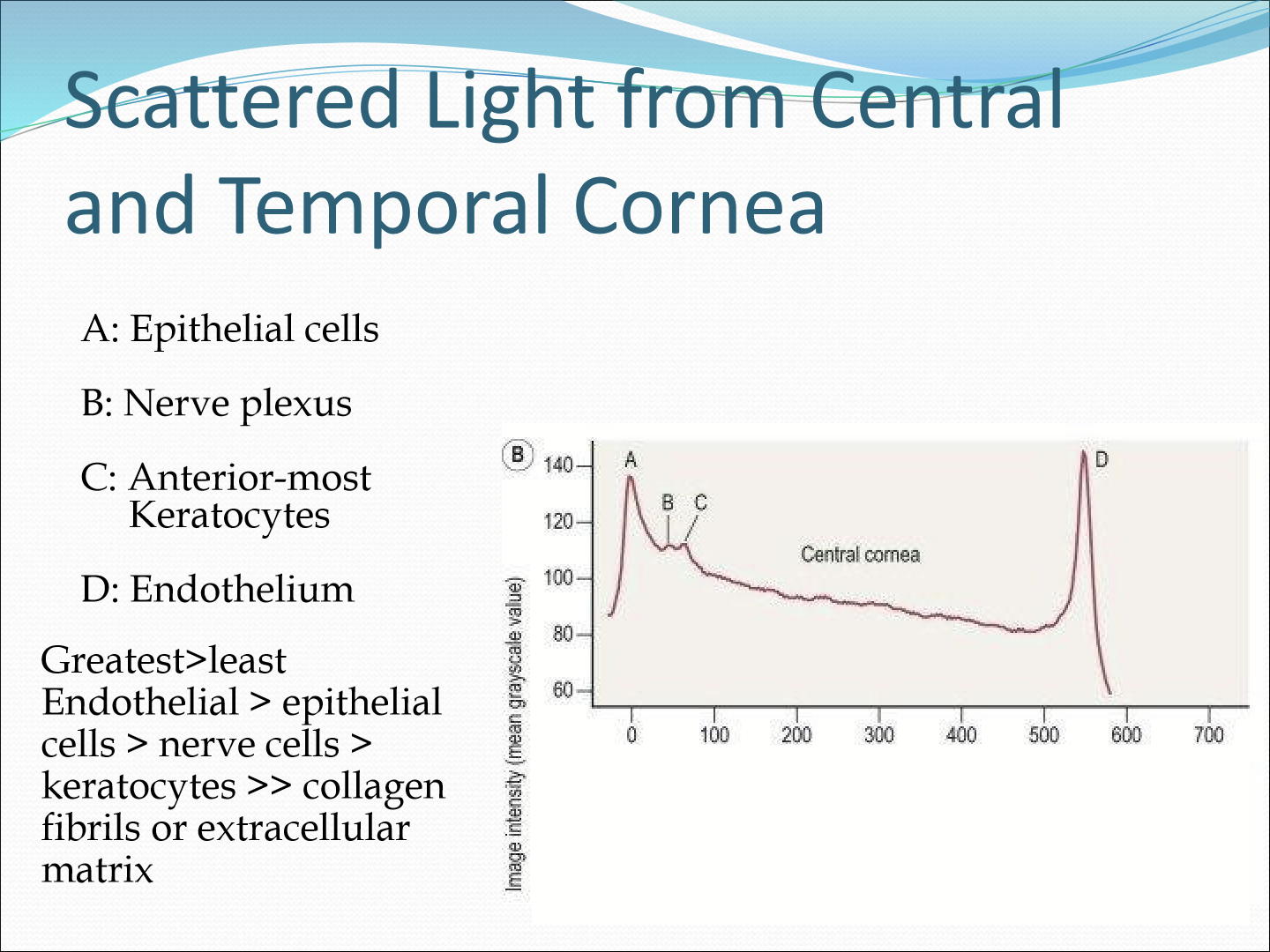
What does the stromal transparency theory state?
It says that the distance between scattering structures has to be less than ½ of the wavelength to create destructive interference to cancel out all scattering light in any direction except the forward direction.
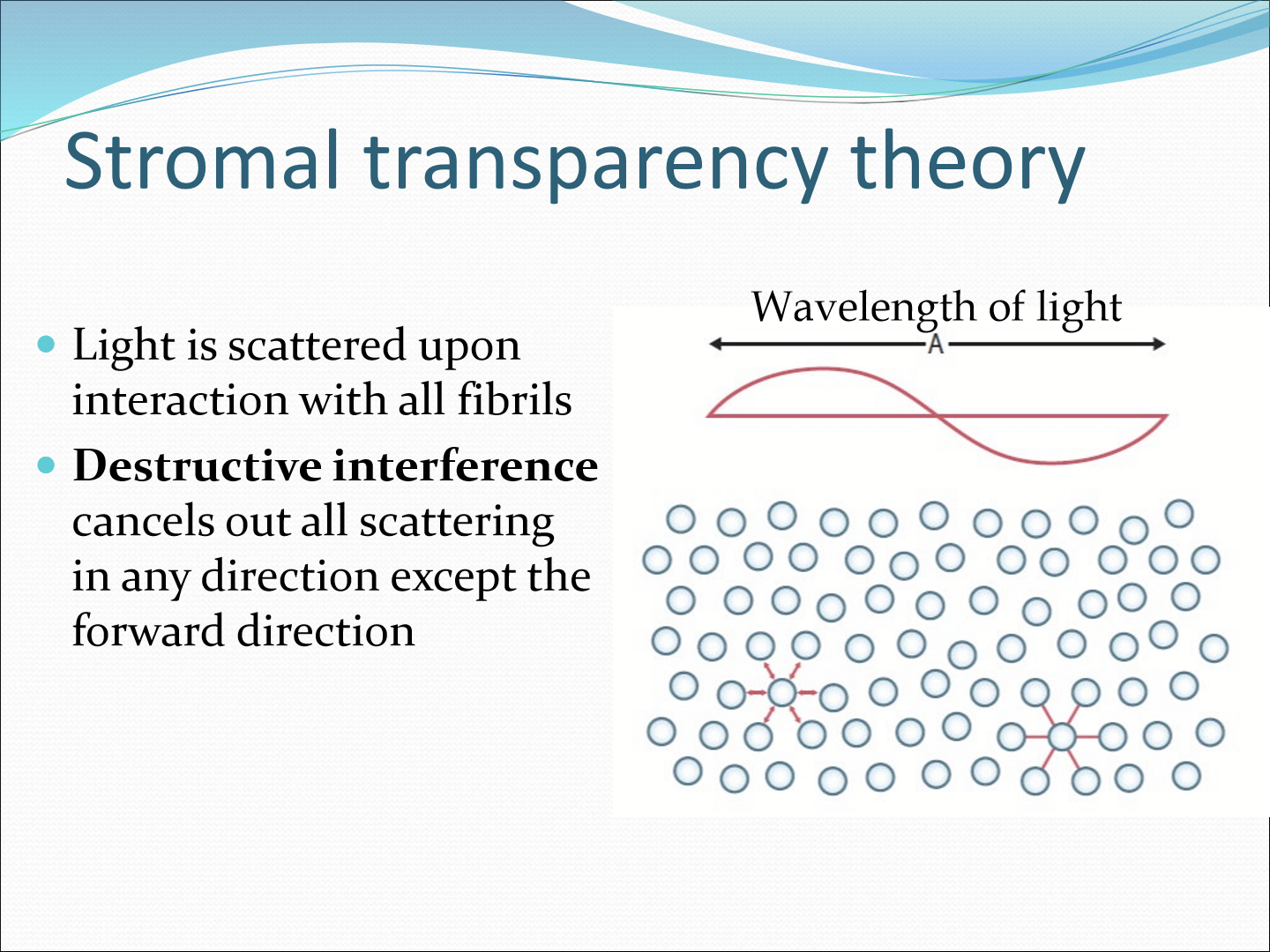
How does the stroma achieve transparency?
Uniformity of collagen fibril diameter (~25nm) and restriction in the range of distances between fibrils (~60nm)
How does GAGs help maintain corneal transparency?
The GAGs provide a repulsion force that maintains spacing between fibrils.
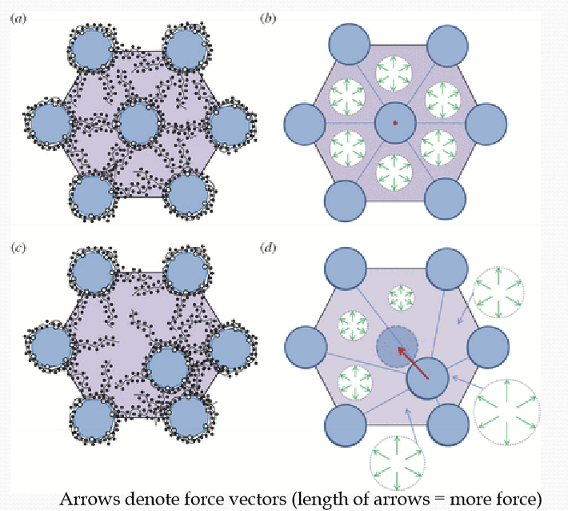
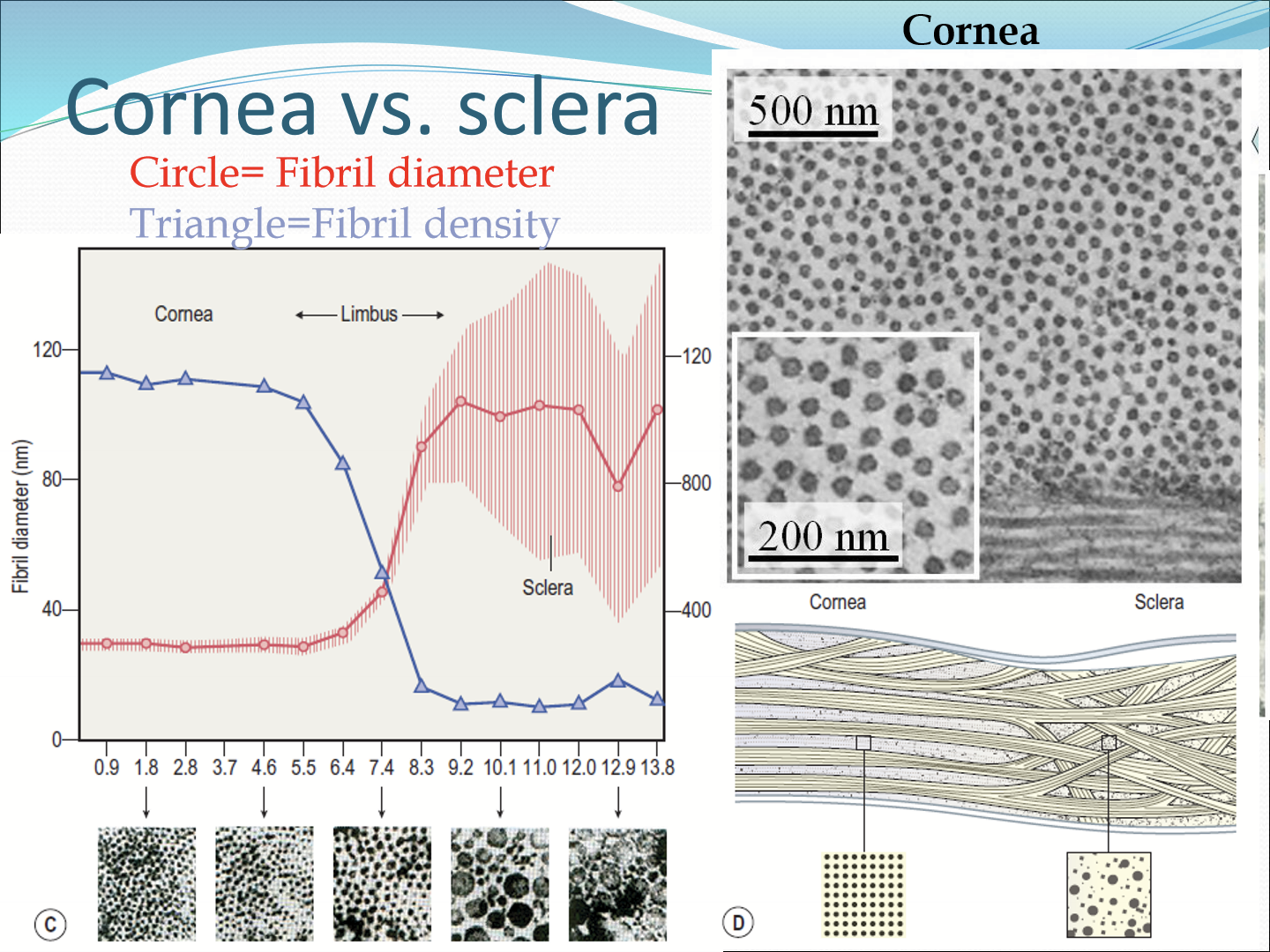
How does fibril diameter change?
It gets bigger the more posterior you go.
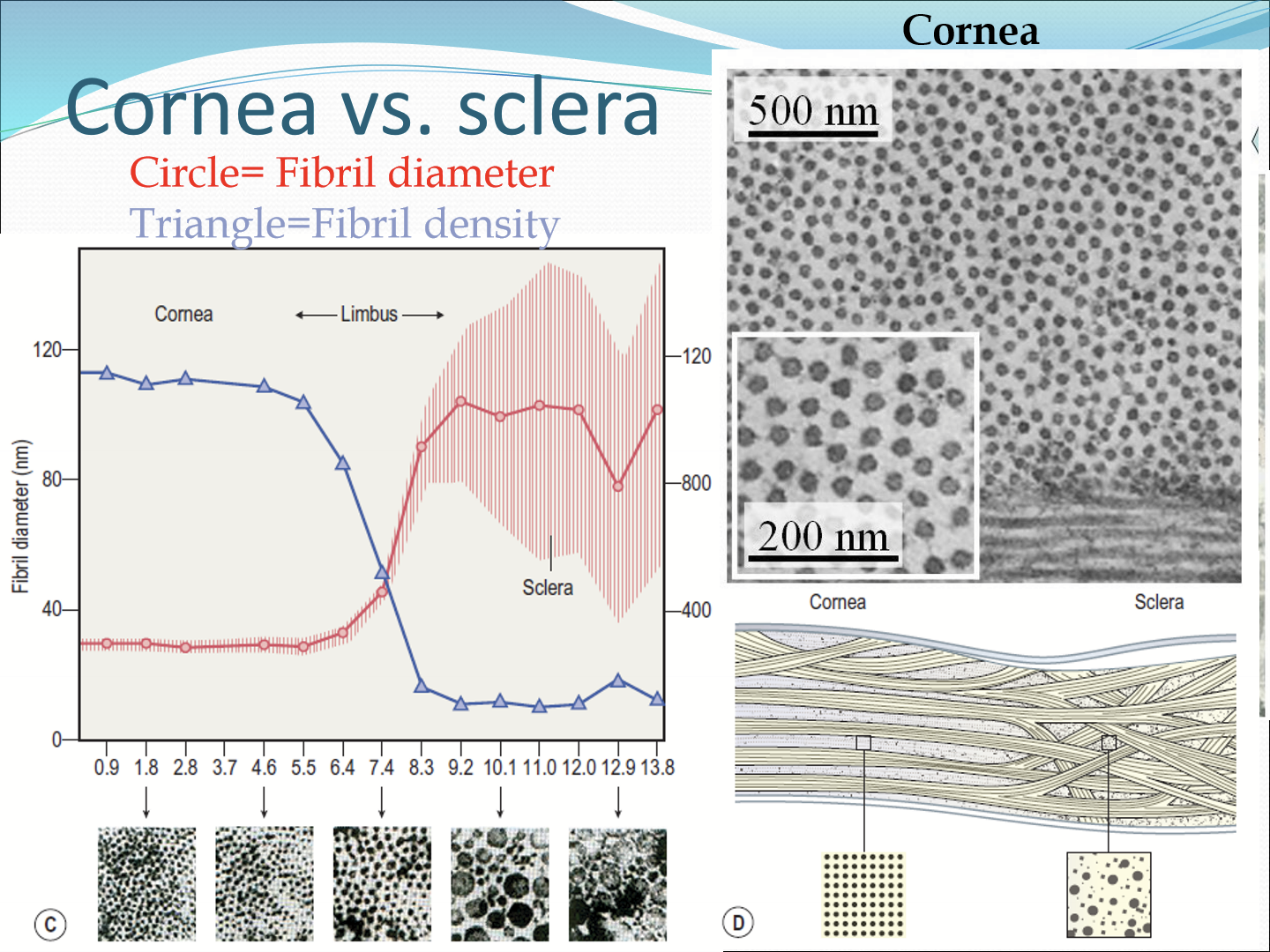
How does fibril density change?
It gets less dense the more posterior you go.
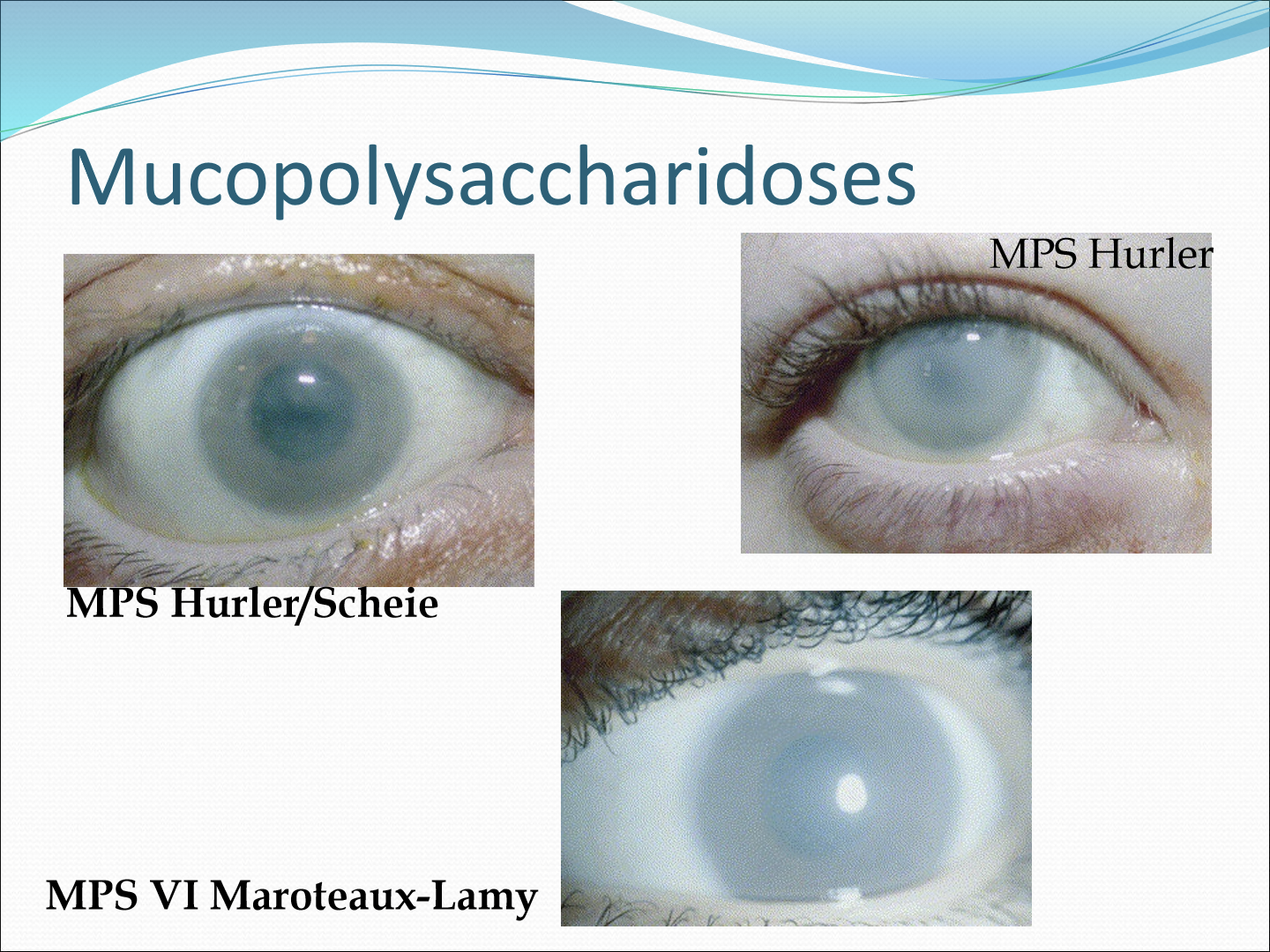
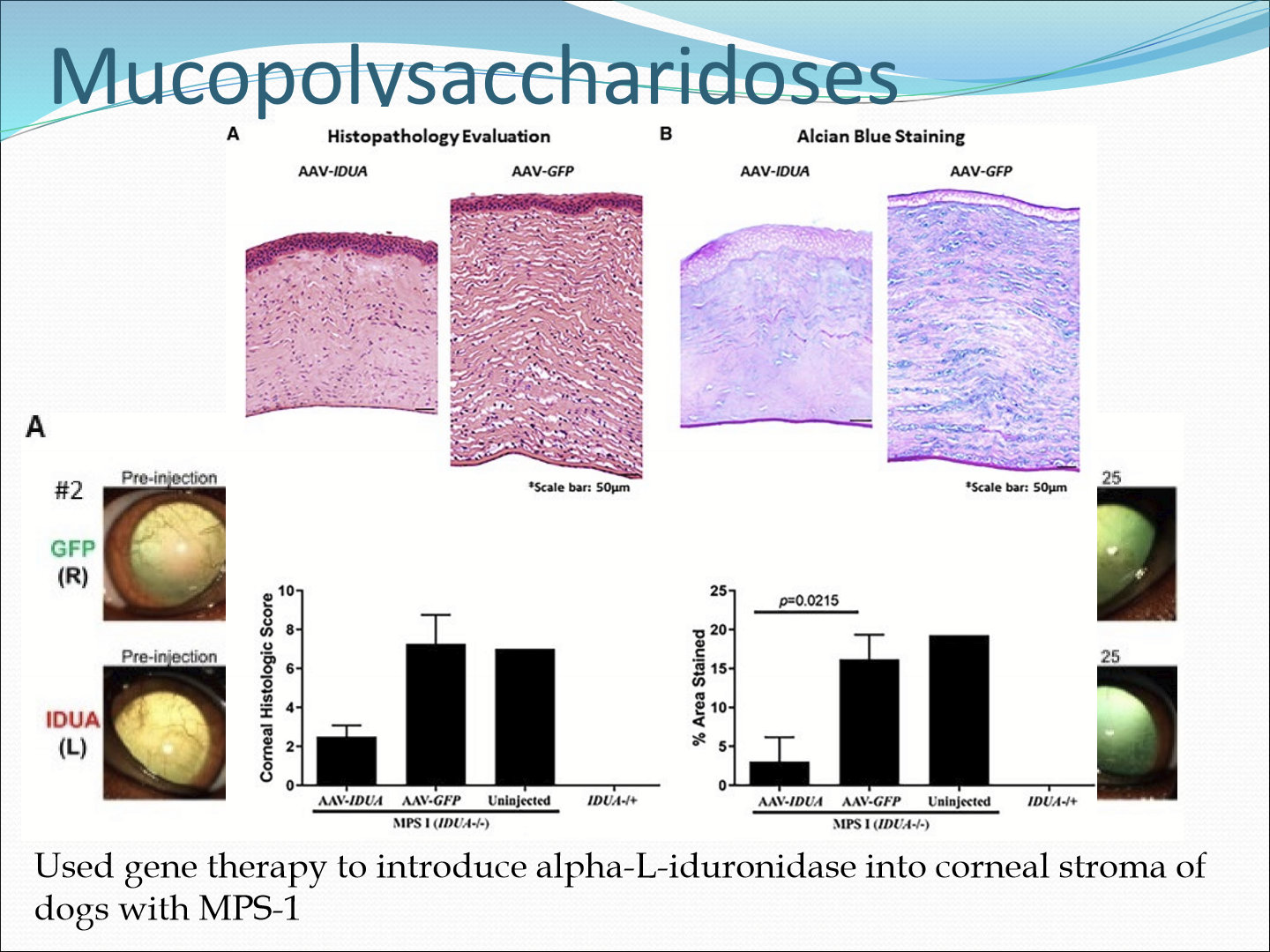
What is Mucopolysaccharidoses?
It is a group of inherited metabolic diseases that affect the breakdown of GAGs, causing GAGs to accumulate in the stromal tissue and disrupt fibril lattice structure. This causes the cornea to be cloudy
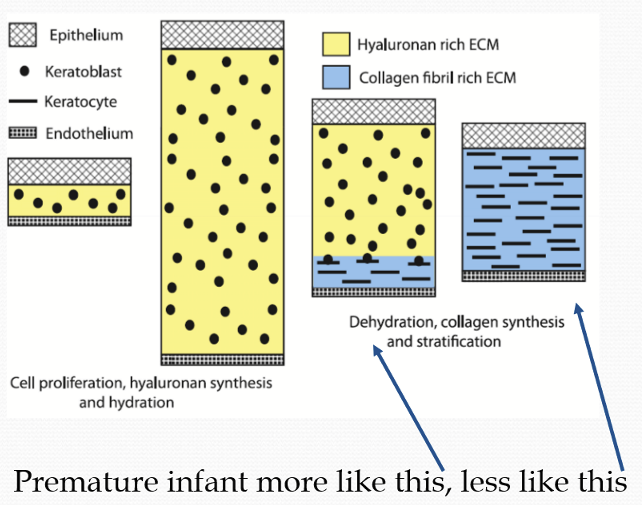
Why do premature infants have less transparent corneas than full-term infants?
It is due to the incomplete development of stromal fiber organization
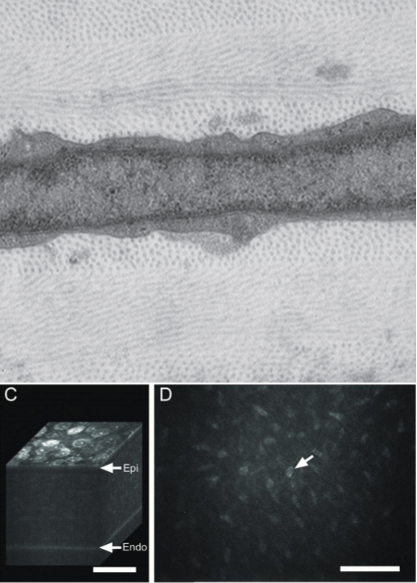
How do keratocytes contribute to transparency?
They do scatter light, but minimizes it by having thin cytoplasm and express large quantities of crystallin protein in the thin cytoplasm
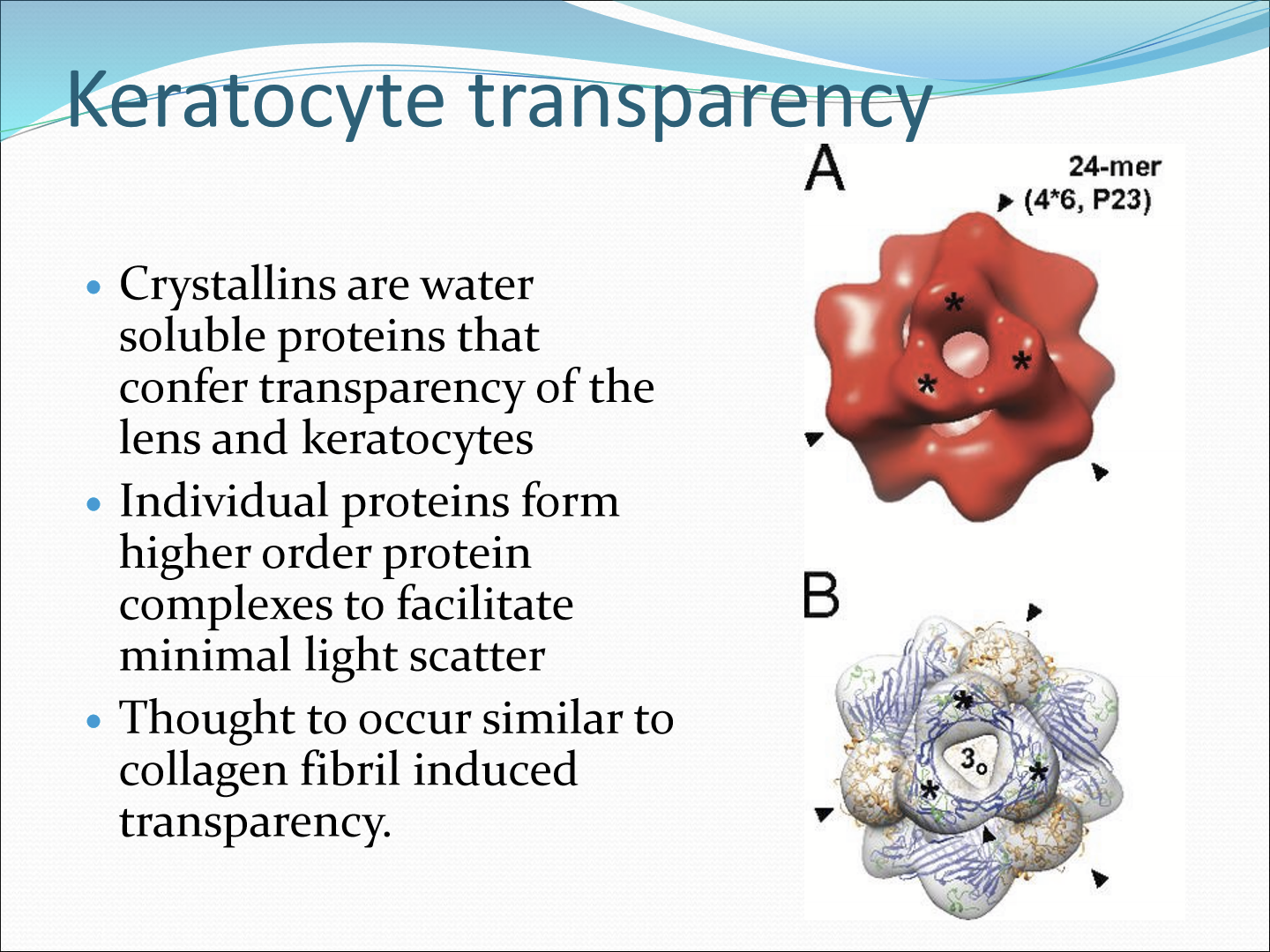
What are crystallins?
They are water soluble proteins that allow transparency of the lens and keratocytes. They are individual proteins that form high order proteins that complexes to facilitate minimal light scatter.
What causes opacity in cornea wound healing?
The transformation of keratocytes to highly reflective myofibrils.
Why is the cornea avascular?
There is active inhibition of the blood and lymphatic vasculature formation. A balance of pro and anti angiogenic factors are present in the cornea, and disruption can lead to neovascularization
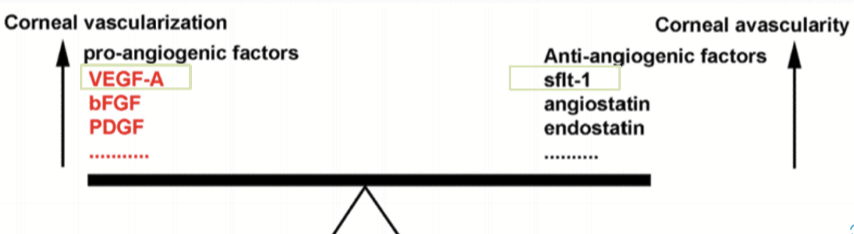
When can vascularization occur?
When the cornea is damaged or/and lack of oxygen
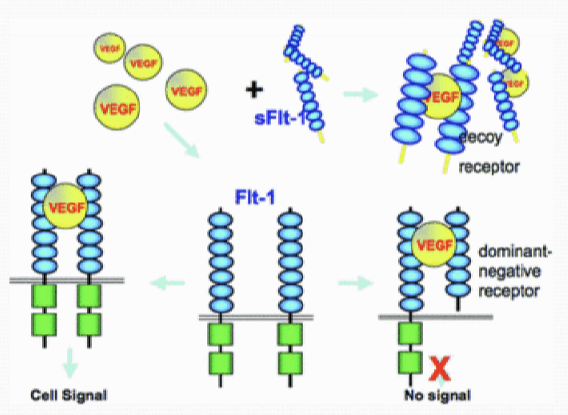
What does sFlt-1 do?
It is a anti-angiogenic factor. It works by binding to VEGF and prevents its function.
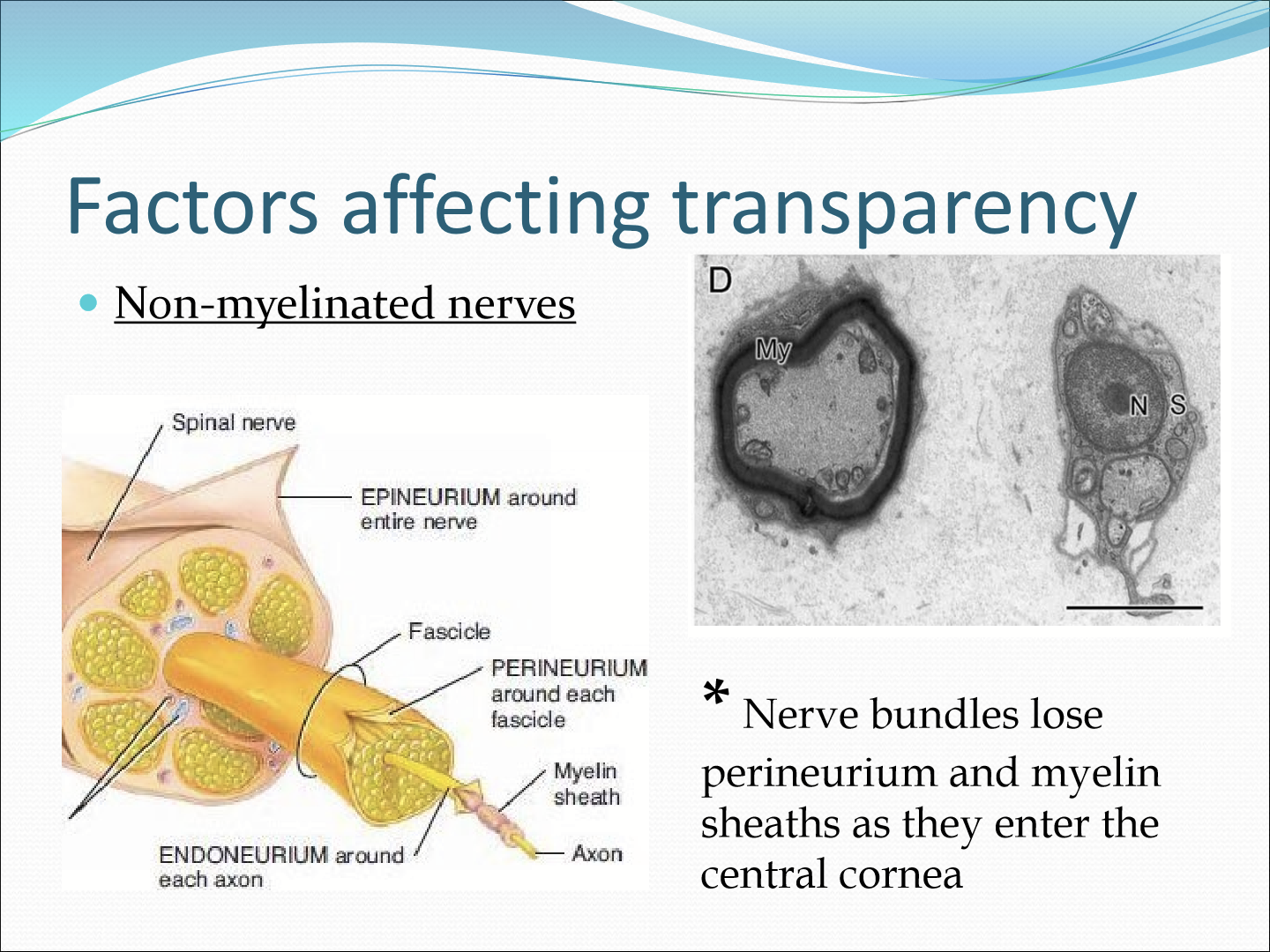
What happens to the nerve bundles when they enter the cornea?
They lose their perineurium and myelin
What proteins to the corneal epithelium express?
Large amounts of crystallin protein like keratocytes.
What modifications do corneal epithelium undergo to promote transparency?
Large amounts of crystallin proteins, relatively thin, sparse cytoplasmic organess, NON KERATINZED
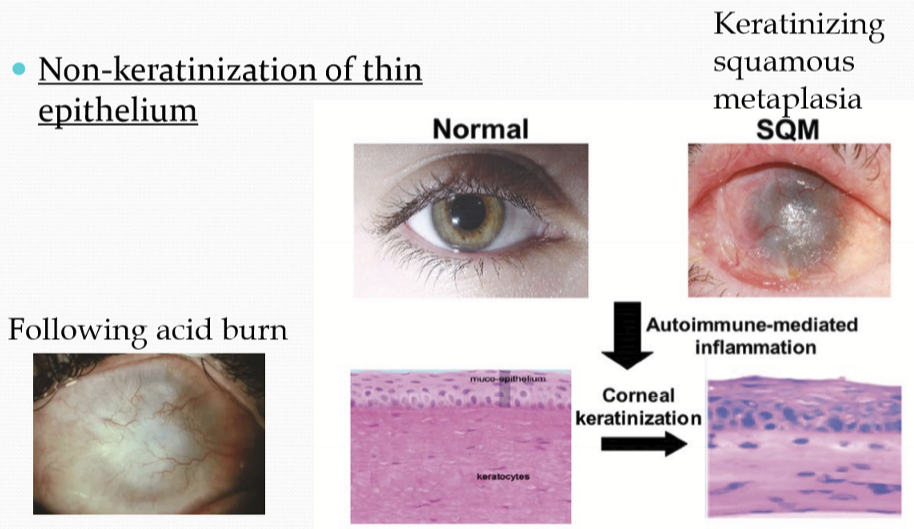
What causes the corneal epithelium to undergo squamous metaplasia?
With chronic irritation, goblet cells are lost, thus mucin production is lost and causes the eye to become dry and loss transparency.
How much UV light is absorbed by the cornea?
UVC (100-280nm): 100% absorption
UVB (280-315nm): 90% absorption
UVA (315-400nm): 60% absorption
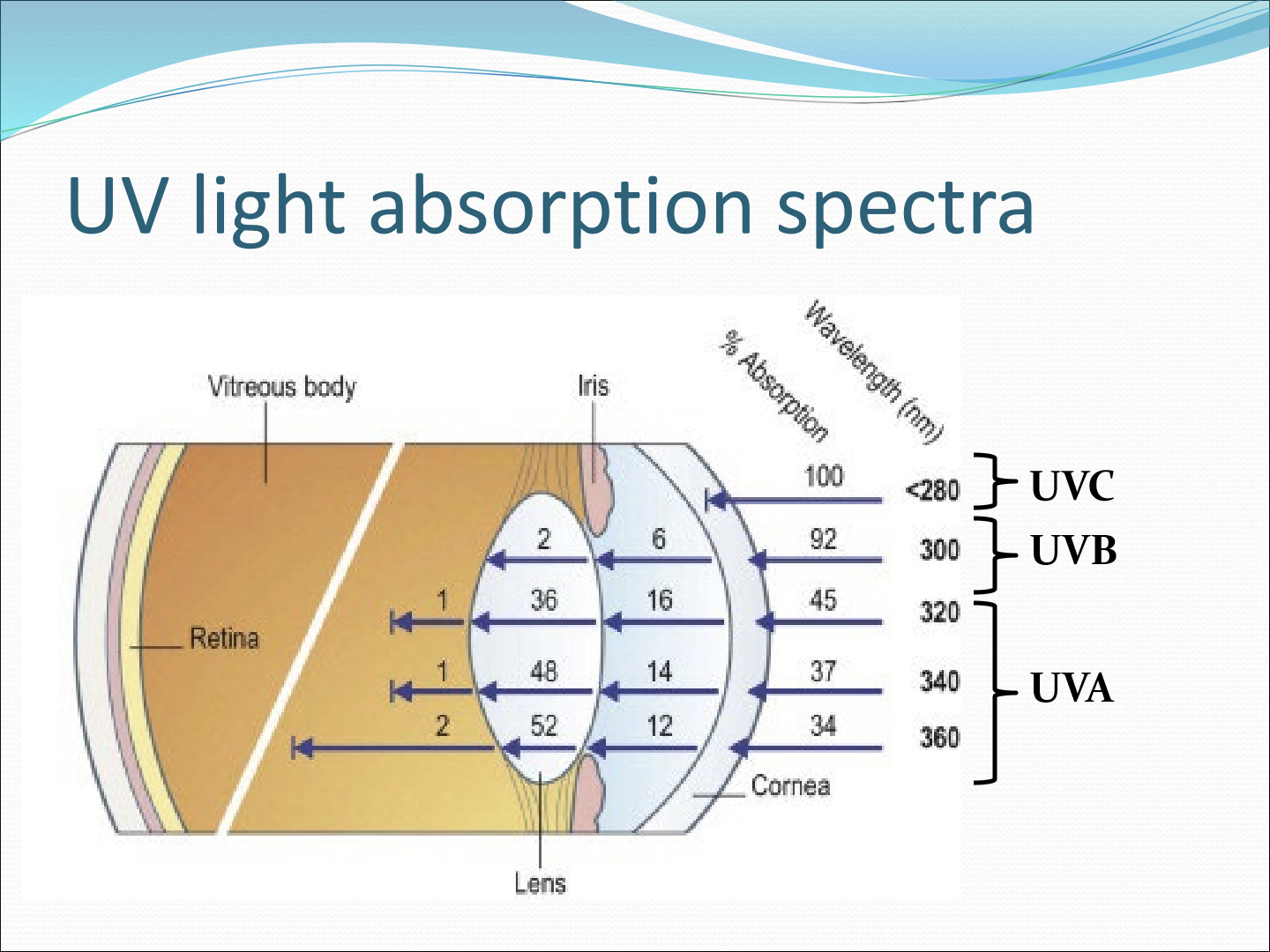
What part of the cornea absorbs UVC?
Epithelium
What part of the cornea absorbs UVB?
Bowman’s and anterior stroma
Why is the cornea more susceptible to UV damage than skin?
Absence of melanin
What does UV overexposure do to the epithelium?
It induces apoptosis and generates reactive oxygen species
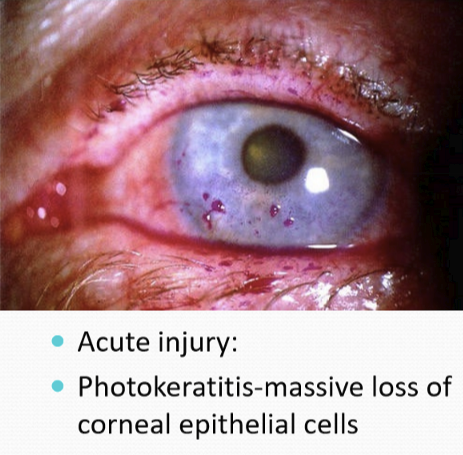
What happens in acute UV damage to the corneal epithelium?
Photokeratitis: massive loss of corneal epithelial cells
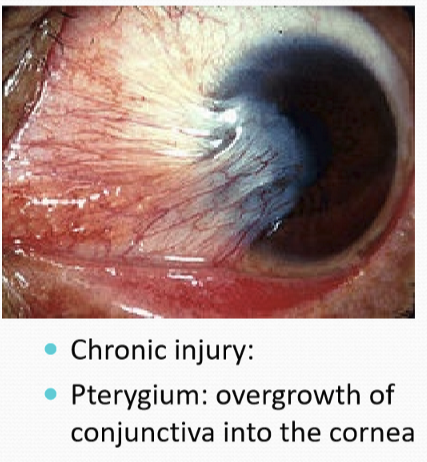
What happens in chronic UV damage to the corneal epithelium?
Pterygium: overgrowth of conjunctiva into the cornea
What is found in large amounts in the corneal epithelium and stroma to absorb UV light?
Ascorbic acid
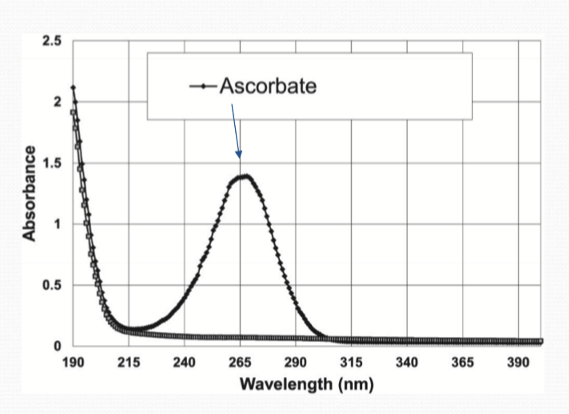
How does Ascoribc acid mitigate ROS?
Ascorbic acid functions as an electron donor, reducing the oxygen radicals
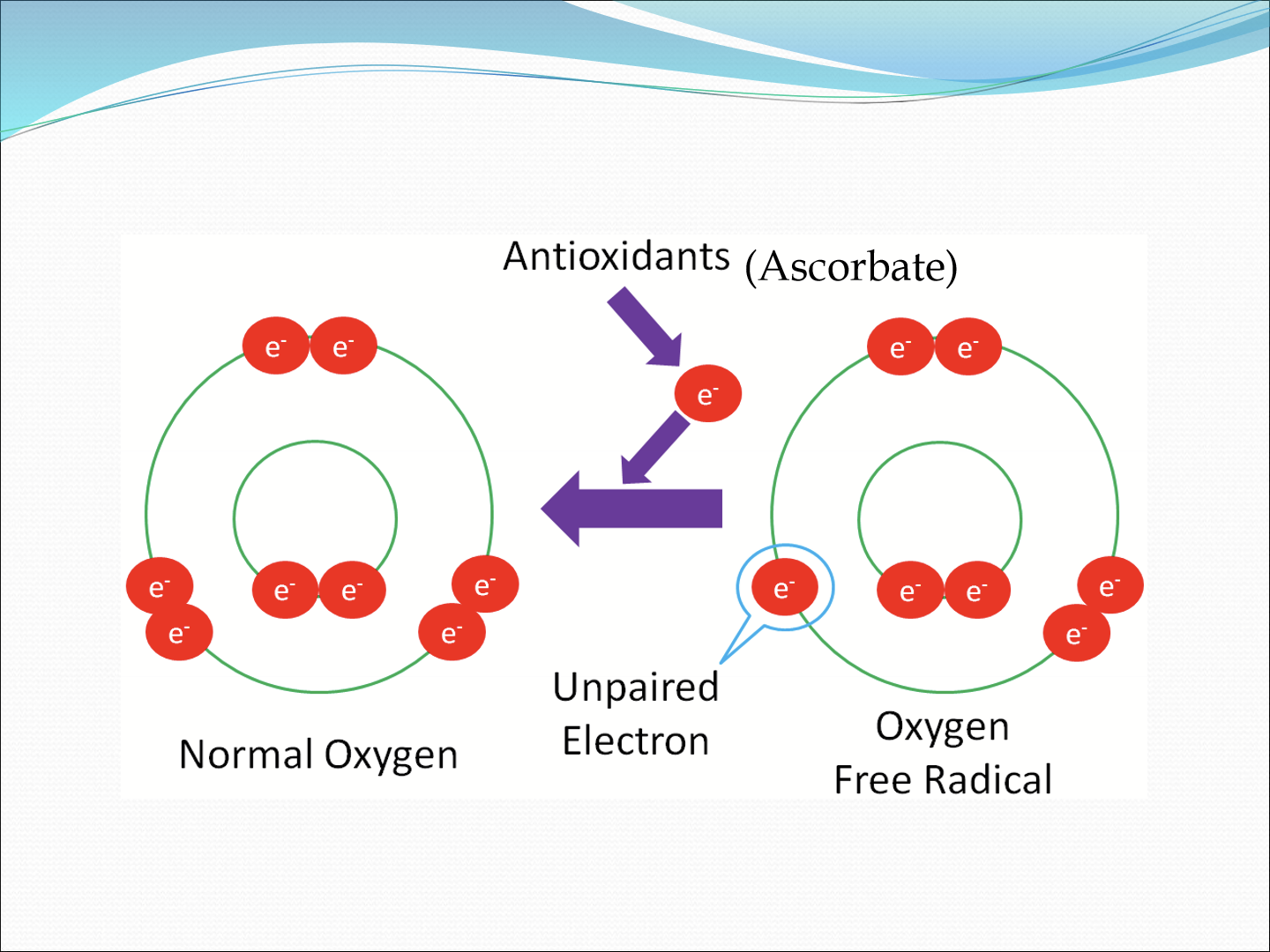
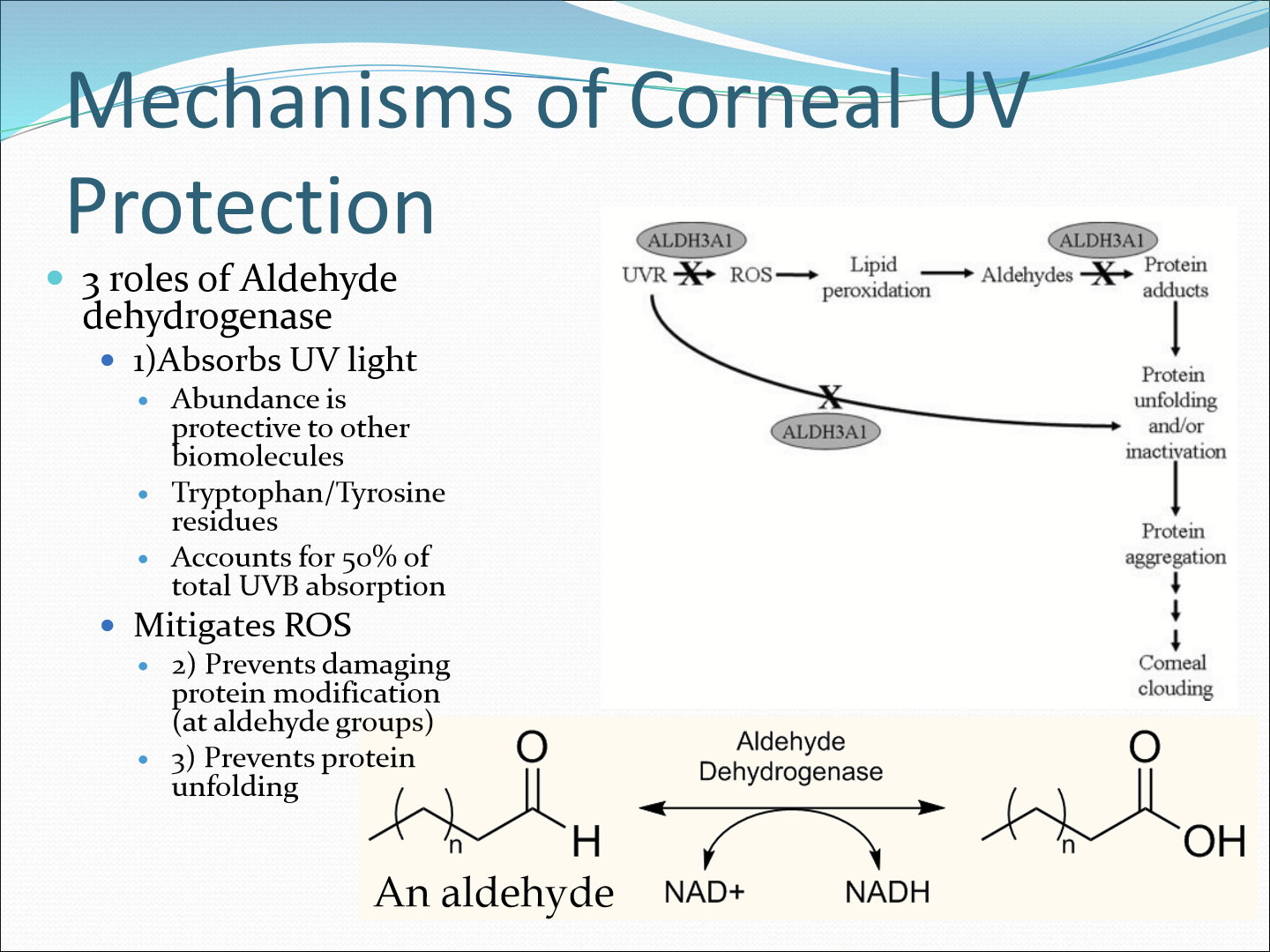
What also protects the cornea from UV damage?
Aldehyde dehydrogenase, found in corneal crystallin and water.
How does aldehyde dehydrogenase work?
It absorbs UVB light from the tryptophan and tyrosin residues
Mitigate ROS by preventing damaging protein modifications (by converting aldehydes to carboxylic acids) and prevents proteins unfolding