Important Things for Exam 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
2 categories of stroke
hemorrhagic and ischemic
define ischemic stroke
blood flow is blocked to the brain
more common than hemorrhagic
associated with permanent brain infarction
define hemorrhagic stroke
sudden bleeding in the brain
what is the function of the CSF
transports nutrients and waste
shock absorption
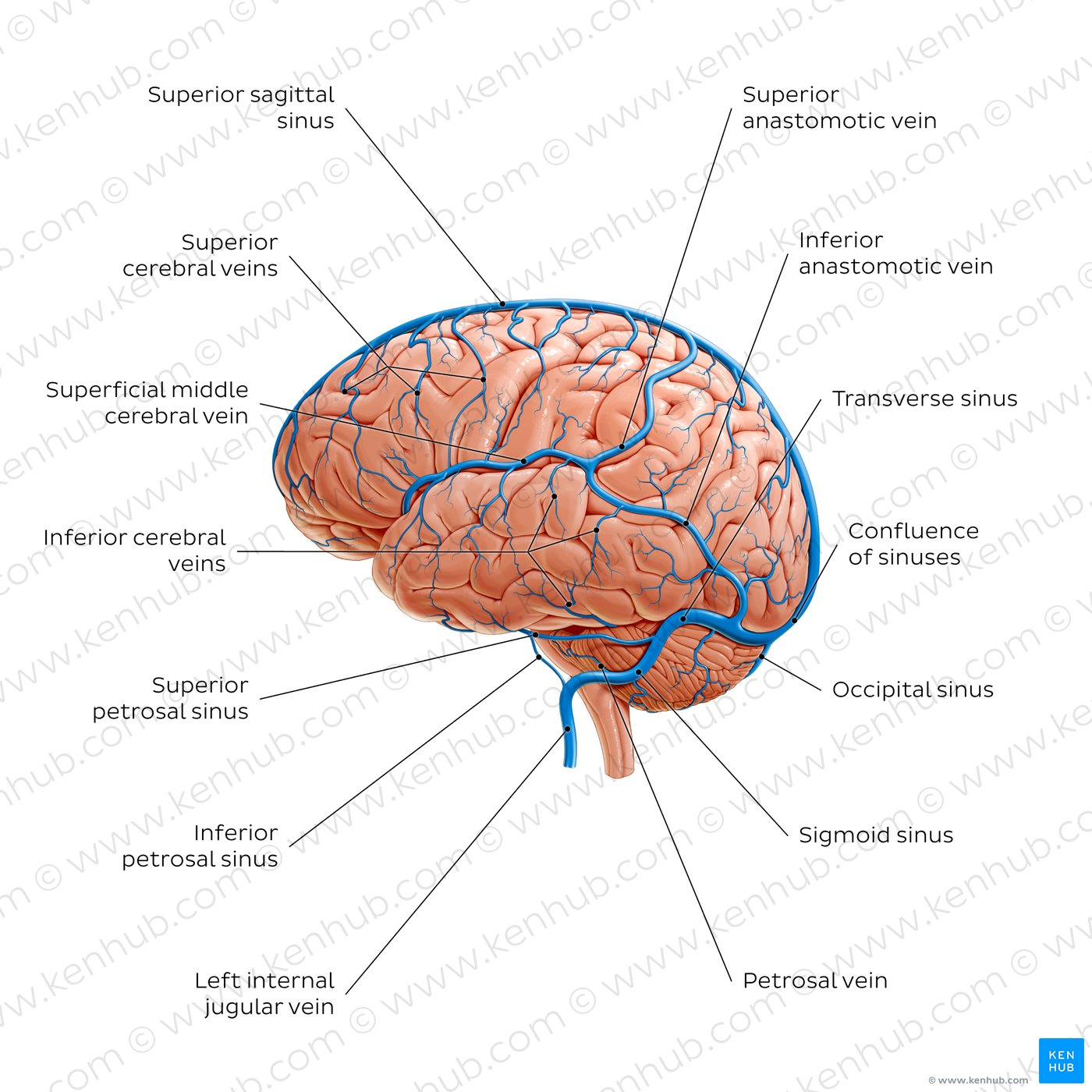
label the venous system of the brain
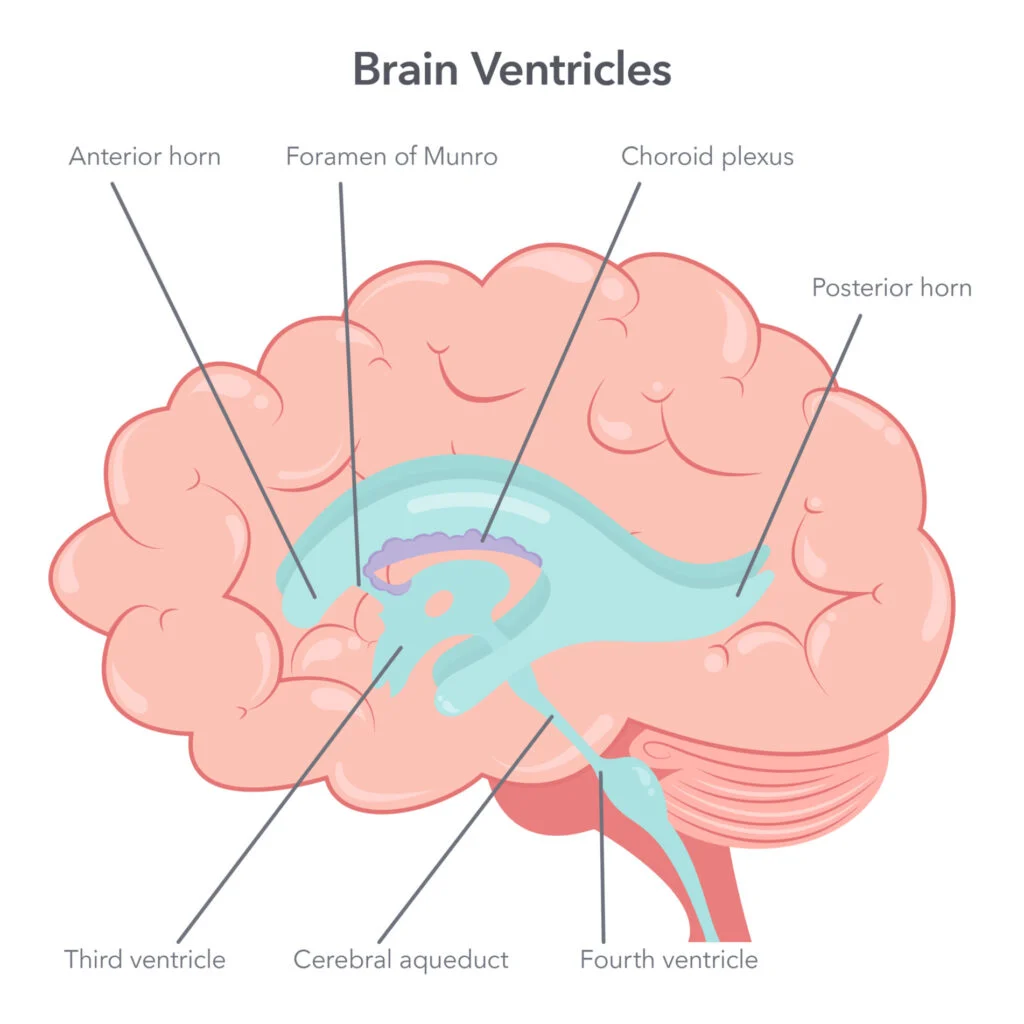
label the ventricles of the brain
label the arteries of the brain
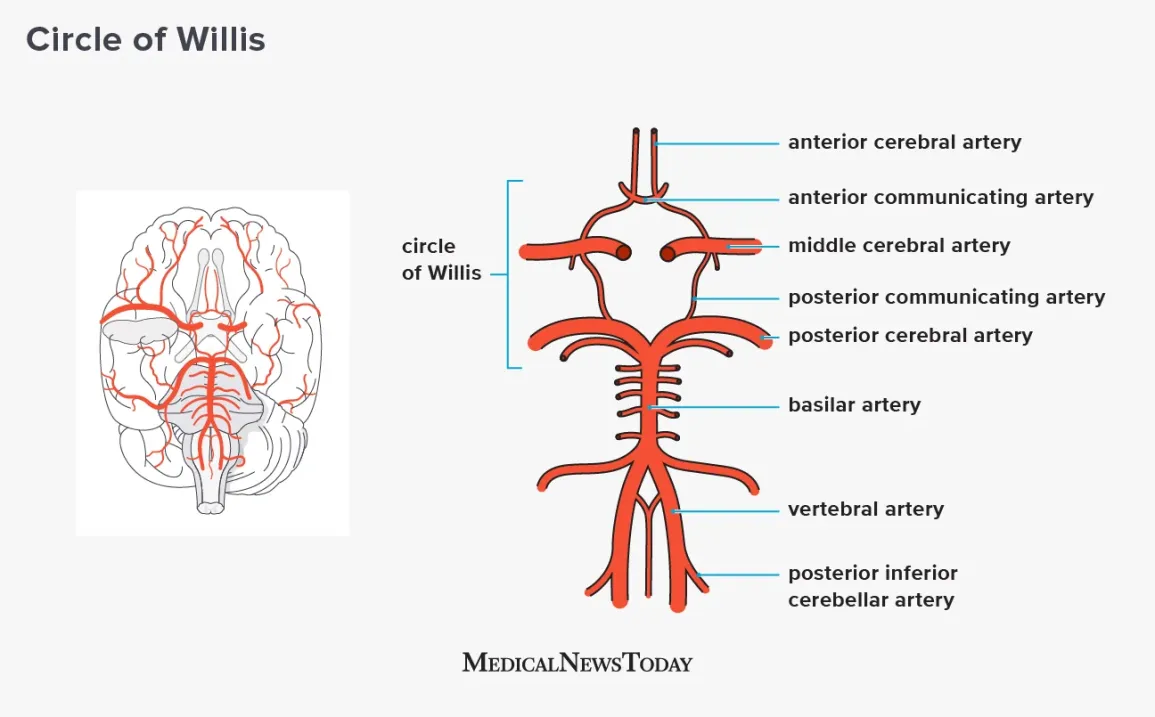
what does the basilar artery supply
brainstem (controls alll major body functions)
ACA stroke is more likely to affect what body parts
lower extremities
MCA stroke is more likely to affect what body parts
hands and face
TIA (transient ischemic attack)
focal brain ischemia that causes sudden transient neurological deficits and is NOT accompanied by permanent brain infarction
will have negative results on imaging
ABCD2 score of what indicates high risk of stroke
>4
ABCD2 score determines what
likelihood of stroke after TIA
what are the common causes of ischemic stroke
thrombosis
embolism
systemic hypoperfusion
cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
define the difference between the ischemic core and the penumbra
penumbra is salvageable while the ischemic core is not
F.A.S.T
face drooping
arm weakness
speech difficulty
time to call 911
wernicke’s aphasia
comprehension of spoken words is impaired
broca’s aphasia
speech output is severely reduced
tPA
tissue plasminogen activator
clot buster medication; needs to be given within a certain amount of time to reverse or negate a stroke
TNK
tenecteplase
faster and more benefits than tPA
principles of neuro rehab
ICF
teamwork
person-centered care
prognosis
neural plasticity
motor control
functional movement re-ed
skill acquisition
exercise prescription
health promotion
self management
mindset
behavior change
what are the levels of consciousness
coma
stuporous
somnalent
lethargic
alert
name the cranial nerves, their function, and whether or not their sensory, motor, or both
go over cranial nerve assessment
levels of sit to stand
flexion momentum (start to lift off)
momentum transfer (lift off —> max DF)
extension (max DF —> end hip ext)
stabilization