Cultivation and Isolation of Bacteria
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are the different types of stains?
- Gram stain
- Ziehl-Neelsen/Kinyoun/Modified
- Fluorochrome
- Acridine Orange
Gram positive pathogens stain ______.
purple
What is the order of a gram stain procedure?
- Fixation
- Crystal violet
- Wash
- Iodine treatment
- Wash
- Decolorization
- Wash
- Counter stain (safranin)
- Wash
- Blot dry
Ziehl-Neelsen/Kinyoun stain is used for ______.
mycobacteria
Ziehl-Neelsen is associated with the use of ______ temperatures, while Kinyoun is associated with ______ temperatures.
hot, cold
The primary stain used in Ziehl-Neelsen is ______.
Carbol-Fuschsin
The decolorizer used in Ziehl-Neelsen is ______.
3% HCl in ethanol
______ is used as the counter stain in Ziehl-Neelsen.
Methylene blue
Modified Z-N/Kinyoun is used for partially ______ organisms.
acid-fast
______ is the primary stain and ______ is the counter stain used in Modified Z-N/Kinyoun.
Carbol-Fuchsin, methylene blue
______ is the decolorizer used in Modified Z-N/Kinyoun.
1% H2SO4
Fluorochrome staining is used for ______.
mycobacteria
Fluorochrome is the primary stain used on all specimens sent for mycobacterial ______.
culture
In Fluorochrome staining, ______ is used as the primary stain.
Auramine-Rhodamine
In Fluorochrome staining, ______ is used as the counterstain.
K permanganate
What is the decolorizing solution for Fluorochrome staining?
0.5% HCl in 70% EtOH
What are the 4 different types of plating media?
- All-purpose/non-selective
- Enriched
- Selective
- Selective/Differential
All-purpose/non-selective media supports the growth of most ______ bacteria.
non-fastidious
All-purpose/non-selective is a ______ agar.
nutrient
Blood agar is a type of ______ agar consisting of Trypticase Soy Agar with 5% sheep red blood cells.
enriched
With blood agar, an MLS should be acutely aware of ______ after colony formation.
hemolysis
What are the types of hemolysis that can present on blood agar?
- Alpha
- Beta
- Gamma
Alpha hemolysis produces a ______ discoloration surrounding the colonies.
greenish
This greenish discoloration is due to ______ hemolysis of the RBCs in the blood agar.
incomplete
Bacteria that produce alpha hemolysis on blood agar are always ______ negative.
catalase
Catalase negative bacteria causes an accumulation of ______, causing alpha hemolysis coloration.
H2O2
Beta hemolysis on blood agar produces a ______ zone around the colonies.
clear/colorless
This clear zone is caused by ______ hemolysis of RBCs on the blood agar plate.
complete
Organisms that produce a beta hemolytic zone on blood agar are always ______ positive.
hemolysin
Gamma hemolysis means there is ______ hemolysis/discoloration.
no
Chocolate agar is a type of enriched media that consists of RBCs that are ______ before they are mixed into the agar.
lysed
Chocolate agar supports the growth of ______ organisms such as Neisseria and Haemophilus.
fastidious
What is the purpose of selective agar?
Inhibit the growth of some bacteria and promote the growth of others
Through what mechanisms can selective agar function through?
- Nutrient manipulation
- pH
- Osmotic adjustments
- Oxygen tension
- Dyes
- Antimicrobial agents
What are the three types of selective agar?
- Phenylethyl alcohol (PEA)
- Columbia Nalidixic Acid (CNA)
- Thayer-Martin
Selective/Differential agar ______ between the bacteria that does grow.
differentiates
What are the types of selective/differential agar?
- MacConkey
- Hektoen
- Mannitol Salt Agar
MacConkey agar is selective for ______.
gram negative rods
MacConkey agar differentiates between bacteria that is/is not ______.
lactose fermenting
Colonies that are the same color as the MacConkey agar plate are _______.
non-lactose fermenters
Colonies that are pink against the MacConkey agar plate are ______.
lactose fermenters
Hektoen agar is selective for ______.
gram negative rods
Hektoen agar differentiates between bacteria that are _______ fermenters.
lactose/sucrose
Colonies that appear green on Hektoen agar are _______ fermenters.
non-sucrose, non-lactose
If these green colonies have a black center, they are ______ positive.
H2S
Colonies that appear orange on Hektoen agar are _______ fermenters.
lactose and sucrose
Mannitol Salt Agar plating that yields a yellow color means the corresponding bacteria _______.
ferment mannitol
Mannitol Salt Agar plating that yields no change in color (stays red) means the corresponding bacteria _______.
don't ferment mannitol
Mannitol Salt Agar is ______ selective, along with anything that can grow in high ______ levels.
staph, salt
Enrichment broth is used for ______ the number of organisms present in a sample.
increasing
Transport media is used to maintain organism ______.
viability
What are some of the transport medias used in microbiology?
- Cary-Blair
- Amies
- Stuart
What are the two types of media inoculation techniques?
- Dilution streak
- Quantitative cultures
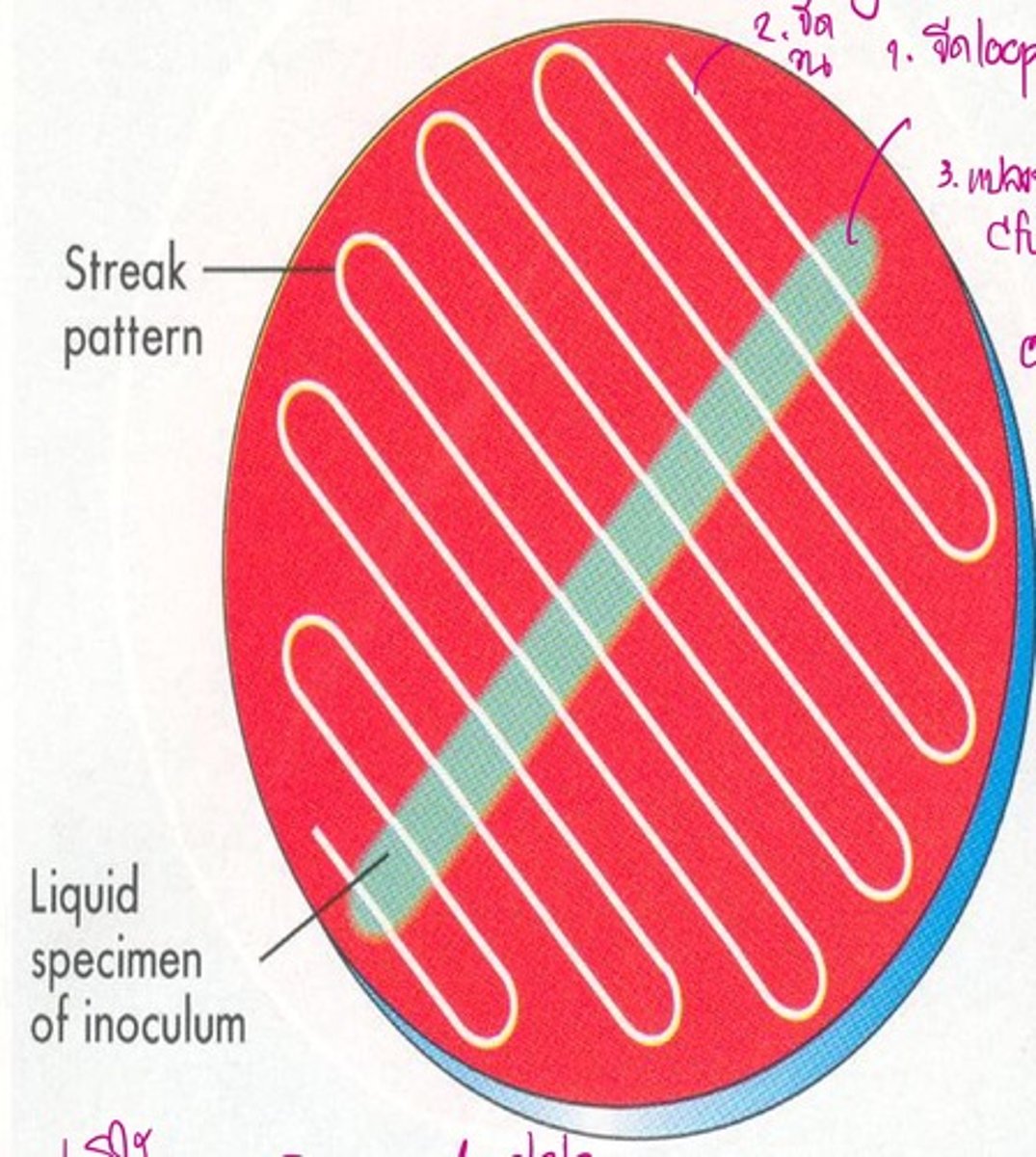
Dilution Streak Plating Technique
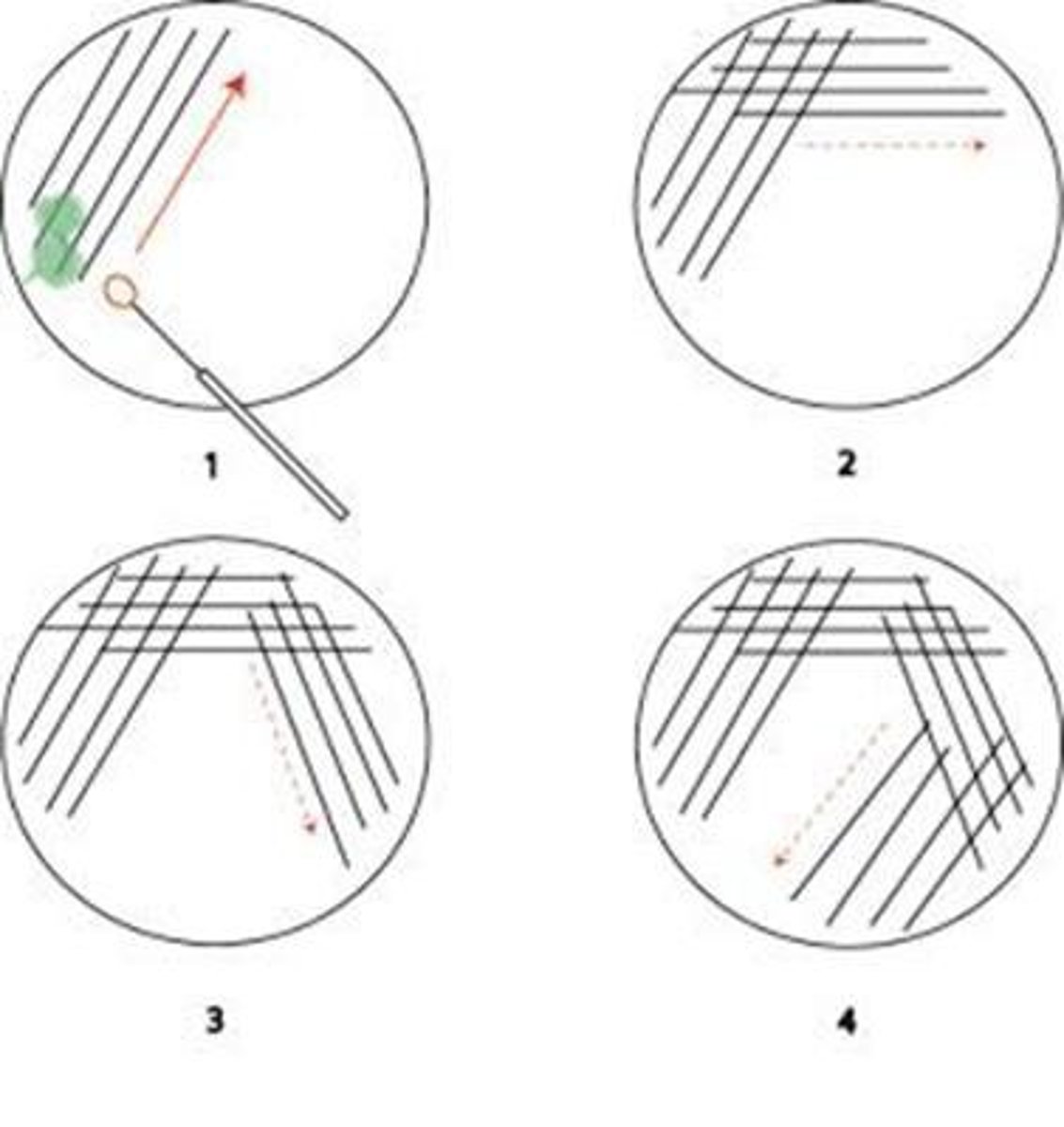
Quantitative Culture Plating Technique
What is the optimal temperature used for media incubation?
35C (+/-2C)
For aerobic bacteria, what should be the atmospheric compound levels, from highest to lowest?
N2 --> O2 --> CO2
For microaerophilic bacteria, what should be the atmospheric compound levels, from highest to lowest?
N2 --> CO2 --> O2
For anaerobic bacteria, what should be the atmospheric compound levels, from highest to lowest?
N2 --> H2 --> CO2
The optimal incubation time for media is ______.
24 hours
What components are observed when looking at colony morphology?
- Hemolysis
- Size
- Margin
- Elevation
- Density
- Color
- Consistency
- Odor