UNIT 3 CHEMISTRY
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Open system
Can exchange energy and matter
Closed system
Can exchange only energy
Equilibrium
When the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of reverse reaction, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products.
Position of Equilibrium
The relative amounts of reactants and product at equilibrium
Factors that affect position of equilibrium
adding or removing a reactant or product
changing the pressure by changing the volume of the sealed container (for equilibria involving gases)
dilution (for equilibria in solution)
changing the temperature.
What is Le Chatelier principle
If an equilibrium system is subjected to change, the system will shift to partially oppose the change
Explain what would happen if you add a product or reactant (collision theory)
When the concentration increases, the amount of collision increases, speeding up the forward reaction, breaking equilibrium. Then, as the concentration of the product increases the reactant decreases thus the rate of the forward reaction rate decreases and the rate of the reverse reaction increases until they become equal again
What is the Gas Particles and Pressure relation in equilibrium context
Gas Particles increase - Pressure increase
Gas Particles decrease - Pressure decrease
How does a system react to a change in pressure
A system will react to a change in pressure by partially opposing the change by reducing or increasing the pressure. The reaction will move left or right.
If a change in pressure occurs, what is something you need to remember that is important (related to the change after intial equillirbum)
If the pressure decreases, all reactants and products will go down in concentration and will be less than what the equilibrium concentrations were regardless after the shift.
Same for if pressure increase, all reactants and products concentration will be higher than the initial equillbirum even after the shift
How does a system react to change in pressure when the gas particles are even on both sides of the reaction
a change in pressure will not shift the position of equilibrium. , the system is unable to oppose the change applied and there is no overall net reaction.
How does a system react to a change in Dilution
Dilution by water reduces the number of particles per volume. This results in the reaction moving to the side that produces greater number of particles to bring back equilibrium as stated by le chatlier principle. However, the concentration decreases instantaneously, and will be lower even after equilibrium
If H20 is a liquid or solvent is it included in the KC
No
On a graph, dilution intialy goes down in what typa way
Straight down, immediate change
How does a system react to change in temperature
net reverse reaction (fewer products) for exothermic reactions
net forward reaction (more products) for endothermic reactions.
Main principle is that when temperature is increased - the reaction will want to absorb energy to counteract the increase in energy
When temperature is increased, reaction will want to produce and energy (exothermic)
The Kc value is only affected by what factor
Temperature
If the reaction quotient is greater than the Kc the system
shifts to the left to acheieve equillbirum, more reactants are formed
If the reaction quotient is less than the Kc the system
the system ‘shifts to the right’ to achieve equilibrium and more products are formed
If you have a reaction and its equilibrium, what do you do to the reverse reaction’s equillibrum
you do the reciprocal, 1/
If the coefficient of the equation is doubled, what happens to the Kc value
value of Kc is squared
If the coefficients of the equation is halved, what happens to the Kc value
value of Kc is square rooted
For an exothermic reaction, what happens to the Kc value if temperature increases
The Kc value decreases due to the shift of equilibrium to the left, favoring the reactants.
For an endothermic reaction, what happens to the Kc value if temperature increases
The Kc value increases because the equilibrium shifts to the right, favoring the products.
What happens to the rate graph curve when there is a Le Chatelier’s response such as temperature change
The concentrations are changing smoothly
What happens to the graph curve when there is a change in volume/pressure
All of the species will either initially drop or increase very sharply
What happens to the concentrations of a system when the volume is halved
The concentrations of all species will double
what happens when Ionic compounds such as NaOH and BrOH are added in solution of an equilibrum reaction
The ionic compounds dissasociates into its respective elements, from here you can work out where it will go and then see the shift in equiullirbum
How to calculate the average rate of reaction
by measuring the change in concentration of a reactant or product over a specific time period.

Important information regarding adding a solution in an equiulilburm reaction
Identify Whether the Solution Will Dissociate and Produce an Acid or Base
See Whether the Reaction Involves an Acid or Base that It Will React With
When can you use ICE tables
ICE tables can be used to calculate the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium in a chemical reaction, particularly when initial concentrations and changes in concentration are known.
A concentrated acid or base contains…
more moles of solute per litre than a dilute acid or base
In context of acid and bases, “strong” and “weak” refer to…
the relative tendency to accept or donate protons
The stronger an acid,
the weaker its conjugate base.
The stronger a base
The weaker its conjugate acid
at 25C what is the concentration of H30 and OH in neutral solutions/pure water
[H3O+] = [OH−] = 10−7 mol L−1
at 25C what is the concentration of H30 and OH in acid solutions
[H3O+] > 10−7 mol and [OH−] < 10−7 mol
at 25C what is the concentration of H30 and OH in basic solutions
[H3O+] <10−7 mol and [OH−] > 10−7 mol
collision theory for an endothermic reaction
Remember that, for an equilibrium
system, an increase in temperature
increases the proportion of molecules
with the necessary energy to overcome
the activation energy barrier for the
endothermic reaction to a greater
extent than for the exothermic reaction,
and so the endothermic reaction will be
favoured
formula for moles

definiiton of Kc
The equilibrium constant is the ratio of the equilibrium concentrations of the products over the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants raised to the power of their coefficients.
If the value of Ka is large
the concentration of the products of the dissociation
reaction are high and therefore favoured. That is, the acid dissociates readily and is
therefore referred to as a strong acid.
If the value of Ka is small
the acid does not readily dissociate making it a weak
acid.
seven strong acids

pH = pKa at half-equivalence is ONLY valid in titrations involving one weak species and one strong species.
For it to be a buffer solution it
must contain a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa
both components must be present in sufficient amounts
for the mole ratio stoichemtry thing
on the bottom fraction put the mole of the one you already know, and on top the one u tryna find
for titration curves, and using stoichemtry calculations you have to use the equivalence point because
In titration, the equivalence point is when the number of moles of acid = number of moles of base
When identifying if an acid is weak on a titration curve identify
buffer region, starting pH
Redox reactions, predicting whether a spontaneous reaction will occur or not
The one being reduced must be below the one being oxidised in the reactivity series (or must have a higher E∘E^\circE∘ value in the reduction potential table).
What is the oxidisation number of a free element
0
Oxidisation number of hydrogen
With nonmetals —> +1
In Metal hydrides —> -1
Oxidisation number of oxygen
Normally 2
With Fluroine it is +2
It is -1 in peroxides (O - O bond)
Oxidisation number of halogens
Is normally -1
Except if it is with Oxygen (oxygen will be -2)
Except if it is with another halogen that is above them in group 17
Steps for balancing a complex redox reaction
Balance all chemicals other than Hydrogen and Oxygen
Balance Oxygen by adding H2O
Balance Hydrogen by adding H+
Balance the charges by adding electrons
What is a galvanic cell and therefore what is the electrolytic cell
A galvanic cell is a type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Electrolytic is electrical energy into chemical energy
maximum cell voltage/ cell potential difference
whats the formula
more positive E - less positive E
(reduction) - oxidisation
In electrolysis what charge is the electrode on the anion and cation
The Anion’s electrode is positive (connected to positively charged terminal)
The Cathode’s electrode is negative (connected to negatively charged terminal)
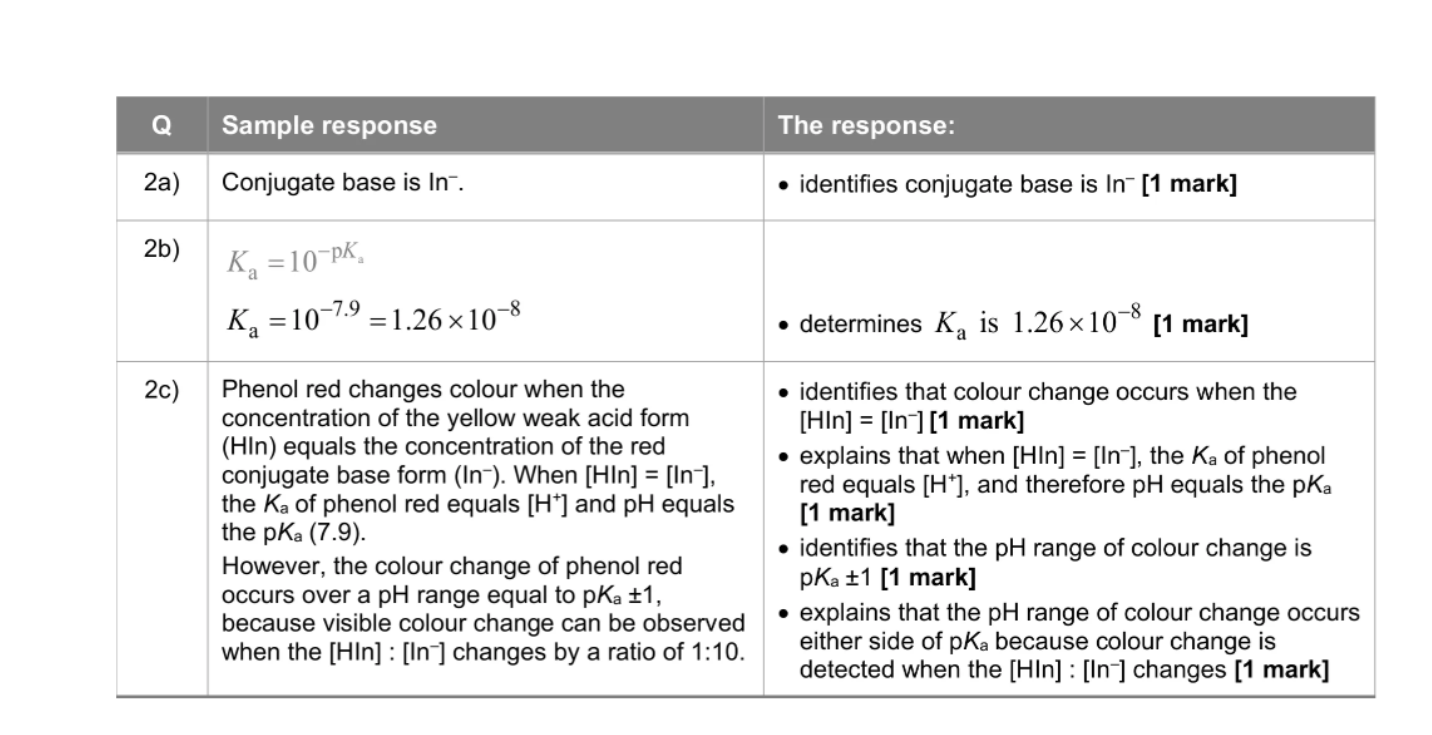
What’s an end point
The end point of a titration using an indicator is the pH at which the indicator changes colour most sharply, which corresponds to its pKa value.
Hln —> H++ ln-
At low pH (acidic), there’s lots of H⁺, so the equilibrium shifts left → mostly HIn → one colour.
At high pH (basic), H⁺ is removed, equilibrium shifts right → mostly In⁻ → the other colour.
Elimination reaction of Alcohol into alkene
What’s removed: H₂O
Reagent: Concentrated acid (H₂SO₄ or H₃PO₄)
Conditions: Heat (~170 °C)
Type: Acid-catalysed elimination
difference between