Clin Lab Pulmonary
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
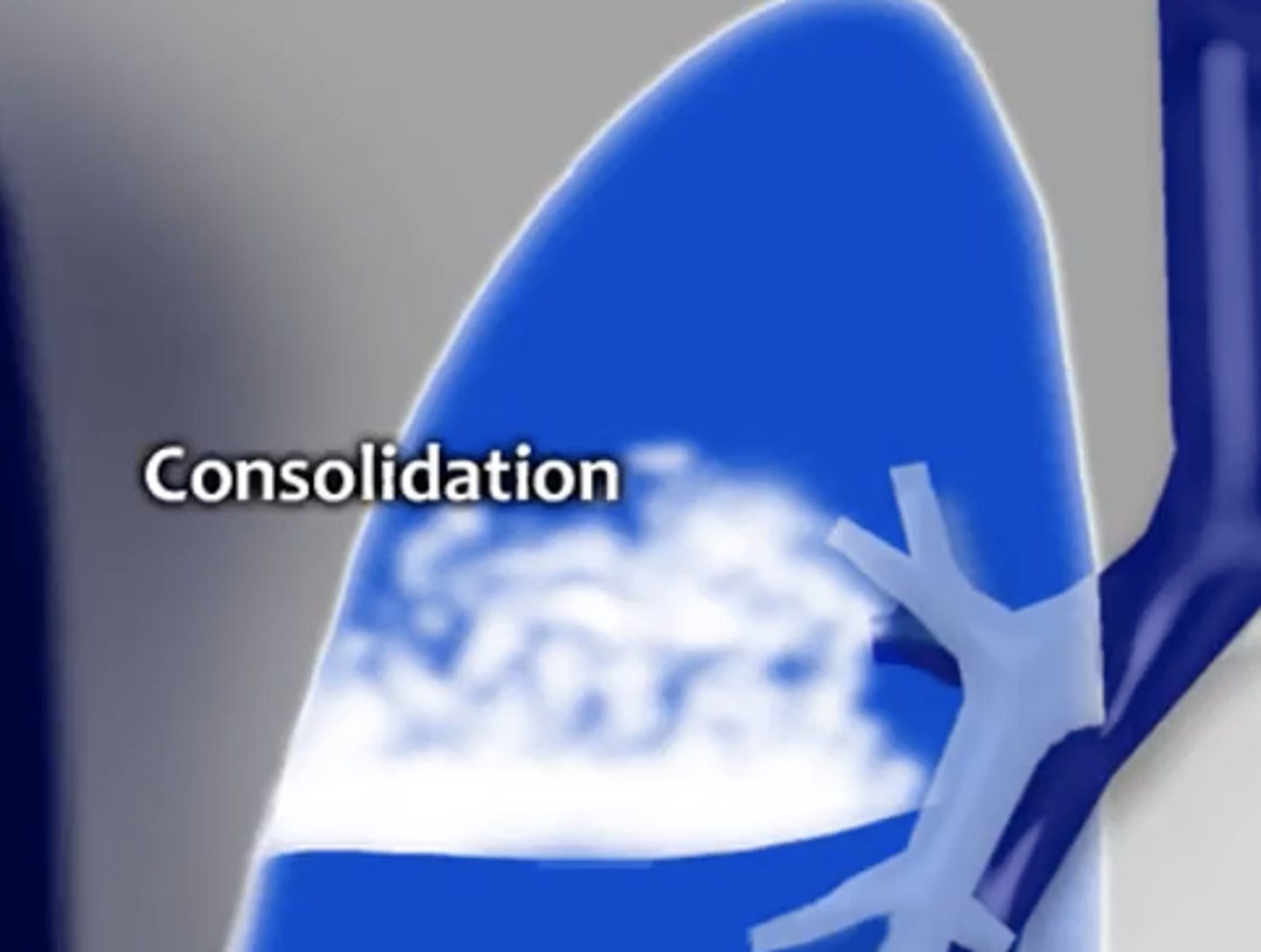
consolidaton
water, pus, blood, cells in the lung parenchyma
effusion
fluid in pleural space
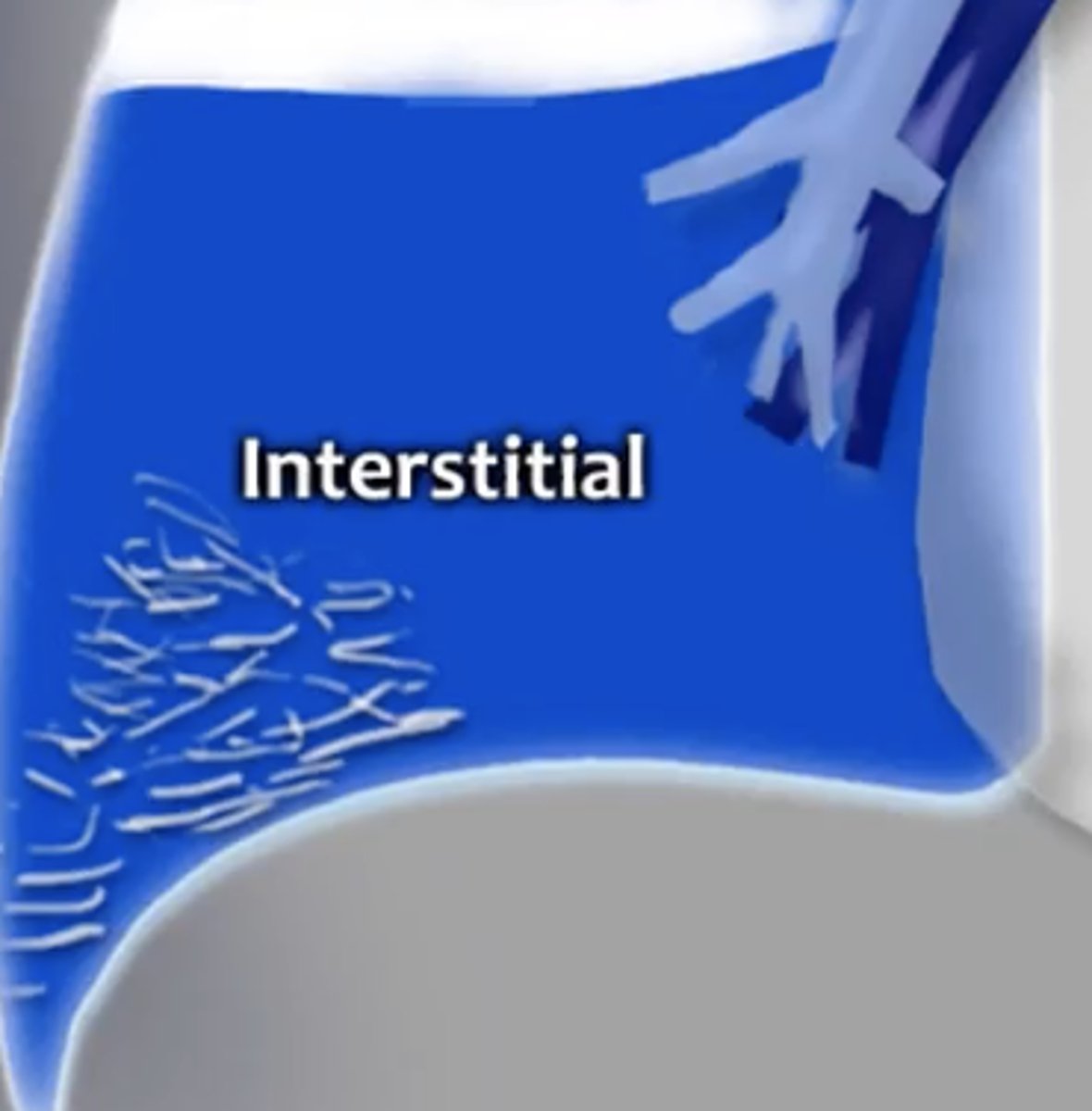
interstitial
reticular pattern is thickening of interstitial fiber network by fluid, fibrous tissue, or infiltration
atelectasis
collapsed lung; incomplete expansion of alveoli
cephalization
increased vascular marking upward toward the head (normal vascular marking are less in apex and greater centrally to base)
posterior anterior (PA)
CXR where patient has to be able to stand up
anterior posterior (AP) chest xray
CXR done when pt cannot stand up; makes heart appear large so cannot evaluate cardiomegaly
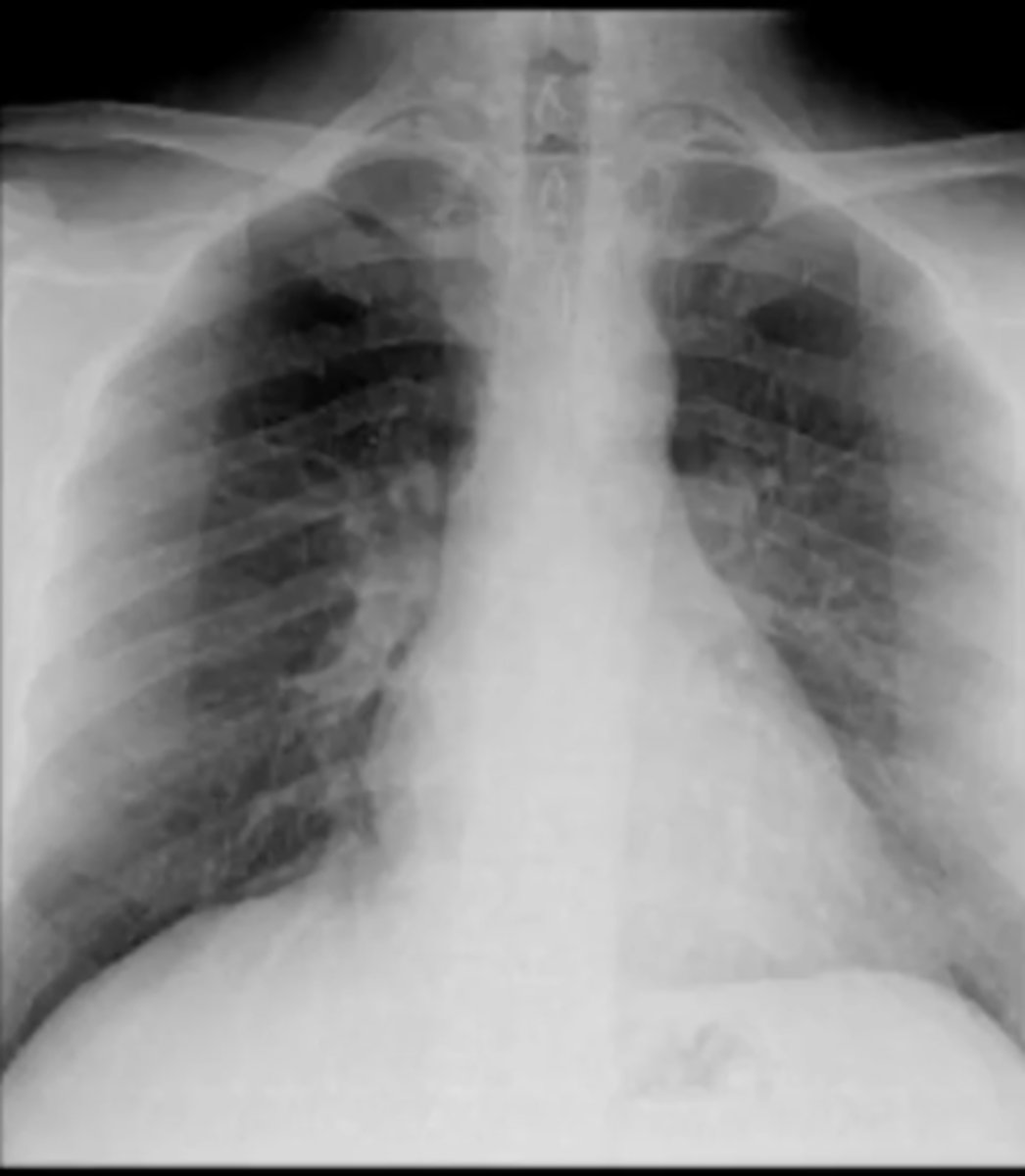
lateral CXR
CXR where patient has to be able to stand up; good for looking behind the heart and in front of sternum (anterior mediastinal mass)
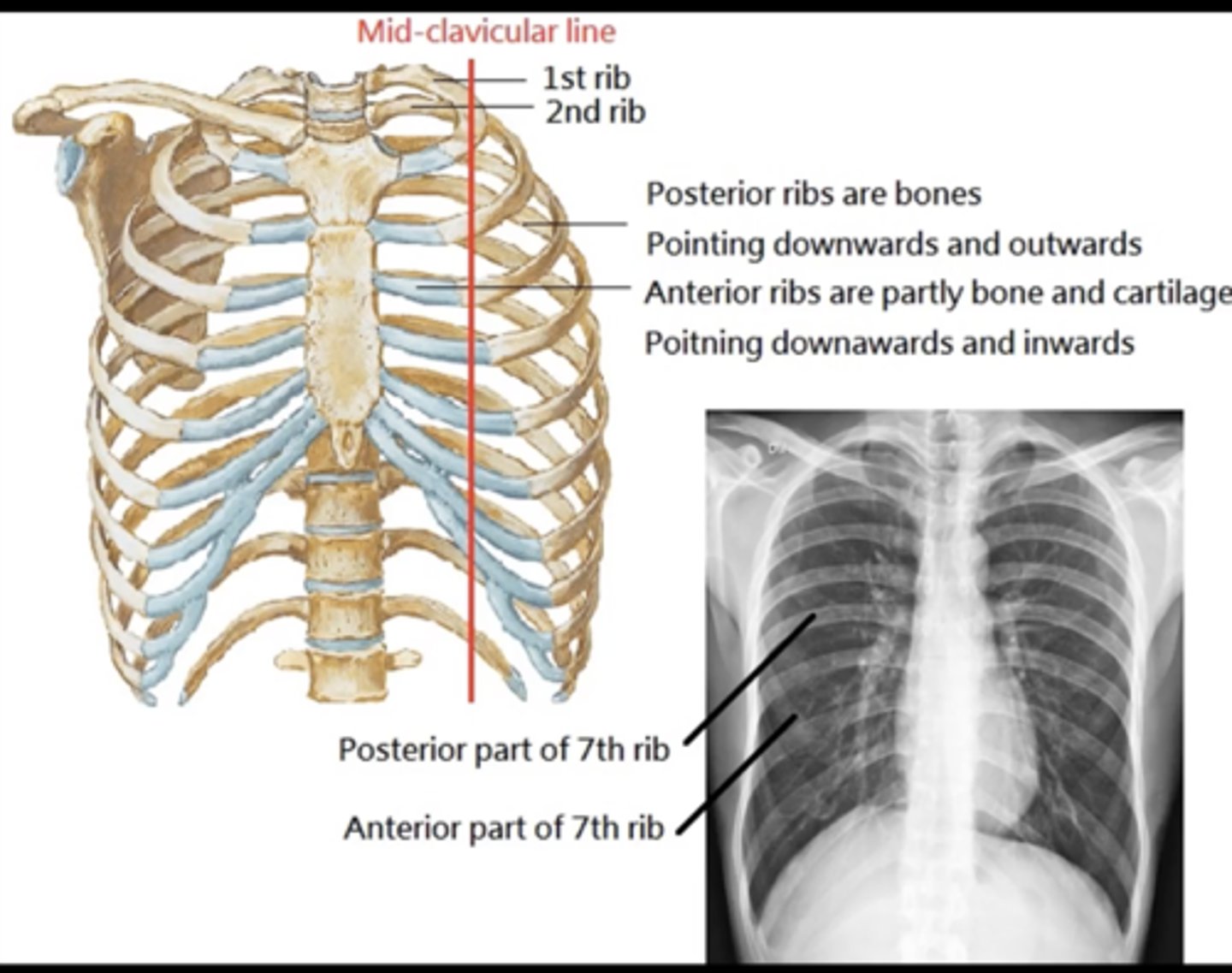
distance of edge of clavicle to spinous process should be equal
(evaluating AP CXR) rotation
(<8= hypoinflation; >10= hyperinflation)
count ribs; should be minimum of 8 posterior ribs
(evaluating AP CXR) inspiration
- vertebrae visible behind heart
- diaphragm visible to spine
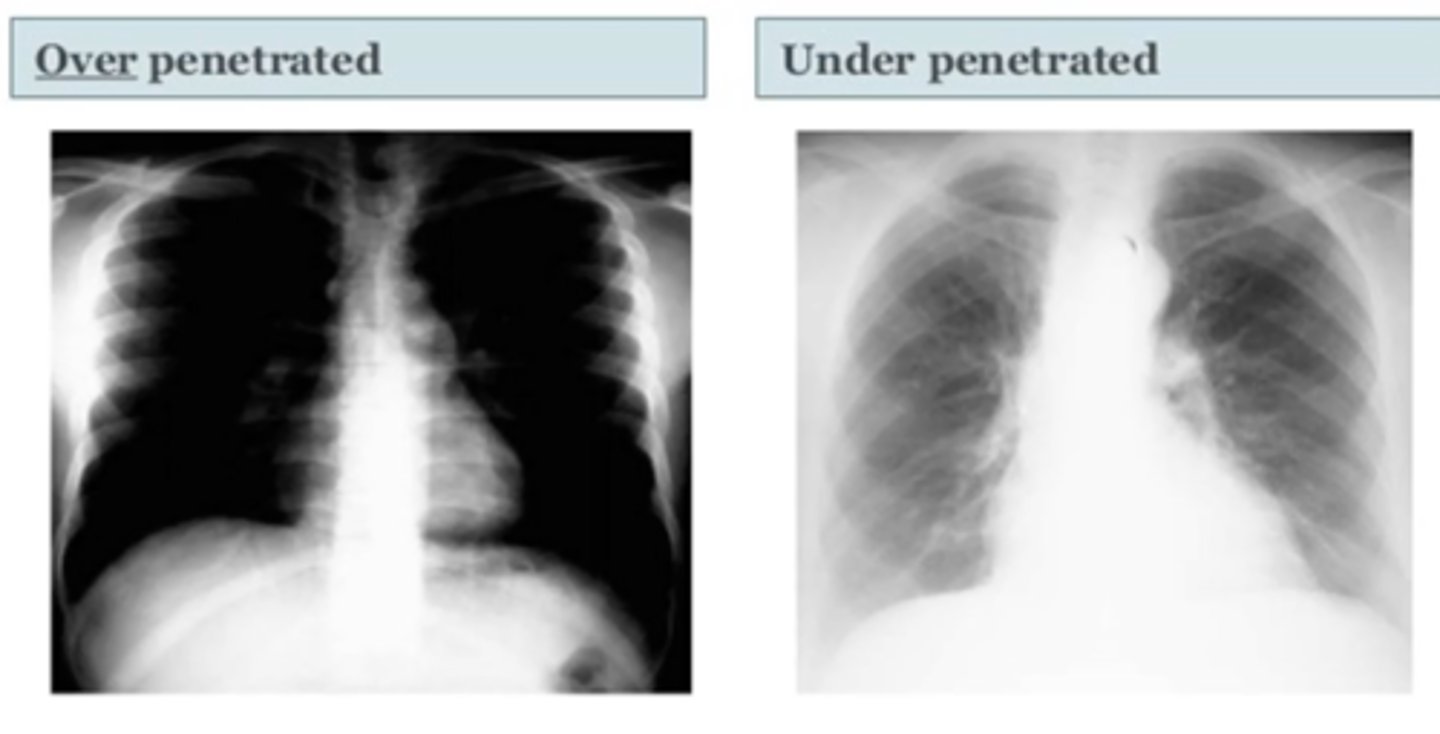
(evaluating AP CXR) exposure
whiter at the top of vertebrae (bc of shoulder muscle) and clearer as you move down spine
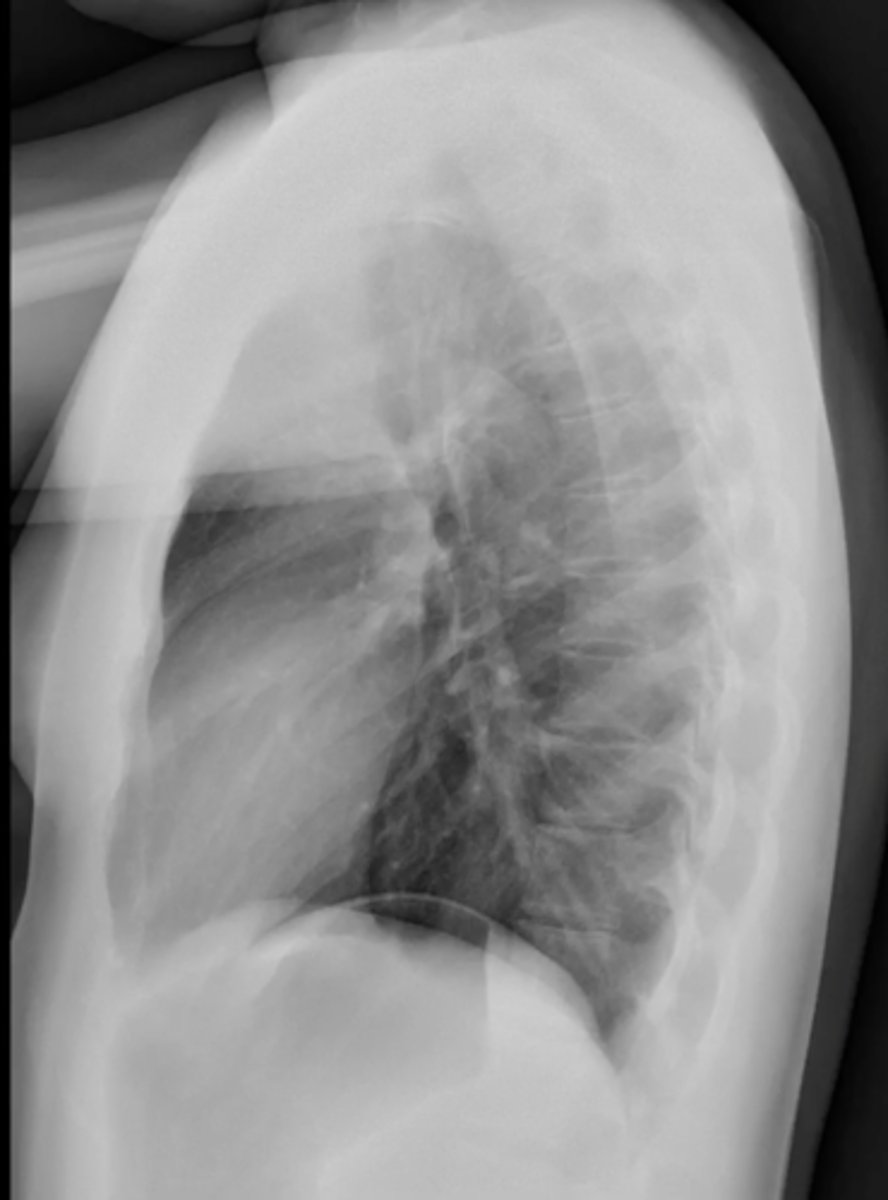
(evaluating Lateral CXR)
exposure
1. bones - look for fractures
2. mediastinum size
3. right paratracheal stripe
4. cardiac silhouette
5. airway (trachea, diaphragm)
6. pulmonary vasculature and hilum
7. lungs
steps to read PA CXR (external --> internal)
normal: <8
(evaluating AP CXR) mediastinum size
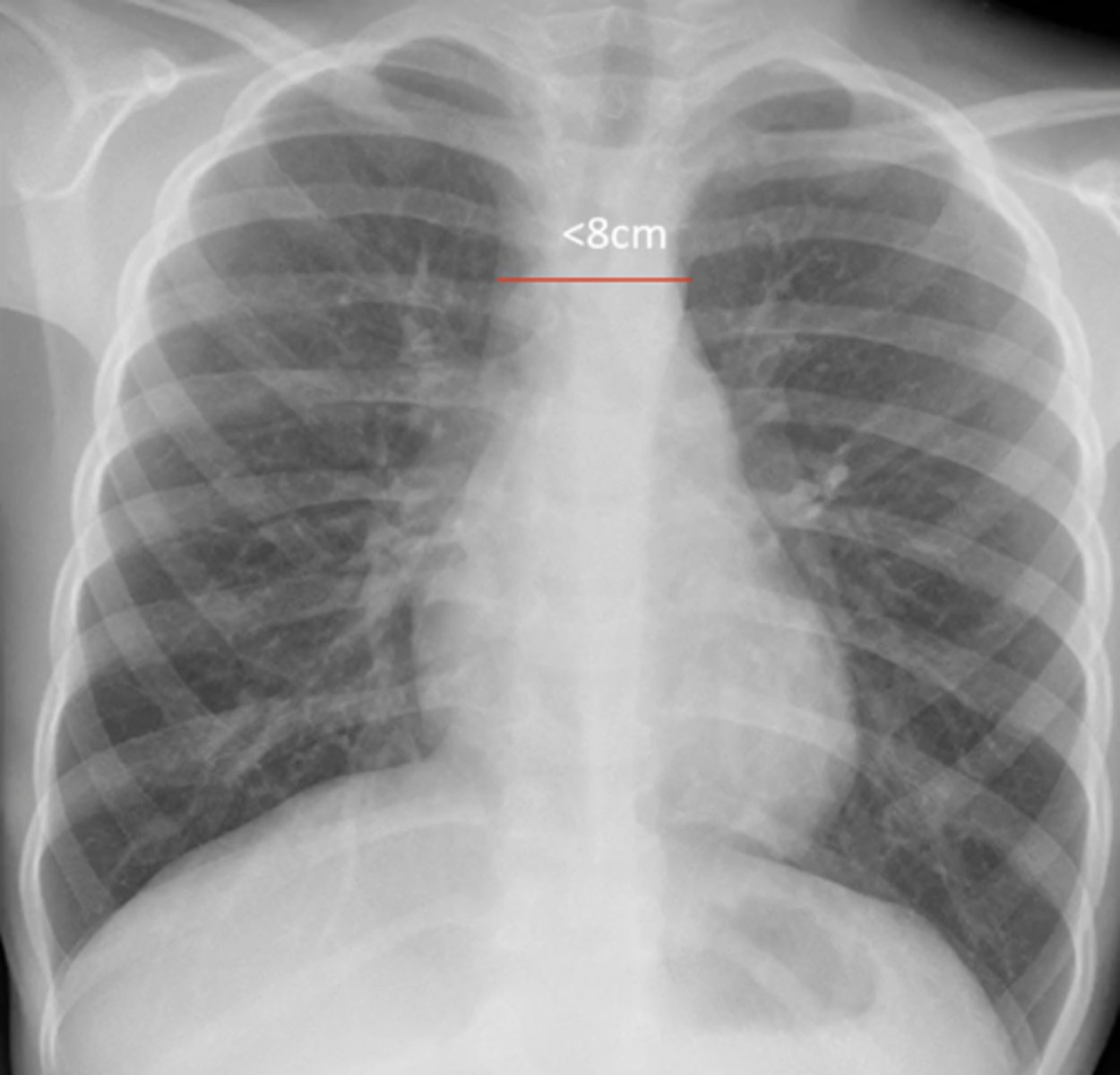
concern for aneurysm if >8cm
(evaluating AP CXR) widened mediastinum

represents right tracheal wall, adjacent pleural surfaces and any mediastinal fat
(evaluating AP CXR) right paratracheal stripe
if >4mm concern for a mass or tumor
(evaluating AP CXR) widened paratracheal stripe
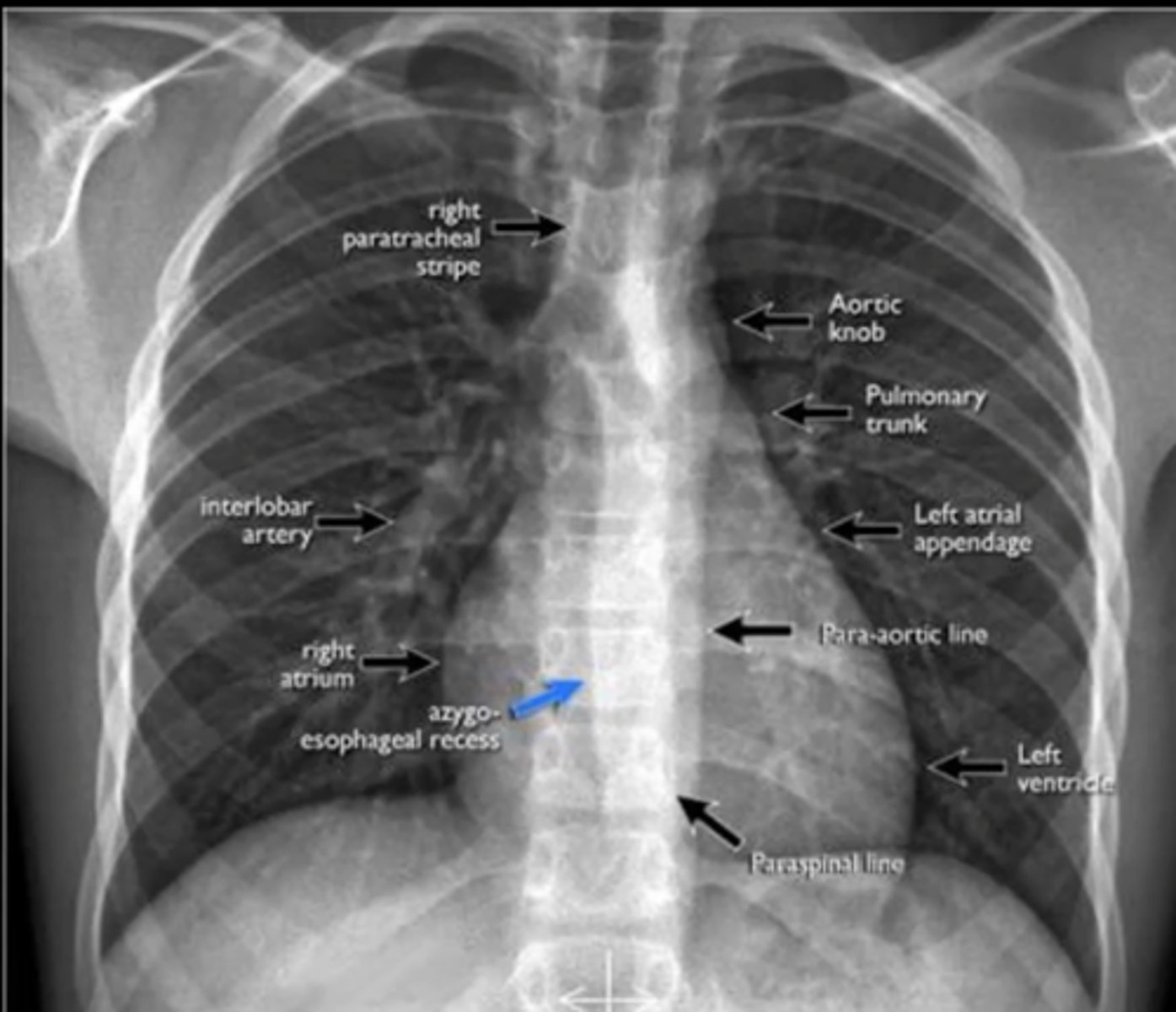
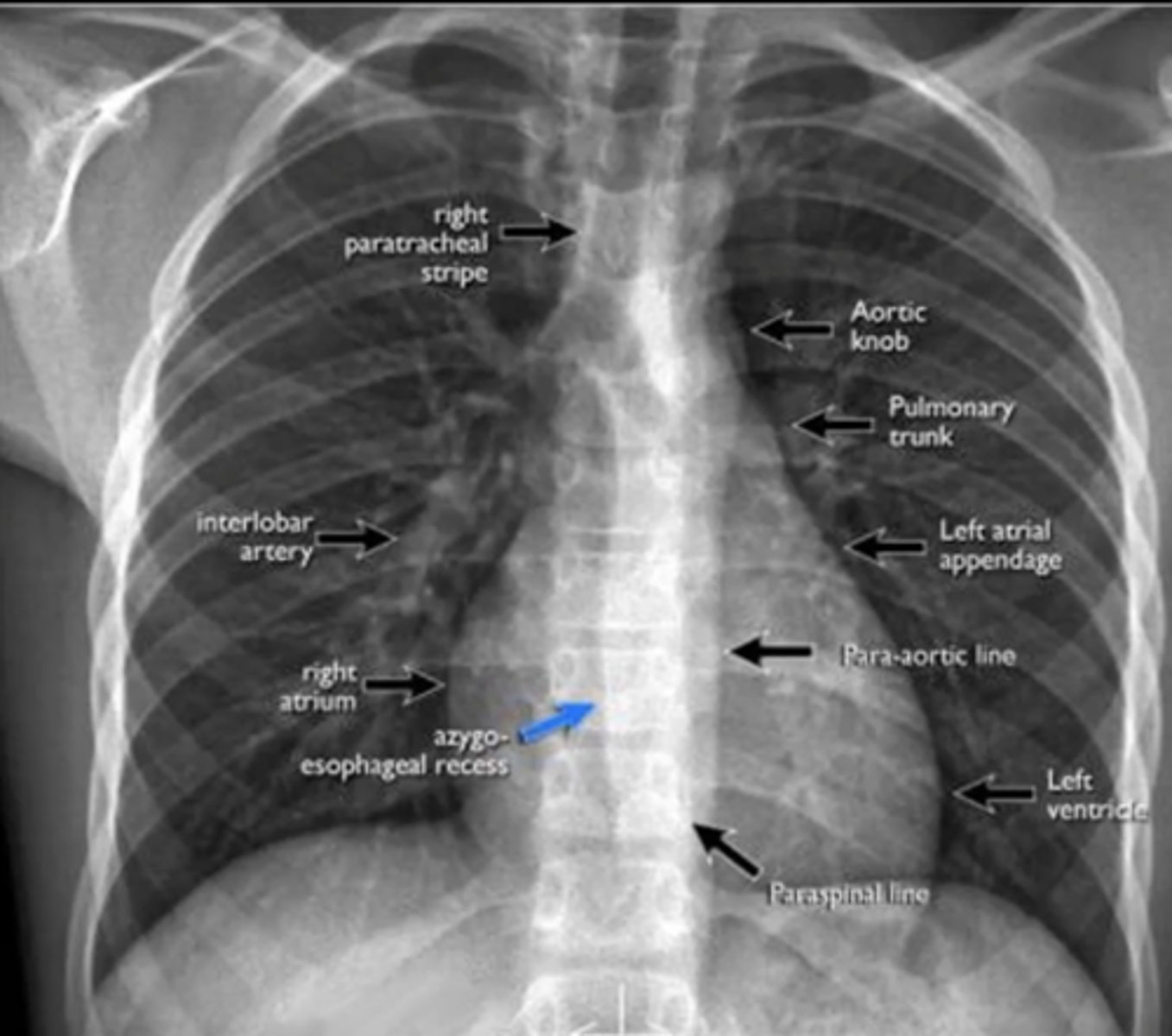
visualize: aortic knob, pulmonary trunk, left atrial appendage, para-aortic line, left ventricle, right atrium, interlobar artery (NO RIGHT VENTRICLE VISIBLE)
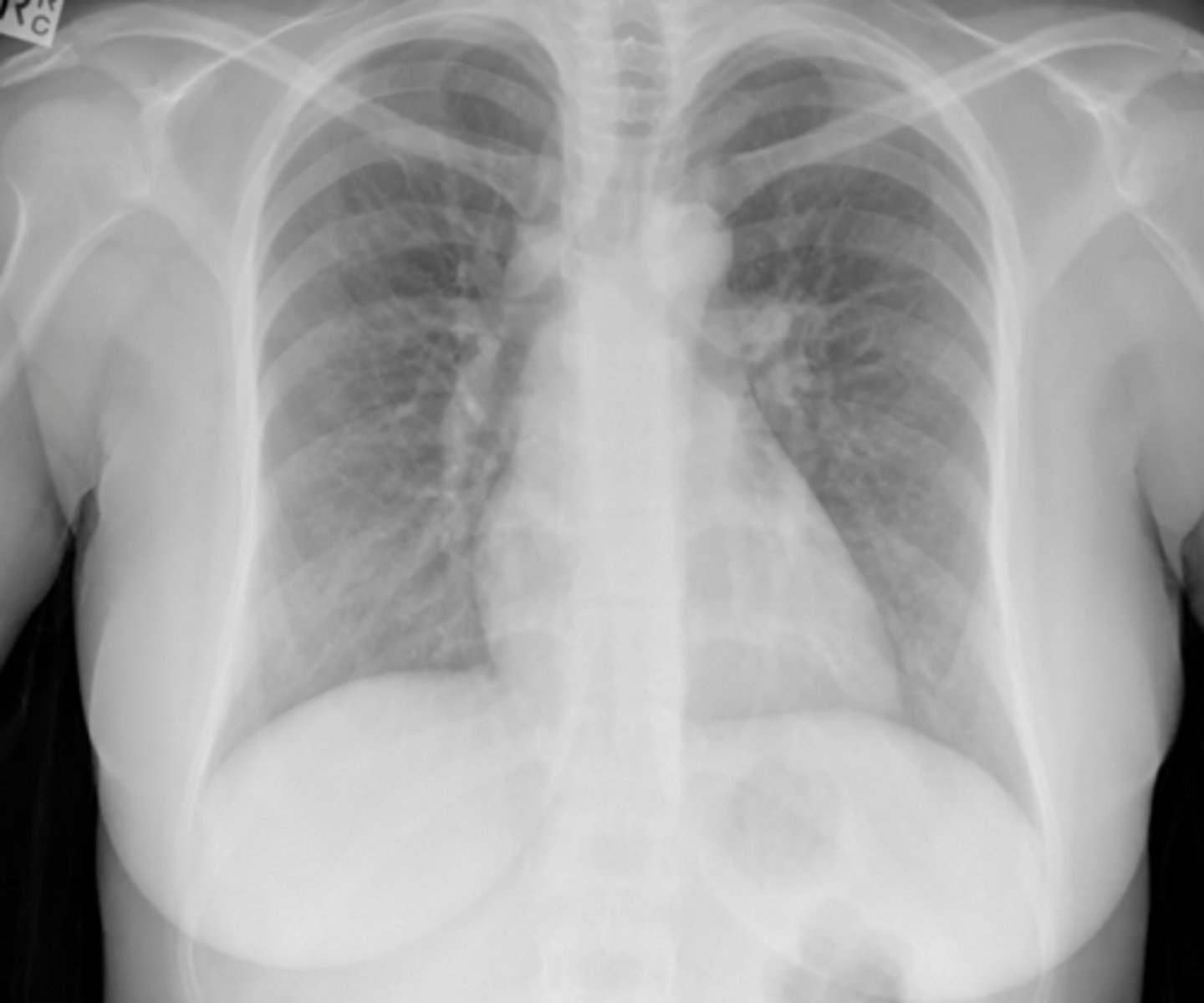
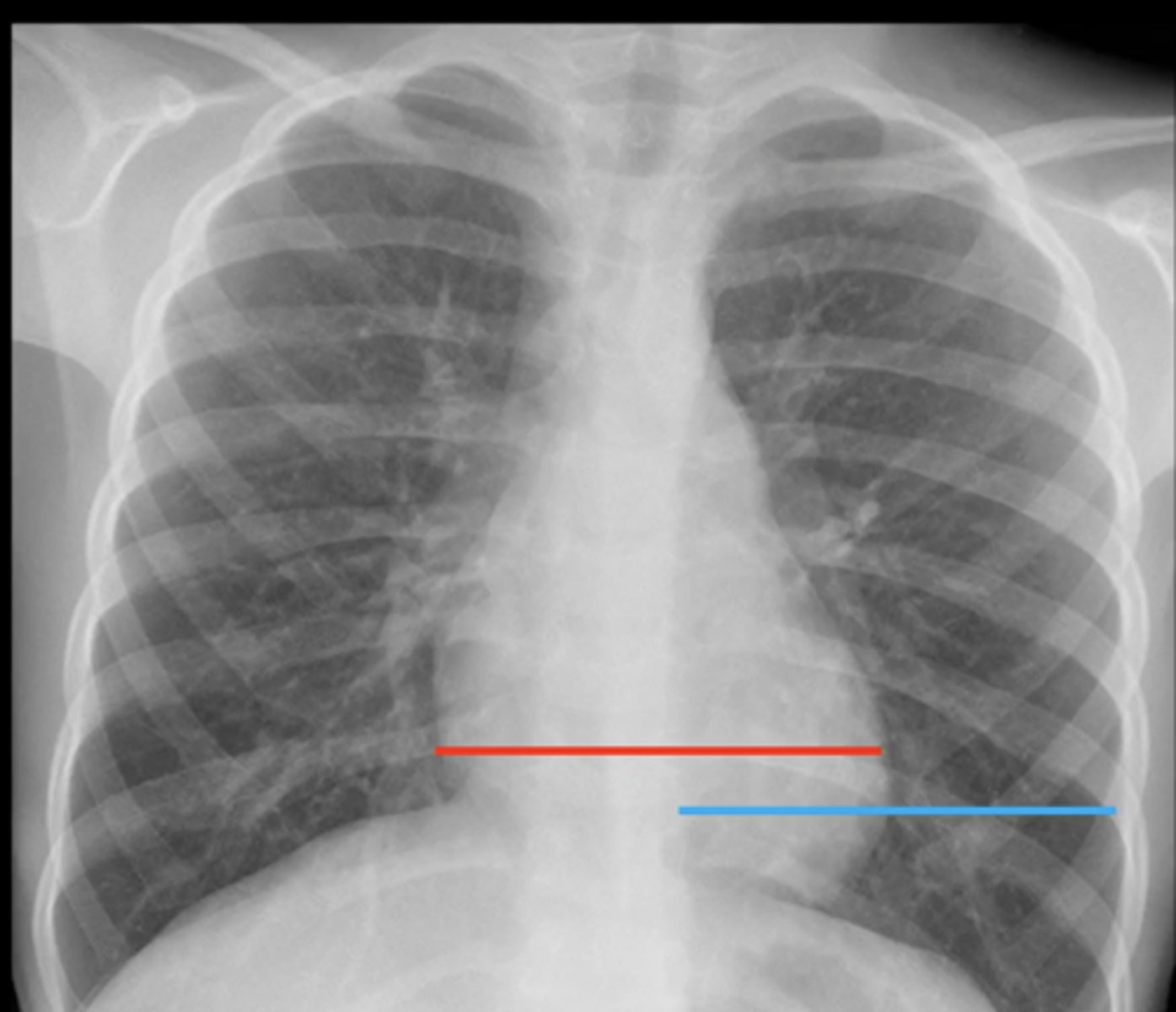
(evaluating AP CXR) cardiac silhouette
silhouette should be <1/2 of the total thoracic diameter (blue line)
(evaluating AP CXR) normal size of cardiac silhouette?
waterbottle heart
(evaluating AP CXR) cardiomegaly where the entire heart is enlarged bc of fluid around the heart (effusion) or dilated cardiomyopathy
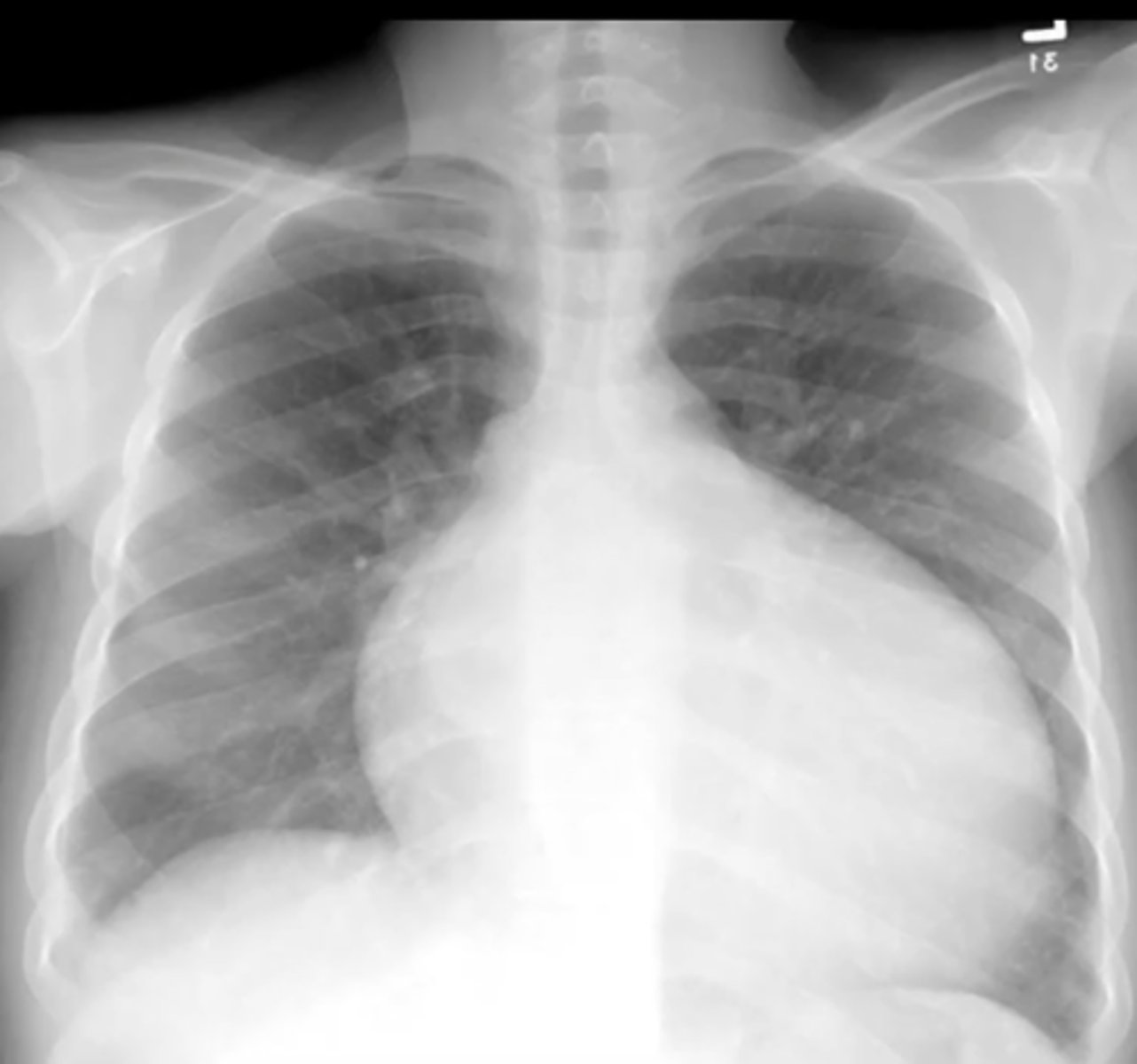
left ventricular hypertrophy
(evaluating AP CXR) cardiomegaly where only left ventricle is enlarged; usually caused by HTN
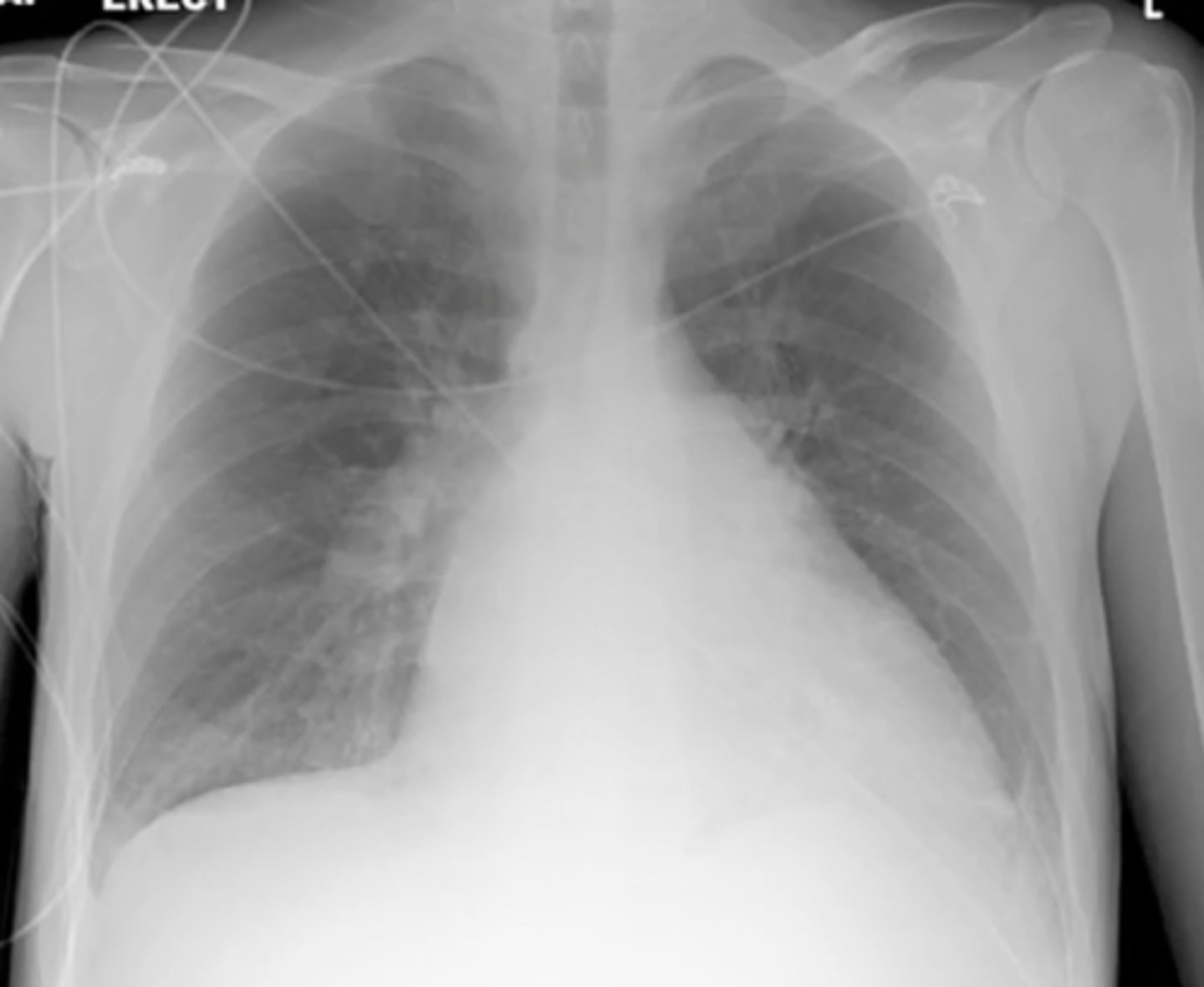
Dextrocardia
(evaluating AP CXR) displacement of the heart to the right
trachea: midline, brandhing
diaphragm: dome shape, clear costophrenic angles
(evaluating AP CXR) airway eval
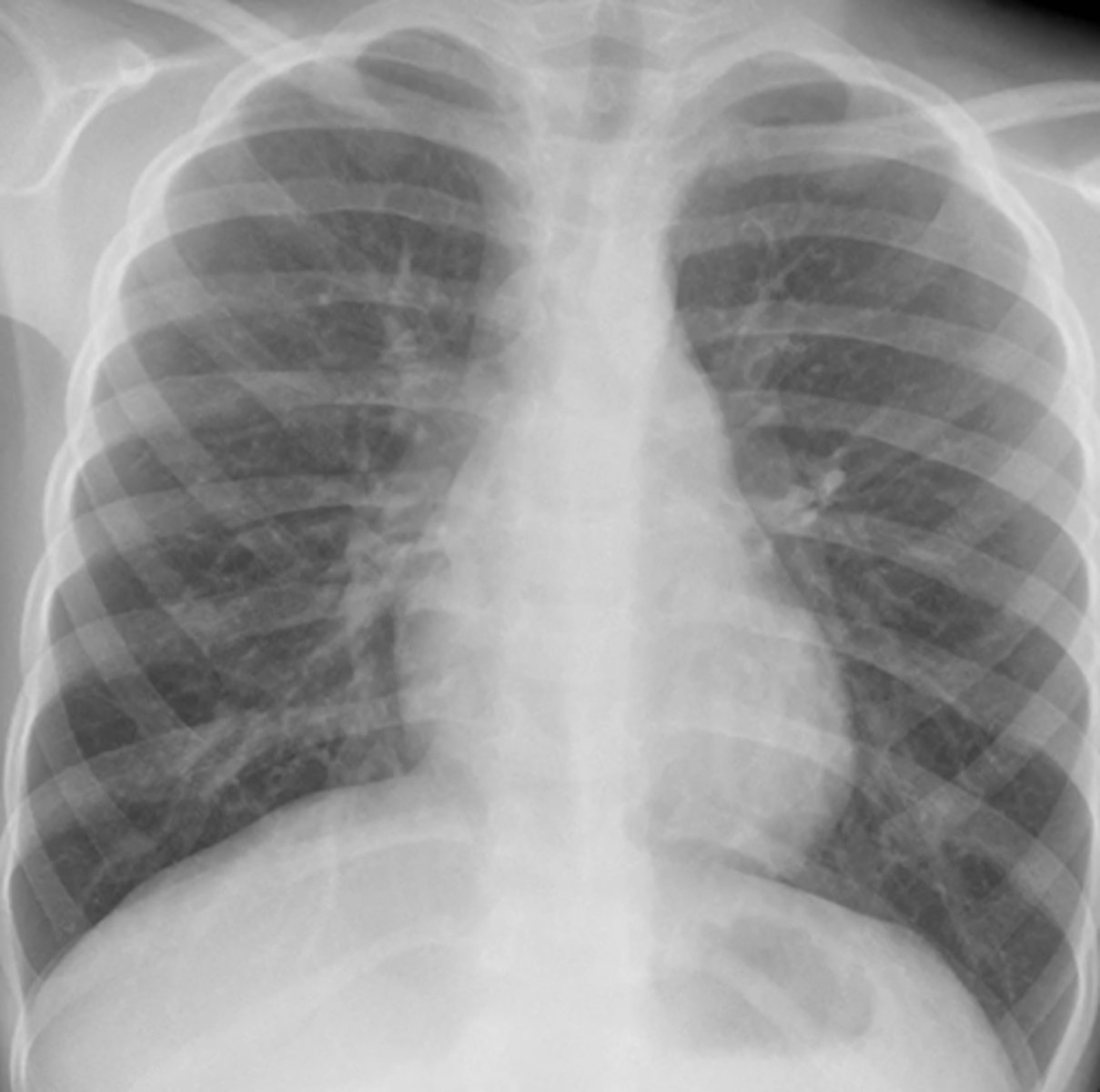
flattened diaphragm
(evaluating AP CXR) seen in diagnosis of COPD bc of hyperextension of lungs
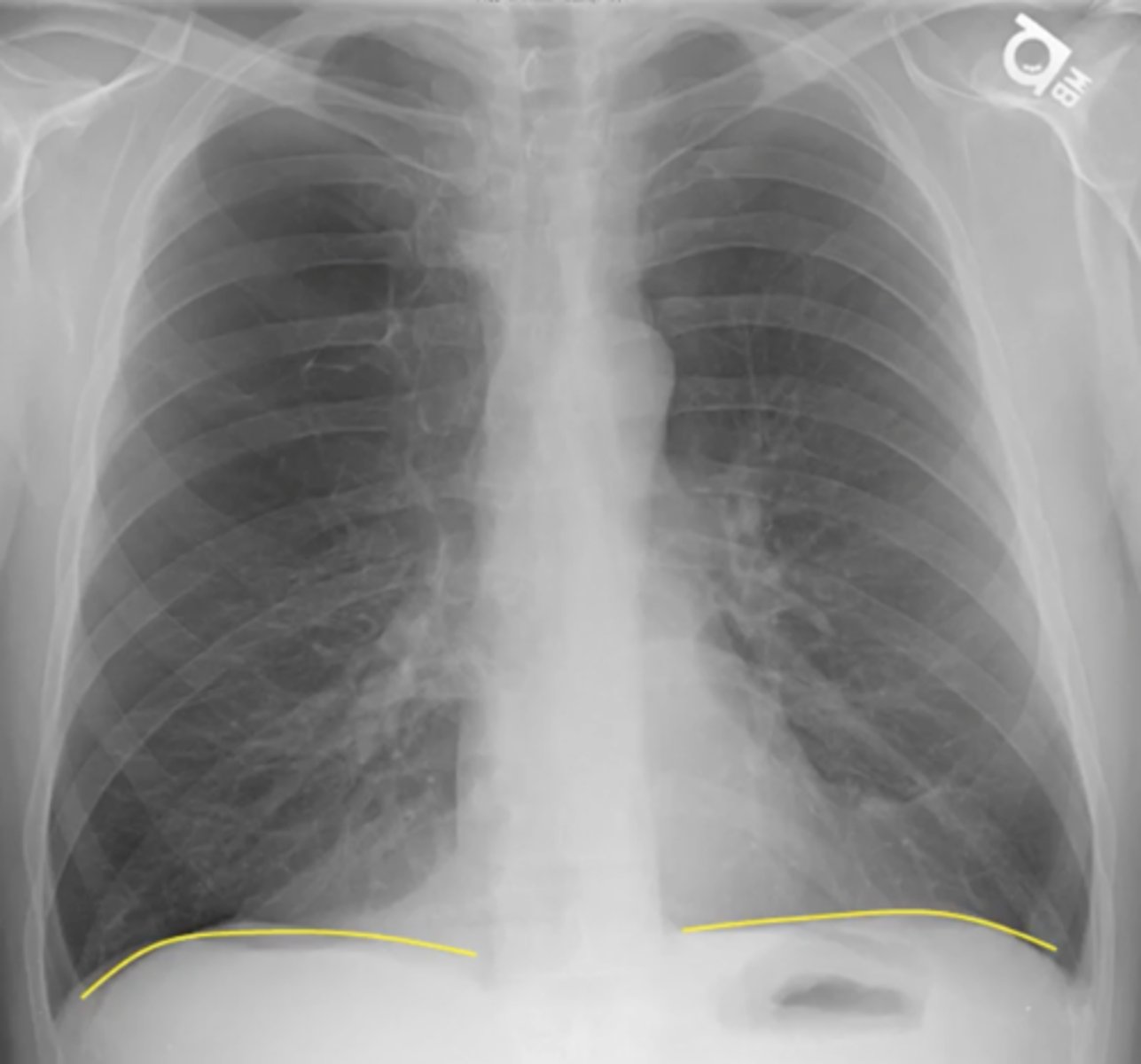
pleural effusion
(evaluating AP CXR) fluid in the pleural space (not lung itself)
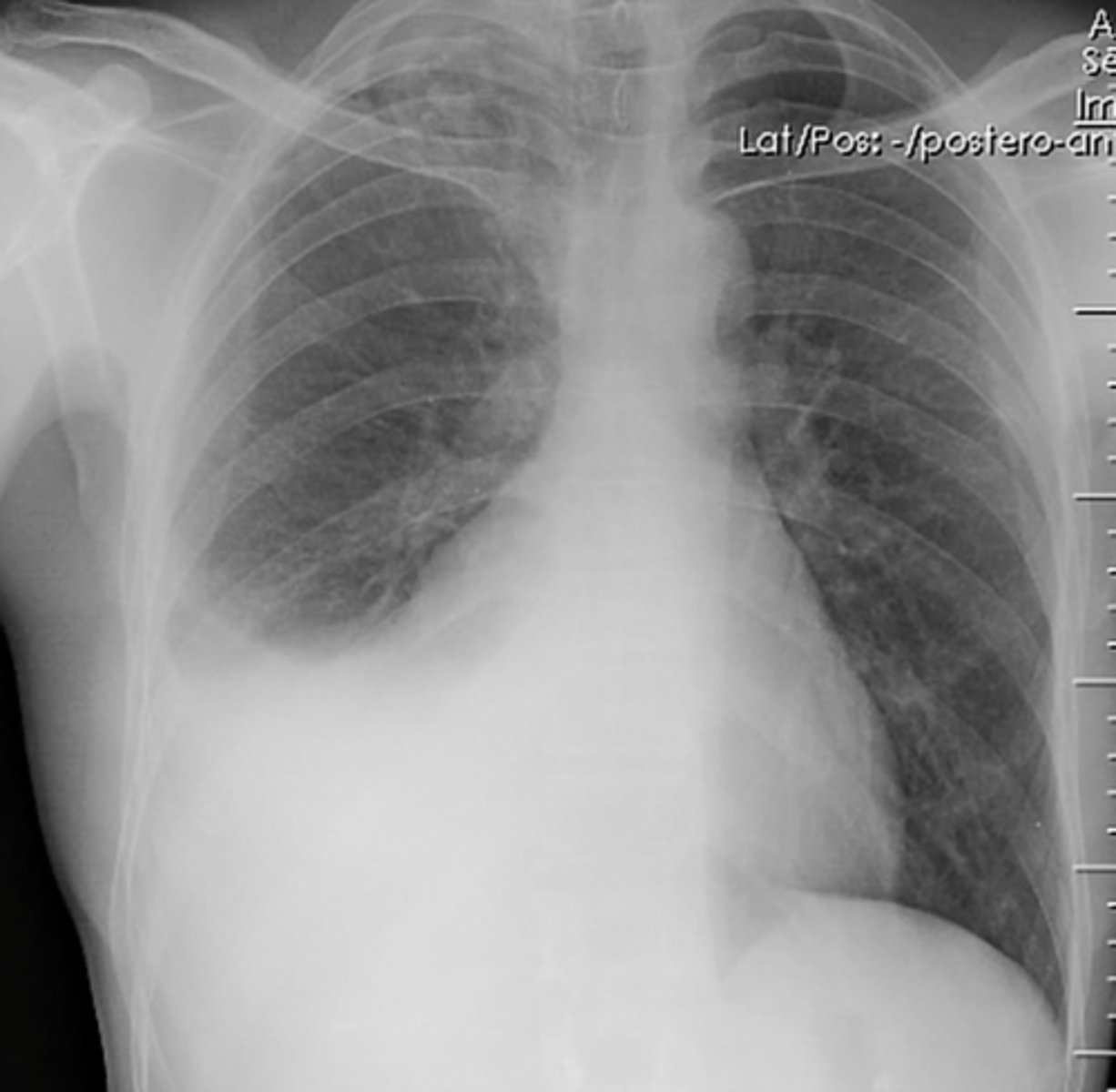
largest at hula and taper at periphery inferior markings more prominent than superior
(evaluating AP CXR) normal pulmonary vasculature and hilum
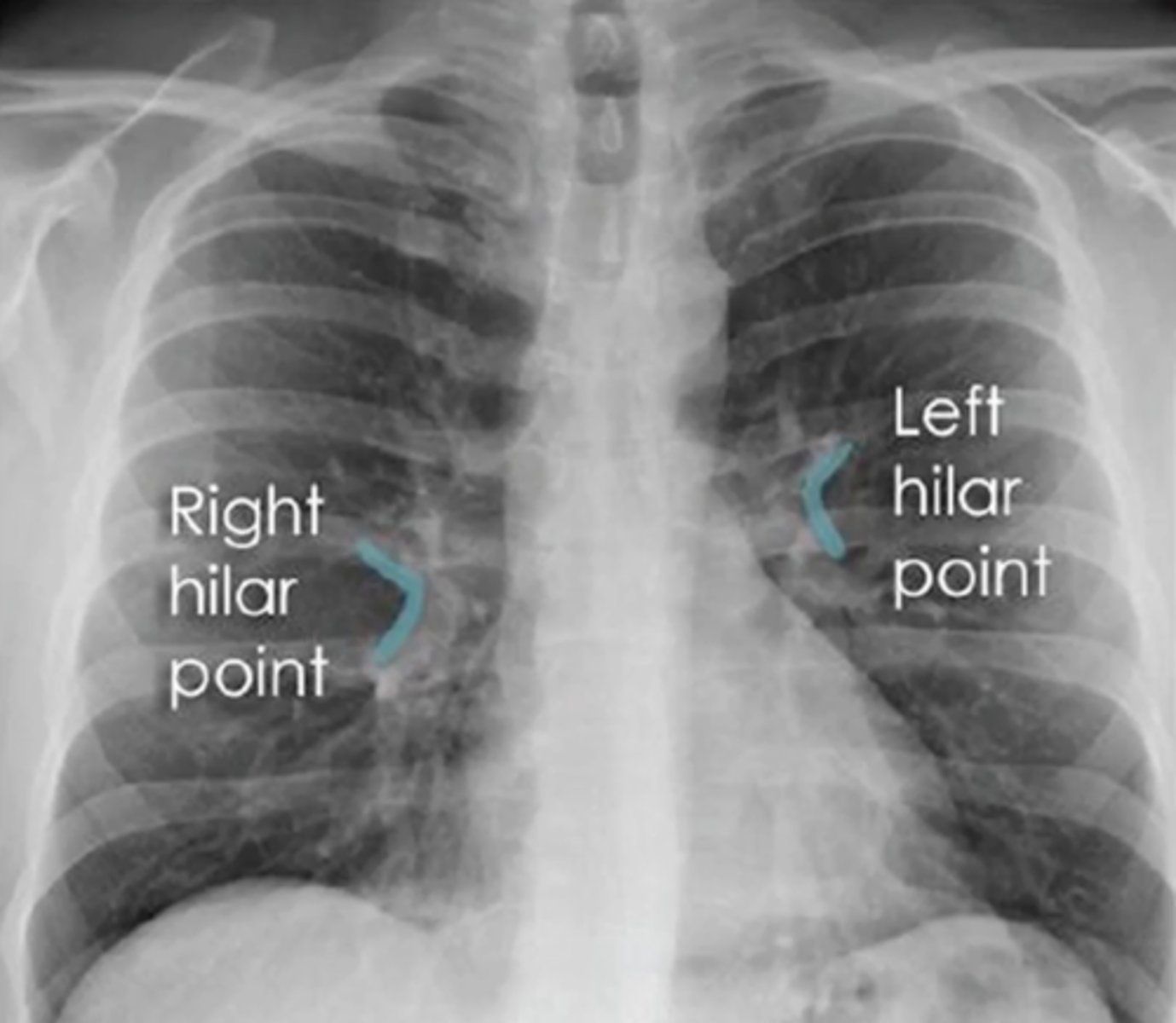
pulmonary hypertension
(evaluating AP CXR) enlarged pulmonary vessel; enlarged aortic arch
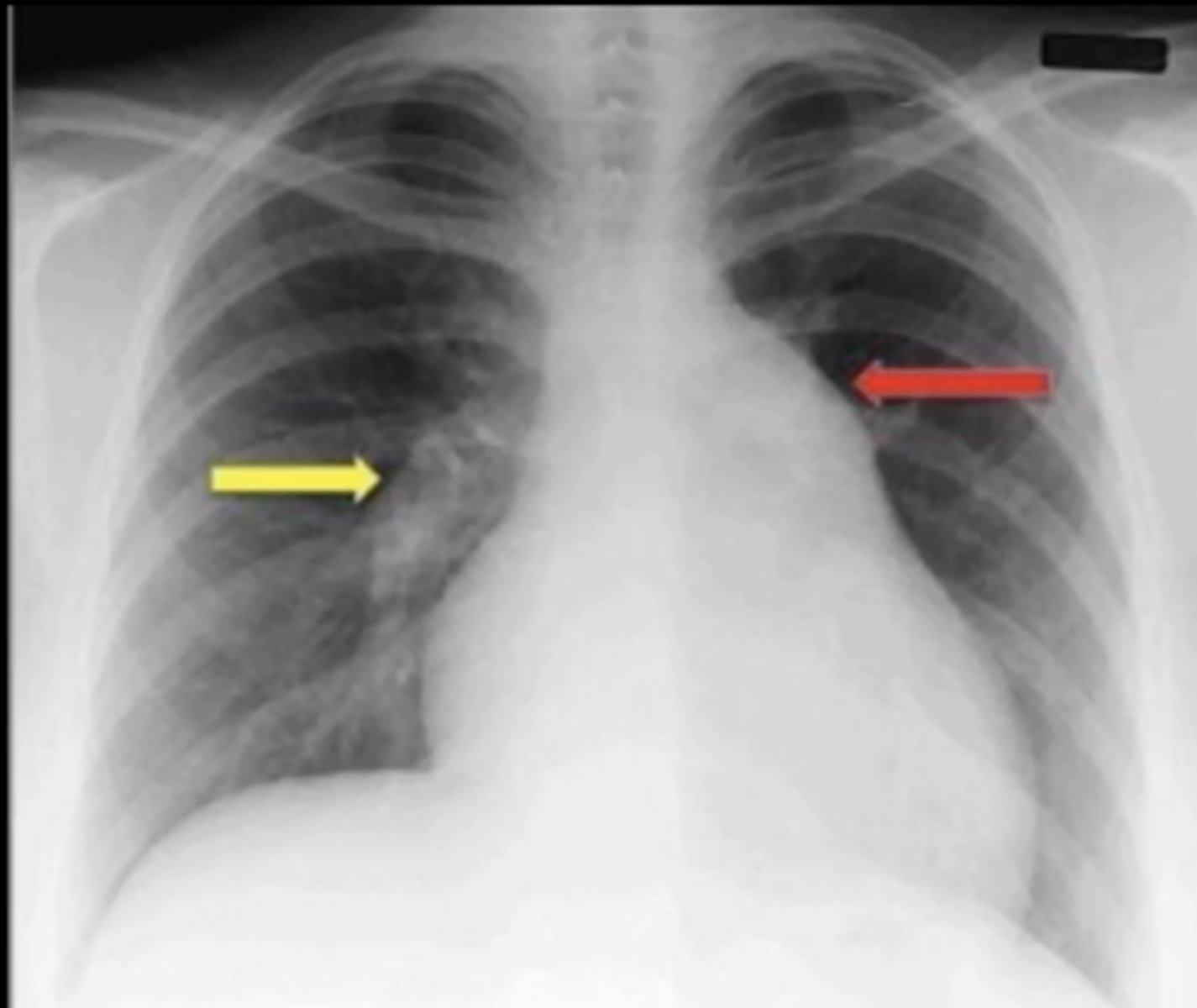
pulmonary HTN
(evaluating AP CXR) 2 enlarged pulmonary vessels
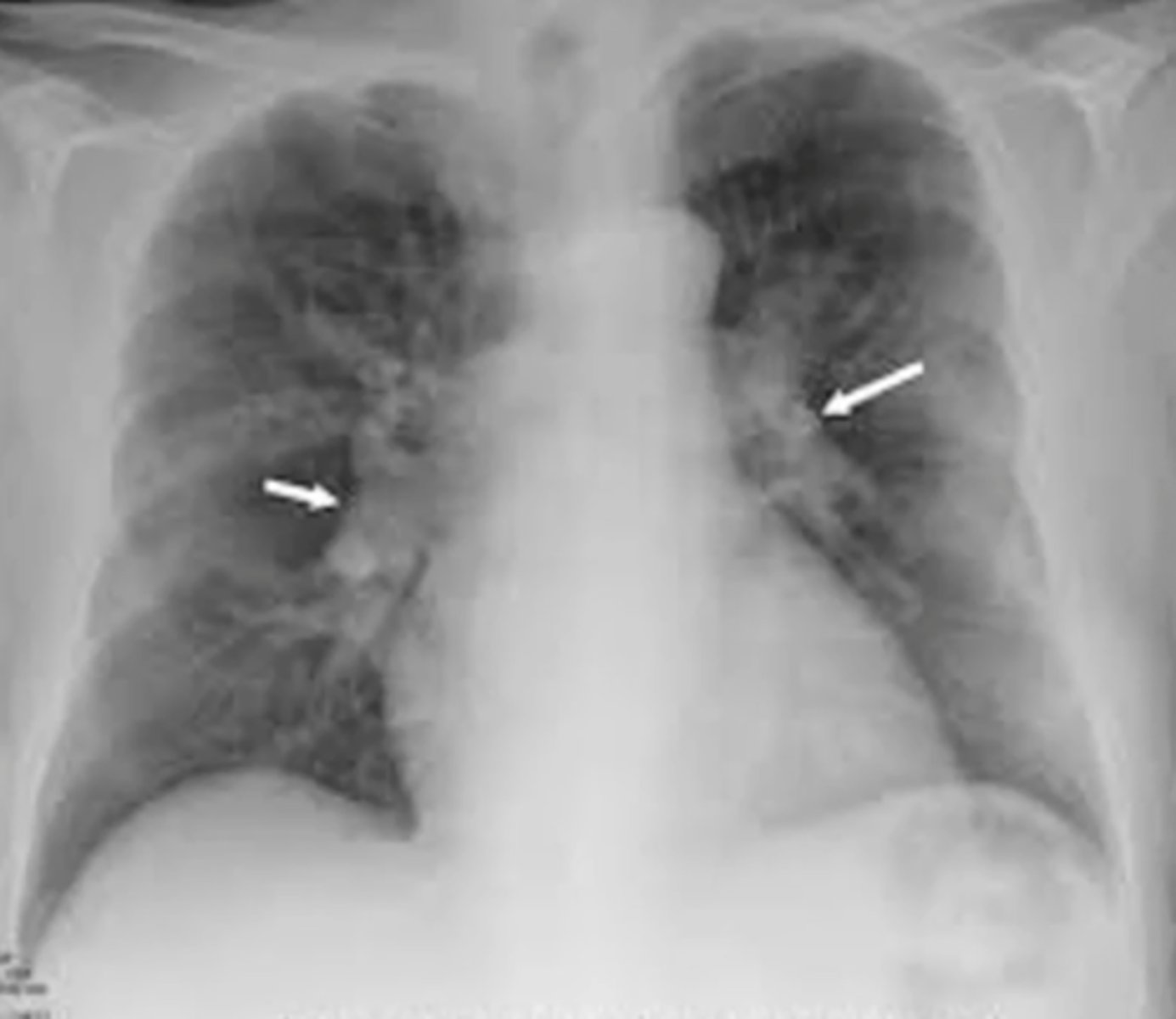
suspicion for sarcoidosis
(evaluating AP CXR) masses on hilar region (bilateral hilar LAD)
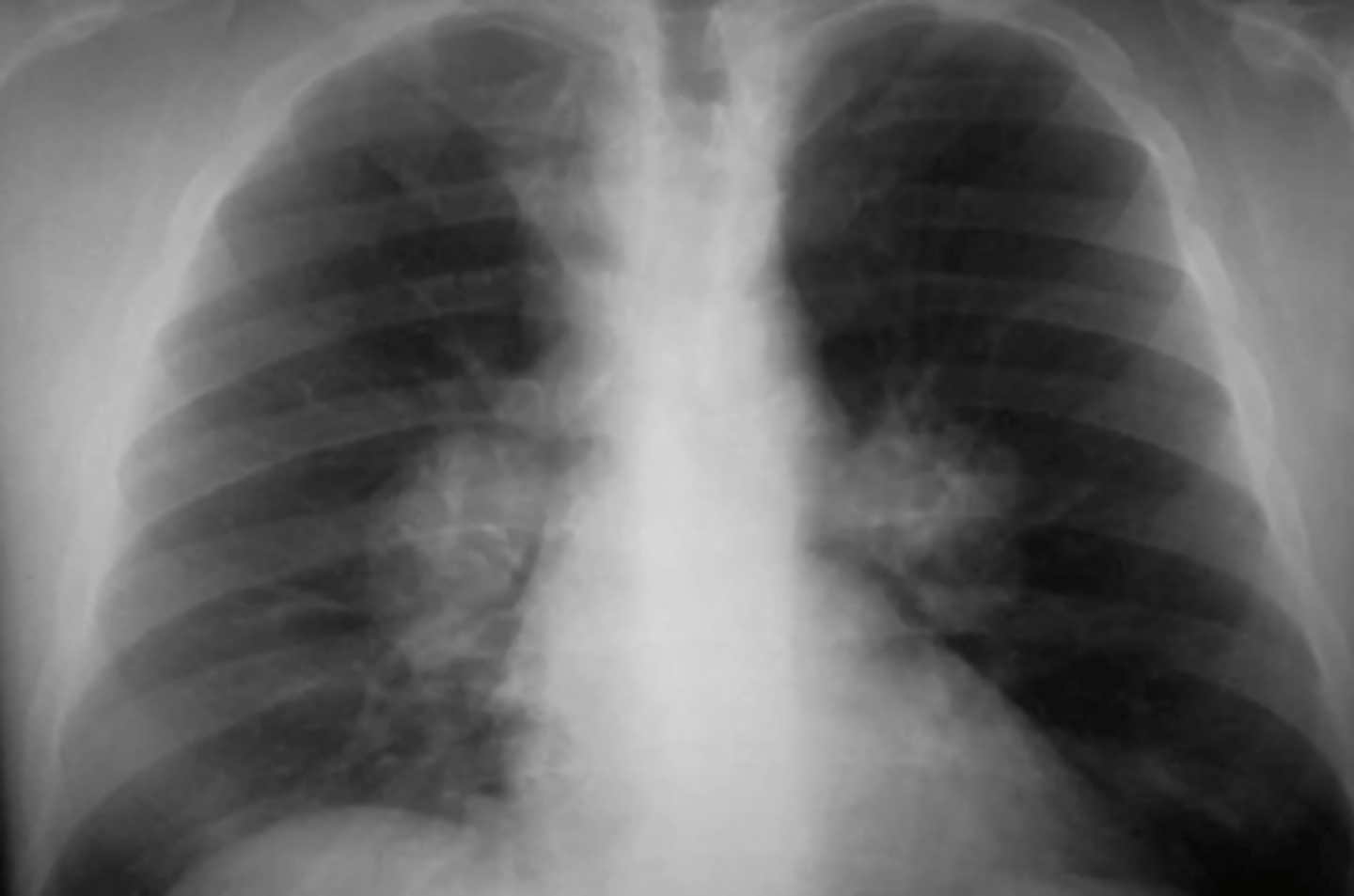
CHF
(evaluating AP CXR) fluid in major fissure, cephalization, Kerly B lines
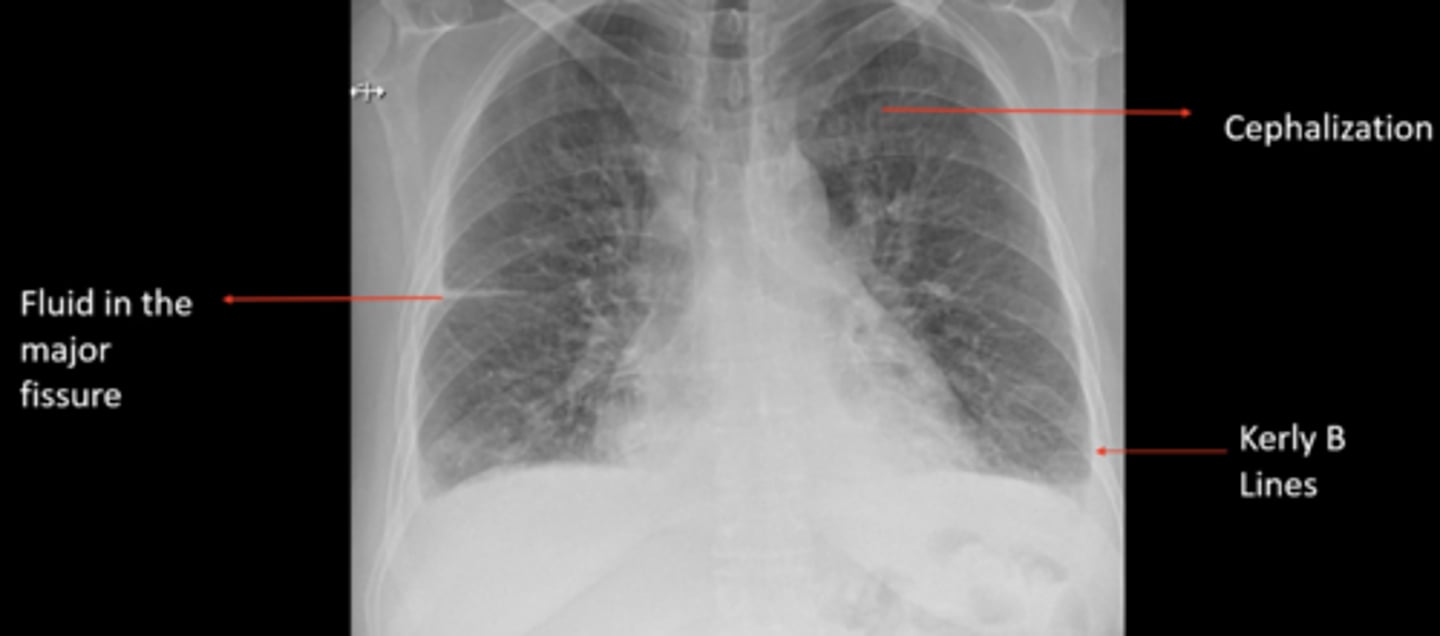
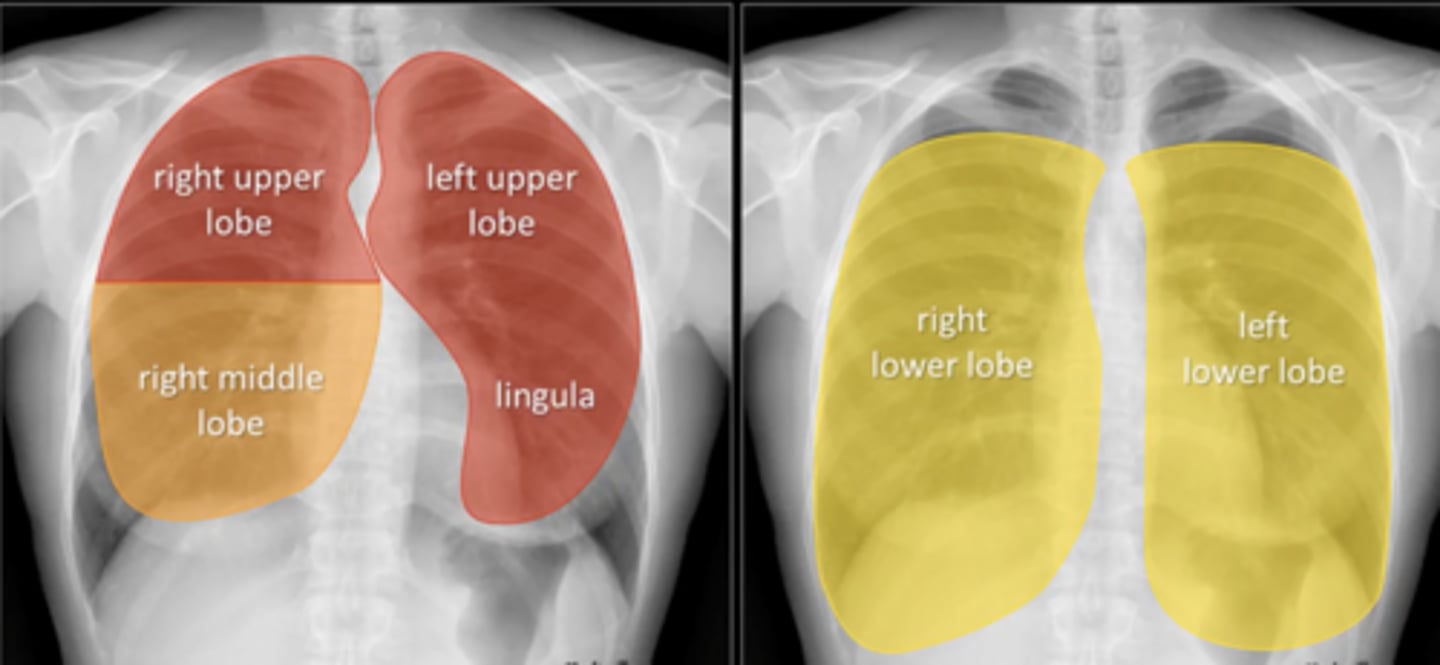
upper/middle lobes: situate the heart
lower lobes: situate diaphragm
(evaluating AP CXR) evaluation of lung position
minor fissure
What fissure separates the RUL from RLL and the RML from RLL?
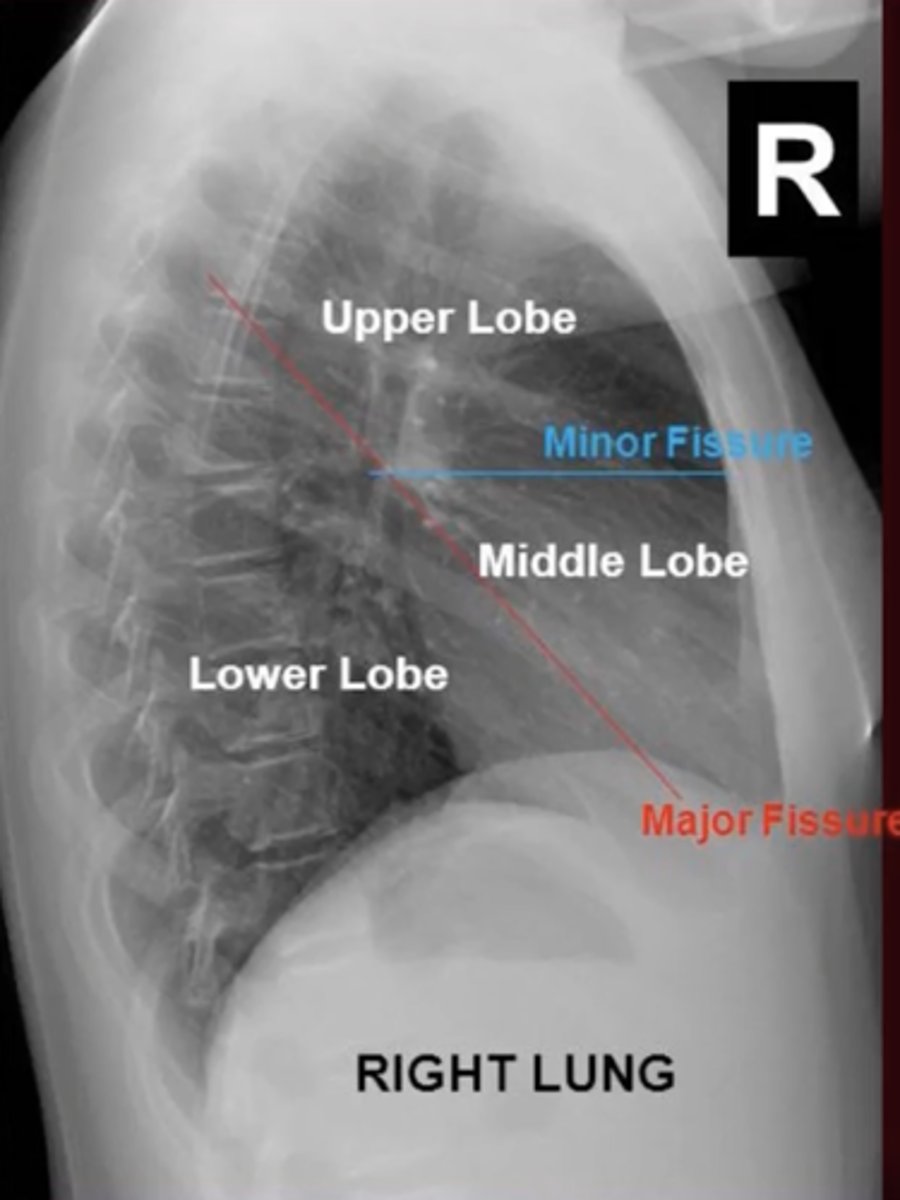
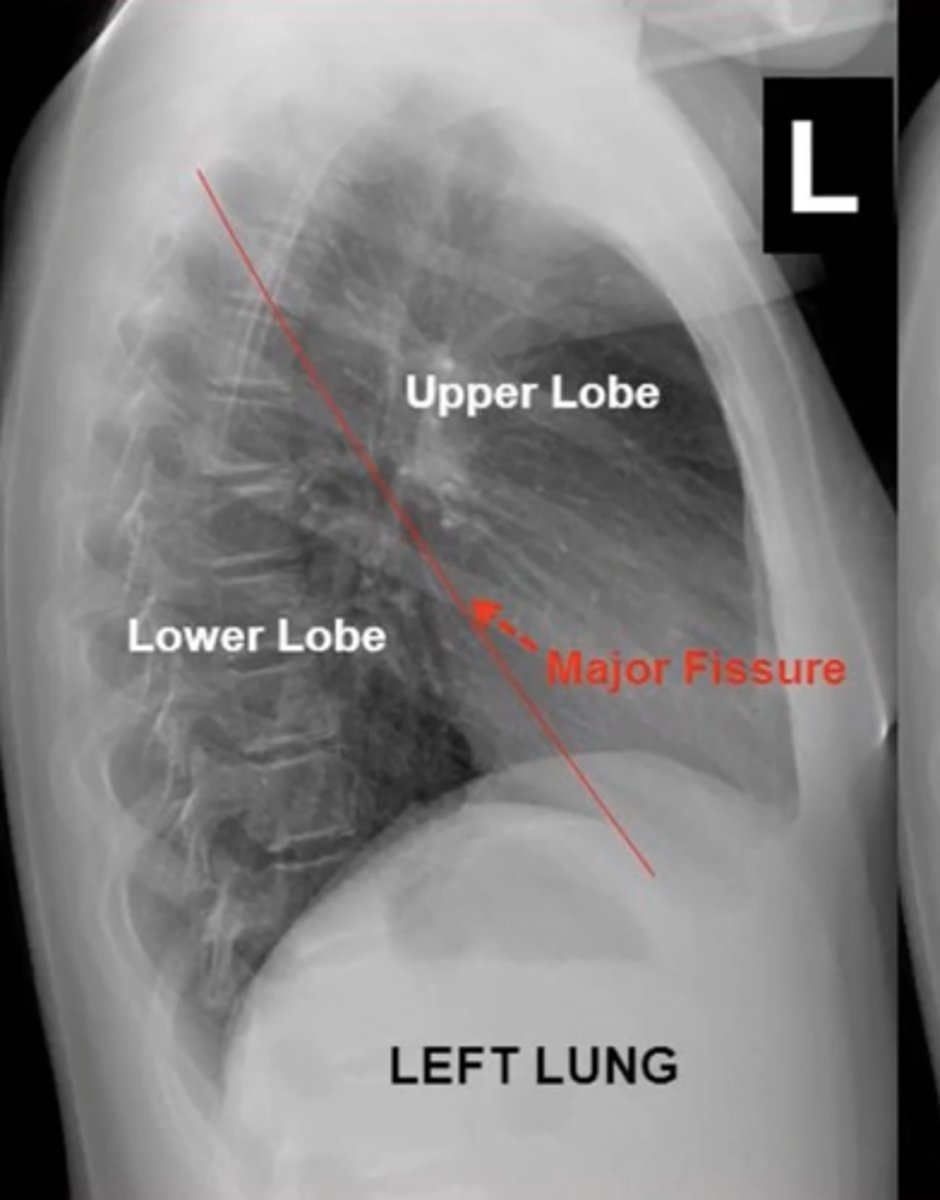
major fissure
fissure seperates LUL from LLL?
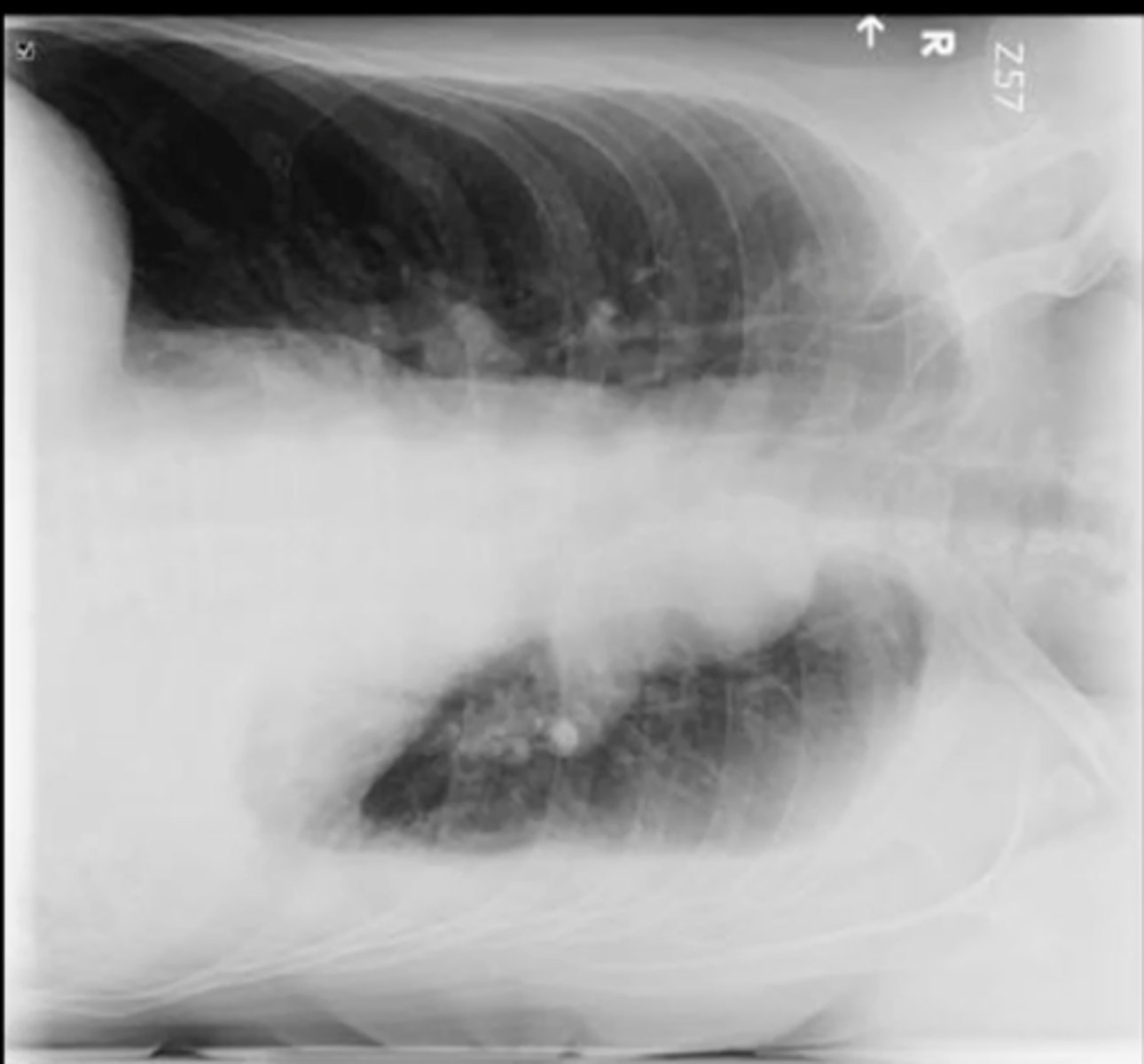
pleural effusion - free flowing fluid (can perform thoracentesis bc >1cm of fluid)
left lateral decubitus xray
1. anterior mediastinal space - should be clear
2. lateral cardiac silhouette
steps to read lateral CXR
white in space on lateral CXR
(4Ts --> thymoma, thyroid, terrible lymphoma, teratoma)
mediastinal mass
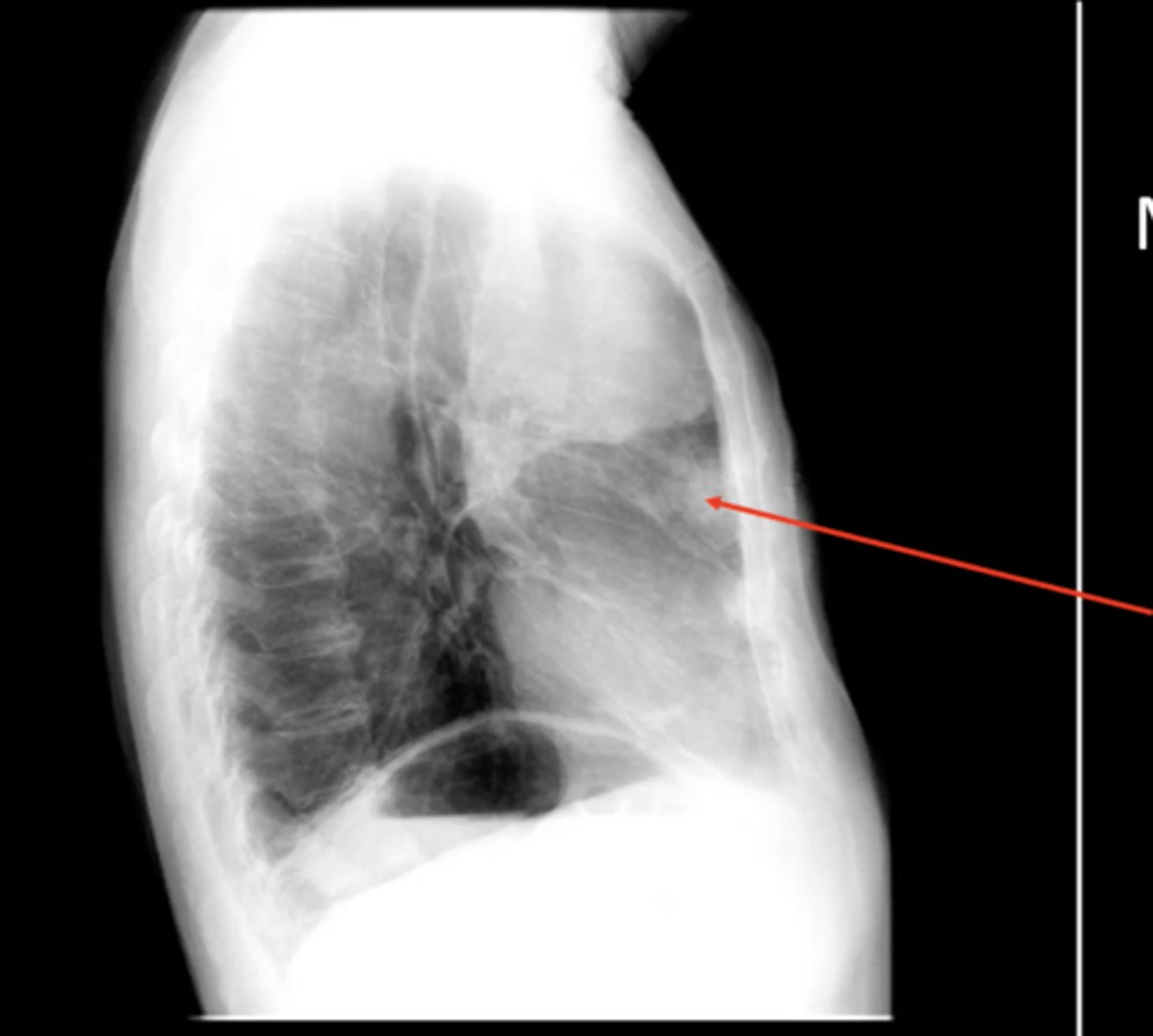
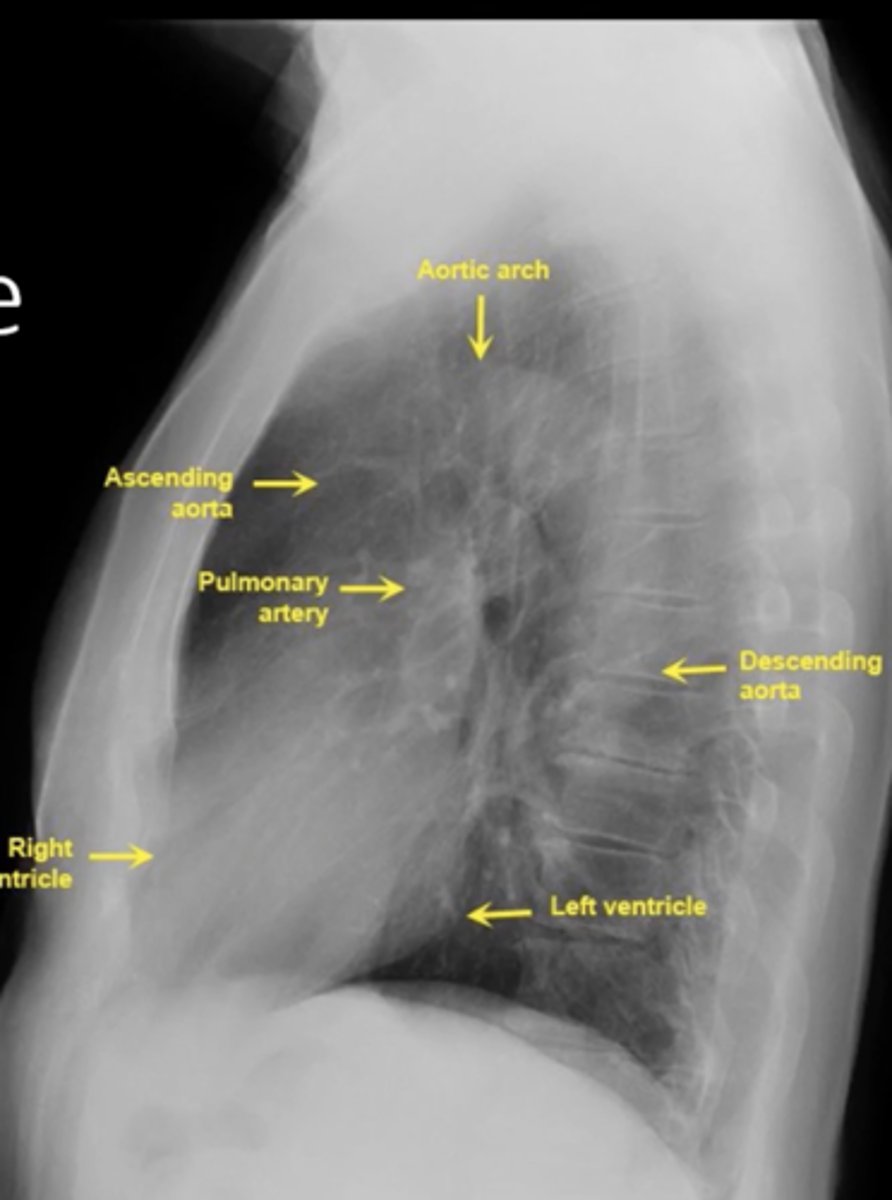
visualize: aortic arch, ascending aorta, pulmonary artery, right ventricle, left ventricle, descending aorta
lateral cardiac silhouette
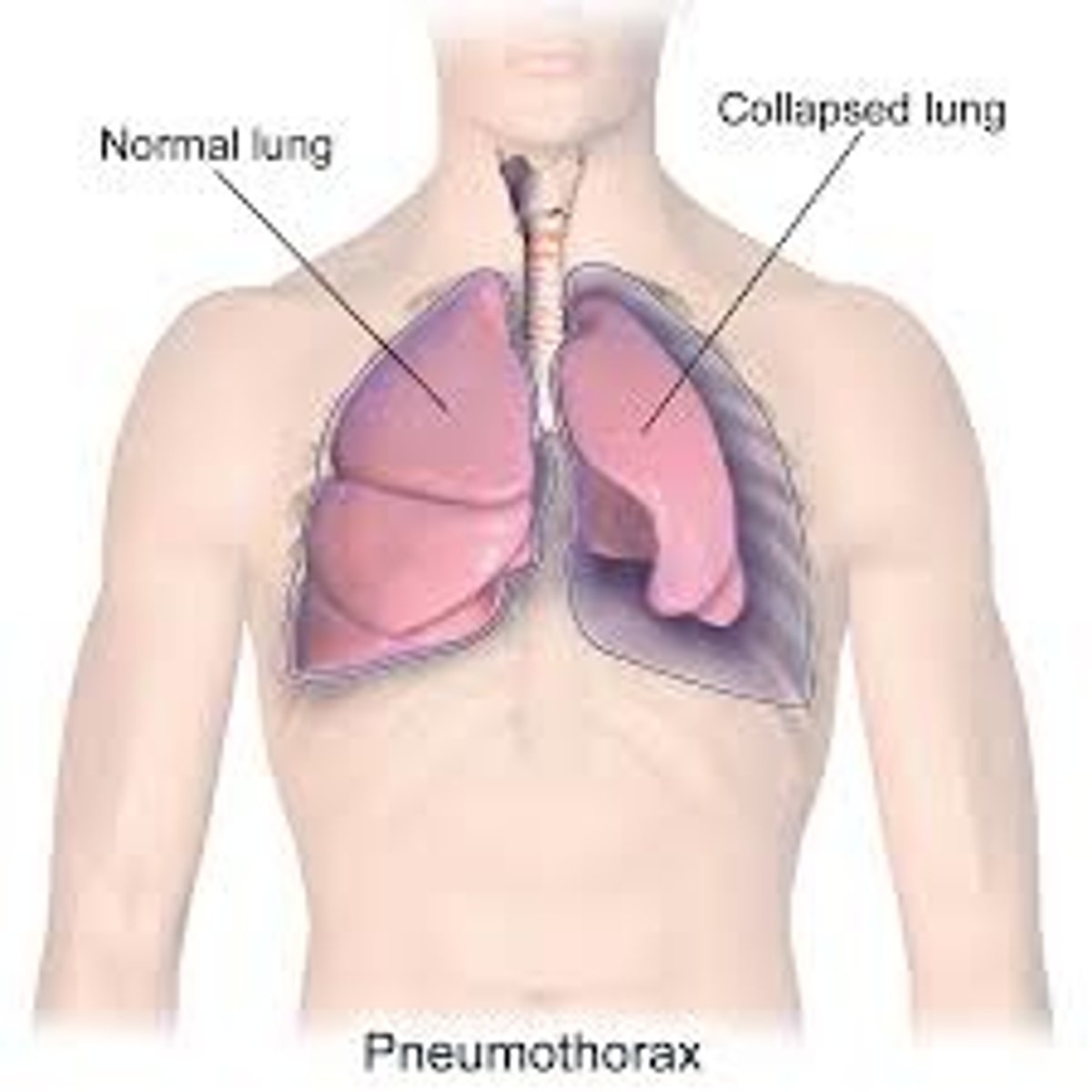
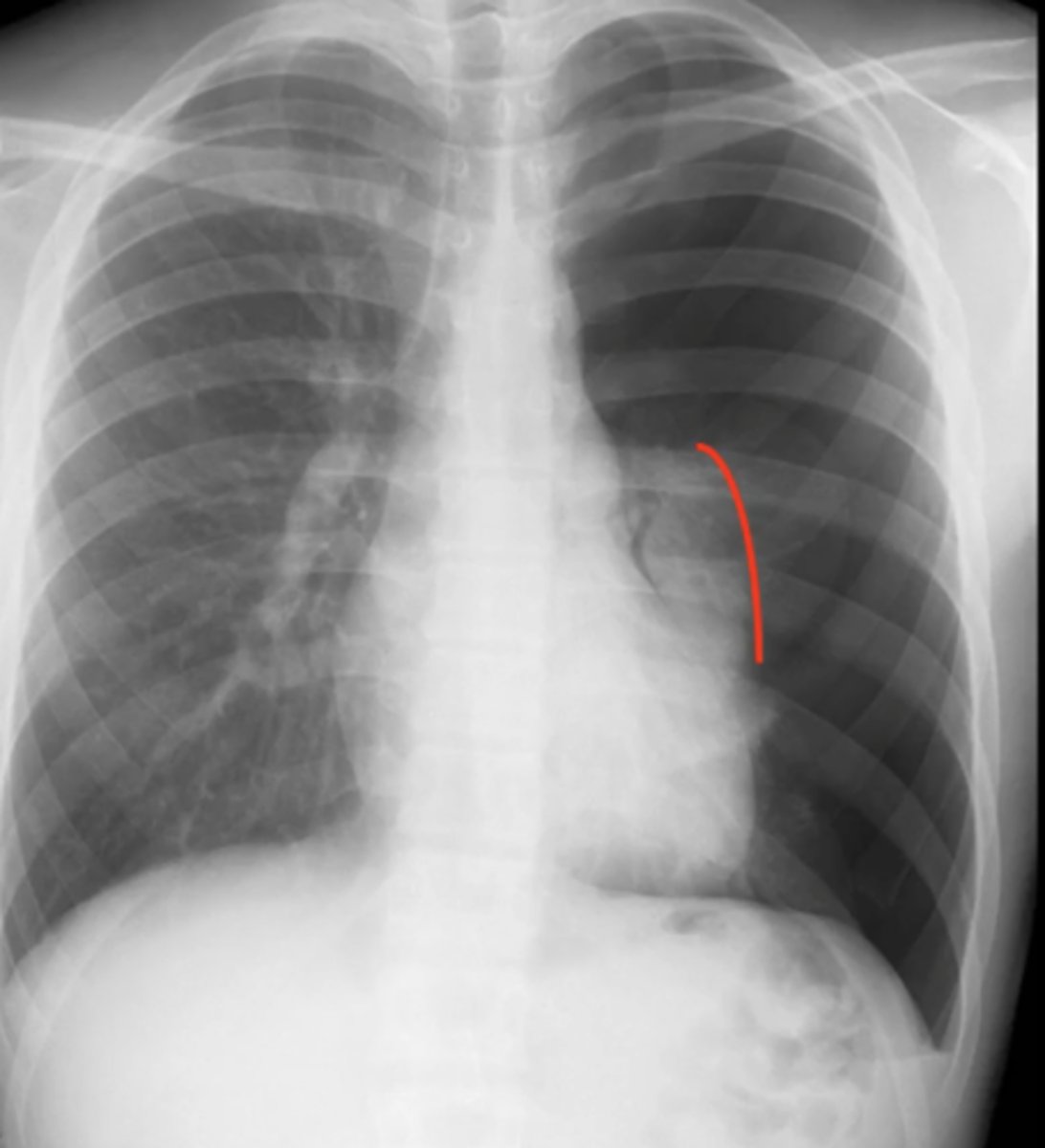
large pneumothorax
(CXR examples) large loss of air markings on the right side; rest of lung is filled with only air
tension pneumothorax
(CXR examples) right lung shows only air; tracheal deviation to the left
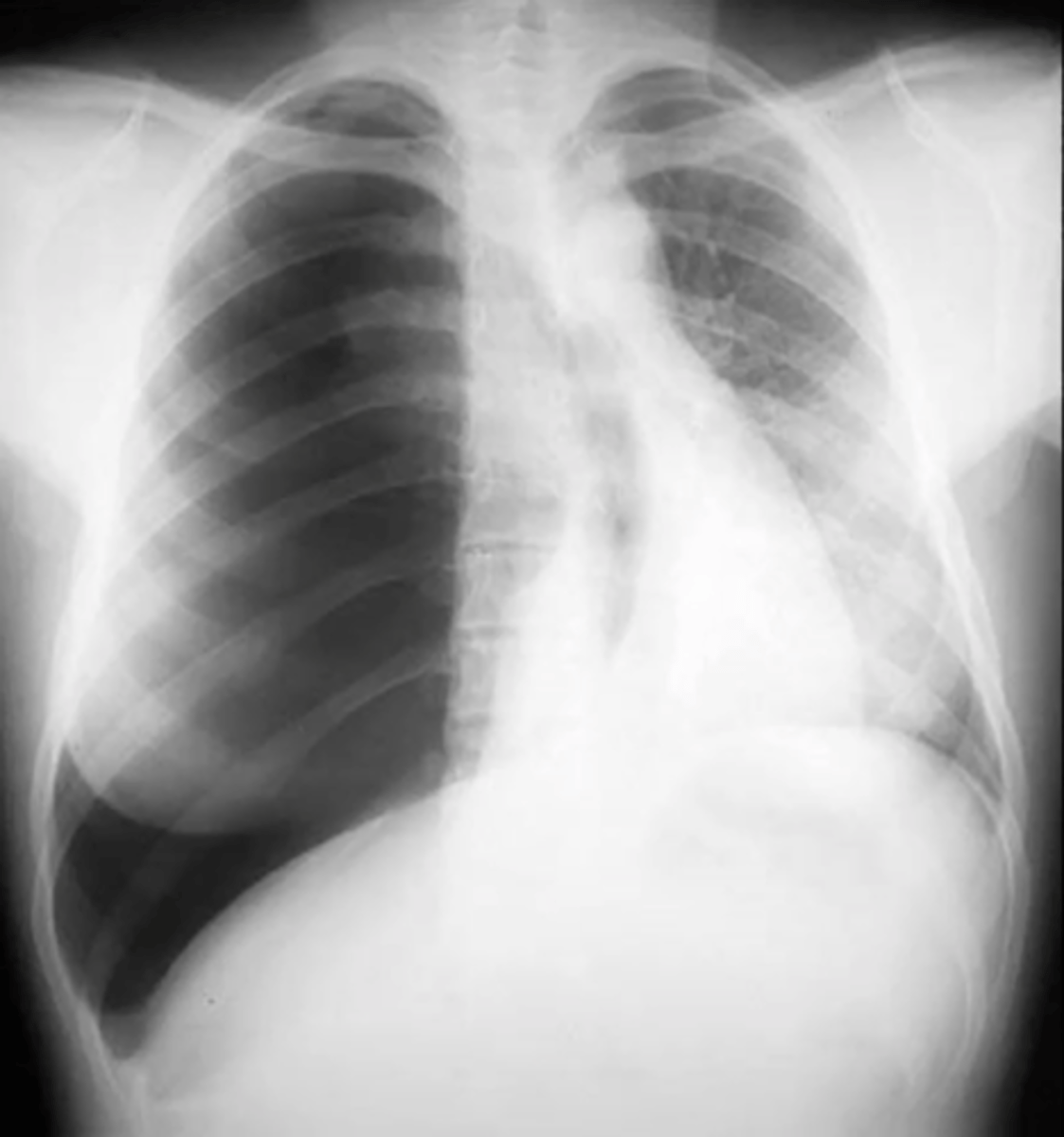
plate atelectasis
(CXR examples) lung collapses on itself; forms a plate like line
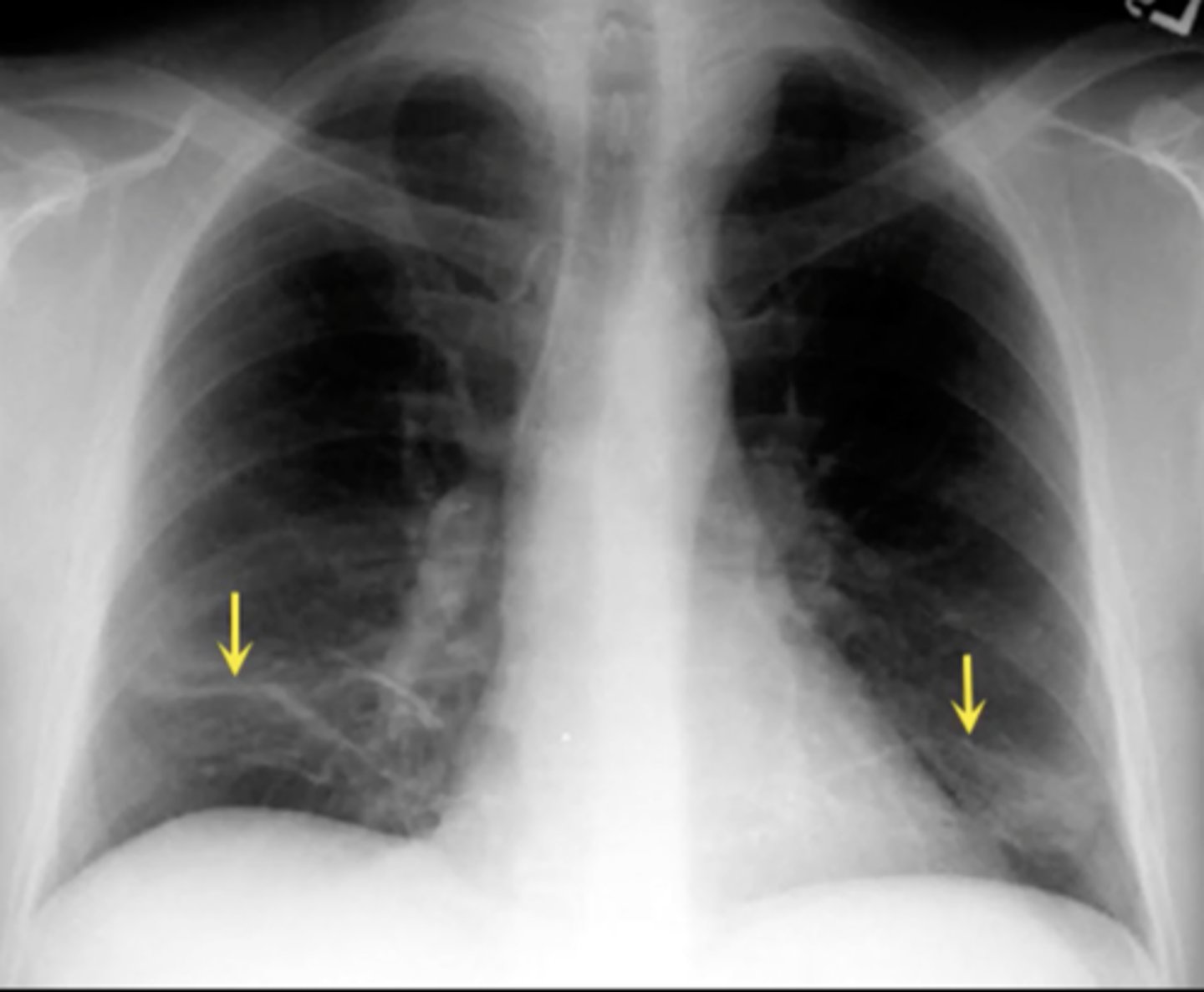
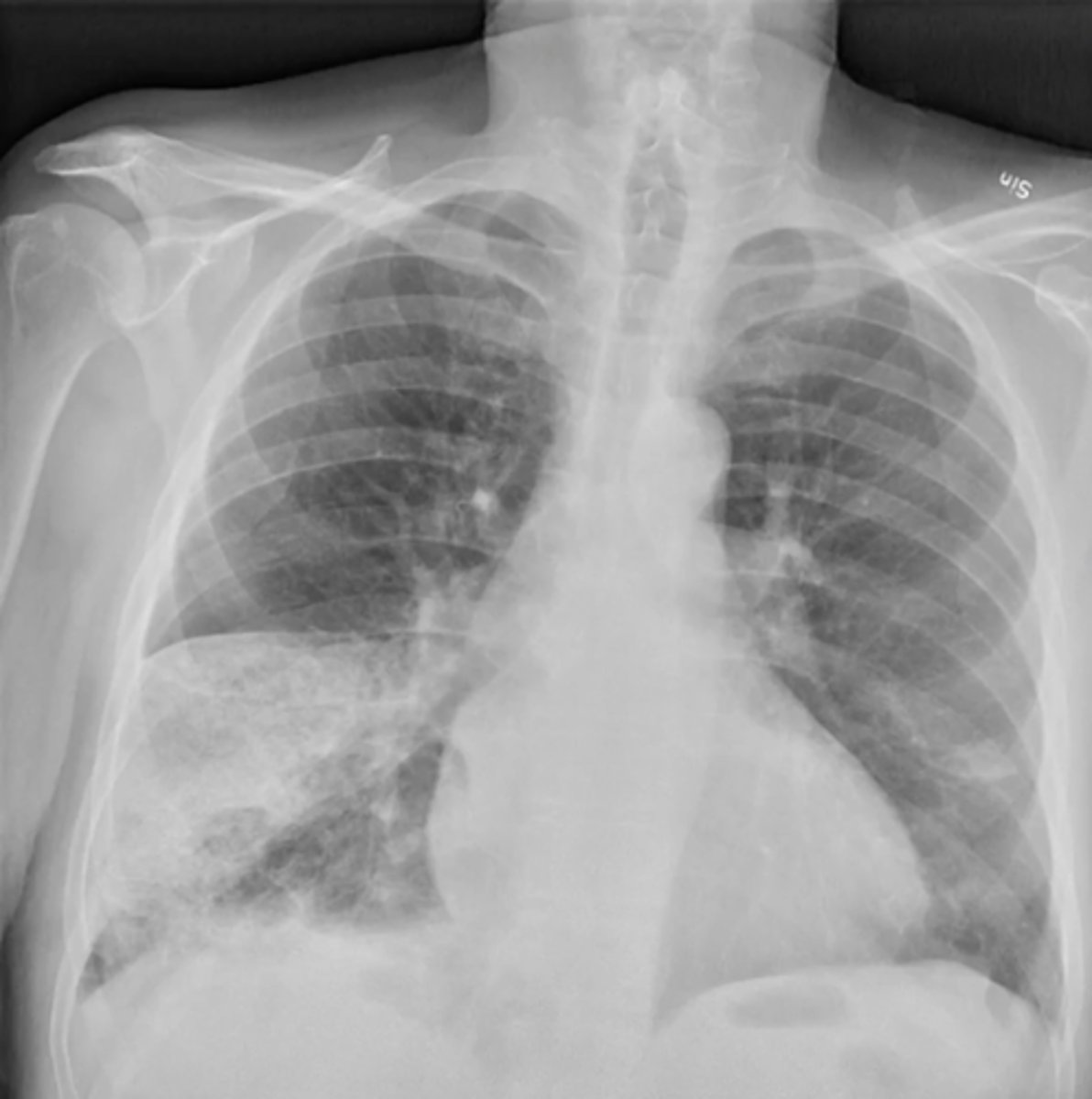
atelectasis of right upper lobe
(CXR examples) right lobe is collapsed and pulling up the diaphragm; on the left there are pulmonary nodules
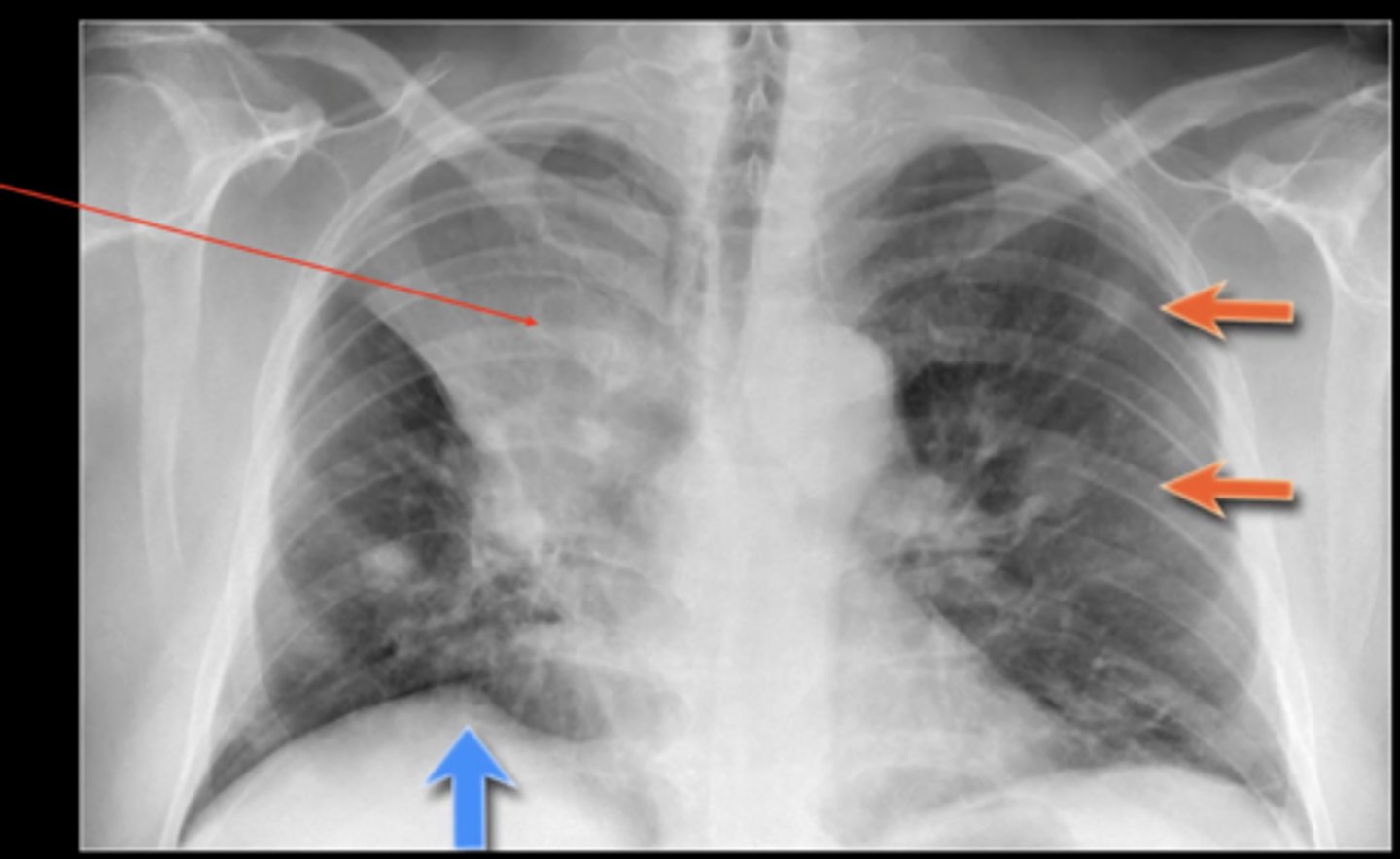
atypical pneumonia
(CXR examples) patchy reticular opacities; especially in perihylar lung; mostly caused by mycoplasma and chlamydia
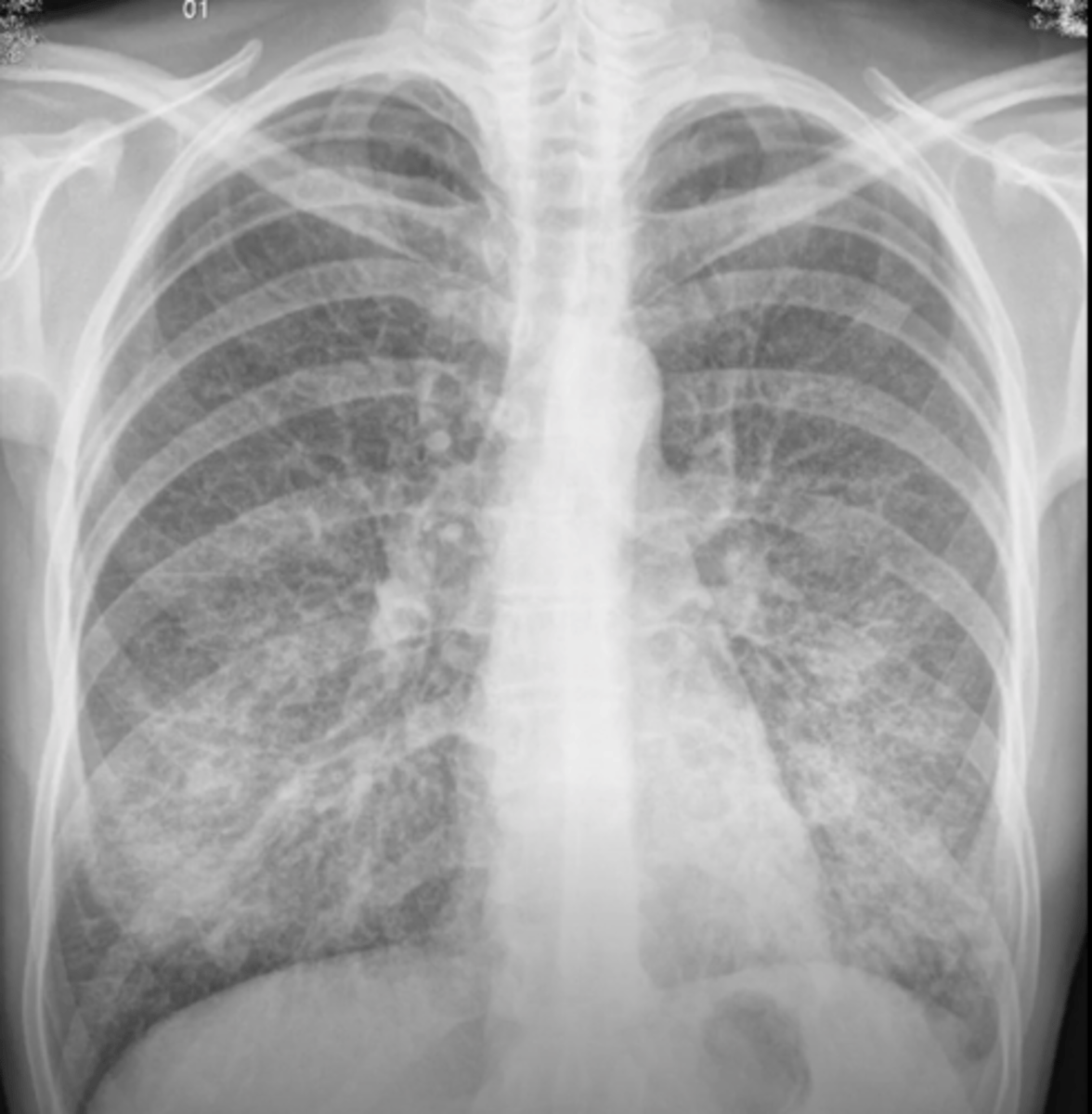
honeycombing
variable sized cysts on a background of densely scarred lung tissue; easier to see on CT scan
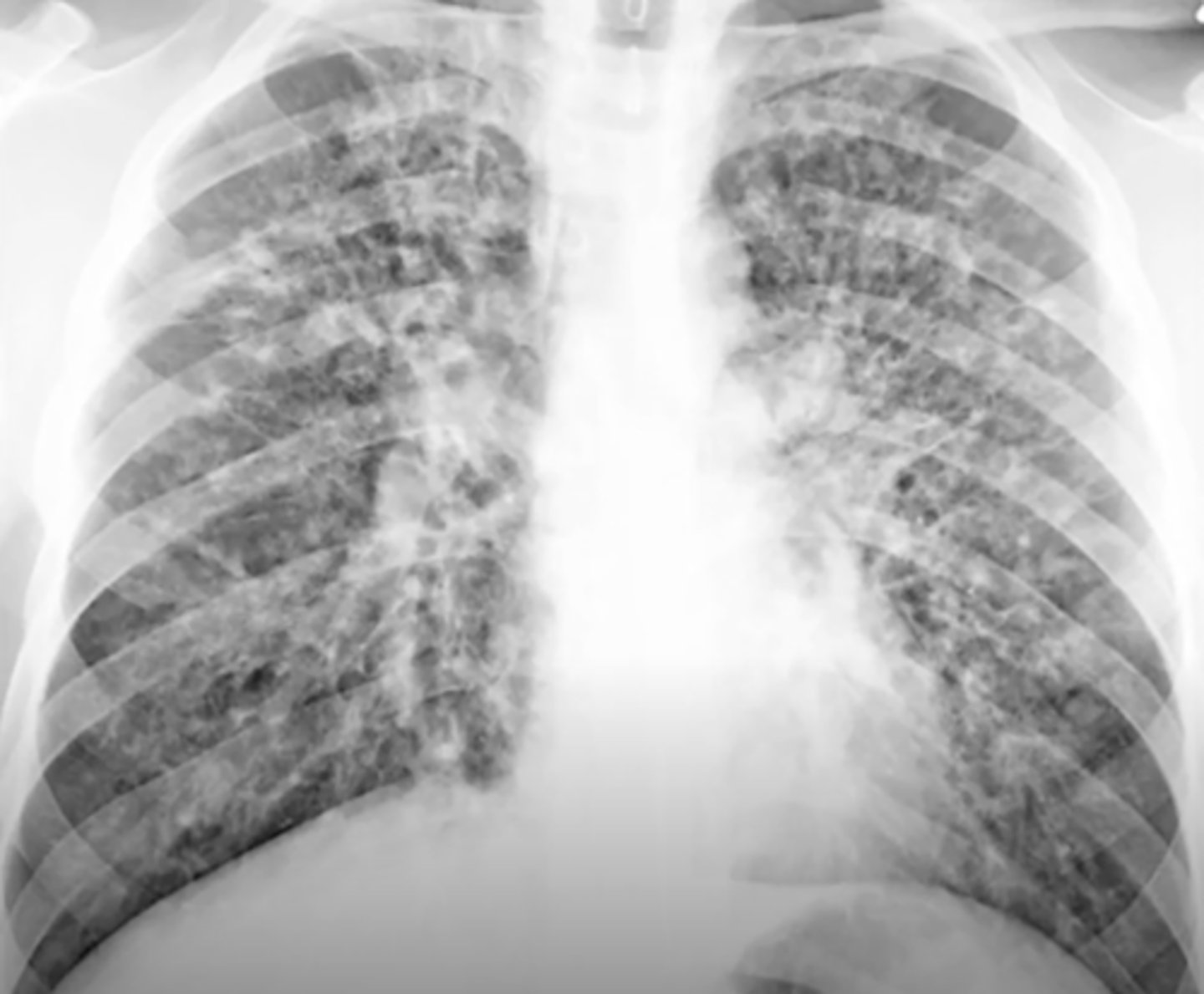
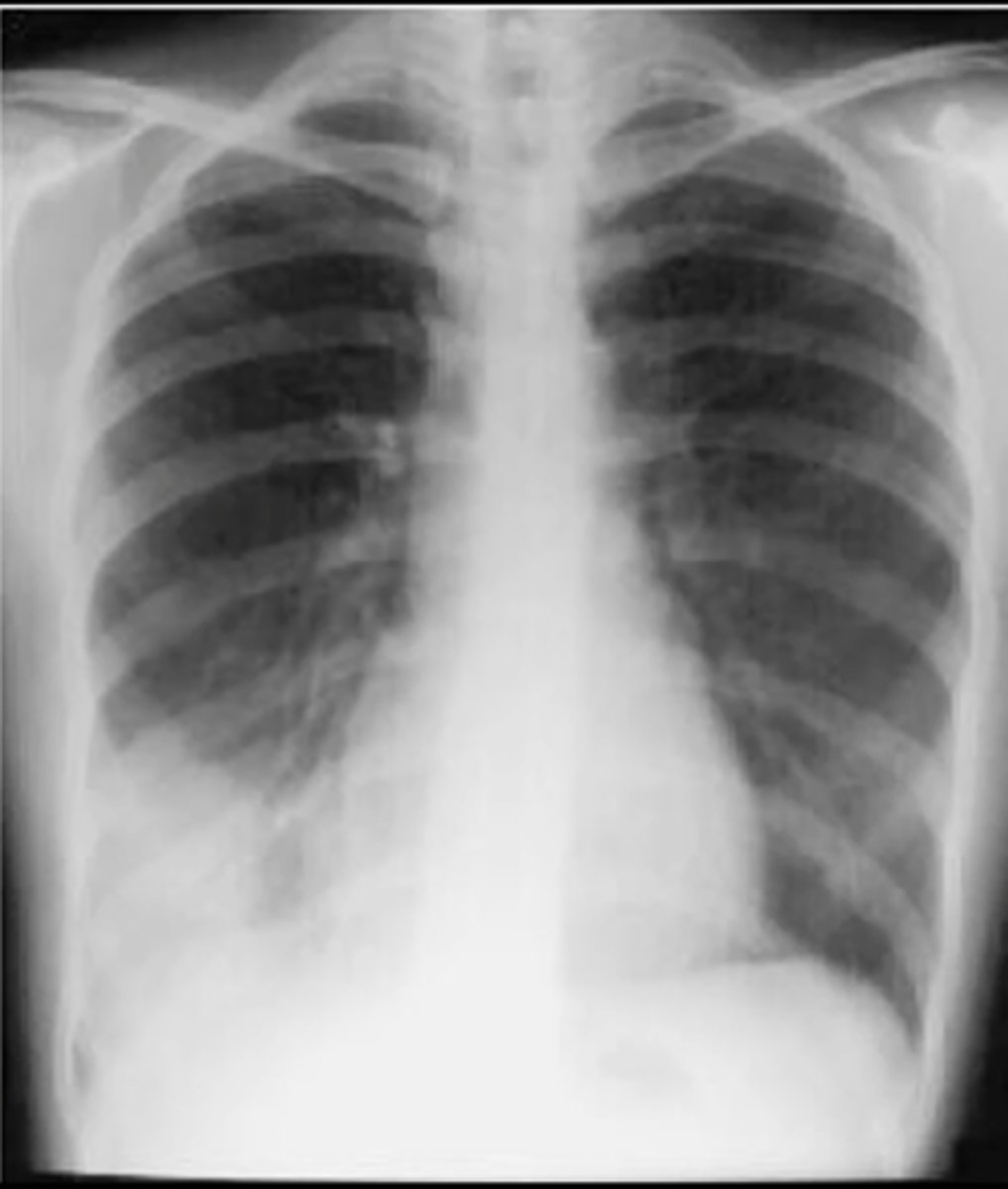
RLL consolidation
air bronchiolgrams and near the diaphragm on the left bottom (RLL of patient)
wedge shaped defect in pulmonary embolism
the clot deoxygenated lungs, so lung tissue dies
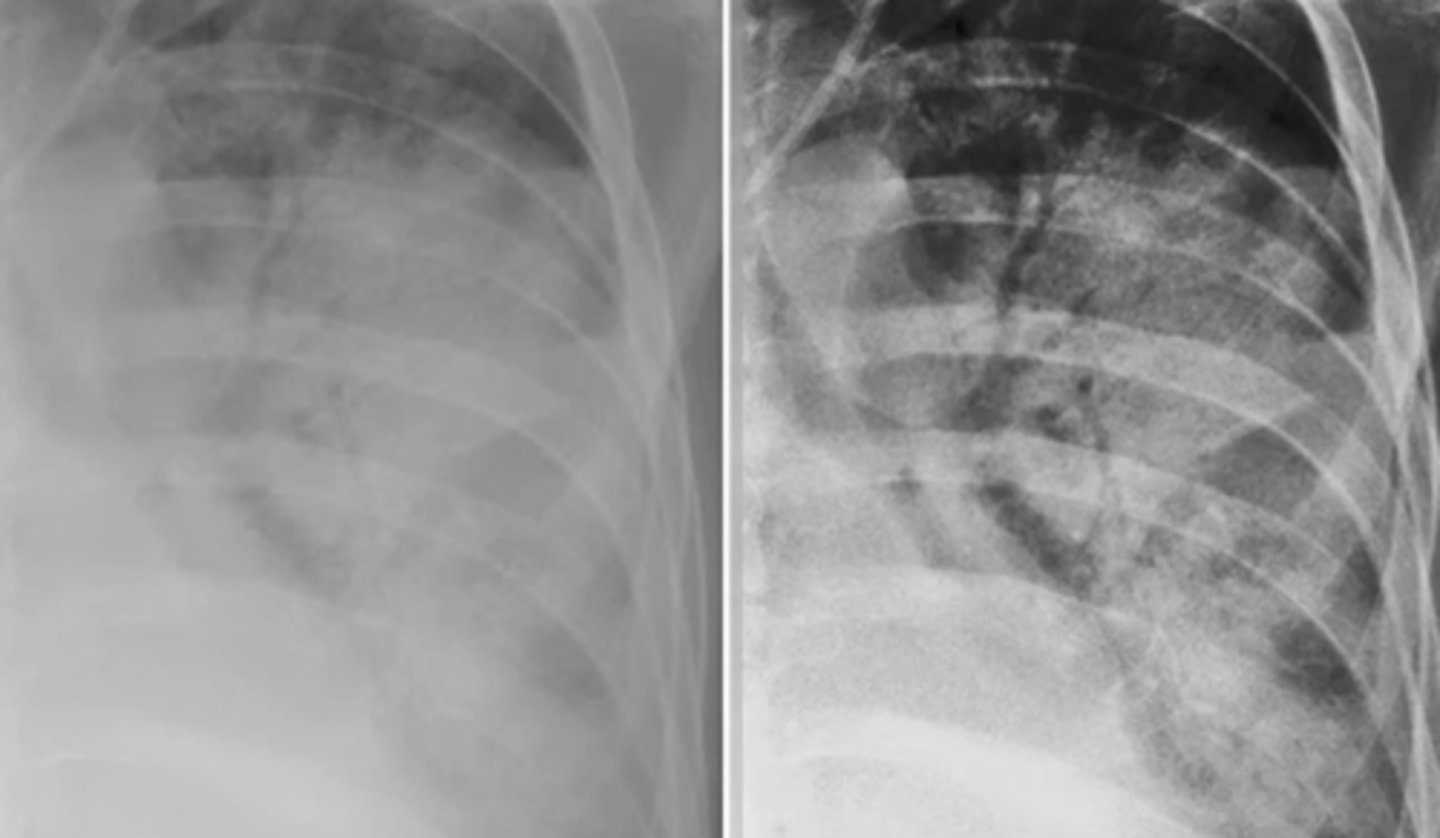
air bronchograms
Lucent tubular shadows running through areas of consolidation
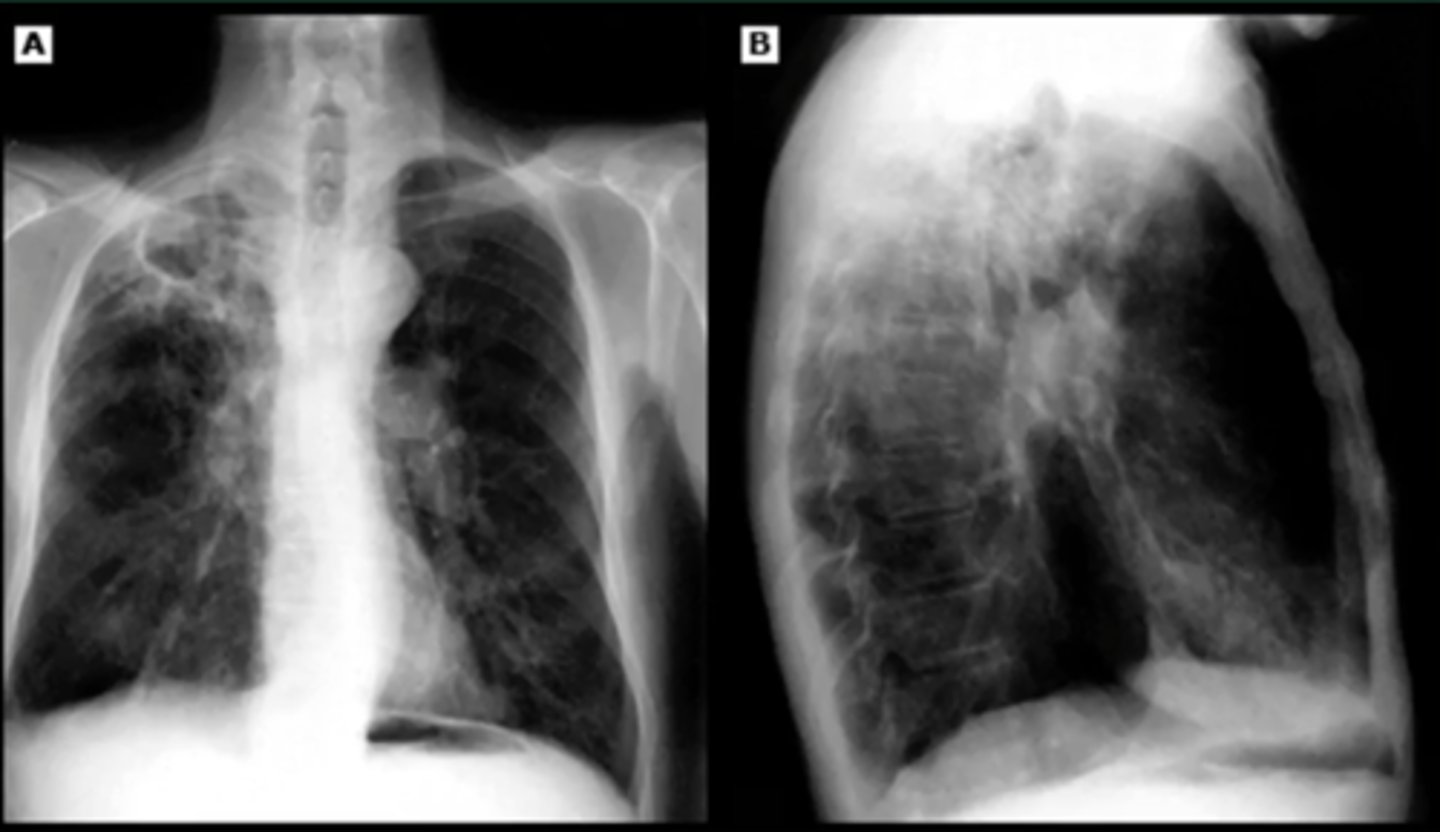
tuberculosis
cavitary lesion in the RUL
ET tube
tube that goes down the middle of the spinous processes (down trachea) and should not go past the bifurcation of the trachea
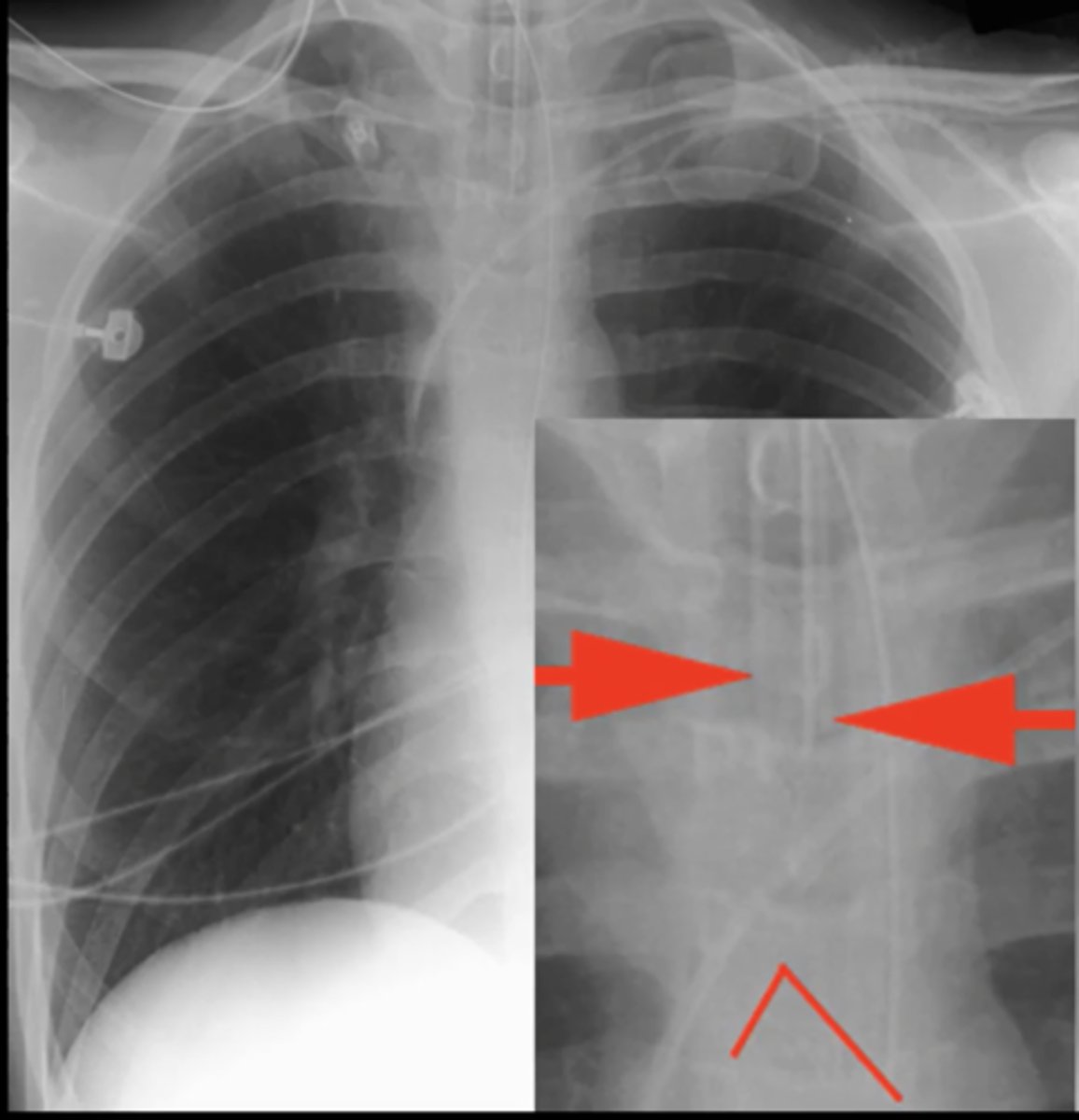
IJ line (central line)
tube that goes into internal jugular and goes into the right atrium
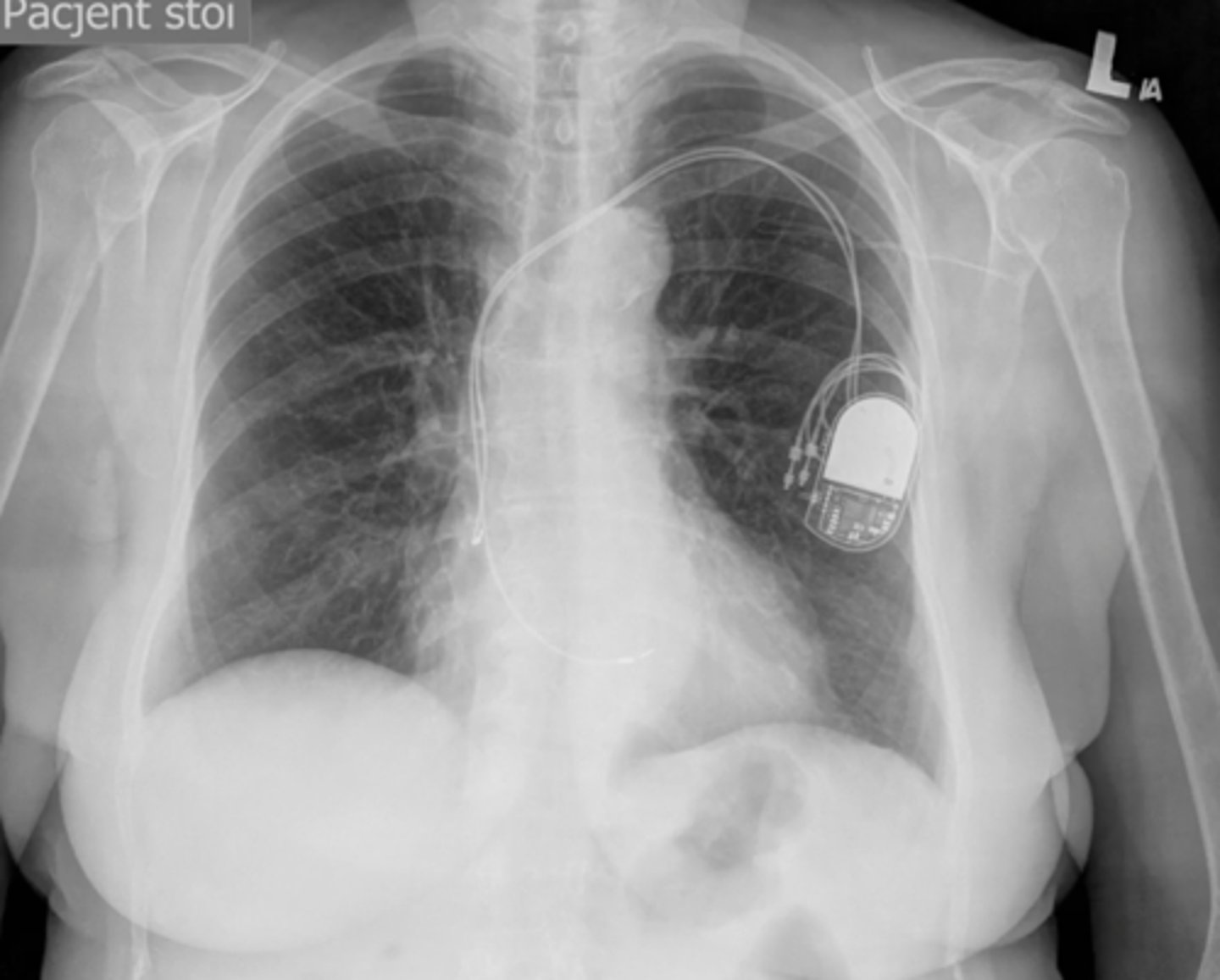
pacemaker
device that connects to the right atrium and ventricle
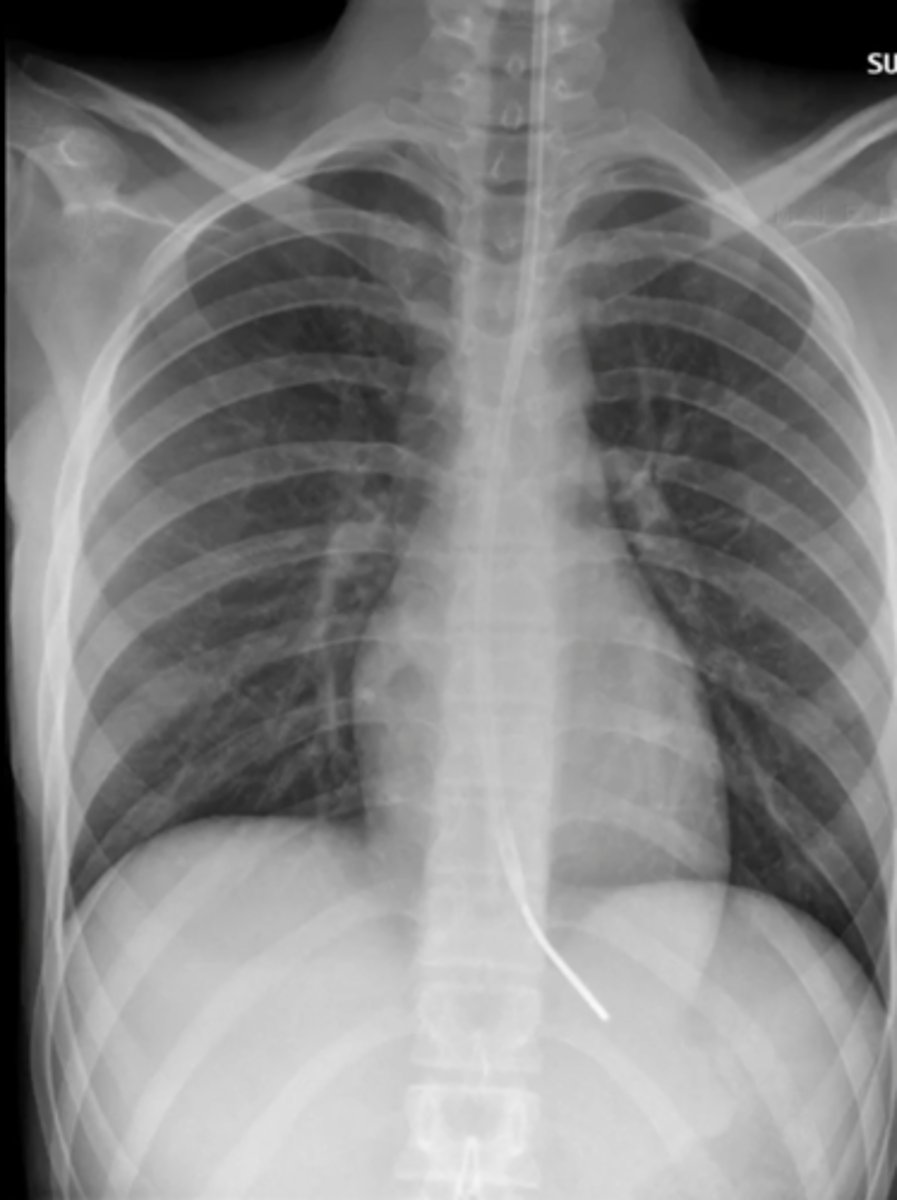
NG tube
tube inserted through nose and into stomach
office spirometer
in office measurement of respiratory function
- spirometry
- TLC: vital capacity + residual volume
- DLCO: diffusion lung capacity
what is included in a full pulmonary function booth
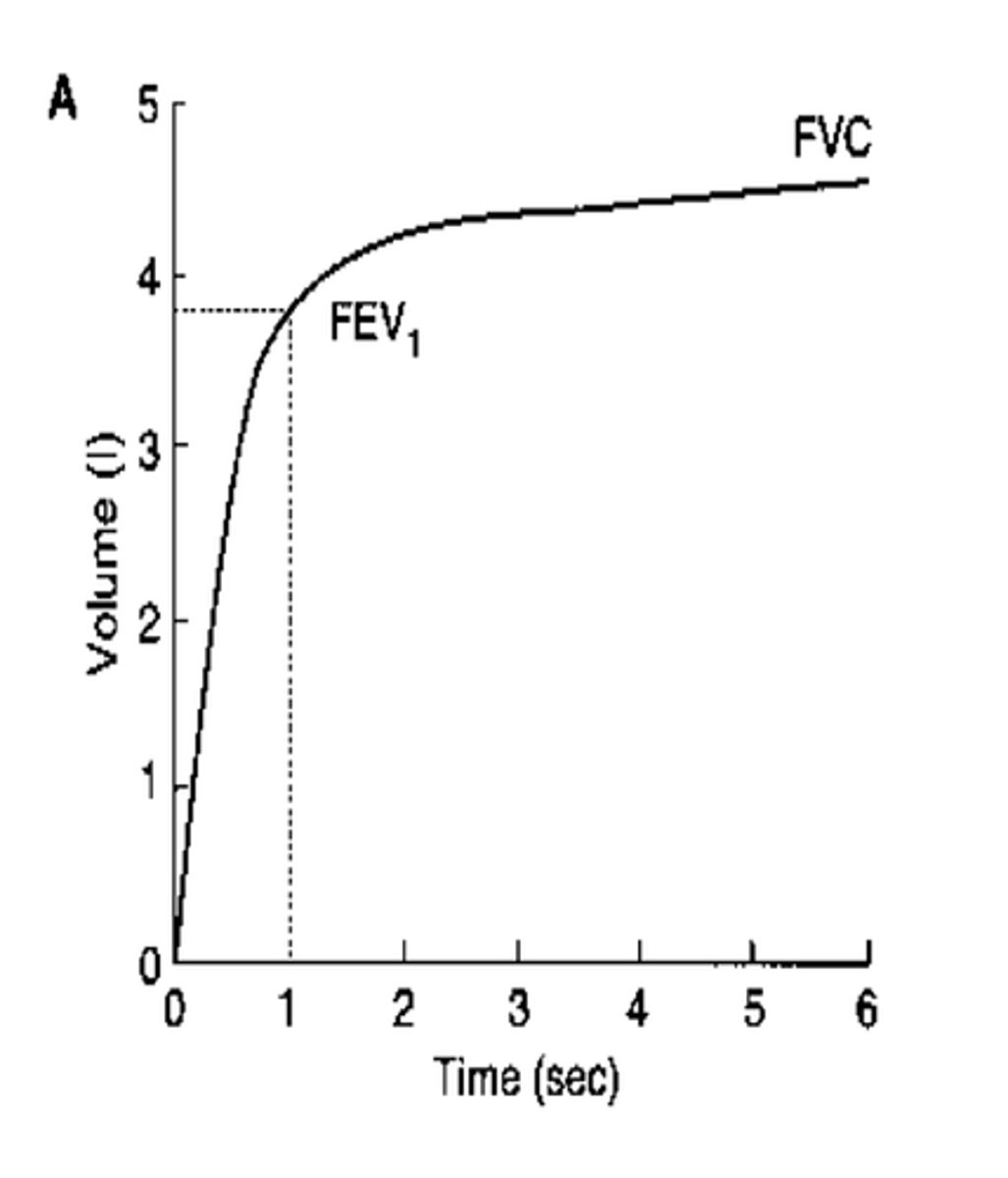
FVC (forced vital capacity)
The amount of air forcefully expired after a maximal inspiration; how much you can hold in the lungs
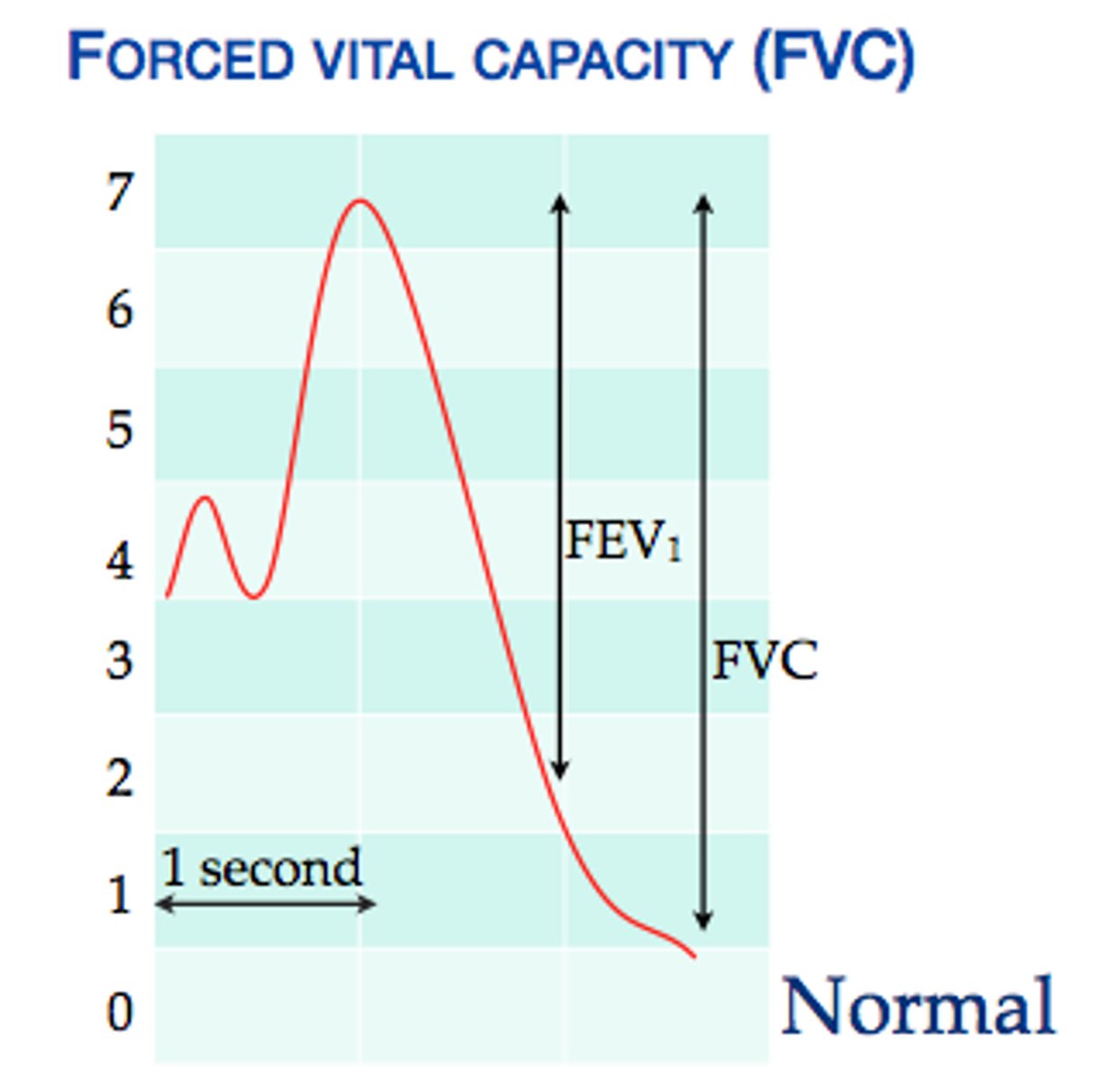
FEV1
forced expiratory volume in 1 second
FEV1/ FVC ratio
percentage of the total volume (FVC) that is exhaled in the first full second of expiration (FEV1). used to evaluate for obstruction
FEF 25-75%
mid expiratory flow rate: gives the flow rate during middle half of the maneuver
small airway obstruction
what does a low FEF 25-75% indicate
obstructive pattern pft
FVC: normal or low
FEV1: low
FEV1/FVC: low
RV: high (air trapping)
TLC: high (hyperinflation)
restrictive pattern pft
FVC: low
FEV1: normal
FEV1/FVC: normal
RV: normal or low
TLC: <80% of predicted
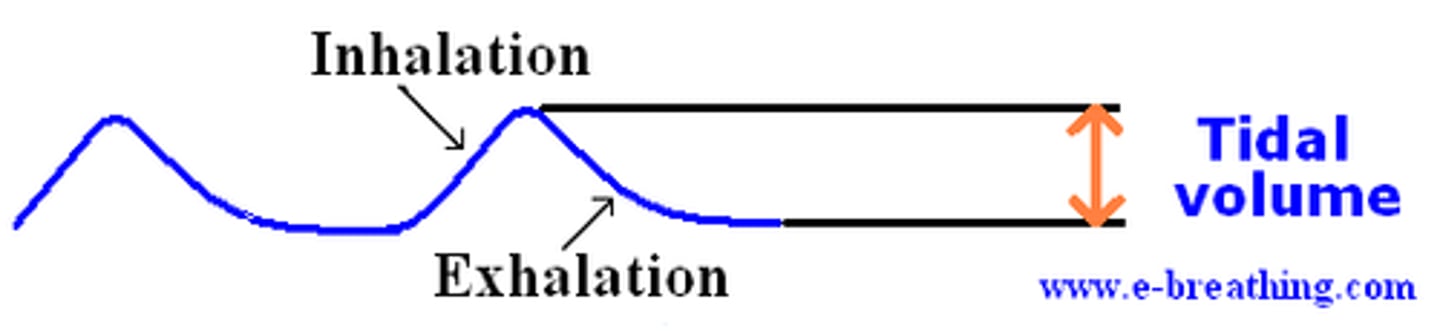
tidal volume (TV)
amount of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
maximum amount of air contained in lungs after a maximum inspiratory effort (includes residual volume)
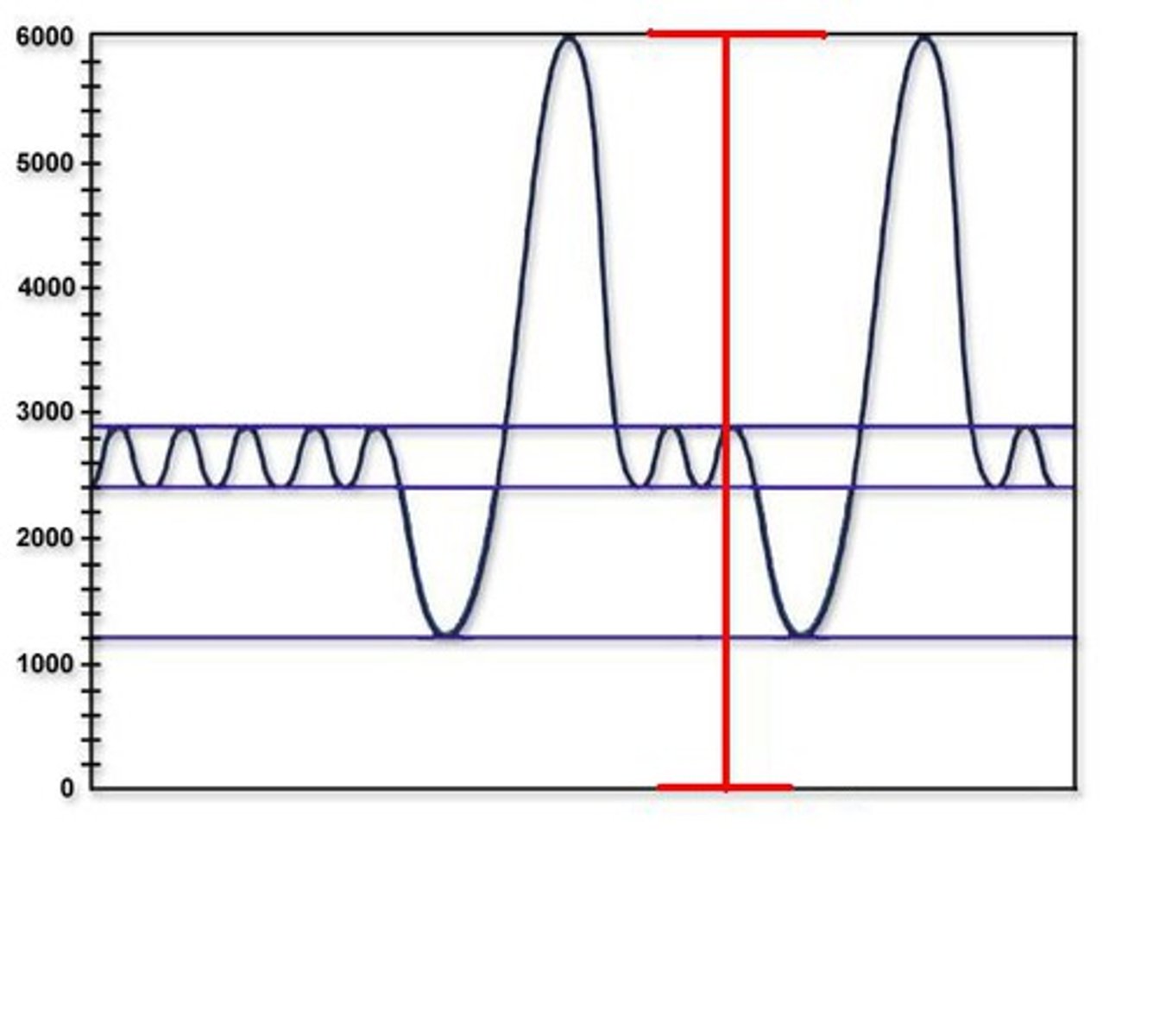
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal tidal volume expiration
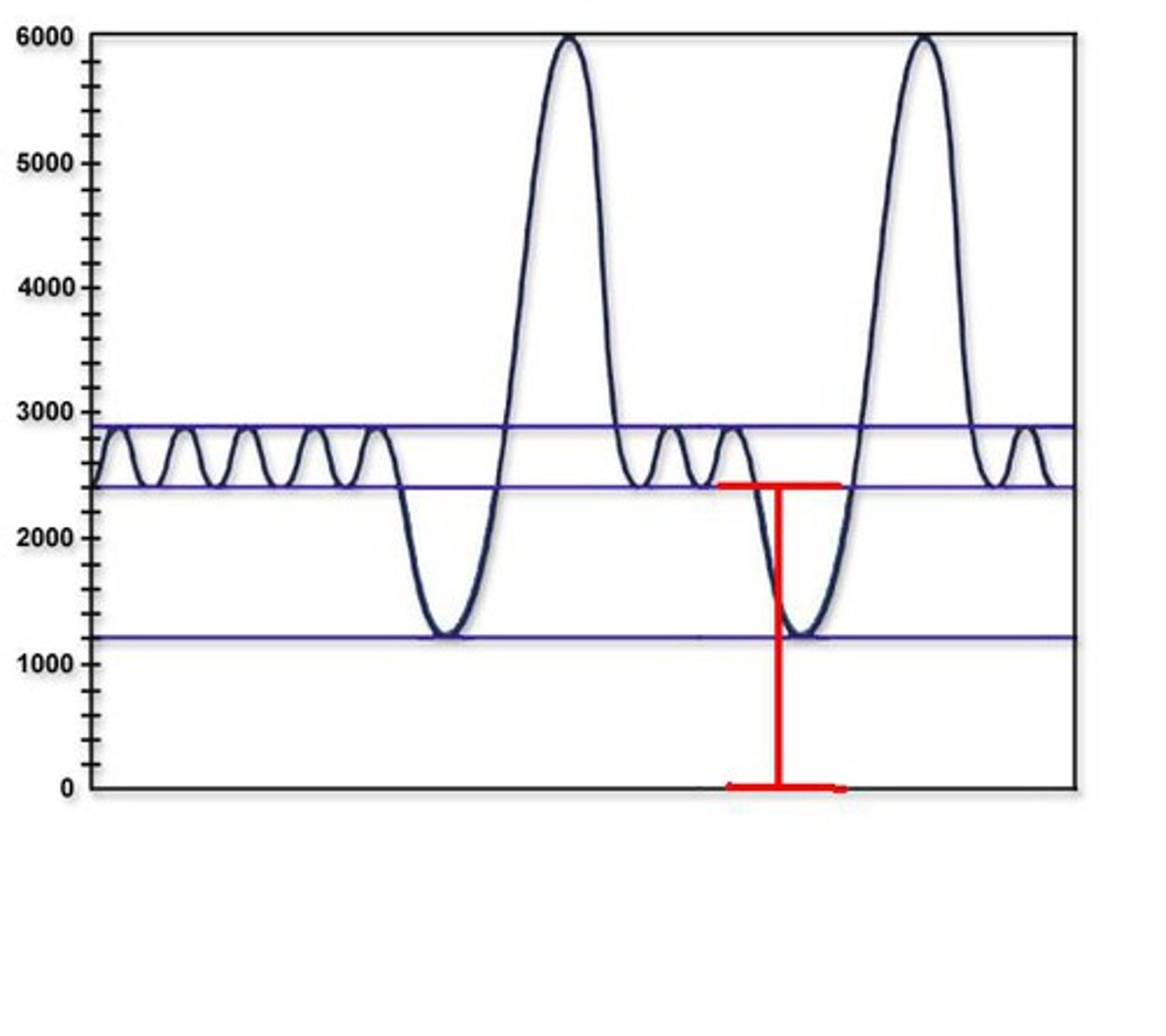
- avoid short acting inhaler on morning of test (can cause false normals, only use if testing for efficacy of medications)
- wear comfortable, nonrestrictive clothing
- give BEST EFFORT!
patient education for spirometry
- coach patient to take deep breath and then rapidly expire into the spirometer
- repeated x3 and averages are used
spirometry technique
Normal Spirogram
FEV1/FVC usually >80%
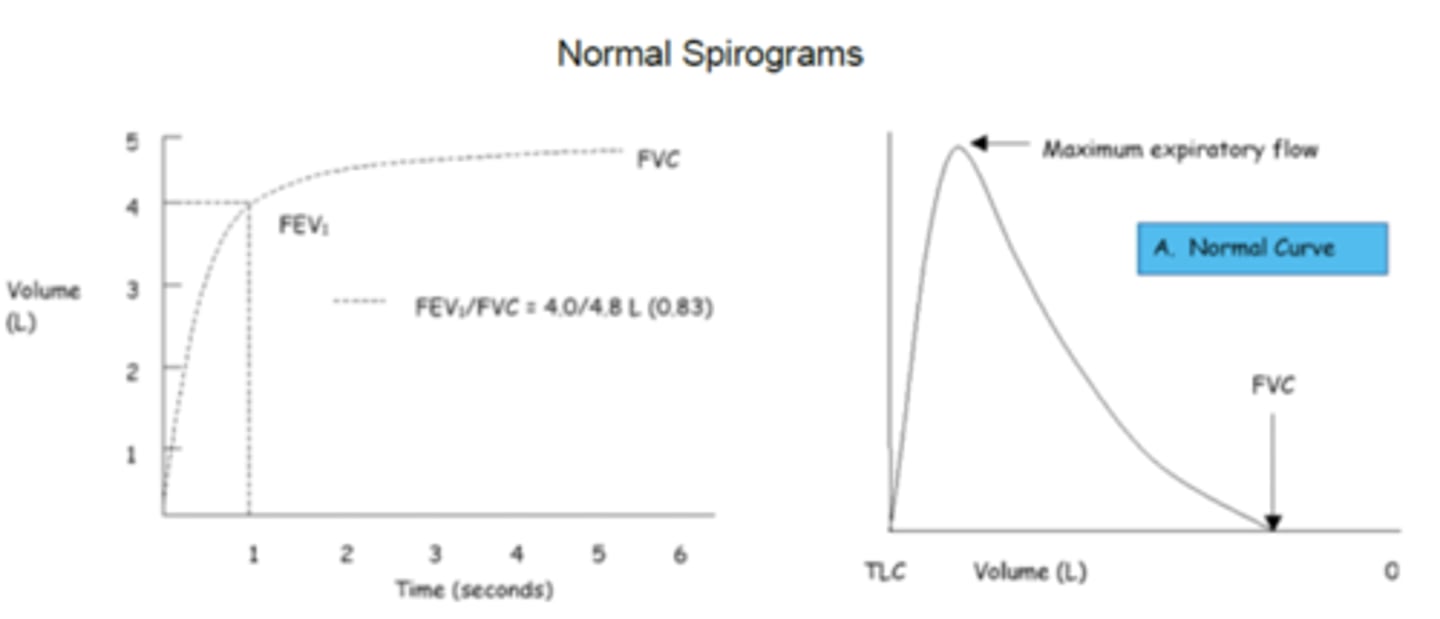
FVC
FEV1
FEV1/FVC ration
FEV6
FEF 25-75%
which values does spirometry give
Low FEV1/FVC ratio + normal FVC --> obstructive only
- adults:
(interpreting PFTs) What lab values are concerning for an obstructive disorder
Low FEV1/FVC ratio + Low FVC --> obstructive and restrictive
FEV1/FVC:
- adults:
(interpreting PFTs) What lab values are concerning for a mixed pattern disorder
Low FEV1/FVC ratio + normal FVC (tells us obstructive pattern)
Post bronchodilator increase in FEV1 or FVC by >12% --> reversible
(interpreting PFTs) What lab values are concerning for REVERSIBLE obstructive disorder (asthma)
Low FEV1/FVC ratio + normal FVC (tells us obstructive pattern)
No significant change in FEV1 or FVC after bronchodilator (<12% increase) --> Irreversible
(interpreting PFTs) What lab values are concerning for IRREVERSIBLE obstructive disorder
normal FEV1/FVC ratio + low FVC
- adults:
(interpreting PFTs) What lab values are concerning for a restrictive disorder
mild: >80%
moderate: 50-79%
severe: 30-50%
very severe: <30%
what FEV1 values determine severity of obstruction
FVC: normal --> no restriction
FEV1: 81% (below LLN) --> mild
FEV1/FVC: 81% (below LLN) --> obstructive
bronchodilation test: >12% increase --> reversible
example: what pattern is seen in the following PFTs
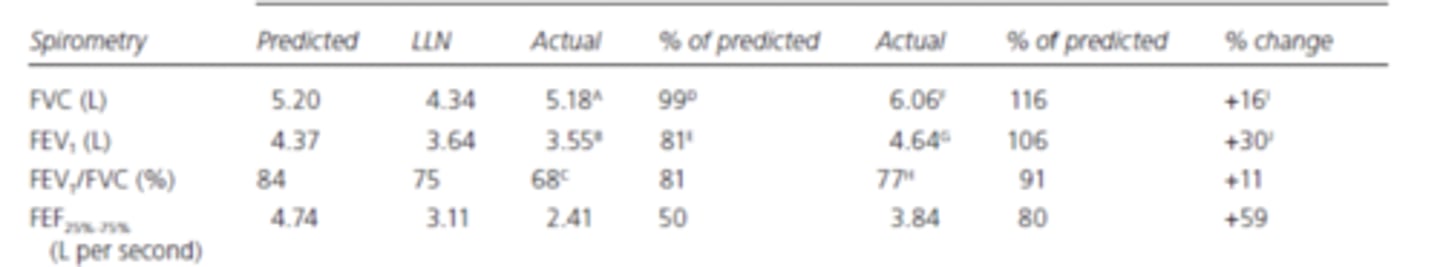
normal: 76-140%
mild: 61-75%
moderate: 40-60%
severese: <40%
what DLCO levels indicate the severity of the disease
loss of surface area (ex: blebs in COPD) or a thickened alveolar wall
- w/ normal spirometry: anemia, pulmonary vascular diseases
- w/ obstruction: bronchiolitis, cystic fibrosis, emphysema, COPD
- w/ restriction: ILD (interstitial), pneumonitis
what causes a low DLCO
- altitude
- asthma
- polycythemia
- severe obesity
what causes a high DLCO
forced expiratory time
- pts 60+ with >9 seconds are at COPD risk
the number of seconds it takes for the person to exhale from total lung capacity to residual volume (deep breath in and out as quick as possible)
measures force of air exhaled; used to monitor asthma
peak flow meter
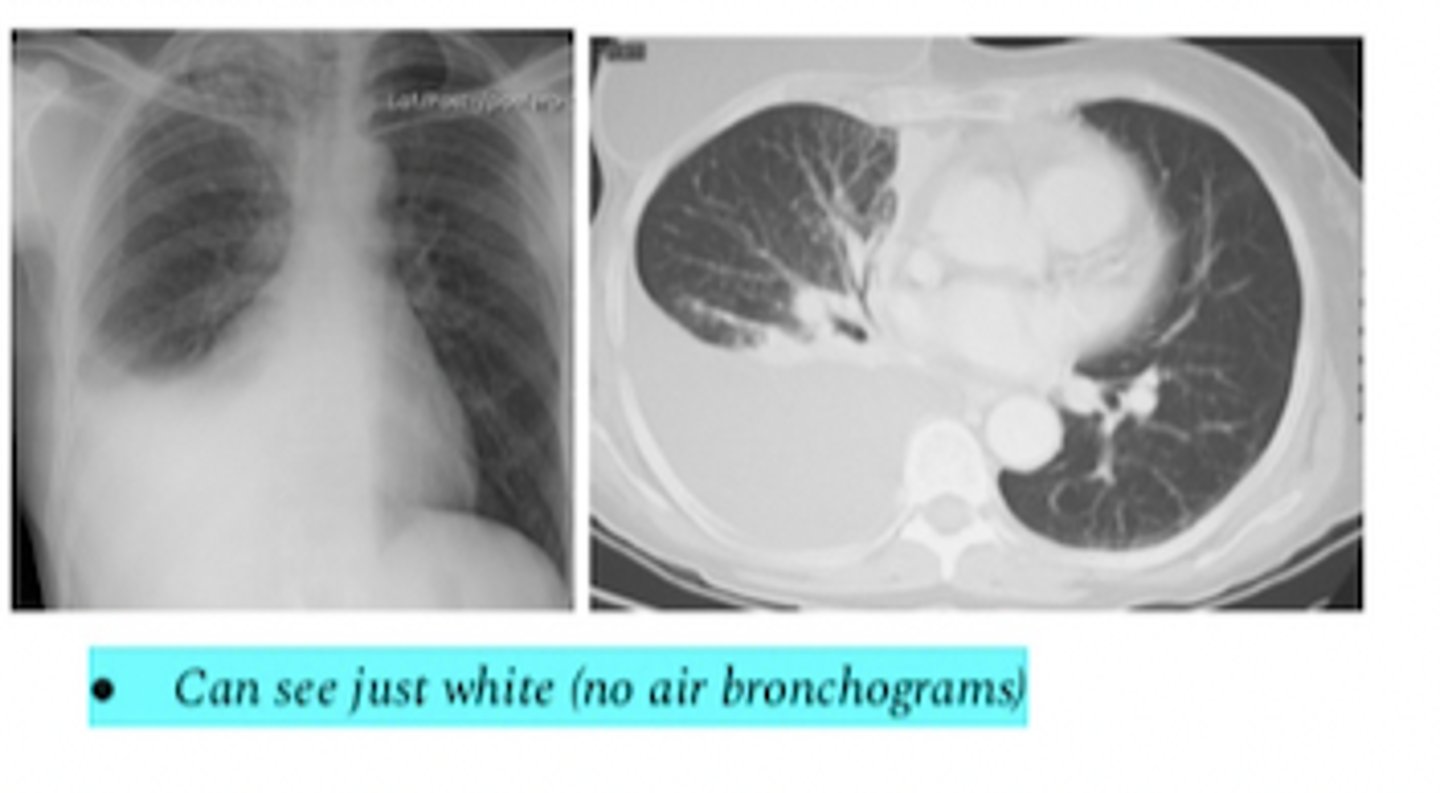
pleiural effusion
what does this xray and CT show
assess local tumor extension, chest wall invasion, and blood vessel invasion
indication for thoracic mri
eval of pulm embolism in pt w a c/i to CT angiogram
indication for VQ scan
<1cm fluid from chest wall
INR >2
PLT <50,000
CR >6
contraindication for thoracentesis
TB, pleurisy, lymphoma, sarcoidosis, chronic rheumatoid pleurisy
what does lymphocyte dominant pleural fluid indicate?
chylothorax (TAG >110) or cholesterol effusion
what causes white pleural fluid
adenosine deaminase (ADA) > 40
what test is done to confirm TB
pleural protein/ serum protein >0.5
pleural LDH/ serum LDH > 0.6
pleural LDH > 2/3 ULN
lights criteria for exudative pleural fluid (usually indicates infection, inflamm, or malignancy)
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure - one setting)
tx for osa
Mild: 5-15
Moderate: 15-30
Severe: >30
apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) classifications