Benign Diseases
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Adhesiolysis
Surgical removal of adhesions
Anovulation
Failure to ovulate
Hirsutism
Excessive hair on a woman
Hydatidiform mole
Genetically abnormal pregnancy that develops into a grape-like mass within the uterus
Hysteroplasty
Reconstructive surgery of the uterus
Involute
Collapsing and rolling inward
Menorrhagia
Abnormally heavy or prolonged menses
Lysis
Breaking up of tissue
Oligoanovulation
Infrequent ovulation
Oligomenorrhea
Infrequent menses
Placenta accreta
Growth of the placenta into the myometrium
Placenta previa
Implantation of the placenta in the lower uterine segment of the cervix
Red degeneration
Hemorrhage into a leiomyoma that has outgrown its blood supply
Tamoxifen
Antiestrogenic drug used to decrease the occurrence of certain estrogen-sensitive breast cancers
Uterine dehiscence
Partial separation of the myometrium at the location of the uterine scar
Gartner’s Duct Cyst
Remnant of the mesonephric duct
single or multiple
usually asymptomatic
If large, they can cause symptoms such as dyspareunia
Benign cervix conditions are causes by:
abnormal uterine fusion
abnormal cervical fusion
DES exposure
Enlarged cervix caused by:
Nabothian cysts
Cervical polyps
Cervical fibroids
Cervical stenosis
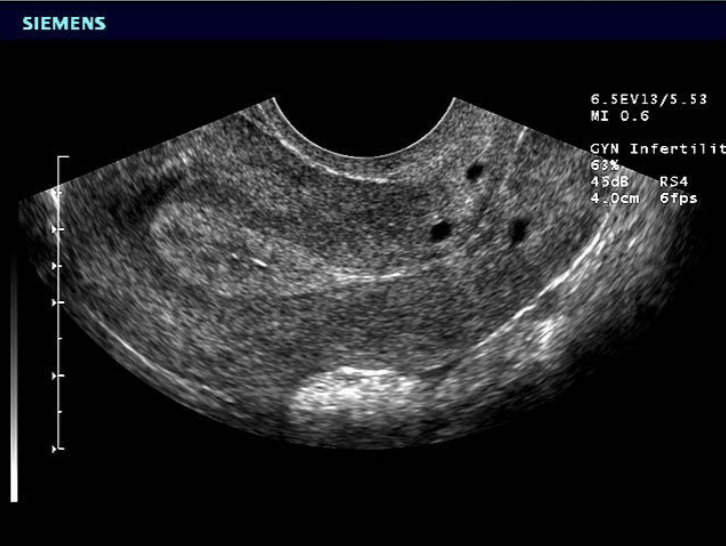
Nabothian Cysts
Considered normal in adults
may be multiple or single
Size ranges from 3mm - 3cm
require no treatment
often occur after pregnancy or chronic cervicitis
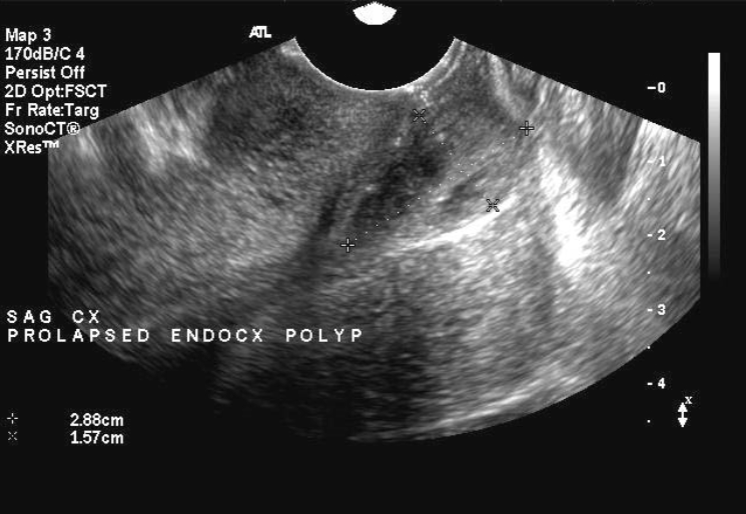
Cervical Polyp
Most common benign cervical lesion
Most often occur in multigravitas, peri or post-menopausal patients
usually asymptomatic
Cervical polyps U/S appearance:
Attached by a stalk to cervical wall
May be difficult to see on US due to size
“teardrop” appearance
Cervical Fibroids
8% of fibroids (myomas, leiomyomas, fibromyoma)
Most are small and asymptomatic
Observe for growth
Common during reproductive years
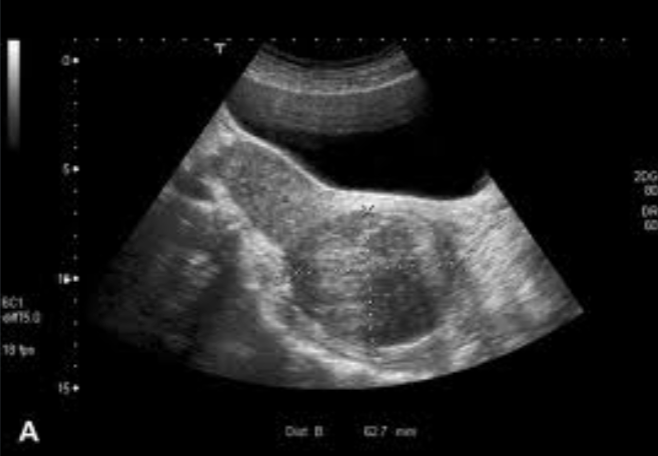
Cervical fibroid symptoms include:
Dyspareunia
Dysuria
Urgency
Genitourinary obstruction
cervical obstruction
prolapse
bleeding
obstructed labor
Cervical Stenosis
Stenosis of the uterine cervix is the pathologic narrowing of the uterine cervix
Defined as cervical narrowing that prevents the insertion of a 2.5 mm wide dilator
1/5 of patients have history of diethylstilbesterol (DES) exposure while in-utero
also associated with endometriosis
If the cervical stenosis is severe enough it may result in proximal obstruction resulting in:
hematometra → women of childbearing age with cervical stenosis are less likely to show evidence of hematometra than postmenopausal patients
hydrometra
pyometra
Other potential consequences of cervical stenosis include:
infertility
difficulty with fertility treatments such as:
embryo transfer
intra-uterine insemination
Causes of cervical stenosis:
congenital
chronic infection - cervicitis
trauma
from previous instrumentation
cone biopsy/loop electrosurgical excision procedures (LEEP)
cryotherapy
laser treatment
stenosis secondary to a tumor/mass:
cervical polyp
cervical cancer
post-radiation therapy
Cervical endometriosis
Cervical Stenosis Diagnosis:
Hysterosalpingogram
Narrowing of the endocervical canal or complete obliteration of the cervical os
prevents catheter insertion
Ultrasound
thickened or normal endocervix appearance
CT
may have hydrometra and/or hematometra
cervix may be normal in appearance
uterine cavity may be fluid distended
further complications such as hematosalpinges may be visualized
Endometrial polyps
Common lesion
Usually occur in 40’s
Malignant potential
Most appear hyperechoic
Large polyps associated with bleeding
Best diagnosed by sonohysterography
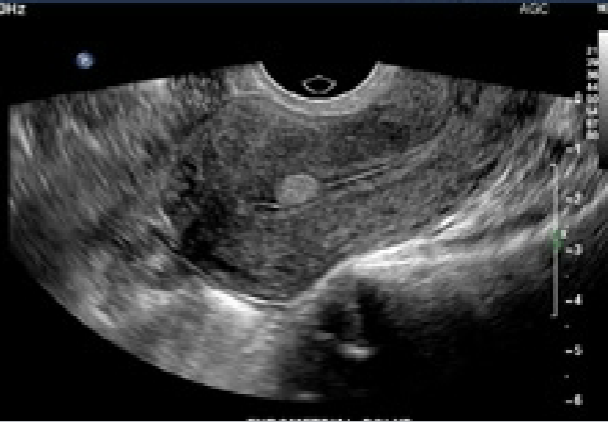
Sonohysterography
Ultrasound-guided procedure used to evaluate endometrial cavity and lining
Physician inserts speculum and catheter with balloons
Removes speculum
Sonographer inserts TV probe
Physician injects saline through catheter
Image lining of uterus
Fibroid AKA:
Leiomyoma
Myoma
Fibromyoma
Fibroid
Tumor of smooth muscle origin
Most common tumor of the female pelvis
Occurs in 20-30% of women of reproductive age
African American females > caucasian females
can be single or multiple
leading cause of hysterectomy
Fibroid causes:
etiology unknown
Typically arise after menarch and regress after menopause
estrogen-influenced
can increase in size during pregnancy
Fibroid signs / symptoms:
may be asymptomatic
can cause heavy bleeding
menorrhagia
can cause spotting/bleeding between periods
enlarged uterus on pelvic exam
urinary frequency if pressing on bladder
Fibroid Locations
Intramural
Submucosal
Subserosal
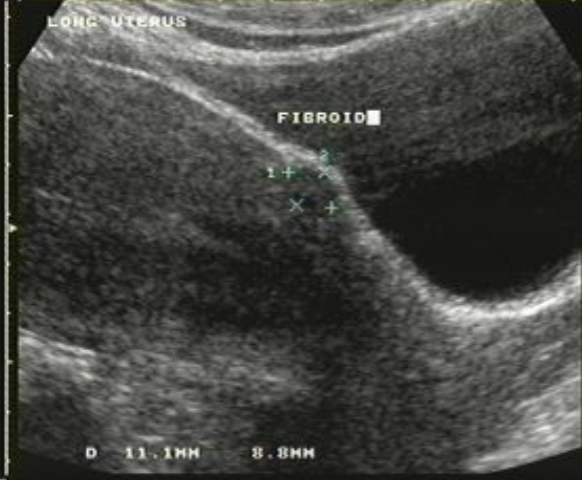
Intramural Fibroid
Located within the myometrium
95% of fibroids located here
may enlarge to cause pressure on adjacent organs
may lead to infertility
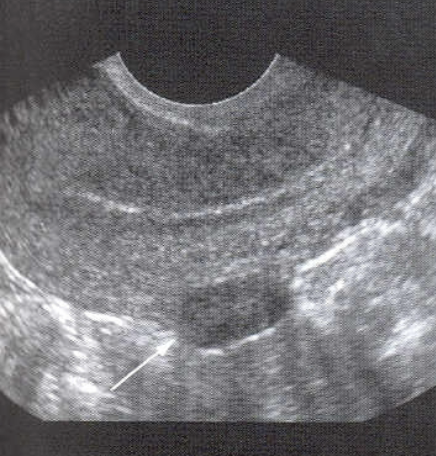
Submucosal Fibroid
Beneath endometrium and protrudes into endometrial cavity
Least common
Causes most symptoms
Can cause infertility
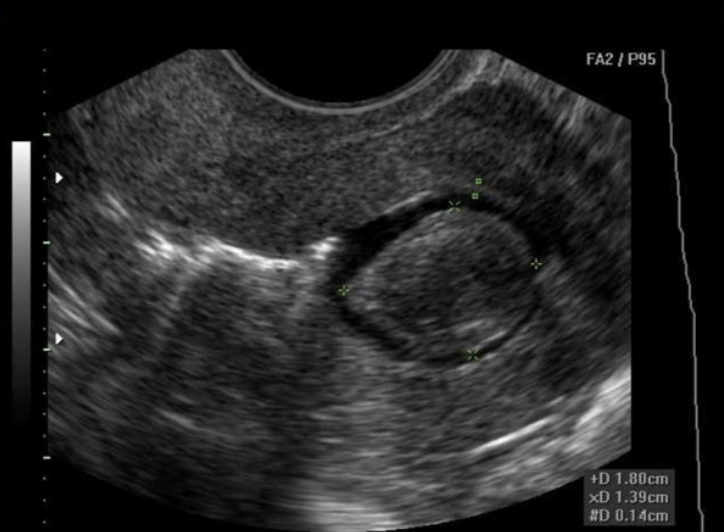
Subserosal Fibroid
Serosal surface → outside the uterus
Pendunculated - on a “stalk” or peduncle
May twist and cause severe pain
Fibroid Degeneration
Fibroids demand blood supply, when they outgrow their blood supply, degeneration may occur
Cystic degeneration - liquefaction necrosis
Calcific degeneration - after menopause
Degeneration process can cause significant pain
Myomectomy or hysterectomy may be performed to reduce pain
Fibroids U/S appearance:
Depends on number and size
Uterine enlargement
Hypo- to hyper- echoic
Heterogenous texture
Distorted uterine contour
May displace endometrium
Calcification causes shadowing
Trandsabdominally → able to appreciate large fibroids
Transvaginally → small fibroids
Ovarian Cysts
Most fluid-filled pelvic masses are ovarian in origin
Ovarian cyst prognosis
Less than 3cm usually regress spontaneously
3-5cm follow up ultrasound 6-8 weeks
may regress w/ BCP’s
>10cm usually do not regress
surgical removal
greater potential for malignancy
Ovarian Cyst U/S appearance:
Assess: Size, Location, Composition, and Age of Patient
Smooth, well-defined borders
Absence of internal echoes
Increased posterior enhancement
Functional Cysts
Ovarian Follicles
Follicular cysts
Corpus Luteum “Cyst”
Theca Lutein Cyst
Ovarian Follicle
Anechoic structures within ovary
Approx. 10 days prior to ovulation, ovaries may contain multiple small follicles
Single follicle becomes dominant
2-2.5 cm
1-3 days prior to ovulation, dominant follicle is seen as a “cloudy cone”
Follicular Cyst
Results from either non-rupture of dominant mature follicle or failure of immature follicle to undergo normal process of atresia
May be multiple
Usually unilateral
Range 1-10 cm (usually 2 cm)
usually asymptomatic → regress spontaneously
Any simple cyst measuring less than 5 cm in an ovulating woman should be re-evaluated in 6-8 weeks
Ruptured cysts will have free fluid in the cul-de-sac (likely posterior cds)
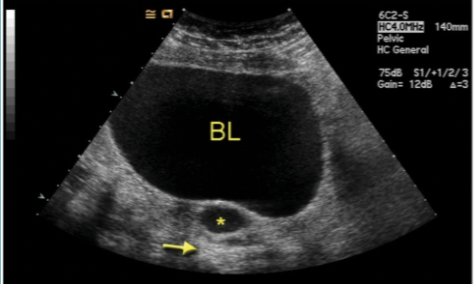
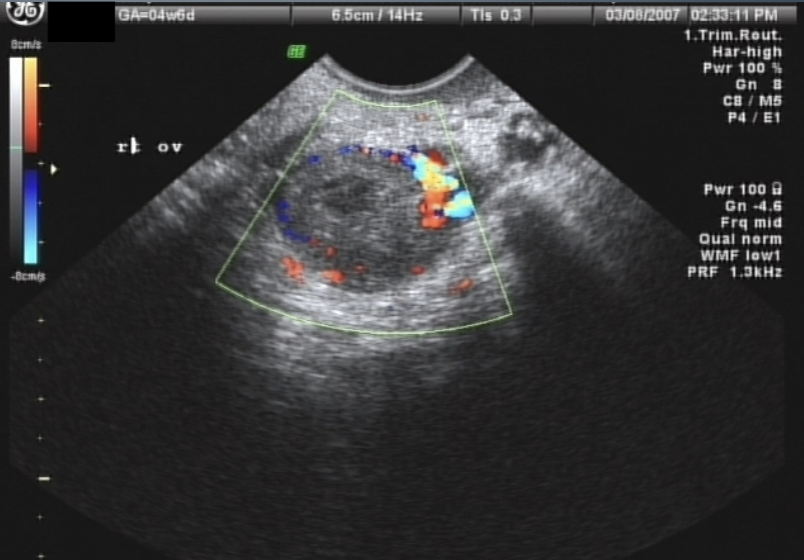
Corpus Luteum “Cyst” AKA:
“Great Pretender” cyst → variable appearance
Corpus Luteum “Cyst”
as dominant follicle ruptures, corpus luteum develops (1.5-2.5 cm)
not considered a true cyst until >3cm, may measure up to 6-8 cm in diameter
Unilateral and unilocular
Corpus Luteum “Cyst” U/S appearance:
hypoechoic w/ irregular or thick borders around a central anechoic area
may contain hemorrhage
demonstrates peripheral blood flow → “Ring of Fire” sign
Corpus Luteum “Cyst” signs / symptoms:
pain
nausea
vomiting
enlarged, tender ovary
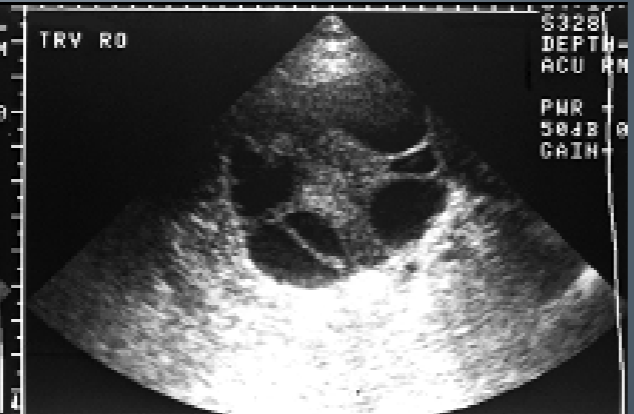
Theca Lutein Cyst AKA:
Hyperreactio luteinalis
Theca Lutein Cyst
largest of functional cysts
may range in size from 3-20 cm
multiloculated, bilateral fluid filled
patients will have high hCG levels
often associated with Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (Molar Pregnancy)
Theca Lutein Cyst
May be seen with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
complication of infertility drug therapy
will persist for several months after trophoblastic evacuation
like other cysts, may undergo hemorrhage, torsion, or rupture
Theca Lutein Cysts tend to appear:
Multi-loculated
thin-walled
large
bilateral
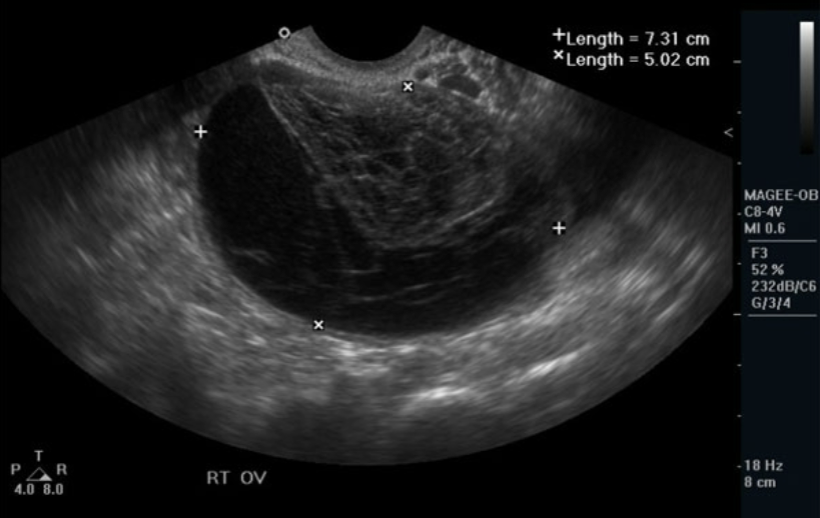
Hemorrhagic Cyst
Any type of cyst may become hemorrhagic
Bleeding within the cyst
Typical with follicular or corpus luteal cysts
Will vary in US appearance
stage of bleed
internal debris
septations
free fluid
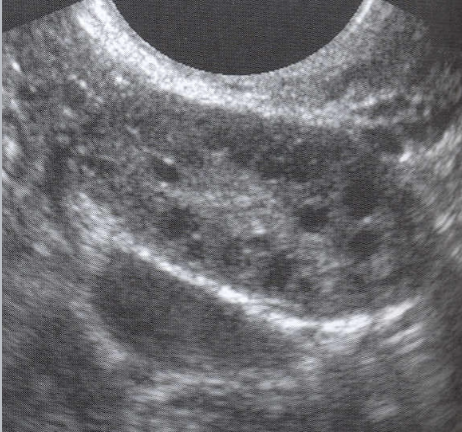
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOS)(PCOD)
Most common androgen disorder
Endocrine Disorder
Obesity
Oligomenorrhea
Anovulation
Caused by thick capsule covering ovary
Hirsutism
Infertility
Hypertension
Insulin Resistance and/or increased risk of Diabetes
Polycystic Ovarian Disease AKA:
Stein-Leventhal Syndrome
PCOS U/S appearance:
Bilateral enlargement
Contain multiple (12 or more), tiny peripheral cysts 2-9 mm
Ovarian volume >10 cm
25% of pt’s have normal appearing ovaries
The US appearance of PCOS may appear in women whose ovaries are treated with FSH
“String of Pearls” or “Black Pearl Necklace”
Benign Cystic Teratoma AKA:
Dermoid or Dermoid Tumor
Benign Cystic Teratoma
Most common germ cell tumor of the pelvis
Most frequently visualized ovarian tumor in women under 20
Made from same germ cell layers that make up hair, skin, glandular tissues, bone, and fat
malignancy is rare
Benign Cystic Teratoma characteristics:
Usually asymptomatic, but may present with pain or palpable mass
Teratomas may twist, butt rarely rupture
Bilateral in 10-15% of cases
Benign Cystic Teratoma treatment:
surgical treatment
young patients → wait to preserve function of ovary
can usually remove tumor without removing entire ovary
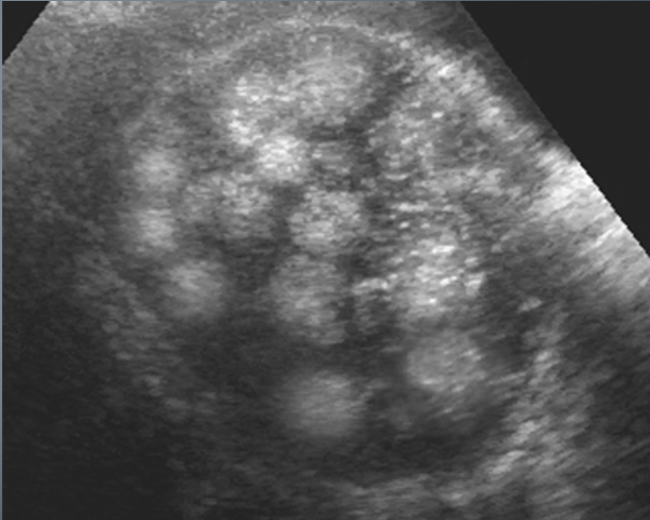
Benign Cystic Teratoma U/S appearance:
varies
cystic mass
complex mass w/ calcifications
fat-fluid level within complex mass
diffusely echogenic mass w/o shadowing
predominantly solid with echogenic foci that represent calcium or fat with or without shadowing
“Tip of the Iceberg”
Epithelial Tumors
Arise from ovarian epithelium
Includes:
Serous Cystadenoma
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Brenner Tumors
Clear Cell
Mixed Epithelial
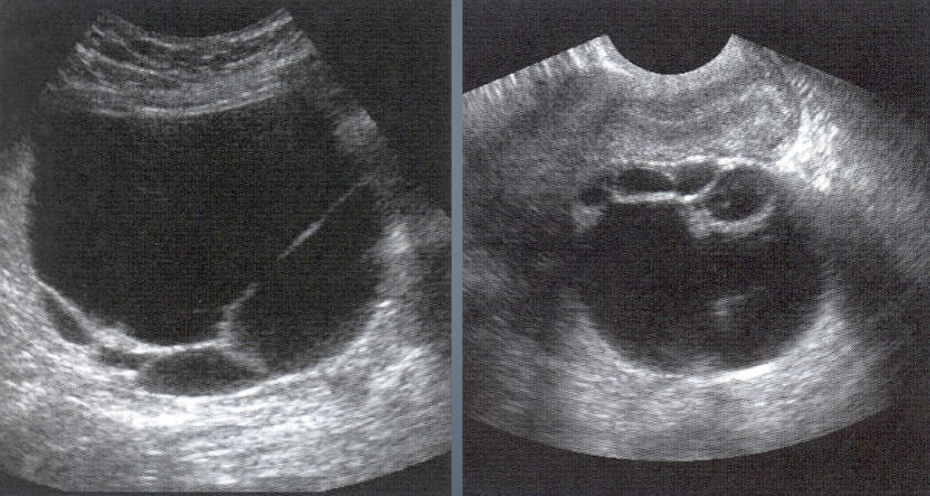
Serous Cystadenoma
Most common type of ovarian cystic tumor
Seen mostly in post-menopausal women (both types)
Contains thin serous fluid
Usually unilocular
May have thin septations
May have papillary projections
Bilateral - 25% of the time
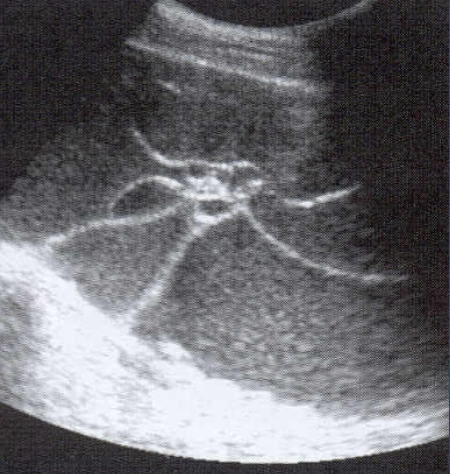
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Contains thicker, mucinous fluid
More frequent chance of malignancy
Usually multi-locular
VERY LARGE! ( may reach up to 30 cm)
multiple septations
may contain debris
bilateral in <5% of cases
Brenner Tumor
Solid ovarian tumors
2% of all ovarian neoplasms
Arise from ovarian epithelial surface
Seen at any age → but usually around 50
Brenner Tumor signs / symptoms:
may be asymptomatic
pelvic mass
pain
abnormal uterine bleeding
Brenner Tumor U/S appearance:
usually unilateral
solid, hypoechoic
microscopic to 30 cm in size
Can be associated w/ Meigs Syndrome
Meigs syndrome
Ascites, pleural effusion, and ovarian neoplasm
Granulosa Stromal Cell Tumors
Hormone producing
Least common
Include:
Fibromas
Thecomas
Granulosa Cell Tumors
Ovarian Fibroma
5% of all ovarian tumors
ages 50-60
usually unilateral - but may be multiple
appear hypoechoic with shadowing
5-16 cm
can also be associated w/ Meigs Syndrome
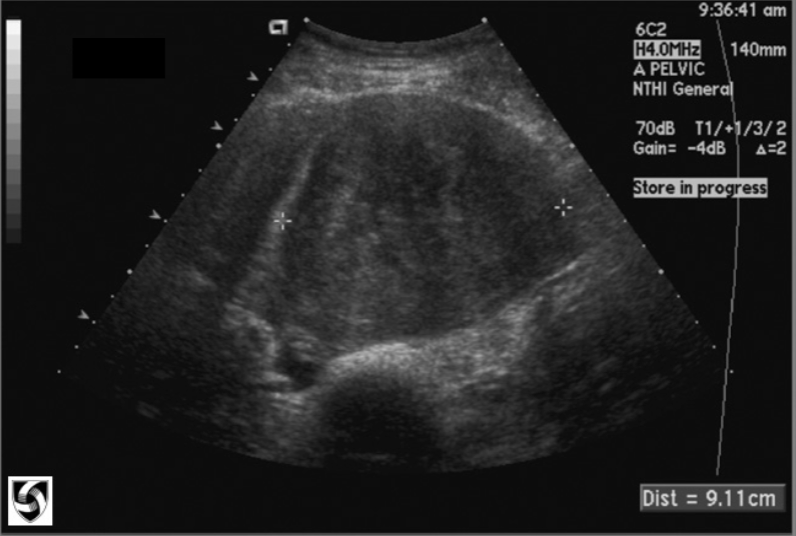
Thecoma AKA:
Fibrothecomas
Thecoma
Estrogen-producing
Solid
1-2% of ovarian tumors
Abnormal uterine bleeding due to estrogen
Usually unilateral
May measure up to 30 cm
Most frequently occur in post-menopausal women
Shadowing is common
Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors AKA:
Sertoli-stromal cell tumors
Arrehnoblastoma
Androblastoma
Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors
Masculinization effects from elevated testosterone levels
Unilateral
Very rare
Pain or abdominal swelling
Young women <30 y/o
Solid echogenic mass
Can be malignant
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
Had ovary removed, but some ovarian tissue is left
This tissue may develop cysts or tumors
Paraovarian Cyst / Paratubal Cyst
Arise in broad ligament
Asymptomatic unless hemorrhage
Simple, thin walled unilocular cysts up to 18 cm
Size does not change based on menstrual cycle