carbon cycle - stores and fluxes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
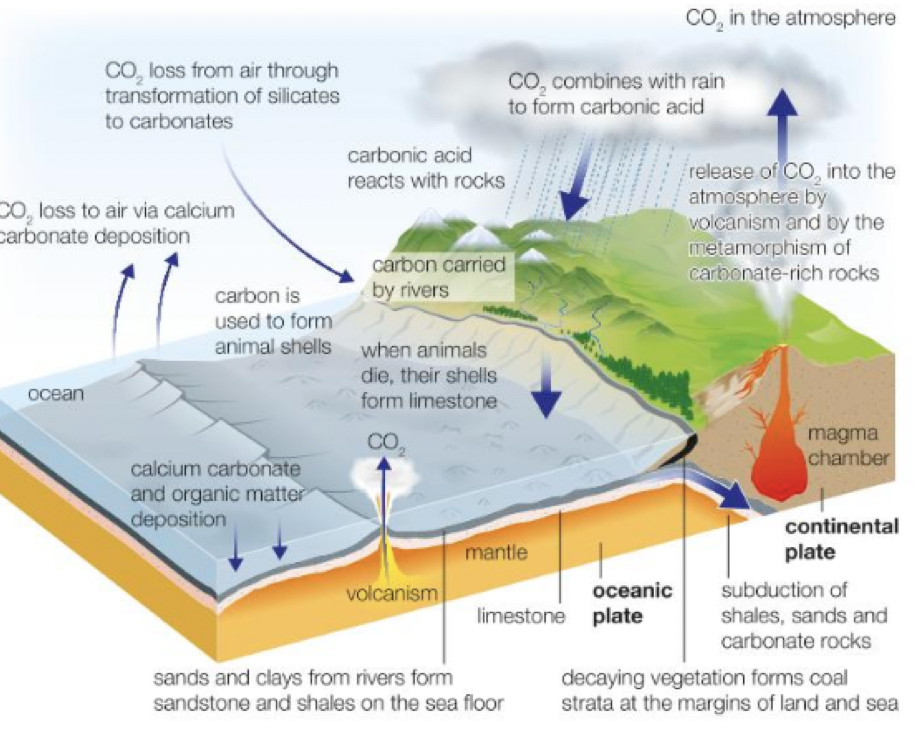
geological carbon cycle
three forms of carbon:
inorganic- found in rocks was bicarbonates and carbonates
organic- found in plant material and living organisms
gaseous- found as CO2 and CH4 (methane)
carbon sink/ source
a carbon sink is any store which takes in more carbon than it emits, so an intact tropical rainforest is an example. A carbon source is any store that emits more carbon than it stores so a damaged tropical rainforest
carbon sequestration
it is the transfer of carbon form the atmosphere to other stores and can be both natural and artificial. For example a plant sequesters carbon when it photosynthesise and stores the carbon in its mass
main carbon stores
marine sediments and sedimentary rocks:
66,000-100,000 million billion metric tons of carbon
oceans:
second biggest with 38,000 billion metric tons of carbon
fossil fuels deposit:
humans have developed to exploit home rapidly- 4000 billion metric tons of carbon
soil organic matter:
deforestation and agriculture and land use can change- 1500 billion metric tons of carbon
atmosphere:
human activity has caused levels to increase by 40% since Industrial Revolution- 750 billion metric tons of carbon
terrestrial plants:
vulnerable to climate change- 560 billion metric tones of carbon
combustion
when fossil fuels and organic matter such as trees are burnt, they emit CO2 into the atmosphere that was previously locked inside of them. This may occur when fossil fuels are burnt to produce energy, or if wildfires occur.
decomposition
when living organism die, they are broken down by decomposers which respire, returning CO2 into the atmosphere. Some organic matter is also returned to the soil where it is stored adding carbon matter to the soil
diffusion
the ocean can absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, which has increased ocean acidity by 30% since pre-industrial times. Seawater becomes more acidic which is harming aquatic life by causing coral bleaching
sedimentation
this can happen on land or in the sea, for example when shelled marine organisms die, their shell fragments fall to the ocean floor and become compacted over time to form limestone. Organic matter from vegetation and decaying marine organism is compacted over time to form fossil fuel deposits.
weathering and erosion
inorganic carbon is released slowly through weathering; carbonation weathering occurs when CO2 in the air mixes with rainwater to create carbonic acid which aids erosion of rocks such as limestone. Marine organisms use the carbon in the water to build their shells
metamorphosis
extra heat and pressure form s metamorphic rock, during which some carbon is released and some becomes trapped
volcanic outgassing
there are pockets of CO2 found in the earths crust. During a volcanic eruption or form fissure in the Earths crust, this CO2 can be released