Concept 6.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
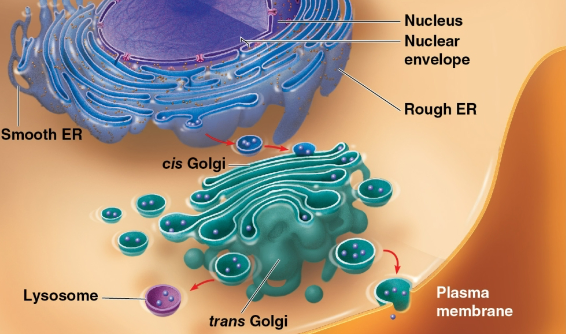
Endomembrane system
System that consists of the:
Nuclear envelope
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
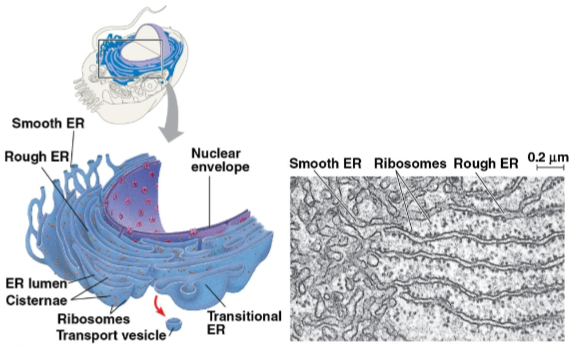
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Organelle that accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
Continuous with the nuclear envelope
Divided into smooth and rough ER based on ribosomal presence
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)
Endoplasmic reticulum section that
does not have ribosomes
synthesizes lipids
detoxifies drugs and poisons
stores calcium ions
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)
Endoplasmic reticulum section that
has bound ribosomes, secreting glycoproteins
distributes transport vesicles
creates membrane for the cell
Transport vesicles
Secretory proteins surrounded by membranes
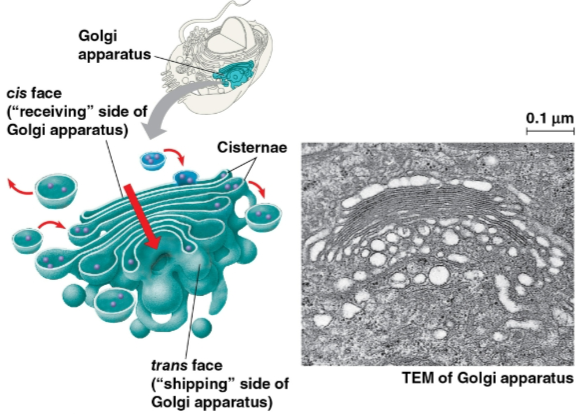
Golgi apparatus
Flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
modifies products of the endoplasmic reticulum
makes certain molecules
sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
Lysosome
A membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest (break down) macromolecules
Has an acidic environment to support lysosomal enzymes
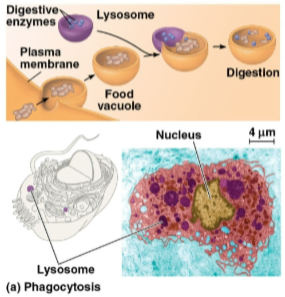
Phagocytosis
Engulfing another cell for food, creating a food vacuole that is digested by lysosomes
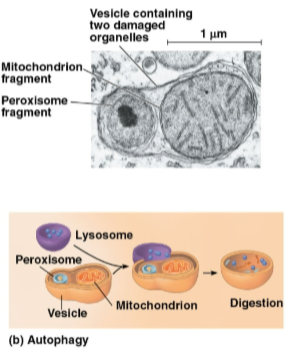
Autophagy
The process in which lysosomes recycle the cell’s own organelles and macromolecules
Vacuoles
Large vesicles derived from the ER and Golgi apparatus
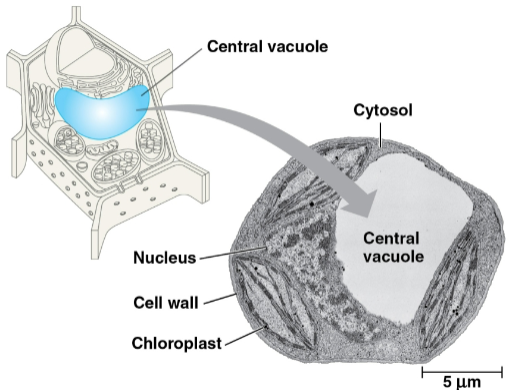
Central vacuoles
Vacuoles found in mature plant cells that contain a solution called sap
Serves as the plant cell’s main repository of inorganic ions, including potassium and chloride