BIO311D LO1-LO4
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Typical human cells, e.g., normal skin cells, have ______ chromosomes.
46
Typical human cells, e.g., normal skin cells, have ______ pairs of chromosomes.
23
Typical human cells, e.g., normal skin cells, have ______ pairs of homologous chromosomes.
23
Typical human cells, if normal, have ______ chromosomes during anaphase in mitosis.
[Don't guess the number, draw what happens in the anaphase in mitosis to answer the question]
92
How do the two members of a pair of homologous chromosomes typically differ from each other?
the precise sequence of the DNA within each of the chromosomes
In most cases, an animal with a diploid number of 2n = 24 chromosomes will have chromosomes in its gametes and chromosomes in its somatic (body) cells.
12; 24
Homologous pairs of chromosomes:
Consist of two chromosomes the same size and with the same genes
Are found in diploid cells
Are found in somatic cells
Are found in zygotes
don't separate during mitosis.
Separate in meiosis I
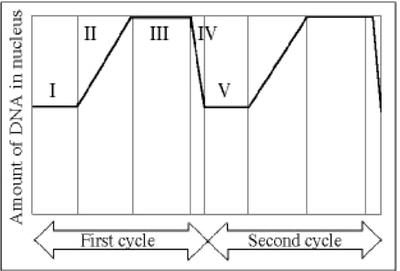
This question tests your understanding of the change in DNA amount along the cell cycle.
Read the graph (both x and y axes) , then answer the question: which letter(s) represents the S phase, and which letter(s) represents the metaphase?
II represents the S phase, and III represents the metaphase.
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves:
formation of a cleavage furrow.
contraction of a ring of actin microfilaments.
Suppose that a cell has 12 chromatids at the prophase of mitosis. Is this cell before or after DNA replication (DNA synthase)? What does each chromatid/chromosome look like?
After DNA replication, there are two sister chromatids (identical copies) per chromosome attached by cohesin proteins in the centromere region. Each chromosome shows a X shape.
Suppose that a cell has 12 chromatids at the prophase of mitosis. How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are there?
3
Suppose that a cell has 12 chromatids at the prophase of mitosis. After mitosis and cytokinesis end, the two resulting daughter cells should have how many chromosomes each?
6
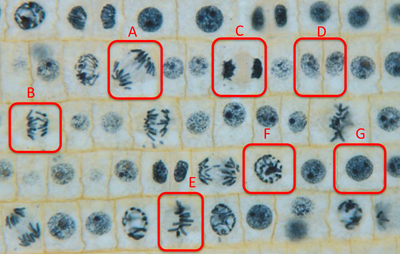
Identify the phase of mitosis. Select all that apply.
Both A and B are in anaphase.
G is in interphase, F is in prophase
Both D and G are in interphase.
D shows two daughter cells are in interphase.
E is in metaphase.
C is in telophase.
Which of the following processes typically occur during the prophase of mitosis in animal cells?
nucleoli disintegrate
nuclear membrane divides into many small vesicles
kinetochore microtubules connect to chromosome kinetochores
chromatin of the chromosomes condenses
a system of microtubules organizes between the two poles of the cell
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. Each cell has ______ chromatids during prophase I.
120
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. Each cell has ______ chromatids during prophase II.
60
Which of the following statements are FALSE?
During meiosis II, paired homologous chromosomes move up to the equator of the cell.
In meiosis II, ploidy is reduced.
During anaphase I, sister chromatids separate.
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. Each cell has ______ chromosomes during prophase II .
30
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
Each diploid cell has eight homologous pairs.
Homologous pairs of chromosomes:
[Select all 7 correct answers.]
Separate in meiosis I
don't separate during mitosis.
don't pair up during mitosis.
Are found in diploid cells
Consist of two chromosomes the same size and with the same genes
pair up in prophase I
separate in anaphase I
Typical human cells, if normal, have ______ chromosomes during anaphase in mitosis.
92
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. The gamete has ______ pairs of homologous chromosomes after meiosis.
0
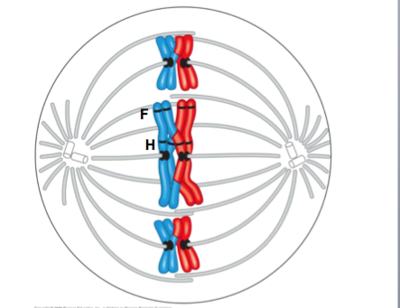
Which of the following accurately describes the organism from which the cell was isolated?
n = 3
2n = 6
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. Each cell has ______ chromosomes during S phase.
60
This chromosome has two chromatids, joined at the centromere. What process led to the formation of the two chromatids?
The two chromatids were formed by duplication of a chromosome.
Which are the sources of genetic variety in sexually reproducing species?
crossing over
fertilization
independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis I
A few cichlid species are 2n=60. The gamete has ______ chromosomes after meiosis.
30
Gametes differ from body cells in
having only one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes.
being haploid.
having half the amount of genetic material.
In goats, a recessive gene causes the goats to "faint" when they are startled. A farmer breeds two goats. What parent genotypes are needed to result in 100% fainting goat offspring?
aa X aa
All of the following combinations are possible in the gametes of an organism that is AaBb EXCEPT
aa
In pea plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers.
If out of 100 offspring 74 are purple-flowered and 26 are white, what were the probable genotypes AND phenotypes of the parents?
Both parents are purple with Aa
Monohybrid cross
When Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants, all the offspring were yellow seeded. When he took these F1 yellow-seeded plants and crossed them to green-seeded plants, what genotypic ratio was expected?
1:1
In humans, one form of polydactyly (extra fingers and toes) is controlled by a single autosomal gene with two possible alleles; the dominant allele leads to polydactyly, the recessive is for the normal number of fingers and toes. A woman with this form of polydactyly whose extra digits were removed when she was a baby mates with a man who also has this form of polydactyly and who also had his extra digits removed when he was a baby. Their first child is born with the normal number of fingers and toes.
What are the odds that their second child will also be born with the normal number of fingers and toes?
1/4
In a dihybrid cross, SsYy x SsYy, what fraction of the offspring will be homozygous for both traits?
1/4
In peas, the allele for tall (T) is dominant over short (t), and the unlinked gene for seed color has the allele for yellow seeds (G) dominant over green seeds (g). What is the predicted phenotypic ratio for offspring from this cross: Ttgg x ttGG
1 tall, yellow: 1 short, yellow
In summer squash, white fruit color (W) is dominant over yellow fruit color (w) and disk-shaped fruit (D) is dominant over sphere-shaped fruit (d).. If a homyzygous squash plant with white, sphere-shaped fruit is crossed with a heterozygous plant with white, disk-shaped fruit, what will the phenotypic ratios for the offspring?
All are white fruits
Half are disk-shaped
Yellow fruit and dwarf vines are recessive traits in tomatoes. Red fruit and tall vines are dominant. cross a dwarf and homozygous red plant with a yellow and heterozygous tall plant. What percent of the offspring will be totally heterozygous?
50%
In cats, the allele (B) produces black color but (b) produces a yellow color. These alleles are incompletely dominant to each other. A heterozygote produces a tortoise shell color. The alleles (B) and (b) are sex-linked as well. Cross a tortoise shell female with a yellow male.
What percent of their offspring will be yellow?
50%
A woman is red-green colorblind, and she mates with a man who has normal color vision. Knowing that red-green colorblindness is controlled by a gene on the X chromosome, what can you predict for their children with regard to inheritance of color vision?
all of the boys and none of the girls will be colorblind.
A woman with normal color vision, but whose father is red-green colorblind, mates with a man who is red-green colorblind. Knowing that red-green colorblindness is controlled by a gene on the X chromosome, what can you predict for their children with regard to inheritance of color vision?
half of the boys and half of the girls will be colorblind.
If one of your parents is blood type A and the other is type AB, which of the following blood types would you NOT be?
O
In a rodent species from an island in the south Atlantic there are three different coat colors found in the population. Studies show that two genes (each with two alleles) determine the coat color in this species, and a dihybrid cross produces offspring with the coat colors in a 9:3:4 ratio. This is an example of _____.
epistasis
You test cross heterozygous purple-flowered, long-pollened pea plant with homozygous recessive plant, and get mostly purple-flowered short-pollened plants and white-flowered long-pollened plants, with a very few purple-flowered, long-pollened or white-flowered, short-pollened plants.
What is the most likely explanation?
The genes are linked.
A round seeded plant (R) is dominant to a wrinkled seeded plant (r). What parental genotypes will produce offspring that are 50% homozygous dominant and 50% heterozygous?
Rr X RR
A tall plant of unknown genotype is test-crossed (meaning it is crossed with a recessive tt plant). Of the offspring, 869 are dwarf and 912 are tall. What is the genotype of the unknown parent?
Tt
In guinnea pigs, black eyes are dominant to red eyes. If out of 100 offspring 52 have red eyes and 48 have black eyes, what are the probable genotypes AND phenotypes of the parents?
Aa X aa, one heterzygous black, the other is homozygous red
In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers.
If out of 100 offspring 74 are purple flowered and 26 are white, what were the probable genotypes AND phenotypes of the parents?
Both parents are purple with Aa

In rabbits, gray hair is dominant to white hair. Also in rabbits, black eyes are dominant to red eyes. These letters represent the genotypes of the rabbits: A male rabbit with the genotype GGbb is crossed with a female rabbit with the genotype ggBb. What are the phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
1 gray hair black eyes : 1 gray hair red eyes
In peas, the allele for tall (T) is dominant over short (t), and the unlinked gene for seed color has the allele for yellow seeds (G) dominant over green seeds (g). What is the predicted phenotypic ratio for offspring from this cross: Ttgg x TtGg
3 tall, yellow: 3 tall, green: 1 short, yellow: 1 short, green
Yellow fruit and dwarf vines are recessive traits in tomatoes. Red fruit and tall vines are dominant. cross a completely dominant red and tall plant crossed with a heterozygous red and dwarf plant.
What percent of the offspring will have yellow fruit and dwarf vines?
0%
In humans, one form of polydactyly (extra fingers and toes) is controlled by a single autosomal gene with two possible alleles; the dominant allele leads to polydactyly, the recessive is for the normal number of fingers and toes. A woman with this form of polydactyly whose extra digits were removed when she was a baby mates with a man who also has this form of polydactyly and who also had his extra digits removed when he was a baby. Their first child is born with the normal number of fingers and toes.
What are the odds that their second child will also be born with the normal number of fingers and toes?
1/4
Mendelian Genetics – Friedreich’s Ataxia
Kate and John, who are both healthy, are having their first baby. A karyotype (a picture of the chromosomes) reveals that the both of the child’s 9th chromosomes have a defect in their structure that causes Friedreich’s Ataxia (FA), an autosomal recessive disease that leads to severe neurological symptoms generally by age 15.
Which of the following chromosomes must also have the defect?
Only one of Kate's chromosomes
Only one of John's chromosomes
One chromosome from either Kate's mom or Kate's dad
One chromosome from either John's mom or John's dad
A woman is red-green colorblind, and she mates with a man who has normal color vision. Knowing that red-green colorblindness is controlled by a gene on the X chromosome, what can you predict for their children with regard to inheritance of color vision?
all of the boys and none of the girls will be colorblind.
Recall that the gene for red or white eye color in fruit flies is X-linked, with the white color allele recessive. You examine a vial of 100 flies that are all offspring from a single genetic cross. In the vial you find that all females are red-eyed, while the males are about half red-eyed and half white-eyed. The genotypes of the parents were: _____________
XRXr ; XRY
Which of the following statements is true regarding the ABO blood system?
People who have the A antigen normally would not produce the anti-A antibody
When columbines with lavender flowers are mated they produce offspring that make either dark purple, lavender, or white flowers. The ratio is 1 dark purple: 2 lavender: 1 white. This is an example of what kind of non-Mendelian inheritance pattern?
codominance or incomplete dominance
In cats, the allele (B) produces black color but (b) produces a yellow color. These alleles are incompletely dominant to each other. A heterozygote produces a tortoise shell color. The alleles (B) and (b) are sex-linked as well. Cross a tortoise shell female with a yellow male.
What percent of their offspring will be tortoise shell?
¼ offspring
half females
None males can be tortoise
If Mendel's crosses between tall, spherical-seeded plants and short, dented-seeded plants had produced many more than 1/16 short, dented-seeded plants in the F2 generation, he might have concluded that
the spherical seed and tall traits are linked
Mendel's second law of independent assortment has its basis in which of the following events of meiosis I?
alignment of tetrads at the equator
In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. What parental genotypes would produce offspring that are all heterozygous for the purple trait?
AA X aa
In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers.
If out of 100 offspring 74 are purple flowered and 26 are white, what were the probable genotypes AND phenotypes of the parents?
Both parents are purple with Aa
In goats, a recessive gene causes the goats to "faint" when they are startled. A farmer breeds two goats. What parent genotypes are needed to result in 100% fainting goat offspring?
aa X aa
An aquatic arthropod called a Cyclops has antennae that are either smooth or barbed. The allele for barbs (B) is dominant over smooth (bb). In the same organism Non‐resistance to pesticides (N) is dominant over resistance to pesticides (nn). A Cyclops that is resistant to pesticides and has smooth antennae is crossed with one that is heterozygous for both traits.
What are the phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
1:1:1:1
One gene determines red vs. white flowers in pea plants, and another determines axial vs. terminal flowers. Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F1 individuals have red, axial flowers. If you perform a cross between two of these F1 individuals, approximately what fraction of the offspring should have red, terminal flowers? (Assume independent assortment).
3/16
You test cross heterozygous purple-flowered, long-pollened pea plant with homozygous recessive plant, and get mostly purple-flowered short-pollened plants and white-flowered long-pollened plants, with a very few purple-flowered, long-pollened or white-flowered, short-pollened plants.
What is the most likely explanation?
The genes are linked.
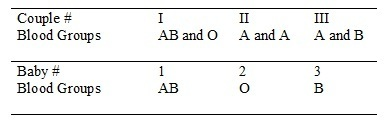
Three babies were mixed up in a hospital. After consideration of the data below, which of the following represent the correct baby and parent combinations?
I-3, II-2, III-1
Sex-linked inheritance
In humans, hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait. If a female who is a carrier for hemophilia marries a male with normal blood clotting, answer the following questions. What fraction of the male children will have hemophilia?
50%
Varieties of Staphylococcus aureus that are resistant to the drug methicillin __________.
already existed in the population before methicillin was developed
Increased in prevalence in response to the use of methicillin
were strongly selected for as methicillin became widely used to treat bacterial infections
do not have an advantage in the absence of methicillin
Which of the following must exist in a population before natural selection can act upon that population?
genetic variation among individuals
Which of the following are examples of analogous structures?
Embryos of fish and birds both make gill slits.
The wings of birds, bats and butterflies.
Natural selection is based on all of the following except
individuals adapt to their environments and thereby evolve.
Which of the following are examples of homologous structures?
[Choose three correct answers]
Rabbits and birds have the same bones in the same order in their forelimbs, even though they use them for different purposes.
The bones of tetrapods
The wings of bats and the arms of primates.
Evolution is best defined as which of the following?
a change in genetic composition of a population from generation to generation
Analogous features share ________ function but not ________ ancestry.
similar; common
Darwin surmised that a few finches migrated to the Galapagos from the mainland. These finches gave rise to the many species of finches on the islands today. This is an example of:
adaptive radiation
A new organism is discovered in the forests of Costa Rica. Scientists there determine that the polypeptide sequence of hemoglobin from the new organism has 72 amino acid differences from humans, 65 differences from a gibbon, 49 differences from a rat, and 5 differences from a frog. These data suggest that the new organism
is more closely related to frogs than to humans.
Traditionally, human males with the genetic disease hemophilia often died before they reached reproductive age. If modern medical treatment allows most hemophiliacs to lead long and fruitful lives, what will happen to the frequency of the allele responsible for hemophilia?
It should increase in frequency.
Over time, the movement of people on Earth has steadily increased. This has altered the course of human evolution by increasing
gene flow
The fact that South and Central American Indians are nearly 100% type O for the ABO blood system is best explained as being the result of:
The founder principle
A mutation that is neither harmful nor beneficial is termed a
silent mutation
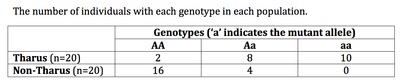
Malaria Resistance and Hardy-Weinberg
The Terai region of southern Nepal is known for high rates of malaria, a disease caused by a parasite transmitted by mosquitos. The parasite causes severe anemia by infecting red blood cells. Two groups of people live in Terai: the Tharus people who are native to the region, and non-Tharus people who have migrated to the region in the last several decades. Native Tharus people have a significantly lower rate of malarial infection than the non-native people living in Terai.
To test the genetic hypothesis, scientists gathered blood samples from Tharus and non-Tharus people and analyzed their alpha-thalassemia genes. Mutations in the alpha-thalassemia gene have been linked to malarial resistance in other populations around the globe. The following table shows their findings.
Given these results, what is the frequency of the mutant allele in the Tharus people?
0.7
In a population of woolybeasts, individuals with long snouts tend to survive better on an island that has burrowing termites. Over time, the woolybeast population consists of individuals with extremely long snouts. This is an example of:
directional selection
Mountains also have an unmatched power to drive human evolution. Starting tens of thousands of years ago, people moved to high altitudes, and there they experienced natural selection that has reworked their biology. In Tibet, for example, people have broader arteries and capillaries. In the Andes, they can dissolve more oxygen into their blood. These different traits of people who live in high altitudes illustrate
adaptive evolution
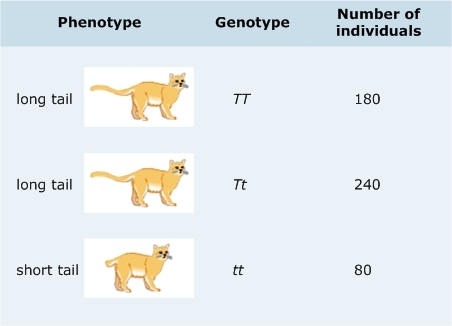
A hypothetical population of 500 cats has two alleles, T and t, for a gene that codes for tail length. (T is completely dominant to t.) The table below presents the phenotype of cats with each possible genotype, as well as the number of individuals in the population with each genotype. Assume that this population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Recall that the Hardy-Weinberg equation is
p 2 + 2pq +q 2 = 1
Use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to predict the frequency of heterozygous cats in the next generation.
0.48
You are maintaining a small population of fruit flies in the laboratory by transferring the flies to a new culture bottle after each generation. After several generations, you notice the viability of the flies has decreased greatly. Recognizing that small population size is likely to be linked to decreased viability, the best way to reverse this trend is to
cross your flies with flies from another lab.
Female guppies tend to choose brightly colored mates. Over time, the population of guppies becomes more colorful. This is an example of:
sexual selection
How might an evolutionary biologist explain why a species of birds has evolved a larger beak size?
Some members of the ancestral population had larger beaks than others. If larger beak size was advantageous, they would be more likely to survive and reproduce. As such, large beaked birds increased in frequency relative to small beaked birds.
From his observations of organisms in the Galapagos Islands, Darwin reasoned that __________.
organisms had adapted to new environments, giving rise to new species
What is the meaning of Darwin’s expression “descent with modification”?
Descent with modification refers to evolutionary change over time.
An evolutionary adaptation is __________.
a trait that gives an organism a reproductive advantage in the current environment
Which of the following must exist in a population before natural selection can act upon that population?
genetic variation among individuals
How can gene flow improve adaptation of population?
Beneficial alleles are transferred to a new population.
Mountains also have an unmatched power to drive human evolution. Starting tens of thousands of years ago, people moved to high altitudes, and there they experienced natural selection that has reworked their biology. In Tibet, for example, people have broader arteries and capillaries. In the Andes, they can dissolve more oxygen into their blood. These different traits of people who live in high altitudes illustrate
adaptive evolution
Cheetahs nearly became extinct but recovery efforts managed to save them. Now, most cheetahs are genetically identical. This is due to:
the bottleneck effect