Multi-Store Memory Model
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
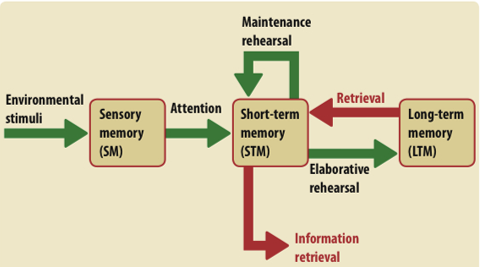
Outline the Multi Store Model of Memory (processes)
proposed by Atkinson and Schiffrin
proposed first model/cognitive explanation as it was previously biological. stores are linked by processing
linear model
stimulus from the environment is registered by the sensory register, which has stores for all the senses
if a certain stimulus has caused attention, it will be moved to the Short Term Memory
through maintenance rehearsal, information in the STM can be kept there for longer
Through prolonged rehearsal, that memory will be transferred to LTM
memories from the LTM can be retrieved to the STM
memories can be forgotten at any point
biologically
sensory information is transported by neurons in the cortex and travels to the hippocampus. transported back to the cortex for permanent storage
Outline the MSM (stores)
Atkinson and Schiffrin
passive stores
proposed first model/cognitive explanation as it was previously biological. stores are linked by processing
Sensory register
coded modality specific
e.g. echoic (auditory), iconic (visual), haptic (tactile), gustatory (taste), olfactory (smell)
capacity is very large - millions of receptors involved
duration- less than half a second
STM
coded acoustically
capacity of 7±2 items
duration of up to 30
LTM
coded semantically
capacity is unlimited, information may be lost through displacement, retrieval failure or interference
duration is unlimited
Case Studies relating to MSM
Patient HM
Scoville
underwent brain surgery to relieve epilepsy and the hippocampus was removed
LTM was severely damaged
he could not transfer any new information to his long term memory but STM was undamaged - anterograde amnesia
Brenda Milner studied him at his home afterwards
managed to remember a number for 15 minutes through repetition but after 5 minutes had forgotten that the test had even taken place
previously believed that memory was monolithic and across the brain
sensory information is transported by neurons in the cortex and travels to the hippocampus. transported back to the cortex for permanent storage - as he didn’t have a hippocampus, his memories couldn’t be consolidated and therefore eroded
Milner also asked him to trace a third star in between the space between to concentric stars whilst looking through a mirror - she found that although he forgot the experiment took place, he improved each time
shows MSM oversimplifies LTM store
KF
Shallice and Warrington
STM for digits was poor for information read out loud but his recall was significantly better when he read the information himself
suggests MSM oversimplifies the STM store
evaluate MSM (limitations)
artificial tasks of supporting evidence may mean that this theory may not apply to everyday life where we have to remember more meaningful information (limitation)
elaborative rehearsal (limitation)
Craik and Watkins believed that elaborative information is needed to transfer information from the STM to LTM - linking this information to information already in the LTM as opposed to repeating that information
alternative explanations (limitation)
WMM and types of long term memory accomadate for the oversimplification of the MSM
evaluate MSM (strengths)
Glanzer and Cunitz (strength)
primacy recency effect
recall is stronger for words at the beginning and end of lists as opposed to the middle
suggests there are separate stores for STM and LTM, primacy being the LTM and recency STM - middle words were in the STM but displaced by later words
supports STM and LTM as explicitly presents STM and LTM as separate
Sperling (Strength)
ppts were presented with 12 letters for 1/20th of a second
had to recall one row
recall for the first row was over 75% suggesting the rows were within the capacity of the SR and it is very large
ppts could only recall the first 5 letters, suggesting letters faded from SR before reaching STM further supporting duration of the SR
Wagenaar (strength)
created a diary of over 2400 events over 6 years
found when tested he had 75% recall of one particular critical detail after 1 year and 45% after 5 years
his sense of remembering (retention judgement) was 80% after 5 years
therefore supports idea that LTM is potentially limitless
Bahrick
392 participants aged 17-74
tested for memory of old photographs and names of their school friends
it was found recall in matching names to faces was 90% after 15
8)% after 48 years
suggests LTM’s duration is verly large, potentially limitless