RAD 110 - Ch 15 Trauma, Mobile, & Surgical Radiography - Key Terms
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Members of the Surgical Team
1. Surgeon
2. Certified surgical technologist (CST)
3. Radiologic technologist
4. Scrub (CST or RN)
Scrub
- Prepares and maintains sterile surgical field and instruments
- Gowns members of surgical team
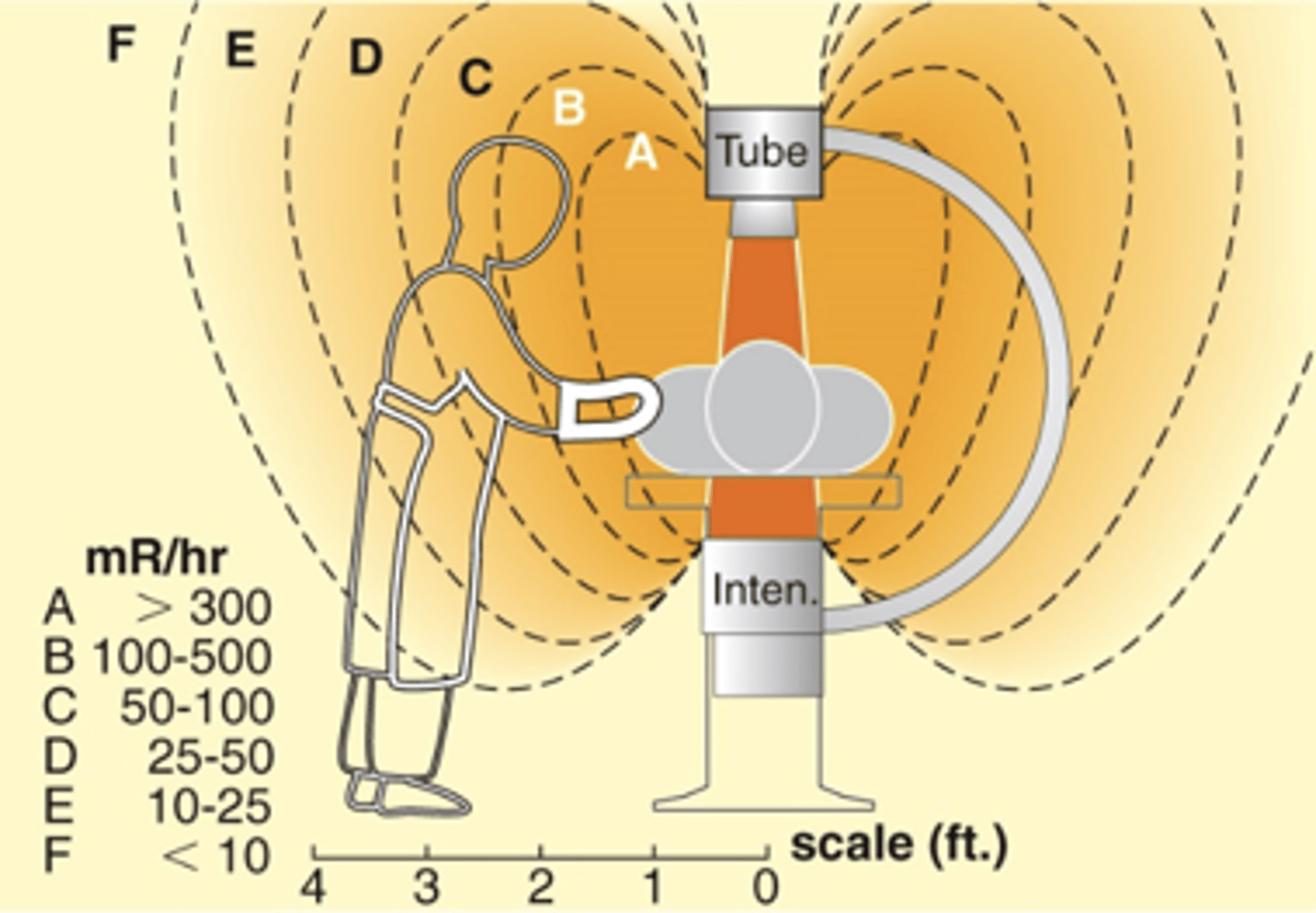
Radiation Protection with C-Arm
- Place x-ray tube under table to reduce head and neck exposure to operator
- Minimize use of boost exposures
- Minimize distance between anatomy and image intensifier
- Provide lead aprons for those remaining in area not behind lead shields
3 Methods of Protecting the Sterile Environment
1. Draping C-arm
2. Draping patient
3. Shower curtain
Technologist's Surgical Attire
- Scrubs
- Shoe covers
- Nonsterile gloves
- Protective apron
- Head cover
- Surgical mask
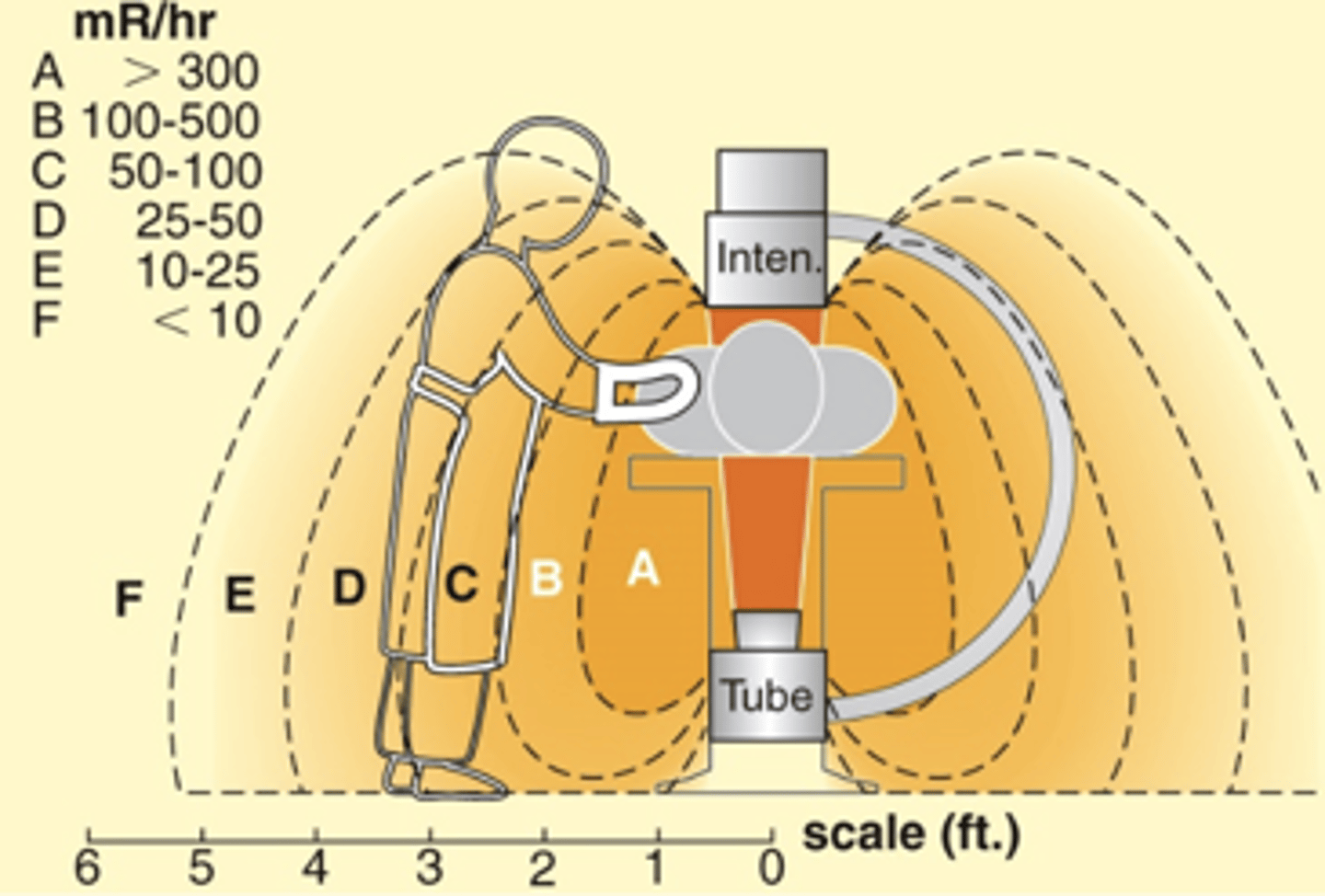
C-Arm Orientation - Vertical PA
- Least exposure to operator
- X-ray tube below
- I.I. above patient
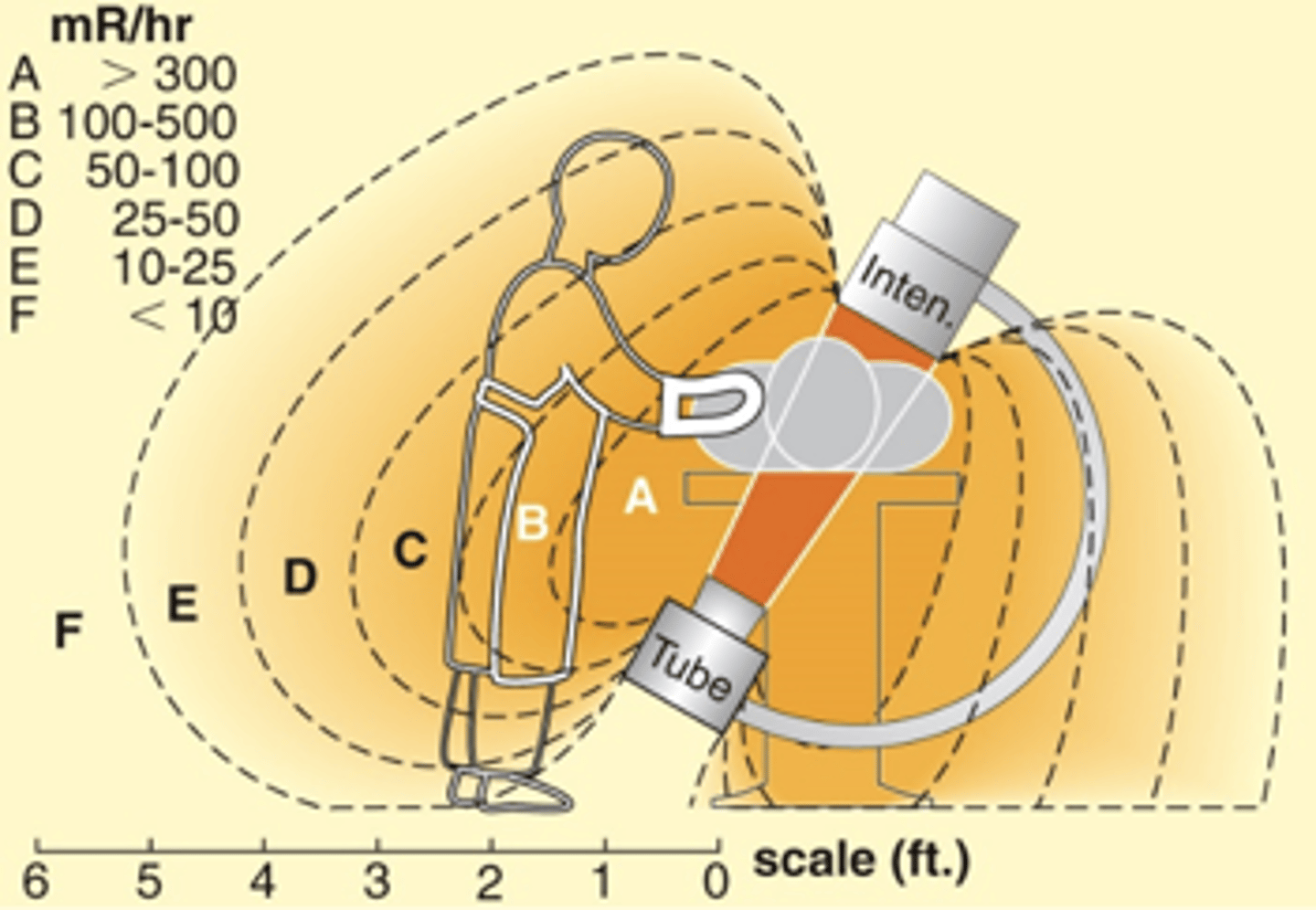
C-Arm Orientation - 30º C-Arm Tilt
- Increased exposure to face and neck by a factor of four
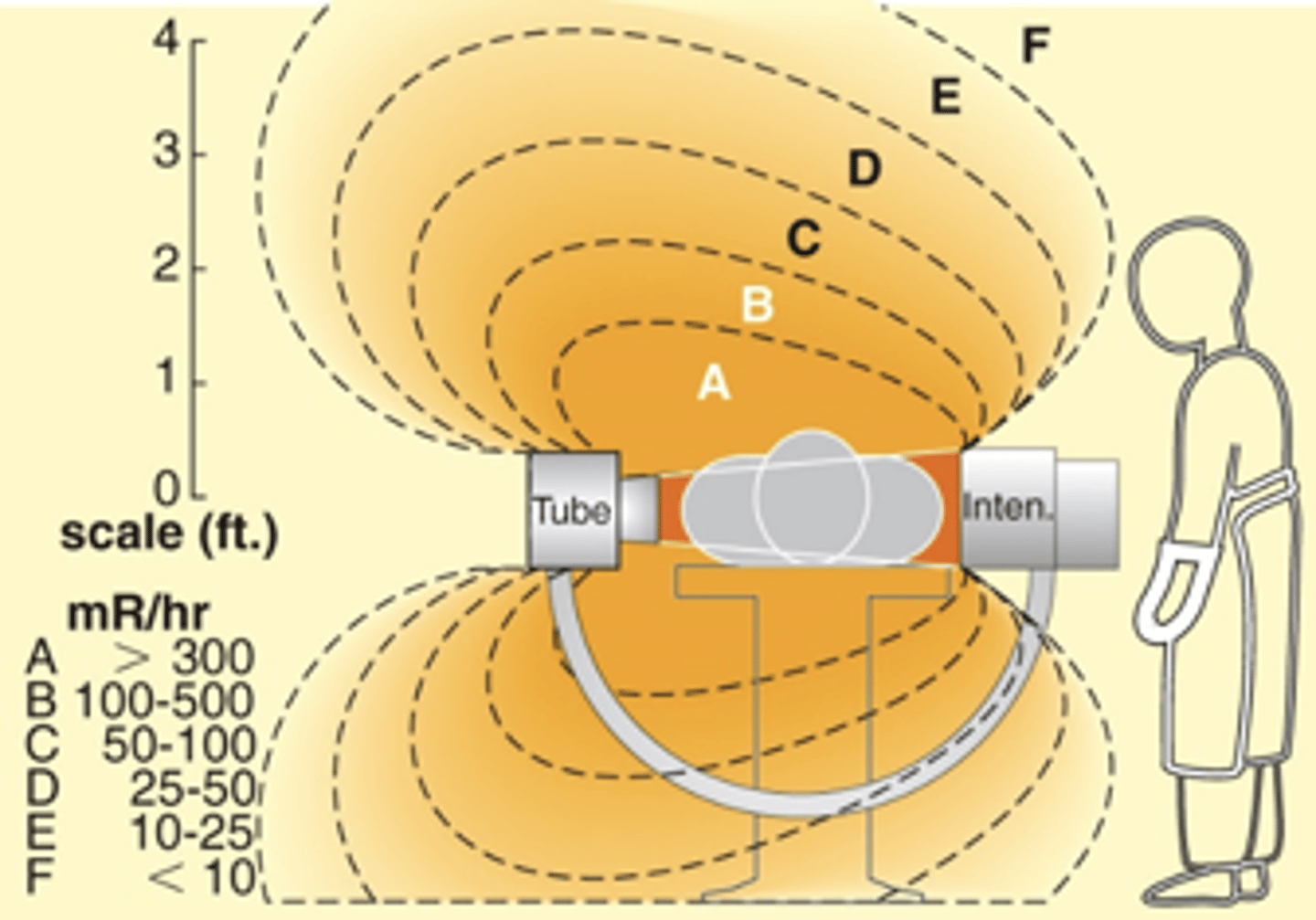
C-Arm Orientation - Horizontal
- Increased exposure at x-ray tube end
C-Arm Orientation - Vertical AP
- Must be avoided, increased exposure to head and neck
Three Cardinal Principles of Radiation Protection
1. Distance
2. Time
3. Shielding
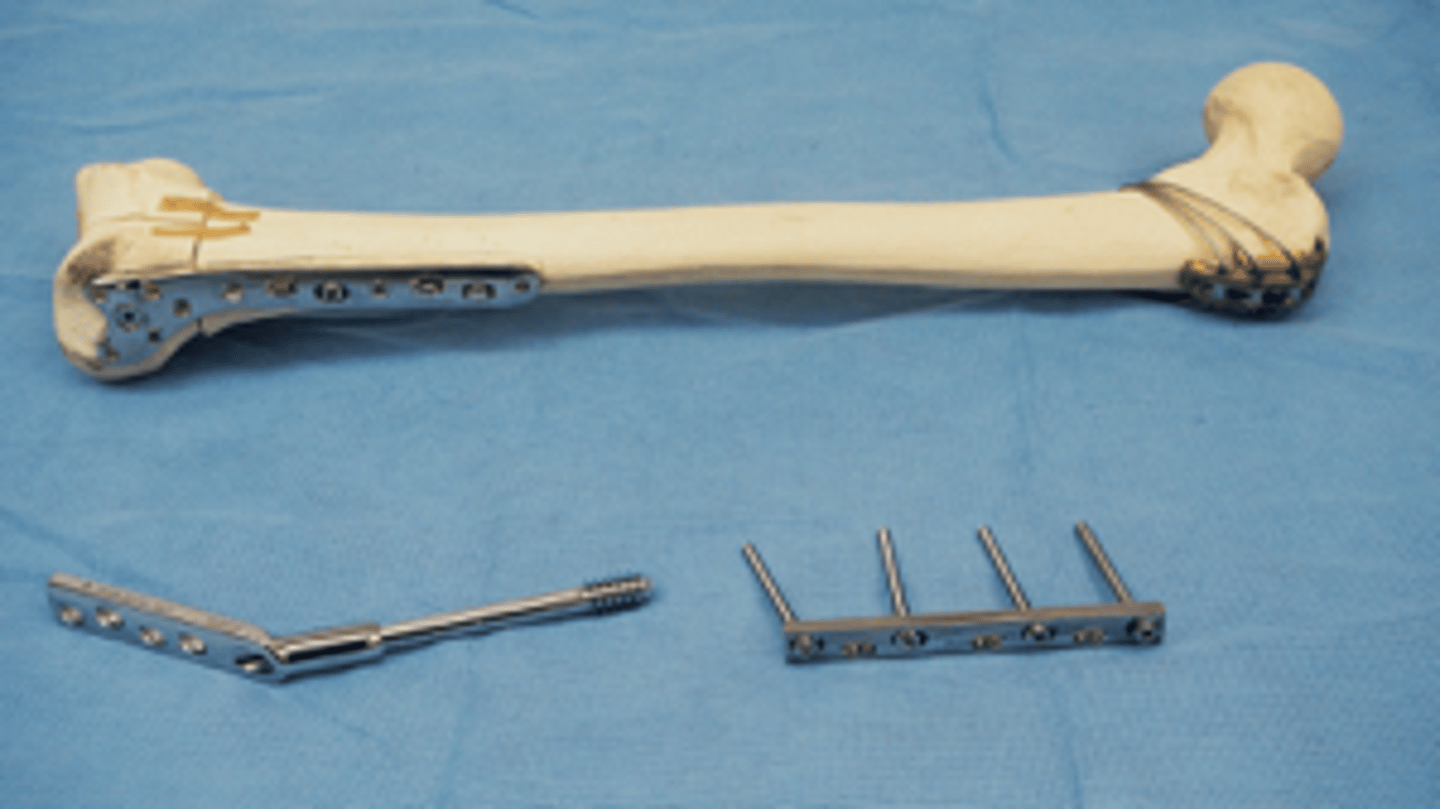
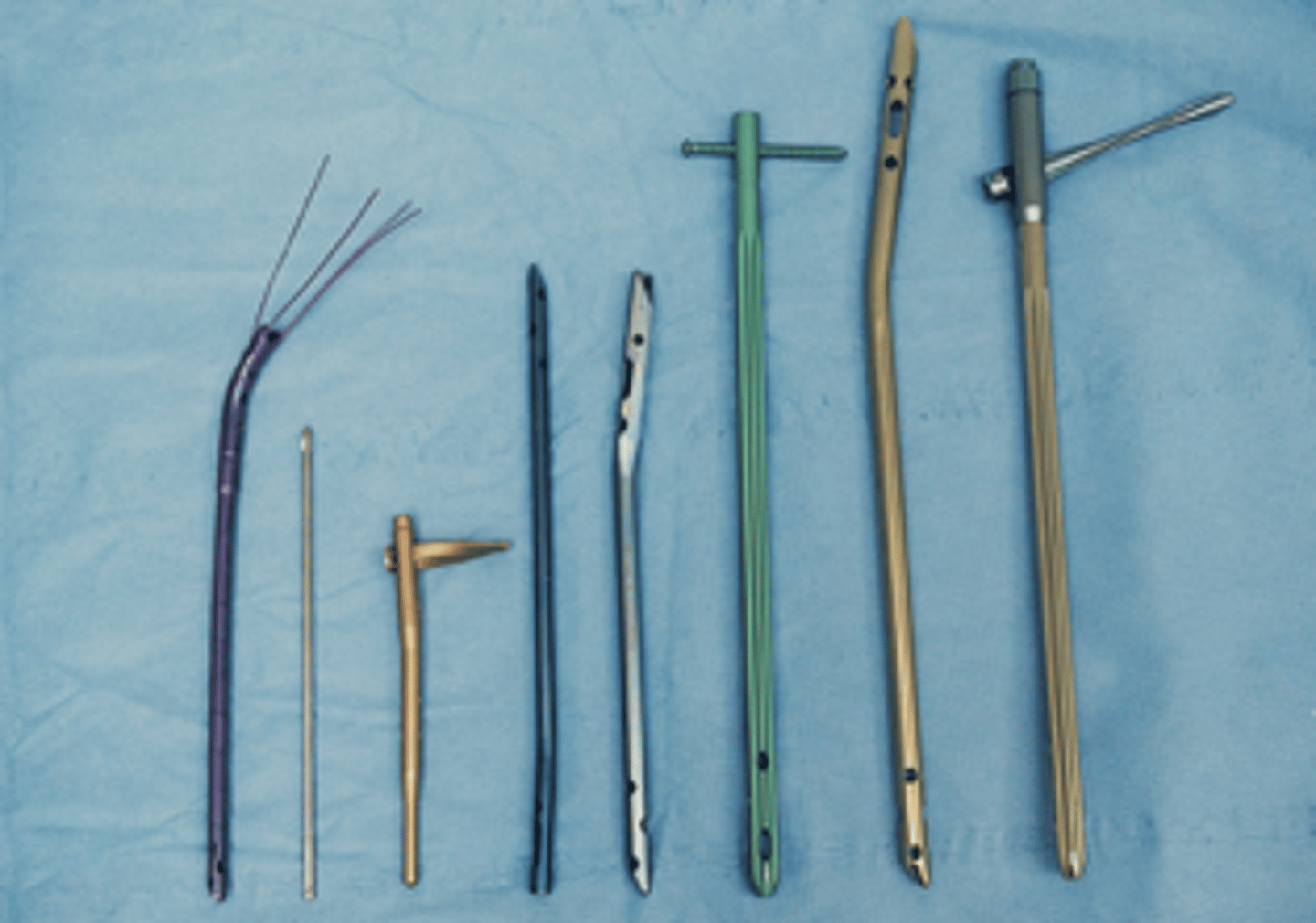
Internal Fixator Devices
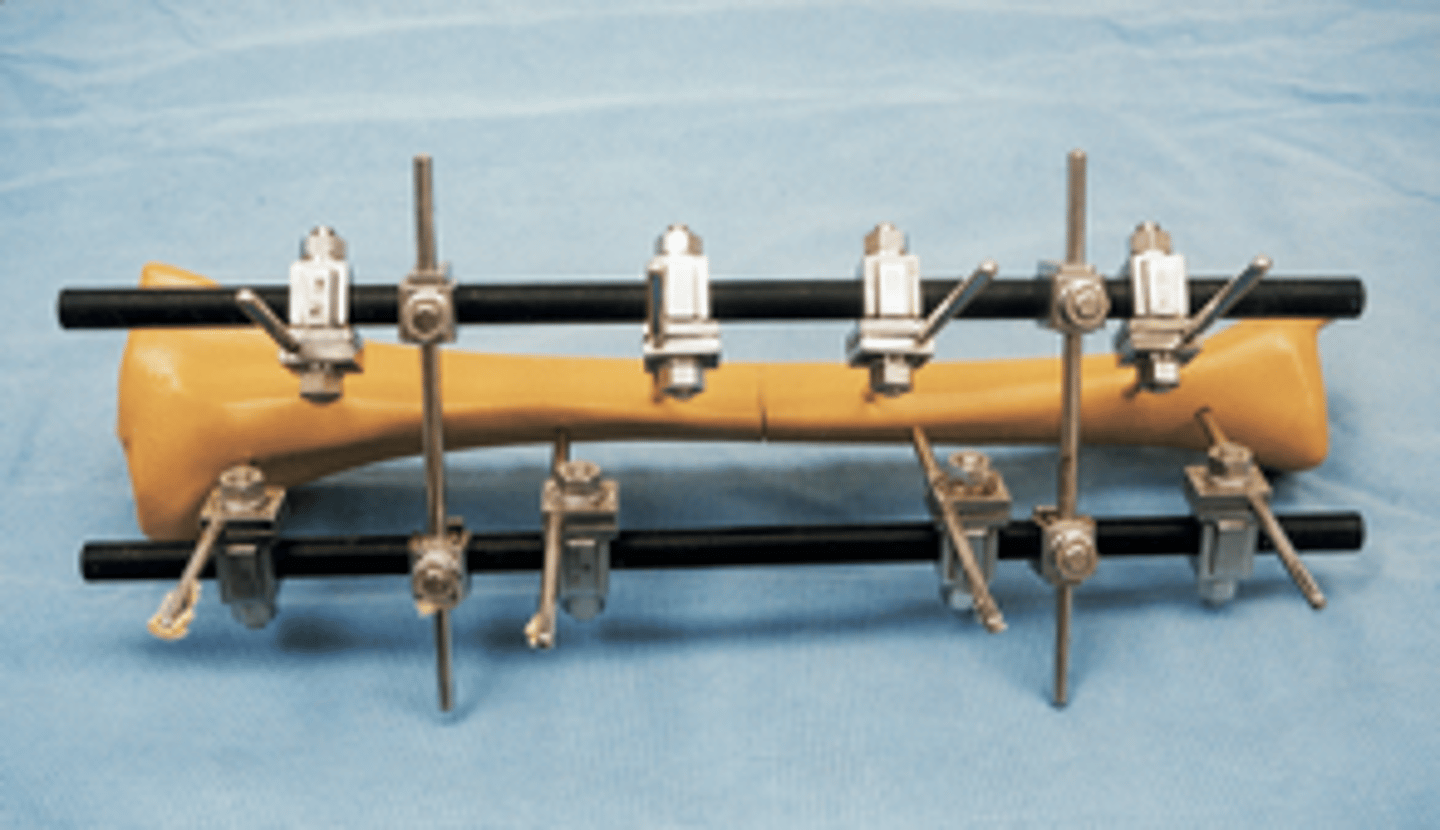
Ilizarov tibial external fixator
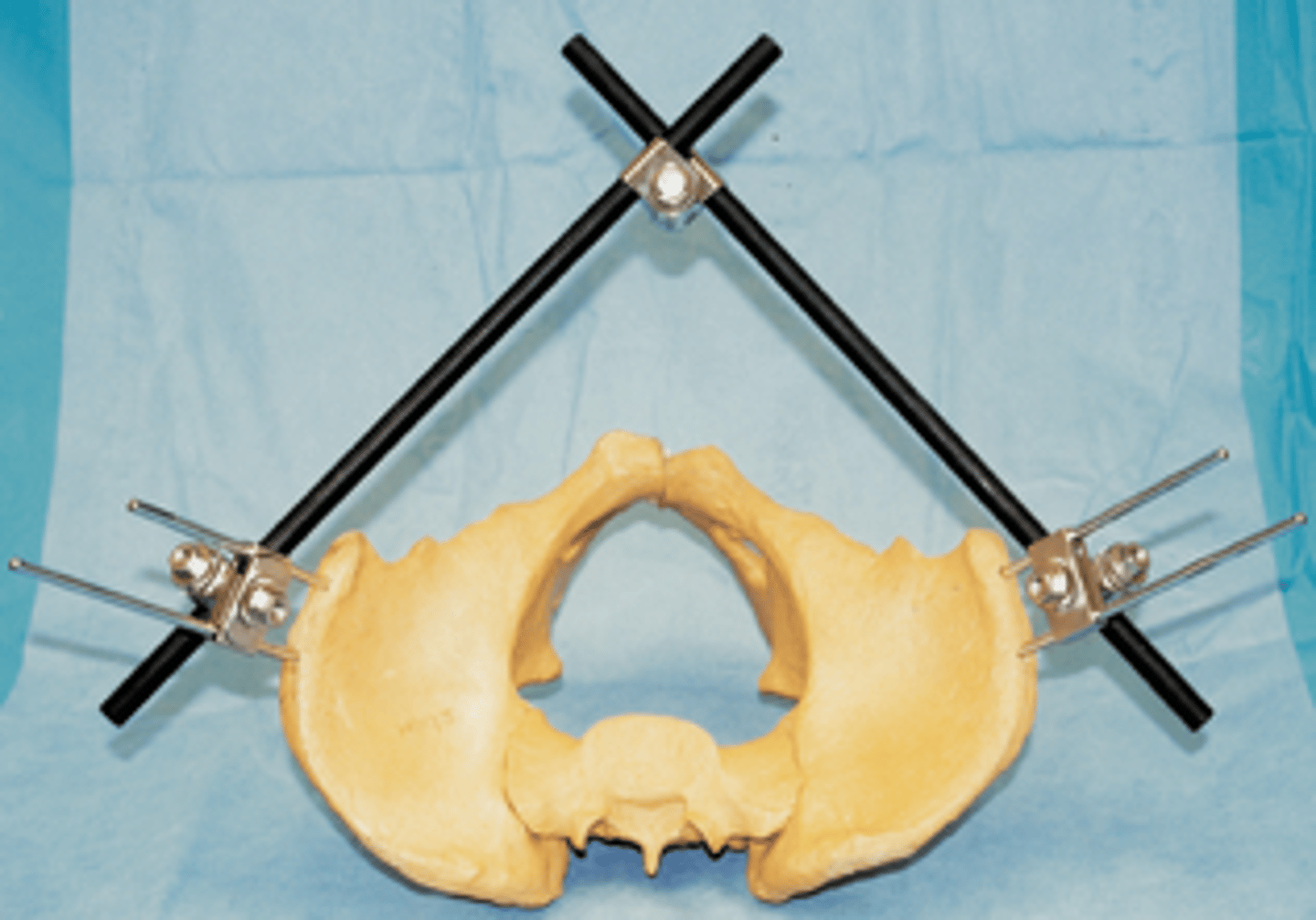
Pelvic external fixator
Intramedullary rods and nails
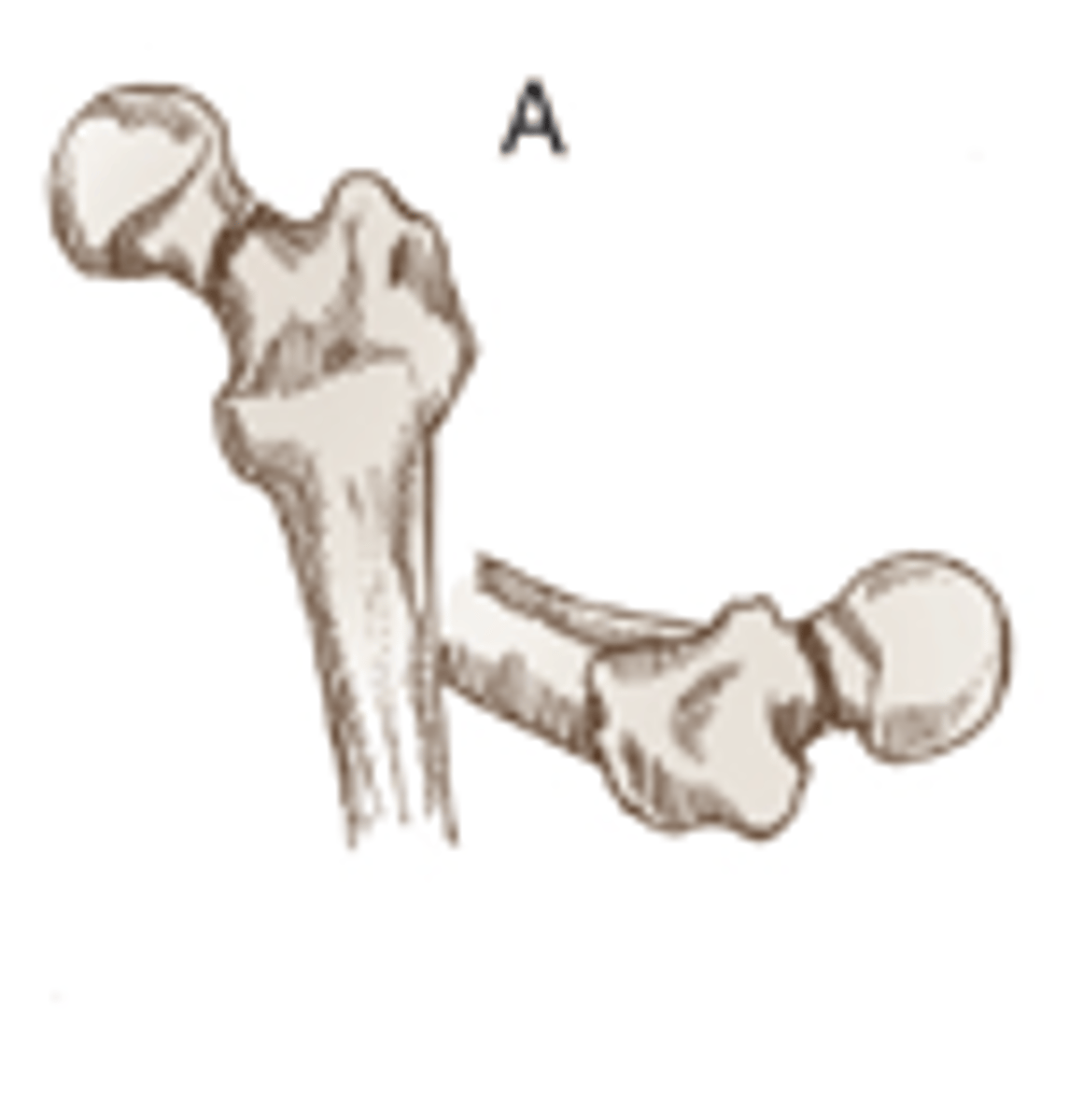
Femoral Neck Fracture
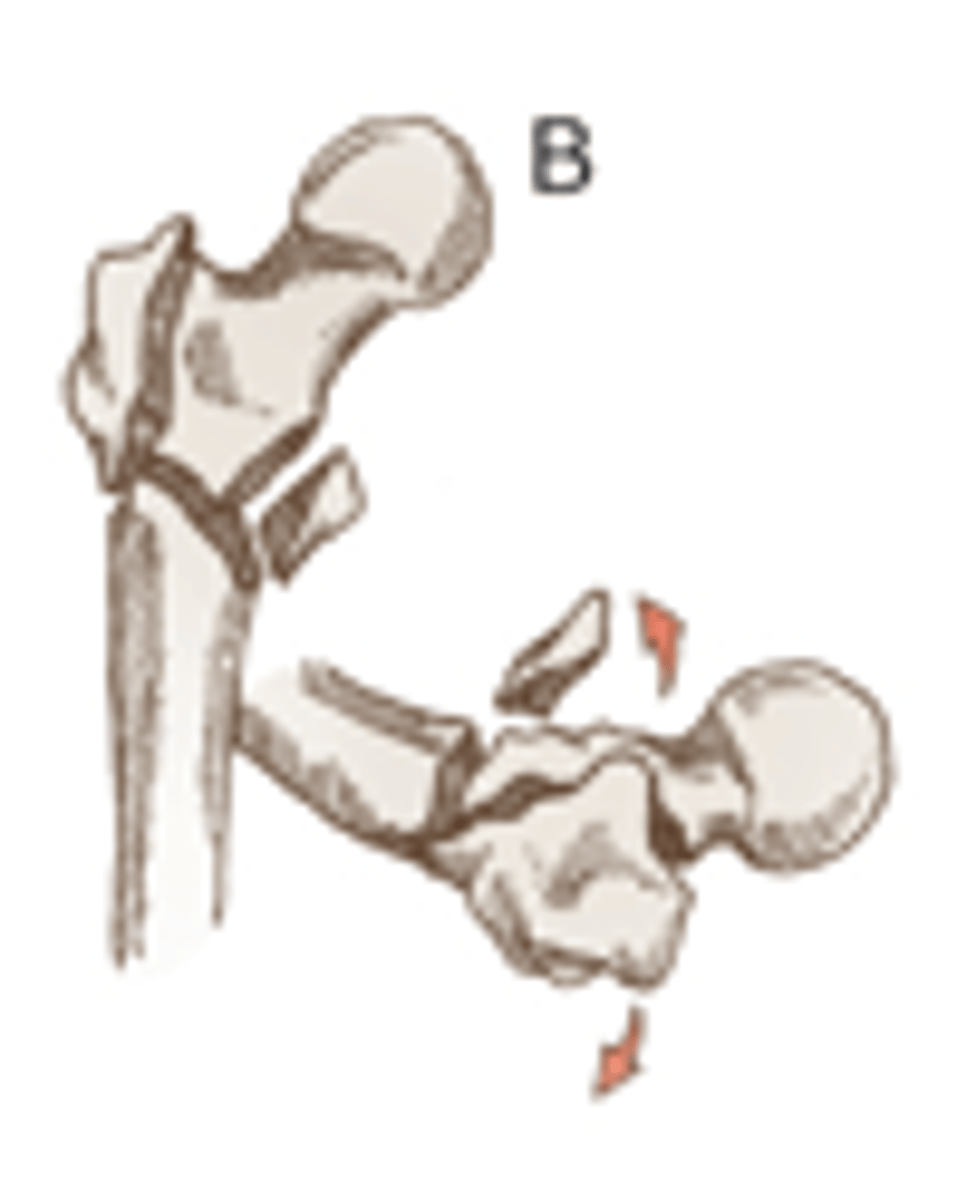
Comminuted subtrochantric fracture
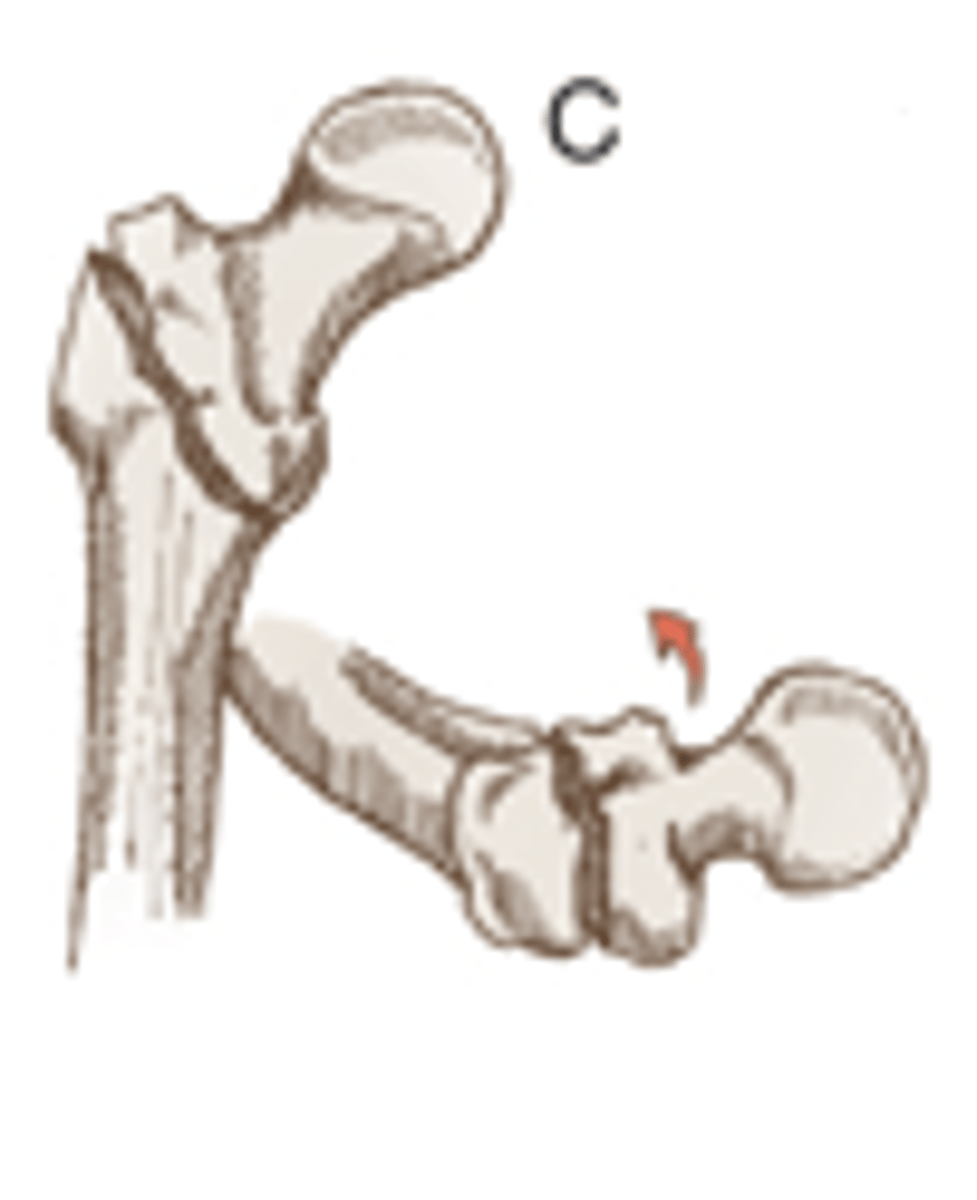
Intertrochanteric Fracture
Sprain
Forced wrenching or twisting of a joint, resulting in partial rupture or tearing of supporting ligaments
Fracture
A break in the bone
Contusion
A "bruise" type injury without a fracture or break in the skin
Apposition
relationship of the long axes of fracture fragments
Types of apposition
1. Anatomic apposition
2. Lack of apposition
3. Bayonet apposition
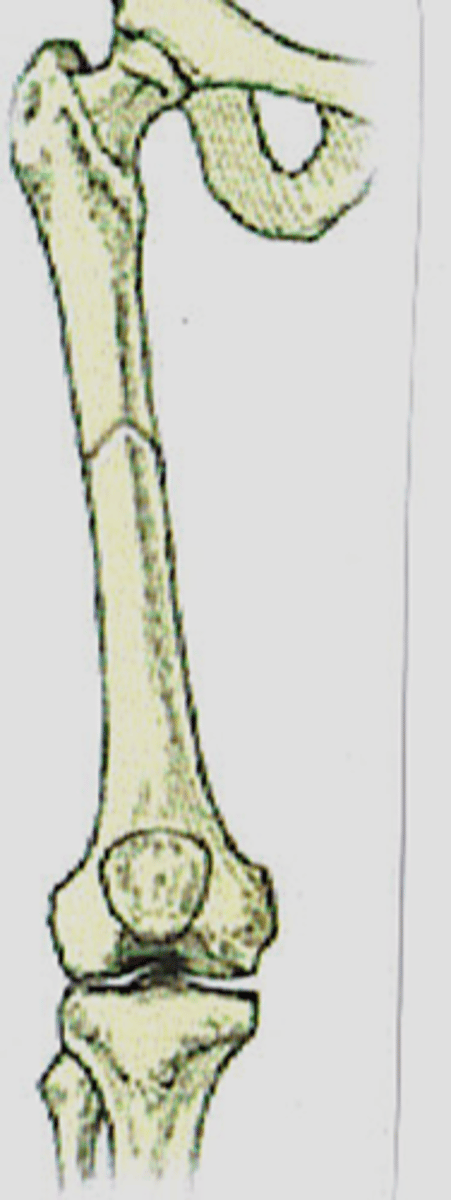
Anatomic apposition
Anatomic alignment of ends of fractured bone fragments, wherein the ends of the fragments make end-to-end contact
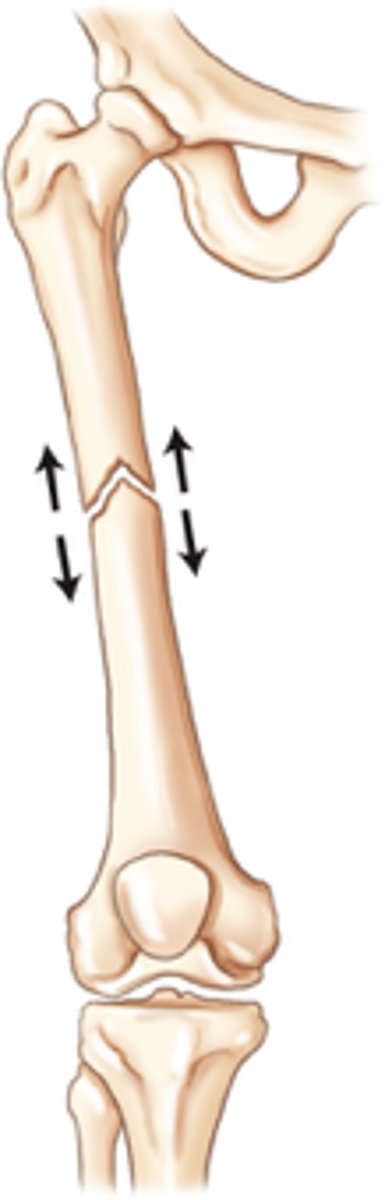
Lack of apposition
the ends of fragments are aligned but pulled apart and are not making contact with each other
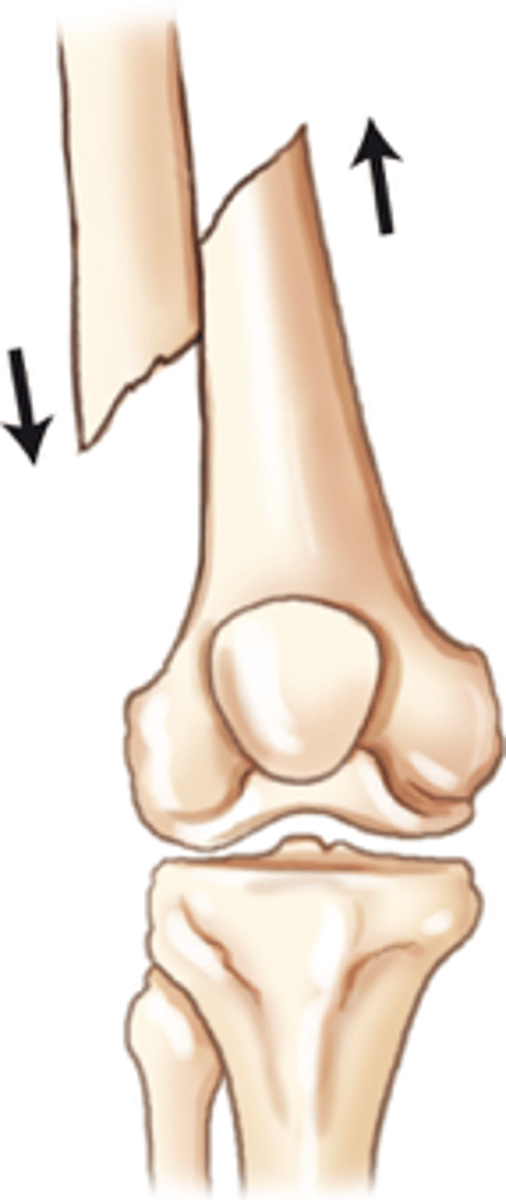
Bayonet apposition
A fracture wherein the fragments overlap and the shafts make contact, but not at the fracture ends
Angulation
loss of alignment
Apex angulation
Describes the direction or angle of the apex of the fracture, such as medial or lateral apex, wherein the point or apex of the fracture points medially or laterally
Types of Apex Angulation
1. Varus angulation
2. Valgus angulation
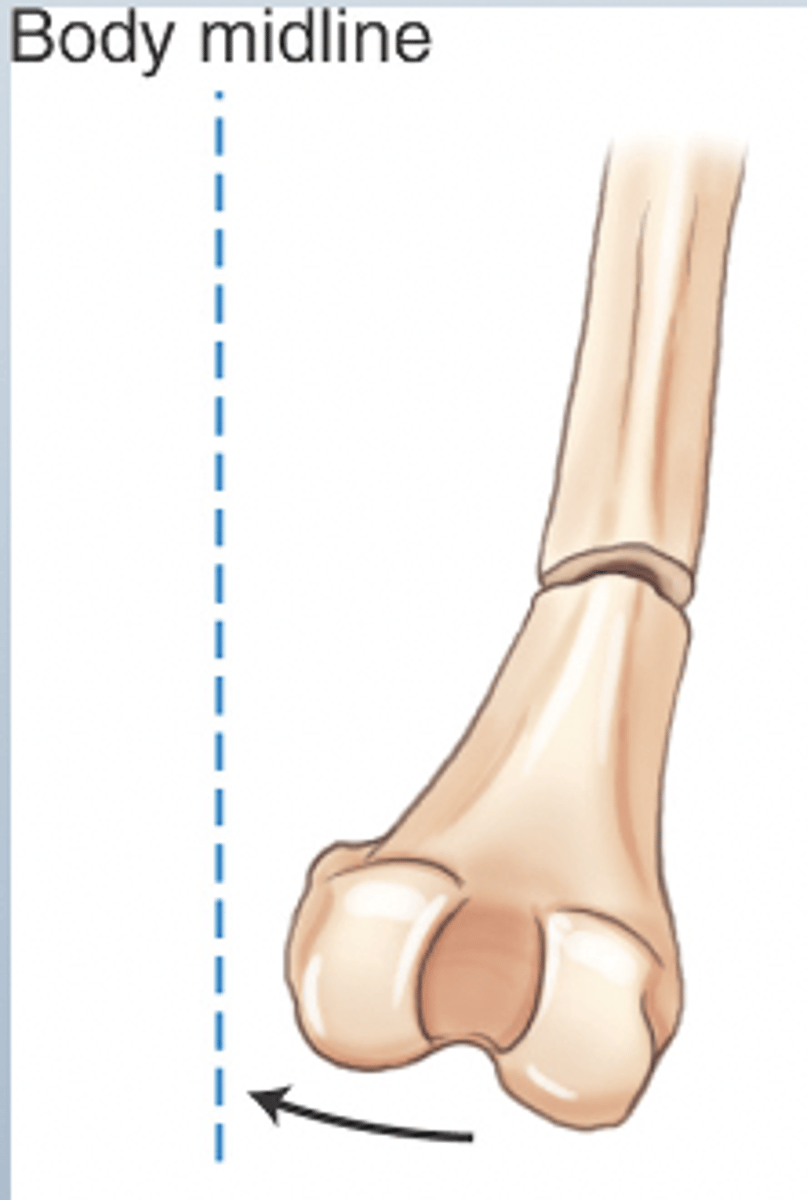
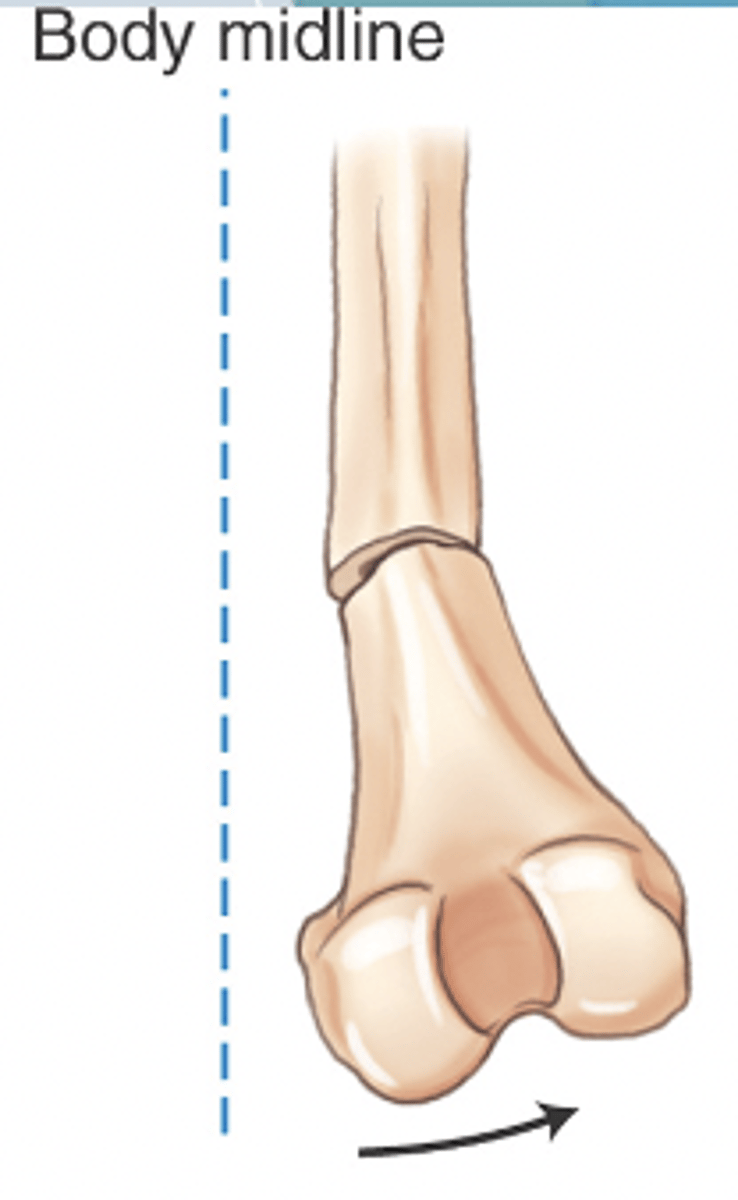
varus angulation
deviating toward midline
valgus angulation
deviating away from midline
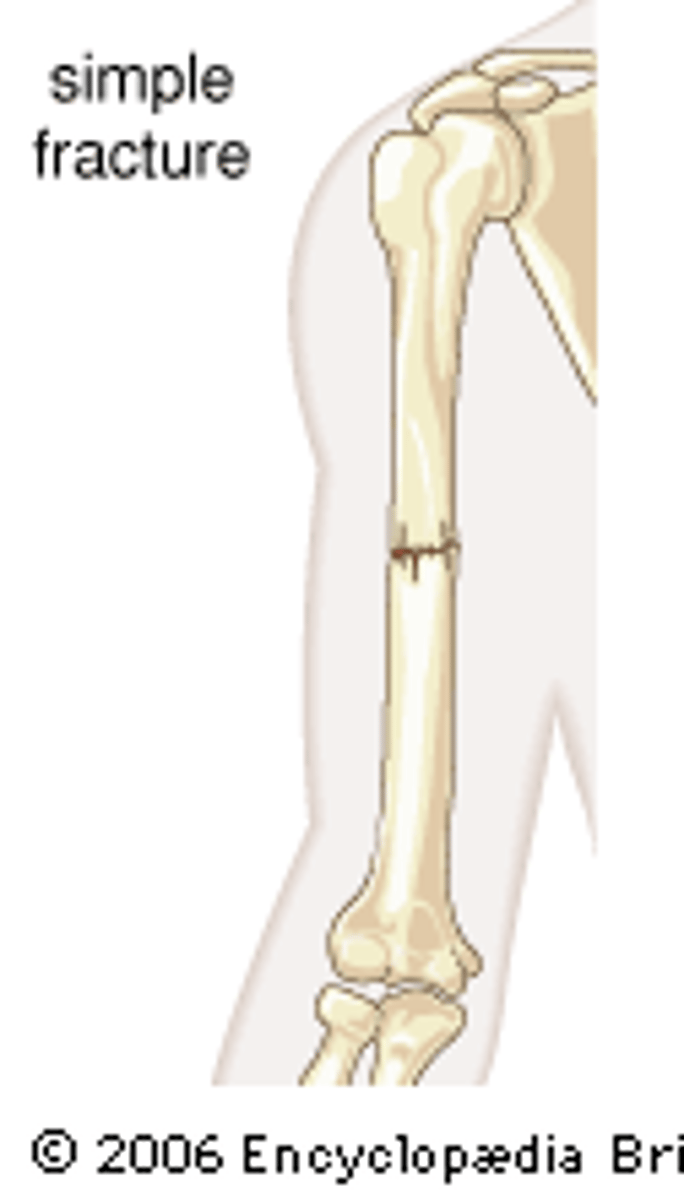
Simple fracture
Bone does not break through skin (closed fracture)
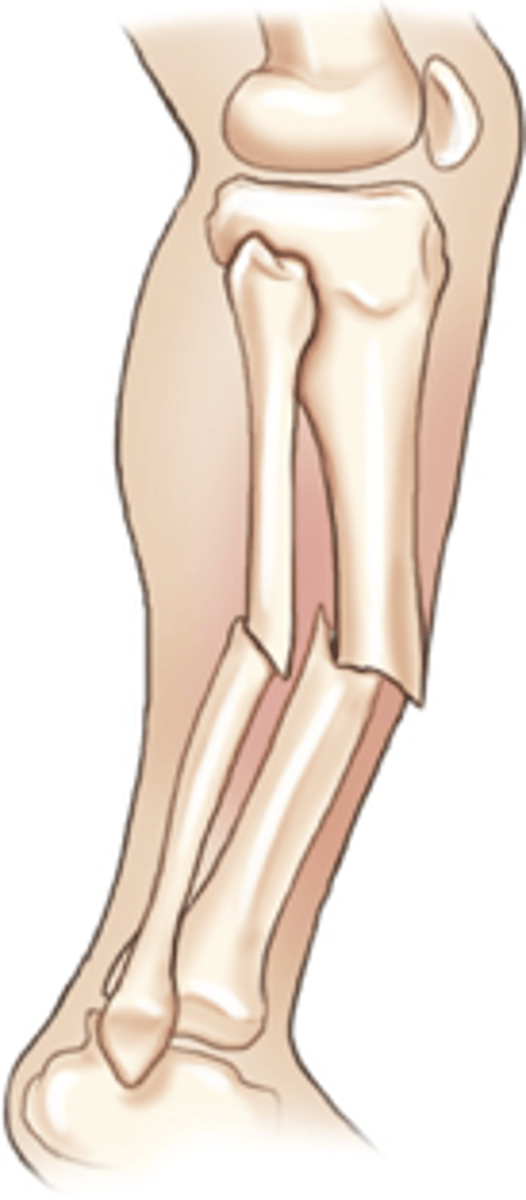
Compound fracture
Bone protrudes through skin (an open fracture)
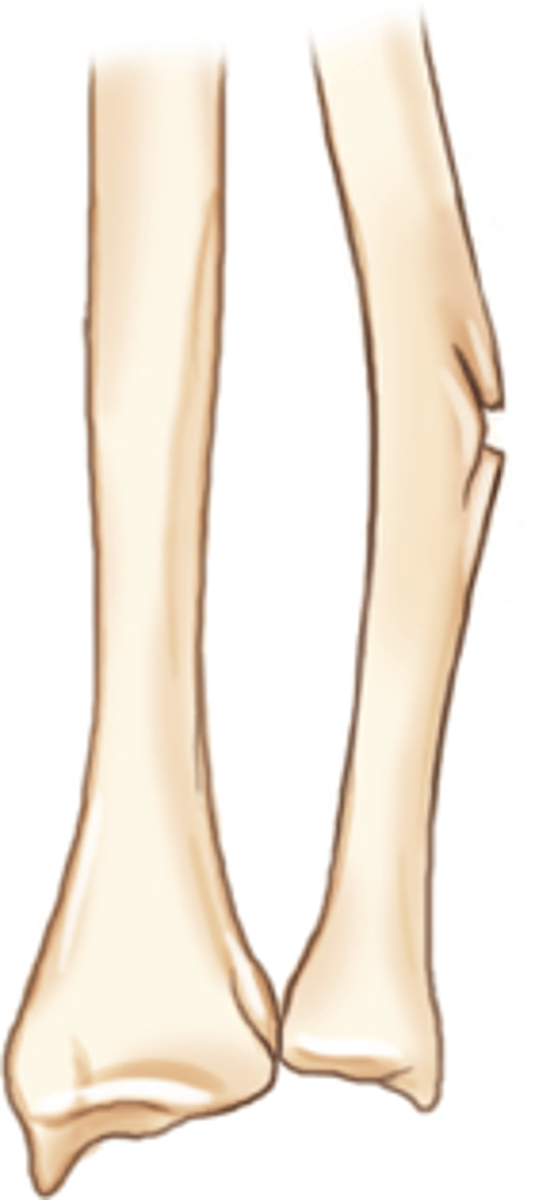
Incomplete fracture
Fracture does not traverse through entire bone
Examples:
- Torus fracture
- Greenstick fracture (imaged)
- Plastic fracture
Complete fracture
Fracture traverses through entire bone
Examples:
- Transverse fracture
- Oblique fracture
- Spiral fracture (imaged)
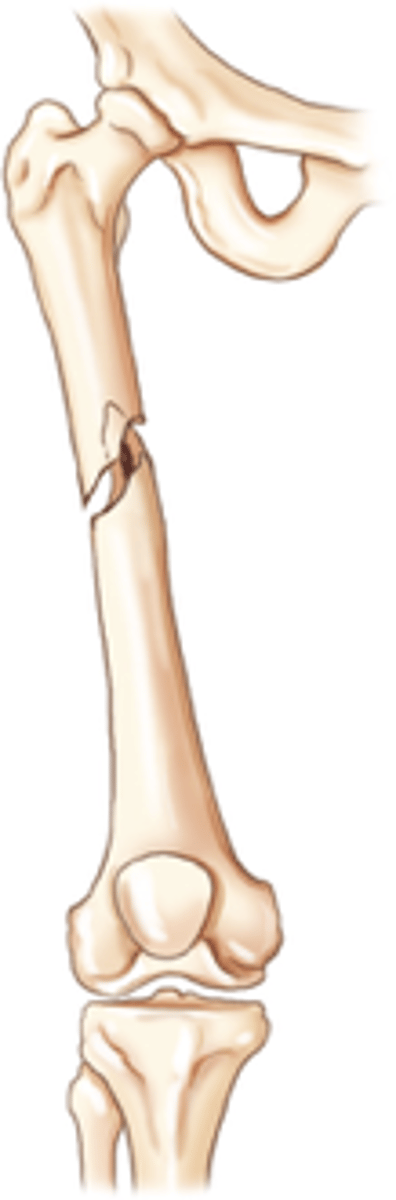
Comminuted fracture
Two or more fragments
Examples:
- Segmental fracture (double-type fracture)
- Butterfly fracture (two fragments)
- Splintered fracture (thin, sharp fragments)
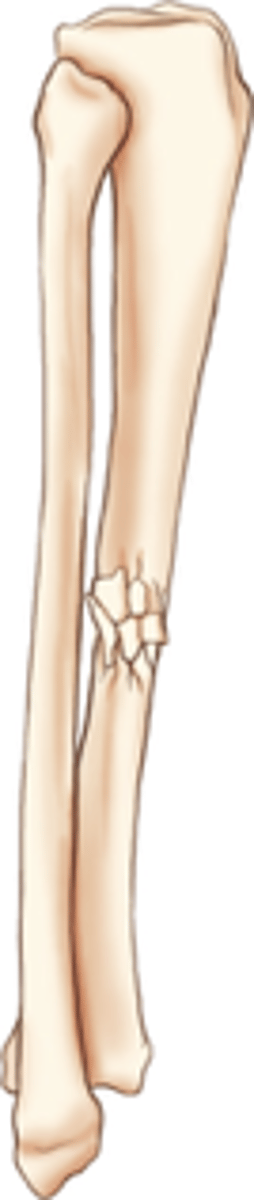
impacted fracture
One fragment driven into another (ends of bones)
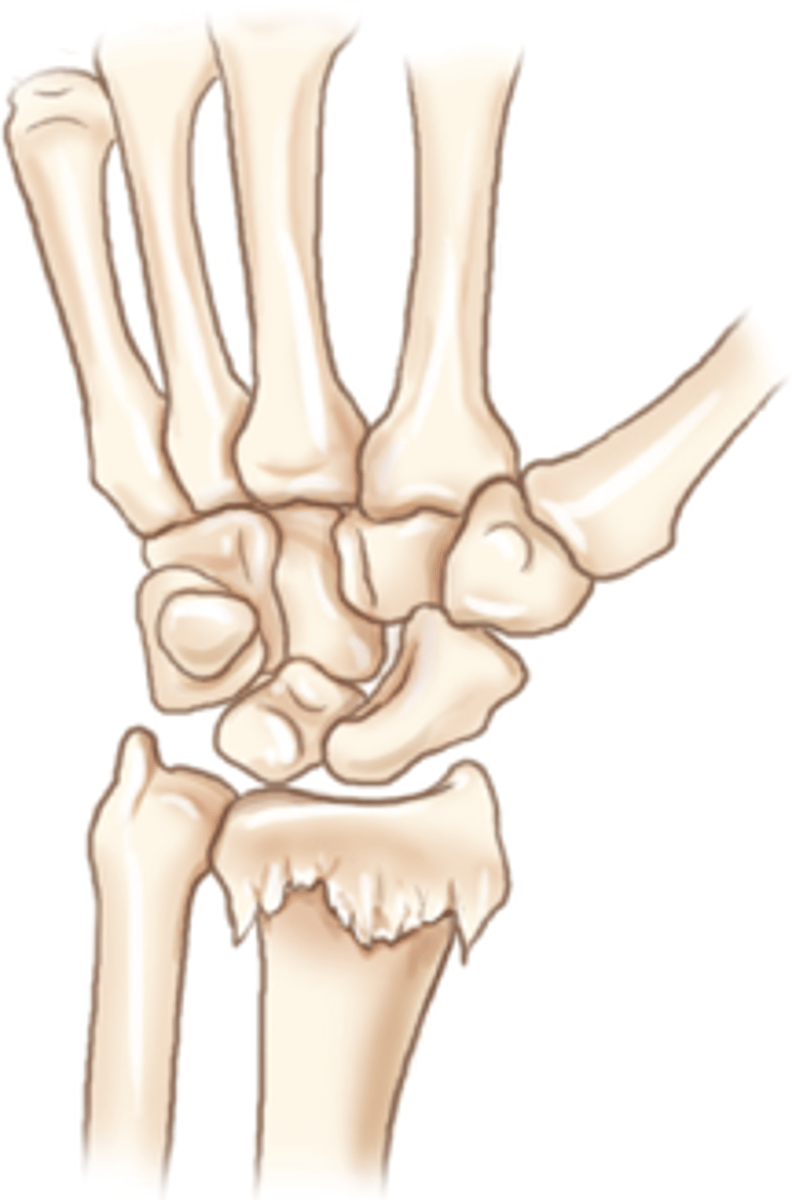
Colles' fracture
Posterior displacement of distal radius

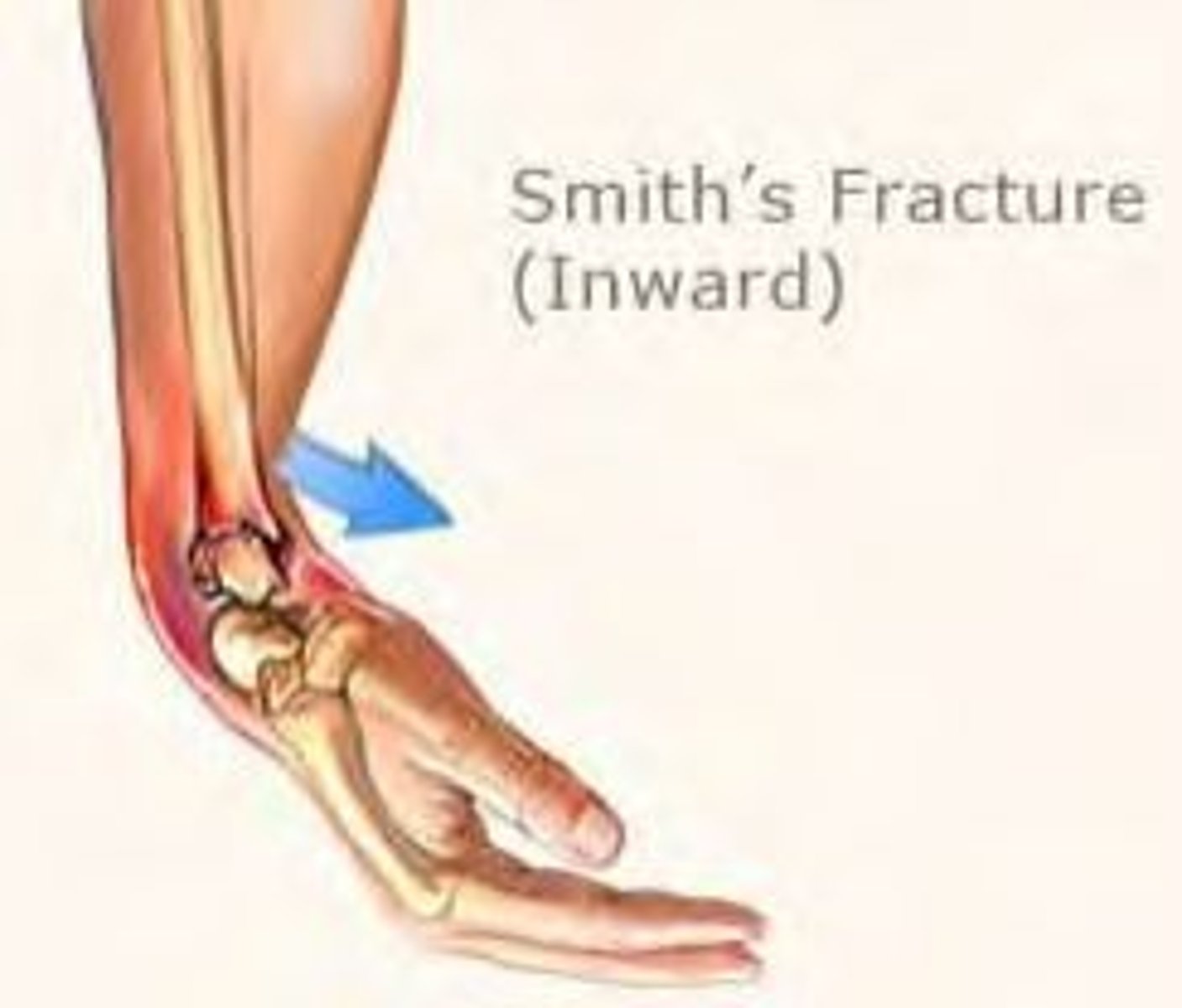
Reverse Colles' (Smith) fracture
anterior displacement of distal radius
Monteggia's fracture
Proximal ulna along with dislocation of radial head
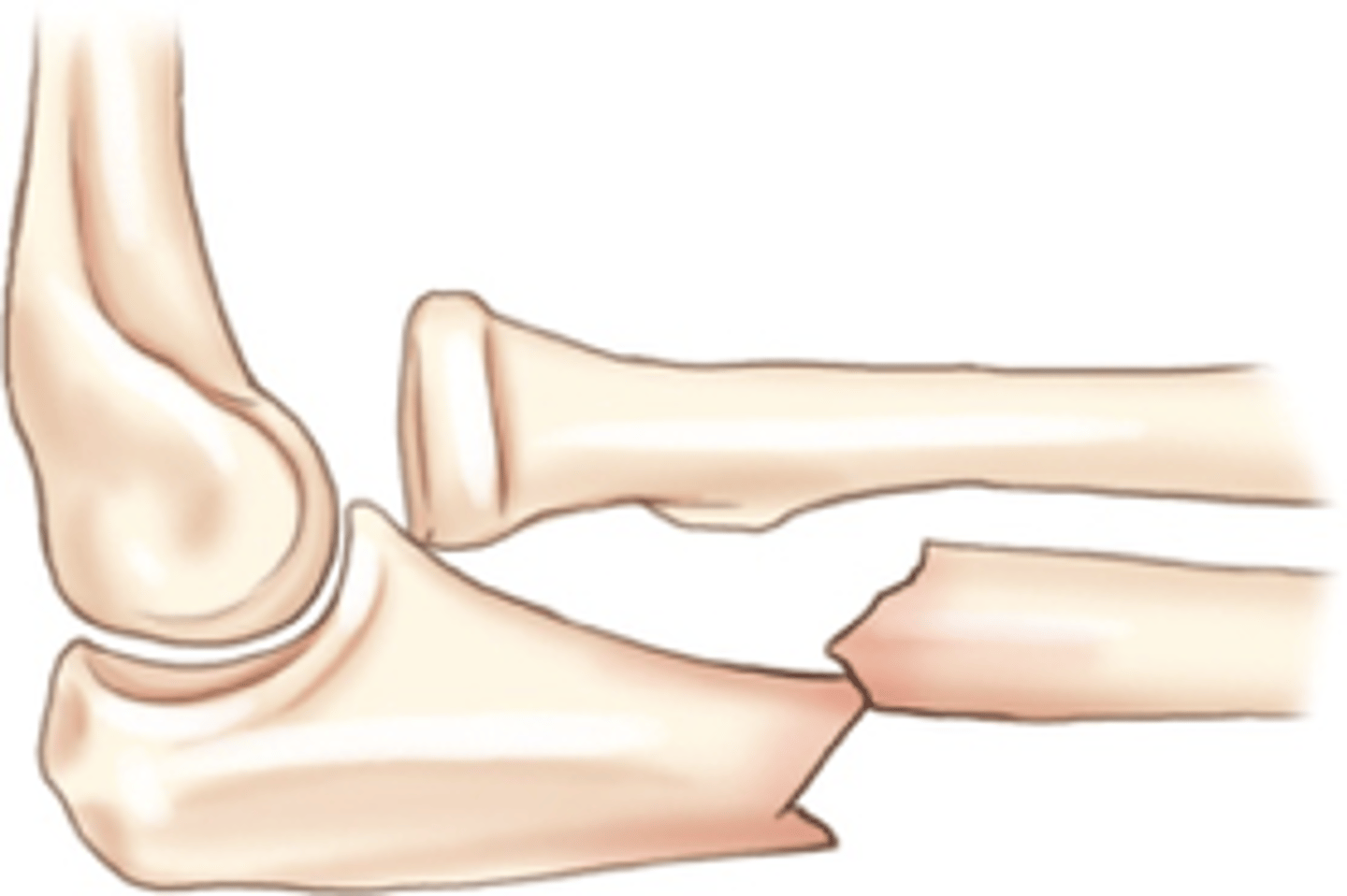
Pott's fracture
Ankle fracture of distal fibula with frequent fracture of medial malleolus
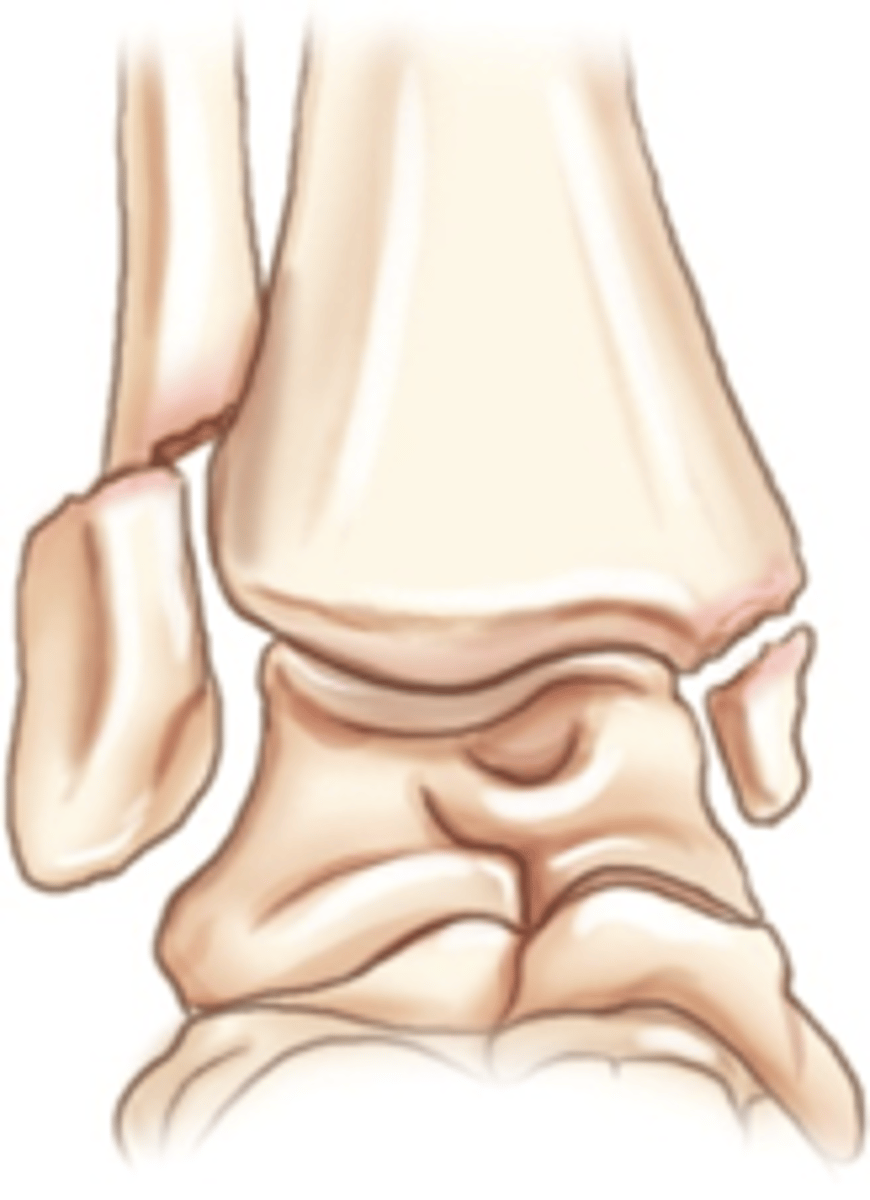
Baseball (mallet) fracture
fracture of distal phalanx
Barton fracture
intra-articular fracture posterior lip of the distal radius
Bennett's fracture
involves the first metacarpal & carpometacarpal joint
Boxer's fracture
fracture of the 5th metacarpal
Hangman's fracture
Bilateral fracture of pedicles of C2 due to hyperextension
- Unstable
Hutchinson's (chauffeur's) fracture
Fracture of the radial styloid process
Nursemaid's elbow
- jerked elbow
- not a fracture
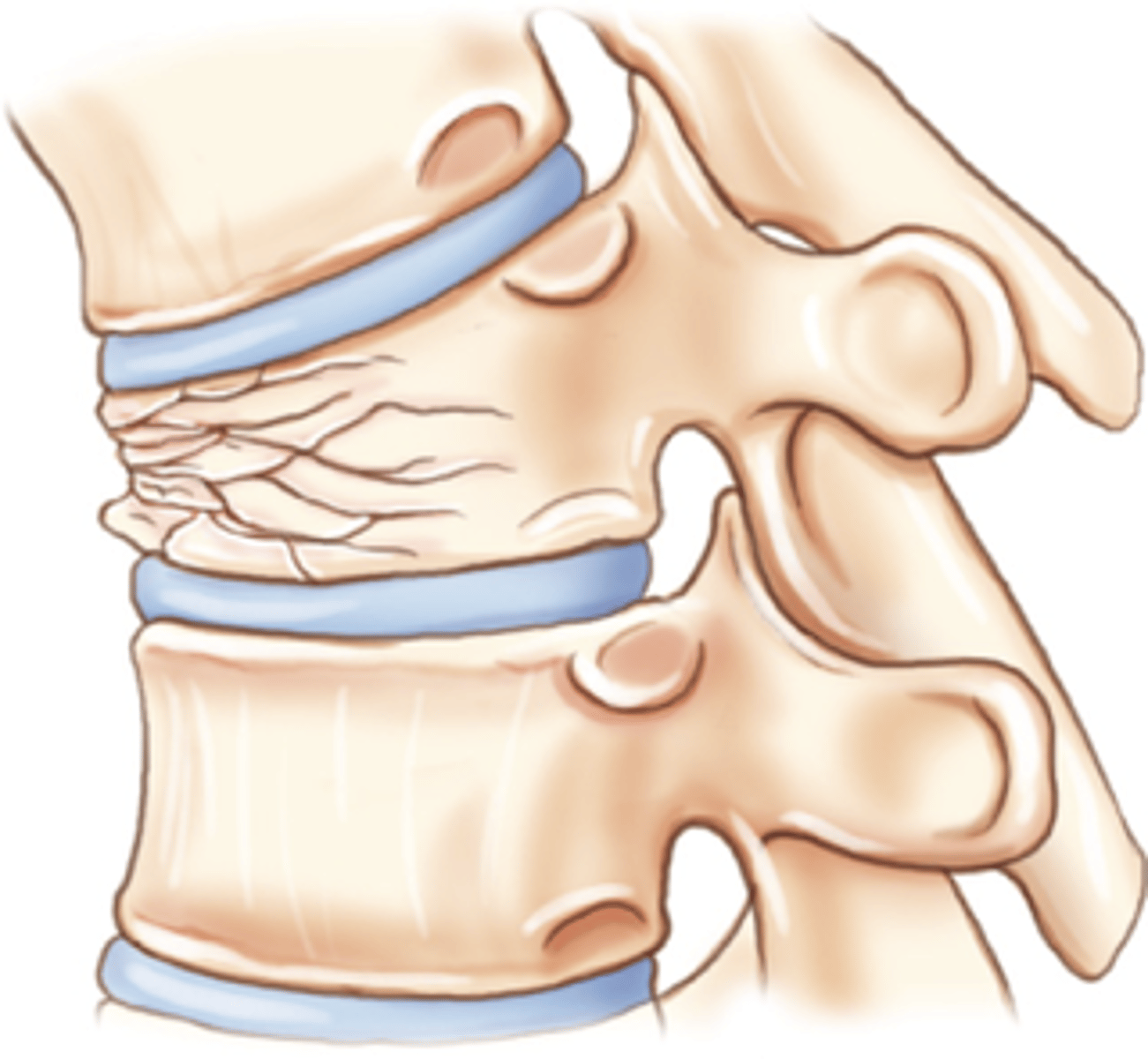
Compression fracture
Vertebral body collapses or is crushed
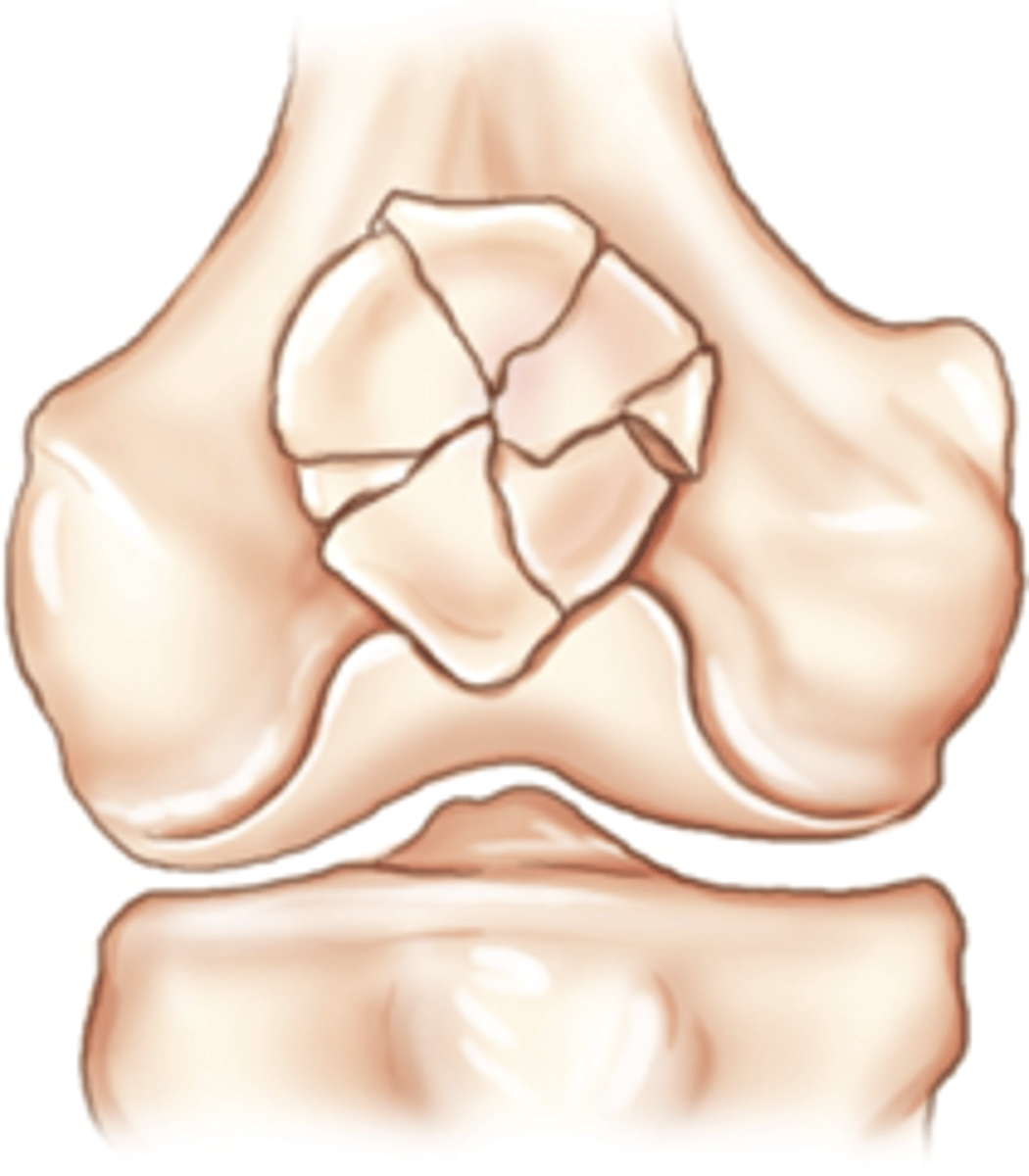
Stellate fracture
Fracture lines radiate from a center point of injury
Tuft fracture
Comminuted fracture of distal phalanx