Multi Hazard Zones + Philippines case study
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Amnas’s summary
physical geography
There are 22 active volcanoes and the Philippines is prone to Earthquakes.
30% of the population live within 30 km of a Volcano. Pacific Ocean – Prone to Tsunamis.
Typhoon belt – The Philippines has on average 15 per year.
High rainfall, steep topography, and deforestation – Landslides.
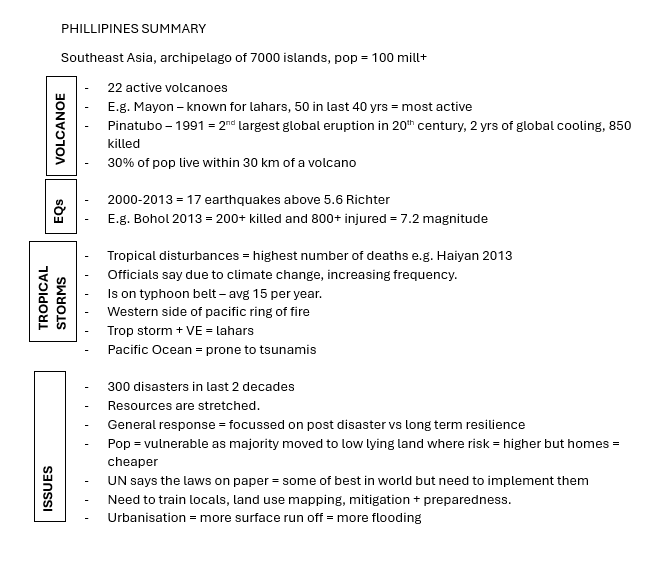
a disaster hotspot...
= when the vulnerability of a population is combined with geophysical, atmospheric and hydrological hazards
the population is exposed to both hazard groups at tectonic plate boundaries and atmospheric storm belts
population number and density is typically high
... a multiple hazard zone
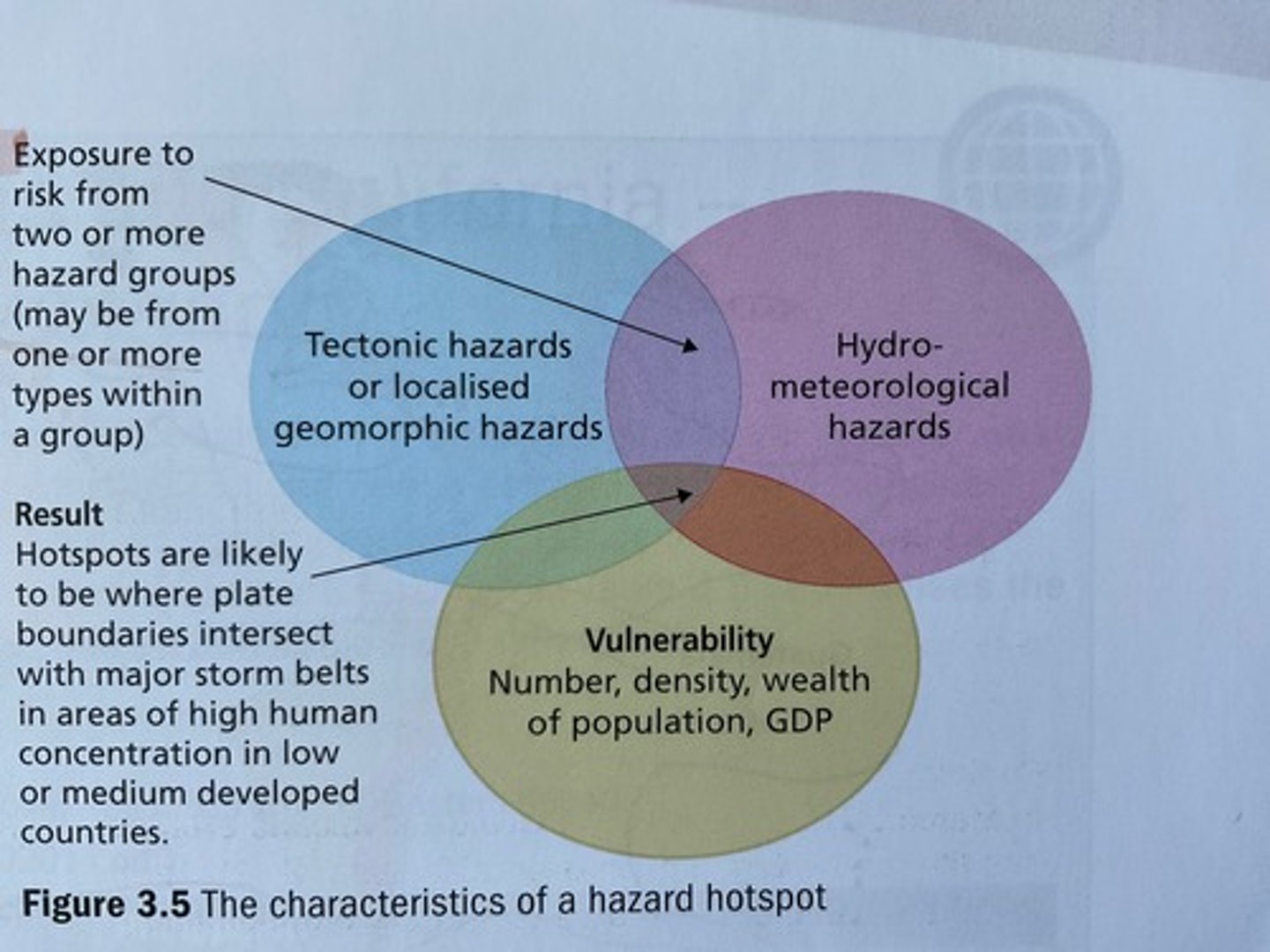
Greatest risk areas around the world
- The red zones are areas that experience drought, hydro-meteorological and geophysical hazards, also known as multi-hazardous areas or "hotspots"
- The red zones typically sit near the equator, along plate boundaries. This would explain both the meteorological and geophysical hazards with the areas.
- Eurasia has many 'red zones' within in it, such as Turkey, Greece, Lebanon, and Cyprus
- In north America, the city of Los Angeles in California is a multi-hazard area
- Central and South America also have a fair share of red zones, such as Hispaniola (Haiti and Dominican Republic) and parts of northern Colombia
- The Philippines is a hotspot for hazards, as are areas of Japan and Western China
Multi Hazard Zone Case Study
The Philippines
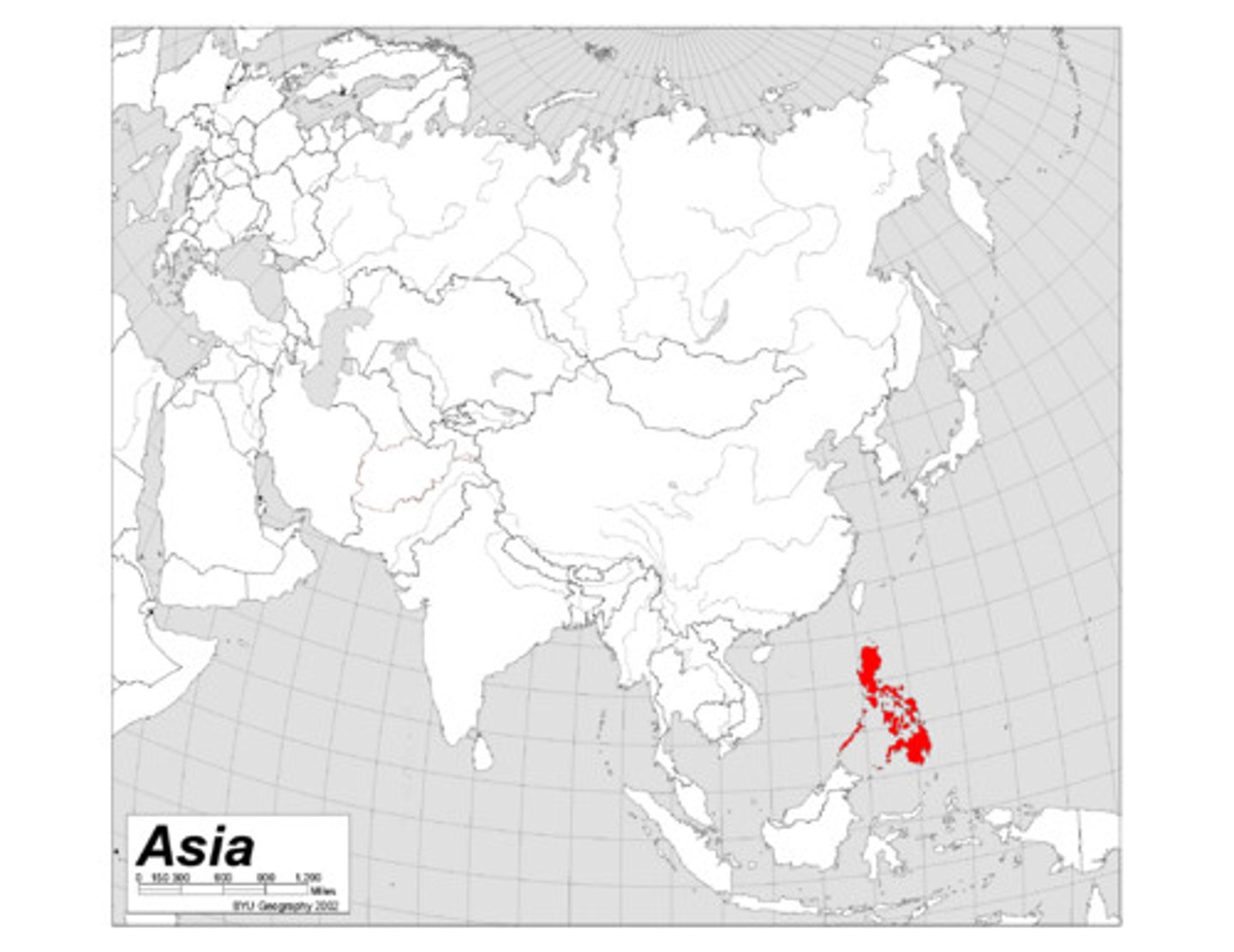
The Philippines
- south east Asia
- consists of an archipelago of over 7,000 islands
- population of 100 million
Geographical position = highly prone to natural disasters
- Western rim of the pacific ring of fire ... earthquakes + volcanic activity
- Situated in area where tropical disturbances cross from the pacific towards SE Asia, making the Philippines the most exposed country in the world to typhoons
... tropical storms = flooding, landslides, lahars (+ volcanic activity)
Philippines economy
Cost of economy = 0.5% GDP
(Disturbances from natural hazards + secondary/indirect effects hinder attempts by the government to reduce poverty and vulnerability)

further vulnerabilities of the Philippines
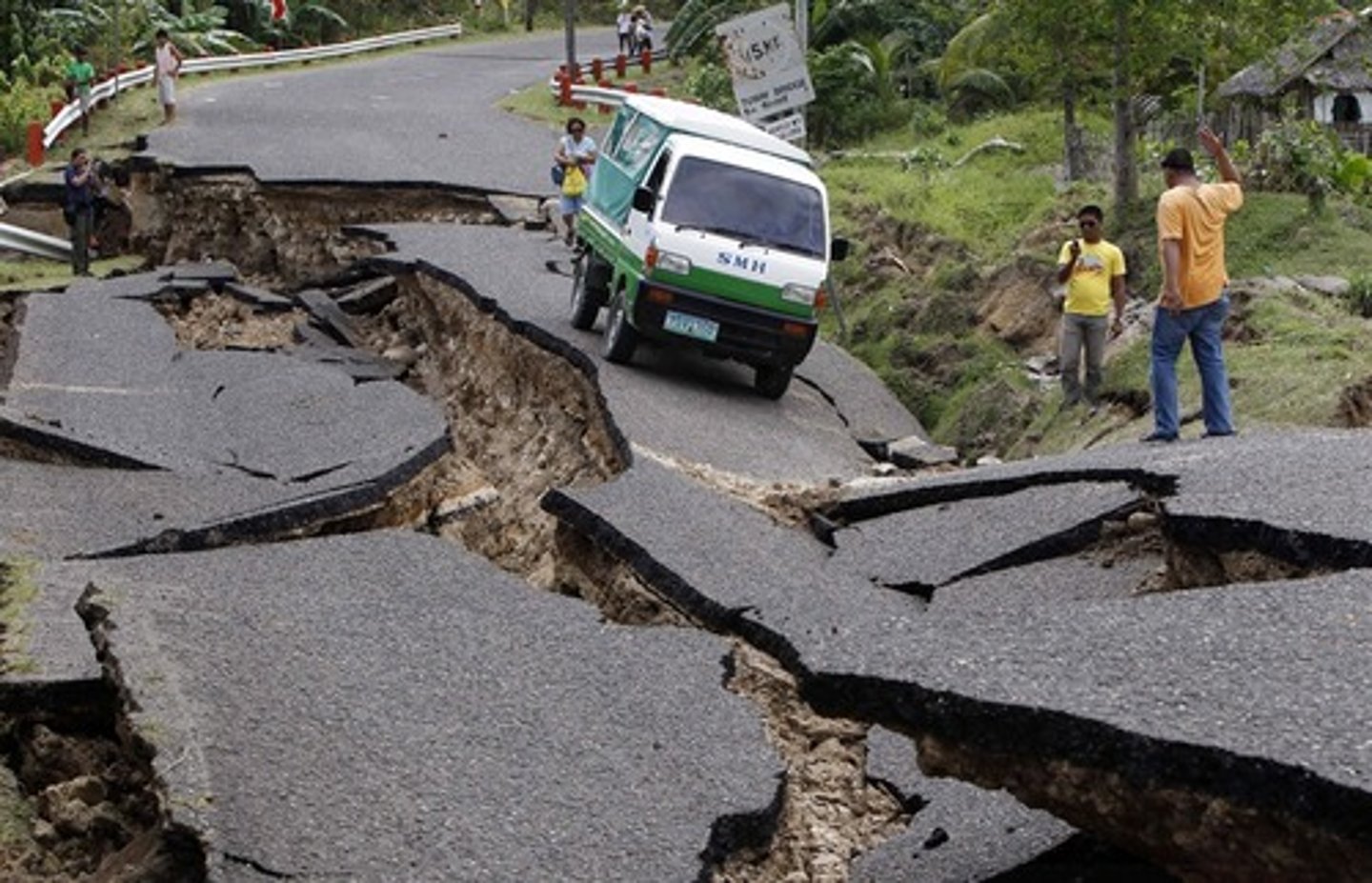
· 2013 Bohol earthquake - magnitude of 7.2
... killed over 200, injured 800, caused damage to 10's of 1000's of buildings
... touched/crossed by 7 typhoons (including Haiyan) & 8 tropical storms
... major volcanoes had intermittent small-scale of lava, steam, and gas
Major threats to the population of the Philippines
Earthquakes
Volcanic Activity
Tropical Disturbances
Earthquakes
= between 2000 and 2013, there were 17 earthquakes with a magnitude of at least 5.6
· 1976 off Mindanao (Moro Gulf)
... magnitude of 7.9
- caused tsunamis which inundated the western shore of Mindanao, killing up to 8,000
· 1990 Luzon
... magnitude 7.8
- killed over 1600 people and caused widespread ground rupturing + soil liquefaction
· 2013 Bohol
... magnitude of 7.2
- killed over 200, injured 800

Volcanic Activity
= 24 active volcanoes on its islands
· Mayon
... most active, has erupted ~50 times in the last 400 years
... most destructive event = 1814
... last eruption = 2014
= noted for its lahars
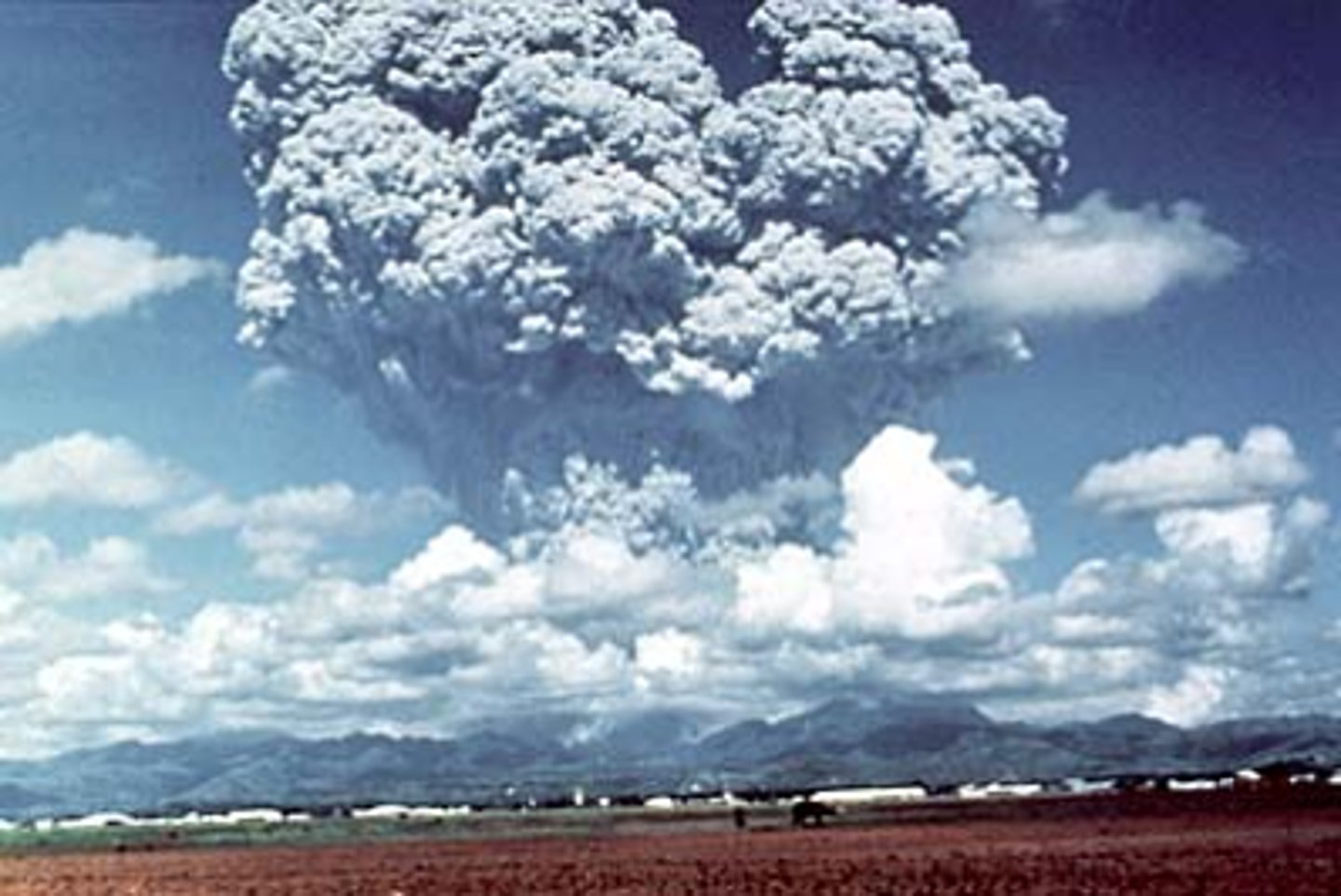
· Pinatubo
... erupted in 1991, 2nd largest eruption on the planet in 20th century
... large numbers of people live in its vicinity (500,000 people within 40km)
... early warnings and evacuations saved at least 5,000 people 1991
- Explosion was so violent that it hurled gases, ash, and steam into the upper atmosphere where they continued to affect global temperatures for at least 2 years (average global temperature fell by 0.5c)
- Followed by the typhoon Yunya, with very heavy rainfall that produced deadly lahars when combined with ash. Final death toll = around 850
· Taal
... one of most active volcanoes, having erupted 33 times on historical record
... eruptions come from a crater lake formed when a prehistoric explosion created the caldera
... thought to be historically responsible for 5,000-6,000 deaths as lies near to populated areas

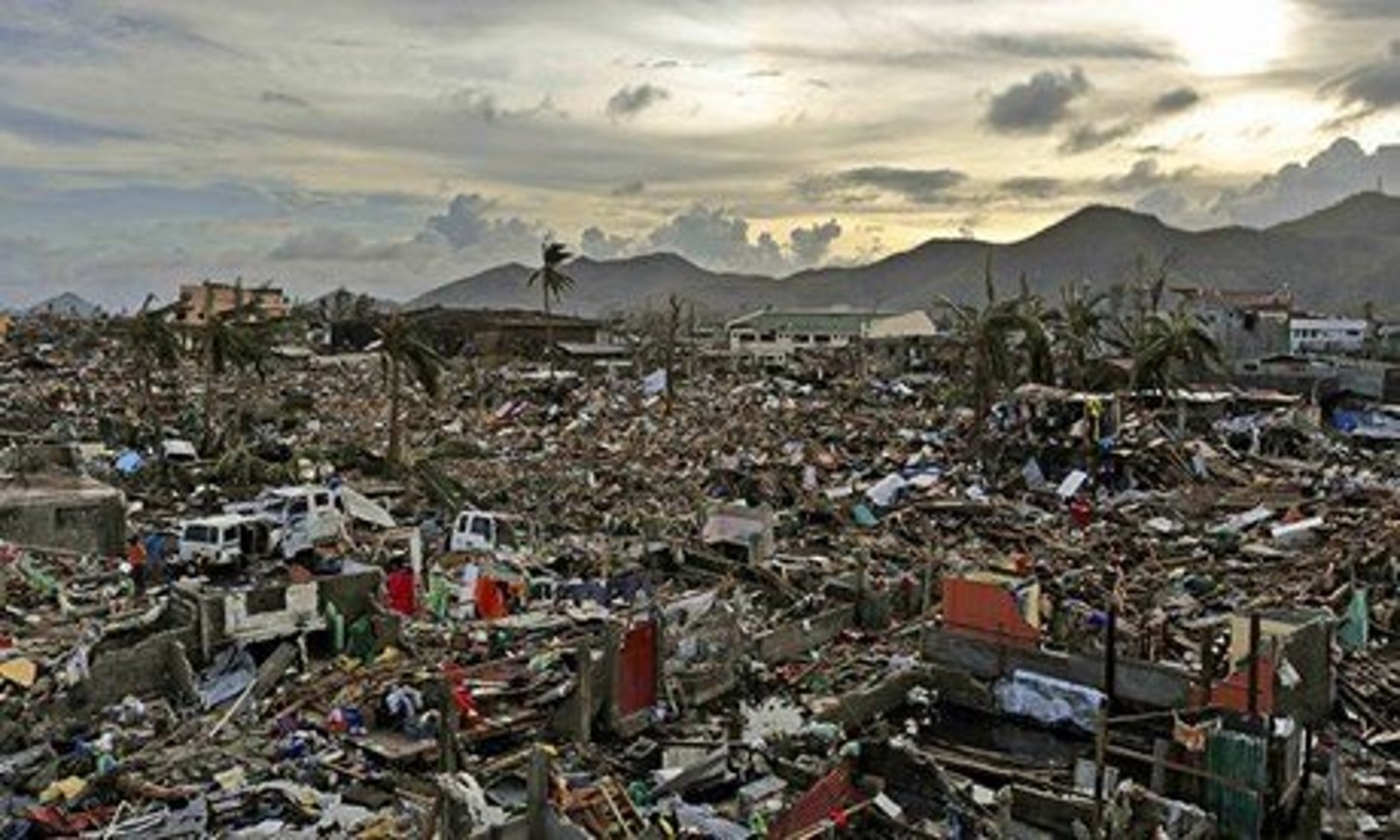
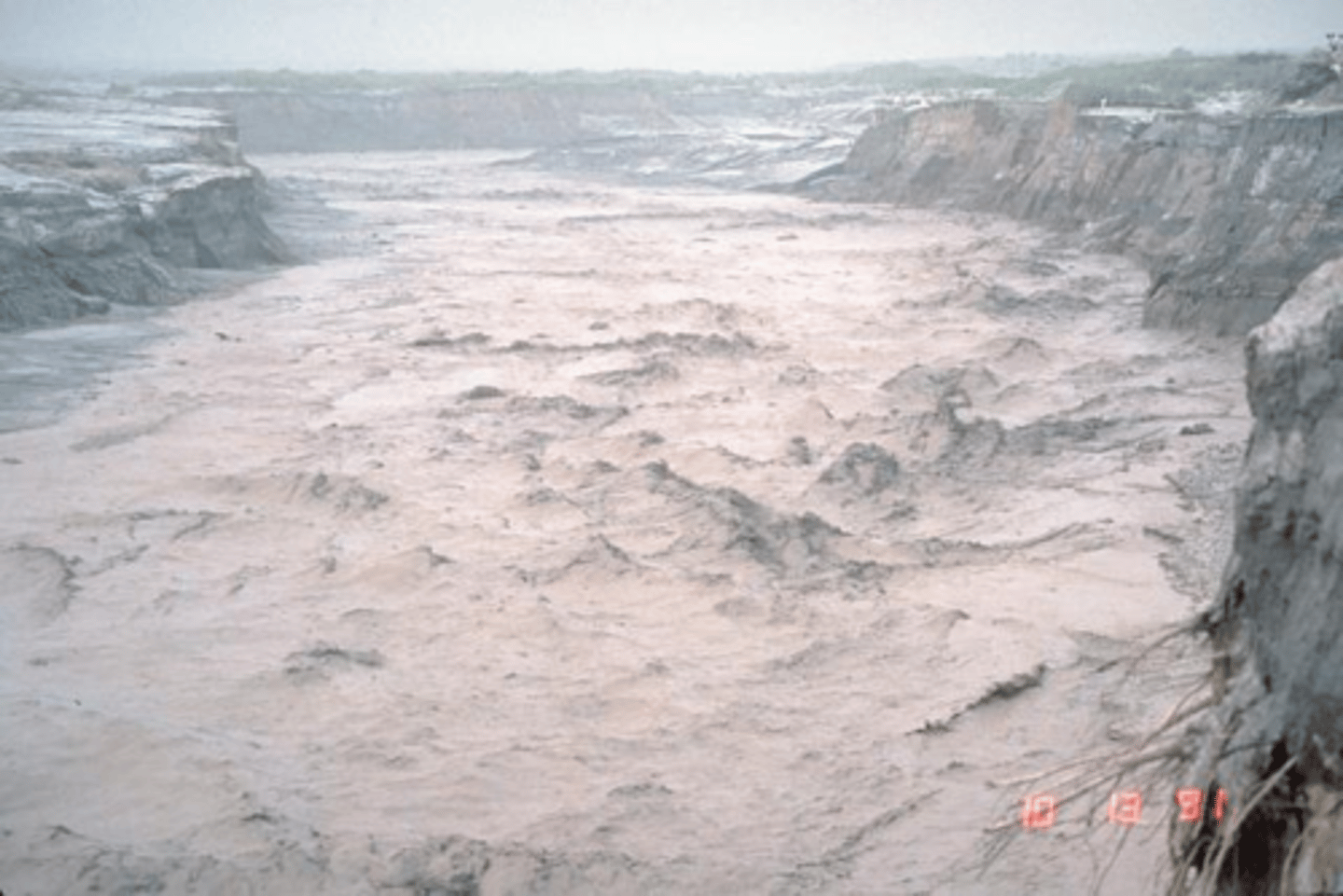
Tropical disturbances
numerous storms cross the country every year bringing with them the risk of severe flooding, landslides, and lahars if combined with a volcanic eruption
... such disturbances account for the highest numbers of deaths from natural hazards in the Philippines, most fatalities being the result of storm surges
e.g., Typhoon Haiyan (November 2013)

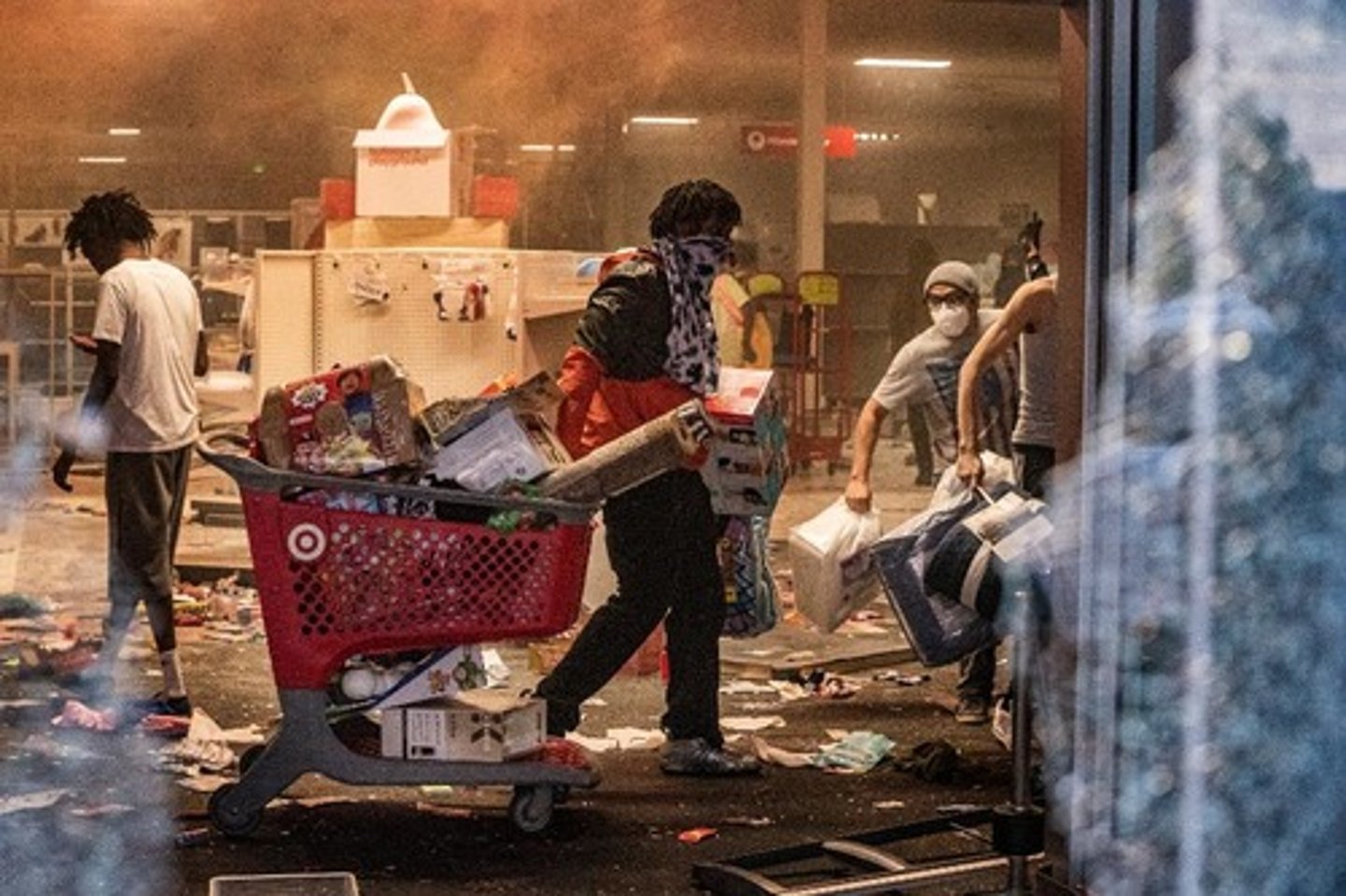
Hazards can lead to...
- Looting
- Violence
- Contamination
- Pollution

Philippines frequency of disasters
· In past two decades the Philippines has experienced over 300 natural disasters
· Filipino officials insist typhoon hazards are becoming more serve due to climate change
vulnerability of filipino population
Majority of population moved to risky low-lying areas which are havens for cheap, crammed housing where there is a clear link between poverty and vulnerability to natural disasters
.. rapid urbanisation has exasperated the problem with tightly packed, poorly constructed housing and environmental degradation (e.g., deforestation - rapid surface run off and increased flooding from unprotected slopes)
Philippines problems with planning and response
Philippines disaster management systems have tended to rely on there response after the event has occured
... should be taking a more effective approach to mitigate against disasters
This could be done by:
- Appropriate land-use planning
- Construction and other preventative measures
- Avoiding the creation of disaster-prone conditions
... there has been widespread emphasis on post disaster relief and short-term preparedness (i.e., forecasting/evacuation) rather than mitigation and post-disaster support for economic recovery
- Current systems tend to be more centralised top-down administrative system than community based systems or local initiatives
- Local initiatives would emphasise the bottom-up approach that will help the most vulnerable communities to cope with the hazards when they occur
Local Initiatives
... together have started programmes at community level
...Aim is to reduce impacts of natural disasters by encouraging people to collaborate in protecting their lives and the resources upon which they depend
Planning + Mitigation
Plans include...
· Co-operation and partnership with governmental bodies in order to gain financial support for mitigation measures and to ensure that the programmes have long-term sustainability
· Training local volunteers in disaster management
· Identifying risk through land use mapping and determining which mitigation measures might be possible
· Initiating mitigation measures which could be physical (sea walls, dykes), health related (clean water supplies) or planning tools (land-use plans, evacuation plans)
- Many commentators have pointed to the great resilience of the Filipino people in the face of the problems in living in a multi-hazard environment
- others have simply described the attitude of the people as "fatalistic"
fatalistic approach
... accept that these events are part of living in such an area and that losses are inevitable from time to time
central government plans of mitigation
The central government is trying to do something about the situation:
o UN claims that the Philippines already has some of the best risk-reduction laws in the world, but unfortunately these are still only on paper
o With a country with over 7,000 islands, too much responsibility for reducing disaster risk falls on the local government where money is not always wisely spent
However...
o Recent government legalisation calls for 70% of disaster spending to be used on long-term plans with only 30% going on emergency aid
o The main problem of living in multi-hazard environments remains because...
..."Resources are stretched - even before we could recover from one disaster, here is the next one"
(government official in the Philippines)