Honors Biology Viruses/Bacteria/Protists Study Guide
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Viruses are very…
small paricles.
Viruses are made up of…
protein and a nucleic acid(DNA or RNA)
Viruses can’t…
eat, grow, get rid of waste, or reproduce on its own.
Host cell-
a living cell that is invaded by a virus for the purpose of reproduction.
Viruses are very specific to the…
kind of host cell they infect,
What do you need to see a virus?
An electron microscope.
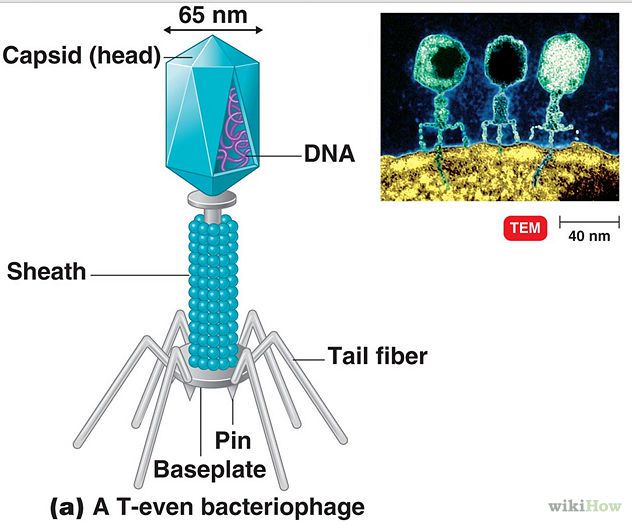
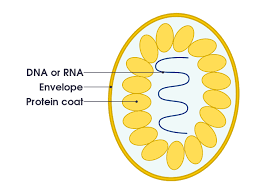
Virus structure-
A core: made up of nucleic acid(DNA or RNA, never both), capsid: The outer coating made of protien. Bacteriophage: a virus that attacks bacteria. Shapes may vary.
Viral infection-
must enter a host cell to replicate. Virus can replicate using the lytic or lysogenic cycle.
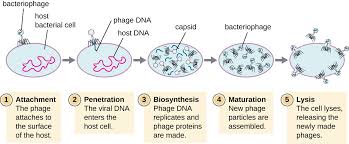
Lytic Cycle-
(*Short Term) process of viral replication inside a host cell occurs in the cytoplasm.
Order of Lytic Cycle-
Attachment- the virus attaches to the surface of the host cell; specific to surface proteins.
Injection- The viral DNA or RNA enters the host and becomes part of the host cell’s DNA
Replication- Viral DNA takes over the host cell and produces viral proteins and nucleic acid.
Assembly- The virus parts are put together to form new viruses.
Lysis and Release- The cell membrane breaks destroying the host cell and releases the new virus particles.
Infections are usually immediate, symptoms appear in a couple days. Ex. Common Cold.
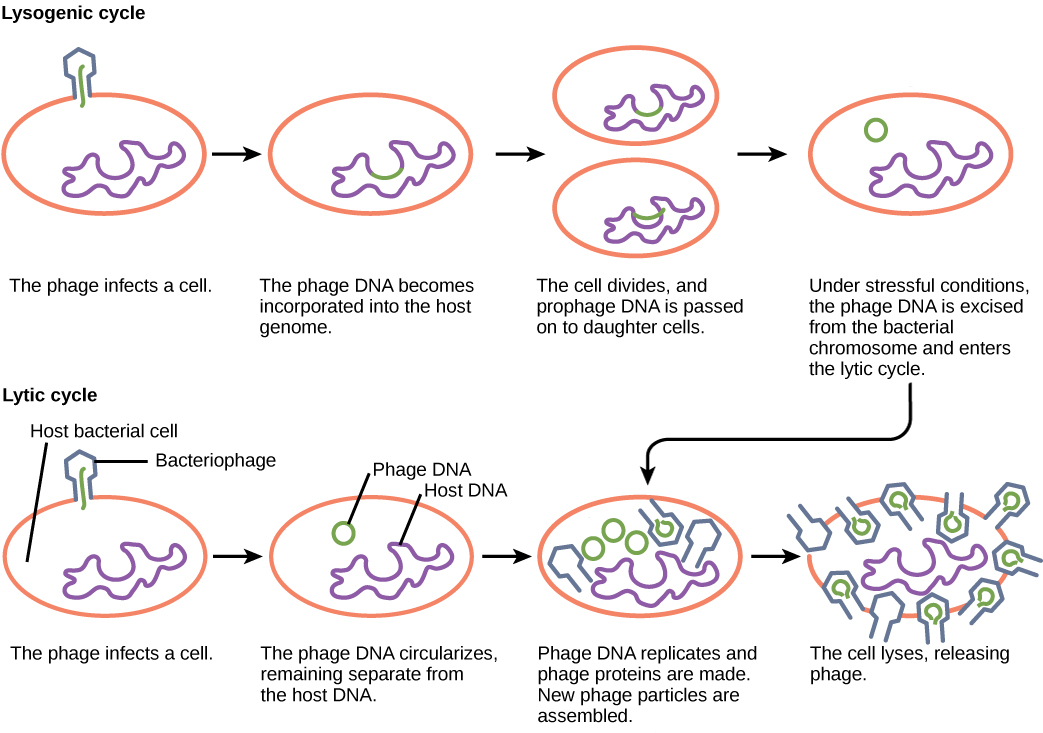
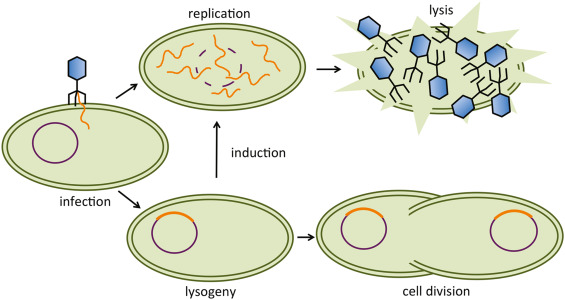
Lysogeneic Cycle
Viral DNA enters the chromosome of the host cell.
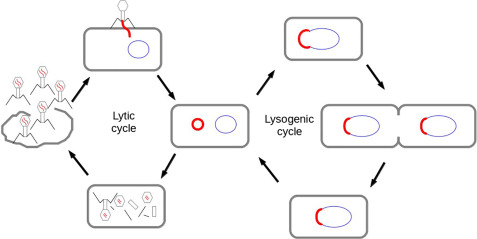
Order of the Lysogenic Cycle
Viral DNA instructs the host cell to make more viral DNA
Infected cell will have viral genes forever, genes may be dormant, but once activated the cell goes into the Lytic Cycle
Why are viruses generally considered non-living?
They lack many characteristics of life.
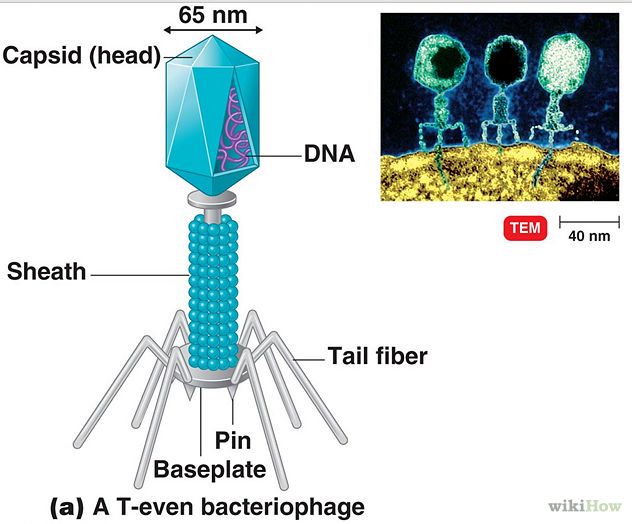
What is the name of the protein coat on viruses that protects its genetic material?
Capsid
What occurs after a virus enters a cell or injects its genetic material into a cell?
The cell follows the virus’s genetic instructions
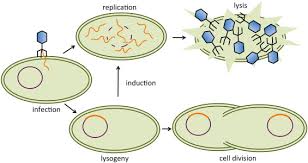
What causes the cell to lyse during the Lytic cycle?
an excessive amount of viruses in the cell.
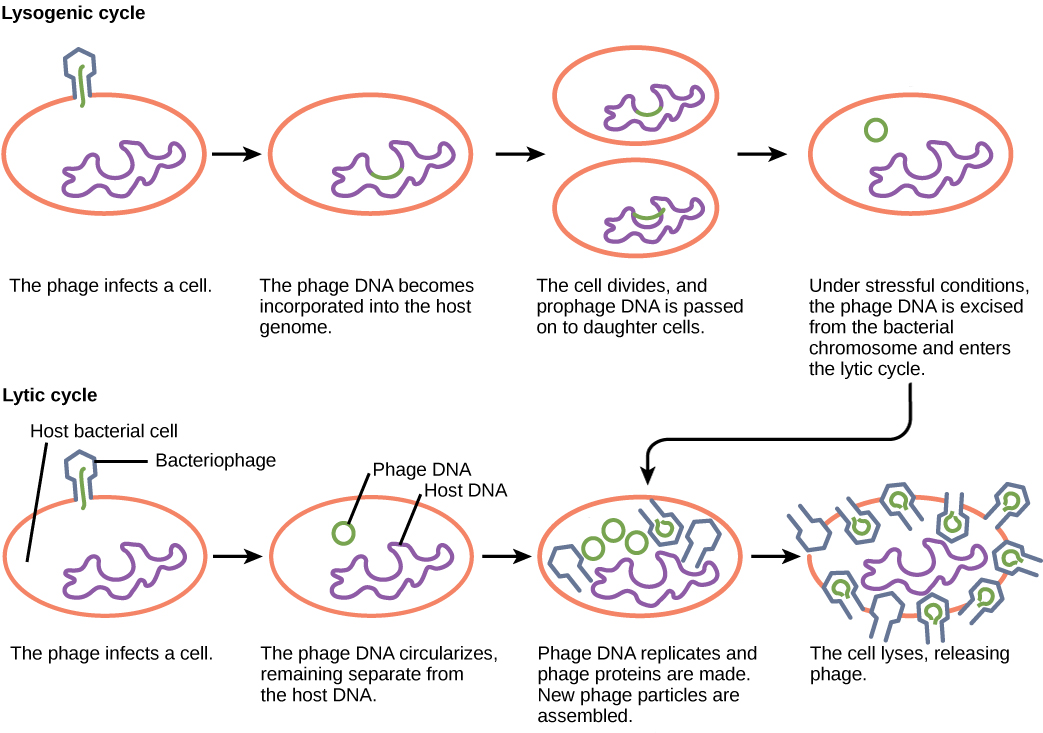
What can trigger the Lysogenic cycle to being the Lytic cycle?
a chemical or lack of food for the host.
What type of cells does HIV target?
Immune cells
Can viruses mutate?
Yes
How can viruses play a useful role?
Gene therapy
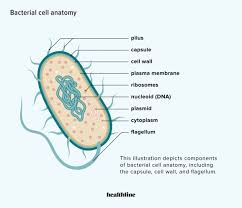
Bacteria are…
prokaryotes(lack a nucleus) and are the simplest living organism.
What are the two domains of bacteria?
Archaea and Bacteria(Eubacteria)
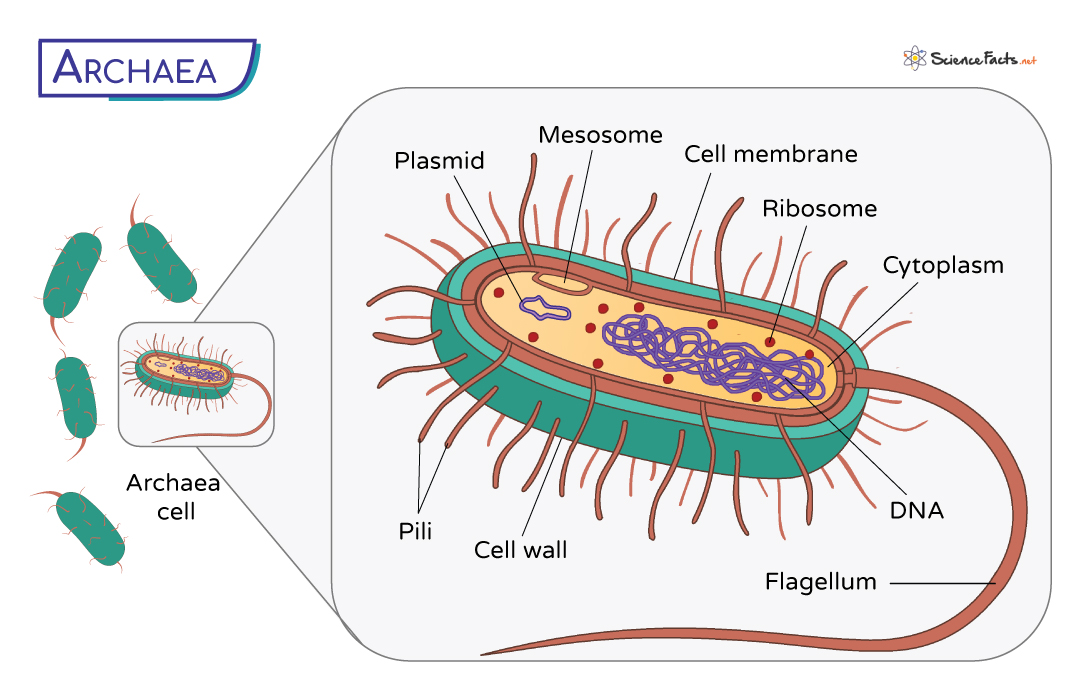
What are some characteristics of Archaea?
No peptidoglycan in cell walls.
may be ancestors to eukaryotic cells.
live in deep oceans, volcanic vents, hot springs, highly acidic or very salty water(extreme conditions).
What are the 3 groups of Archaea?
Methanogens
Thermophiles
Halophiles
What are methanogens(archaea)?
produce methane gas anaerobic(make no oxygen and when exposed to oxygen they die).
What are thermophiles(archaea)?
live in hot, acidic environments and thrive at high temperatures(volcanoes)
What are halophiles(archaea)?
Live in very salty water(dead sea).
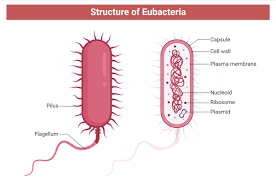
What are the characteristics of Bacteria(Eubacteria)?
Cell walls contain petidoglycan.
Grows best where there is moisture and warm tempatures(20 degrees C to 40 degrees C)
Can be divided into groups based on energy sources.
What are the three groups of bacteria(eubacteria)?
Cynobacteria(chemosynthesis)- photosynthetic , autotrophs, have chloroplasts. added oxygen to the atmosphere.
Chemoautotrophic- get energy from gases; include sulfur bacteria.
Heterotrophic- great variety, many are areobic(need oxygen).
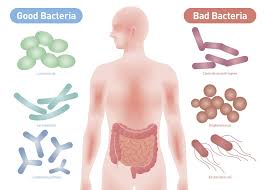
Only 1% of bacteria is harmful, how is the other 99% helpful in us and the enviorment?
Nitrogen-Fixation: the process of turning nitrogen gas from the air to a form plants can use.
Decomposers: break down dead material and return nutrients to the soil.
Norma flora: bacteria needed by the body. It digests your foods in the intestines and prevent them from taking over.
Production of foods: cheese, pickles, yougurt, also some medicines.
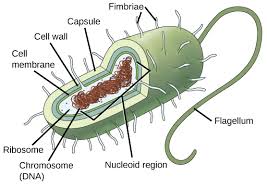
Stucture of prokaryotes
Nucleoid: Area where the chromosome is located
capsule: protects the bacteria. A layer of polysaccharides around the cell wall.
pili: Hair-like structures on the outer surface.
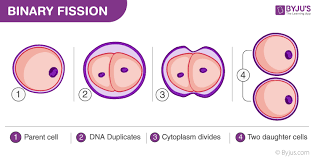
Binary Fisson:
The splitting of one cell into two, asexual reproduction.
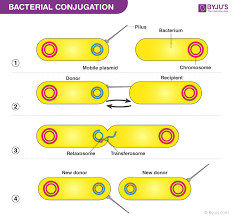
Conjugation:
The transfer of genetic material by direct contact, sexual reproduction.
Diseases caused by bacteria:
Strep throat, syphilis, bubonic plague, typhoid, and cholera.
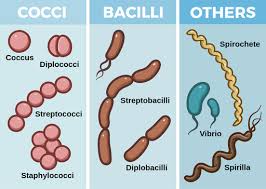
Bacterial shapes
include cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilla (spiral). Diplo are pairs, staphylo are clusters, and strepto are chains.
Where can bacteria be found?
Toothbrush, people, gardens, water, animals, etc.
How are photoautotrophs different from chemoautotrophs?
Photoautotrophs use sunlight for energy(photosynthesis) while chemo autotrophs use oxidation of inorganic chemicals for energy.
How do protists reproduce?
Reproduce asexually through binary fission or sexually.
What is the procedure when making a slide of bacteria?
Place a small drop of water on a clean slide.
Add a small amount of the bacteria to the water droplet and swirl it around.
Let it air dry.
Heat fix the slide through a flame a few times.
Stain the bacteria.

Why is heat fixing so important?
So that the bacteria adhears to the slide and to kill live organisms.
If you get a bacterial infection, how would you treat it?
Take antibiotics.
How can you prevent an infection of pathogenic bacteria?
Having good hygiene, vaccinations, and food safety.
How did the Phylum Ciliophora move?
They use cilia(hair-like stucture) to propel themselves through water.
What are the characteristics of each type of protists?
Protozoans(animal-like): are heterotophs, usually ingest algae, bacteria, or other protozoans.
Algae(plant-like): make their own food though photosynthesis.
Fungus-like: absorb their nutrients from other organisms.
What is the difference between areobic and anaerobic bacteria?
Aerobic bacteria require oxygen for survival and growth, while anaerobic bacteria do not and can be harmed by oxygen.
What are some diseases caused by protists?
Malaria and African Sleeping Sickness
What are the Phylums of the protists we studied? What protis fall into each Phylum?
Phylum Euglenophyta : Euglena
Phylum Ciliophora: Paramecium
Phylum Chlorophyta: Spirogyra & Pediastrum
How are protists classified? What are the three classifications?
Animal-like(protozoa)
Plant-like(algae)
Fungus-like
What are ways a protist moves?
Flagella, cilia, psudoepodia.
What is flagella?
a whip-like appendage that many microbes use for locomotion, or movement
What is cilia?
A hair-like structure that provides movement to some protists
What is psedopodia?
temporary, arm-like projections of cytoplasm that cells use for locomotion by "crawling" or "slithering" from one place to another.