Bio 006 - Cell Communication II & Immune System I
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
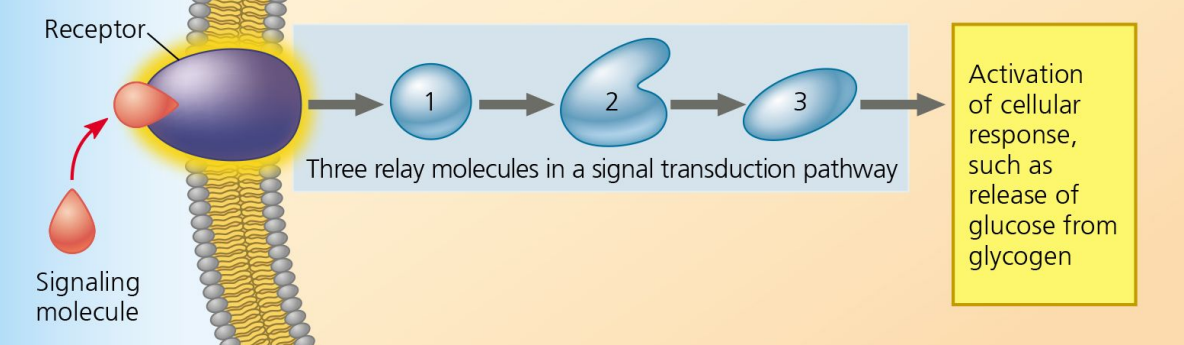
Signal Reception
Step 1 of Cell Communication:
Ligand binds to receptor, changing its shape.
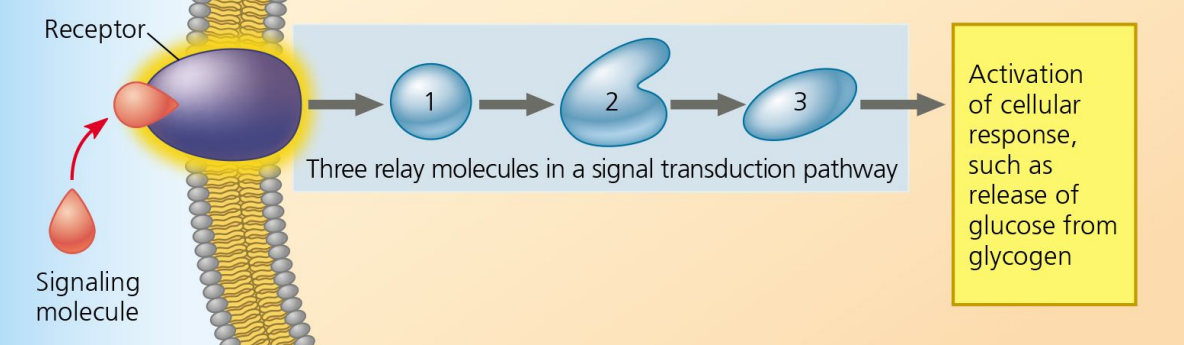
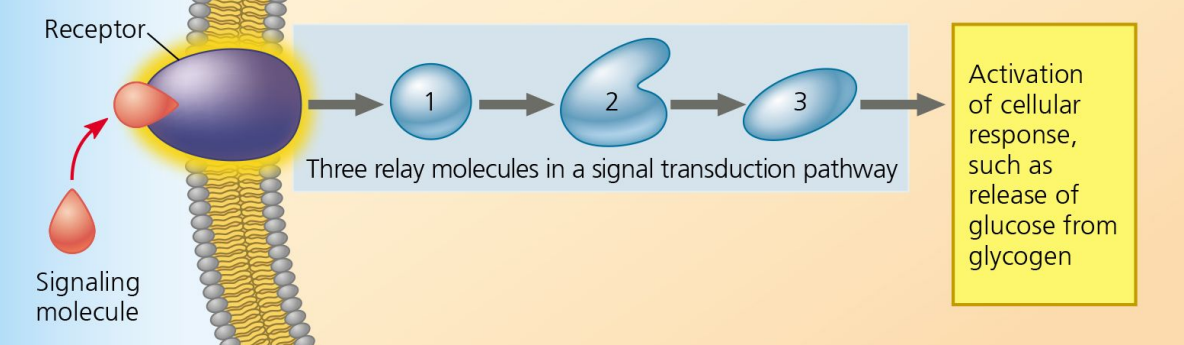
Signal Transduction
Step 2 of Cell Communication:
Chain reaction of relay molecules transmitting signals.
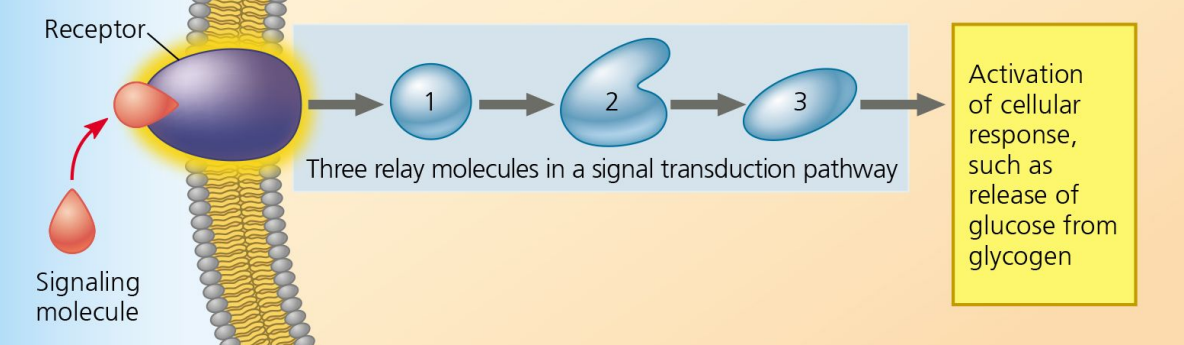
Cellular Response
Step 3 of Cell Communication:
Change occurs within the cell due to signaling.
Ligand
Signaling molecule that binds to receptors.
Receptor
Protein that binds to a ligand.
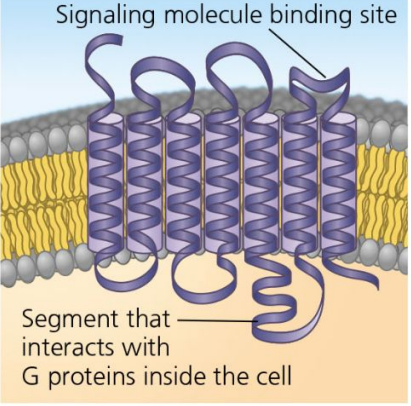
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Made of alpha-helices
Loops serve as binding sites
GDP = inactive, GTP = active
Receptors that interact with G proteins.
which binds to GDP (guanosine diphosphate) OR GTP (guanosine diphosphate)
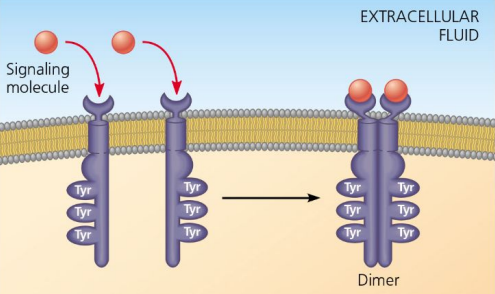
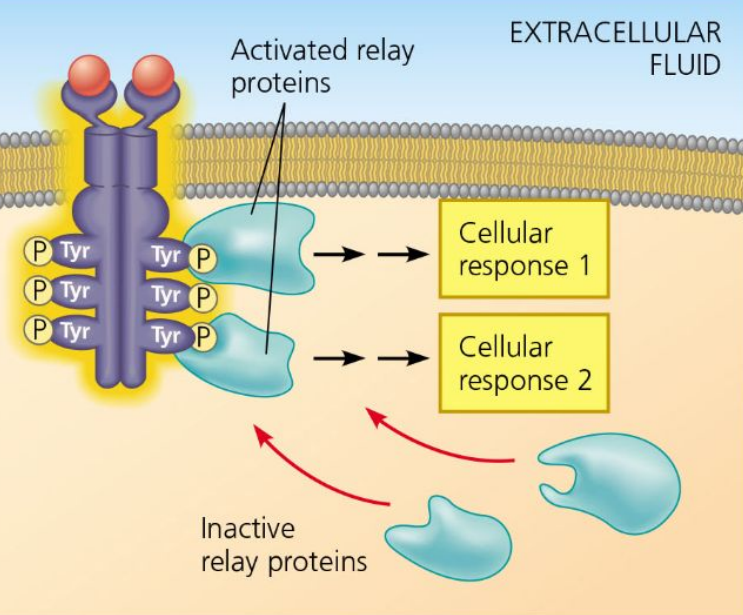
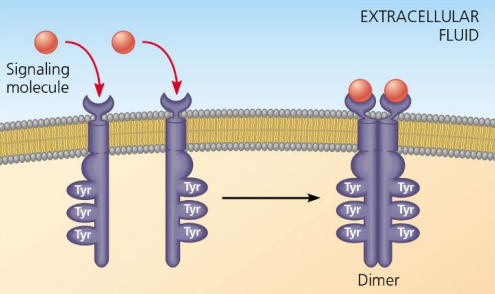
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Receptors that form dimers upon ligand binding.
Each has a set of tyrosines (amino acids)
When BOTH RTKs receive the signal, they snap together
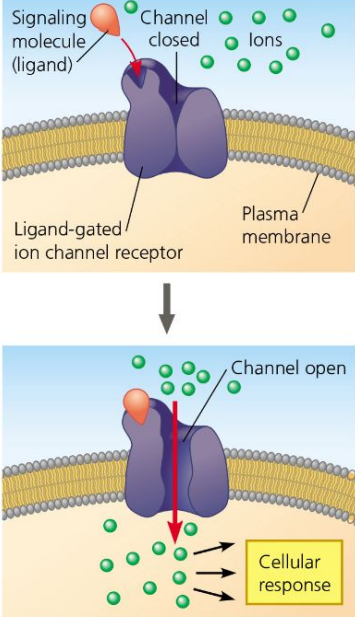
Ion Channel Receptors
Channel proteins that open in response to ligands.
Usually closed, but open when a signal molecule binds
Specifically let in ions such as Na+ or Ca2+
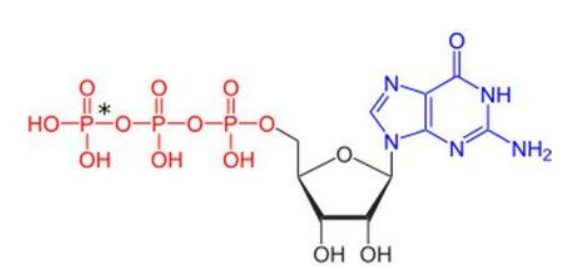
GDP
Inactive form of G protein, binds to G protein.
GTP
Active form of G protein, replaces GDP.
Membrane Receptors
Receptors located in the cell membrane.
Cytoplasmic Receptors
Receptors located in the cytoplasm or nucleus.
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate group to proteins.
Relay Molecules
Transmit signals from receptors to cellular targets in Signal Transduction
protein
Small non-protein molecules or ions
Monomer
Individual unit of receptor tyrosine kinases.
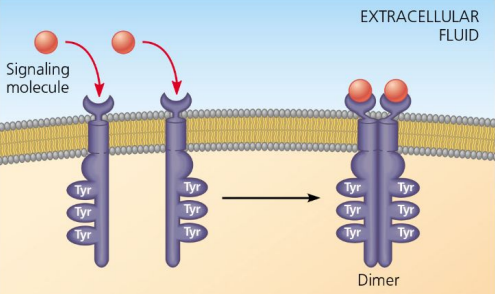
Tyrosines
Amino acids phosphorylated in receptor tyrosine kinases.
Ion Channel
Protein that allows ions to pass through cell membrane.
Na+
Sodium ion, can enter through ion channels.
Ca2+
Calcium ion, can enter through ion channels.
Hormone Receptors
Cytoplasmic receptors that bind hormones.
Conformational Change
Structural change in a receptor after ligand binding.
Cyclic AMP
A common secondary messenger in cells. Used as a Non-Protein Relay Molecule.
Calcium ions
Important ions in cellular signaling processes. Used as a Non-Protein Relay Molecule.
Cellular Response
Outcome of signal transduction pathway activation.
Signal Transduction Pathway
Regulates cellular activities based on signals.
Regulating Transcription
Altering gene expression to produce proteins.
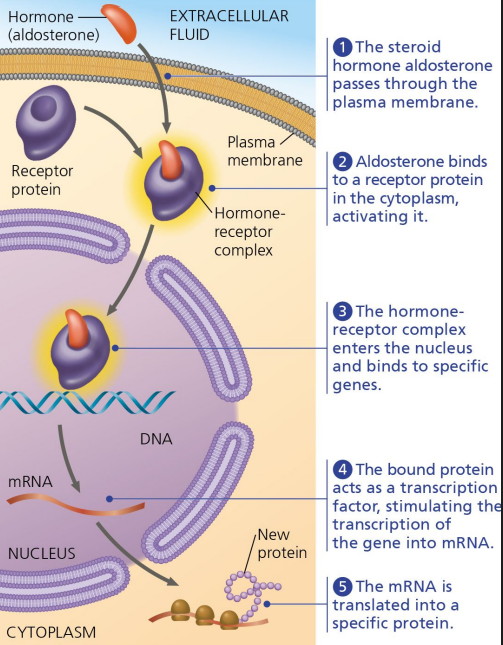
Transcription
Copying DNA into mRNA for protein synthesis. Which the ribosomes then translate into protein
Hormones
Chemical messengers that regulate cellular functions.
Regulating Cytoplasmic Activities
Modifying the use of existing proteins in cells.
Epinephrine
Hormone that activates enzymes in response to stress.
(an example of Regulating Cytoplasmic Activities)
Amplification
Increasing the strength of a cellular response.
Response Variation Factors
Elements affecting how cells respond to signals.
Is the response being amplified?
How many steps in the relay?
Is the response different across cell types?
How efficient is the response?
When does it stop?
Host
Organism infected by a pathogen.
can have immune systems to fight
Pathogen
Disease-causing organism (germ), such as bacteria or viruses (can be prokaryotic & eukaryotic).
Immune System
Defense mechanism against pathogens in organisms.
Innate Immunity
General defense system without memory of pathogens.
Adaptive Immunity
Specific defense that learns and remembers pathogens. Expands overtime.
Physical Barriers
First line of defense against pathogens, like skin.
CRISPR
Bacterial system for cutting foreign DNA.
Defense Mechanisms
Strategies to surround and alert cells to pathogens.
Cleanup Crews
Cells that eliminate pathogens and debris.
Self vs Non-Self Recognition
Immune cells identify body cells versus invaders. Inside mammals.
Mammalian Immune System
Complex barriers and memory cells for defense.
Physical Barriers
First line of defense against pathogens.
complementary
Signal and receptor are ____________: they fit one another in a specific way
dimers
Two monomers bonded together in receptor activation in receptor tyrosine kinases
microbes
Are only pathogens if they make you sick.
bacteria
Keep a DNA log of bacteriophages that have previously attacked