[PCOL and TOXICOLOGY] PPT Introduction to Toxicology (Part 1 intro)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Pupil
Decrease in the size of this is an indicator an substance abuse
Sugar
What can be given to patients who got poisoned
Clinical Examination of Poisoned Patient
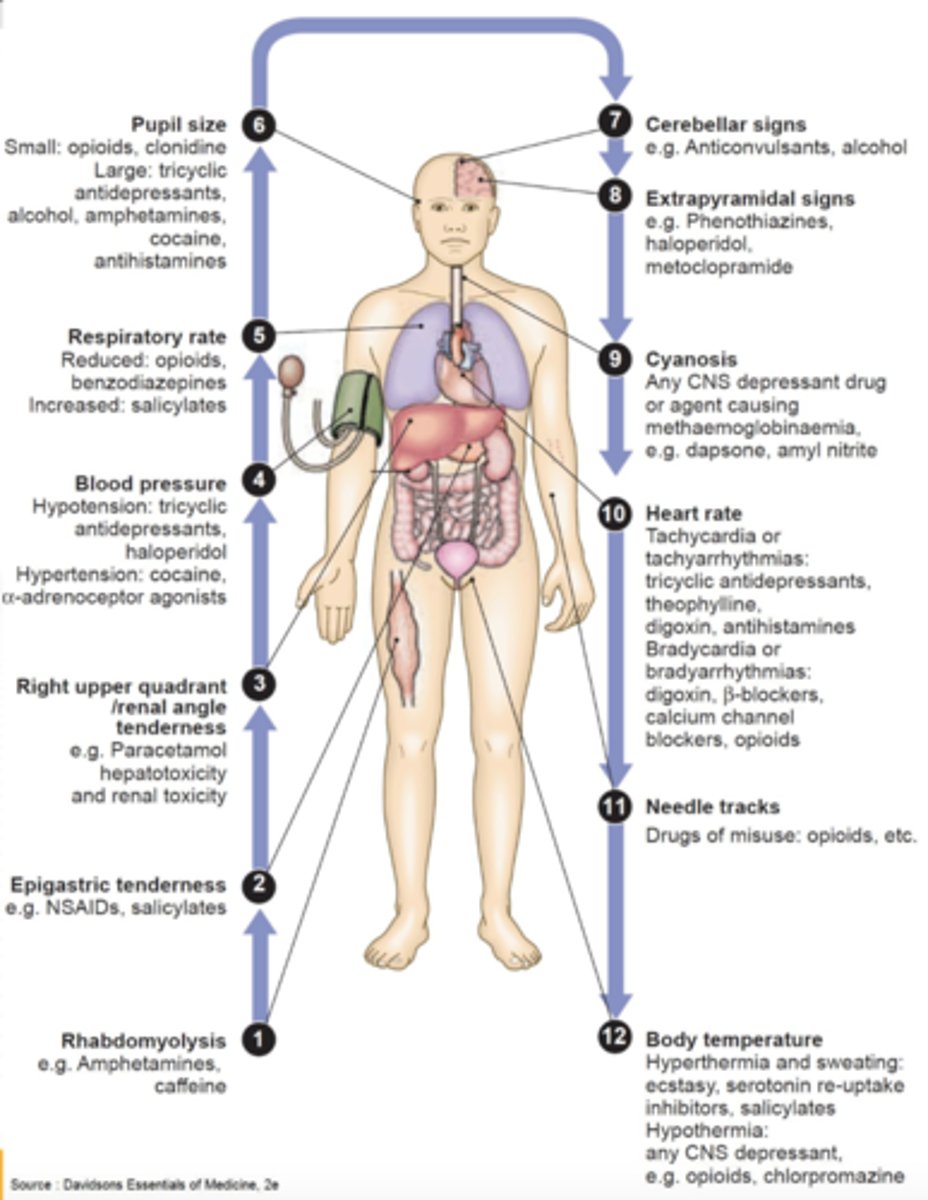
Rhabdomyolysis
Epigastric Tenderness
Right Upper Quandrant/Renal Angle Tenderness
Blood Pressure
Respiratory rate
Pupil Size
Cerebral Signs
Extrapyramidal signs
Cyanosis
Heart rate
Needle tracks
Body temperature
Order of the Clinical Examination of Poisoned Patient
skin
we absorb chemicals through what body sense (commonly now)
Recognition
Prevention
Treatment of adverse effects
Occupational-environmental toxicologists is primary concerned with what (R-PT)
EDTA
Best chalating agent
Occupational Toxicology
Deals with the effects of chemicals found in the workplace
• Emphasis on the:
> Identification of agents of concern
> Identification acute and chronic disease they cause
> Define the conditions they can safely use
> Prevention of absorption of harmful amounts of this chemicals
• Carry out programs for the surveillance of exposed workers and the environment they work
• Regulatory limits and voluntary guidelines have been elaborated to establish "safe" chemical exposure limits for workers
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Who Promulgates the limits
Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs)
• Denotes the standards for specific materials particularly serious toxicity
• These standards are developed following extensive scientific study, stake holder input at hearings, public comment and other steps
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH)
Periodically prepare lists of their consensus versions of "safe" threshold limit values (TLVs) for many chemicals
ecotoxicology
environmental toxicology is Often called _____________, deals with deleterious impact of chemicals, present as pollutants in the environment on living organisms
Environmental Toxicology
Concerned with the toxic effects of chemical and physical agents on population and communities of living organisms within a defined ecosystem
This includes transfer pathways of the agents and their interaction with the environment
Changes in the condition of our planet's air and water is the major international concern
environment
Includes all the surrounding of an individual organism
Particularly air, soil and water
Humans are considered target species
Indicator Species
Are species that provides early warnings of impending human events
Hazard
• Is the ability of a chemical agent to cause injury in a given situation or setting
• The conditions of use and exposure are primary considerations
• To assess the hazard, one needs to have knowledge about both the inherent toxicity of the substance and the amounts to which individuals are liable to be exposed
Use and Exposure
Primary considerations when dealing with hazards
Risk
• Expected frequency of the occurrence of an undesirable effect arising from exposure to a chemical or physical agent
• Risk assessment has become an integral part of the regulatory process in most countries
Hazard
Had a potential harm on you
Risk
The likelihood of a hazard to cause harm
Routes of Exposure
• Route of entry for chemicals into the body differs in different exposure situations
• Industrial setting: Inhalation is the major route of entry
• Transdermal route is also important
• Oral ingestion is relatively minor route
• Primary prevention should be designed to reduce or eliminate absorption by inhalation or topical contact
Oral ingestion
Minor route
Inhalation
Industrial setting major route
reduce or eliminate absorption by inhalation or topical contact
Primary prevention
Quantity, Duration & Intensity of Exposure
Toxic reaction differs from quantity of exposure, duration and rate of exposure
Acute
Indicates a single exposure or multiple exposure that occur over a brief period
from seconds to 1-2 days
Rapidly absorbed this doses of substances that may ordinarily detoxified by enzymatic mechanisms in small doses may overwhelm the body’s ability to detoxify the substance and may result in serious or even fatal toxicity
Chronic
Single or multiple exposure over a longer period
Examples are repetitive handling of chemicals
Exposures to chemicals as air and water pollutants
Environmental Considerations
Poorly degraded chemicals exhibit environmental persistence and can accumulate
Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification
Bioaccumulation
Chemical accumulates within the tissues of the organism, if the intake of a long-lasting contaminant exceeds the organism’s ability to metabolize or excrete the substance
Biomagnification
Magnification of the concentration of a contaminant hundreds or thousands of times as the contaminant passes up the food chain, even if it may be virtually undetectable in water
Elimination
Substitution
Engineering Controls
Administrative Controls
PPE
Give the hierarchy of controls
ESEAP
Elimination
Physically remove the hazard
Substitution
Replace the hazard
Engineering Controls
Isolate the people from the hazard
Administrative controls
Change teh way people work
PPE
Protect the workers with wearing these