Questions from old exams 1-2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Washboarding observed in a section of uterus is most likely caused by which of the following?
loose or worn microtome parts
Agar, gelatin, and Elmer's glue are examples of:
Waterbath additives
In reference to microtomy, what is the clearance angle?
angle of blade in relation to the block face
Bevel angle is
the intersection of the two cutting facets of a microtome blade
A dull blade, too little clearance angle, paraffin accumulation behind the blade, and a warm block may all be causes of this microtomy artifact.
Compression
Melt down and re-embed
Microscopic evaluation of a colon section reveals only two layers.
Review of the paraffin block reveals additional tissue layers deeper in the block.
Which of the following is the best procedure for correction?
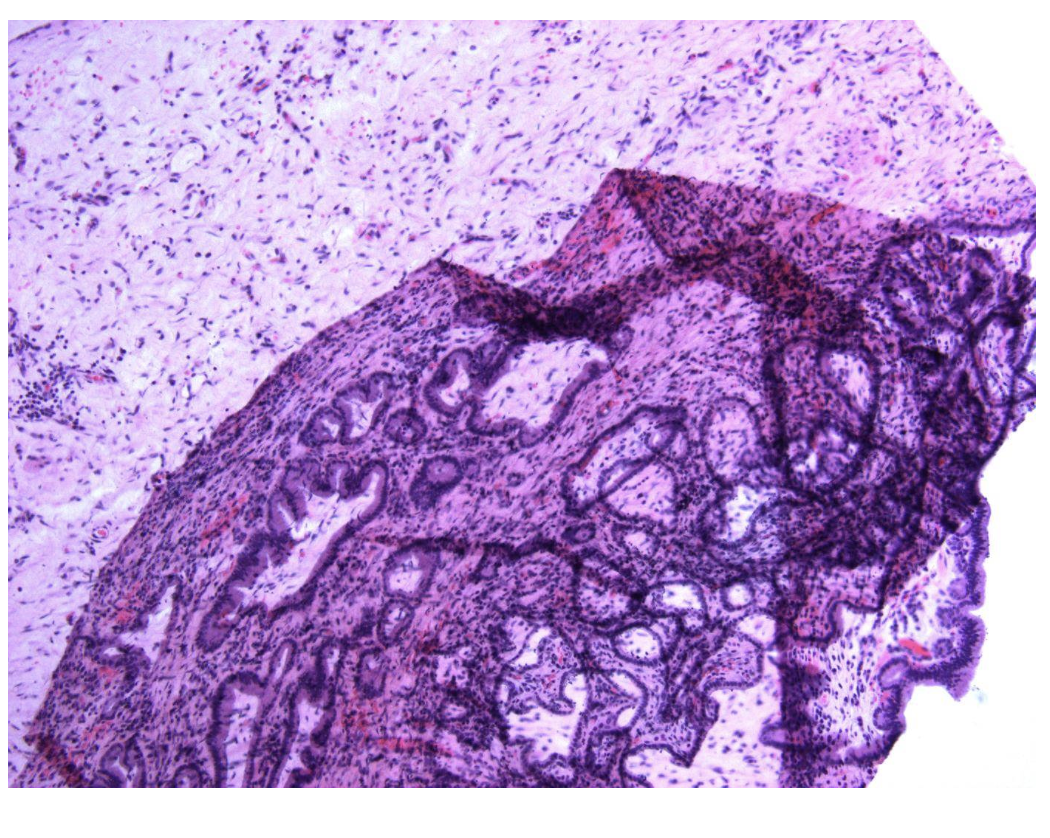
What causes this?
Slide not dried sufficiently
Which of the following methods for cleaning embedding molds is not recommended?
Using the cleaning cycle of the processor.
(is rec = boiling water, mold cleaning station, soaking in xylene)
Holes with ragged edges are seen in a section of liver when viewed microscopically. These were most likely caused by:
Aggressive sectioning
Small intestine should be embedded…
on edge
Incomplete drying can lead to..
wavy sections
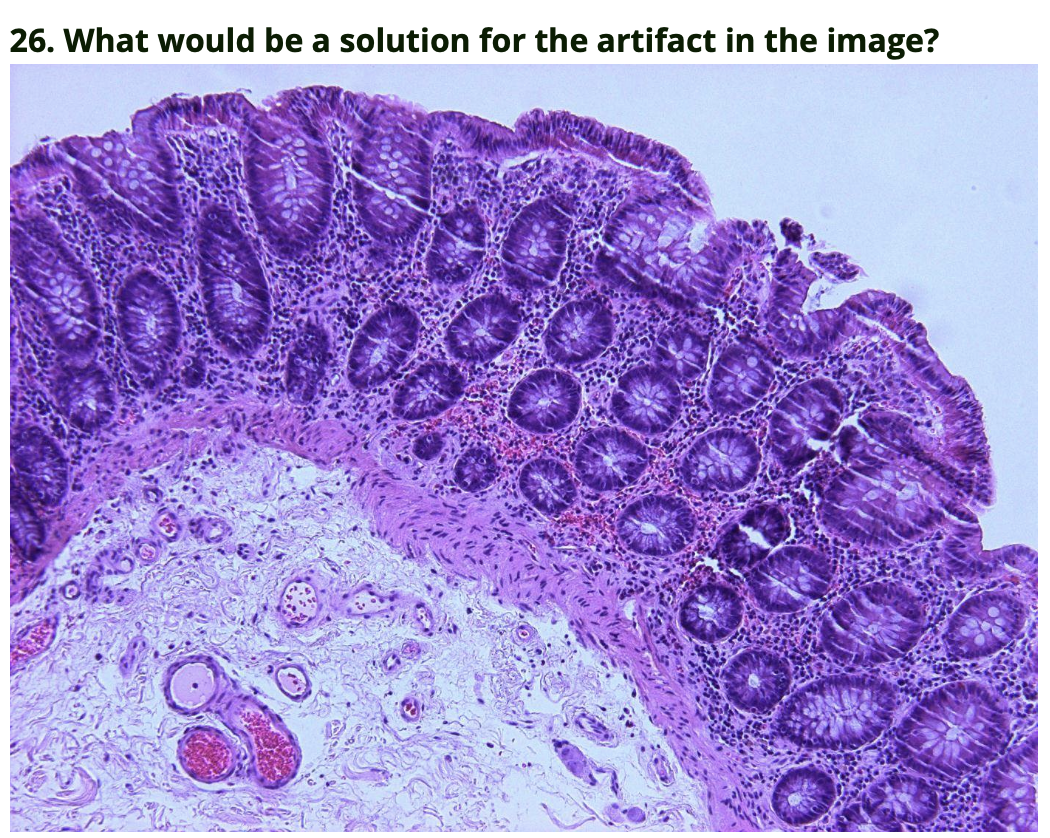
Hydrate longer
When getting thick and thin sections, what is the first thing you should check?
Loose levers/clamps
The temperature of a waterbath should be how many degrees below the melting point of paraffin?
5-10 degrees
Waterbath too cool can cause what?
wrinkles
Which of the following is likely to cause sections to lift from the blade during microtomy?
clearance angle too low
Which of the following tissue types could contribute to washboarding or undulations?
dense, fibrous tissue
Rapid solidifying of paraffin at embedding is important for…
ensuring the best support for tissue
Which of the following artifacts is caused by contamination of the waterbath?
floaters
When sectioning dense fibrous tissue, what waterbath temperature adjustment may be necessary?
increase temp
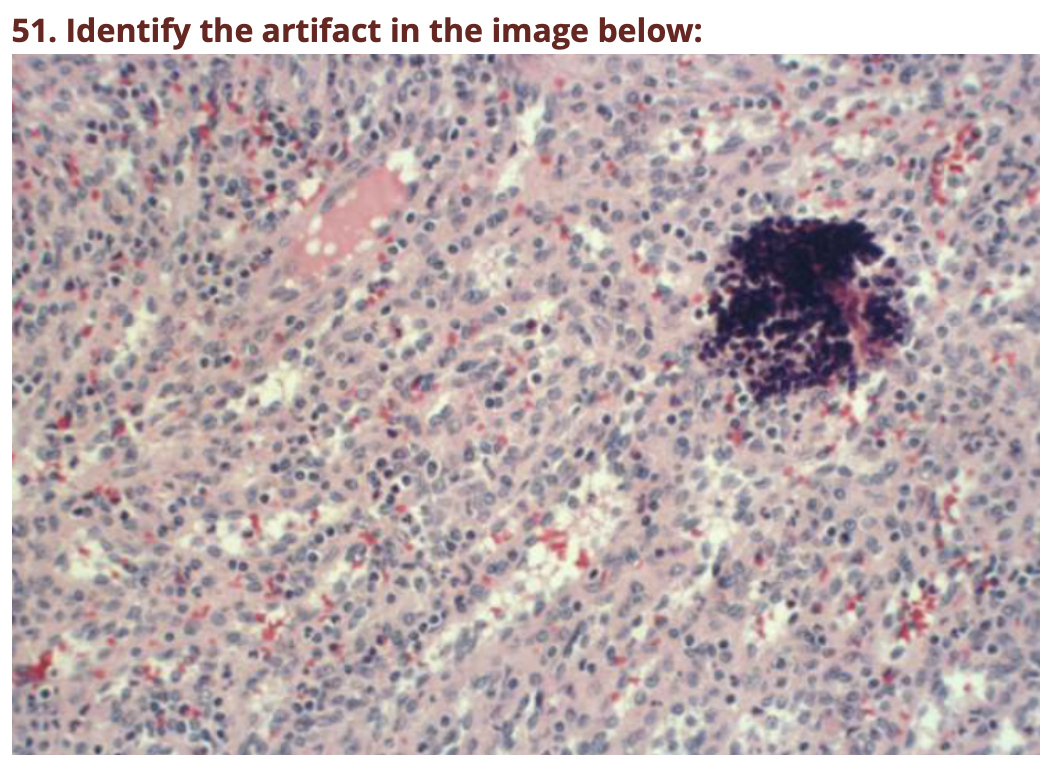
Tissue debris
A ribbon will not form at sectioning. Which can be causes?
Improper clearance angle, dull/dirty blade, loose levers
Microchatter can be caused by…
underhydrated tissue
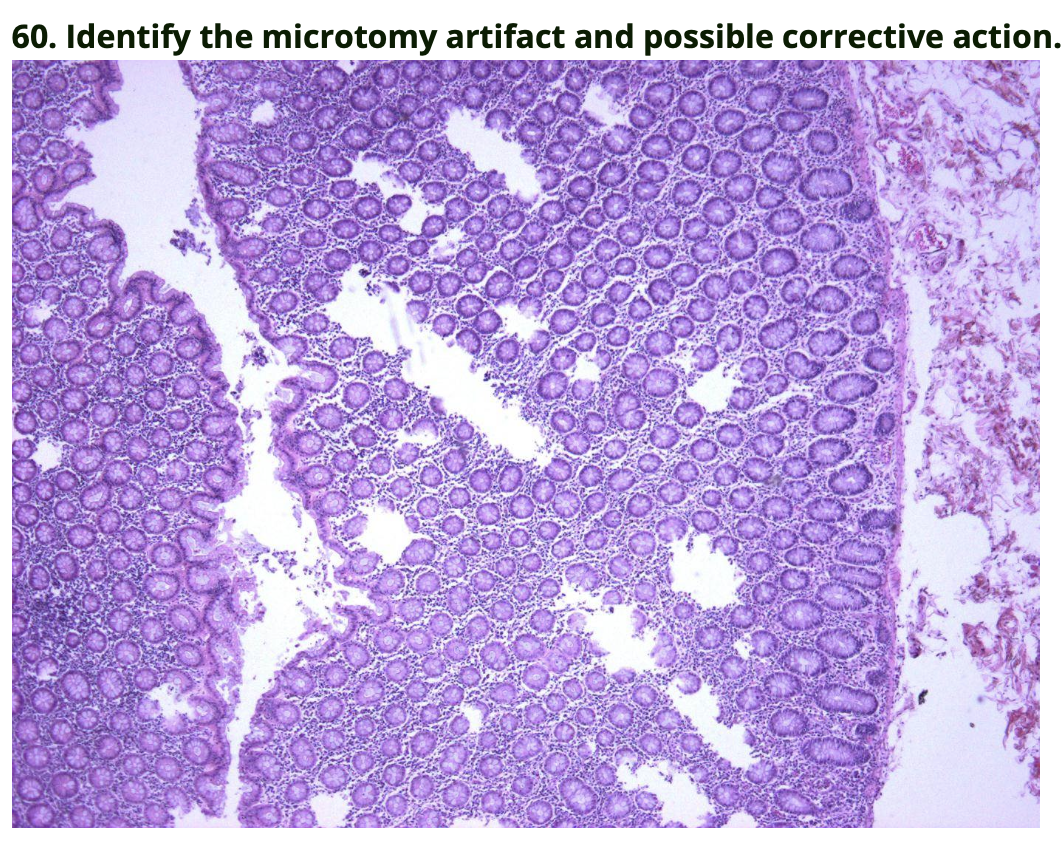
Holes/tears, cut less aggressively
Your sections keep lifting off the blade and sticking to the top of the block when cutting.
Which of the following would be a possible solution?
remove paraffin buildup
What tissue is susceptible to damage if too much pressure applied at embedding?
Brain
What do you put tissues in post fixation?
70% alcohol
Recommended temperature range for all methods that use heat for fixation, i.e. routine processing, primary microwave, and microwave assisted?
45-68
Which formalin solution should CNS tissues be put in?
Formalin ammonium bromide
All additive fixatives:
Chemically rx w/tissue molecules
fixative that penetrates slowly, but cross-links quickly
Glutaraldehyde
Cold ischemic time?
Time from removal from patient to placement in fixative
Formaldehyde is a poor fixative of…
nucleic acids
Formaldehyde penetration…
Pen fast, cross link slowly
Smudgy nuclei w/nuclear bubbling in mucosa is calused by
underfixation
Do not do fixation if ___ is needed.
immunoflourescence
Enzymatic destruction is called…
autolysis
Add copper acetate to fixatives to ___
Protect RBC lysis
e- microscopy pH
7.2-7.4
Which formalin solution is used as a dual purpose fixative for light and e- microsc.?
Modified Millonig formalin
used as a formaldehyde replacement due to lower toxicity and quicker fixation?
Glyoxal
Penetrates slowly, insolublizes lipids and oxidizes carbs?
Chromic acid
What fixative should be avoided for H. pylori demonstration?
Glyoxal
Fixative that lyses RBCs
Acetic acid
Chromate fixatives react with a specific cell type to form a pigment that cannot be prevented or removed in an effect called:
the chromaffin rxn
Chemical that is added to formaldehyde to prevent polymerization to paraformaldehyde?
Methanol
Picric acid ___
dissolves small calcifications
Coagulant fixatives…
denature proteins → Mesh like permeable network
What is a fix and a stain?
Picric acid
what is the maximum concentration of formaldehyde that can be achieved in water?
37-40%
What pigment cannot be prevented but can be removed?
Mercury
EM fixatives?
Paraformal., Osmium tetroxide, glutaraldehyde
A fixation pigment caused by chromate-containing fixatives can be prevented by treating the tissue with _______ prior to exposure to alcohol in processing.
Running water
Mercuric chloride is hazardous, but it produces..
exceptional nuclear detail
Acid hematin/formalin pigment is caused by…
acidic formalin (< 5.5-6)
A disadvantage of formaldehyde is…
it masks proteins antigens in immunohistochem staining
10% formalin contain ___% of formaldehyde?
3.7-4%
Non-coagulant
Which fixative category forms a gel-like network?
How does formaldehyde react with insoluble carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids?
traps them in cross-linked proteins
Chromate fixation pigment can be partially removed with…
acidic alcohol
Formaldehyde ACTION
add., noncoag
Acetic acid ACTION
nonadd., coag
Zinc salts ACTION
add., coag
STEL (15 minutes short term exposure) for formaldehyde is…
< 2ppm
Soluble carbs are ___ during fixation
lost
Replacement for mercury?
Zinc salts
Specimen has remained in 10% NBF for a prolonged period of time. When an H&E slide from the specimen is examined microscopically, a black to dark brown pigment is observed adjacent to the RBCs.
Pigment cause?
Fixative becoming acidic
General function of fixatives?
Protect tissue against distortion during processing
Fixative for phospholipids?
Calcium formalin
Fixation for touch preps and blood smears
Desiccation
It is necessary to add buffer salts to formalin solutions to prevent:
formation of formalin pigment
Formalin pigment can be removed w/
alkaline alcohol
Nuclear bubbling is more commonly seen in tissue fixed in 10% formalin because it…
is a poor nuclear fixative
Microwave fixation is what type of fixation method?
Physical
Formaldehyde + water =
paraformaldehyde
Buffering formalin to a neutral pH is accomplished by adding…
sodium phosphate, monobasic and dibasic
Zinc chloride is the most preferred zinc salt due to a lower health risk.
T/F?
False
Zinc salt precipitation is caused by…
Phosphates in buffered formalin, carbs in water, heat/P/vacuum on processor
The change in the tertiary structure of proteins causing the molecule to become inactive and insoluble.
Denaturation
Fixative category that removes molecularly bound water from tissue
Nonadditive