Lab 12 Animal Diversity & Behavior
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
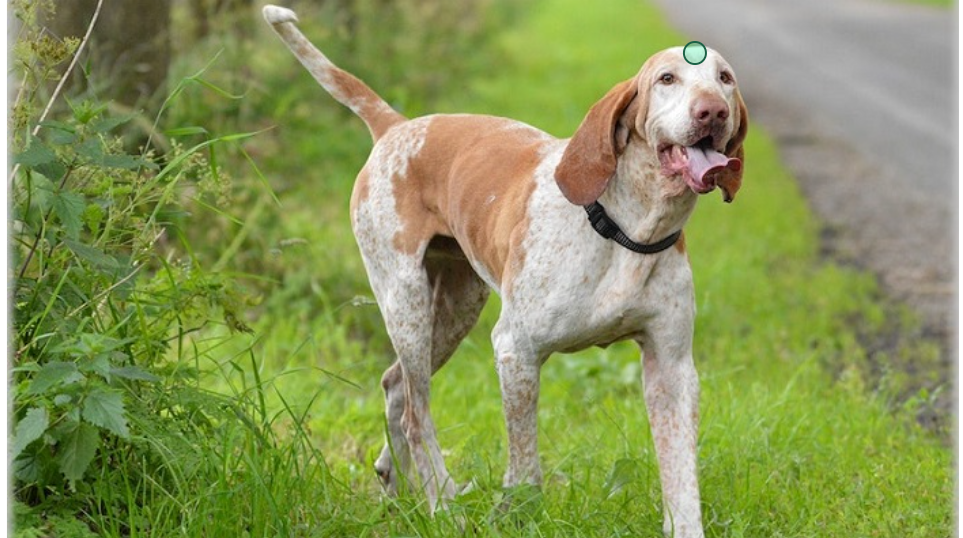

It will be helpful for you to know anatomical directions (dorsal, ventral, anterior, and posterior) when you dissect a preserved crayfish. Anterior end of this dog.
The anterior is the front end of a four-legged animal (and other non-bipeds), where the head is.

The non-venomous scarlet kingsnake (left) and venomous Eastern coral snake (right) occur in the same habitats in the Eastern United States. What type of mimicry is happening here?
Batesian mimicry
characteristics which apply to all animals.
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotrophic
Sort the following biological structures in order from smallest (least complex) to largest (most complex).
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organisms
What is motility?
The ability to move
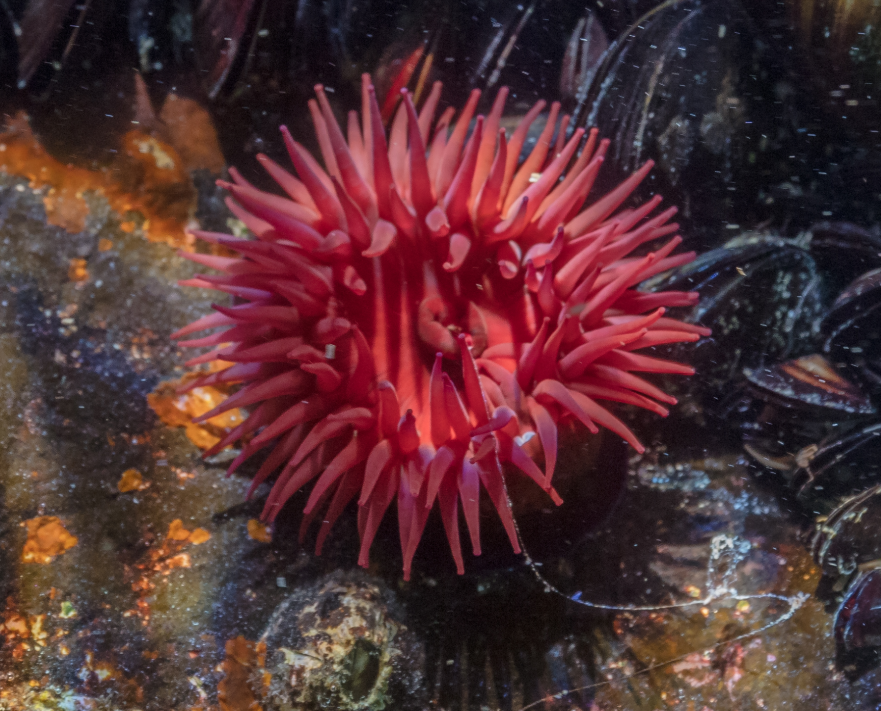

What type of symmetry does this sea anemone have?
Radial symmetry
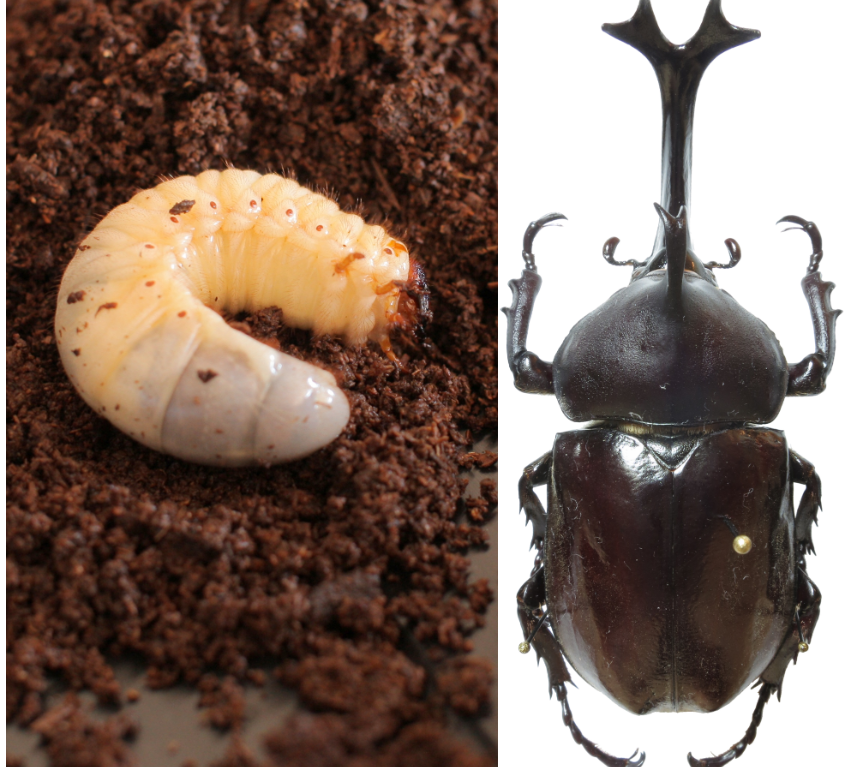

To the left is a juvenile larva of the species Allomyrina dichotoma, the Japanese rhinoceros beetle. An adult of the same species is on the right.
What type of development occurs in this species?
Metamorphosis (indirect development)
Which of the options below accurately describes a difference between free-living planarian worms (Dugesia) and parasitic tapeworms (Taenia)?
Planarians have a digestive system with a pharynx, but tapeworms simply absorb nutrients through their epidermis.
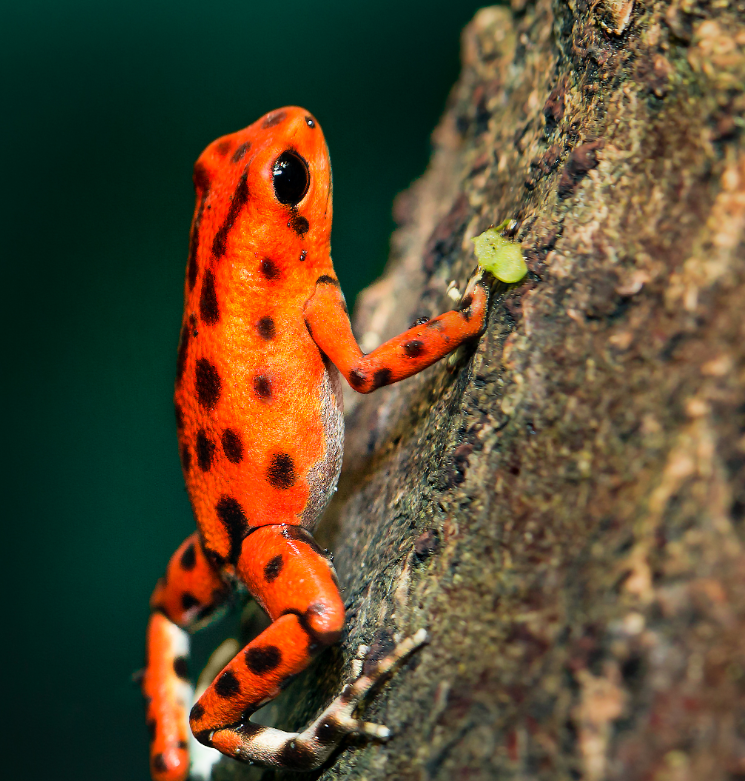

The brilliant orange and black coloration of this poison dart frog is an advertisement that this animal is poisonous. This frog provides an example of:
Aposematism. Aposematism is bright, warning coloration. Although aposematic animals may look pretty, you'll be sorry if you touch or eat them.
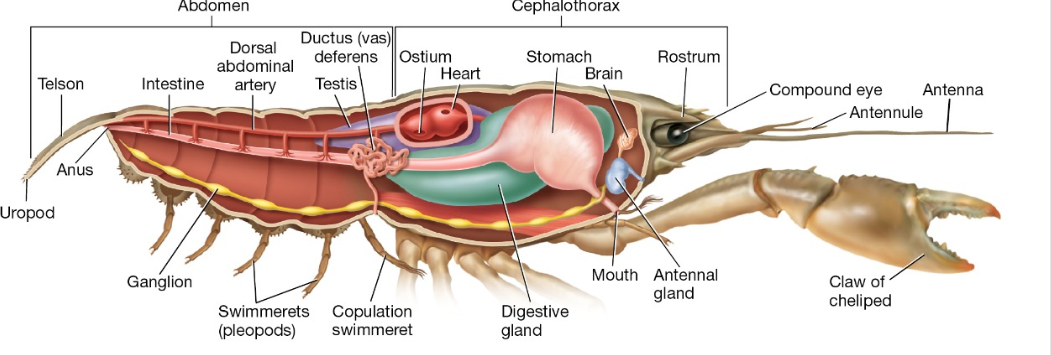
On which surface are locomotor structures called swimmerets located in this crayfish?
The ventral surface
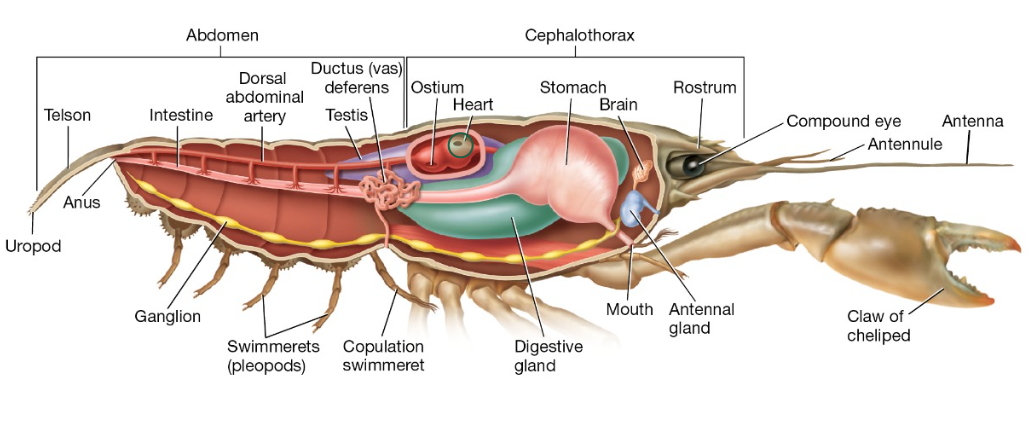
Find and click on the heart of this crayfish. It will be one of the features you can see during your on-campus dissection.
Of which phylum do crayfish and pillbugs belong?
Arthropoda