BE202-Chapter2_Review Note
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
State an advantage of organelle compartmentalization
Allows organelles to have a distinct internal compartment that contains specialized chemicals for carrying out particular functions
5 types of membranous organelles
Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria
4 types of non-membranous organelles
Ribosomes, proteasome, vaults and centrioles
Describe the structure of rough ER
consists of flattened interconnected sacs
outer surface contains ribosomes
Describe the function of rough ER
synthesize and release proteins into ER lumen
transport within or outside the cell
Describe the structure of smooth ER
a network of interconnected tubules and lack ribosomes
Describe the function of smooth ER
collects proteins from rough ER
package the proteins and transport it throughout the cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
a fluid-filled membranous system distributed throughout the cytosol
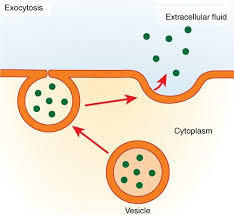
Exocytosis
Materials inside the cell are released to the exterior.
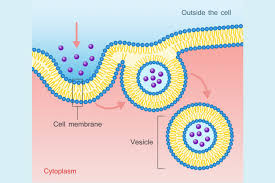
Endocytosis
Materials outside the cell are taken into the cell.
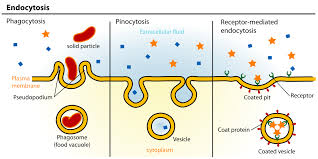
Describe the different forms of Endocytosis
Pinocytosis
a droplet of ECF is non-selectively internalized
Receptor-mediated Endocytosis
selective process that enables cells to internalize specific large molecules from its environment.
Phagocytosis'
a process which large multi-molecular particles are internalized
Which organelles serve as the intracellular “digestive system”?
Lysosomes
it contains hydrolytic enzymes
breaks down raw ingredients
remove worn-out organelles
Compare lysosomes with peroxisomes
Lysosomes
contains hydrolytic enzymes to break down raw ingredients
Peroxisomes
contains oxidative enzymes and perform detoxifying activities by removing hydrogen atoms
Distinguish among Cellular Respiration, oxidation phosphorylation, and chemiosmosis
Cellular Respiration
collection of intracellular reactions, where the molecules are broken down to form ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation(O.P)
process where ATP synthesizes using energy released by electrons while transferred to oxygen
Chemiosmosis
last step of O.P and involves the production of ATP via the activation of ATP synthase
Describe the Structure of Mitochondria
enclosed by double membrane
outer membrane that surrounds the organelle
inner membrane contains multiple folds (cristae)
most inner cavity formed by cristae (matrix) is filled with gel-like solution
Role of Mitochondria in Cellular Respiration
major role in ATP production
Citric acid cycle reaction occurs in the matrix
O.P reaction take place on the inner membrane
Distinguish between the oxidative enzymes found in peroxisomes and those found in mitochondria
in Peroxisome
uses oxygen for detoxification
in mitochondria
uses oxygen in synthesizing ATP
Cell epend energy on what three categories of activities?
synthesis of new chemical compounds, membrane transport processes, and mechanical work
List each component of cytoskeleton
microtubule, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
Describe the function of microfilaments
major role in cellular contractile systems
including muscle contraction
Describe the function of microtubules
maintaining the shape of cells
coordinating complex intracellular movements
serves as the main structural component of cilia and flagella
Describe the function of Intermediate filaments
resist mechanical stress placed on cells