Part 1: Electron Beam Therapy & Mass Stopping Power
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
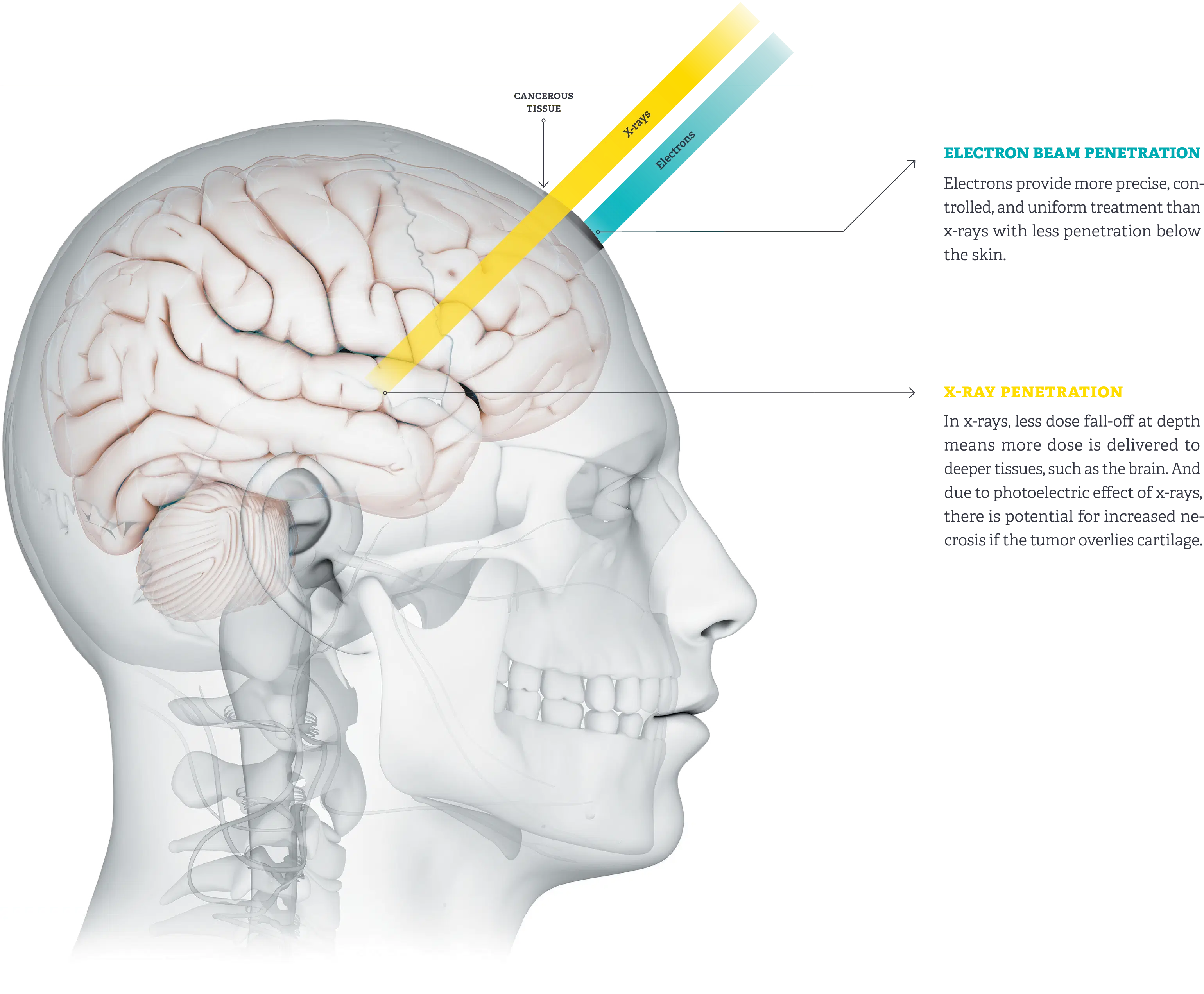
What is the advantage that electron beams offer?
Being able to tx superficial lesions with virtually no dose to underlying tissues
Which was the first machine to have electron therapy?
Van de Graff
Electron therapy began as an alternative to ___ therapy
KV
Besides Van de Graaff, what other machines have electron beam capability?
Van de Graaff
Linacs
Betatrons
What are the most useful energy ranges for electron energy?
6-20 MeV
(6 is the lowest and 20 is the highest)
What are the 3 Major Characteristics of Electron Beams?
Sharp fall off of dose
Tho this characteristic tends to fade with increasing energy
No exit dose
skin sparring is only modest or non-existent
Extra:
What does “sharp fall off of dose” mean?
Is there really no exit dose?
You start off with a really high dose at the surface, and then it rapidly falls off at around 80% to 0 in no time
There is a bit of exit dose because when we tx with electrons we generate a few x-rays in the patient’s body which can exit from the other side.
What sites are commonly treated with electron therapy?
Mnemonic: CHi BS
Chestwall for breast
some H&N ca’s:
Parotid salivary gland
Boost dose for superficial nodes or scars
Skin & lip

Field arrangement for parotid salivary gland? Reasoning?
single e- field coming in from a straight lateral.
Reasoning: When you tx with e- you minimize the dose to the other parotid & maintain salivary function reducing risk of xerostomia.
fyi: Cuz the parotids are just below the masseter muscles
term. Chestwall
def. all the tissues between the skin and the lungs
Extra: Why do we boost scars?
seeding of scars: e.g. During a lumpectomy scar examination, the pathologist determines there are + margins cuz scalpel had some cancer cells on it, which could have been seeded/ spread as the scalpel was coming out of the patient.
Why do electrons interact with tissue very differently than x-rays?
electrons have:
(-) charge
mass
How does an electron react in tissue?
elastic and inelastic collisions
term. Mass Stopping Power
def. The rate of energy loss per gram per cm²
FYI: rate of E loss/ gram/ cm²
Explain Mass Stopping Power in your own words.
Energy is speed.
↑ Speed = ↑ Energy
X-rays travel at the speed of light, e- travel at sub-light speeds
↑ e- interact with stuff = ↑ slow down = they lose Energy
Mass Stopping Power relates to how much Energy (speed) is lost as electrons interact with matter
Extra:
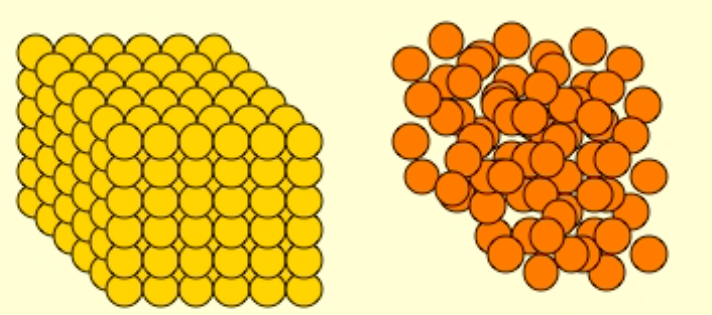
Label Low density vs High Density
yellow= high density
orange = low density
the __ the z# (atomic #)/ density = the ↑ the Mass Stopping Power
Lower
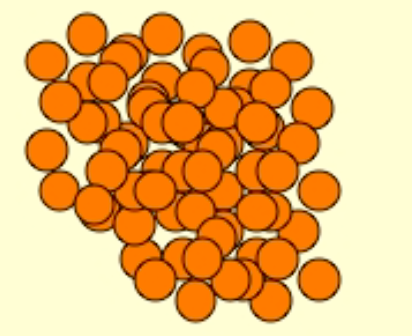
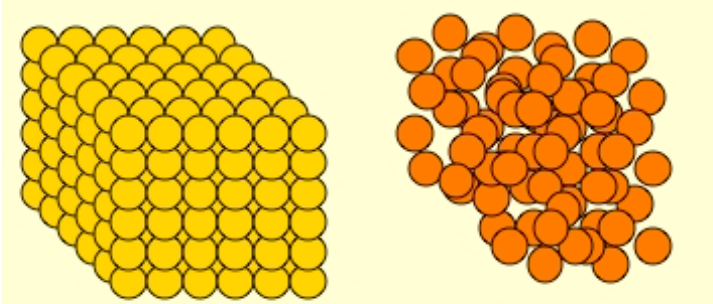
How come low z# material has a higher Mass Stopping Power (slows e- down more) than high z# materials?
(looking at the picture wouldn’t it make sense that the high z# material would have a greater mass stopping power?)
high z# materials = fewer e-/ gram
e- beams depend mostly on collisions with other e- (as opposed to photon beams)
high z# materials = e- more tightly bound = less available for interactions
FYI: e- from e- beam have to knock out e- in patient’s body, and that’s how dose is deposited
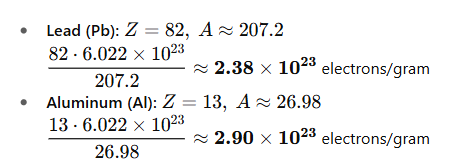
term. Delta Rays
def. electrons scattered with enough Energy to cause further ionization & excitations in other atoms
FYI: An atom is ionized creating a recoil e-, if the recoil e- has enough E to cause other interactions in other atoms, then that recoil e- has a new name: Delta Ray
What accounts for the energy transferred by Delta Rays
Restricted mass collisional stopping power
(low/high) Z# materials are sued for making scattering foils.
What material is commonly used?
Why?
high
lead
↑ Z# = ↑ big atoms = ↓ likely to get their e- knocked out
Big atoms create a pinball effect, e- bounce all over the place, which scatters the beam. The scattered beam get’s down to the patient more uniformly rather than having an unscattered pencil beam.
high z# scatters the dose (e- bounce around)
low z# absorbs the dose (e- from beam interact with other e-)
What 2 types of scattering system are there?
Dual scattering system
Magnetically scanned beam (powerful magnets tear apart/ unravel the pencil beam)
Pro and Con of Magnetically Scanned Beam vs Dual Scattering beam
Advantage: No scattering foil which creates some Brems x-ray contamination;
Disadvantage: It’s much more complex
Pencil beam measures__ in diameter
3mm
When in electron beam mode:
what is moved out of the way?
What gets put in place?
x-ray target & flattening filter
scattering foil
scattering foil & target are mounted in a carrousel system
Where is electron beam energy defined (characterized) at?
at the skin surface
(i.e. it measured at the skin surface and that’s where we call it, 6 MV, 9MV, 20MV etc.)
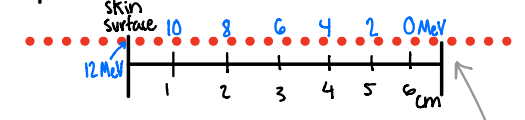
Bottom line for mass stopping power = the rate of energy loss of electron beam energy is approx. ___ (measurement) in ____ (medium)
the rate of energy loss of electron beam energy is approx. 2 MeV/ cm in soft tissue and water
how much energy will a 12 Mev electron have at
0 cm in tissue
1 cm in tissue
2 cm in tissue
3 cm in tissue
4 cm in tissue
5 cm in tissue
6 cm in tissue
12 MeV
10 MeV
8 MeV
6 MeV
4 MeV
2 MeV
0 MeV
What is the Dmax for electron beams?
e- DON’T follow a linear relationship with Energy regarding Dmax Depth
While Dmax depth is not a very useful terminology for electron beams, isodose curves are still used in planning tx. (fyi: cuz the maximum depth is usually at the surface with electrons)
fyi: But the isodose curves are very individualized for each tx, they vary depending on field size & shape