Physics SAT4 - Light and Atoms
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
EM Waves
Composed of an oscillating E field and B field
How EM Waves are Produced
Charged particle produces E field that oscillates with charge movement, moving charge produces oscillating B field
Plane of Polarisation
The direction of oscillation, i.e. the E field
Polarised Light
Light with the plane of polarisation on the same plane, restricted to 1 plane
Constructive Interference
Occurs when waves are in-phase, PD = m x lambda
Destructive Interference
Occurs when waves are out of phase, PD = (m+1/2) x lambda
Coherence
Two waves maintain a constant phase relationship, must have same wavelength/frequency
Monochromatic Light
Light of a single colour (wavelength/frequency), not necessarily coherent
Incandescent Light
White light produced by a heated substance, not monochromatic or coherent
Diffraction
The bending and spreading of waves when passing an obstacle, slight width approx. equal wavelength
Bright Fringes
When waves are in-phase at the optical screen
Dark Fringes
When waves are out of phase at the optical screen
Creates Coherency
Passing an incoherent light through a single slit
Transmitting Antenna
Attached to AC, causes charge oscillation and transmits EM wave in that plane
Receiving Antenna
Charge oscillates as it receives EM wave in the same plane, interpreted as signal
Conditions for Antennae
Must be in the same plane (both vertical/horizontal) to receive signals
Young’s Double Slit Experiment
Distance between successful maxima (delta y) is assumed to be constant
Intensity Pattern
Drops off from the central maxima, but intensity curve is modulated due to single-slit effects
Transmission Diffraction Grating
Many slits, d = 1/lines per m
Benefits of Diffraction Grating
Produces more constructive/destructive interference, fringes are bright and sharp, and easy to compare spectra to known elements
White Light Pattern
Central maximum is white, inner maxima are violet as it has small wavelength, further out maxima are red as it has larger wavelength
Photons
Bundles of energy/quanta that behave as a particle
Photon Properties
Zero mass, zero charge, travel at speed of light
Photoelectric Effect
EM radiation incident on metallic surface causes electrons to be released, proof of the particle model of light
Photoelectric Effect Process
Light passes through opening in evacuated tube and hits photosurface, which emits electrons. Some electrons reach collecting plate and attracted to now positively charged photosurface. thus moves through external circuit and current detected.
Einstein’s First Postulate
Monochromatic light consists of discrete quanta, called photons
Einstein’s Second Postulate
Photons are absorbed or emitted on an all-or-nothing basis
Einstein’s Third Postulate
If absorbed by the material, a photon transfers its entire energy to one electron, emitting it instantaneously
Electron Energy Variability
Variation in KE of emitted electrons, as electrons require more energy to emit from lower shells
Work Function
Minimum energy required for the least attracted electron to be emitted
Threshold Frequency
Frequency of photon required for least attracted electron to be emitted
Light Intensity
Greater intensity means more photons and more electron emission, but does not affect electron energy
Stopping Voltage
When charge of collecting plate is negative enough so that only most energetic electrons make it across - as V increases, charge becomes more negative
X-Rays
Electrons accelerated across large potential difference to strike a metal target, resulting in high energy photons being released
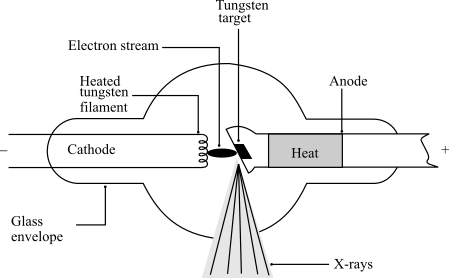
X-Ray Process
Electrons released by filament as thermal energy is provided, electrons accelerate across V and gain KE, electrons interact with target metal and release photons in x-ray spectrum
High Attenuation
Material scatters more x-rays, caused by thicker/denser material and greater effective atomic number
Low Attenuation
Material absorbs more x-rays
X-Ray Image Creation
Photographic film is white, turns black when protons hit (i.e. dense areas stay white)
Optimising X-Rays
Greater hardness (energy), decreased exposure time
Increased Filament Current
Greater intensity due to increase in electrons and thus more photons emitted. Energy remains same
Bremsstrahlung
Continuous spectrum of x-ray frequencies
Characteristic Peaks
Sharp peaks in intensity on x-ray spectrum for given frequencies
Max Frequency Photon
The highest frequency produced on an x-ray spectrum
de Broglie Wavelength
Wavelength of moving particles dependent on momentum
Davisson Germer Experiment
Electrons accelerated to 54eV, scattered electrons produce intensity graph that varied with angle
Continuous Spectrum
Continuous range of frequencies/wavelengths/energies of light produced through incandescence, distribution dependent on temperature
Incandescence
All particles in constant random motion, thus oscillating, which produces all frequencies of EM radiation and hence continuous random spectrum
Increased Average KE
Increased temperature, oscillating at higher frequencies
Emission Spectrum
Specific lines produced through exciting electrons, black with coloured bands
Absorption Spectrum
Continuous spectrum with black bands of emitted light, typically corresponding to emission spectrum
Ground State
n=1, electrons requires most energy to emit
Ionisation Energy
Energy requires to remove an electron from the ground state
Photon Absorption
When photon energy corresponds exactly to energy difference, electron jumps to matching energy level
Photon Emission
When excited, electrons will eventually drop to ground state and release photon with energy corresponding to E-level transition
Multiple Photon Emission
Excited electrons make multiple jumps down and release multiple electrons
Lyman Series
Electron drops to ground state, emits UV photon
Balmer Series
Electron drops to n=2, emits visible light
Paschen Series
Electron drops to n=3, emits infrared photon
Production of Absorption Lines
Hydrogen must be heated to excite electron, sit in n=2 instead so visible light is emitted
Fraunhofer Lines
Core of sun produces white light through incandescence, outer layers have electrons existing in energy levels thus the Sun produces absorption spectrum
Fluorescence
Process of converting single high energy proton into multiple smaller energy photos through absorption/emission
Fluorescence Process
High energy photon absorbed, jumps to high energy state, jumps to ground state and emits series of lower energy photons
Stimulated Emission
If electron in metastable state and photon matching energy transition is incident on atom, forced transition occurs. Incident photon not absorbed, and emitted photon is identical
Benefits of Stimulated Emission
Coherent, uni-directional and monochromatic light, only occurs when there is population inversion (majority of electrons in metastable state)
Lasers
Use stimulated emission to produce EM radiation, concentrated in a small area and travel over large distances
Population Inversion
Substance must have a metastable state, with majority of electrons in an excited state
Production of Coherent Light
Atoms must be in population inversion, higher E level must be metastable, and mirrors are used to trap emitted photons in system
Fermions
Particles that have mass
Gauge Bosons
Particles that are force carriers
Antiparticles
Identical to their particle counterparts with opposite quantum numbers
Quarks
Fundamental particles that make up hadrons
Leptons
Fundamental particles with six flavours (electron, muon, tau) with neutrino counterparts
Baryons
Hadrons that are made up of 3 quarks, B=1
Mesons
Hadrons that are made up of 1 quark and 1 anti-quark (B=0)
Quark Baryon Number
1/3
Quark Confinement
Quarks cannot be observed in isolation
Lepton Family Number
Have +1 corresponding to their type, and 0 for all other families
Gravity
Fundamental force that acts between anything with mass, weakest
Electromagnetism
Fundamental force that acts between charged particles, relatively strong
Strong Nuclear Force
Fundamental force that acts between quarks/hadrons, strongest but very short range
Weak Nuclear Force
Fundamental force that acts between leptons during beta decay, weak
Photons
Gauge boson particle for electromagnetism
EM Force through Bosons
Virtual photons are instantaneously emitted by charge, causing recoil as photons have momentum. If repel, shoot toward like charge. If attract, shoot toward opposite charge.
Gluons
Gauge boson particle for strong nuclear force
W+, W- and Z0
Gauge boson particles for weak nuclear force
Graviton
Theoretical gauge boson for gravity, not yet observed
Active Medium
Materials in a laser used to emit the light, can be solid, liquid or gas
Pump/Energy Source
Device in a laser that supplies energy to the active medium to excite electrons and lead to a population inversion
Optical Cavity
Structure in a laser that encases active medium and consists of parallel mirrors, which reflect photons back to stimulate photon emission AND allow light to escape as laser beam
Parts of a Laser
Active medium, pump/energy source, optical cavity