Lecture 30: introduction to the immune system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is the immune system and what is it made up of?
its used to fight off pathogens
its made up of cells, organs, proteins and tissues
it also recognises abnormal cells like cancer cells(sometimes are not fought off as they identify as self therefore arent attacked)
what are the main components of the immune system?
organs and cells(thymus and spleen which produce wbc to fight off infection)
lymph system(helps immune cells travel around the body)
circulatory system
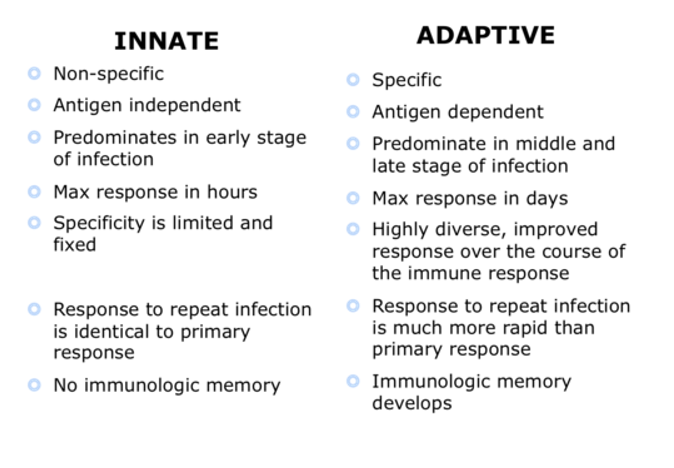
what are the subsets of the immune system?
acquired immunity and innate immunity
acquired is specific and occurs overtime
innate is non-specific and from birth
what is innate immunity ?
natural
non-specific defense mechanism
fast and initial response of the body to eliminate microbes
what is the function of innate immunity?
physical barriers such as skin, tears, mucus all protect against pathogens
sometimes bacteria can get around the barriers
innate immunity uses phagocytosis to remove pathogens
sometimes backup is needed so signal to adaptive immune system
what are the components of innate immunity?
physical/structural: barriers such as mucous lining in nasal passages
chemical barriers: stomach acid(some pathogens are ingested through food)
protective cells: natural killer cells, white blood cells
also sneezing, coughing and vomitting
what are some of the physical and chemical barriers
skin, hair, cilia
mucus membranes
mucus
blood brain barrier
tears
digestive enzymes in mouth
stomach acid
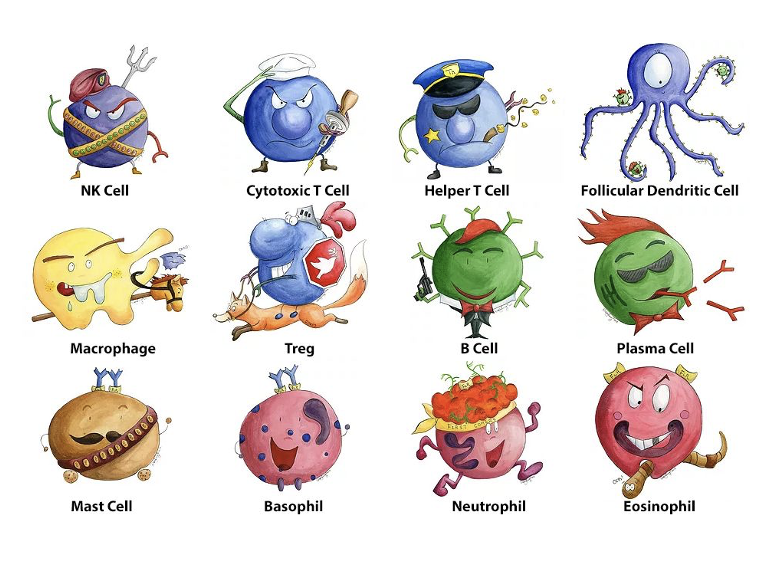
what are the cellular components of innate immunity and what do they do?
Macrophages, Neutrophils and Mast cells
involved in the removal of pathogens via phagocytosis
Natural killer cells
eliminate infected or abnormal host cells
Dendritic cells
microbicidal
secrete chemicals which activate other immune cells
what is inflammation
when physical barriers are breached, innate immunity triggers an inflammatory response
releases signalling molecules such as cytokines and chemokines
they recruited immune cells to the site of infection
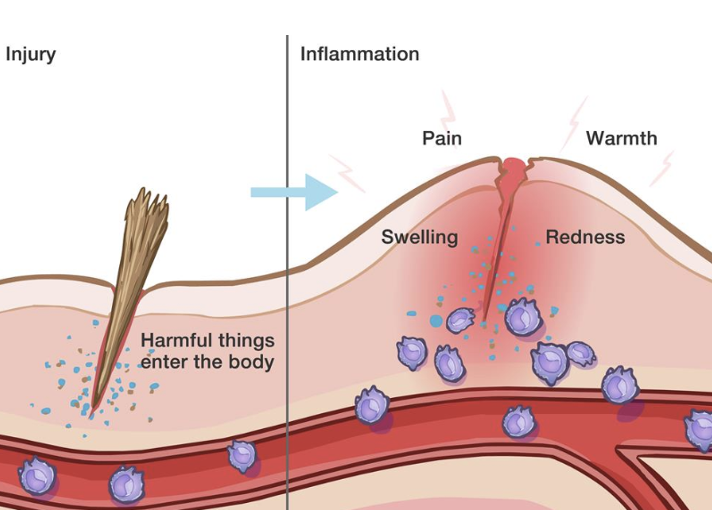
what are the classical signs of inflammation
associated with heat, pain, redness and swelling
what are the 2 main things inflammation does?
helps eliminate pathogens
helps promote tissue repair
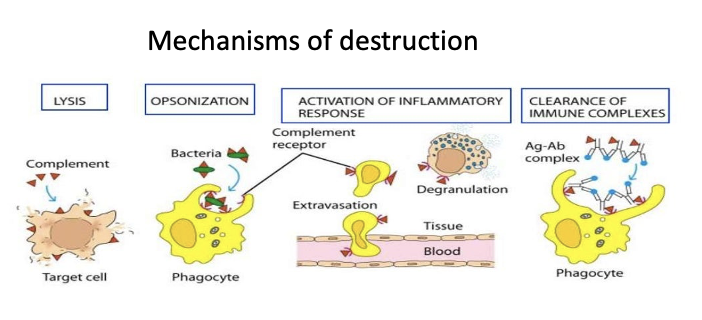
what is the complement system?
a cascade of plasma proteins in innate and adaptive immunity
they are produced in the liver but circulate the blood which helps destroy pathogens
activation of immune cells
bridge between innate and adaptive immunity
what is adaptive/acquired immunity?
specific and targeted defense mechanisms
initiated when innate response doesnt clear the pathogen
detect specific antigens(proteins) on the pathogen
remembers pathogens and provides a longer lasting protection
slow response
what are the 2 branches of adaptive immunity?
cellular immunity(cells)
humoral immunity(production of proteins)
what is the function of adaptive immunity?
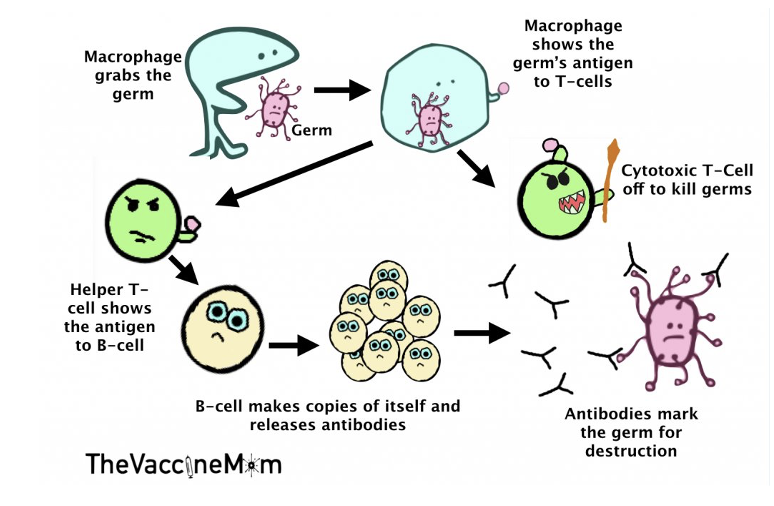
made up of T and B cells
T helper cells help the B cells b sending chemical signals to activate B cells to target pathogen and produce antibody to identify pathogens
T killer cells identify infected host cells and sends chemical signals to cause them to be eliminated form the body(cytotoxic)
what is cell mediated immunity?
dendritic cells present the antigen to the T cells to produce a response
Cytotoxic t-killer cells attack and kill infected cells
T helper cells help B cells produce antibodies
regulatory T cells help maintain immune balance and prevent excess responses
Memory T cells remember the pathogen and bring about a response much faster
what is humoral immunity?
involves B cells
they produce antibodies in response to antigens
they mark the pathogens to be destroyed by phagocytosis etc
overview of adaptive immunity:
what is the comparison between innate and adaptive immunity?

cells overview of the immune system:
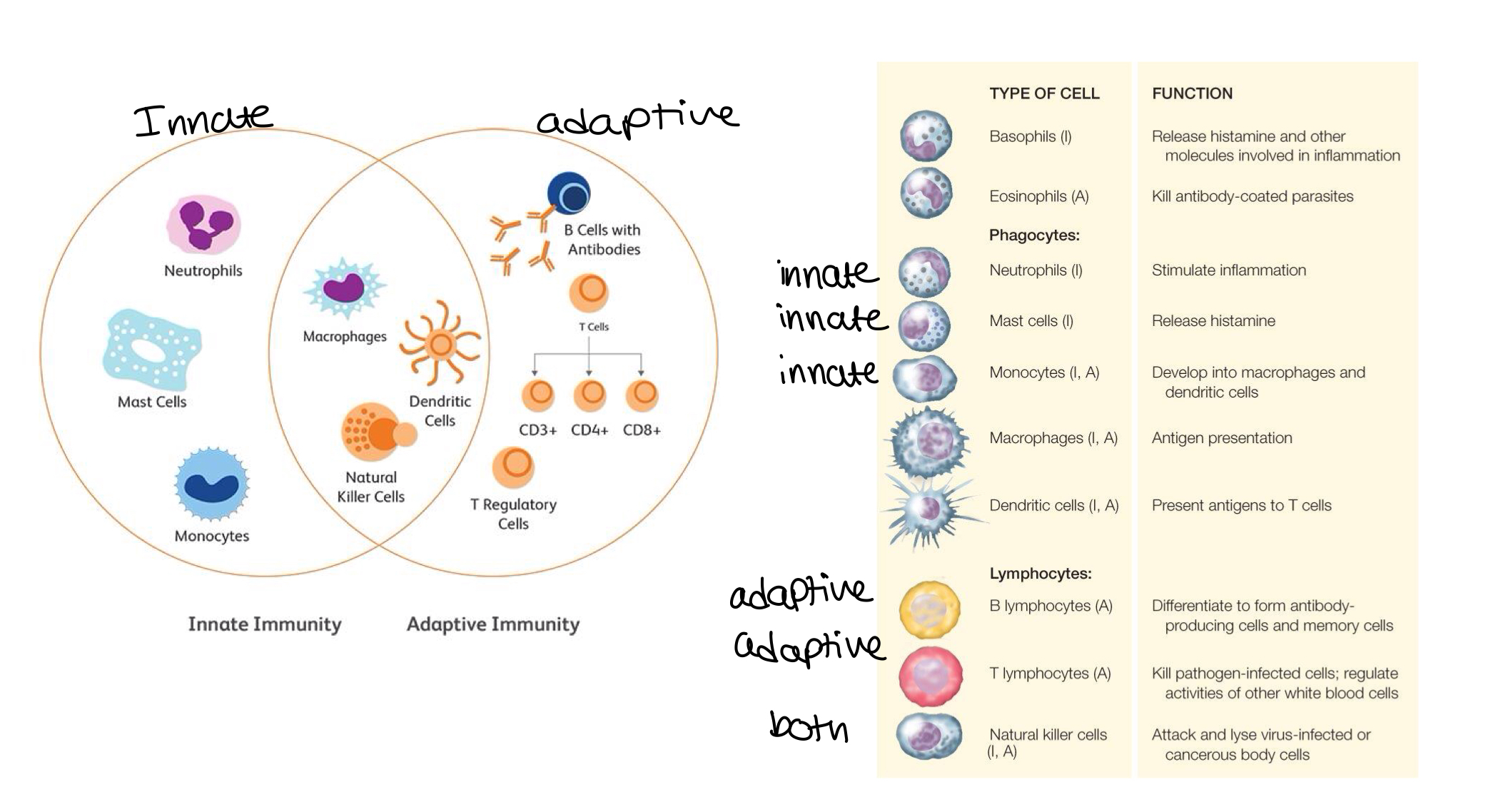
what is immunization?
immune system is stimulated to produce an immune response against specific pathogens
can be through natural infection or vaccines
what is vaccination?
produces immunity to a specific disease
vaccines contain weakened or killed pathogens which introduce antigens which trigger an immune response
forms memory B cells
remembers and eliminates the pathogen when re-exposed
what are the types of vaccines?
Live attenuated vaccine- MMR
inactivated or killed vaccines- hepatitis A
subunit, recombinant or conjugate vaccines- HPV
mRNA vaccines- COVID 19
what are allergies?
an overreaction of the immune system to normally harmless substances such as pollen
hypersensitivity
through inhalation, ingestion or contact with the skin
what are the symptoms of allergies
itching
sneezing
rash
anaphylactic shock- constriction of airways, leads to death sometimes
what is autoimmunity?
when the immune system mistakenly attacks the bodys own cells and tissues
genetic predisposition
environmental factors may trigger an autoimmune response
what are examples of autoimmune diseases?
Rheumatoid arthritis
ulcerative colitis
psoriasis
diabetes
multiple sclerosis