DH105 Dental Anatomy Midterm
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Transverse ridge
If two triangular ridges join, what is the entire ridge called?
distal
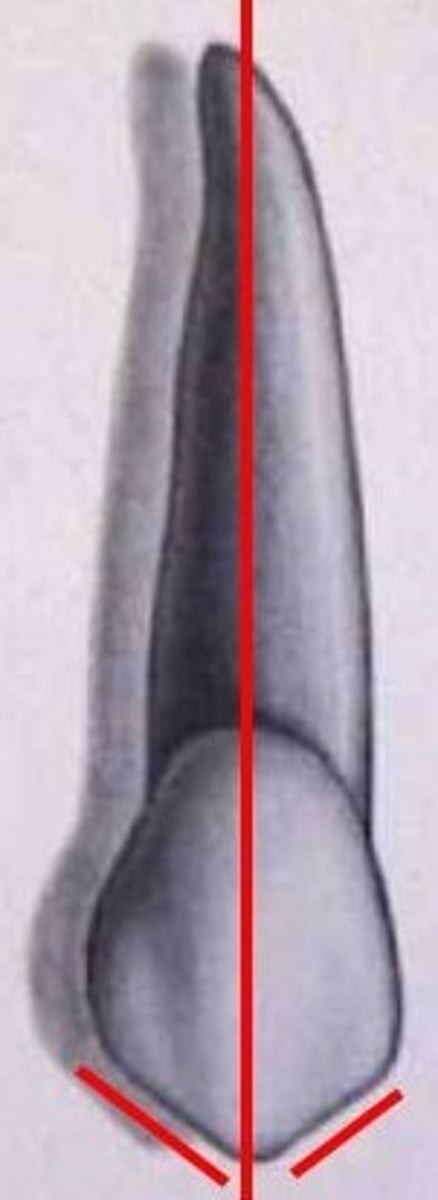
In a facial view of a maxillary central incisor, vertical lines may divide the crown into thirds called 1. mesial, 2. middle, and 3. _______.
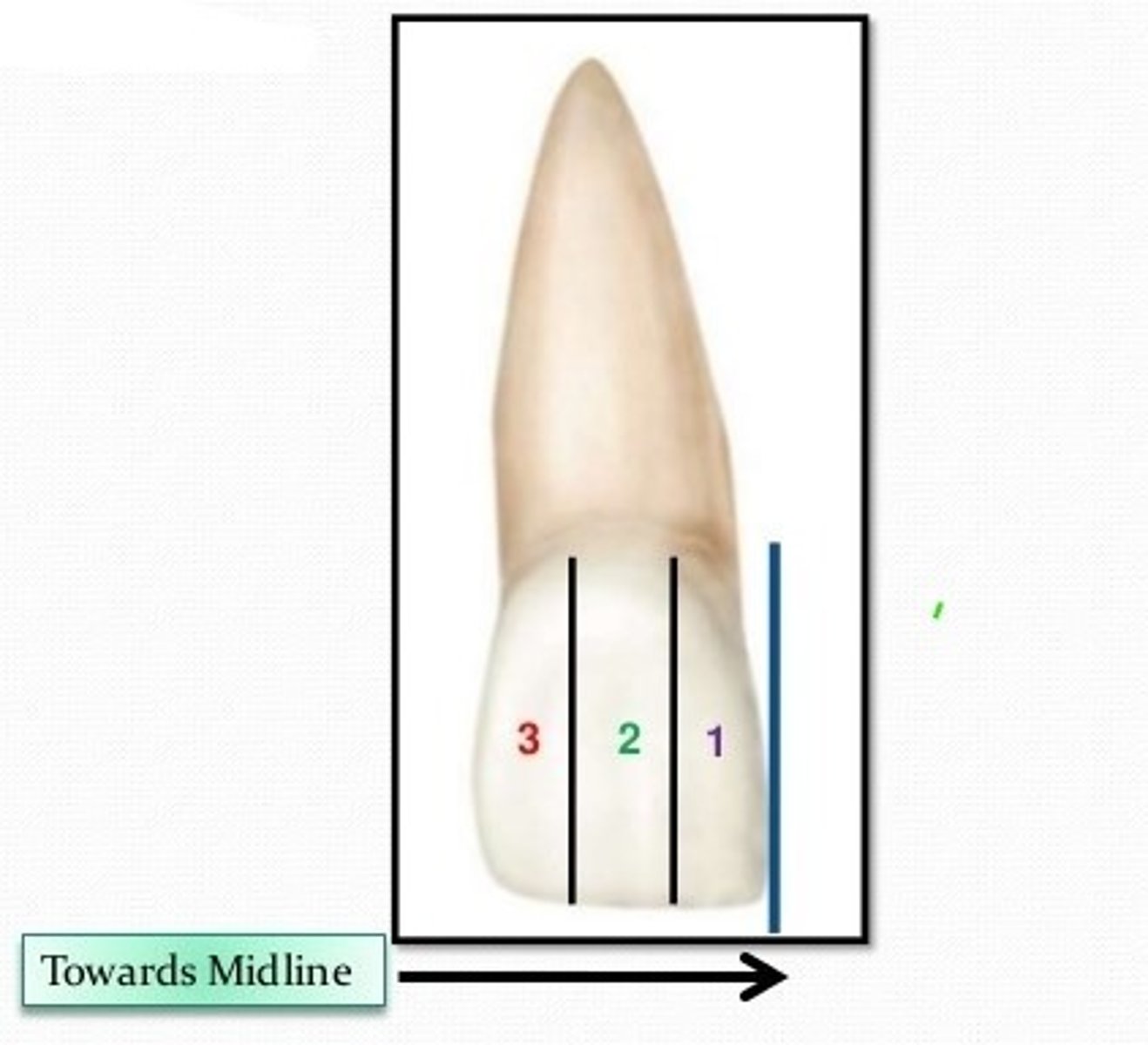
three
On incisors, the number of lobes on the FACIAL surface (which is the same as the number of mamelons on the incisal surface) is:
mesial marginal ridge
The borders of the lingual fossa of the maxillary lateral incisor are the cingulum, the distal marginal ridge, the incisal edge or ridge, and the _____________.
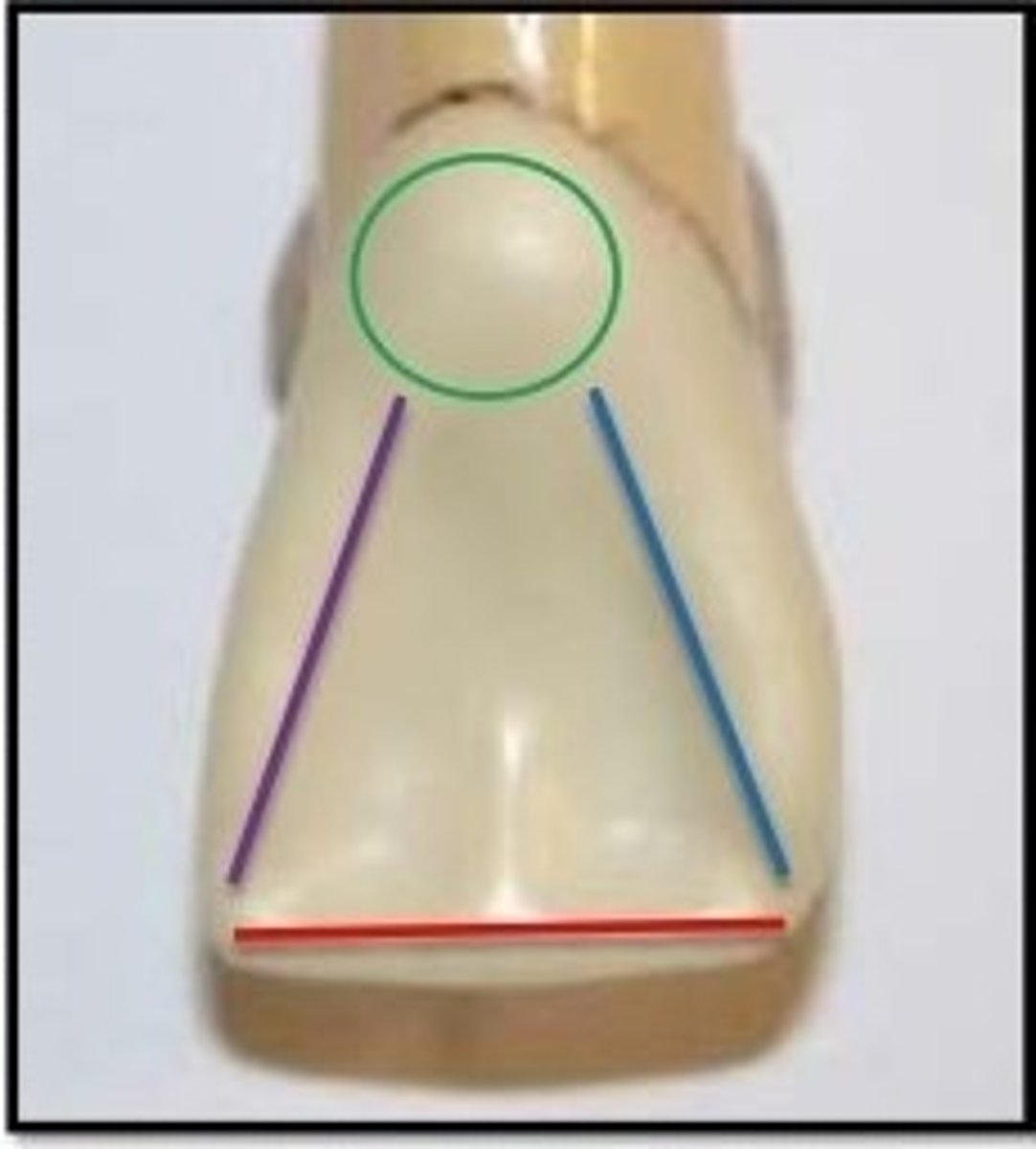
embrasures
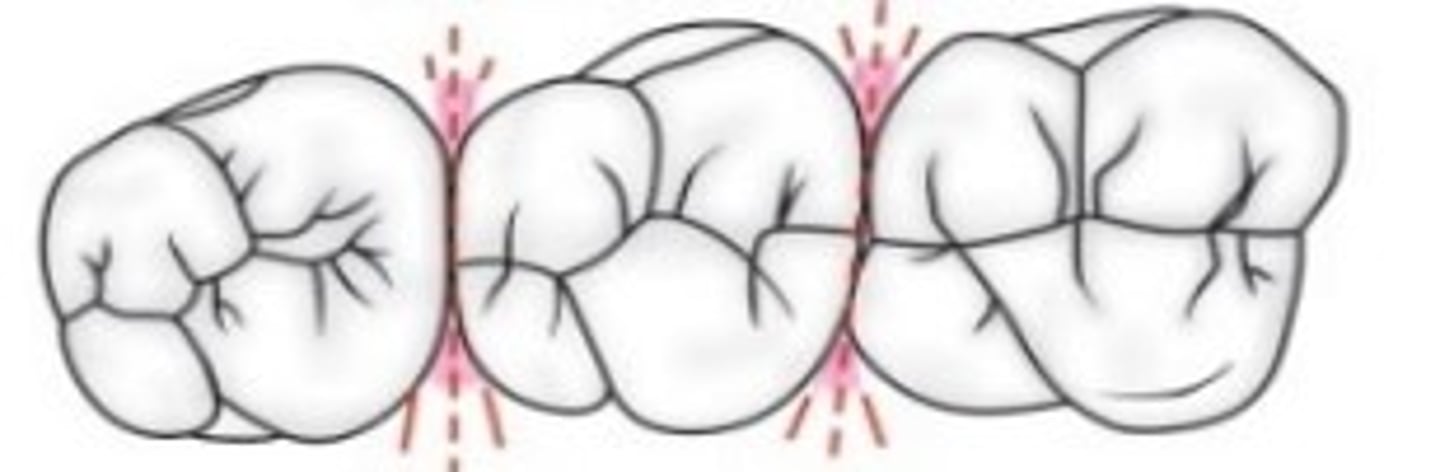
The spaces formed around the point of contact between proximal surfaces of adjacent teeth are called _________.
True
True or false? The CEJ curves more on the mesial of the tooth than on the distal.
False
True or false? The facial height of contour of tooth #8 is located in the middle third of the crown.
Cervix, trunk, furcation, apex
What is the correct order of anatomic landmarks of a tooth with two roots beginning at the cementoenamel junction and moving toward the root tip?
Labial
When referring to mandibular anterior tooth surfaces, what is another term for facial surfaces?
Palatal
When referring to maxillary tooth surfaces, what term is the same as lingual?
Dentin
Which tissue makes up the majority of the bulk of a tooth?
All posterior teeth only
Which tooth crowns have the LINGUAL crest of curvature (height of contour) located in the middle third? (Read all choices before selecting the one best answer.)
Enamel
Which tooth structure is hardest (most calcified)?
mamelons
_____ are rounded incisal extensions of the labial lobes found on newly erupted or unworn permanent incisor teeth.
A root that is almost the same length as the crown
Compared to permanent maxillary lateral incisors, maxillary central incisors are more likely to exhibit:
(what do maxillary central incisors have that maxillary lateral incisors don't?
Less prominent
The marginal ridges and cingulum of the permanent maxillary central incisor are _______ than those of the permanent maxillary lateral incisor.
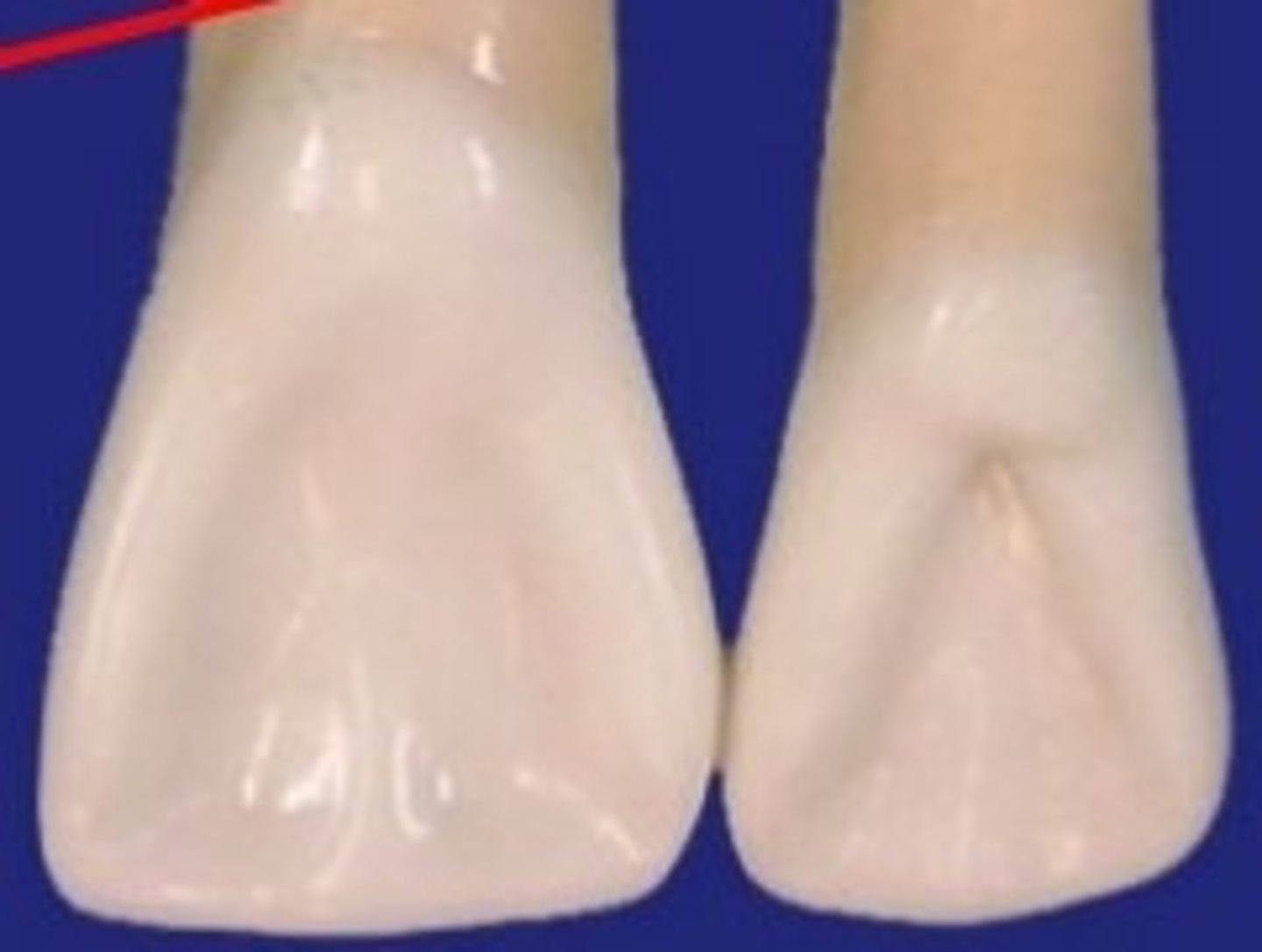
Narrower
When viewed from the facial aspect, the mandibular central incisor is _______ mandibular lateral incisor.
Mandibular central incisor
Which of the following incisors is symmetrical?
Mandibular central incisor
Which incisor is the smallest tooth in the mouth?
Maxillary central incisor
Which incisor is normally the widest (mesiodistally)?
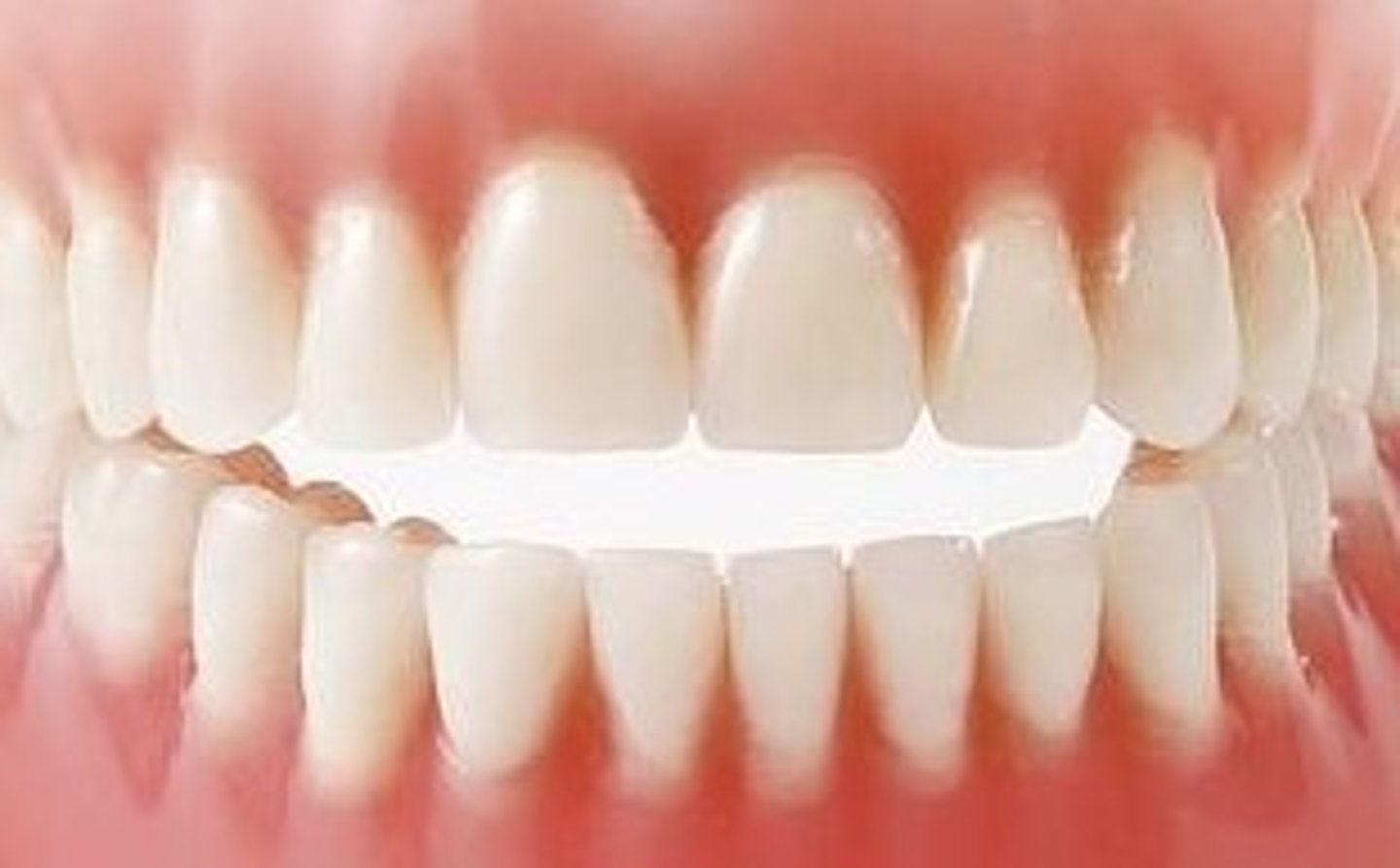
The labial height of contour is in the cervical third
Which of the following characteristics is normally seen on ALL types of permanent incisors?
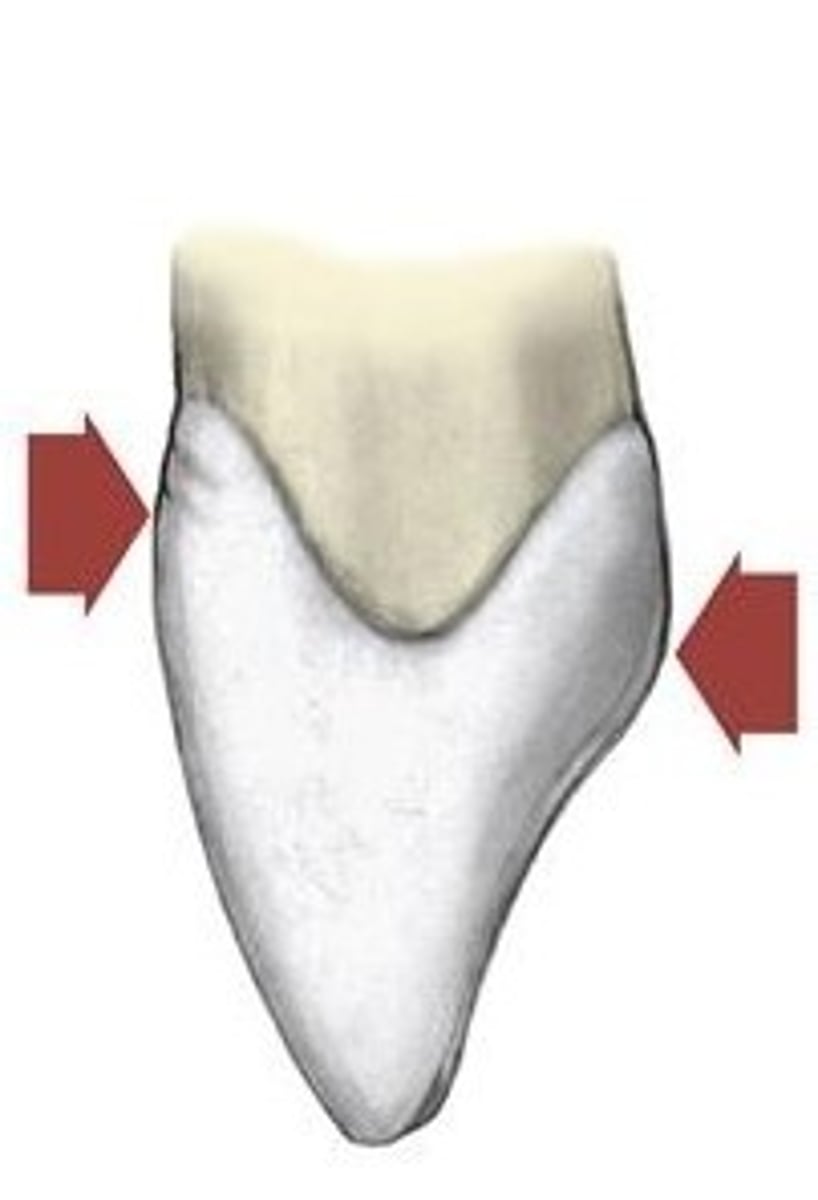
The mesioincisal angles are more square than the distoincisal angles (more rounded)
Which statement is true regarding all lateral incisors (maxillary and mandibular)
Maxillary central incisor
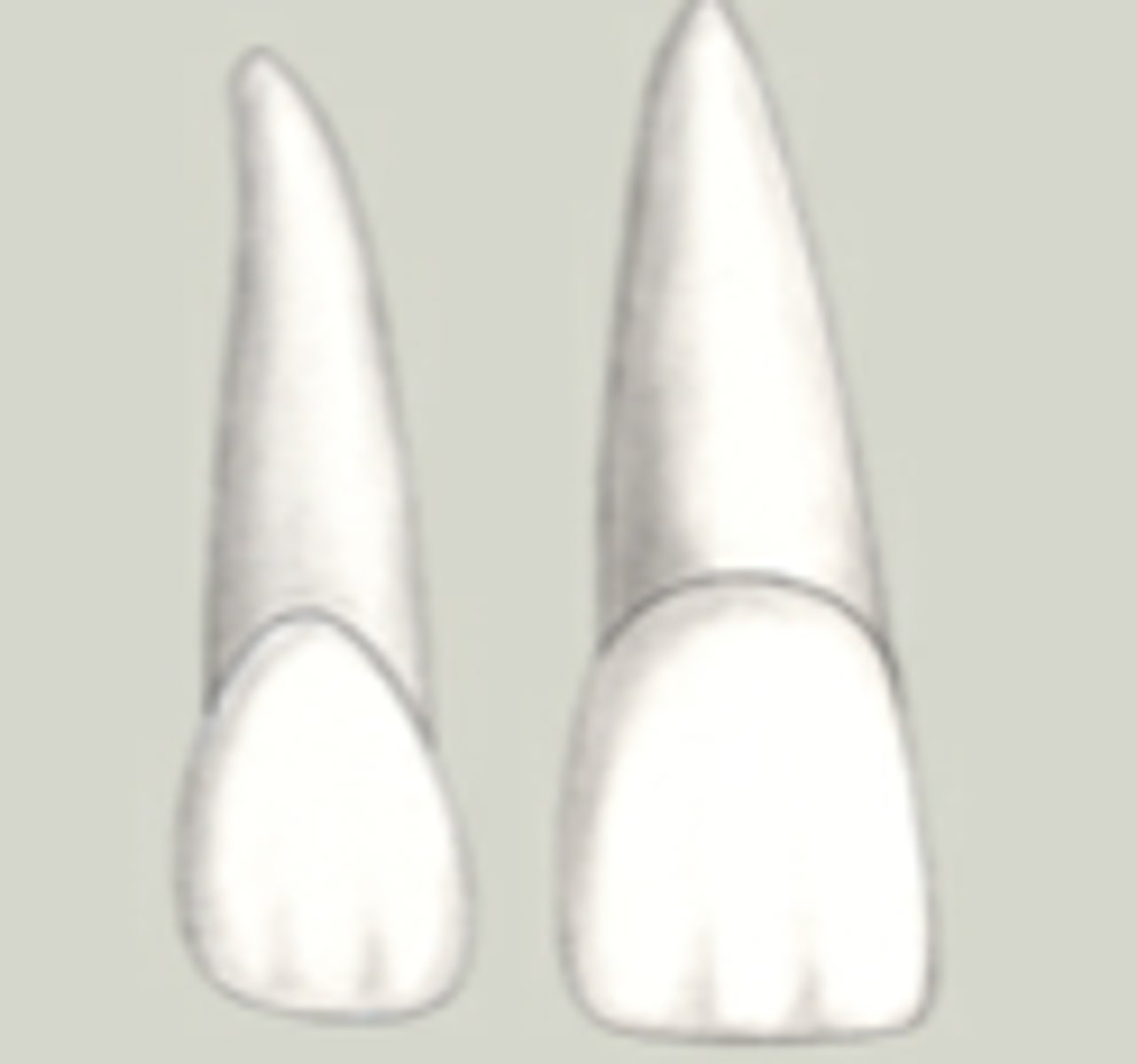
Which tooth has the shortest root relative to its crown?
(smallest crown to root ratio)
shorter than
The crown of the permanent maxillary canine is ________the crown of the permanent mandibular canine.
True
True or false? A distinguishing characteristic of mandibular canines is the relatively straight line of the mesial outline, compared to the distal outline.
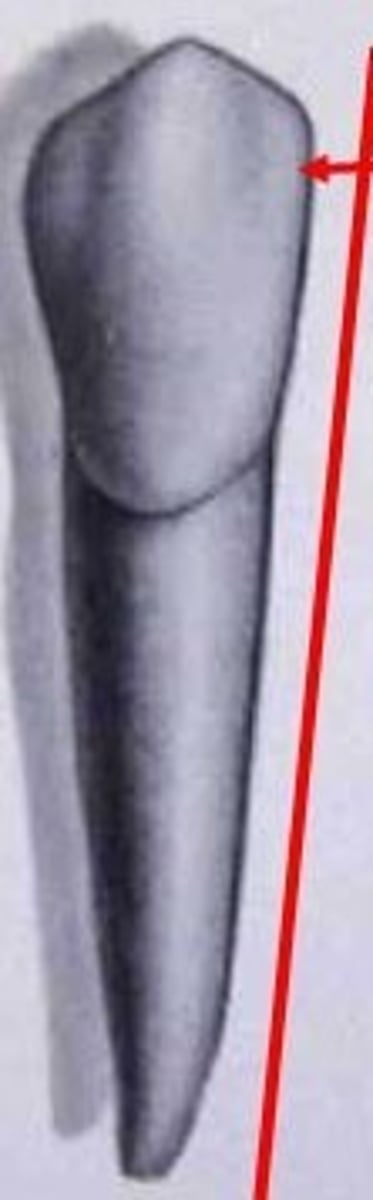
#28
Which tooth has a distinct mesial and distal fossae with a pit that can have 'snake eye' fillings?
False
True or false? On the permanent maxillary canine, the mesial cusp ridge is longer than the distal cusp ridge.
Mandibular second premolar
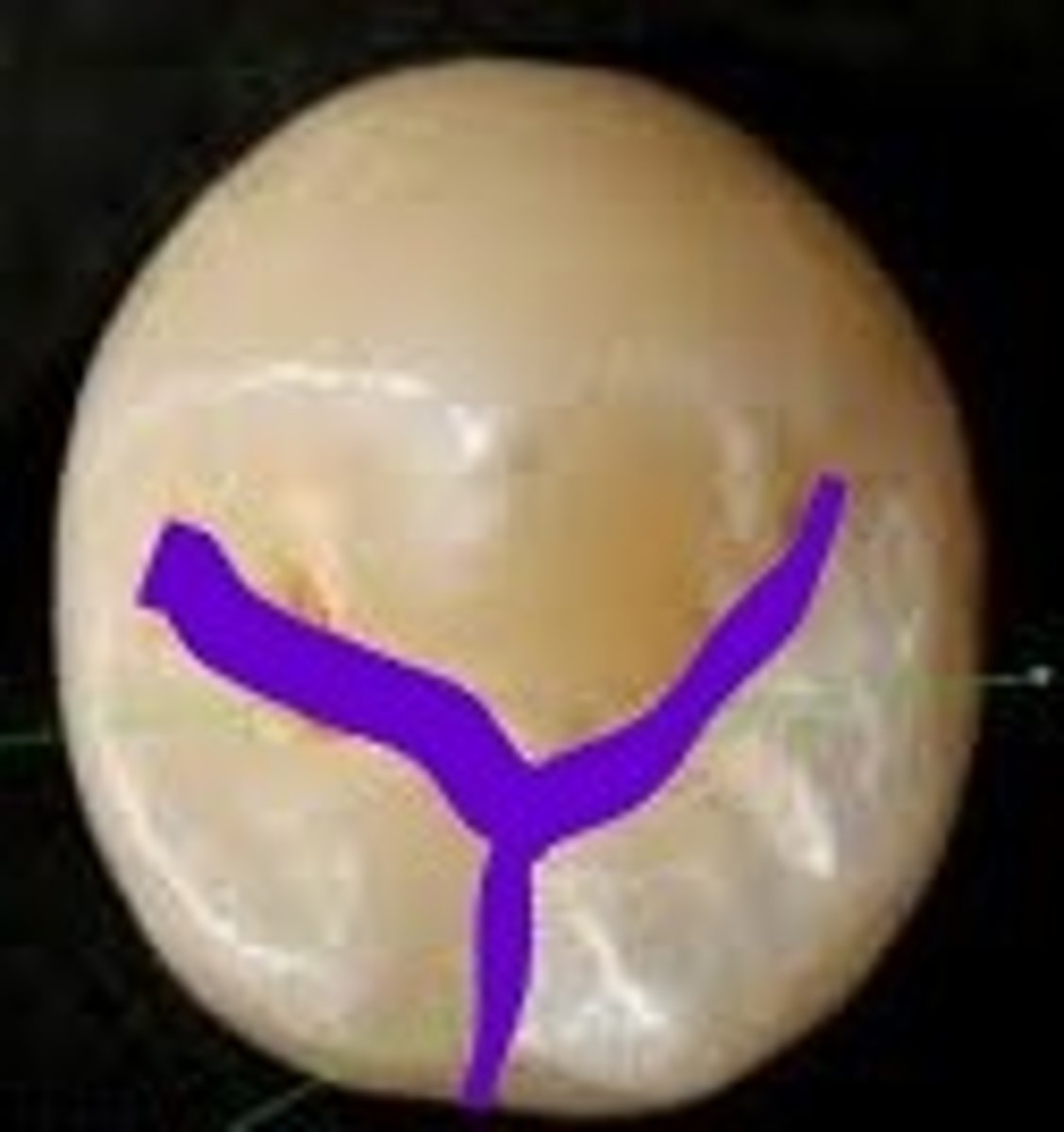
A Y-shaped occlusal groove pattern is characteristic of a:
Mesiolingual, distolingual, and buccal
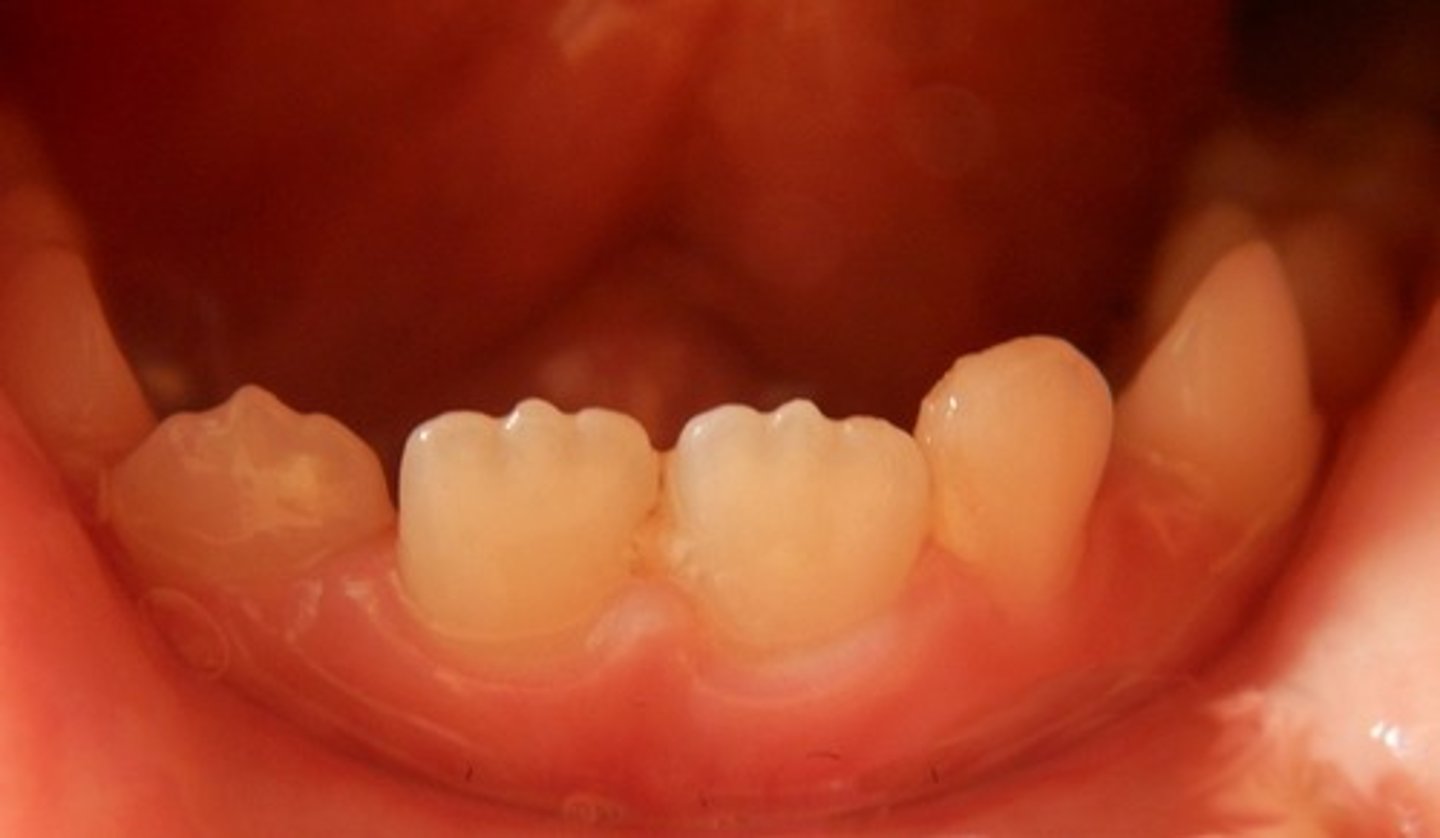
If a mandibular second premolar has three cusps, what are they called?
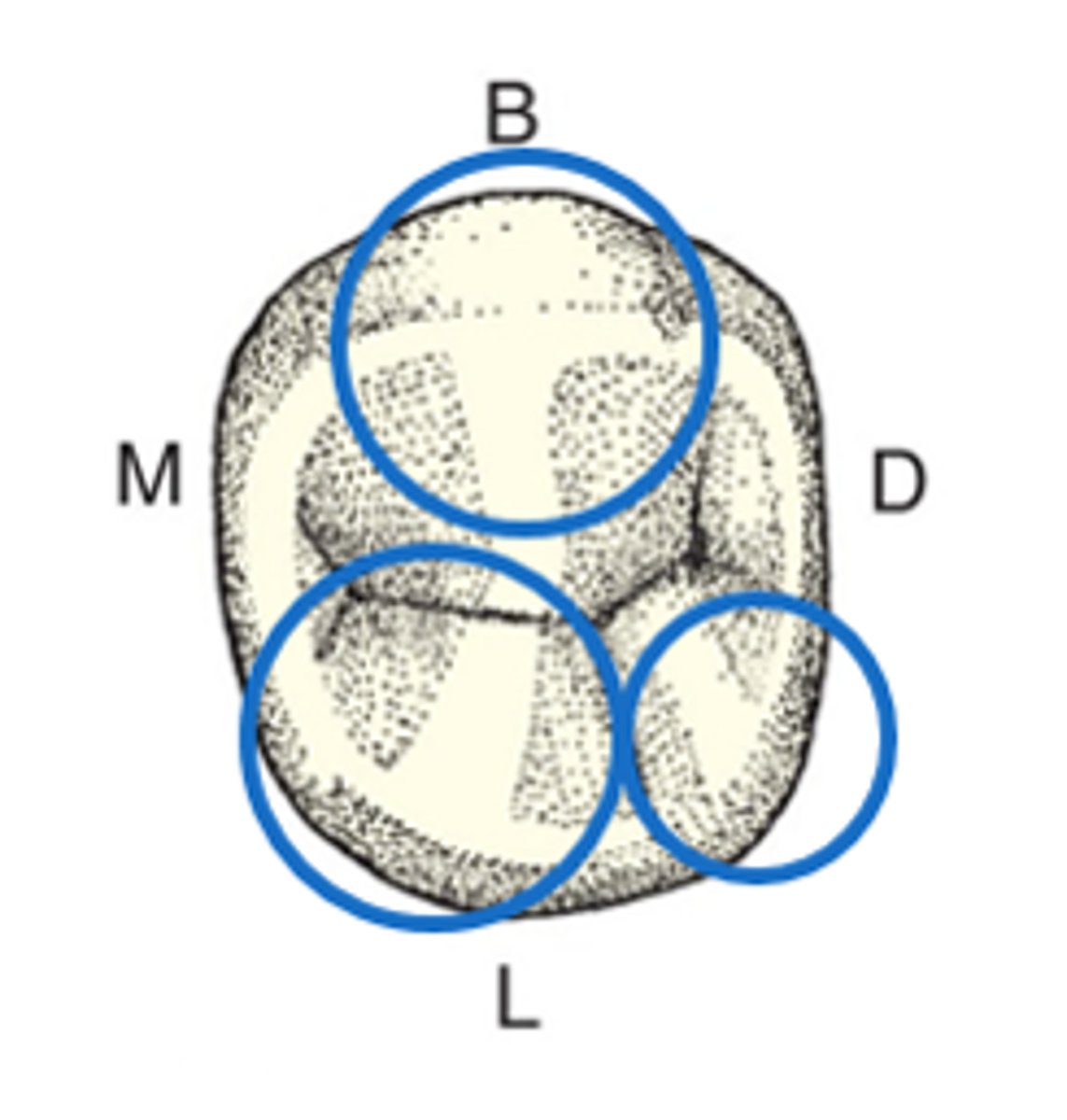
Maxillary first premolar
Which premolar has a pronounced concavity (fossa) on the mesial side of the crown?
marginal ridges
The cusp ridges form the buccal and lingual sides of the occlusal table, and the __________ make up the mesial and distal boundaries of the occlusal table.
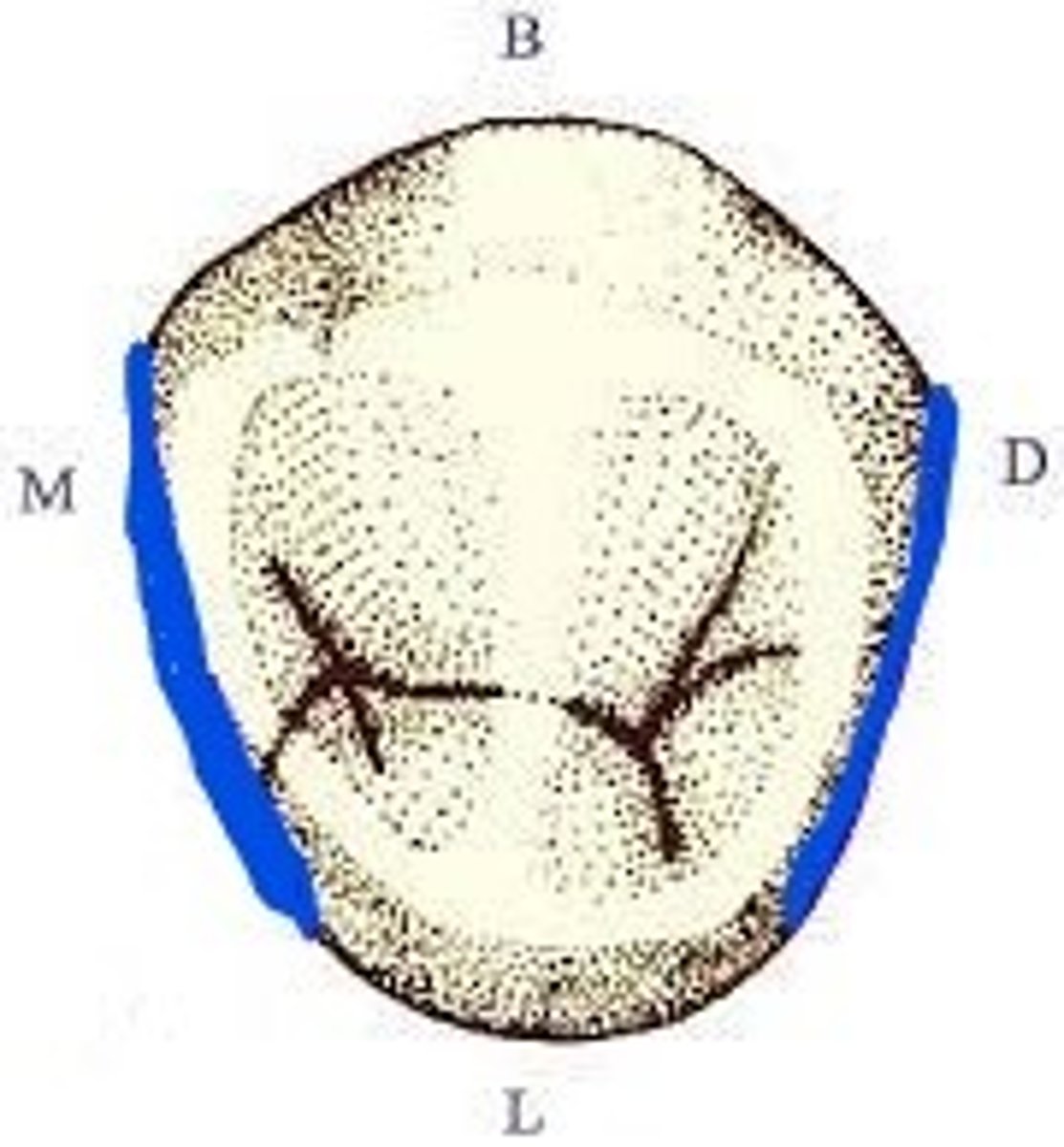
mandibular second premolar
The only single-rooted tooth to have three cusps is the ___________________.
It will be either an incisor or premolar.
True
True or false? Multiple supplementary grooves often are found on a maxillary second premolar.
There is likely to be a mesiolingual groove crossing onto the mesiolingual surface.
When compared to other premolars, which of the following characteristics is unique to a mandibular first premolar?
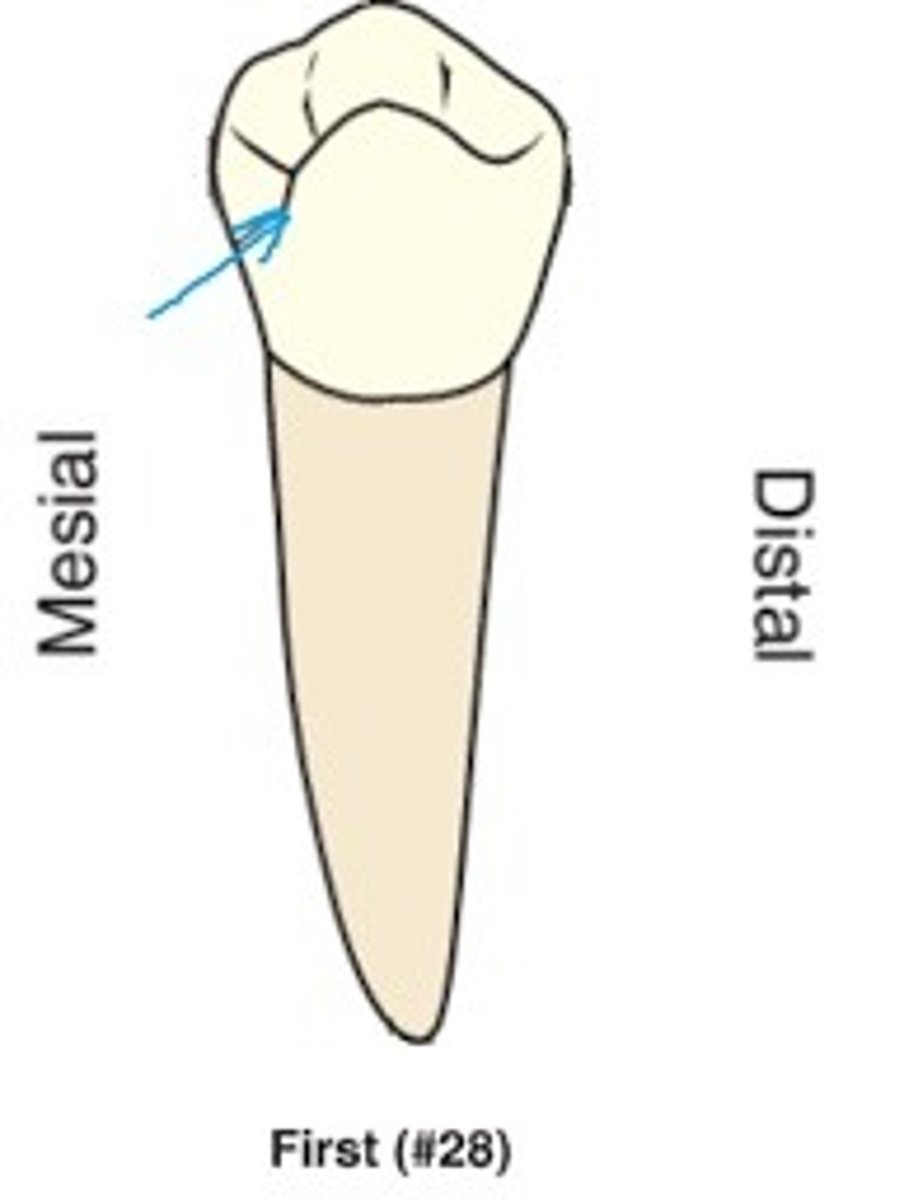
The short lingual cusp is non-functional.
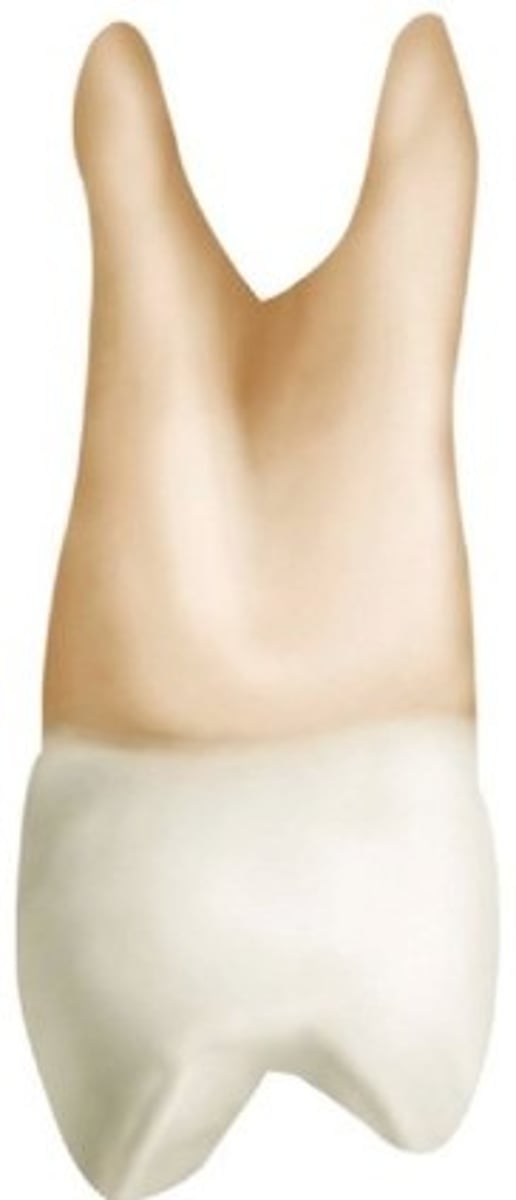
Which of the following characteristics is NOT true about a maxillary first premolar?
Maxillary first premolar
Which premolar has a deep mesial root depression?

Mandibular first premolar
Which premolar has a non-functional lingual cusp (due to the difference in the height of the two cusps)?
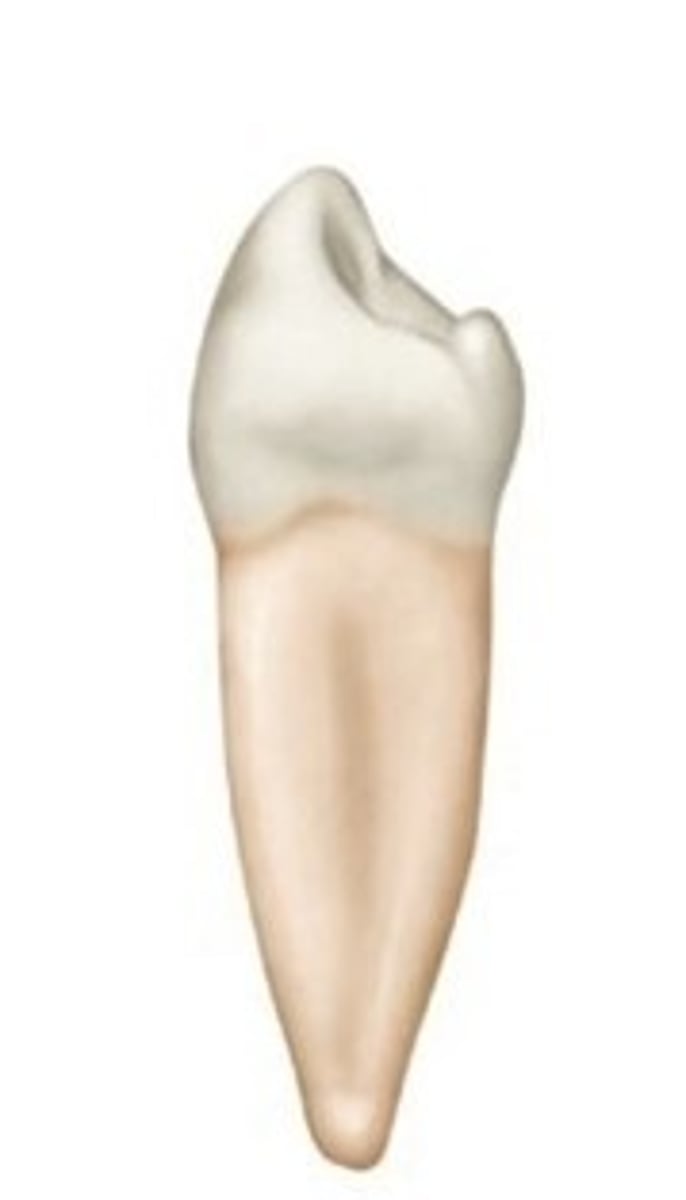
Mandibular second
Which premolars are most likely to have three cusps and a lingual groove?
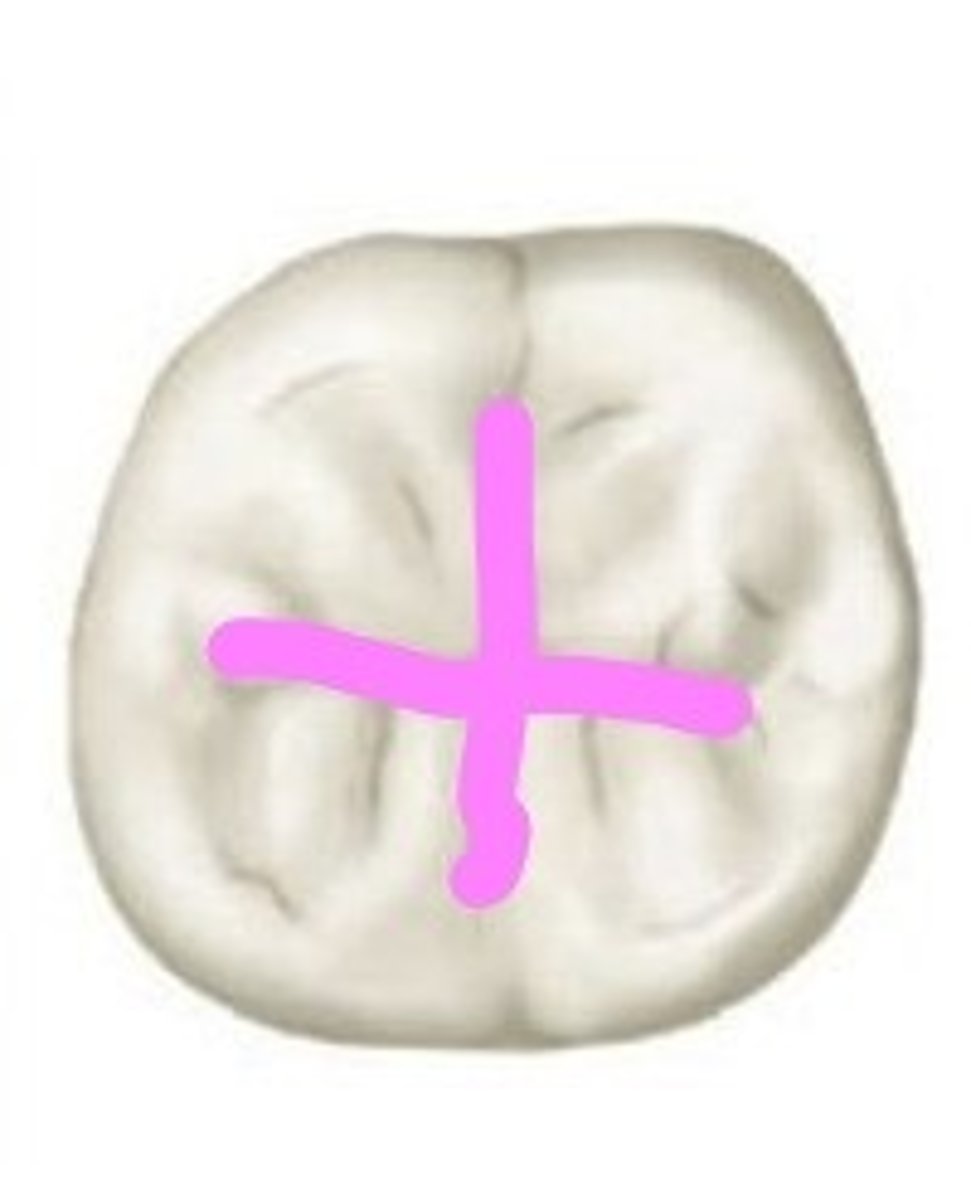
Mandibular second permanent molar
Due to the four cusps being almost equal in size, the “+” groove pattern on the occlusal surface of this MOLAR identifies the tooth as the:
Mesial
From which view is only one root visible on a mandibular first molar?
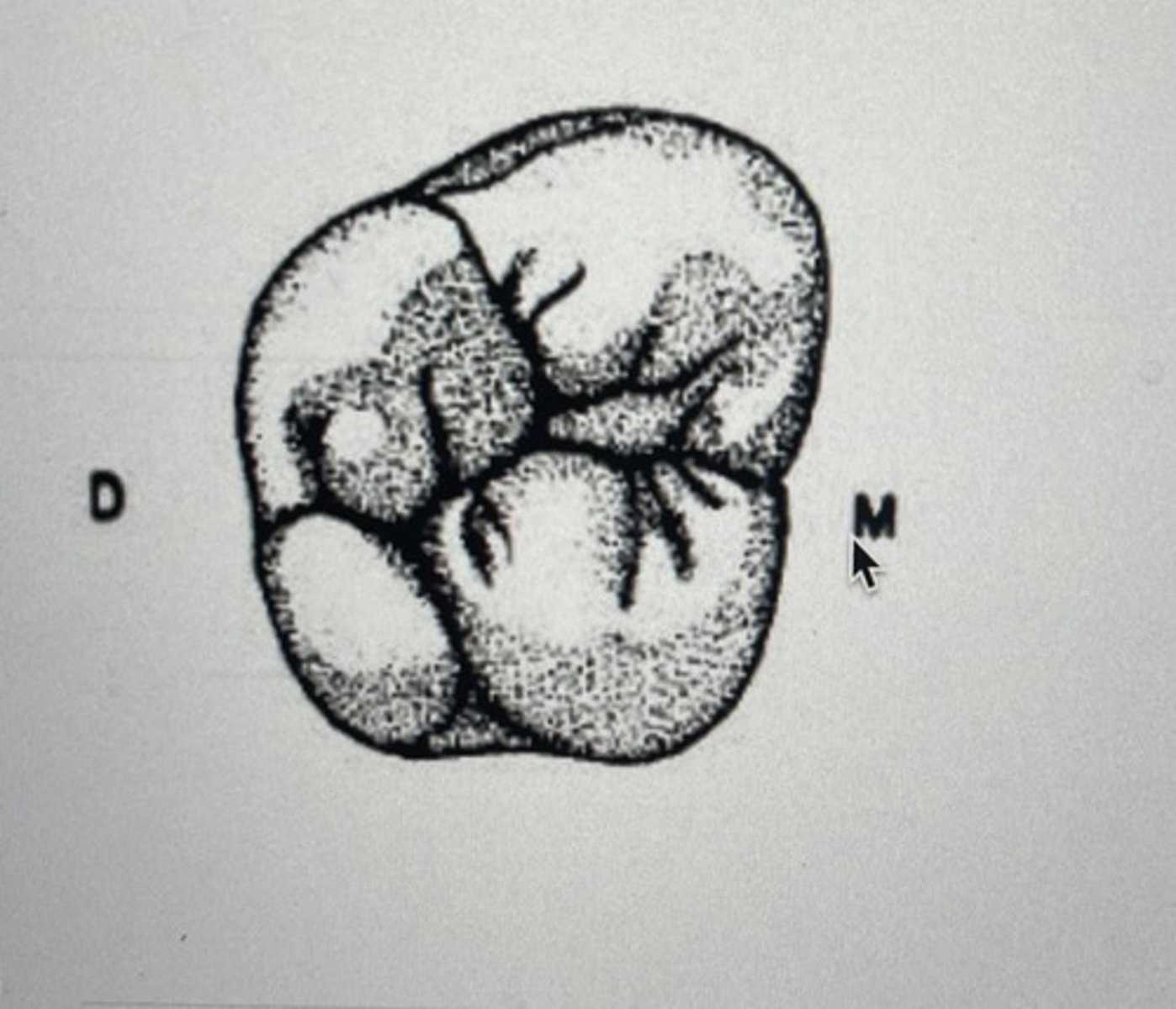
Mesiobuccal, distobuccal, and lingual
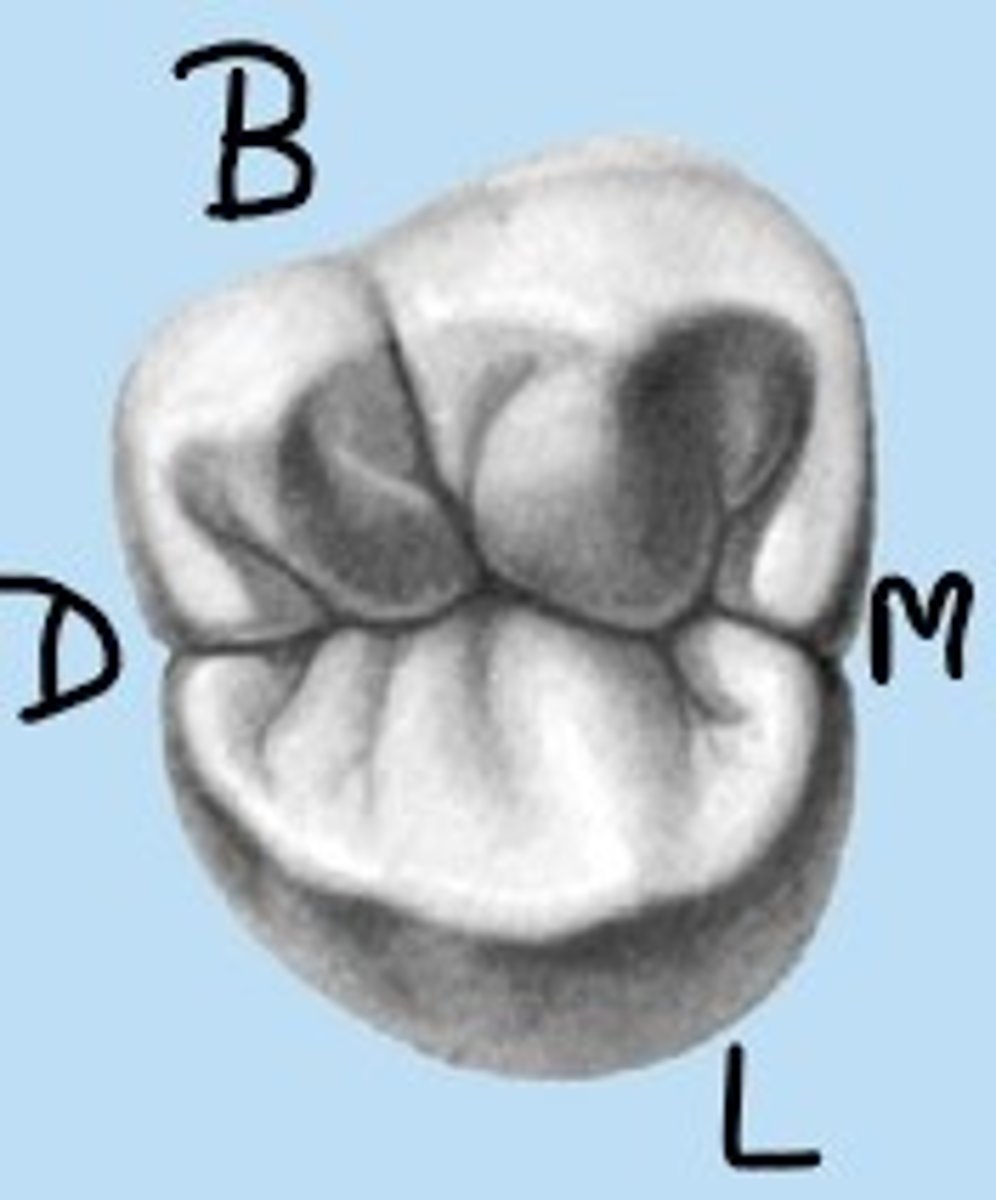
If a permanent maxillary second molar has only three cusps, what are the three cusps called?
distobuccal
Name the two grooves found on the buccal surface of the mandibular first molars, mesiobuccal and ____________
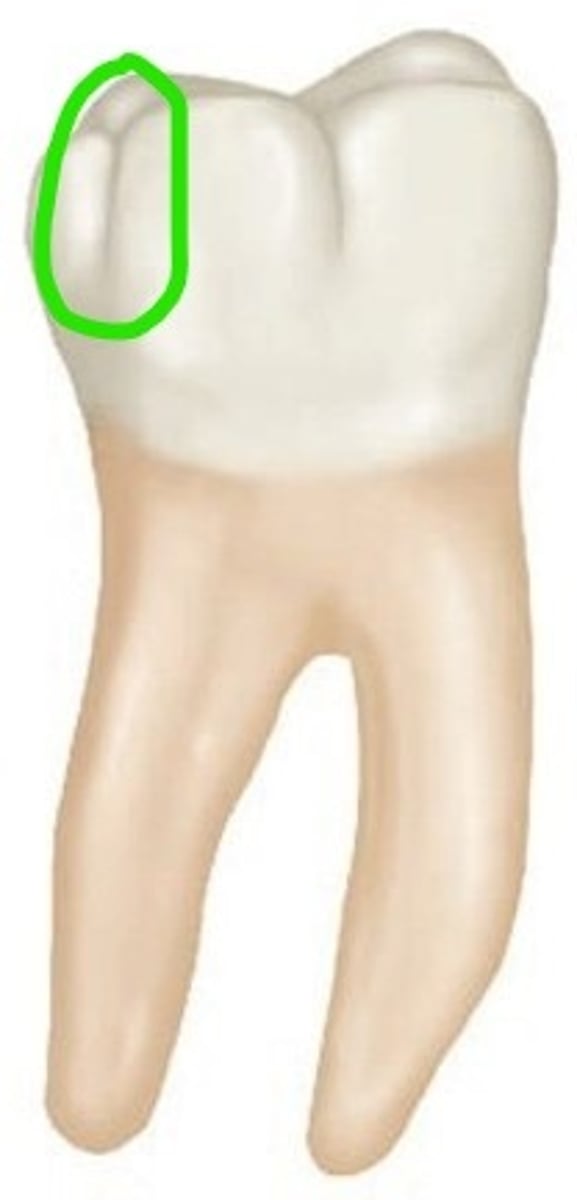
Distolingual
Of the following, which cusp is the smallest cusp on permanent maxillary molars (not including the Cusp of Carabelli)?
mesiolingual cusp
The ___________ cusp of the maxillary first molar is the largest cusp (carries the Cusp of Carabelli).
buccal
The furcation of the mandibular molars may be seen from either a ______or lingual view.
Correct!
True
True or false? A prominent ridge crossing the occlusal surface of the permanent maxillary first molar, (unique to maxillary molar teeth), is called the oblique ridge.
24
During most of their eighth year, children have how many teeth in their mouth (primary and secondary)?
6 months to 2 years
During what age span are primary teeth in the process of erupting (emerging) into the mouth?
12
How many non-succedaneous teeth are in the complete dentition?
Greater divergence of roots
Primary molars differ from permanent molars in that primary molars have:
6 to 7 years
The PERMANENT mandibular central incisor erupts at age:
three
How many roots does a primary maxillary first molar have?
Distal to the tooth "K"
Tooth #19 forms within the mandible (prior to erupting) at which location?
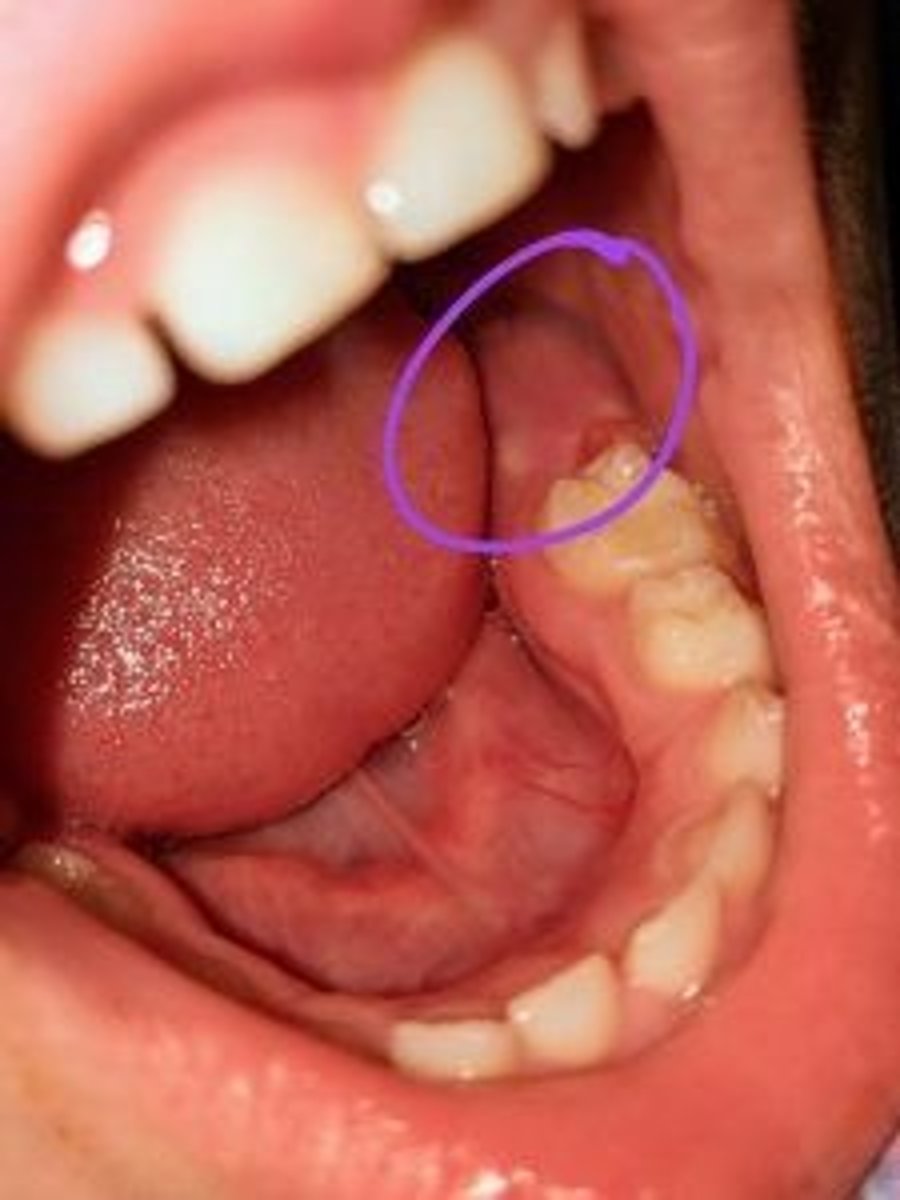
Tooth #8
Using the Universal number or letter, which tooth erupts in place of primary tooth "E"?
Second premolars
What permanent tooth erupts into the space previously held by any of the primary second molars?
The maxillary anterior teeth are lingual to the mandibular anterior teeth
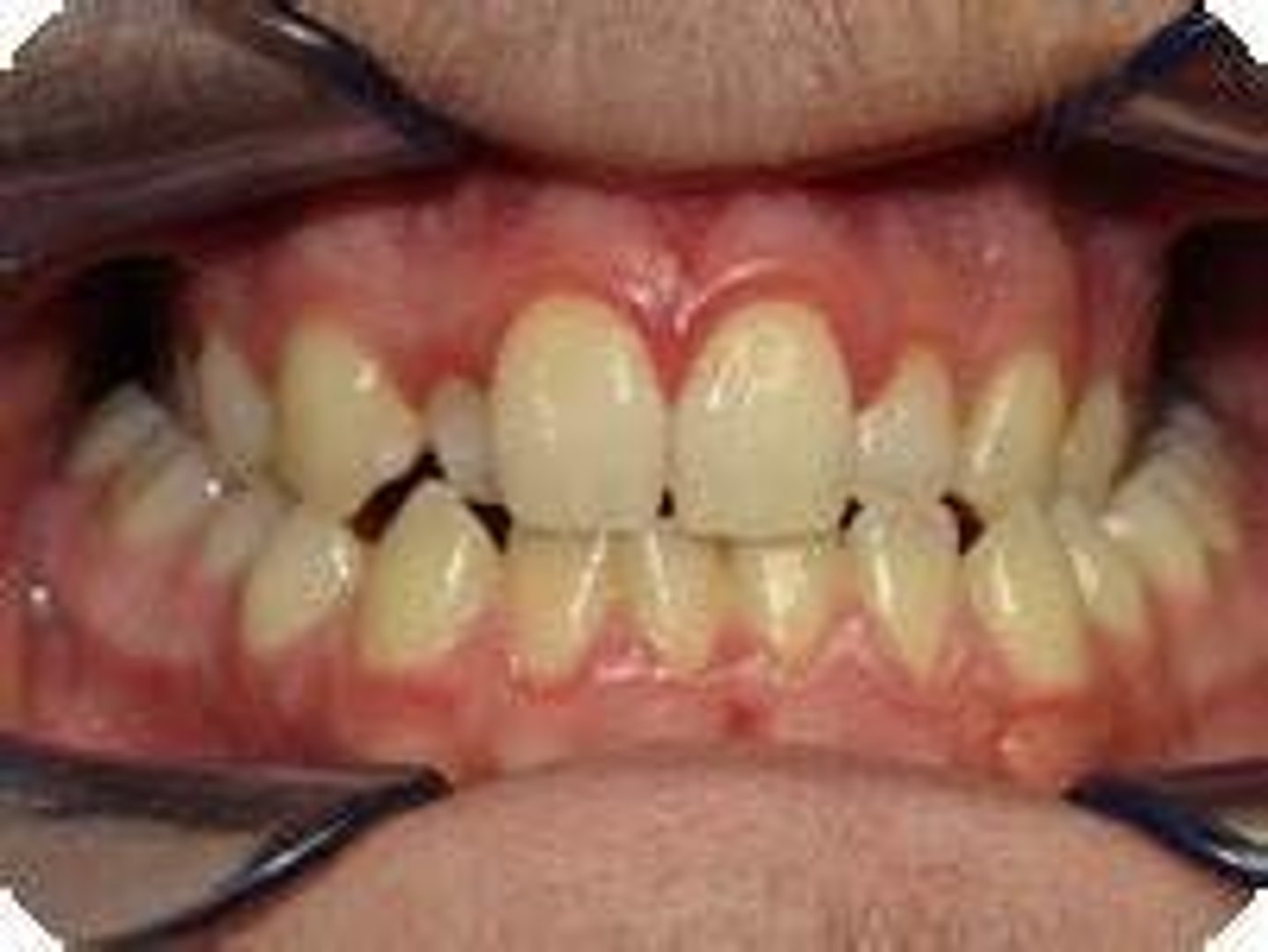
Choose the best description for anterior crossbite.
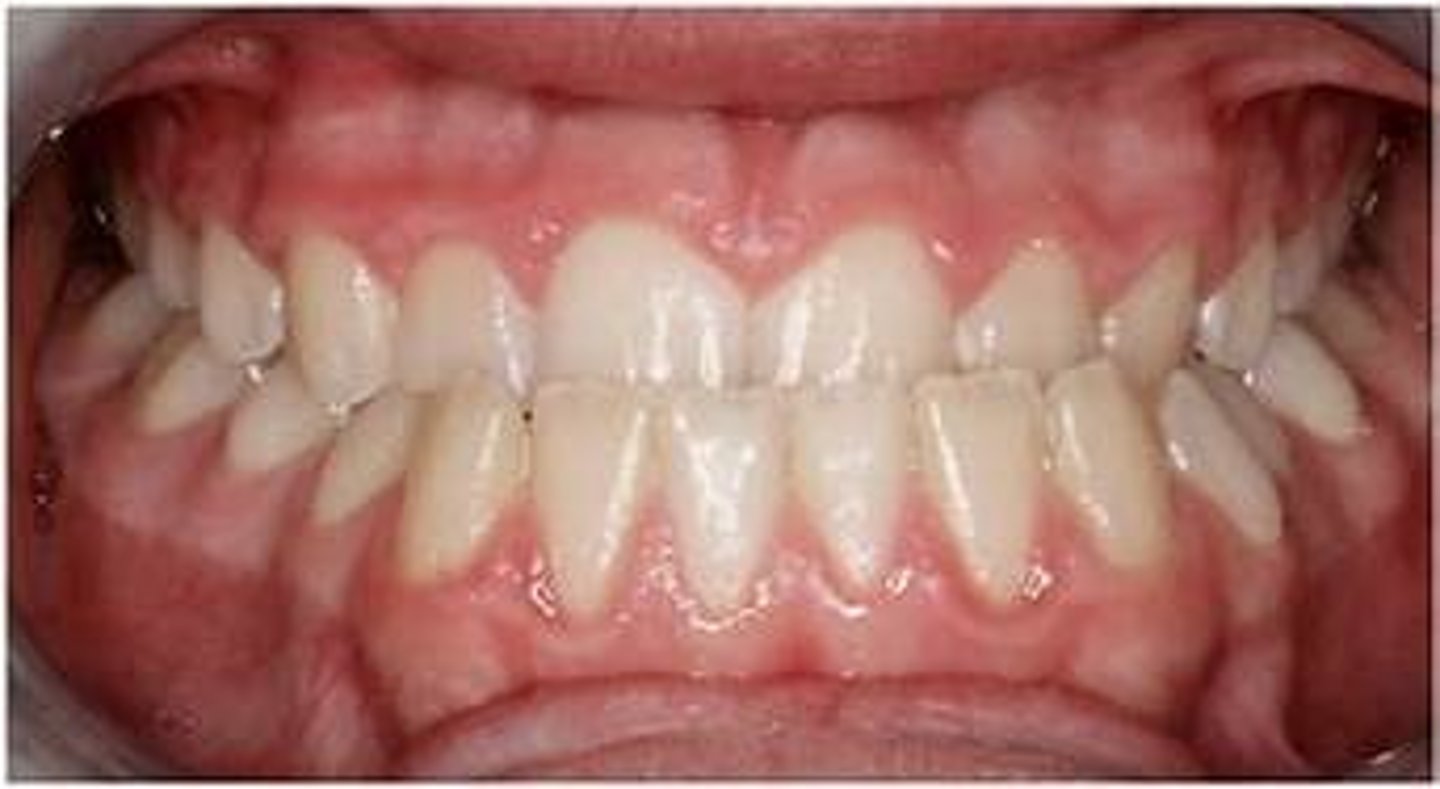
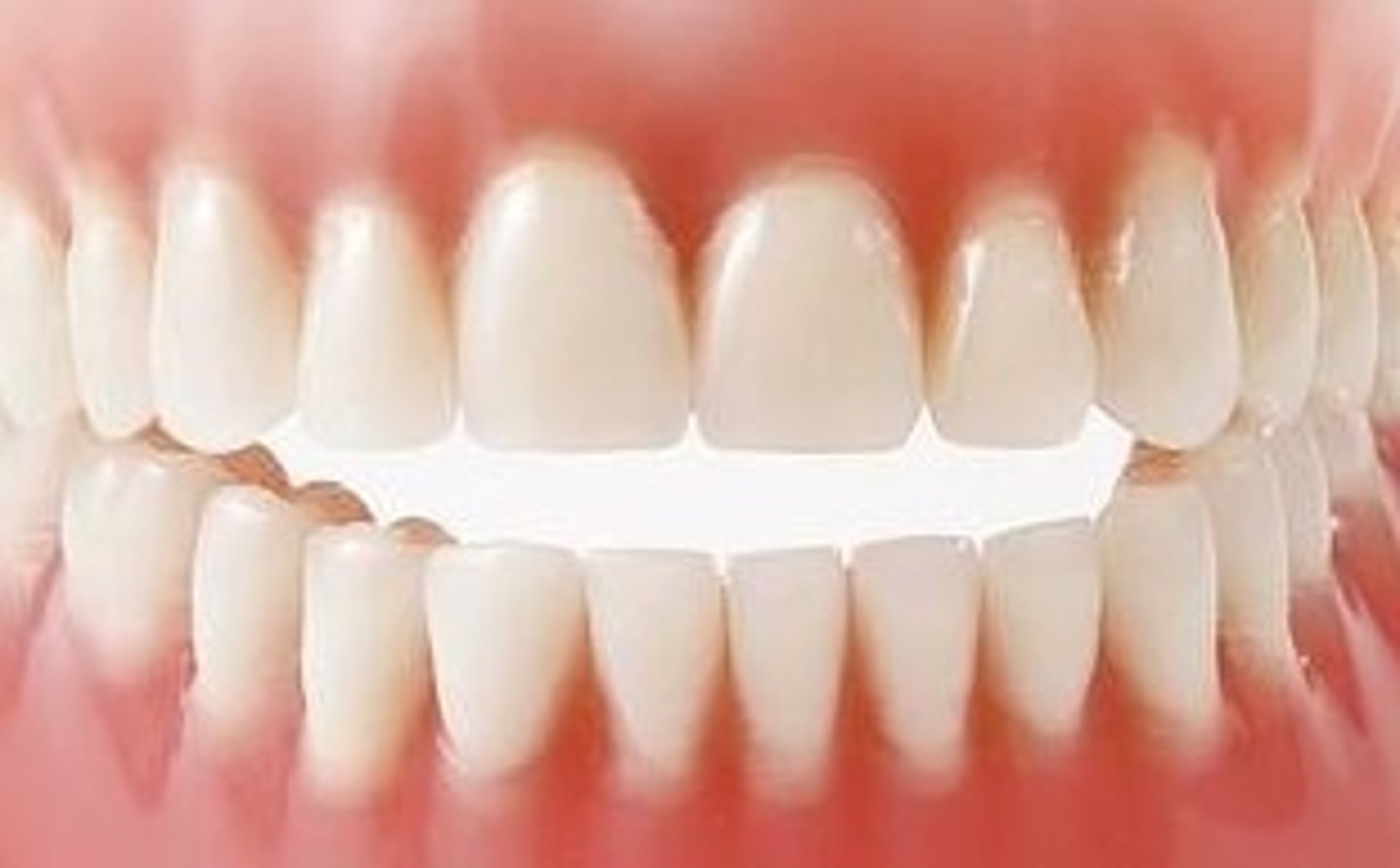
Class I occlusion
When the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar sits even with the mesiobuccal groove of the mandibular first molar it is:
Posterior cross bite
When the mandibular posterior teeth sit more to the buccal than the maxillary posterior teeth, it is termed:
True
In class II malocclusion, the profile is retrognathic, meaning the lower jaw sits back further than in class I occlusion.
Correct!
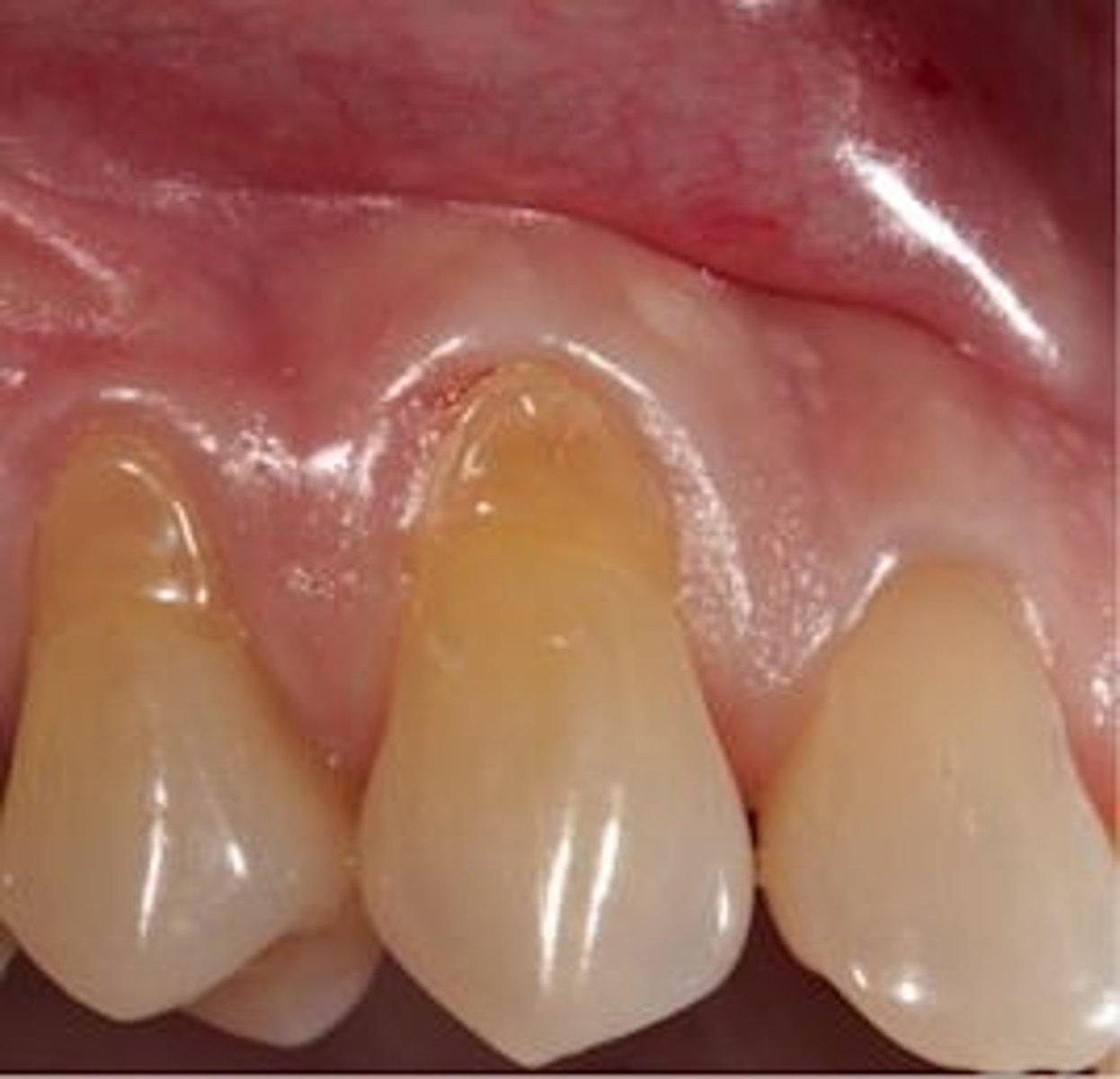
Abrasion
Loss of tooth structure due to mechanical forces (toothbrushing):
Maxillary incisor area
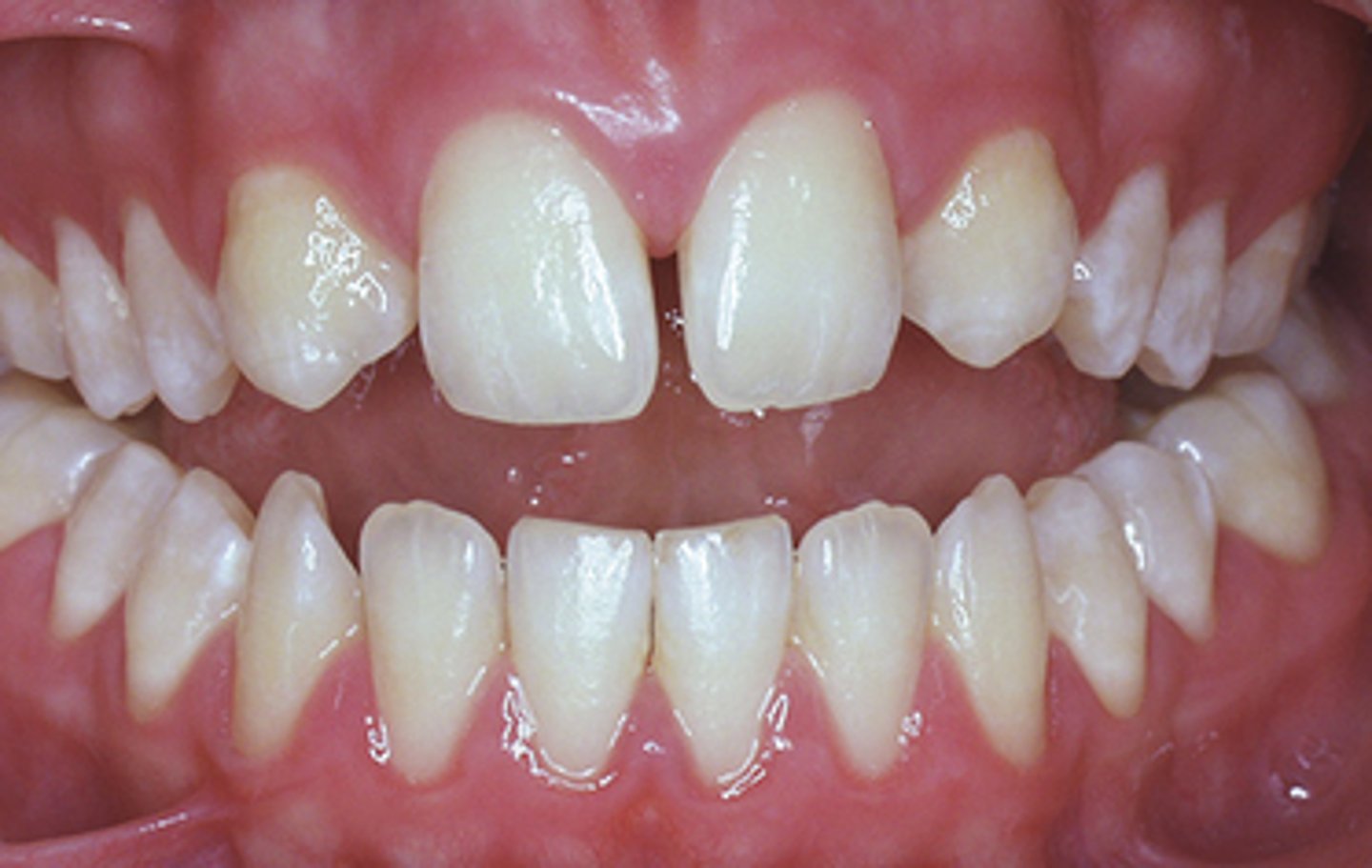
When examining a large group of people, what is the most frequent location where extra (supernumerary) permanent teeth may be found?
#7 or 10
Which two teeth are most likely to be congenitally missing?
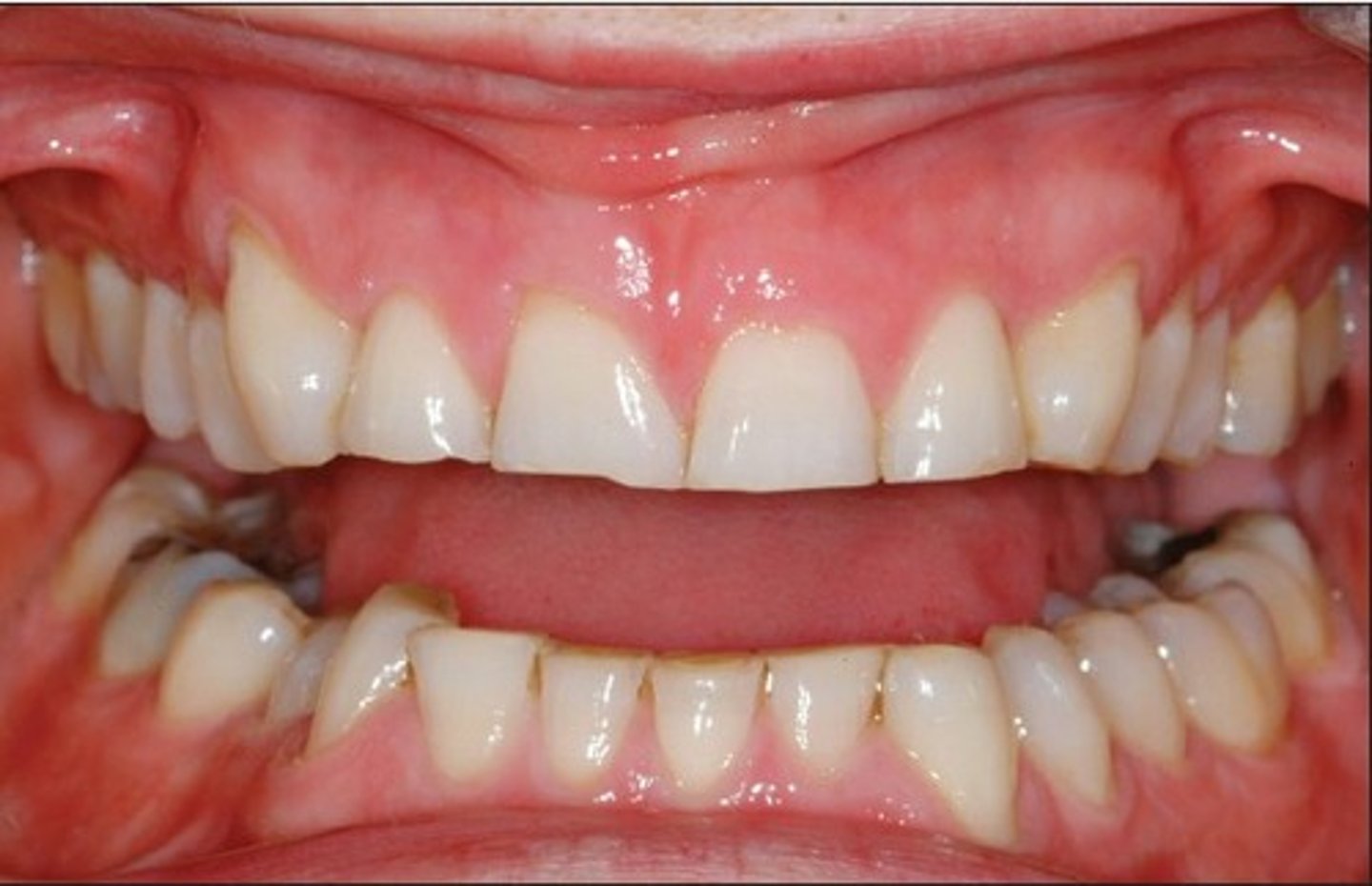
Attrition
Tooth wear caused by tooth-to-tooth contact:
20
How many teeth should be visible in the mouth of a 3-year-old (complete primary dentition)?
cusp
A cone shaped mass found on the occlusal surface of posterior teeth and that is made of ridges is called a _____.
two triangular ridges
A transverse ridge is made up of which two ridges?
three
How many molars are there in one quadrant of a normal adult human dentition?
#S
Which primary tooth is most unique in shape and resembles no other tooth?
eight
How many total premolars are there in the complete adult dentition?
32
How many teeth in a complete adult dentition?
Maxillary left second premola
Using the Universal Numbering System, what tooth is #13?
#23
Using the Universal Numbering System, what tooth is the permanent mandibular left lateral incisor?
8 & 9
Using the Universal Numbering System, what teeth are the maxillary central incisors?
E & F
Using the Universal Numbering System for primary dentition, which teeth are the maxillary central incisors?
1, 16, 17, 32
Using the Universal Numbering System, what teeth numbers are the 3rd molars (wisdom teeth)?