Macropreparat (for practical exam)
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EXAM - macroslides som vi kan få (tatt fra dokument)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
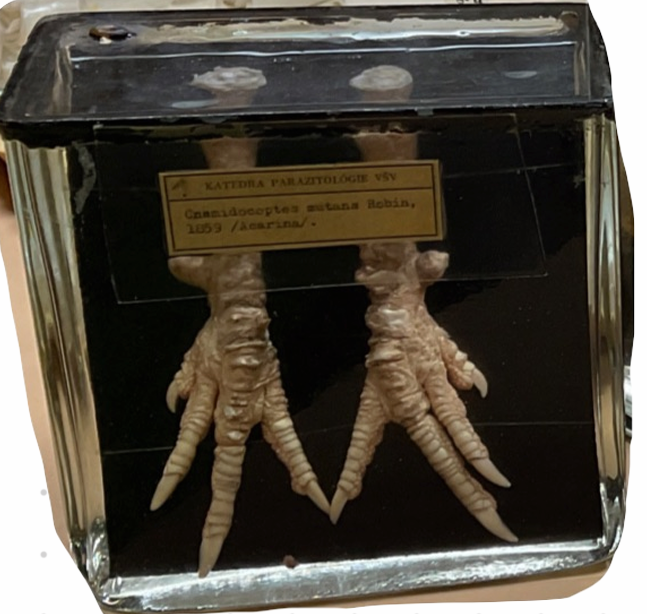

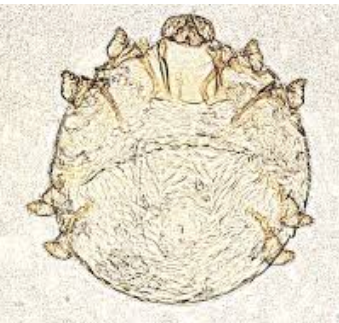
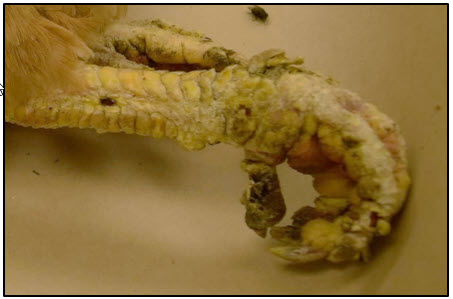
species, morphology, LC?
Cnemidocoptes mutans (burrowing mite)
Order: Astigmata, Family Cnemidocoptidae
Species: C. mutans, C. gallinae, C. pilae, C. prolifecus
Morphology: no spines or pointed scales, no anterior vertical setae, snickers on all legs in adult males, round, convex dorsally.
LC: Vinparous (ala human) - 17-21 days
females burrows in epidermis, give birth L1 → crawls to skin surface → burrows again → creating multi-pockets
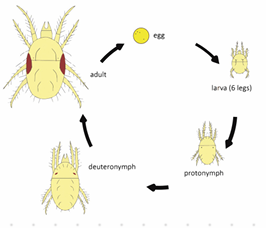
egg → larvae → protonymph → ditonymph → adult
CS:
Mutans: scaly legs, malformation of fat, can go to neck and comb
gallinae: burrow in feather shaft, pain, bird pulls out feathers
pilae: beak and fat of birds
Treatment: ivermectin
Diagnosis: mites on feather shafts or skin scrapings

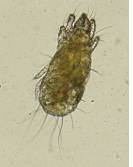
this is?
Acarus siro var. suis
Order: sarcoptiformer
Family: acaridae
flour mite.
Oviparous, egg → 2 nymph stages → adult

this is?
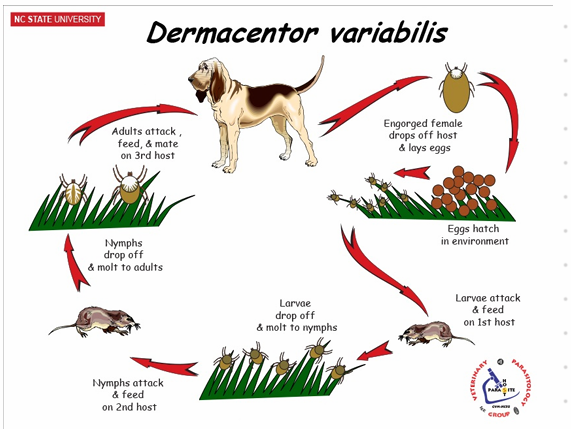
Dermacentor pictus🪲
Order: Ixodida, fam. Ixodidae
Hard Ticks - Ornate sheep tick
Temporary parasites: Feed once per molt
🔍 Morphology
Scutum on dorsal surface
Haller's organ on the first pair of legs (detects CO2 and heat)
Stigmata: Respiratory opening behind the last pair of legs, leading to trachea
Grooves and festoons: Genital pores located anterior-ventrally
Anus: ventrally
Colorful = ornate ticks
Gnathosoma: mouthparts
🧬 Life Cycle (LC)
I. ricinus: 3 years
Hemimetabolous (incomplete metamorphosis)
Egg
Larvae (3 pairs of legs, no spiracle)
Nymph (4 pairs of legs, has spiracle, but no gonopore)
Adult (4 pairs of legs, has spiracle and gonopore)
🦠 Vector
Ixodes ricinus
Babesia
B. divergens
B. canis
Lyme disease
💊 Treatment
Spot-on, spray, Bravecto

?
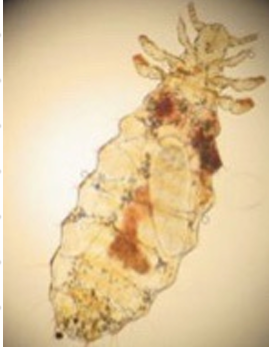
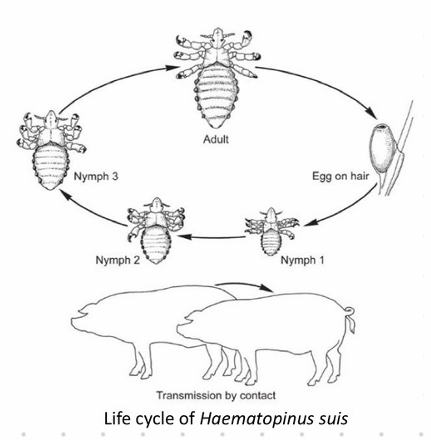
Haematopinus suis
Sucking louse
🐛 Order: Phtiraptera, family: Haematopinidae
Su, Bo, Eq
🧬 Life Cycle (LC)
Hemimetabolous - 1 month
Eggs glued to hairs and feathers hatch in 2 weeks
3 nymph stages
Protonymph
Deutonymph
Tritonymph
Adult
Transmission: animal-to-animal
Permanent ectoparasites
Host-specific
Head narrower than thorax
Distinct claws
💊 Treatment
Pour-on/spot-on organophosphorus insecticides
Rotate medicine to avoid resistance
🩺 Clinical Signs (CS)
Dermatitis (mild)
Pruritus
Anemia (heavy infestations)

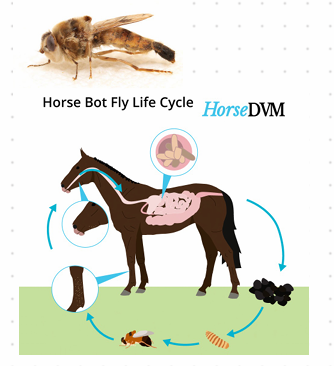
This is?
Order: Diptera🪰 Gastrophilus intestinalis
Family: Oestridae
Myasis: Parasitic infection of the body by fly larvae of Diptera (mammals)
Life Cycle (LC)
Flies lay eggs on host
Eggs hatch after 12-24 hours
Larvae migrate into tissue and molt twice
Larvae feed for 2-4 days, then leave host and pupate on the ground for 1-2 weeks
Adult emerges
Females lay eggs in open wounds of mammals
💊 Treatment
Remove larva with forceps
Lidocaine can be used to extract
Petroleum gel can be used to cut off O2 supply
📍 Location
G. intestinalis: duodenum (common botfly)
G. inermis: esophagus & stomach
G. haemorrhoidalis: stomach, rectum
🐴 LC where FH is horse:
Egg on hair (foreleg) - 1 week
Hatch when licked or eaten
Burrow in front of tongue and migrate to back - 3-4 weeks
Stomach - intestinal wall - 8-12 months
Leaves with feces in summer
Pupate for 1-2 months - Adult
Adult and larva are free-living
Infective stage: L1
Hatch: L1 -> L2 in mouth -> L3 in stomach
Larva has 17 segments with spiracles in butt
🔬 Diagnosis
Endoscopy
Larva in feces
💊 Treatment
Ivermectin

this is?
Gasterophilus intestinalis - Duodenum - common botfly in horses.


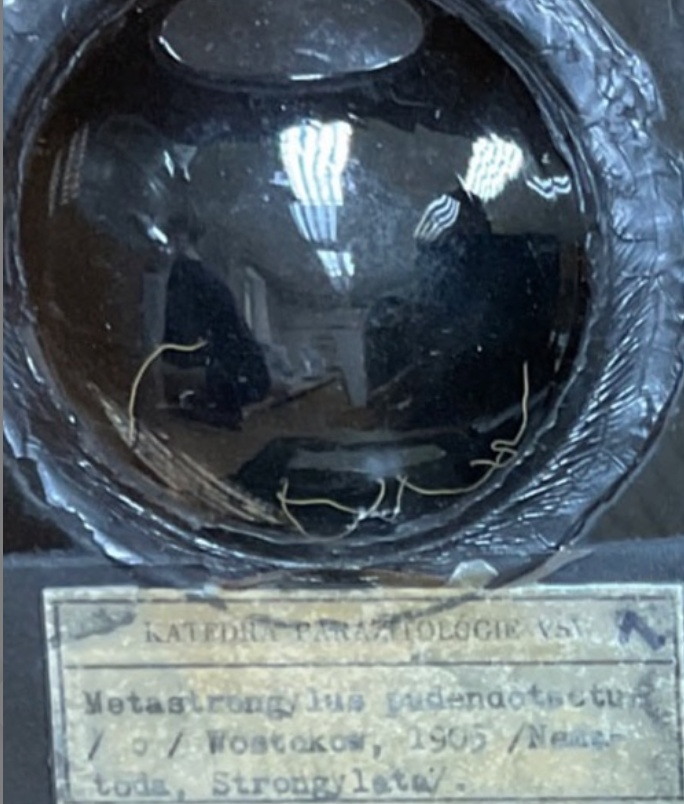
this is?
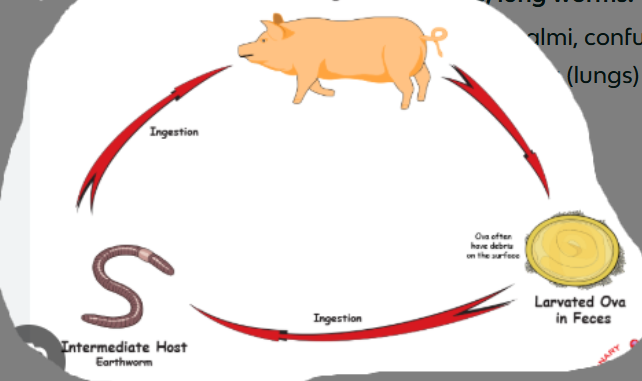
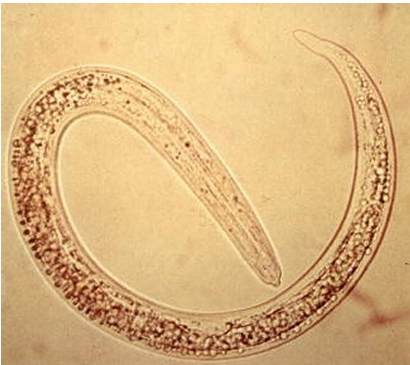
Metastrongylus pudendotectus (Metastrongylus spp., fam. metastrongylidae) Nematode.
also have M. apri, salmi, confusus
Lung worms, found in bronchi and bronchioles of pigs. Worldwide. Indirect LC. Infective stage: L3
FH: pigs
IH: Earthworms
Morphology: 6 cm, mouth 6 lips and hooks, well developed bursa in males, long spicules (hook structure on end), female tail is bent ventrally.
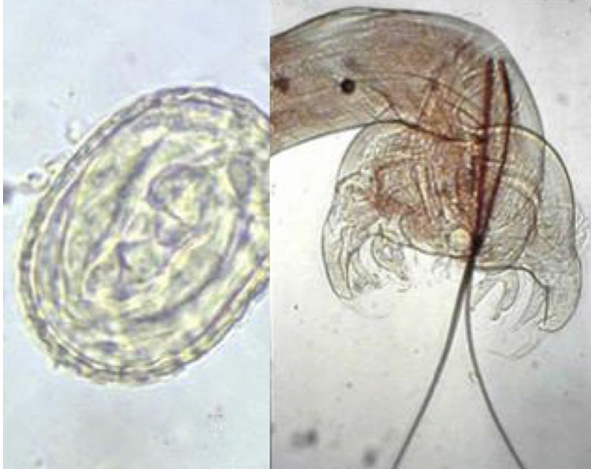
LC: Oviviparous (egg with larva) - 2-4 weeks.
Adults in bronchi of pigs → release eggs with L1 → coughed up → swallowed → feces → soil
The infected feces are ingested by IH, L3 develops
Pigs will eat the earthworms → migrate to lungs via the hepatic-portal system → L5 develops.
Treatment: Ivermectin
Diagnostics: Embryonated eggs in fecal flotation with breza, ovoscopy, necropsy - adults in lungs.


this is?
3 month old pig - 10 000 metastrongylus
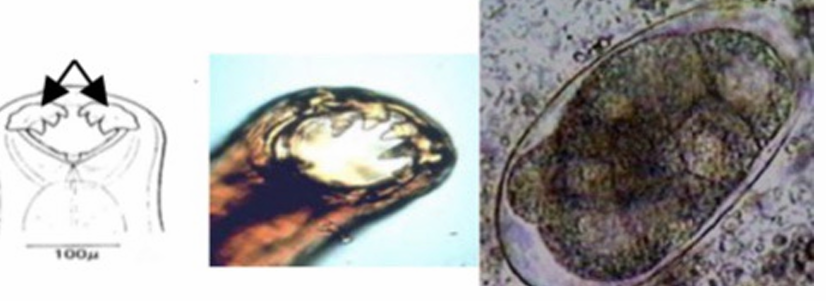
this is?
Metastrongylus

this is?
Metastrongylus
M. elongatus
M. pudendotectus
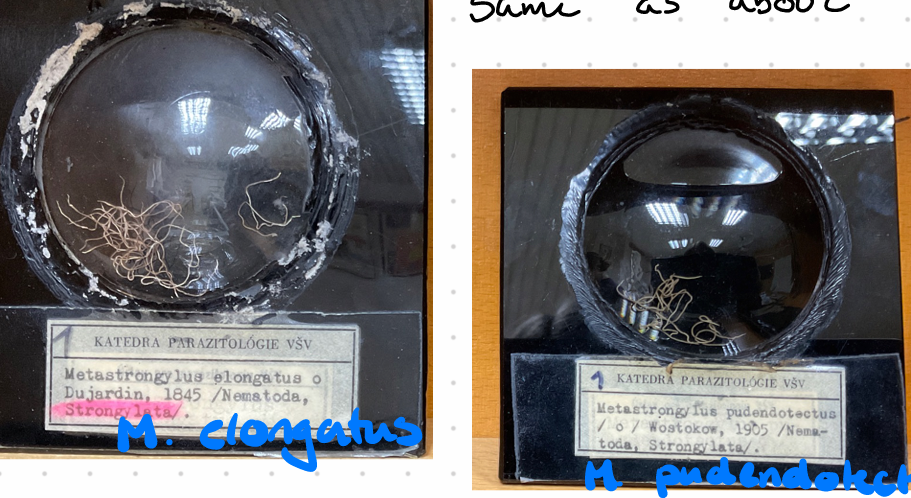

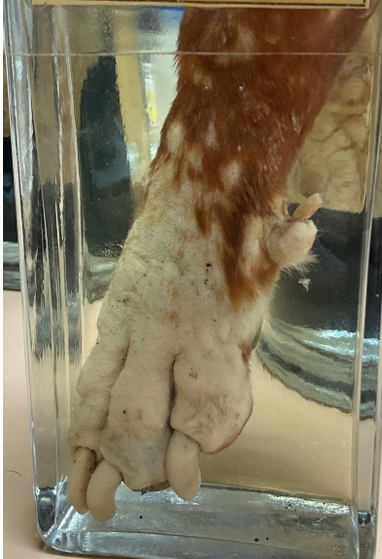
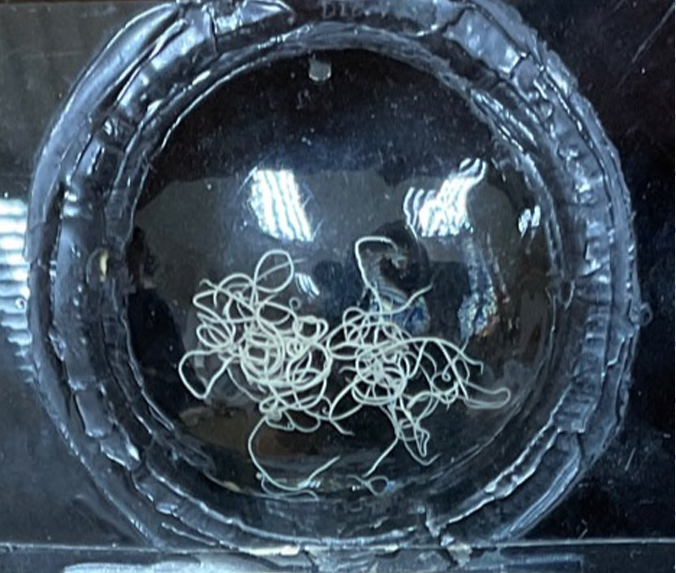
this is?
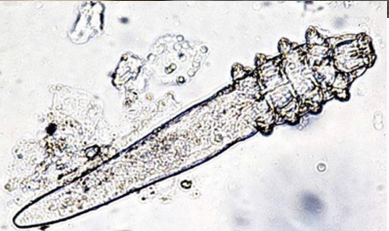
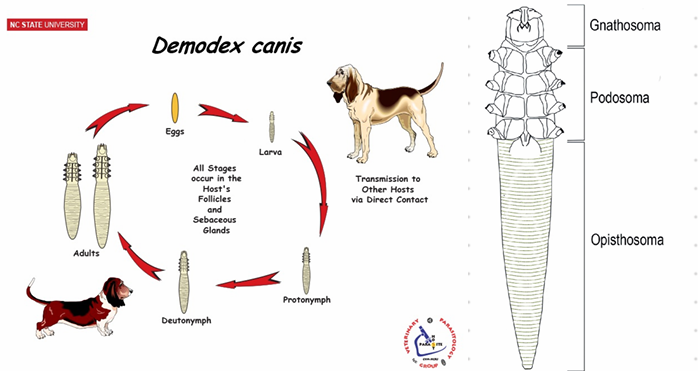
Demodex canis
Order: Prostigmata
Family: Demodicidae
Burrowing mite
🔍 Morphology
Inhabits hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and ducts
Wide mouthparts
4 pairs of short legs
Species-specific (D. cati, D. bovis, D. equi, etc.)
🧬 Life Cycle
Oviparous
Hemimetamorphus (incomplete metamorphosis)
Eggs hatch into larva with 3 pairs of legs
2 nymph molts - 4 pairs of legs
Adult
🩺 Clinical Signs (CS)
Localized: eye, nose, ears - do not itch
Generalized: starts at head and forelimbs, spreads to kidneys and trunk; alopecia & thickening of skin
Pododmodicosis: foot in dogs; alopecia due to bacterial infection; destroys hair follicles
🔬 Diagnosis
Skin scrapings
💊 Treatment
Ivermectin

this is?
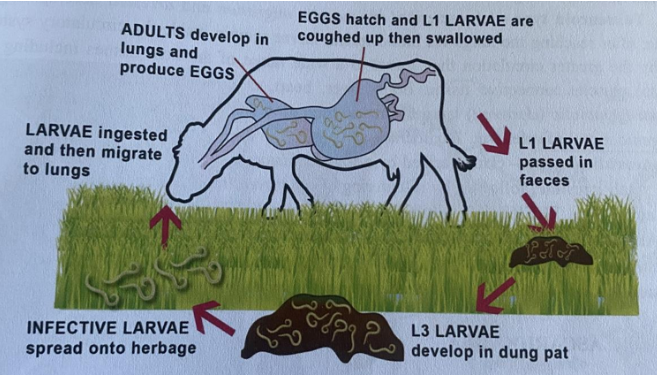
Dictyocaulus viviparus
Order: Strongylida
Lungworm
Family: Dictyocaulidae
🐮 Final Host (FH): Cattle, lama, alpaca
📍 Location: Bronchi & trachea
🔍 Morphology
3-8 cm
Mouth with 3 lips
Males have bursa copulatrix
🧬 Life Cycle (LC)
Direct, ovoviviparous
L1 larvae → feces
L1 → L3 → FH ingest free L3 larvae
Penetrates intestinal walls → lymphatic vessels.
reaches mesenteric lymph gland.
L3 → L4 → migrate to lungs.
Migrate through the parenchyma to the airways.
L4 → adult → adult lays eggs in the bronchi.
eggs coughed up and swallowed → L1 hatches in the intestine.
Prepatent phase: Larva adult in alveoli - bronchiolitis & bronchitis
Patent phase: 1000 adult worms in bronchi - parasitic pneumonia
Post-patent phase: recovery after adults are expelled - inflammation & lesions
Calves in 1st grazing season most affected
Adults have acquired immunity
💊 Treatment
Ivermectin vaccines
🔬 Diagnosis
Fecal flotation, larvoscopy
ELISA
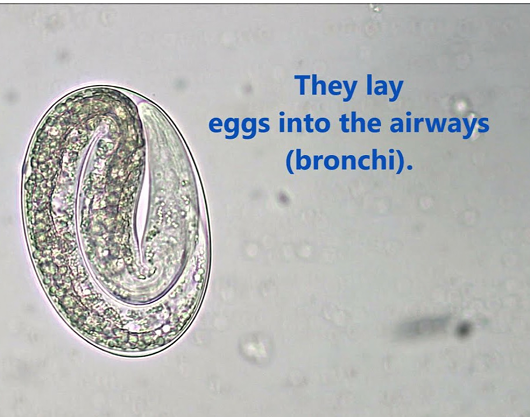
this is?
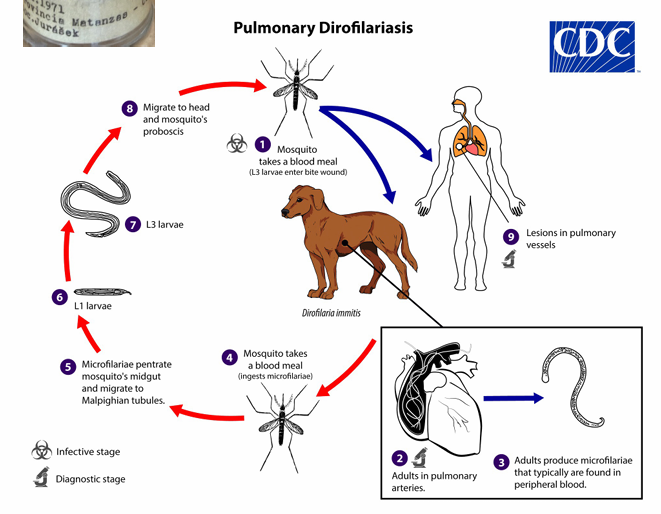
🫀 Dirofilaria immitis (Dirofilaria)
Order: Filaria
Family: Onchocercidae
Tropical
FH: Dogs, wild canids, cats, humans
IH: Mosquito
📍 Location: Heart, pulmonary artery, subcutis
20-30 cm big. 🤫
🧬 Life Cycle (LC)
6 months
Adult in heart - produce microfilariae in bloodstream
Ingested by female mosquito
L3 injected to FH
Subcutaneous & subserosal tissue - 2 molts to L5
Adult migrates to heart
💊 Treatment
Difficult; Ivermectin during mosquito season
🔬 Diagnosis
ELISA & microfilariae in blood
🩺 Clinical Signs (CS)
Vena cava syndrome
Thickening of endothelium
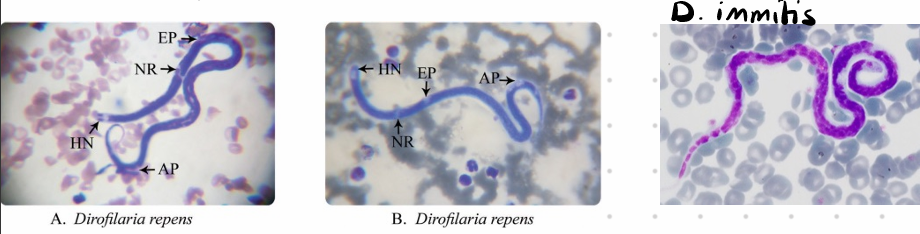
Types:
D. immitis different tail
D. repens

This is?
🐔 Heterakis gallinarum - Nematoda
Order: Ascaridida
Family: Heterakidae
Worldwide
Vector of Histomonas meleagridis (blackhead disease)
FH: Chicken
PH: earthworm
Location: cecum
🧬 Life Cycle (LC)
3-4 weeks
Unembryonated eggs passed in feces
L3 (in egg or PH) is ingested
Released in gut
Migrate to cecum
Adult
No migration!!
H. dispar: duck, goose
H. isolonche: pheasant, wild birds.
🩺 Clinical Signs (CS)
Very pathogenic for poultry - inflammation, thickening of cecum

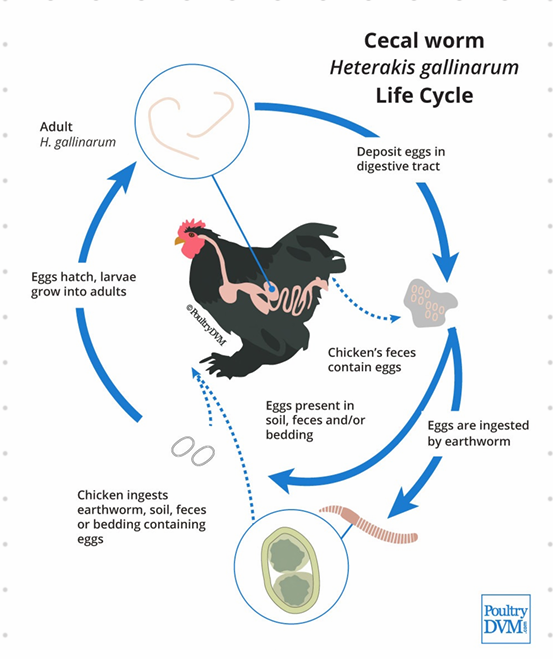


this is? (slay ser ingenting🤣🤣)
Habronema Muscae - nematoda (H. majus, muscae)
Order: Spirurida
Family: Spiruridae
FH: Donkey, horse, mules, zebra, dogs
IH: House flies, face flies, stable flies (feeding on pre-existing wound and moist mucus)
Location:
Adult in stomach
Larva on skin, eyes, prepuce, nostrils & lips
🧬 Life Cycle
Egg or L1 (eggs in H. muscae, larva in H. majus) is passed in feces
Ingested by flies
L1+L3
L3 deposited by flies on skin
On body skin: invades tissue and stops development
Infective L3 around mouth is swallowed - stomach
Adult stage after 2 months total
🩺 Clinical Signs
Conjunctival habronemiasis
Aberrant form
Granulomatous lesions in eyelids, 3rd eyelid, conjunctiva by Habronemia
Cutaneous habronemiasis
Aberrant form
Granulomatous lesions by invasion in skin wounds by both Habronemia and Drachia
Limbs, prepuce, external genitalia, ventral abdomen
Summer sores
Gastric habronemiasis
Large granulomatous mass in gastric mucosa by Draschia larva
Habronemia causes mild gastritis without tumor formation
Treatment: ivermectin
Diagnosis: Clinical signs
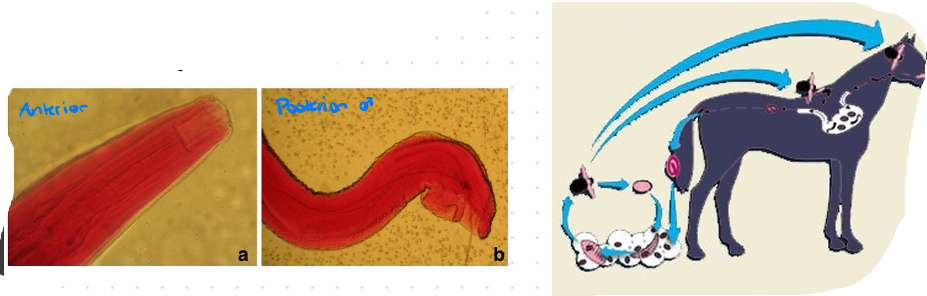

This is?`(legit zero)
Ancylostoma caninum. - Nematoda.
Ancylostoma tubaeforme (cat)
A. brazilience (cat)
Uncinaria stenocephala
Necator americanus
Morphology: Well-developed buccal capsule. Have 3 pairs of teeth used to attach to the mucosa of the intestine. Feeding - blood suckers. Larva migrans cutana by skin penetration. Anterior part bent dorsally, males have well-developed bursa, females lay 16000 eggs per day.
Location: small intestine.
Direct LC.
🧬 Life Cycle
Eggs hatch after 3 days in slightly moist soil
L1 -> L3 after 6 days
Infection by ingestion, mammary, or cutaneous
Ingestion: L3 Intestine Adult
Per skin: L3 Bloodstream Lungs Trachea Coughed-up-swallowed Adult
Somatic migration/transplacental: larva from mother to fetus
Transmammary (only caninum): larva stuck in tissue mammary gland of pregnant dog enter milk
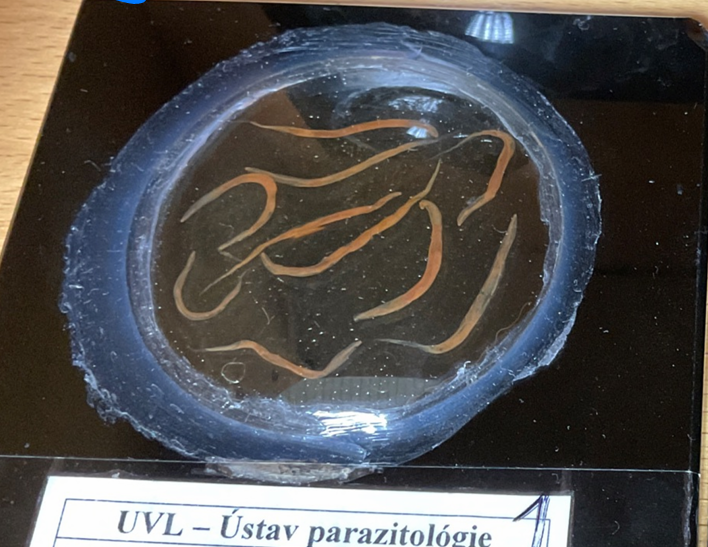
This is?
🐴 Oxyuris equi
FH: horse, location: LI
Common name: pinworms
🔍 Morphology
Females:
Slender, sharp posterior end
Large, esophageal bulb
Swollen cuticle
Males:
Much smaller
🧬 Life Cycle
Direct
Unembryonated eggs in SI hatch L3
Pass into large intestine and goes into the mucosa of cecum and colon
Molt to L4 (8-10 days)
Adult (2 months) elongate & fertilized
Female to anus to lay eggs on perineal skin (yellowish/gray, 8-60000 eggs)
L3 inside egg (3-5 days)
FH rubs anus against surfaces
💊 Treatment: Ivermectin
🔬 Diagnosis: Coprological with perianal swab
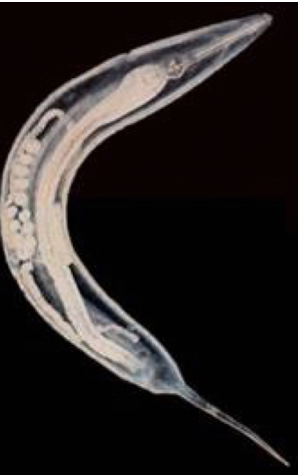

What is this? (just getting worse at this point)
Oesophagostomum Dentatum, nematoda
O. brevicauda
O. quadrispinulatum
O. dentatum
Final Host: Pig, Location: LI and Cecum
🧬 Life Cycle
Direct LC
Unembryonated eggs 45 days
Eggs passed in feces
hatches
Molt L1-L3
Ingested by FH SI & LI and forms cysts
Inside cyst L3-L4
L4 hatches & goes to lumen of LI
Adult
Nodules form in the cecum
💊 Treatment: Ivermectin
🔬 Diagnosis: Coprological (flotation)
🩺 Clinical Signs: All except O. venulosum forms nodules.
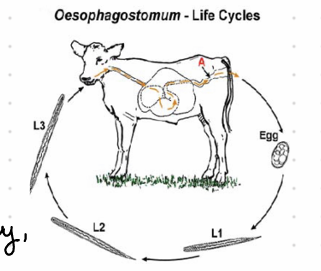

this is? 😒😒
🐔 Dispharynx nasuta, Nematoda
Final Host: Poultry - Chicken turkey, game birds, pigeon
America, Asia & Africa
🧬 Life Cycle
Indirect/Direct
Adult lay egg in proventriculus of FH
Eggs shed in feces
Direct: FH eat contaminated soil fed or water with embryonated eggs
Indirect: FH eat IH (water lice, bugs)
💊 Treatment: Ivermectin

this is?
Trichuris suis, Nematoda (står trichocephalus suis)
Whipworm
Oviparous
Location: LI
🧬 Life Cycle
Unembryonated eggs are shed by host`s feces
L1 larvae develop inside the egg in the environment
Host ingest embryonated eggs
eggs hatch and L1 are released in the SI → large intestine (All 4 moults - happens)
The larvae matures into adults within LI → release eggs.
💊 Treatment: Fenbendazole
🔬 Diagnosis
Flotation (K-M or Breza)
Unembry eggs
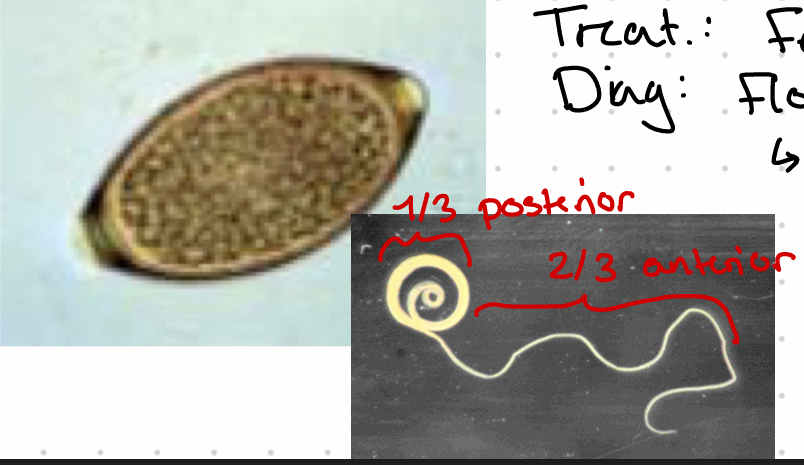

Esophagus 2/3 of body with glands (stichocytes)
Tail of male is coiled.
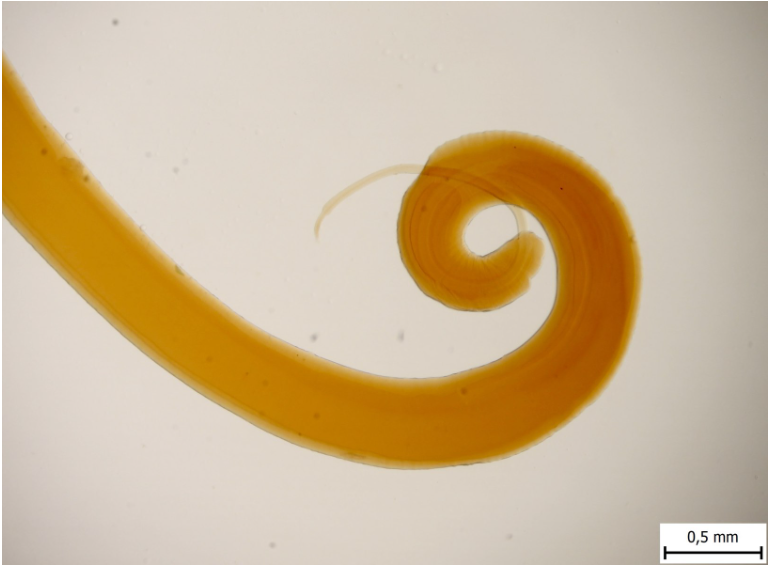


this is?
Trichuris ovis
male on right
female on left (with long thin)
Adult - flaggellate shape, thread-like front part of the body 3-8 cm.
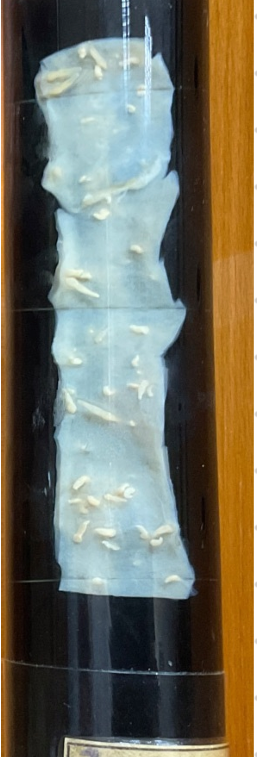
this is?
Polymorphus magnus (Acanthocephala)
Final Host: Duck goose swan chicken
Location: SI
IH: crustaceans
LC: - 30 days
embryonated eggs with acanthor shed in feces
eggs are eaten by IH → acanthella → cystacanth (infective stage forms)
FH ingest IH, cystacanth hatches and attach to SI wall → adults → lays eggs
🔬 Diagnosis: Sedimentation
Treatment: Bitinol
species of polymorphus: Minitus, magnus
“Picture shows adult - P. minitus” - Proboscis anteror - spirus and hooks.
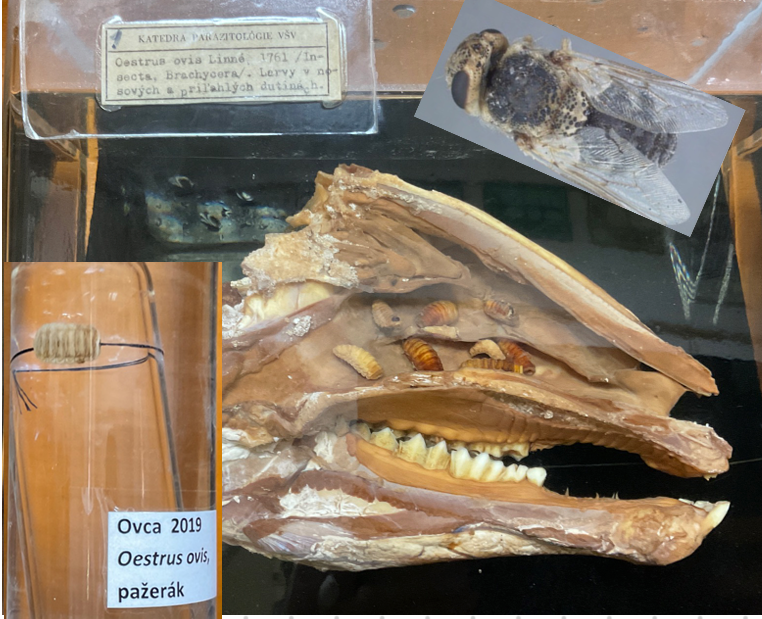
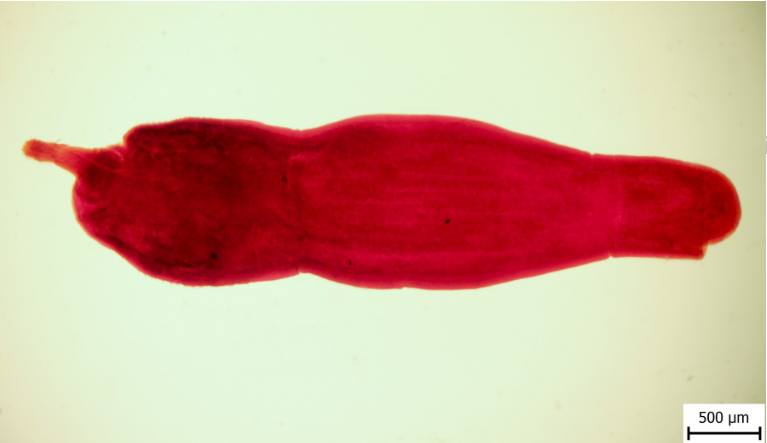

This is?
Oesterus Ovis
Sheep nasal botfly
Worldwide
Larva: large black oral hooks, ventral surface has small spires.
Adults: black spots (esp. thorax)
🧬 Life Cycle
Viviparous
L1 is released by nostrils and mouth and migrate through nose → attach by hooks L2 frontal sinus → L3 migrate to nostrils → fall out by coughing or sneezing → molt into pupar adult
Larva stay in nose and frontal sinus through the winter. Complete migration when weather is warmer in spring
Males dies at fertilization
Adult flies (april -> june) Inside body rest of the year
🔬 Diagnosis: endoscopy, ELISA
💊 Treatment: Ivermectin
Rhinoestrosis in horses.

this is?
Cephenemyia stimulator
Eggs hatch inside females → deposited into nostrils → migrate through nose into throat → L3 → fall out → pupate in soil → adult (2-3 weeks). Mates → egg.
Oviviparous. Deer botfly
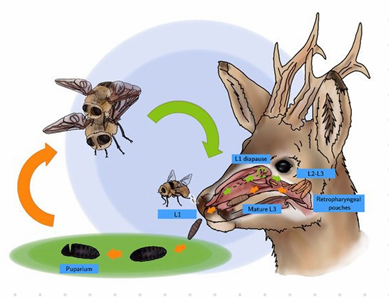

this is?
Melophagus ovinus (Insect)
Vector of blue tongue virus & border disease virus (BDV)
Brown & hairy, host specific, permanent ectoparasite, wingless, small head, D-V flattened, strong legs with tipped claws, 3 pairs of legs, small eyes, when released from pupa they have wings which breaks when attached to host.
LC: whole life in wool of sheep - hemnatophagous (blood sucking)
Chest and neck area or abd. wall
Complete metamorphosis
Viviparous
females produce 1 larva at the time inside mother for 1 week before → pupates.
Pupae is glued to wool
Females live for 4 months
increase in winter, spread by contact
Diagnosis: find adults or viviparous pupa on surface or larvae.
Treatment: Pour-on w/ pupates Pyrethorids, dipping
Cause melophagosis. (abnormal craving/eating)

this is?
Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) - ivermectin treat.
Multiple host species
Females release embryonated eggs with acanthor → in IH (arthropod) → acanthor released → acanthella → cystacanth → IH ingested by FH (fish) → intestine.
FH: fish
IH: arthropods
Alters behavior and color to make them more visible - goes from avoiding light to seeking it.

this is?
Ticks
A. maculatum 140 species
A. americanum
Amblyomma cayennese (ixodidae) - 3 host, large (THE LEFT ONE, BIGGER)
Boophilus Microplus (Izodidae) - 1 host (THE RIGHT ONE)
Vector of hepatozoon americanum (Amblyemma)
Vector of Babesia bigemina (Boophilus)
3 host hard tick where each stage is on separate host over 3 years
Temporary parasite fading 1 time per molt
Females - blood sucker
Found in tropic (Africa America)
🔍 Morphology
Scutum on dorsal surface in male, small area in larva
nymph and female, 1st pair of legs is longer to grasp host and has 6 segments, Haller's organ (ist pair) to detect (O2 & heart)
Stigmata behind last pair of legs which is respiratory opening leading to trachea
Gnathostoma ticks (head) - anterior
soft ticks - ventrally, cannot see head.
Signs: produces local lesions
Diagnosis: finding on skin, soft vs. hard - location of head.
💊 Treatment: spot on spray, bravecto
LC: Hemimetabolous.
Egg → larva (3 pairs of legs) → nymph (4 pairs of legs, spiracle, no gonopore - 3 stages, protonymph, deutonymph, tritonymph) → Adult (4 pairs of legs, spiracle, gonopore)
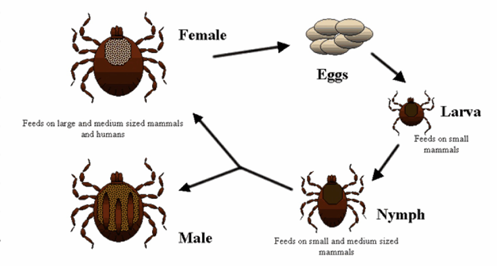

this is?
Hypoderma bovis
Includes species like H. actaeon and H. diana, belonging to the Oestridae family. H. lineatum + bovis - bovine.
Location: Larvae are found under the skin, in the spinal cord (bovis), and esophagus. (H. lineatum)
Adult: Adults are free-living.
Larva: Barrel-shaped and dark brown.
Life Cycle:
Eggs are laid on hair around the hindlimbs and hatch in 4 days.
Larvae migrate into the skin, then to the esophagus/spinal cord for hibernation during winter.
They migrate to the skin surface (30 days), drop off, and pupate for 1-3 months before emerging as adults in May-July.
H. bovis lays single eggs, with larvae migrating along nerves and the spinal cord.
H. lineatus lays eggs in batches, with larvae migrating along muscle or connective tissue.
Clinical Signs:
Nodules with larvae inside.
H. bovis can cause paraplegia due to pressure on the spinal cord.
Dead larvae in tissue release proteolytic enzymes.
Diagnosis: Finding lesions and eggs in summer.
Treatment: Ivermectin is effective if used in Sep-Oct (to avoid larvae dying inside the animal). Adults live briefly to lay eggs and are host-specific.

this is?
Large strongyles - Strongylus vulgaris (Nematode)
In horses, including Strongylus vulgaris, Strongylus edentatus, and Strongylus equinus (migratory)
Worldwide distribution.
Non-migratory species: Triodontophorous serratus, Triodontophorous tenuicollis, Triodontophorous brevicanda minor.
Location: Large intestine and cecum.
Life Cycle:
Direct life cycle.
Adults live in the large intestine and cecum.
Eggs are passed in feces.
L1 larvae hatch, develop into L3 larvae, and are ingested by the final host.
S. vulgaris: L3 penetrates the mucosa, develops into L4 in the submucosa, enters arteries, and migrates to the cranial mesenteric artery, molts to L5, migrates to the intestinal wall, forming nodules around the large intestine, cecum, and colon. Nodules rupture, and adults emerge (6-7 months).
S. equinus: L3 invades the wall of the small intestine, cecum, and colon, encapsulates in nodules, molts to L4, leaves nodules, goes through the peritoneal cavity to the liver (3 months), migrates back to the large intestine by crossing the abdominal cavity or via the pancreas, molts to L5 during the migration back (9 months).
S. edentatus: L3 excyst in the small intestine, penetrates the gut wall, molts to L4 in the subserosa (3 months), often in nodules, migrates to the root of the mesenteric artery, then goes to the liver and lungs before going to the wall of the cecum and right central colon (immature adult in lumen of LI).
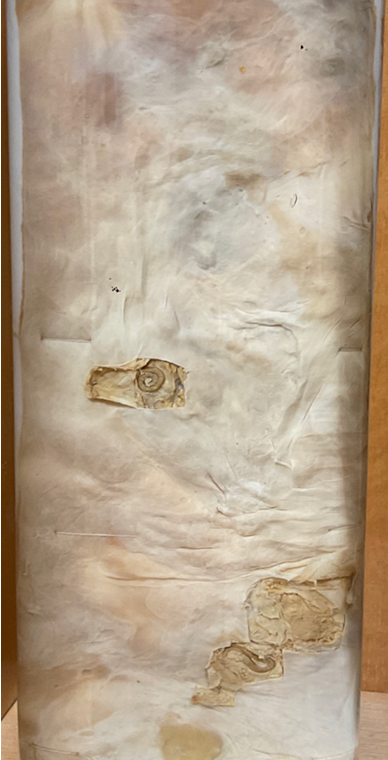
This is?
Alfortiosis of the Peritoneum - Strongylus Edentatus.
S. edentatus: L3 excyst in the small intestine, penetrates the gut wall, molts to L4 in the subserosa (3 months), often in nodules, migrates to the root of the mesenteric artery, then goes to the liver and lungs before going to the wall of the cecum and right central colon (immature adult in lumen of LI).
athogenesis:
Young worms cause inflammation and obstruction of blood vessels.
S. equinus early migration produces hemorrhagic nodules.
S. edentatus L4 in subperitoneal cysts cause pathological changes in the flanks.
Causes severe and fatal colic due to obstructed blood flow to the intestines.
Adult worms create small bleeding ulcers in the large intestine, causing blood loss.
Clinical Signs: Colic and diarrhea.
Diagnosis:
Flotation (fecal egg count).
Necropsy.
Treatment:
Moxidectin.
Ivermectin.
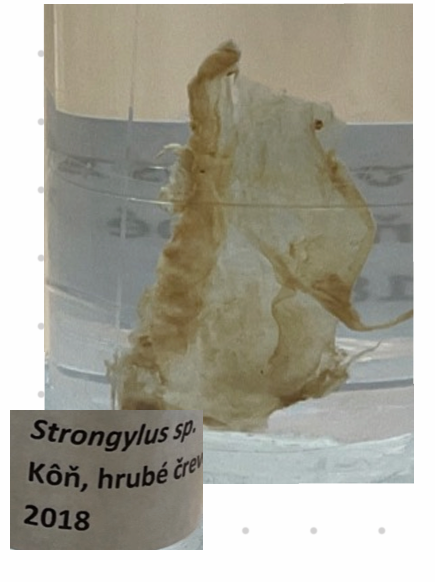
this? (what the sheesh)
Small Strongyles (Cyathostomum) - Nematoda.
Genera: Cyathostomum, Cabellonema, Coronocyclus, Cylicocyclus
In cyst: resistant to most dewormers
L3: does not migrate, sheaths in environment (when eaten, they exsheat).
Location: LI and SI
Life Cycle:
Adults live in the lining of the LI, laying eggs passed in feces → L3
L3 is ingested by the final host and encysts.
L3 can hibernate in cysts in the intestinal wall over the autumn/winter before hatching adults at the right time of year
L3 enters the wall of the cecum and LI, molts to L5, leaves the wall, and goes to the lumen to mature into adults.
Pathogenesis:
Underperformance, loss of condition, feed inefficiency, and predisposition to secondary diseases.
Ulcerated gut wall when L5 leave the wall.
Severe enteritis (Cyathostominosis).
Clinical Signs:
Severe diarrhea and weight loss.
Treatment:
Moxidectin is the best choice, with Ivermectin as another option.
Yearly deworming is recommended.
Diagnosis:
Flotation, necropsy, and larval culture for species identification.
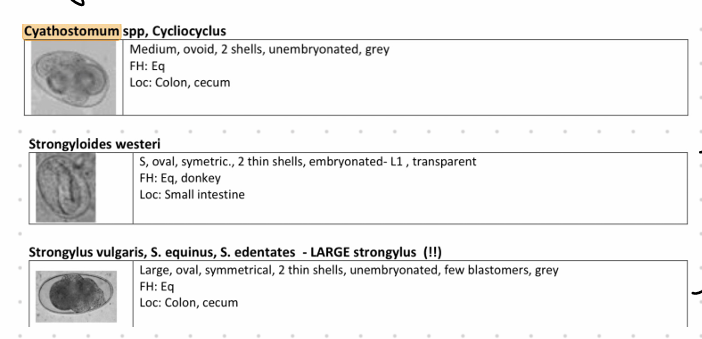


this is?
Angiostrongylus - A. vasorum
Superfamily: Metastrongylida
Family: Angiostrangylida
Morphology: Oviviparous (egg/Larval)
L1: Roar tail with dorsal thorn, rudimentary buccal cavity, lips small and slender, thin spicula
Males: Bursa copulatrix reduced or absent
Location: Pulmonary artery and right heart
Intermediate Host (IH): Snails
Paratenic Host (PA): Frogs
Distribution: Found in Western Europe & Canada
Life Cycle:
40-60 days
L1 excreted in feces ingested by snails molt to L3
Final Host (FH) ingests IH/PA, L3 is released, penetrates the wall of SI, molts to L4, goes through bloodstream to heart and lungs, L4 to L5 to adults
Adults release eggs with L1, which is carried to lung capillaries
L1 hatches, penetrates alveoli, migrates to pharynx, coughed up, swallowed, excreted in feces
Pathogenesis / Clinical Signs:
Chronic disease: Months to years, all positive for anemia, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss
Adult located in large vessels, Larva in lung arteries and capillaries
Leads to circulatory and heart failure
Severe infections: Tachycardia, tachypnoea, cough (with blood), nasal discharge
Diagnosis: Fecal flotation (Baermann method) and L1 in sputum
Treatment: Best: Milbemycin oxime, Fenbendazole: Same, but specific to lungs
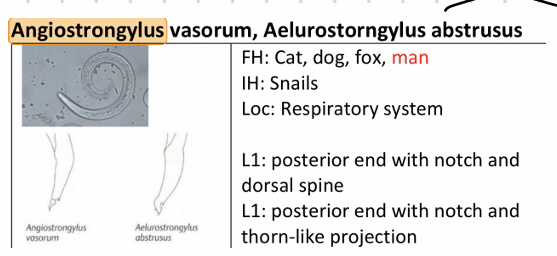

this is?
Tetrameres Fissispina
Order: Spirurida
Family: Tetrameres
Species: fissipinna, americana, crami, confuce
FH: birds, in proventriculus
IH: crustaceans, cochroaches, grass hopper
🧬 Life Cycle
Eggs shed in feces hatch when ingested by IH molt to L3 FH eat IH migrates to glands in proventriculus molt to adult
Males in mucosal surface and upper regions of glands die after mating females is dup in mucosal glands
Bloodsuckers: cause anemia and local erosion
🔬 Diagnosis: Necropsy dark spots on surface of proventriculus

this is?
Gongylonema Pulchrum
Order: Spirurida
Species and Locations:
Gongylonema pulchrum: Found in the esophagus and rumen of various mammals (Ru, Su, Eq, Dur, Man).
G. verrucosum: Found in the rumen, reticulum, and omasum of ruminants (Ru).
G. ingluricula: Found in the crop, esophagus, and proventriculus of birds.
Intermediate Hosts: Coprophagous beetles and cockroaches.
Life Cycle:
Indirect life cycle.
Eggs are passed in feces and ingested by the intermediate host.
L1 larvae hatch and molt to L3 within the intermediate host.
Final host eats the intermediate host, and the parasite molts to an adult in the esophageal mucosa.
Pathogenicity:
Low pathogenicity but can cause irritation.
May cause mild esophagitis in the host.
Diagnosis: necropsy.
this is?
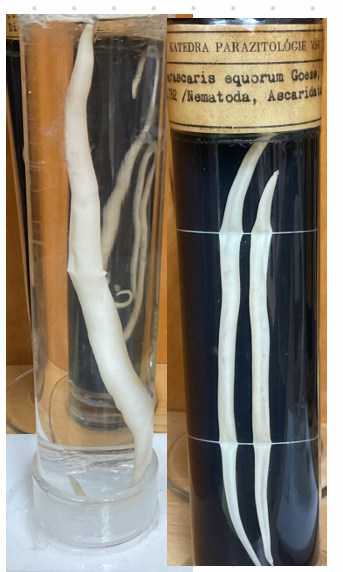
Parascaris equorum - Nematode
Order and Family: Ascaridida, Ascarididae
Worldwide distribution
Morphology:
Females: 50 cm long
Males: 15-20 cm long
Mouth: 3 prominent lips
yellow to white
Large size
Final Host:
Horse & donkeys (especially young foals in SI)
Adults typically have immunity
Life Cycle:
Direct, 10 weeks
Unembryonated eggs passed in feces, develop to L3 inside the egg
Horse ingests egg with L3, hatches in SI
Larvae penetrate the wall, migrate to liver (L3 to L4)
Migrate to heart and lungs, then through bronchi to trachea, are coughed up and swallowed
Molts to L5 (adult) in SI
Pathogenesis:
Petechial hemorrhages in lungs, leading to lymphatic nodules with dying larva and lymphocytes
Nodules more common in older foals with re-infections
Foals may cough, gray/white nasal discharge.
Diagnose: fecal flotation, Treatment by Benzimidazole.
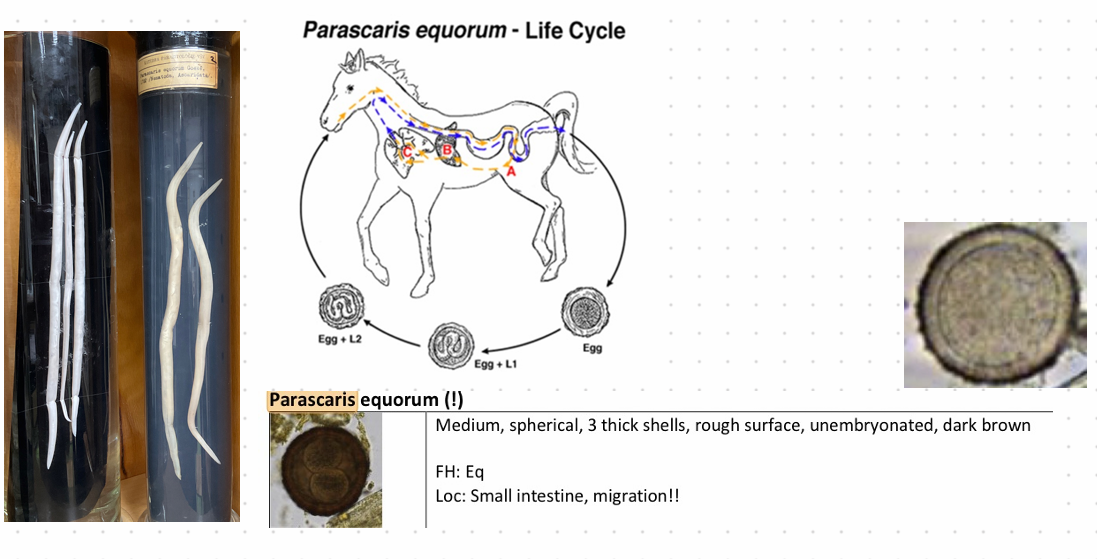

this is?
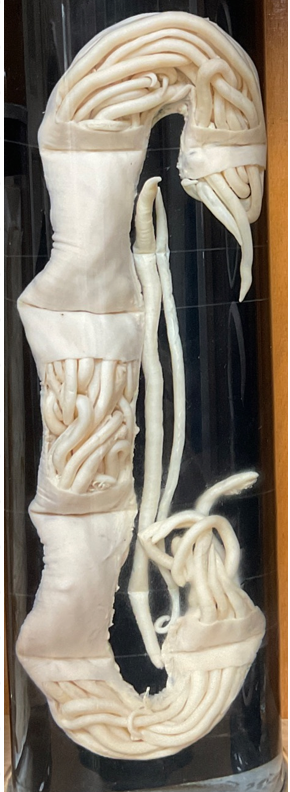
Ascaris suis - Nematode.



this is?
Acarida columbae - Order: Ascaridida


this?
Ascaridia anseris
FH: geese
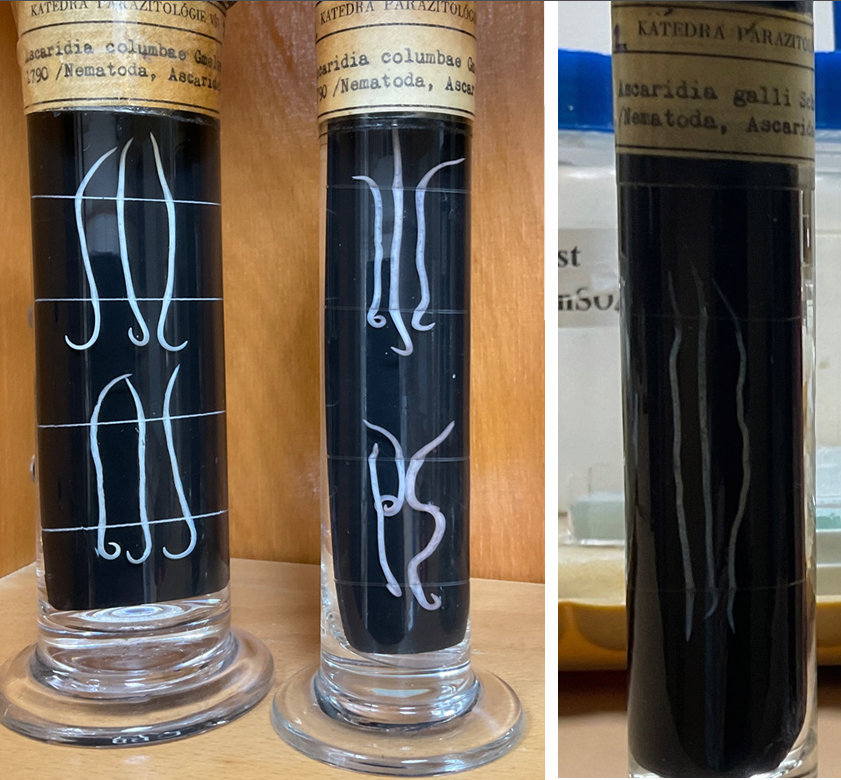

this?
Ascaridia galli

this is?
Toxocara vitulorum

this?



this is?
Baylisascaris spp.
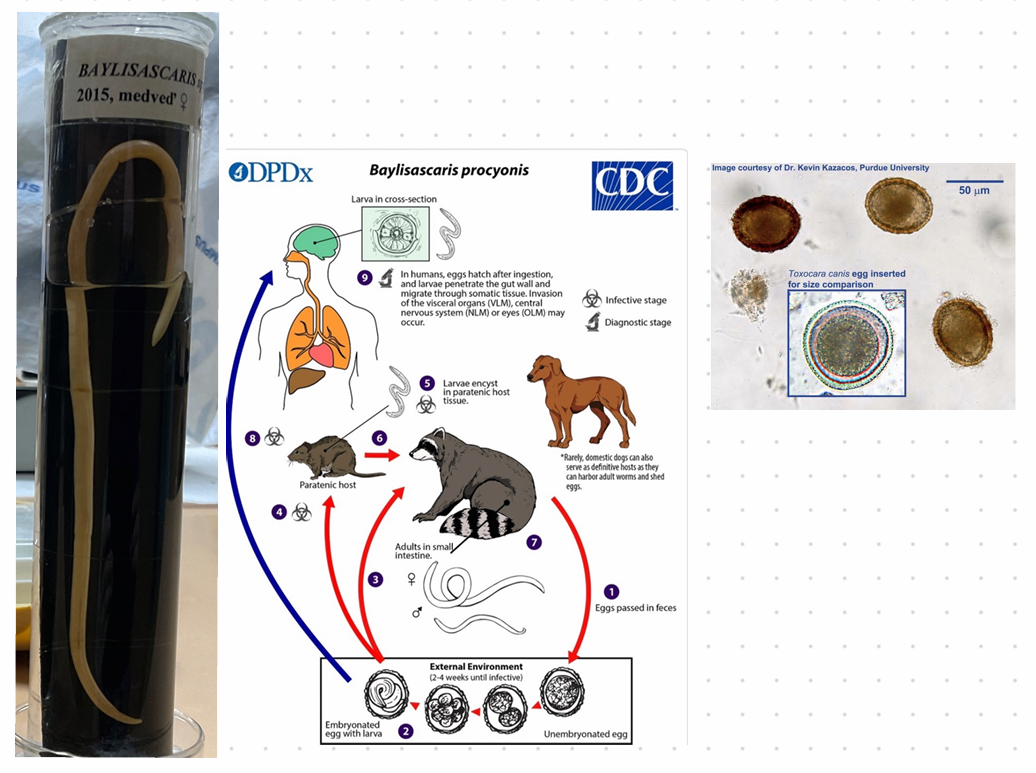


This is?
Toxocara Leonina - nematode


this is?
Toxocara cati
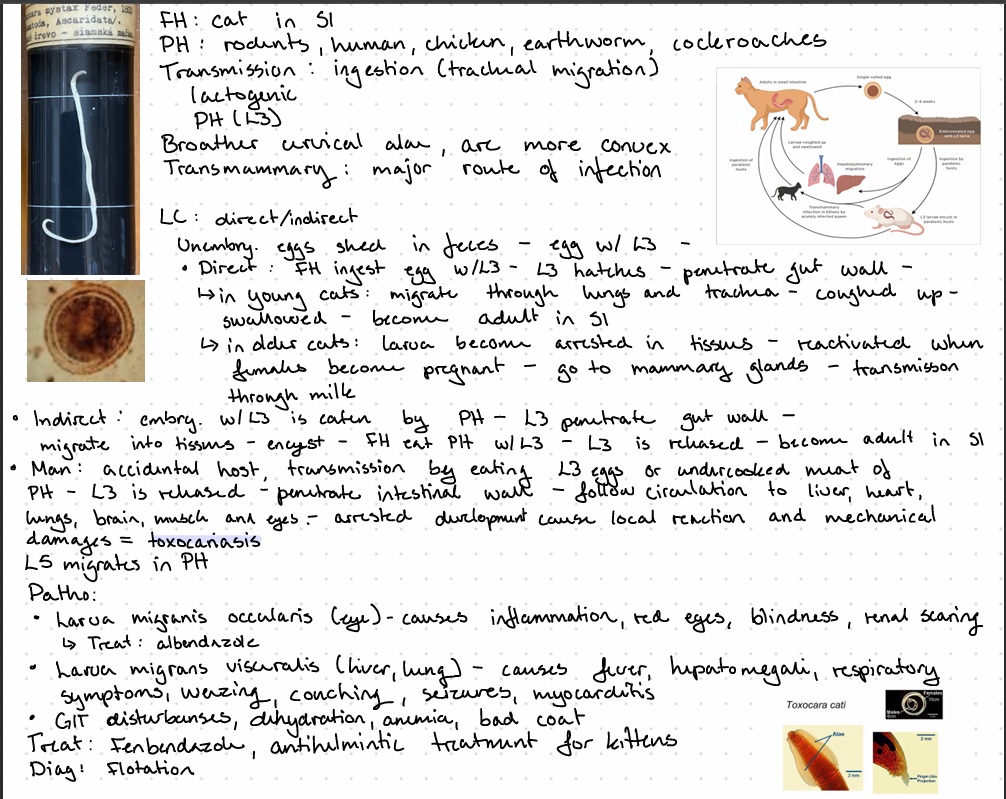

this is?
Toxocara canis


this is?
Stephanurus dentatus - nematode


this?
Gordius equanticus


this? (another shitty)
Syngamus Trachea - nematode
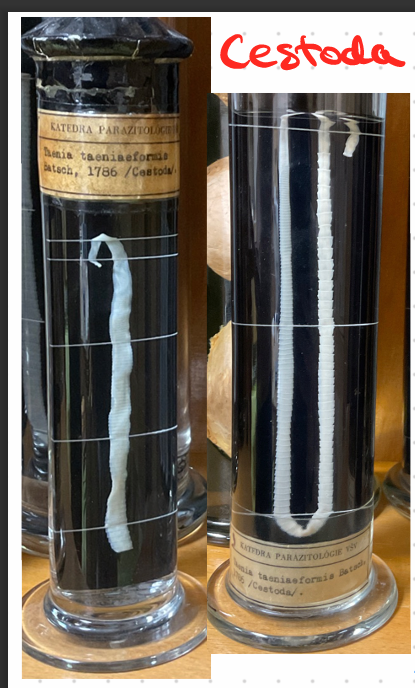



this?
Taeinia Taeniaformis - cysticercus fasciolaris (Cestode)
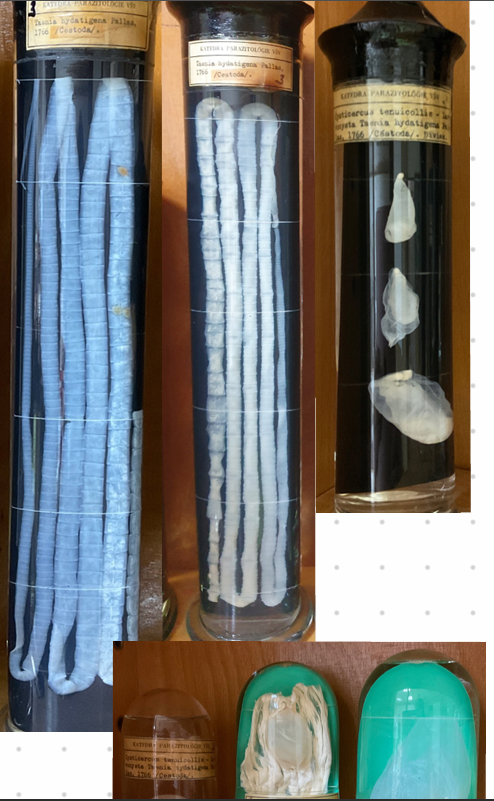
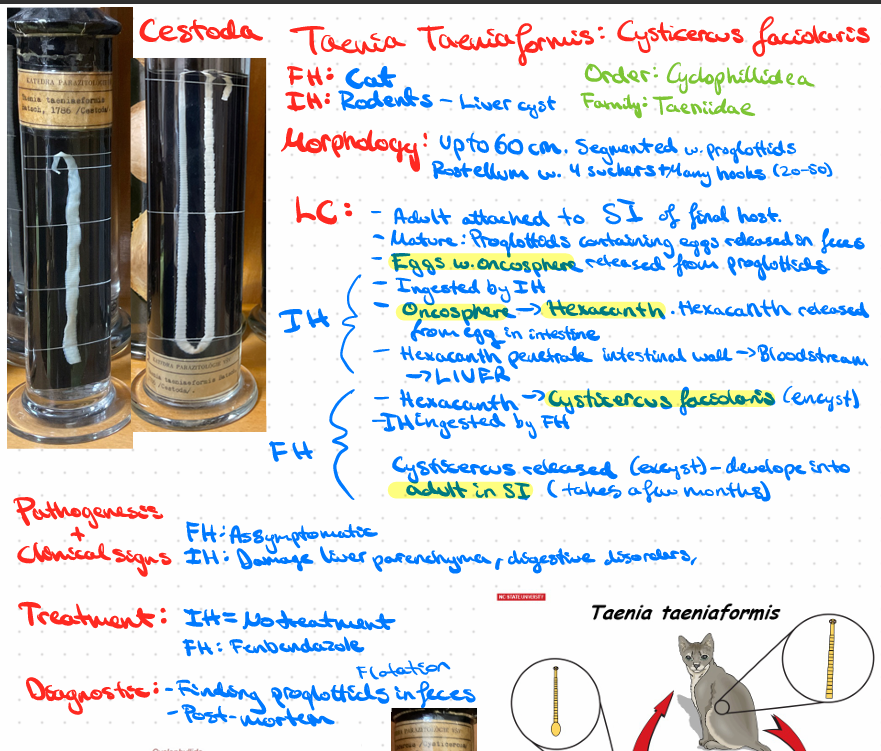
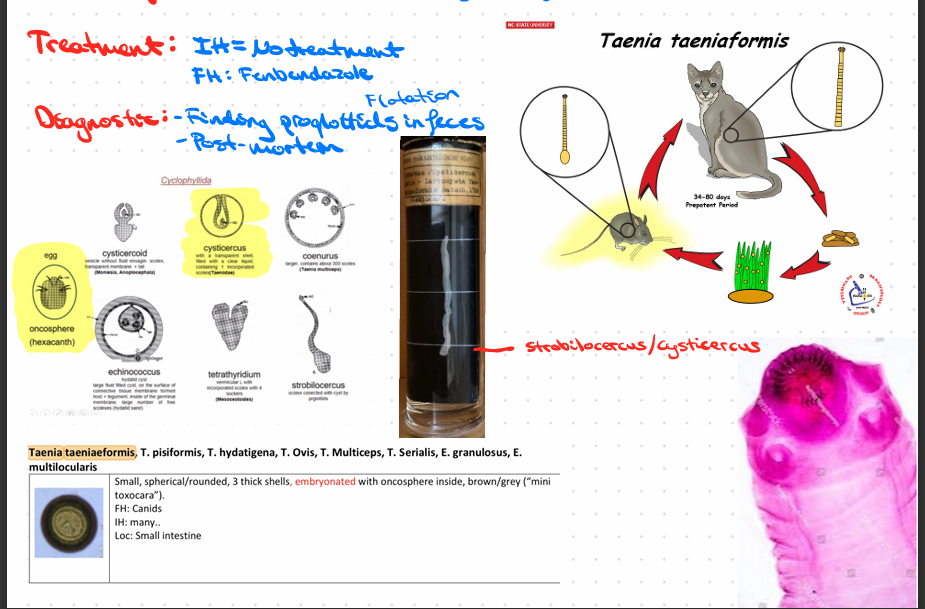

this?
Taenia Hydatigenea - Cysticercus tenuicollis
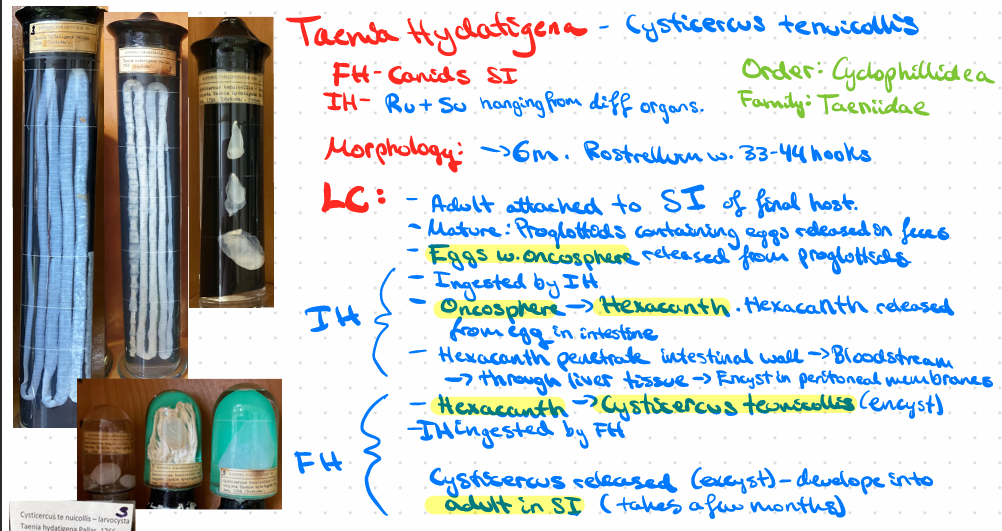


this?
Taenia saginata - cysticercus bovis

THIS?
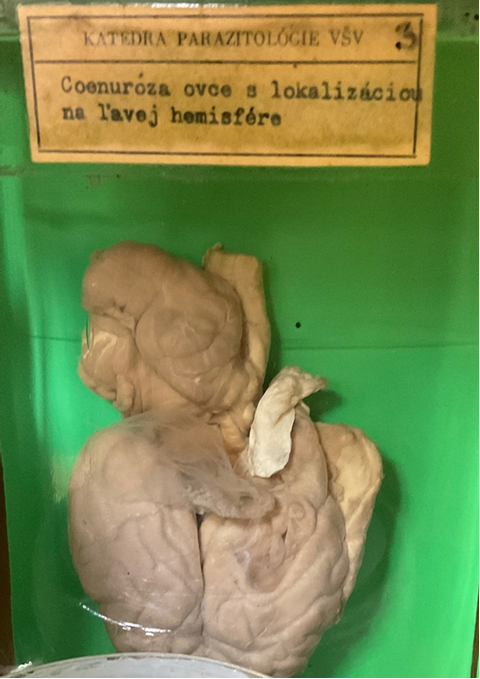
Taenia multiceps - coenurus cerebralis


this?

taenia pisiformis - cysticercus pisiformis
Order: cyclophyllidae
Fam: taeniidae
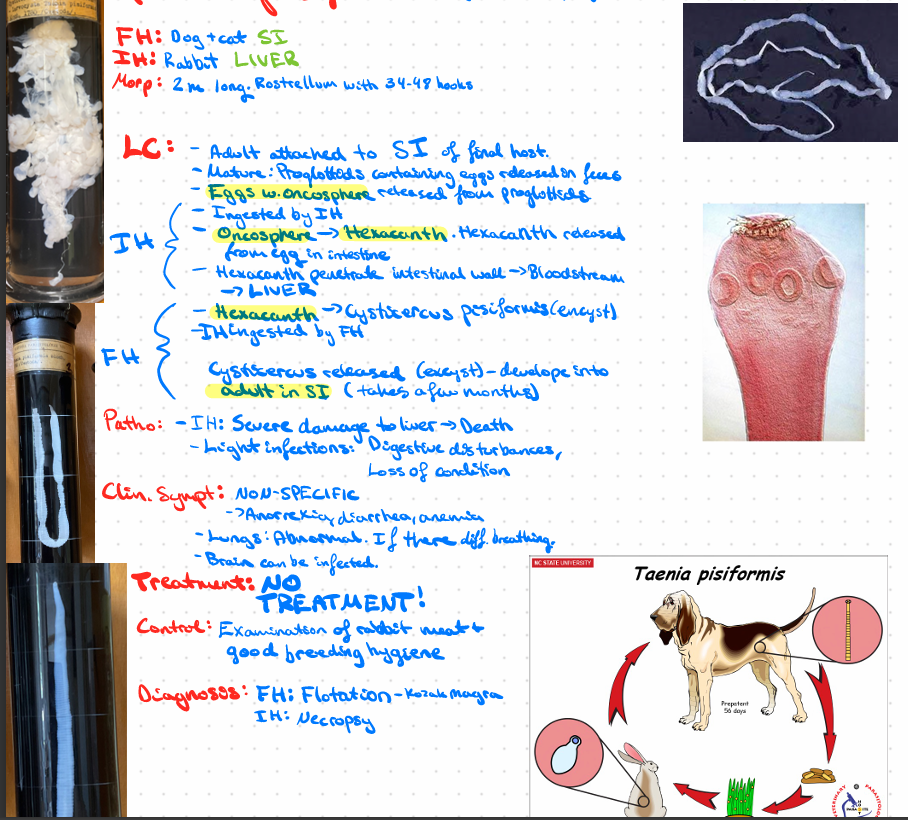

? - WHAT THE FRICK
taenia pisiformis - c. pisiformis (CONGRATS du leste bra hehehehehesakfjre0fujfr9+43

?
Taenia solium - cysticercus cellulosae


?
Cittotaenia ctenoides - Cestode


?
Echinococcus granulosus - Hydatid cyst

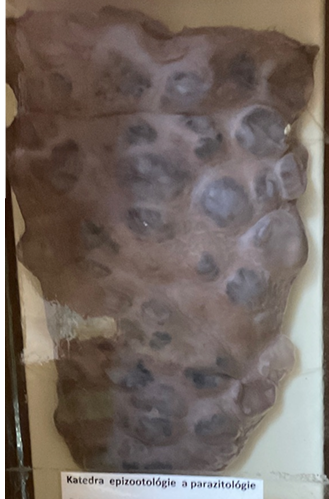
this?
Echinococcus multilocularis - Alveolar cyst


this?
Moniezia expansa - Small ru, Cestode
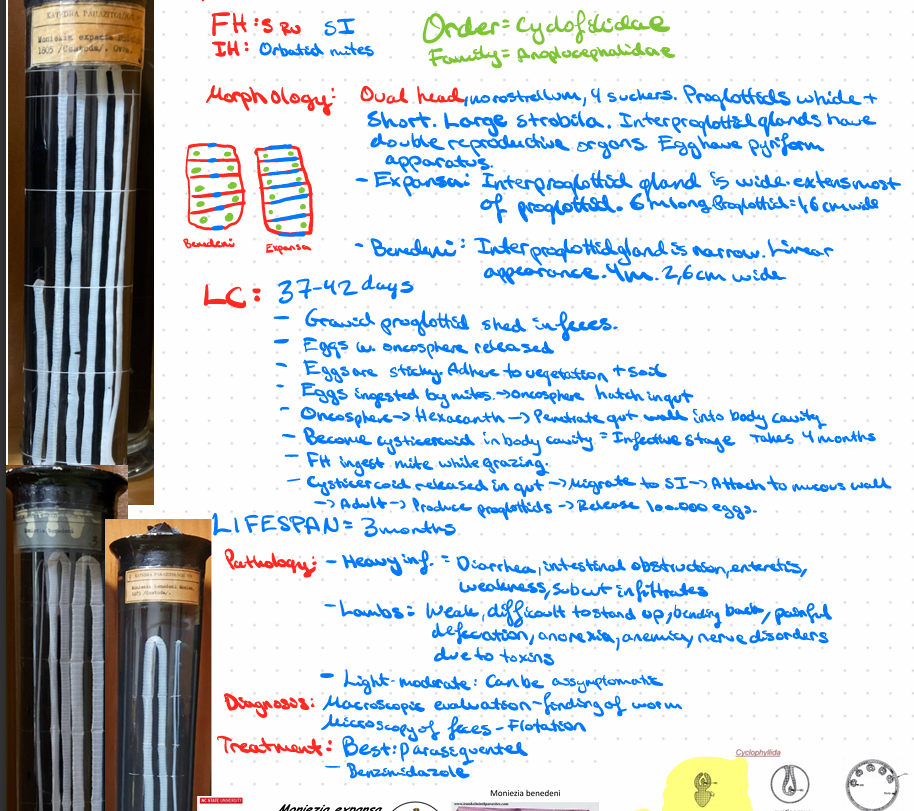
????
Moniezia benedeni i guess
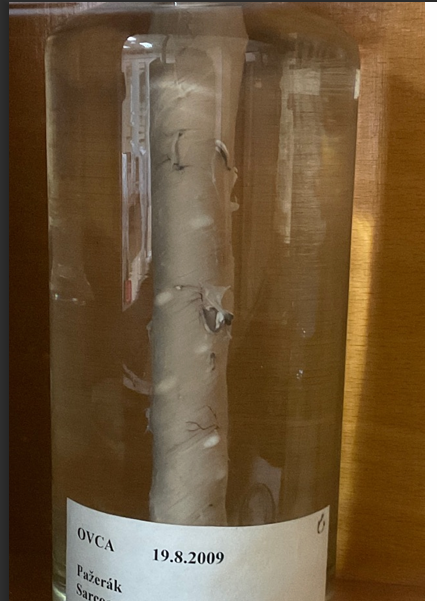


this?
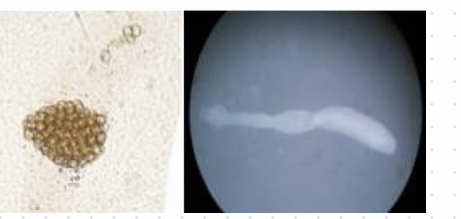
Sarcocystis sp.
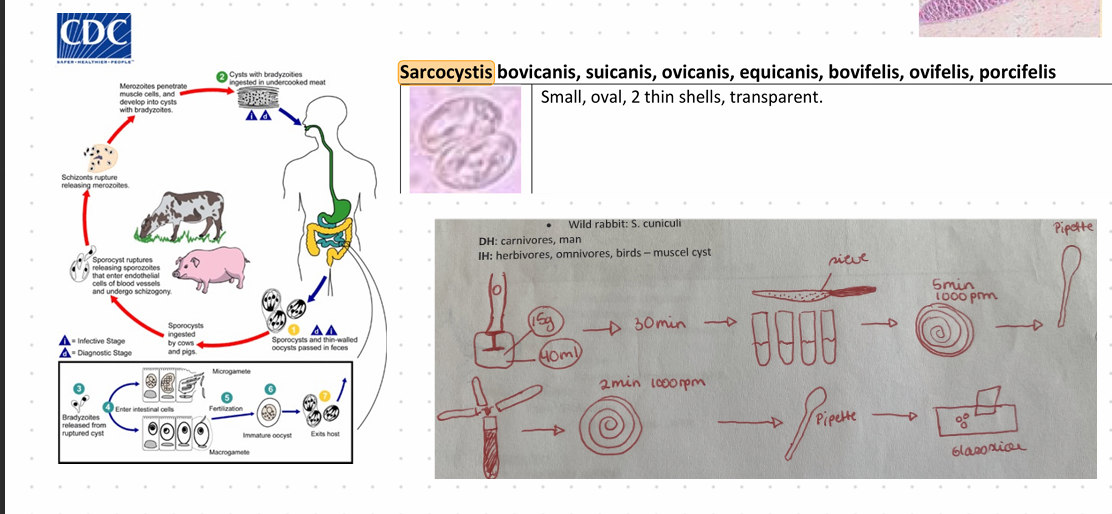


??
Eimeria stiedai - protozoa
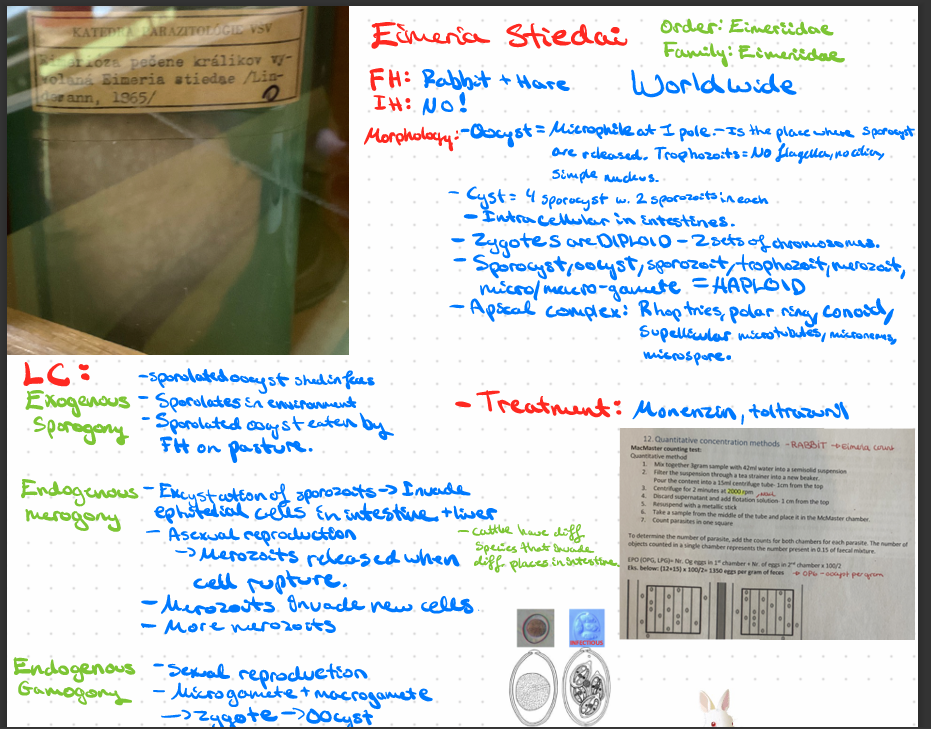
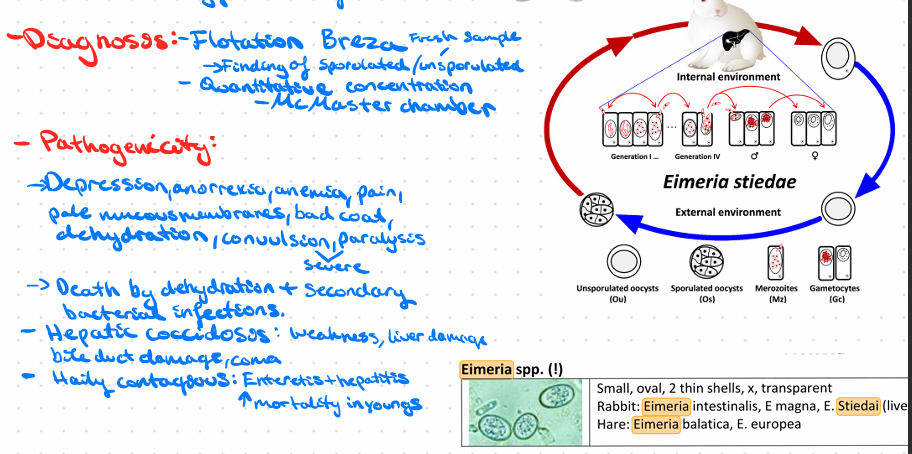
??KJ)J)jhew09fjhrefgh4w3er
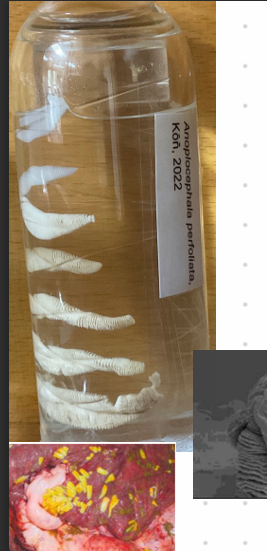
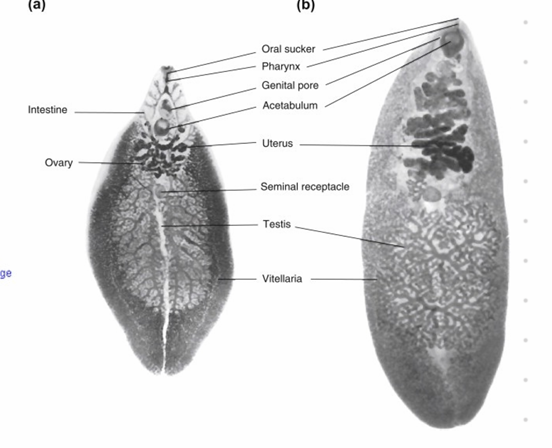
Anoplocephala perfoliata + magna (CESTODE)


THE?
Gammarus Pulex: Amphispoda



this is?
Fasciola hepatica - Trematode, worldwide
Order: Eccinostomidae
Fam: Fasciolidae
Common liver fluke


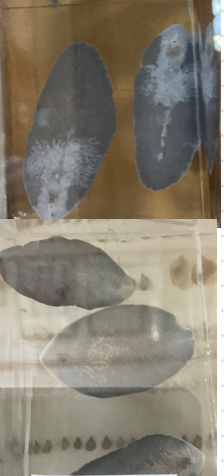
this?
Fascioloides magna - Trematode


this?
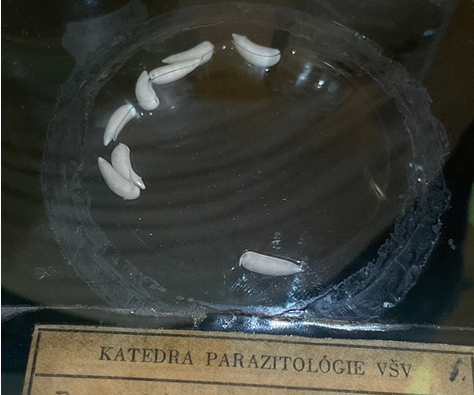
Paramphistomum cervi - trematode
order - amphistomida
Fam: paramphistomida
P. cervi, daubneyi, ichikawai, microbothrium
Alike F. hepatica eggs, just different color.

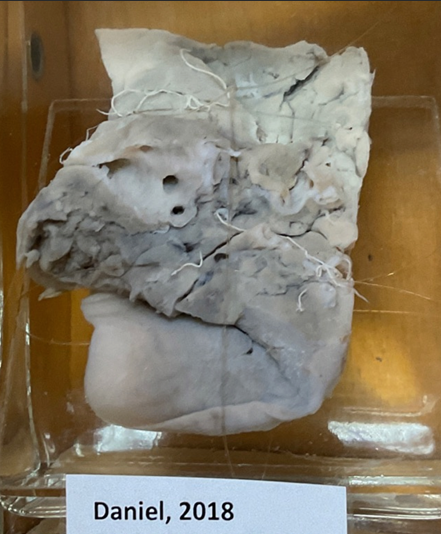
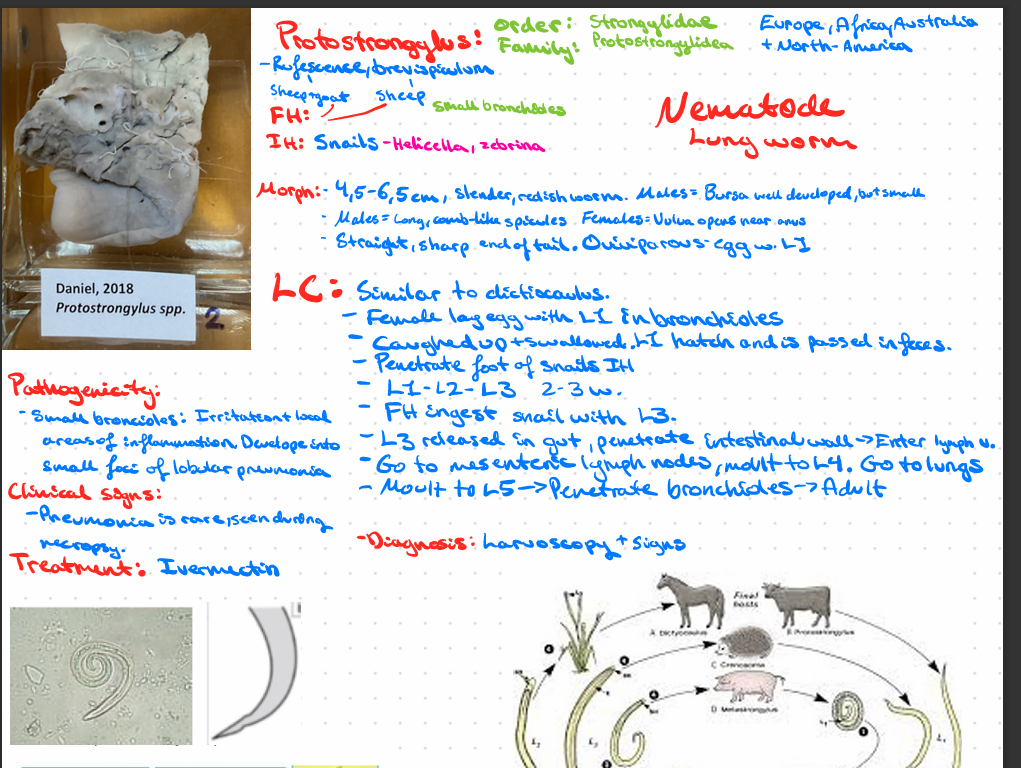
this?
Protostrongylus spp.
protostrongylus rufescens, brevispiculum, muellerius capillaris, cystocaulus ocreatus - FH (cattle), IH (snail), located in respiratory
Protostrongylus pulmonalis - rabbit, respiratory.

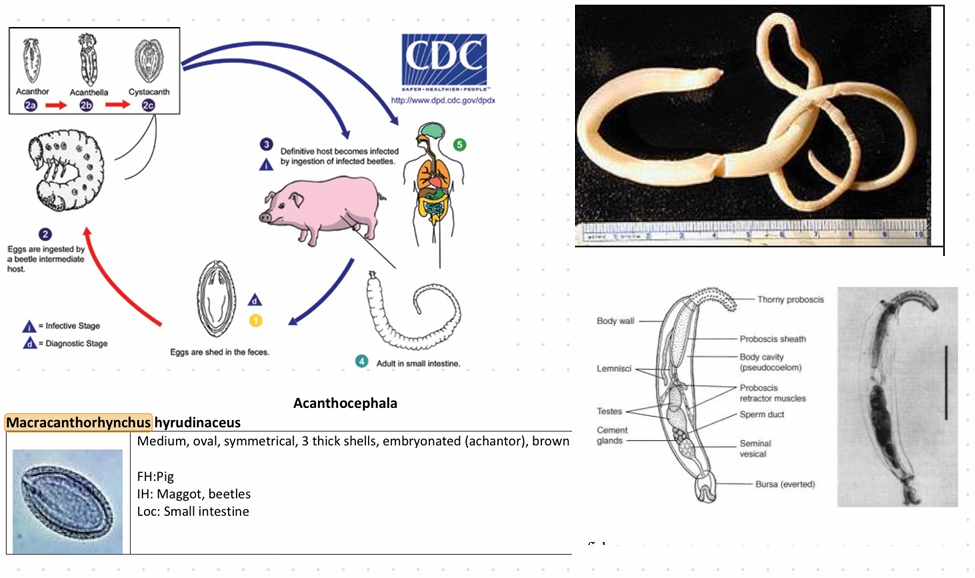
this?
Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus
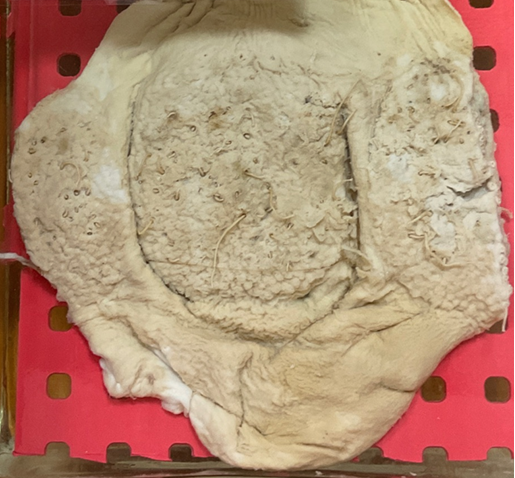


this?
Contraceum rudolphii


this?
Dictyocaulus filaria


this?
Mesocestoides - lineatus, corti
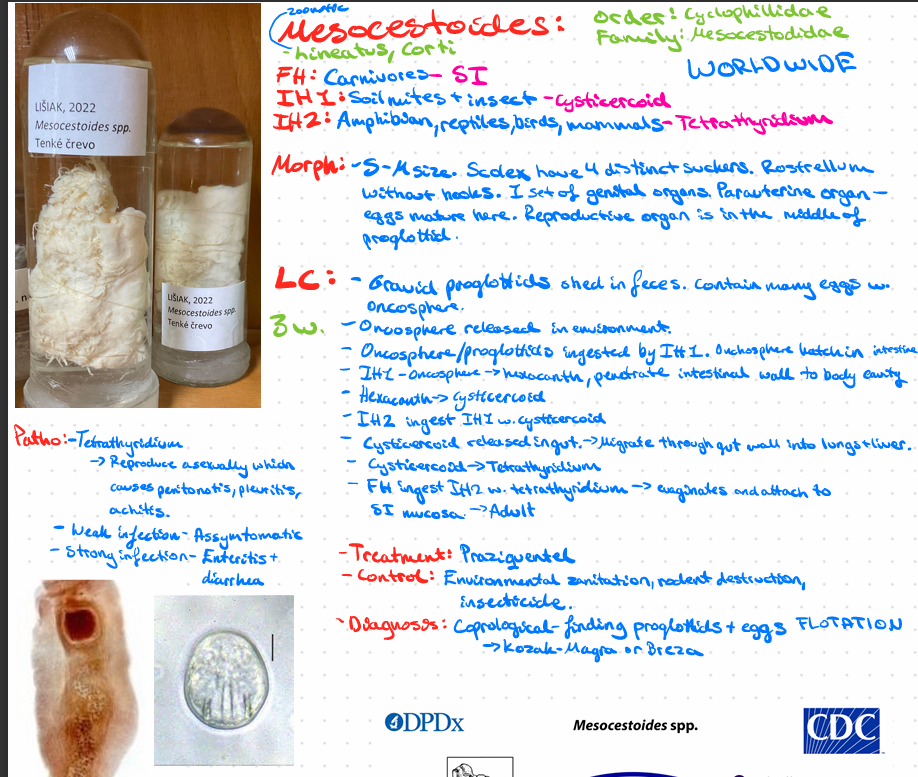

this?
Drepanidotaenia lanceolata/HYMENOLEPSIS LANCEOLATA!


?
Choanotaenia infundibulus - Poultry, SI
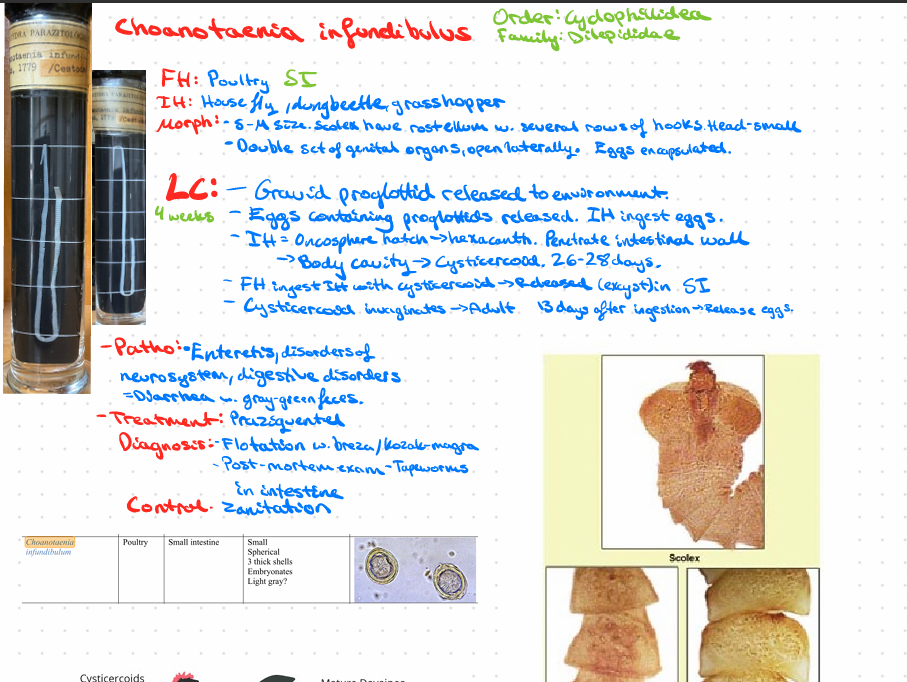

?
Gallus gallus

?
Raillietina - Echinobothriday - cesticullius, tetragona
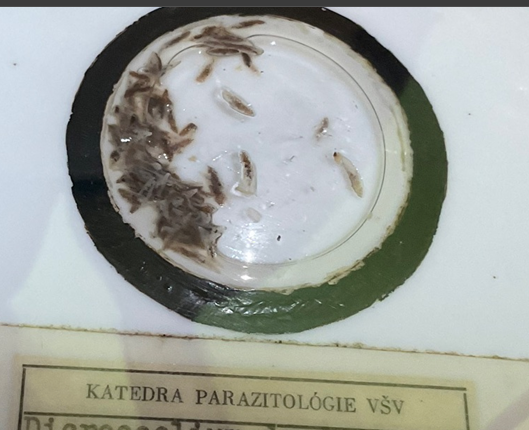
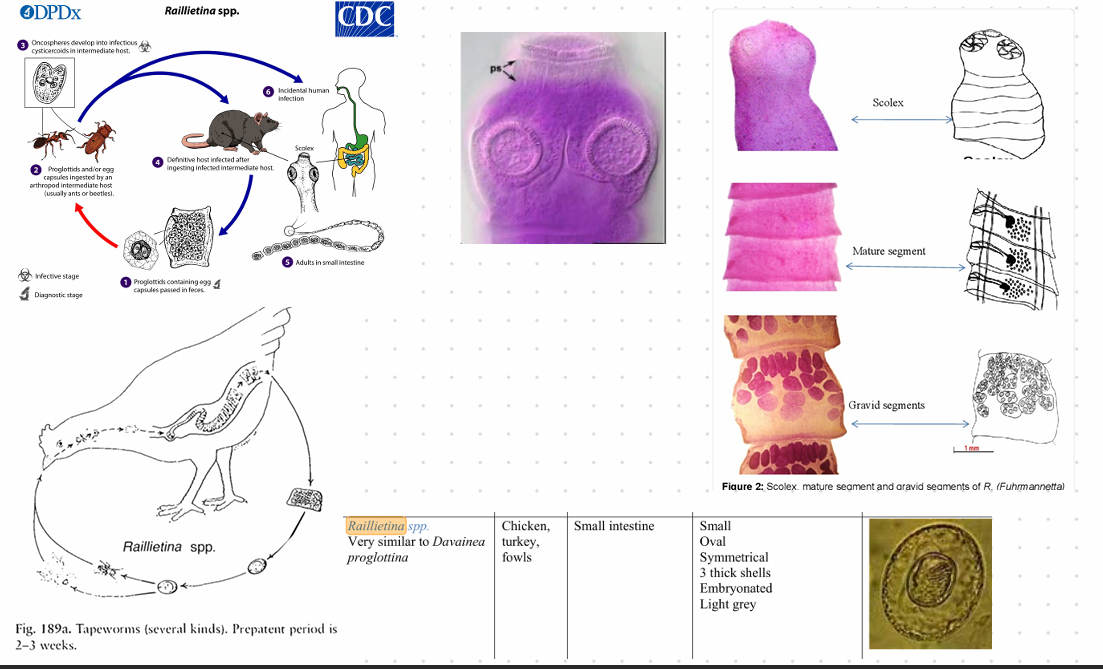


this?
Dicrocoelium dendriticum - trematoda
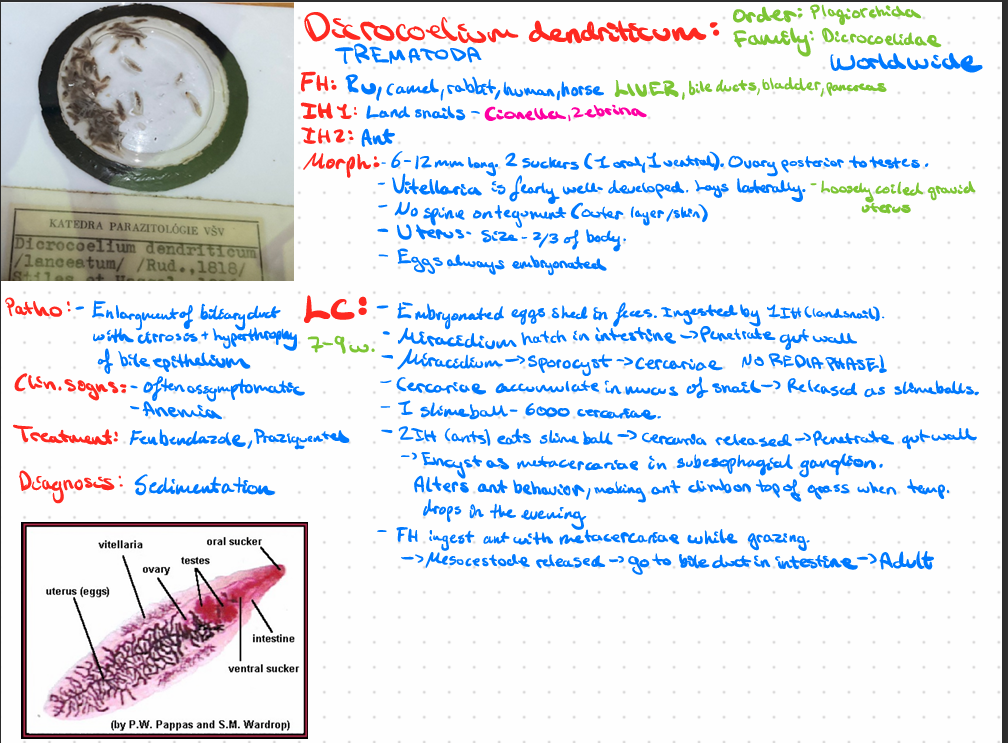
explain tick organs - its BODY
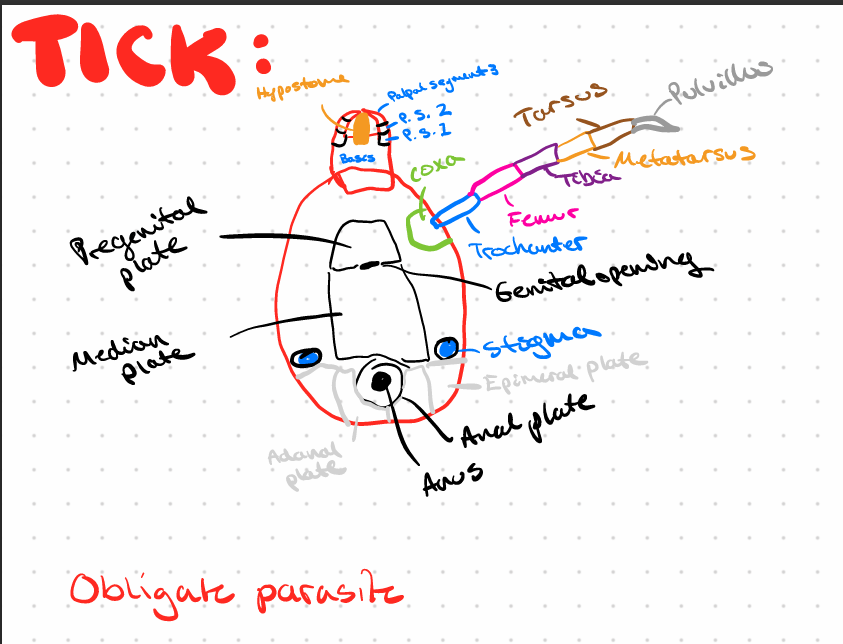
MITES - BODY EXPLAIN
