Nucleotide Metabolism
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the ribose donor in purine synthesis?
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP), from the pentose phosphate pathway
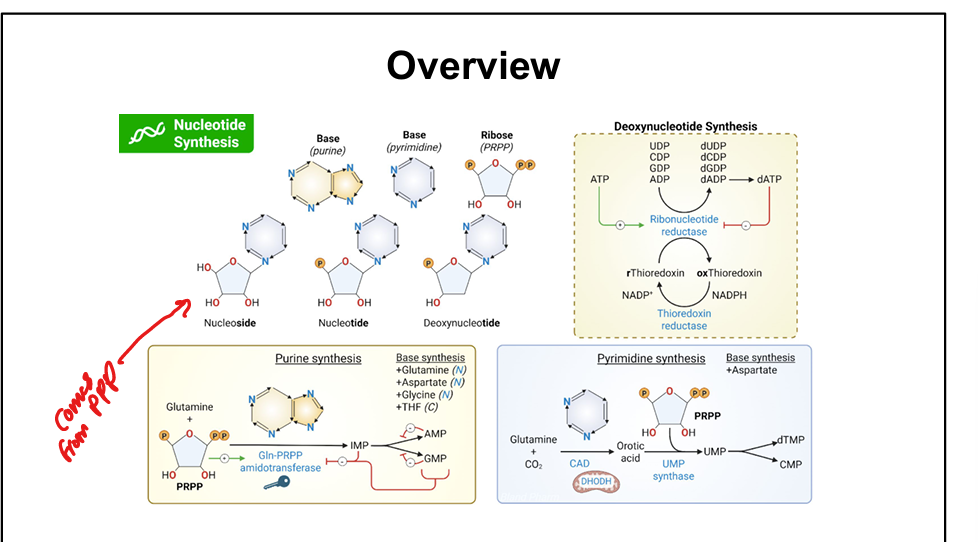

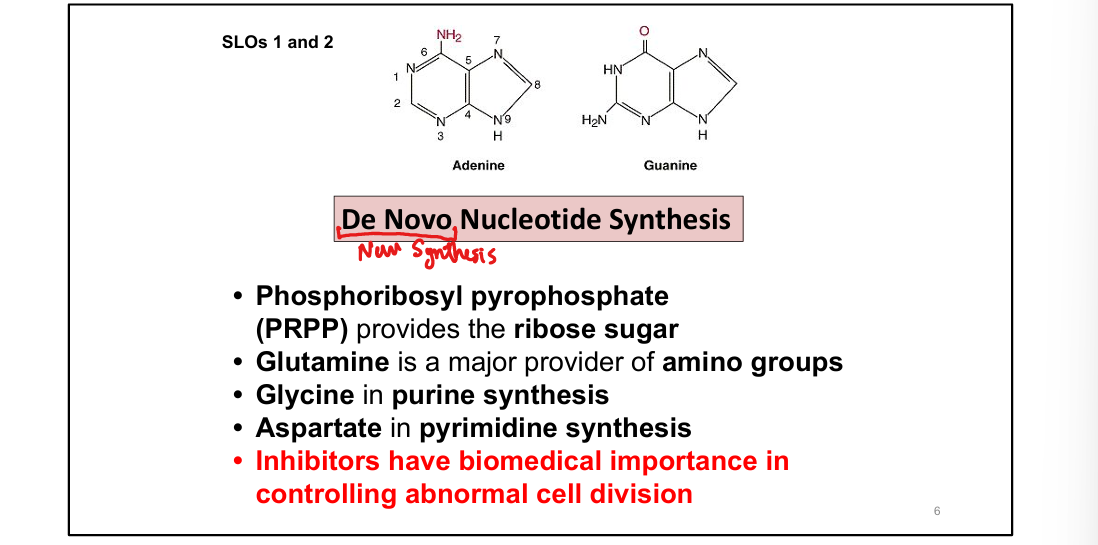
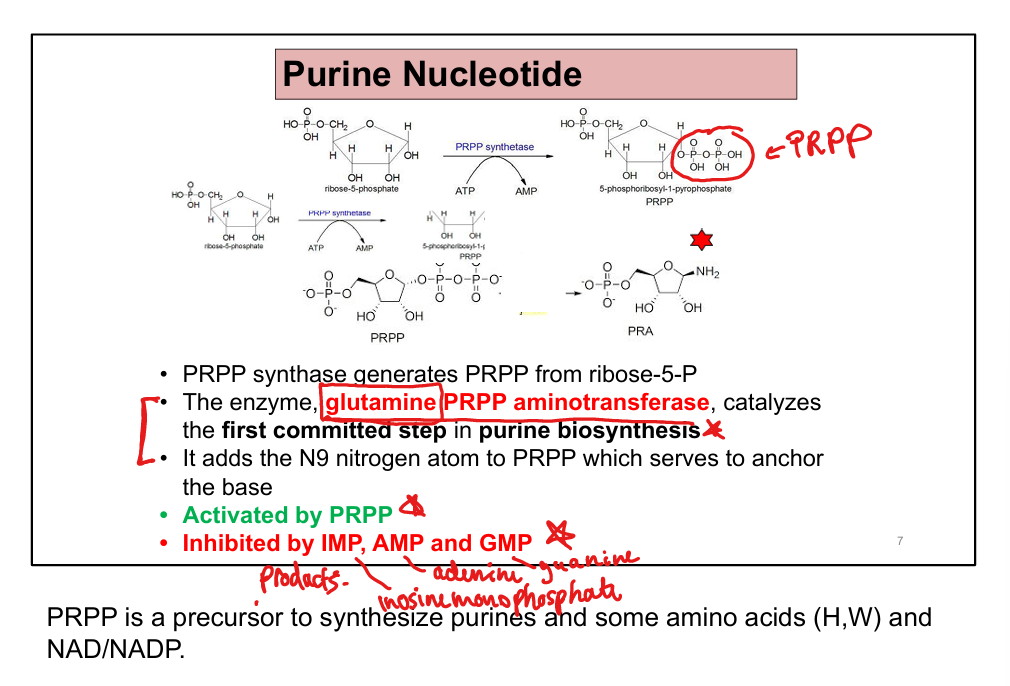
What is the committed step of de novo purine synthesis?
PRPP + glutamine → phosphoribosylamine via glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase

What activates glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase?
PRPP
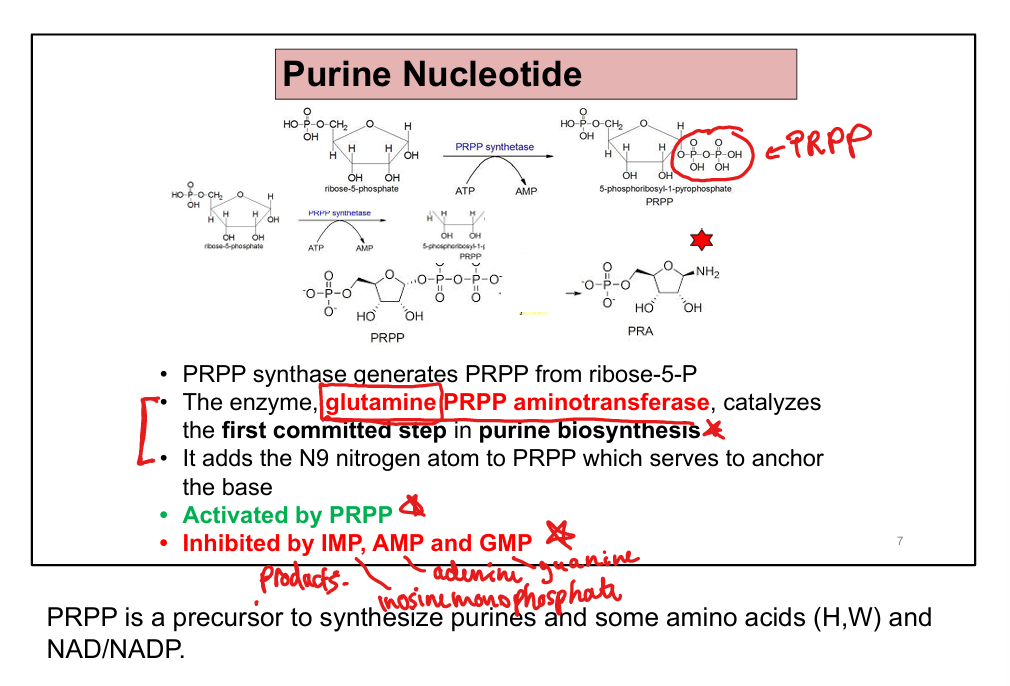

What inhibits glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase?
IMP, AMP, GMP (feedback inhibition)

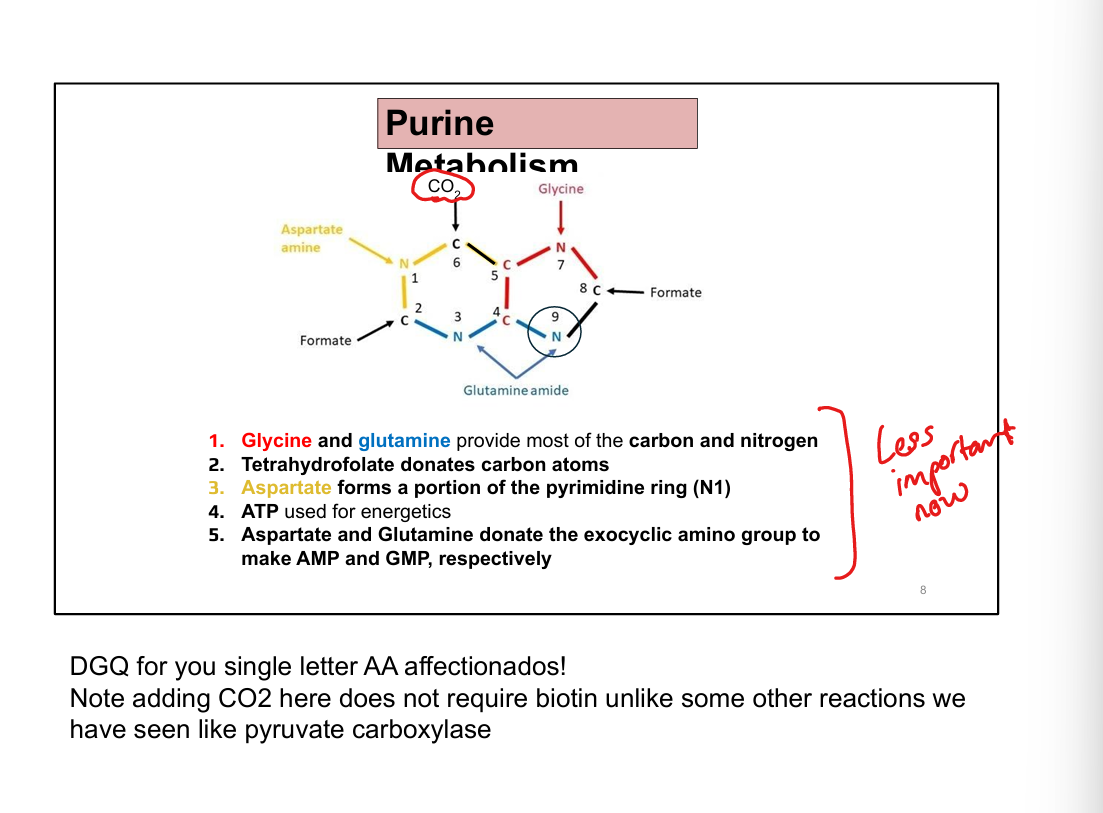
What are the key nitrogen and carbon donors in purine synthesis?
Glutamine, glycine, aspartate, CO₂, and tetrahydrofolate (THF)

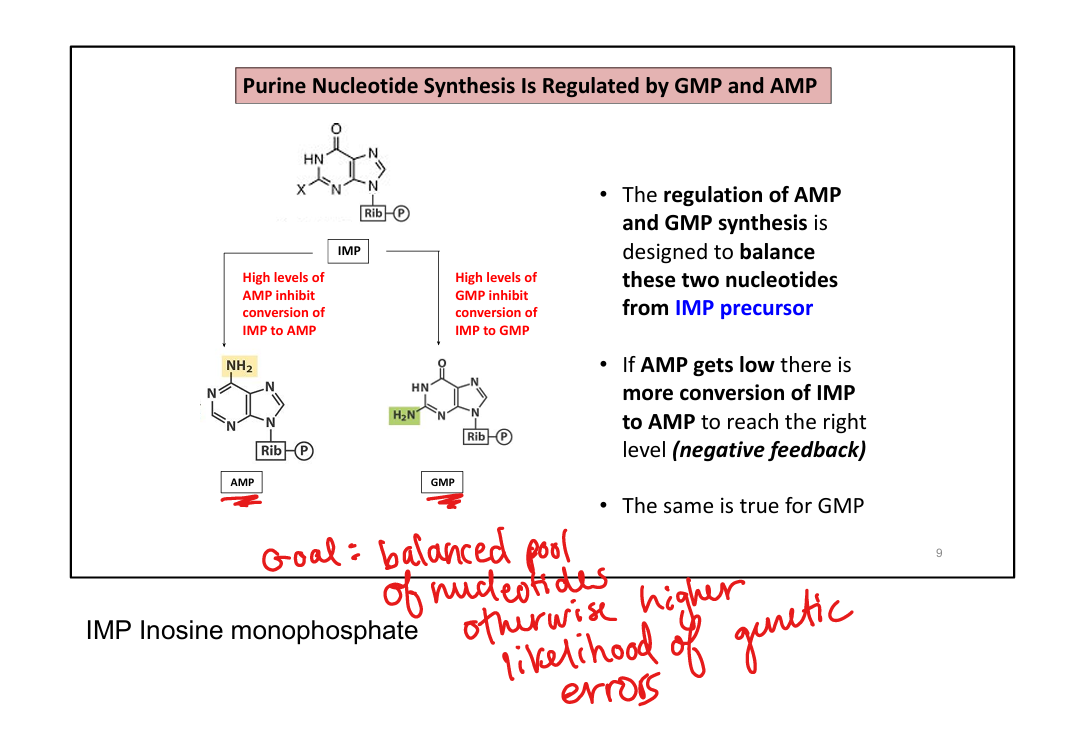
What is the role of IMP in purine synthesis?
Branch point intermediate for AMP and GMP synthesis

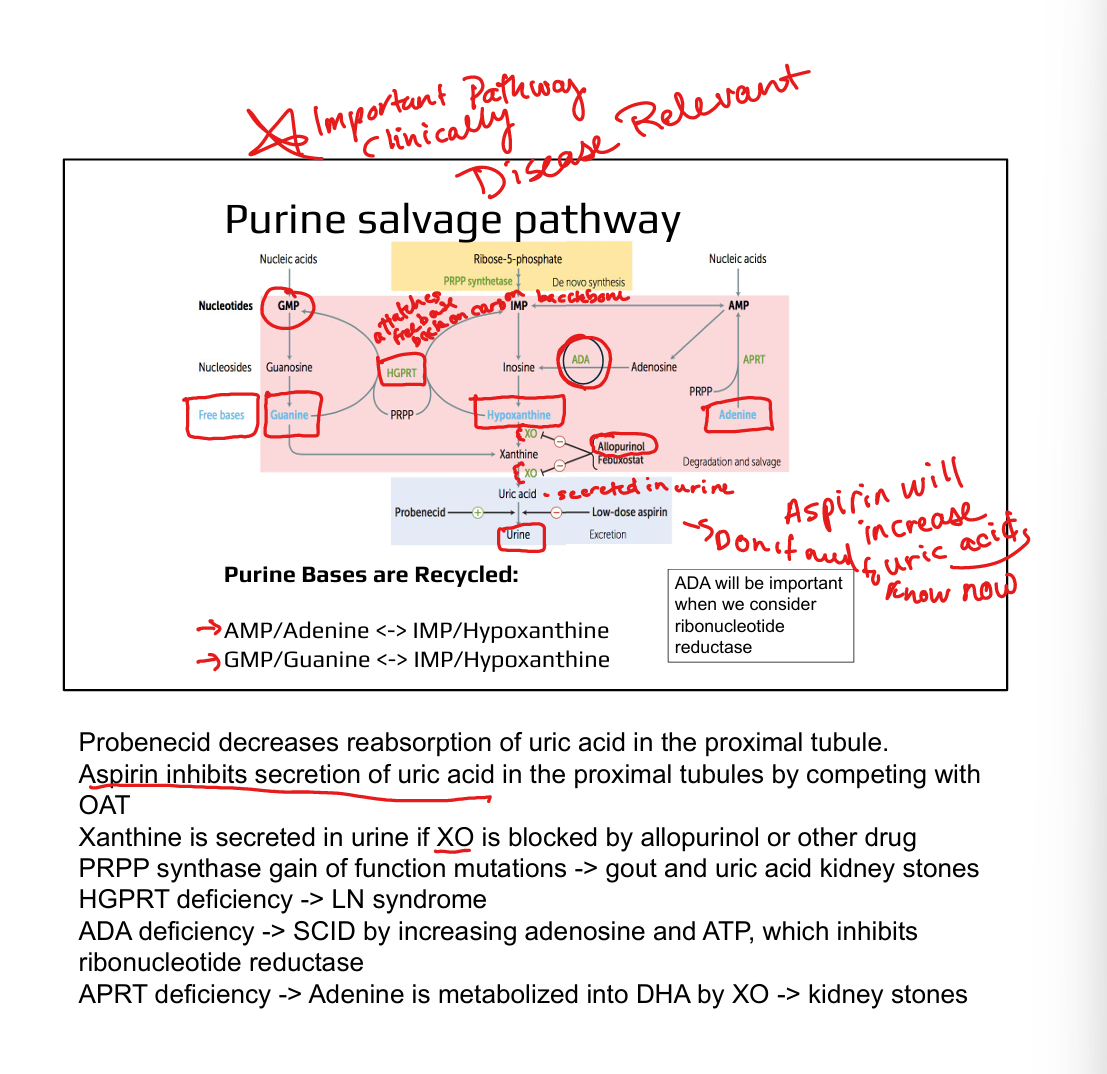
What enzymes are involved in purine salvage?
HGPRT (hypoxanthine/guanine), APRT (adenine)
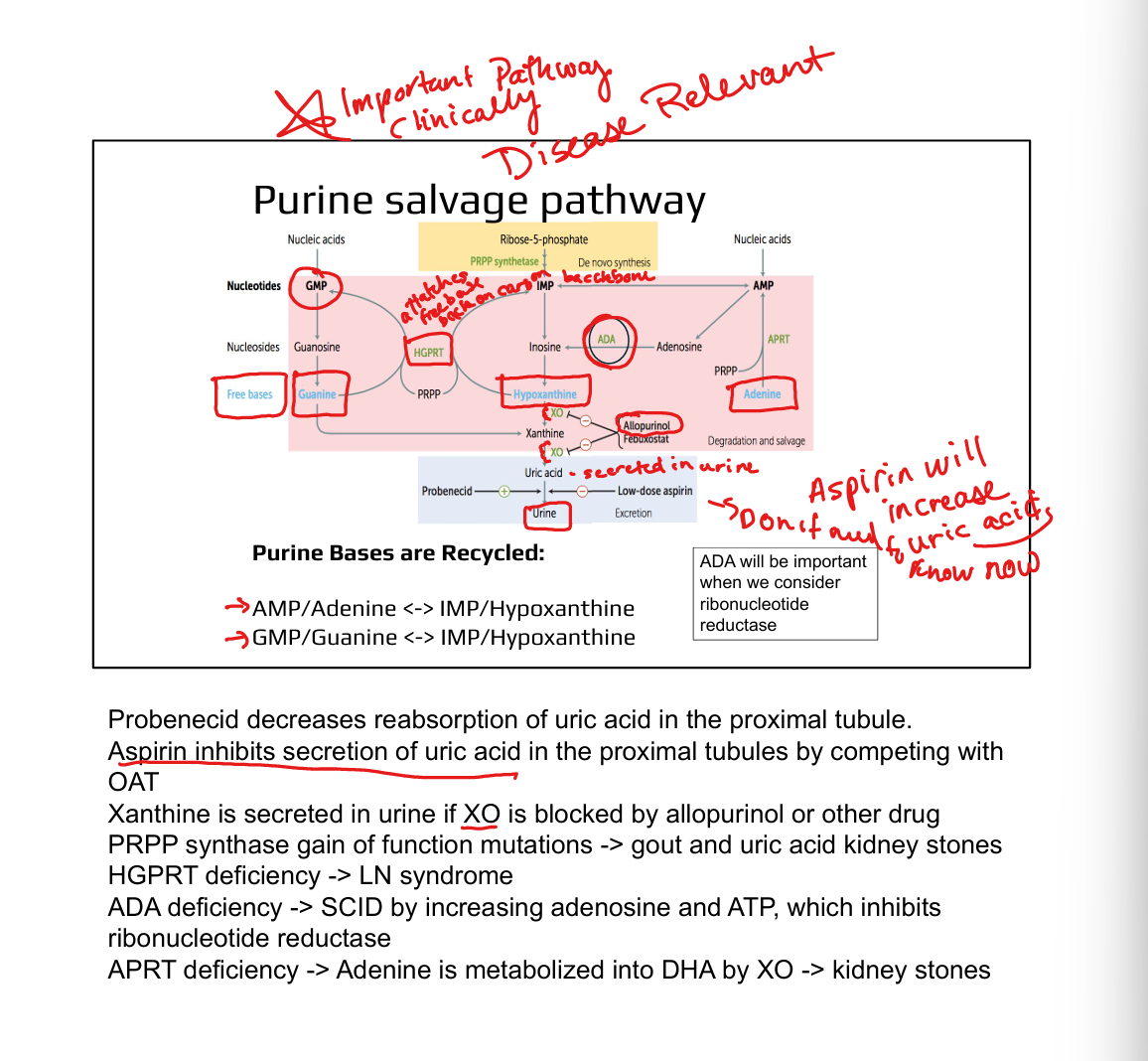

What is the clinical significance of HGPRT?
Deficiency causes Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (X-linked, self-mutilation, hyperuricemia)
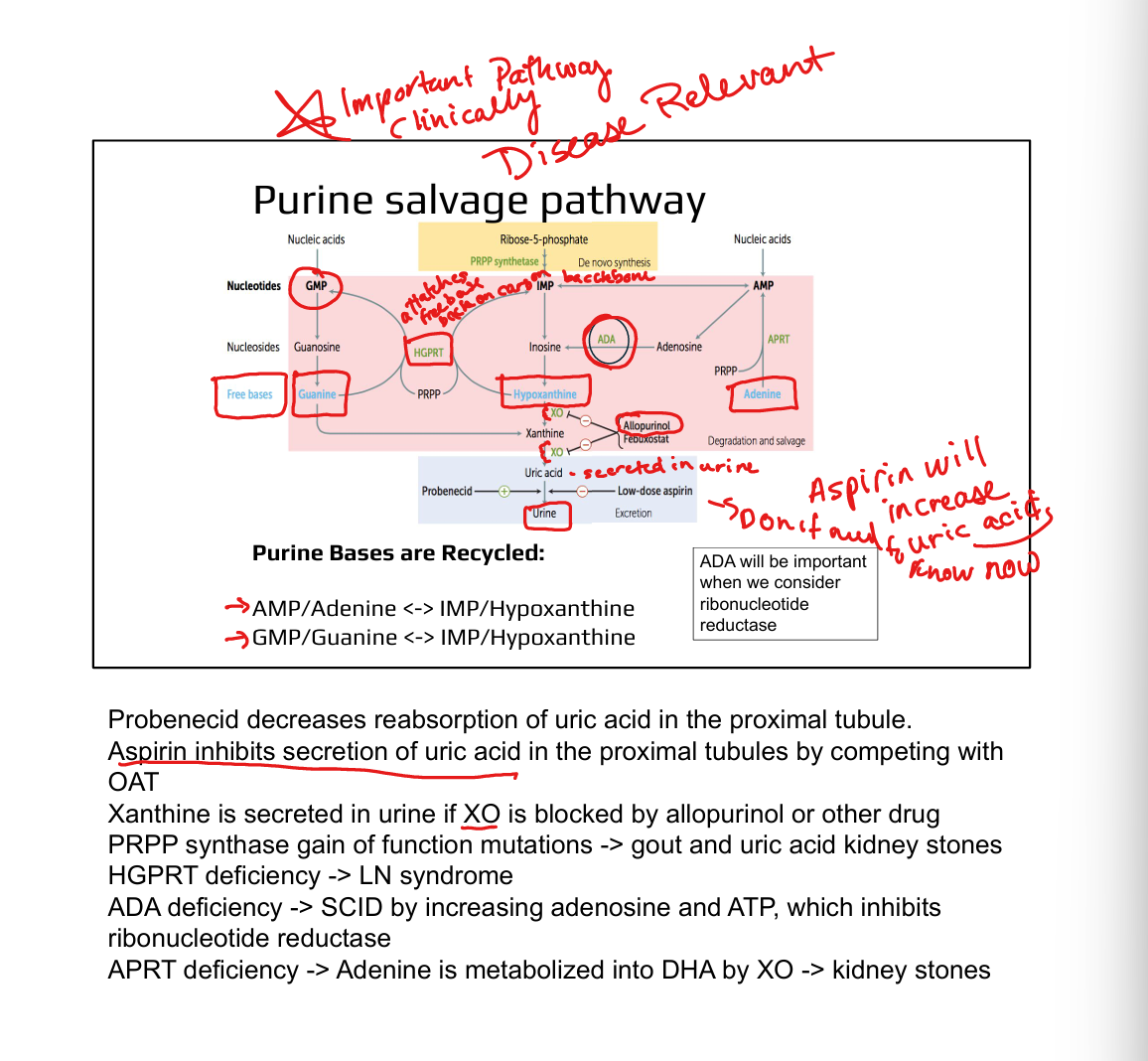

What causes gout?
Hyperuricemia due to excess uric acid from purine degradation
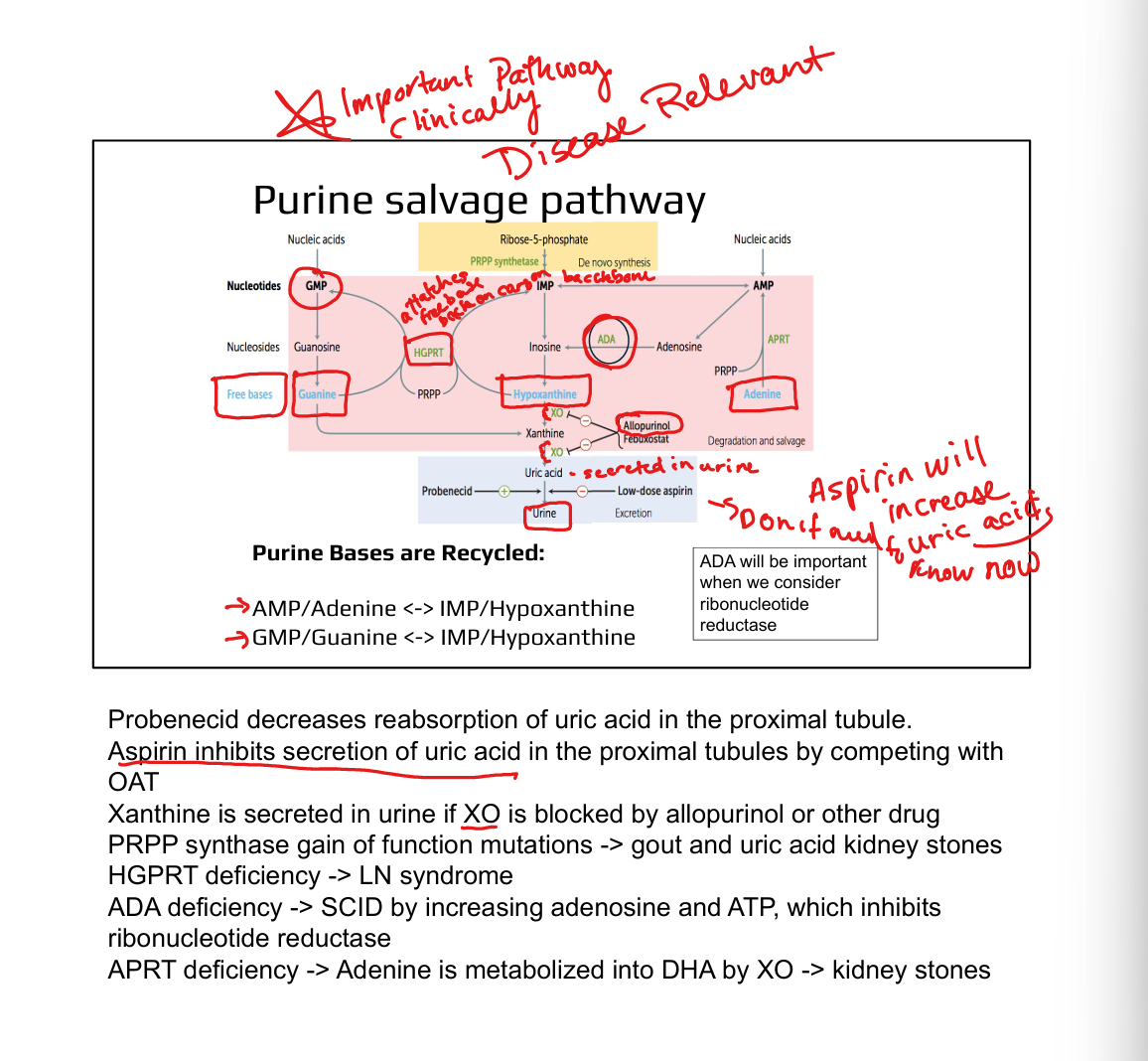

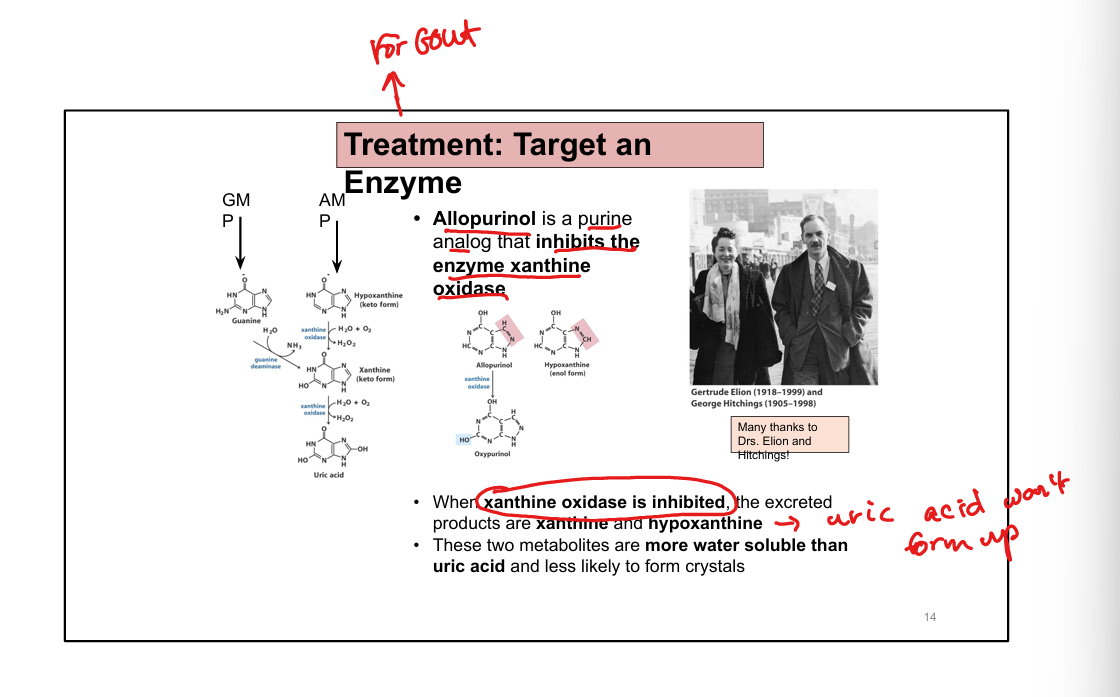
What enzyme is targeted in gout treatment?
Xanthine oxidase (inhibited by allopurinol or febuxostat)
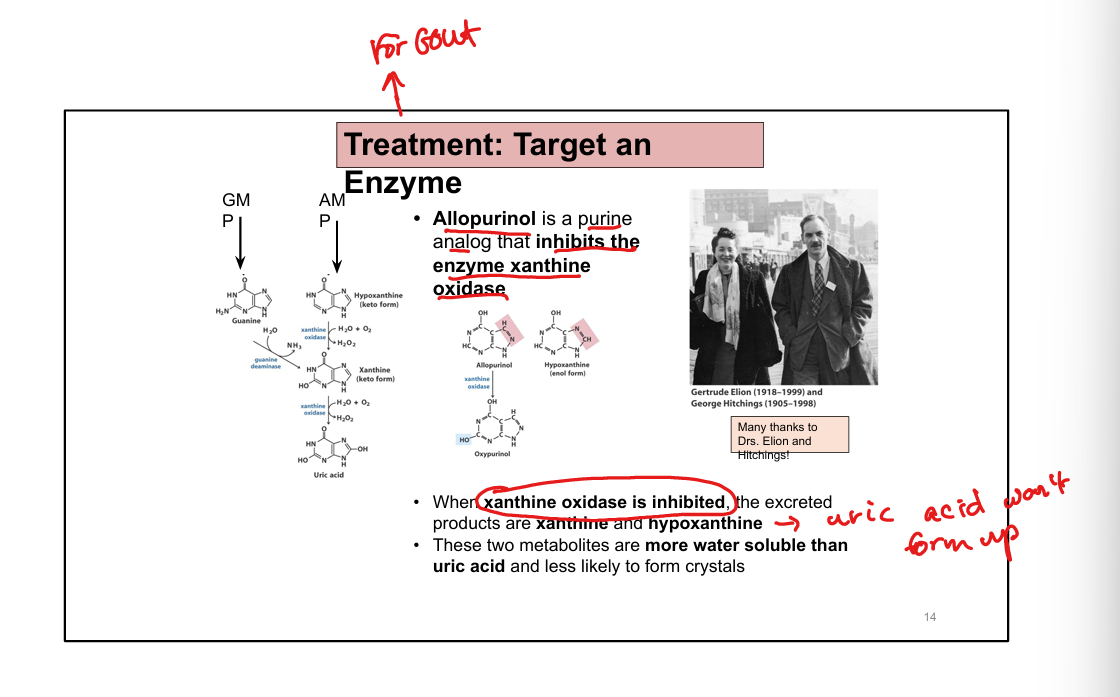

How does allopurinol work?
Inhibits xanthine oxidase → ↓ uric acid, ↑ soluble hypoxanthine/xanthine

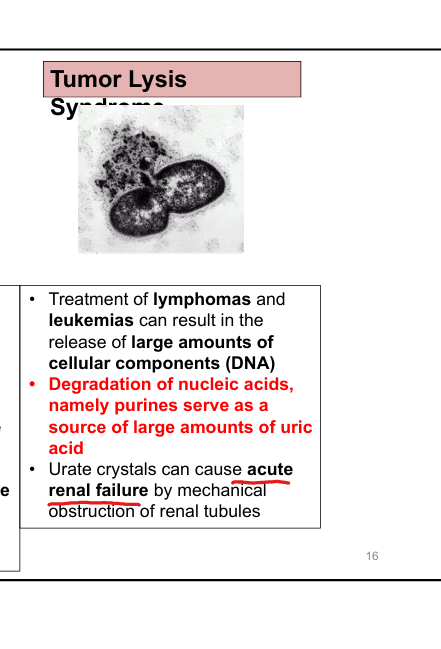
What is tumor lysis syndrome?
Massive cell lysis → purine release → uric acid overload → acute kidney injury

What is ADA deficiency?
Adenosine deaminase deficiency → ↑ dATP → inhibits ribonucleotide reductase

What is the clinical consequence of ADA deficiency?
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
What is the biochemical defect in Lesch–Nyhan syndrome?
HGPRT deficiency → impaired salvage → ↑ PRPP → ↑ de novo synthesis → ↑ uric acid


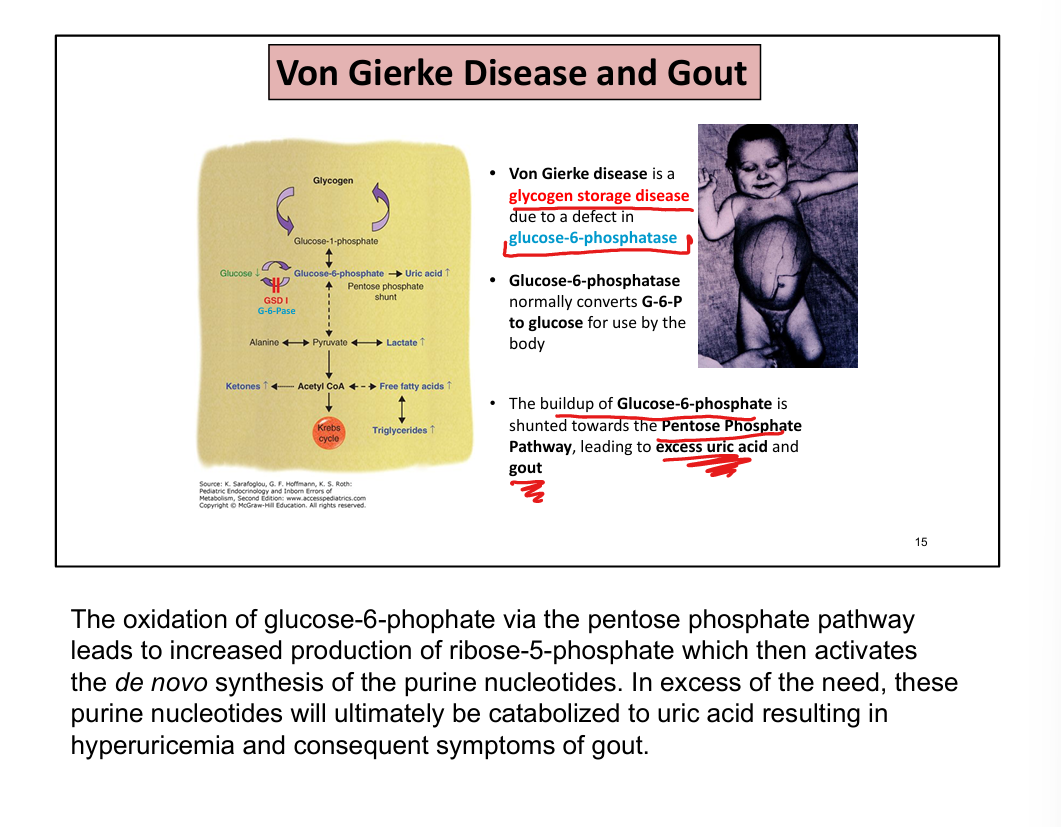
What is the link between Von Gierke disease and gout?
↑ G6P → ↑ PPP → ↑ PRPP → ↑ purine synthesis → ↑ uric acid

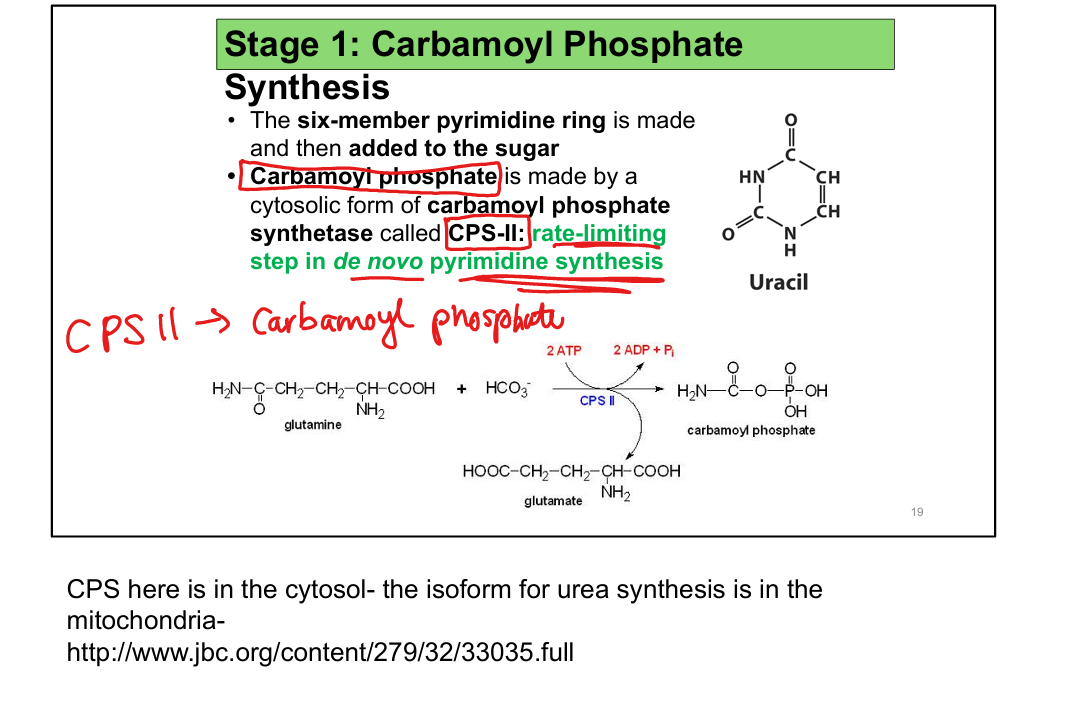
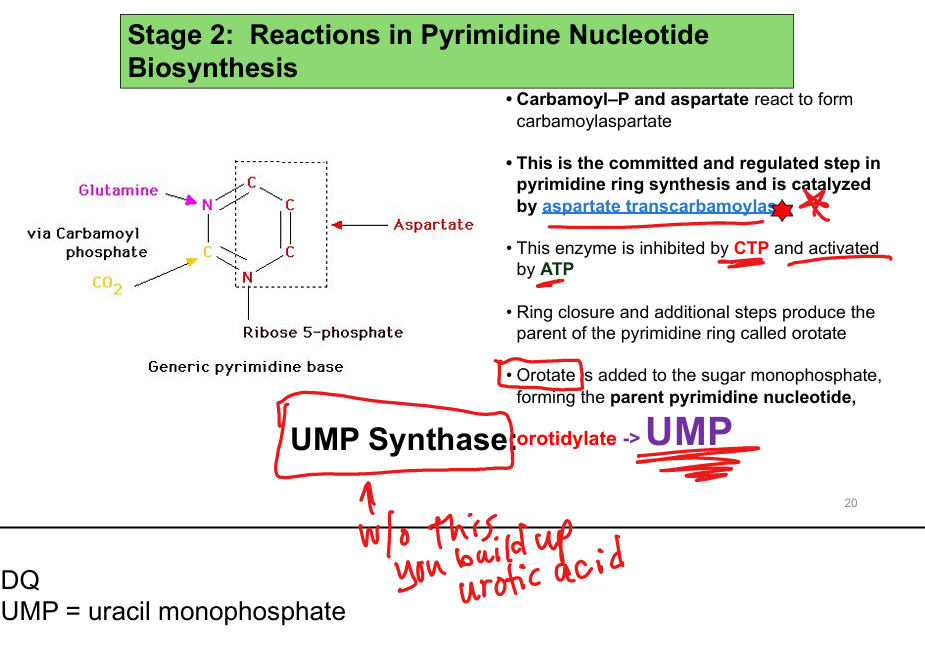
What is the rate-limiting enzyme in pyrimidine synthesis?(Someone call CPS for those rotten kids on the pyrimid)
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II)

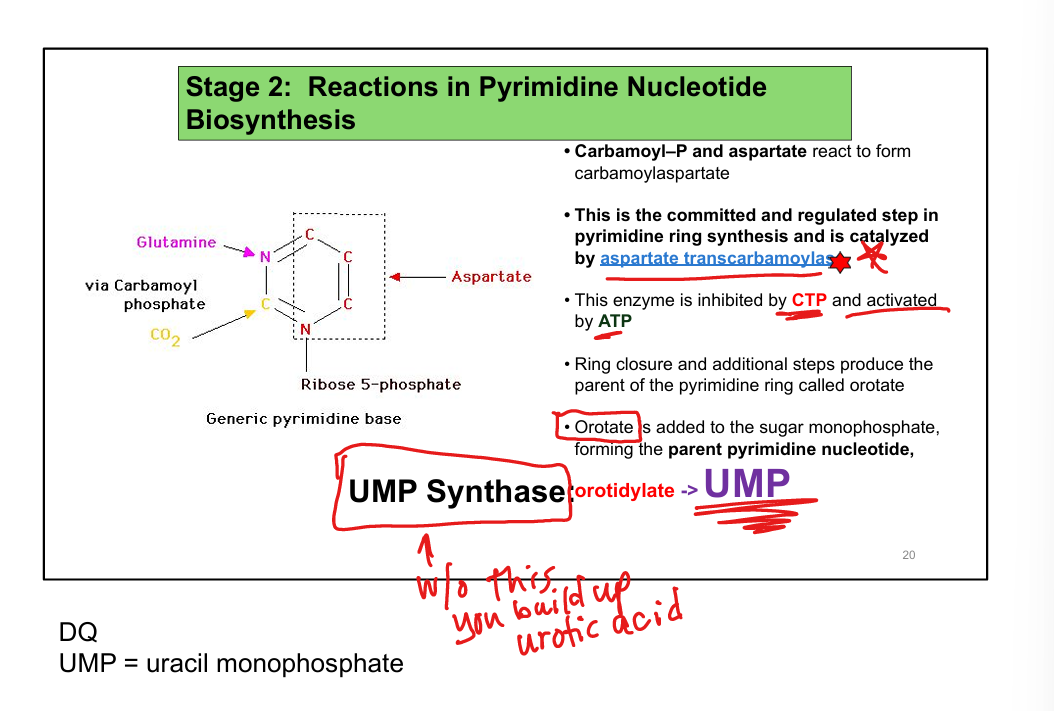
What is the committed step of pyrimidine synthesis?
Carbamoyl phosphate + aspartate → carbamoylaspartate via aspartate transcarbamoylase

What is the difference between purine and pyrimidine synthesis?
Purines are built on PRPP; pyrimidines are synthesized first, then attached to PRPP
What is the role of UMP synthase?
Converts orotate to UMP; deficiency causes orotic aciduria

What regulates Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (CPS II)?
Activated by PRPP, inhibited by UTP

What is the role of glutamine in pyrimidine synthesis?
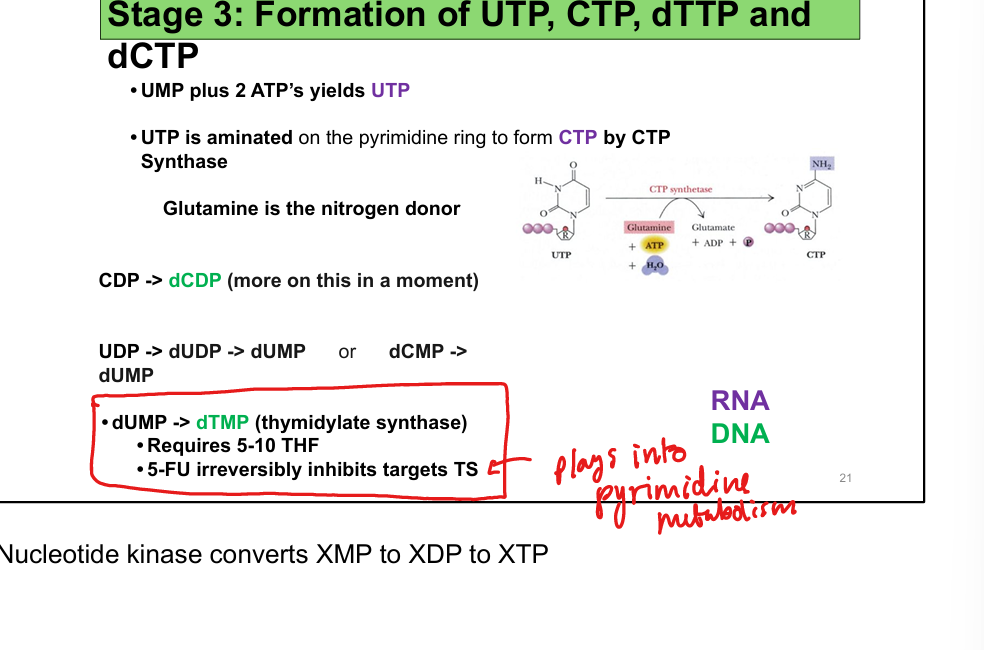
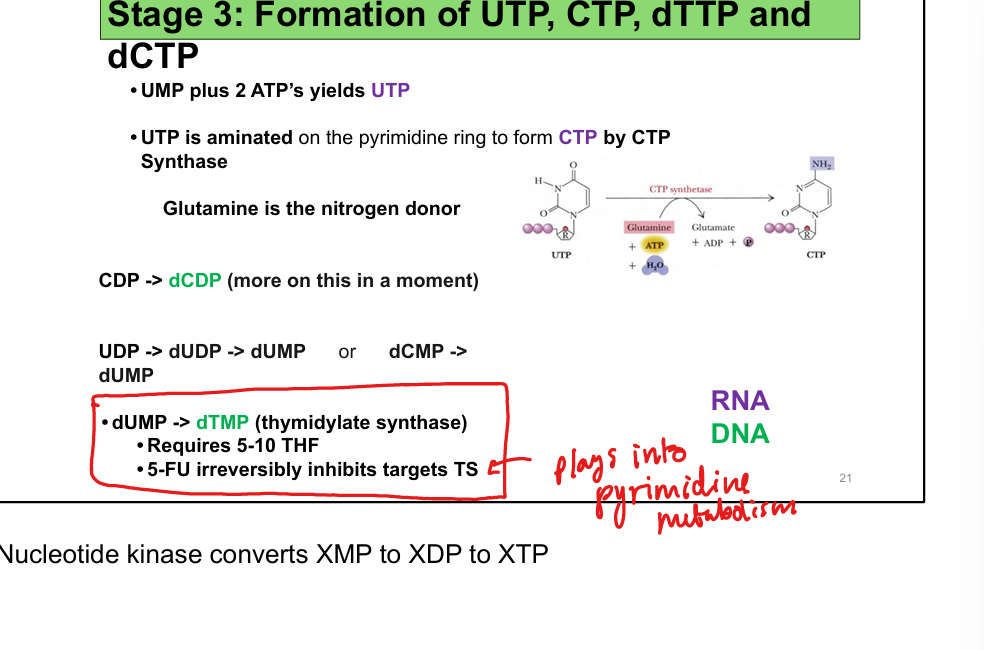
Nitrogen donor for carbamoyl phosphate and CTP synthesis

What is the role of 5,10-methylene-THF in pyrimidine synthesis?
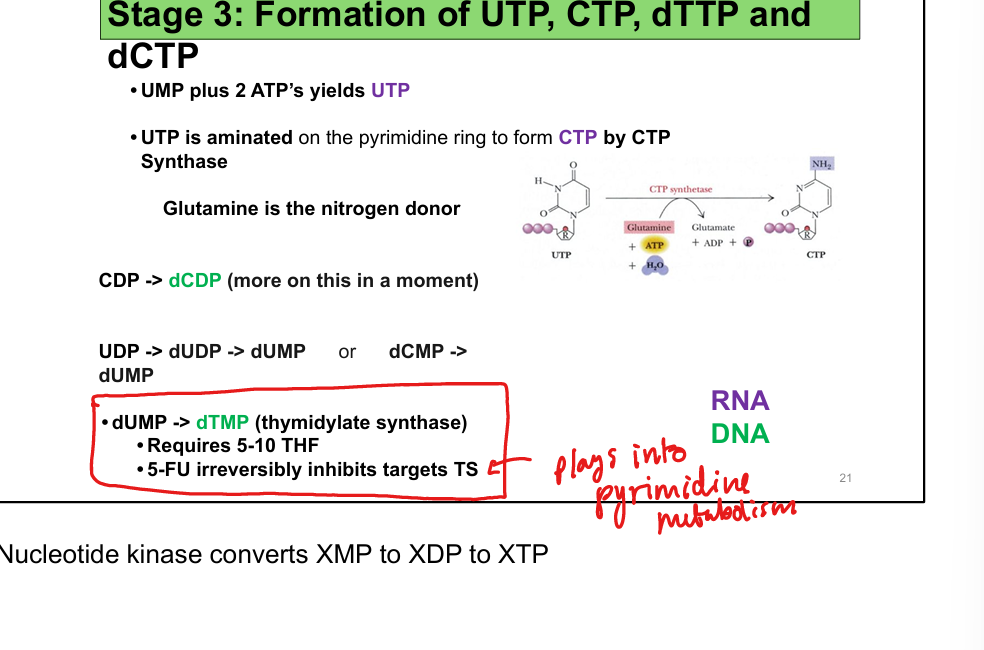
Required for dUMP → dTMP via thymidylate synthase

What causes orotic aciduria?
Deficiency of UMP synthase (orotate phosphoribosyltransferase + OMP decarboxylase)
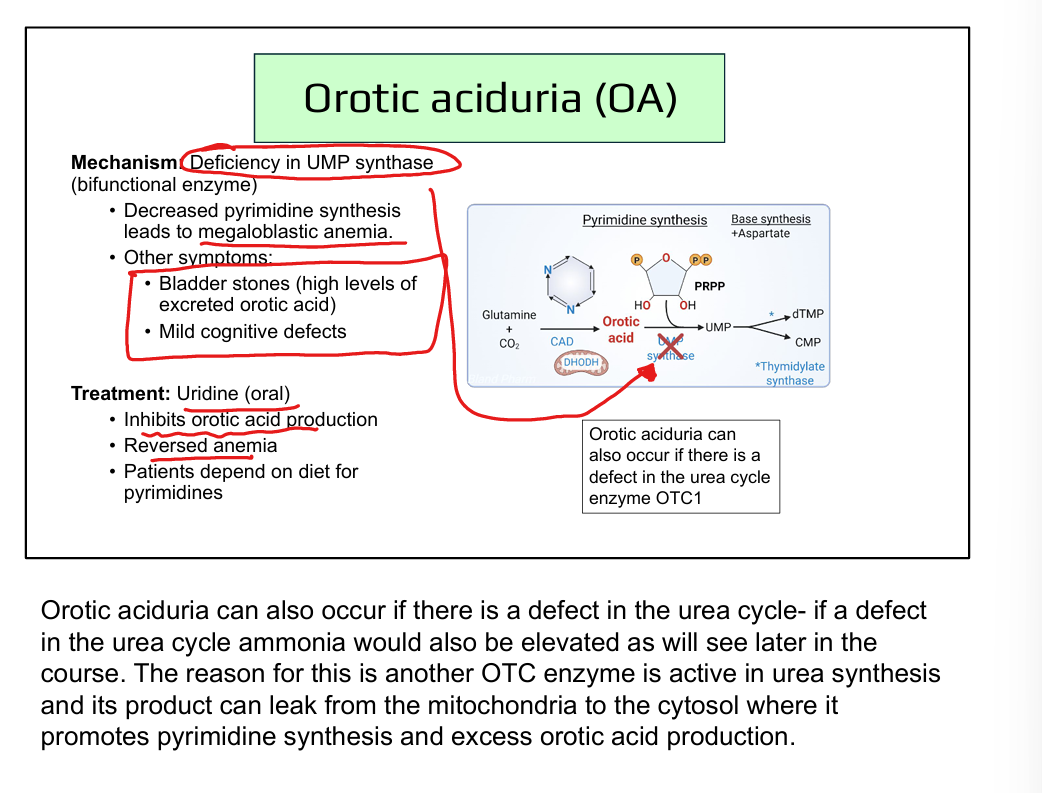

What are symptoms of orotic aciduria?
Megaloblastic anemia(decreased nucleotide synthesis), growth delay, orotic acid crystals in urine
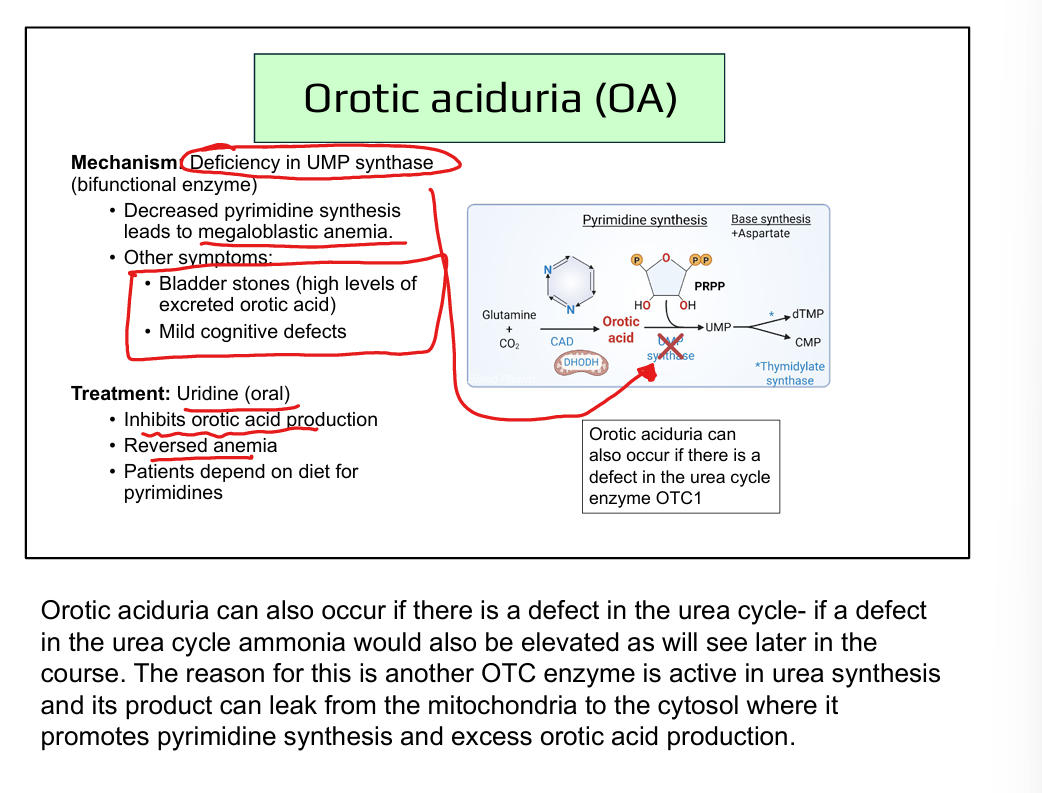

How is orotic aciduria treated?
Uridine supplementation (bypasses UMP synthase)
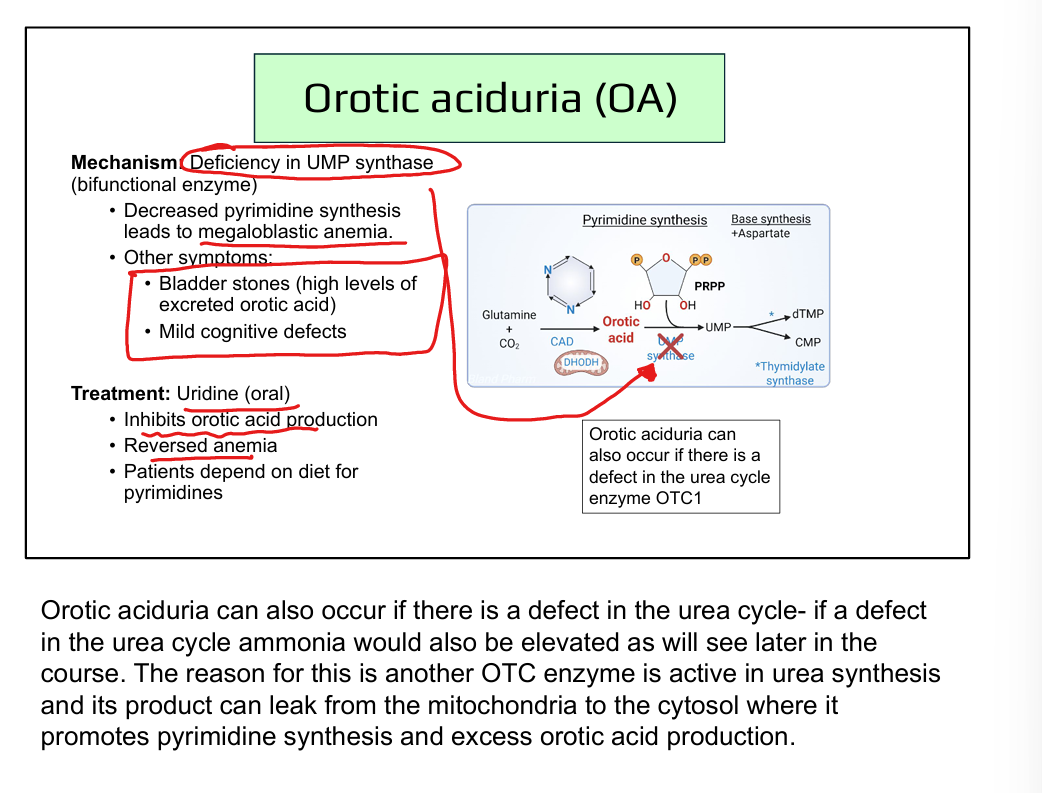

How is orotic aciduria differentiated from urea cycle defects?
UCDs also show hyperammonemia; OA does not
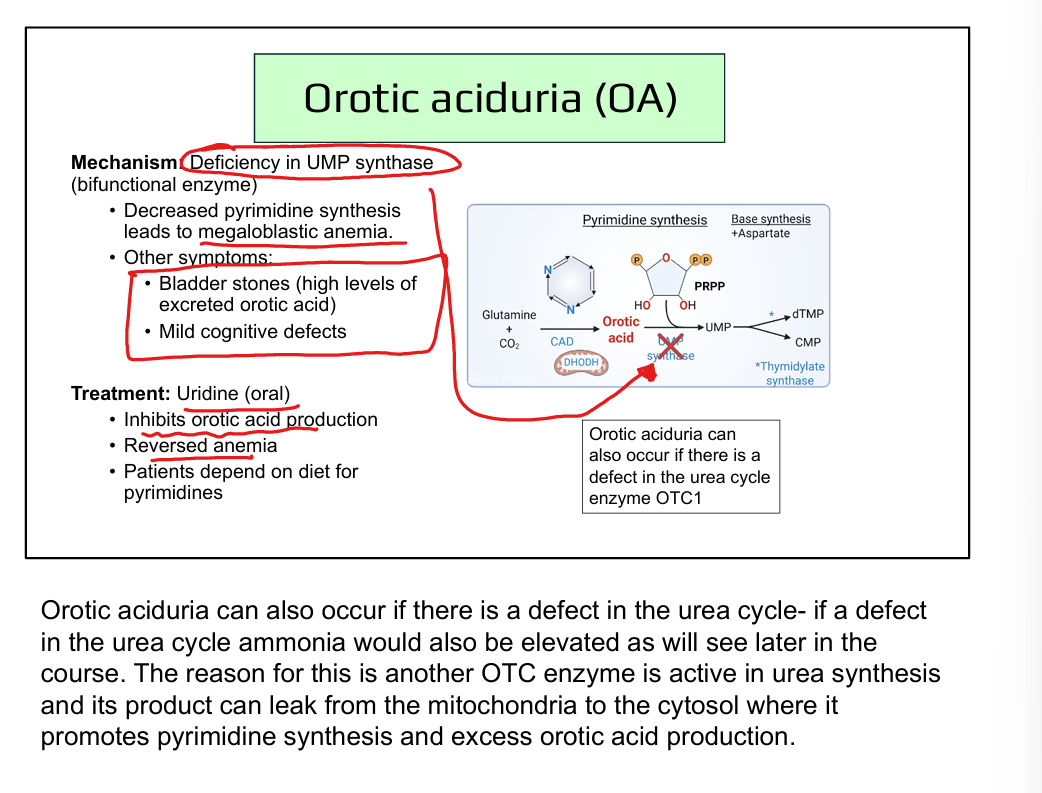

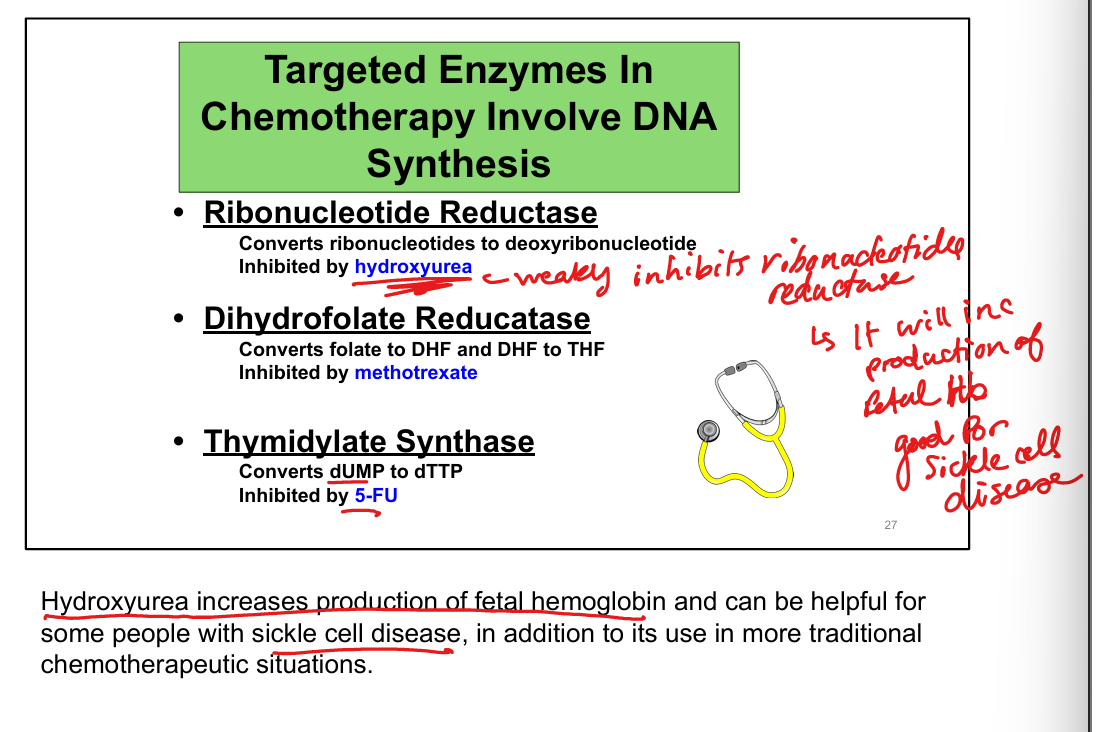
What is the mechanism of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)?
Converted to 5-FdUMP → irreversibly inhibits thymidylate synthase → ↓ dTMP
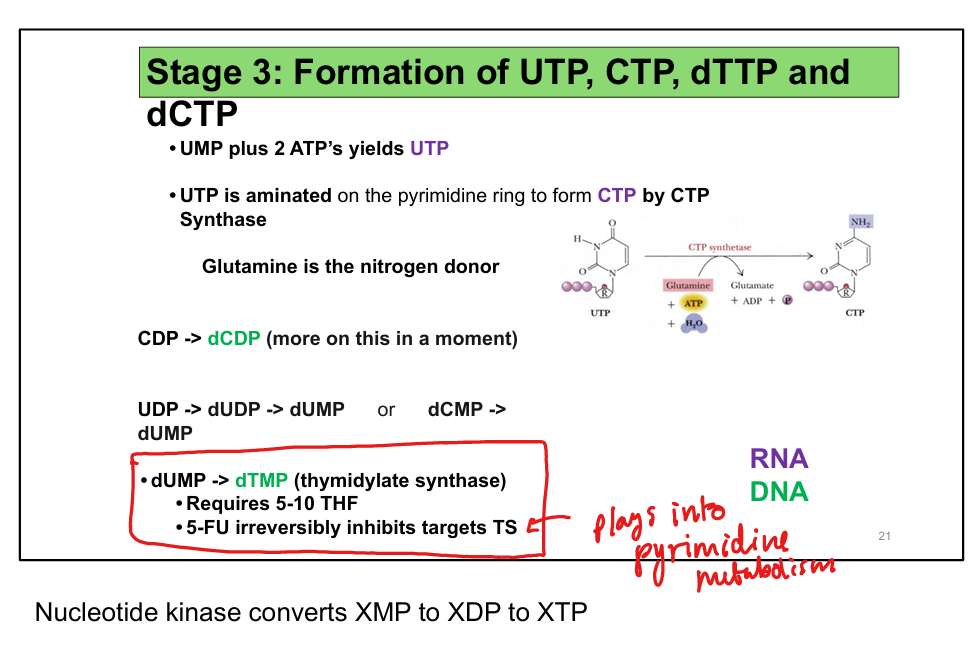

What is the clinical use of 5-FU?
Cancer chemotherapy (e.g., colon, breast)
What does ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) do?
Converts ribonucleotides (NDPs) to deoxyribonucleotides (dNDPs) for DNA synthesis
How is RNR regulated?
ATP activates; dATP inhibits (feedback inhibition)
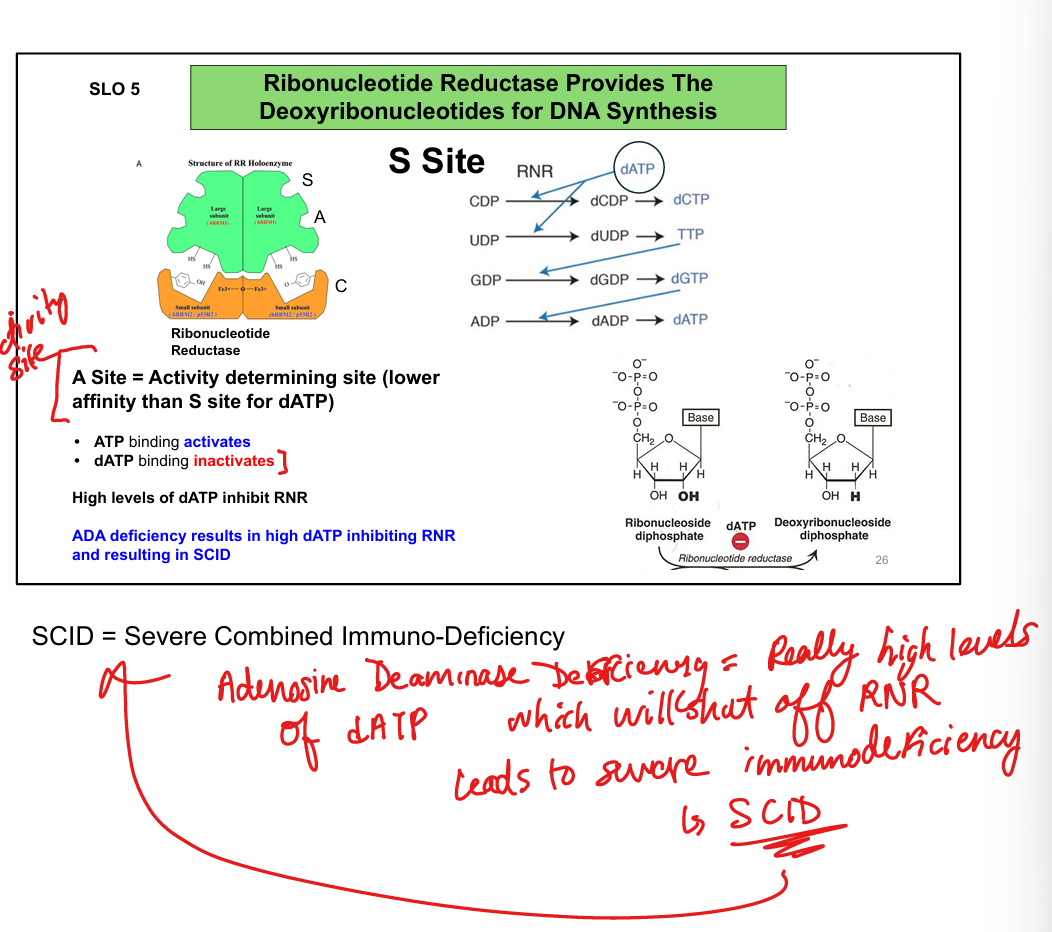

What is the S site of RNR?
Determines substrate specificity (e.g., dGTP → promotes ADP reduction)
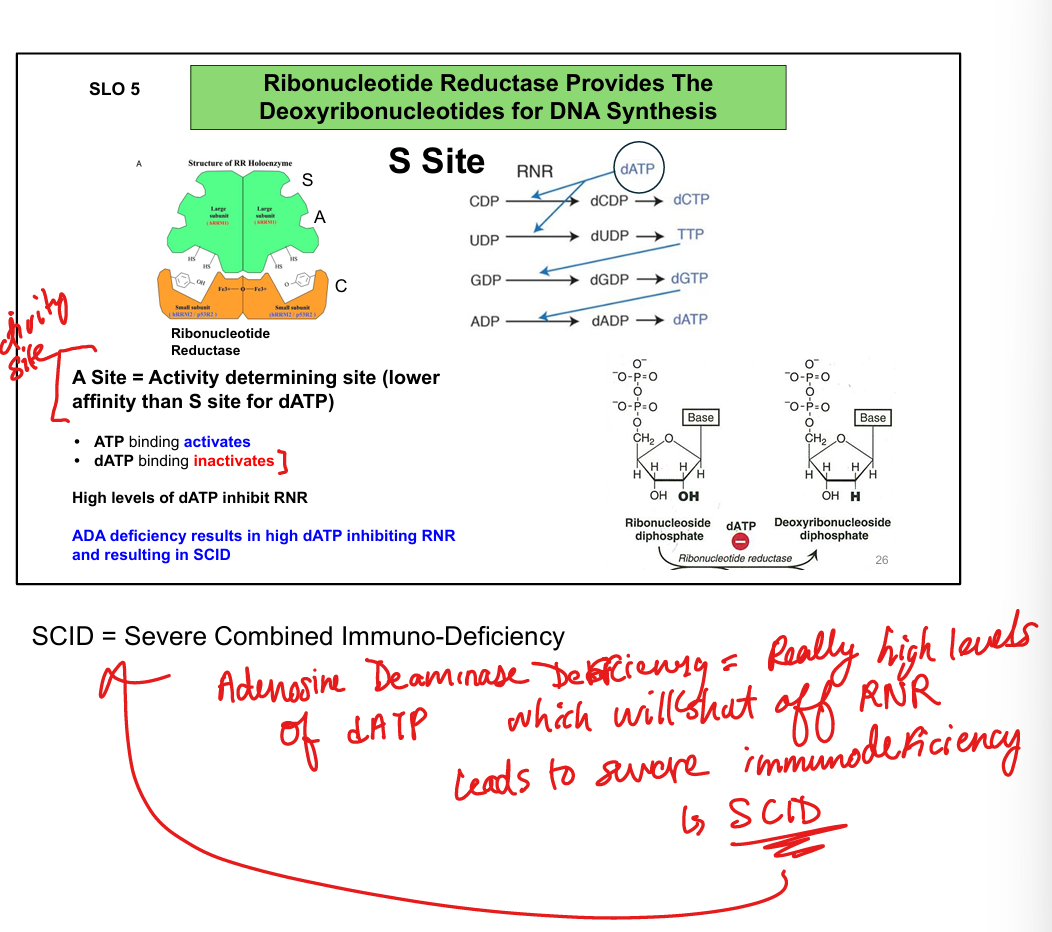

What is the A site of RNR?
Determines overall activity (ATP = ON, dATP = OFF)
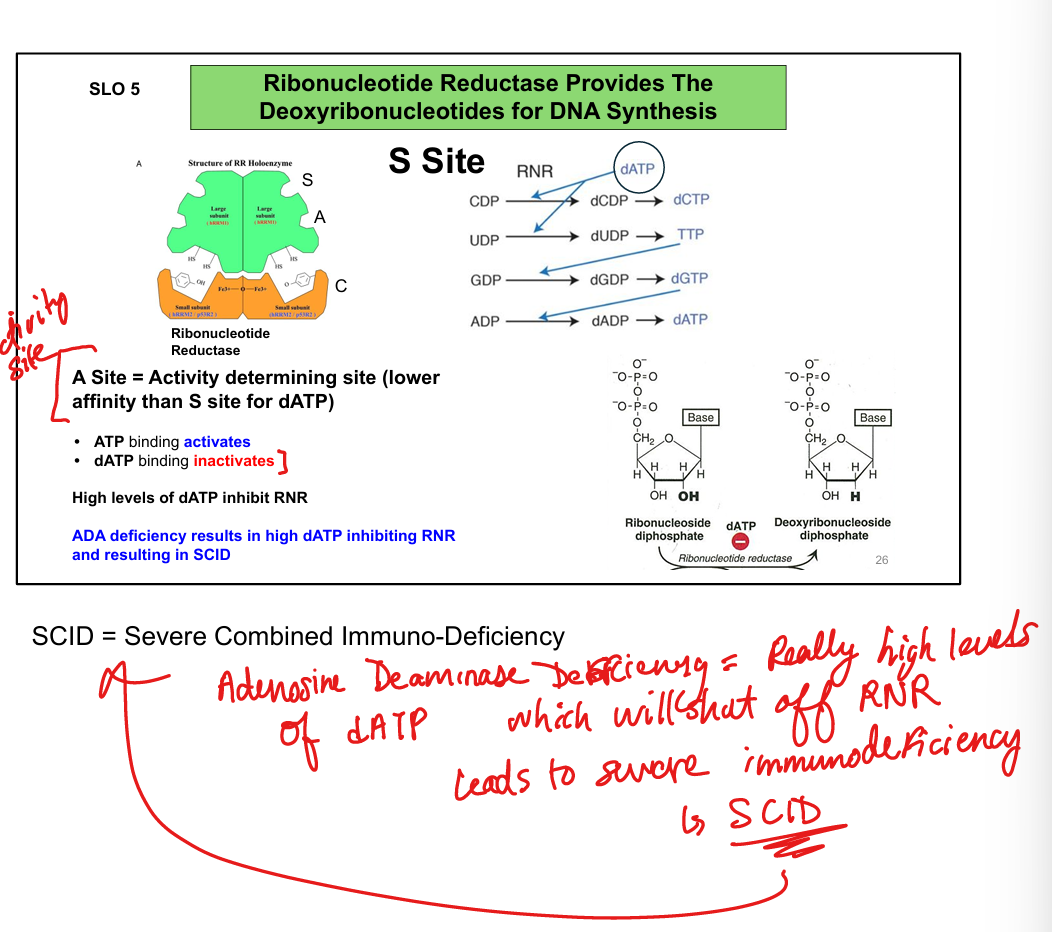

How does ADA deficiency affect RNR?
↑ dATP → inhibits RNR → ↓ dNTPs → impaired DNA synthesis
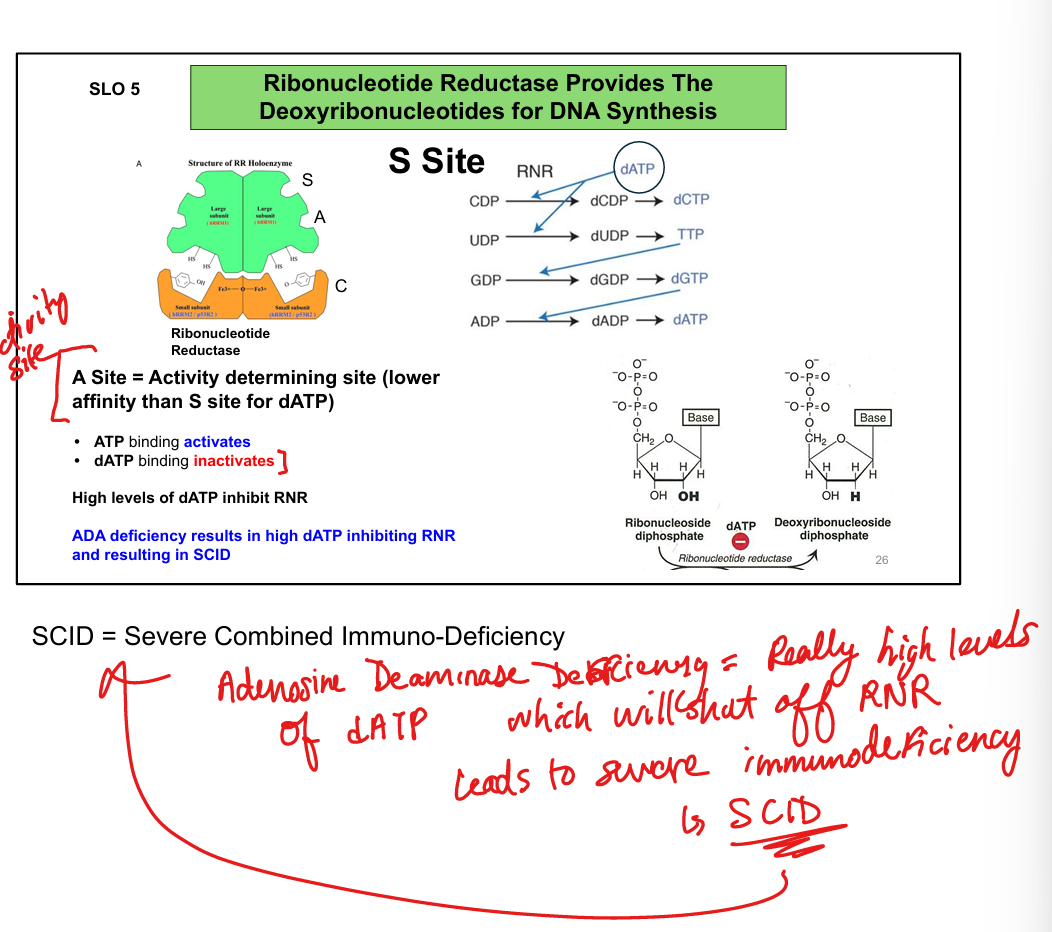

Why does ADA deficiency cause Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency (SCID)?
Lymphocytes fail to proliferate due to lack of dNTPs → immunodeficiency

What drug inhibits RNR?
Hydroxyurea (used in cancer and sickle cell disease)

What is megaloblastic anemia?
Not enough nucleotide synthesis