Med admin and safe injection/safety and security
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Nursing drug knowledge
generic names
trade names
classifications
indications
pharmakinetics
metabolism
excretion
effects
adverse effects
allergic reactions
mild
anaphylactic
tolerance
toxic
idiosyncratic
Drug dose and serum drug levels: therapeutic range
concentration of drug in the blood serum that produces the desired effect without causing toxicity
Drug dose and serum drug levels: peak level
the point when the drug is a its highest
Drug dose and serum drug levels: trough level
the point when the drug is at its lowest concentration, indicating the rate of elimination
Drug dose and serum drug levels: half-life
amount of time it takes for 50% of blood concentration of a drug to be eliminated from the body
Medication reconciliation: administration assessment
prescribed medications
PTA medications
allergies
pregnancy and lactation status
dietary supplements and herbal and “natural” remedies
Aging and drug response
decreased gastric motility
decreased total body water
decreased lipid content in skin
decreased liver function
decreased kidney function
adverse CNS effects
altered peripheral vascular tone
Critical thinking
proper order
calculating adult medication dosages
patients condition
equipment decisions
documenting medication administration
patient teaching
Medication orders
verbal orders
telephone orders
standing orders
PRN orders (as needed)
stat orders
one time order
Parts of the medication order
patients name and a secondary identifier (date of birth, medical record number)
date and time the order is written
name of drug to be administered
dosage of the drug
route by which the drug is to be administered
frequency of administration of the drug
signature of the prescribing provider
Parts of the medication order: how often?
daily
BID (twice a day)
TID (3 times a day)
QID (4 times a day)
ac (before meals)
pc (after meals)
HS (at bedtime)
5 rights: dr tim
dose
route
time
individual/patient
medication
6 other rights
reason
assessment
documentation
response
refuse
educate
3 checks
removing medication from med cart
comparing medication to MAR
students have an additional check: instructor checks ALL meds
rechecking to EMR/MAR at bedside prior to admission
Identifying the patient
utilizing 2 patient identifiers
name
birthdate
MRN
comparing with the EMR
Right time (when is my medication administration considered late?: medications given more frequently than Q6 hours Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 or short acting insulin (regular, Aspart/novolog)
administer within 30 minutes before or after the scheduled time
Right time (when is my medication administration considered late?: medications given Q6 hours or less frequently (Q6, Q8, Q12)
administer within 60 minutes before or after the scheduled time
Right time (when is my medication administration considered late?: daily, weekly, or monthly medications
administered within 2 hours before or after the scheduled time
Mechanisms of drug action?
physiologic effect
pharmacokinetics
absorption (w/food?)
lipid solubility
pH
blood flow (patho?)
protein binding
metabolism
excretion
weight
biologic sex
Oral medication administration: enteral
PO
Feeding tubes
sublingual and buccal routes
solid
liquid
scored (breaking the pill)
SR, XL, CR
enteric coated
For oral medications..
brown syringes mean oral dose ONLY
Topical medications
lotions, creams, ointments and medicated powders
trans-dermal patches
eye drops
nose drops/mists
ear drops
rectal-suppositories
vaginal creams + suppositories
Parenteral medications: intradermal (ID)
TB tests
allergy test
Parenteral medications: subcutaneous administration (SubQ)
insulin administration
heparin
Parenteral medications: intramuscular administration (IM)
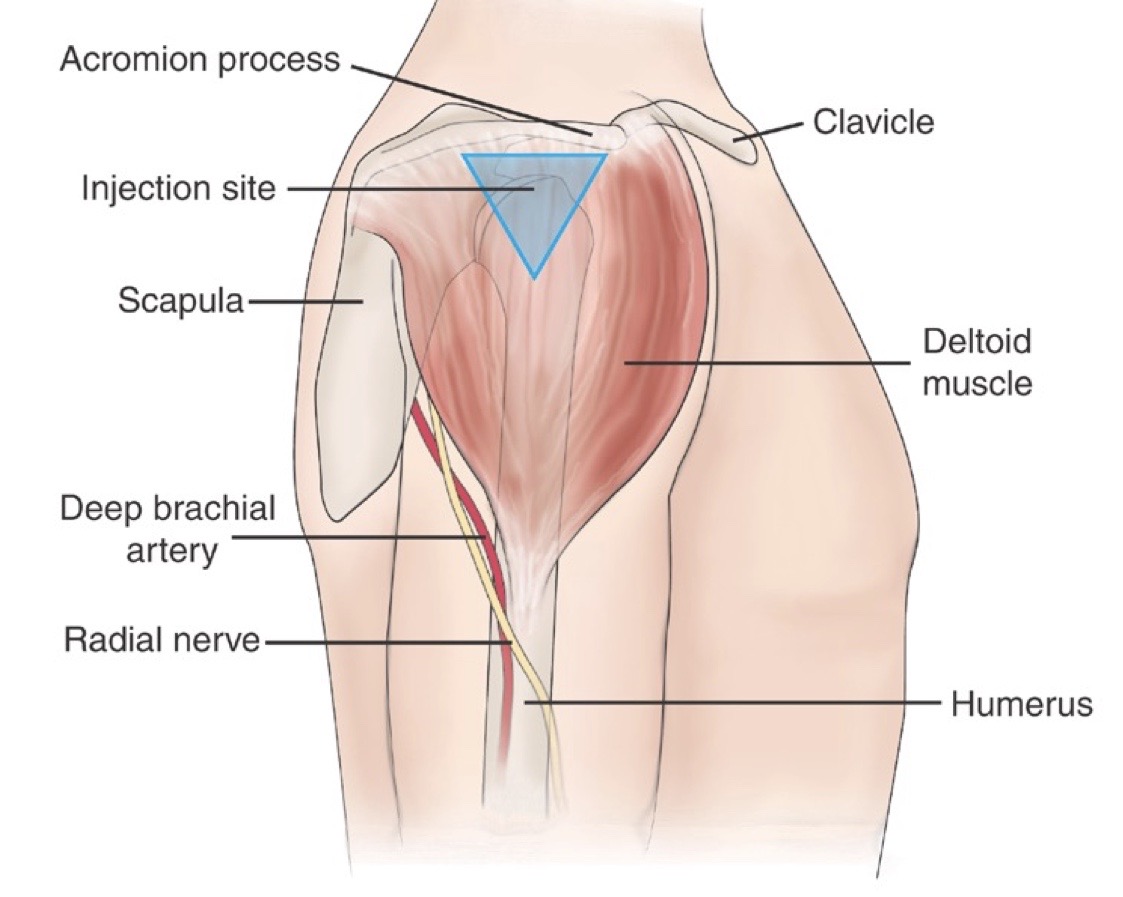
deltoid site
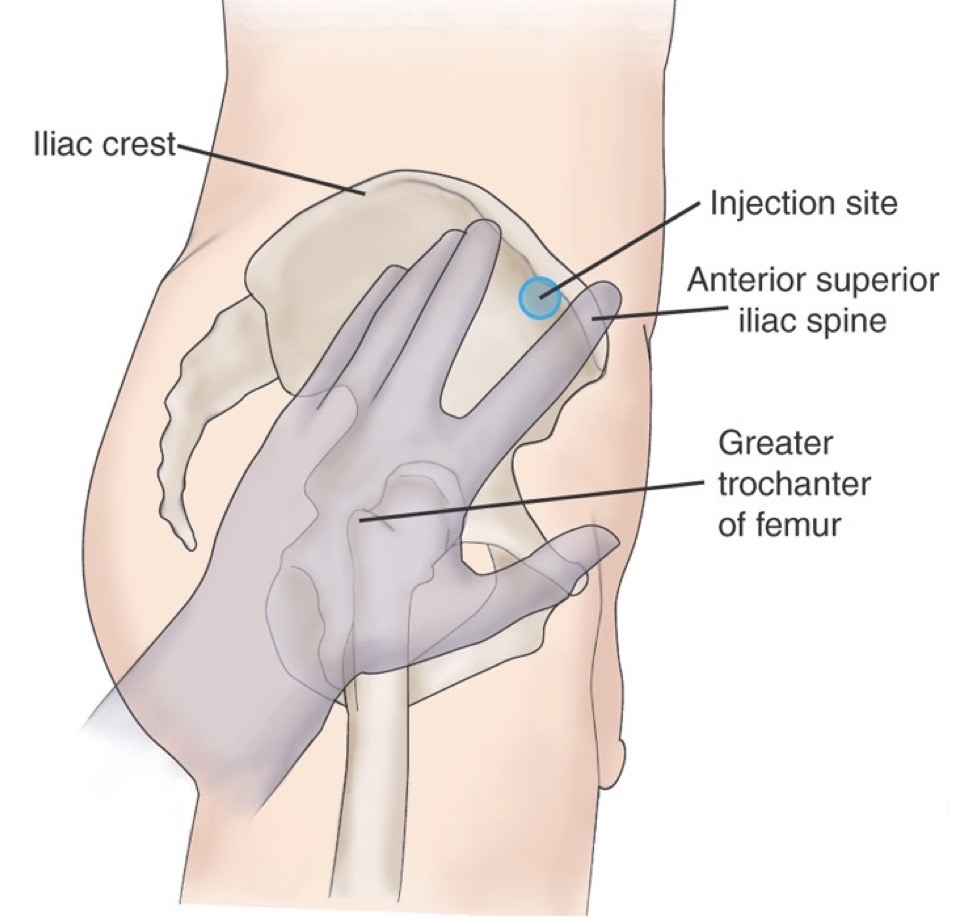
ventral gluteal
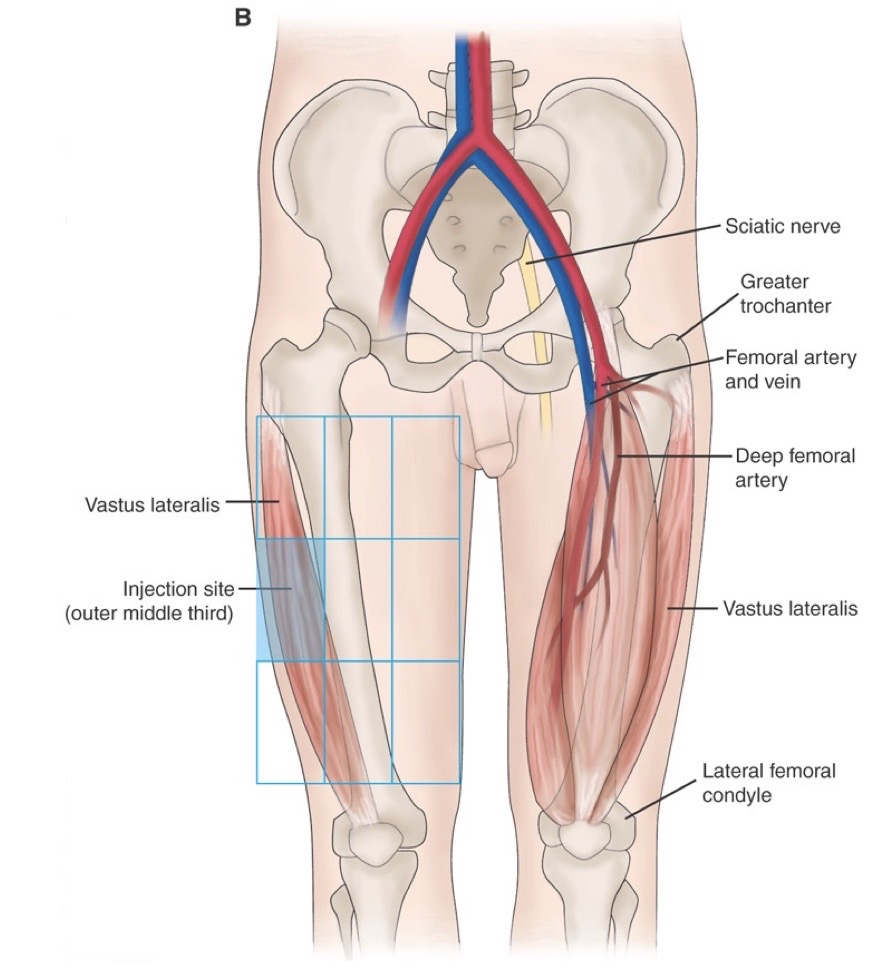
vastus lateralis sites
Needles
length
gauge
needleless systems
safety guards
sharps containers
Injection specifics: intradermal
¼ - ½ inch
25G, 27G
LESS THAN 0.5 mL
angle 5-15 degrees
no aspiration and no massage of sites
Injection specifics: subcutaneous
DRUG SPECIFIC SYRINGES
3/8 - 5/8 inch
25G - 30G
1 mL maximum volume
45-90 degree angle
to pinch or not to pinch
no aspiration and no massage of sites
don’t forget to rotate sites
Injection specifics: intra-muscular
5/8 inch - 1.5 inch needle
20G - 25G
know your sites
up to 3 mL volumes in large muscles
gentle pressure NOT massage
what is the z-track method?
NEVER recap used needles
no aspiration
Z-track method
for intramuscular injections
to prevent leakage of medication into the needle track, thus minimizing discomfort
There is no reported evidence that aspiration with or without blood return
confirms needle placement
eliminates the possibility of an intramuscular injection into a non-subcutaneous blood vessel
Aspiration
not indicated for SC injections
not indicated for IM injections of vaccines and immunizations
may be indicated for IM injections of large molecule medications, such as penicillin
Organizations which state aspiration is NOT necessary for immunizations and vaccines are:
centers for disease control (CDC)
advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP)
department of health services (DHS)
american academy of family physicians (AAFP)
U.K. department of health (DoH)
world health organization (WHO)
NEVER:
recap, bend or break a used needle - straight to the sharps container
Controlled substances
locked
narcotic counts
report any discrepancies
record partial doses
What we need to document
electronic charting
incident reports for medication errors
patient education/teaching
Electronic charting: drugs given
sites and parameters
Electronic charting: doses missed
explanation of why
Electronic charting
drugs given
doses missed
refused medications
Medication errors
check patients condition immediately; observe for adverse effects
obtain a set of VS
notify nurse manager and primary care provider
complete form used for reporting errors, as dictated by the facility policy. (SHARE) not indicate that this form was completed in the patient chart
Needles: vastus lateralis
5-8” to 1”
Needles: deltoid (adults)
5/8” to 1½”
Needles: ventrogluteal (adults)
1” to 1½”
Intramuscular site selection: infants and toddlers and biological (infants and toddlers)
vastus lateralis
Intramuscular site selection: children
vastus lateralis or deltoid
Intramuscular site selection: adults
ventrogluteal or deltoid
Intramuscular site selection: biologicals (children and adults)
deltoid
Intramuscular site selection: medications that are known to be irritating, vicious, or oily solutions
ventrogluteal
Vastus lateralis injection site
Deltoid injection site
Vastus gluteal injection site
NEVER:
recap, bend or break a used needle → STRAIGHT TO THE SHARPS CONTAINER
Controlled substances
locked
narcotic counts
report any discrepancies
record partial doses
What we need to document
electronic charting
drugs given
doses missed
refused medications
incident reports for medication errors (SHARE)
patient education/teaching
What we need to document: drugs given
sites and parameters
What we need to document: doses missed
explanation of why
Medication errors
check patients condition immediately; observe for adverse effects
obtain a set of VS
notify nurse manager and primary care provider
complete form used for reporting errors, as dictated by the facility policy. (SHARE) not indicated that this form was completed in the patient chart
Healthcare failures which lead to laps in safety
failure to recognize
failure to rescue
failure to plan
Maintaining emergency preparedness avoiding failure to plan: general preparation
CPR training
fire drills
code pink drills
preparing for mass trauma terrorism
Maintaining emergency preparedness avoiding failure to plan: course specific preparation
skills check offs
competency based education grading
medication calculation quizzes
QSEN competencies
patient-centered care
teamwork and collaboration
evidence based practice
quality improvement
safety
informatics
QSEN defines safety as:
minimizing risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance
TJC 2024 National patient safety goals for hospitals
identify patients correctly
improve staff communications
use medications safety
label medications
medication reconciliation
use alarms safety
prevent infection
hand hygiene
identify patient safety risks
prevent mistakes in surgery
Fire safety RACE: R
rescue anyone in immediate danger
Fire safety RACE: A
activate the fire code and notify appropriate person
Fire safety RACE: C
confine the fire by closing doors and windows
Fire safety RACE: E
evacuate patients and other people to safe area
BIG 3 in safety errors: #1
medication errors
a medication error is a breakdown or failure at any point in the medication use process
Types of medication errors: omission
drug not prescribed
drug not dispensed
drug not administered
drug not taken
Types of medication errors: communication
vague instructions
Types of medication errors: commission
wrong drug or dose prescribed
wrong drug or dose dispensed
wrong drug administered
wrong patient
frequency timing or duration of the drug is incorrect
wrong route
allergic reaction
drug interaction
Student barriers to building a safer culture
near miss
no harm to patient
lack of learning
how do we overcome these barriers?
acceptance of corrective feedback
BIG 3 in safety errors: #2
falls
one of the never events
Fall risk factors
> 65 years old
history of fails
females
cognitive impairment
altered gait
medications - which ones?
incontinence
unsafe environment
sensory deficits
orthostatic hypotension
depression
assistive devices
confusion or disorientation
new environment
Fall prevention interventions
complete fall assessments
frequent rounding
place on fall precautions
treaded socks
offer assistance to the toilet Q2
bed in low position and bed alarms ON
personal items within reach
call light within reach/answer call lights promptly
BIG 3 in safety errors: #3
improper use of restraints
a restraint is any involuntary method chemical or physical of restricting an individuals freedom of movement, physical activity, or normal access to the body
ANA believes only when no other viable option is available should restraint be employed
Recommended use of restraints
imminent danger to others
imminent danger to the patient
profound disruption of treatment
The hazards of restraints and side
impaired circulation
altered skin integrity
altered nutrition and hydration
aspiration/difficulty breathing
incontinence
increased possibility of serious injury due to fall
depression
anxiety
death
What the evidence shows: routine use of restraints
does not lower the risk of falls or fall injuries
they should NOT be used as a fall prevention strategy
What the evidence shows: restraints can add
to the risk of fall-related injuries and deaths
limiting a patient’s freedom to move around leads to muscle weakness and reduces physical function
Safety event reports
must be completed after any accident or incident in a health care facility that compromises safety
describes the circumstances of the accident or incident
details the patient’s response to the examination and treatment of the patient after the incident
completed by the nurse immediately after the incident
is not part of the medical record and completion of a safety event report should not be mentioned in EMR documentation