Neurophysiology: Conduction Velocity (axon diameter)
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 11.6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Speed of AP movement down the axon is determined by…
Axon Diameter: larger the diameter, faster the impulse
Myelination: continuous vs saltatory conduction; degree of myelination (sheath thickness)
A Fibers
Faster (15-120 m/s)
large (5-20microm); myelinated, short ARP (absolute refractory period)
Sense Danger- do something about it FAST
motor neurons to skeletal muscles
sensory neurons (touch, temp, joint position)
B fibers
Slower
Smaller, light myelination, longer ARP and A’s
Visceral sensory
autonomic moto neurons
C Fibers
Slowest
Smallest; unmyelinated, longest ARP
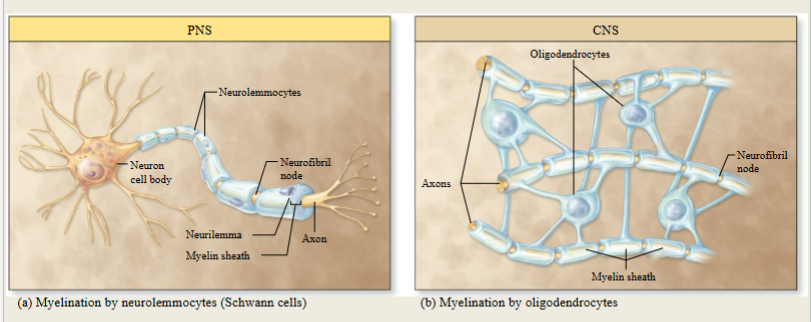
myelination axons
myelin does not conduct electricity; it is an insulator that prevents ion movement
electrical currents only at the nodes of Ranvier
high concentration of V-G Na+ Channels at nodes
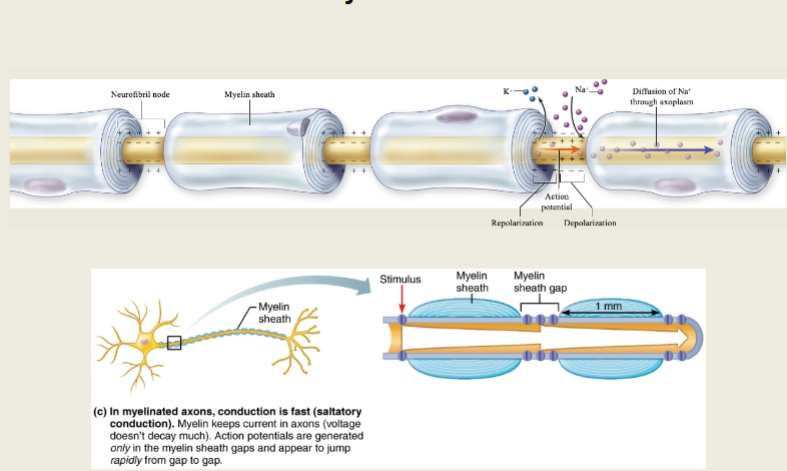
APs jump from one node to the next
Advantages of Saltatory Conduction
Less energy expended by Na+/K+ pump to resent RMP
increased conduction speed
smaller axon diameters
*allows people to have small diameter axons with rapid APs, rather than space consuming large diameter axons
What is the purpose of generating and propagating an AP down the axon to the axon terminal branches?
Releases of chemicals stored in vesicles
chemicals are used to transmit information from the neurons to another cell, with myelination it can be done quickly