SOC 150 Exam 4 - CSUN Carter Fall '19
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Economy
a system of producing goods and services
Technology
knowledge of how to control natural and social elements; one of the elements of an economy
Physical capital
implements used to gather, produce, and distribute; one of the elements of an economy
Human capital
knowledge, skill, and motivations among those who occupy positions and play roles in the economy
Property
socially constructed rights to own, possess, and use physical and symbolic objects of value
Entrepreneurship
the way the other elements are organized for gather, producing, and distributing
Capitalism
private ownership of means of production, market competition, pursuit of profit
Socialism
public ownership of means of production, central planning, the distribution of goods without profit
Capitalists believe...
market forces should determine products and pries, profit is good
Socialists believe...
an item's value is based on the work that went into it, the government should protect workers from exploitation, profit is immoral
Oligopoly
the rule of the many by few
Industrialized societies
the movement of workers out of primary industries and into secondary and tertiary industries
Primary industries
produce raw materials (farming, fishing, mining, forestry)
Secondary industries
turn raw materials into finished products (mills and factories).
Tertiary industries
service oriented (education, government, police and fire, etc.)
Outsourcing
occurs when a society transfers their production of goods and services to industrializing societies where labor costs are lower
Religion
a unified system of beliefs and practices aligned with a society's sacred elements
Sacred
something or someone holy
Profane
something or someone nonreligious
All religions involve
a concern with the sacred and supernatural, rituals, beliefs about the nature of the supernatural, cult structures
Cosmology
a set of beliefs concerning the nature of the universe
Cults
a new religion with few followers, whose teachings, and practices are at odds with the dominant culture and prevailing religion
Sects
a loosely organized religious group that is similar to but larger than a cult
Churches
a bureaucratized organization with structured rules and some sort of hierarchy of authority
Ecclesia
a religious group that is integrated into the dominant culture to such a degree that it is difficult to differentiate where one begins and the other ends
Functionalist perspective on religion
religion answers existential questions, supports government, is an agent of social control
Conflict theory on religion
religion supports the status quo of a society and maintains social inequality
Symbolic interactionist perspectives
religion provides values and meaning in people's lives.
Kinship structures serve
to regulate sex drives so that social organization is possible
Kinship
represents people who consider themselves related by blood, marriage, or adoption
Nuclear family
spouses and children
Extended family
nuclear family, plus grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins
Polygamous family
multiple spouses
Endogamy
the practice of marrying within one's own group (normal)
Exogamy
the practice of marrying outside one's own group
Patrilineal systems
trace descent on father's side
Matrilineal systems
trace descent on mother's side
Bilateral (or bilineal) systems
trace descent of both father's and mother's side
Patriarchy
men dominant women
Matriarchy
women dominate men; there is no historical example of it
Egalitarian
authority is shared between men and women
Kinship in Hunter/Gatherer societies
vitally important; the primary basis of social organization
Kinship in Horticultural societies
extremely important; provided the basic framework of the social system
Kinship in agrarian societies
for individuals, it remained important but for societies in this period, it ceased to be the chief integrating force
Kinship in the industrial era
changed from historical kinships in three main ways: average size declined, type of family has changed, growing difficulty for young adults to form their own families
Functionalist perspective on kinship
believes the family provides socialization, care, regulation of sexual activity, social placement
Conflict perspective on kinship
sees the family promoting inequality because property is inherited through the family, and the family is generally patriarchal
Collective behavior
the action of behavior of people in groups and crowds
Crowd behavior is
unanimous, emotional, and intellectually weak, and therefore represents great threats to social order.
Emergent Norm Perspective on collective behavior
focuses on uncertainty, observation, circular reinforcement, and action motivated by emergent norms
Uncertainty in collective behavior
collective behavior can occur whenever people find themselves in a situation where they are confused or don't know what to do
Observation in collective behavior
when people don't know what to do, they look around to see what other people are doing
Circular reinforcement in collective behavior
when a group member engages in a behavior, all other group members wait to see what will happen
Action motivated by emergent norms
because people conform to the norms of their social surroundings, they will follow the group's new emergent norms.
Social movements
unconventional collectives with varying degrees of organization that attempt to promote or prevent social change
A collectivity
a collection of people that is not as structured as a group
Reform/moderate social movements
moderate and seek modest change within an existing system
Revolutionary/radical social movements
radical and seek fundamental changes of a system rather than changes within a system
Instrumental social movements
seek to change the structure of society
Expressive social movements
address problems and needs of individuals or seek to change individuals' behavior
Progressive social movements
seek to improve the future, especially for marginalized groups
Conservative social movements
seek to prevent change or resurrect the past
Social Movement Combinations
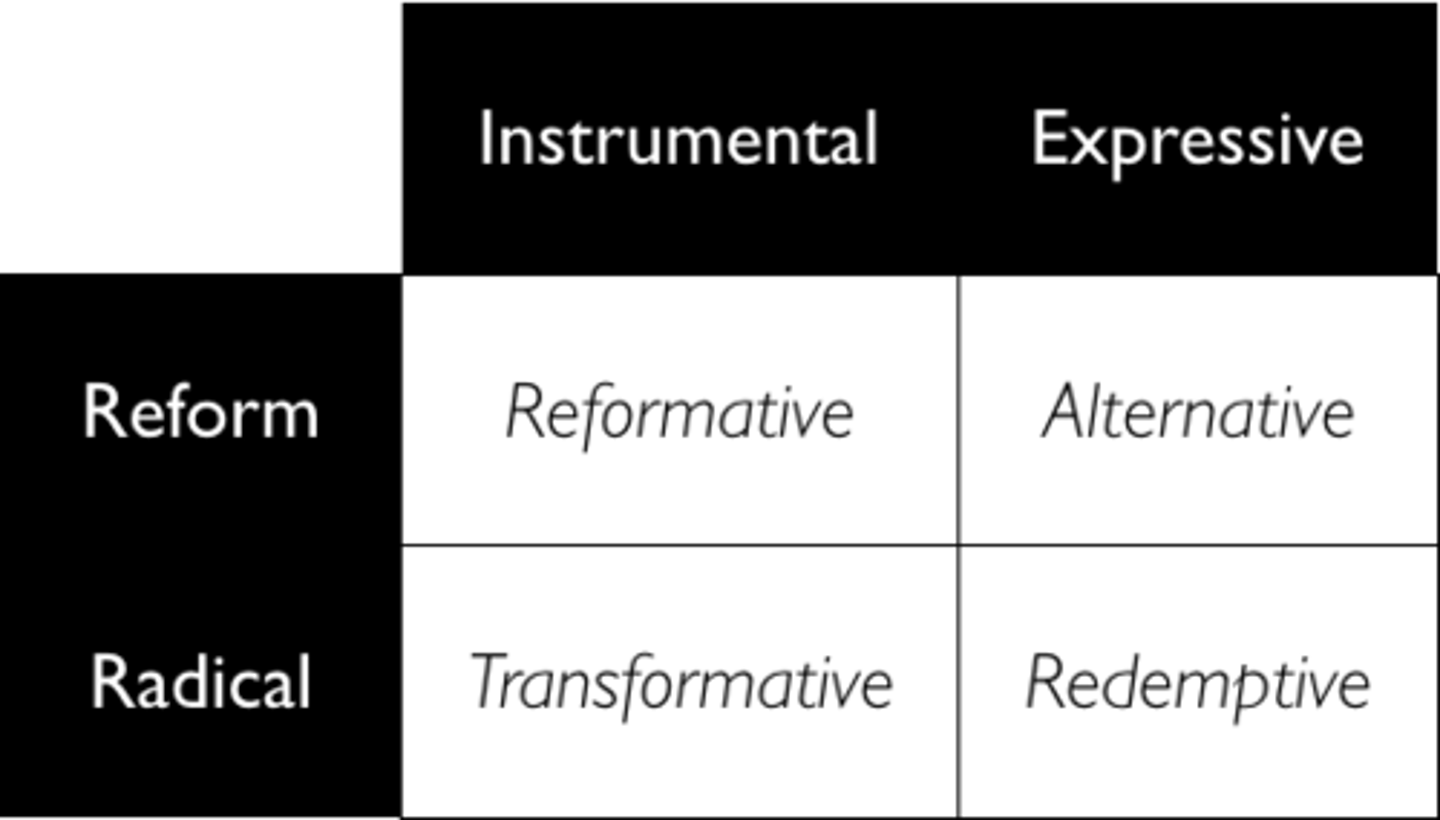
Reformative social movements
seek to change an entire community or society, but in a limited way. The goal is to change society's attitude about a specific issue
Alternative social movements
seek to create change in some people's thoughts or behavior in a specific area
Transformative social movements
seek to completely destroy the old social order and replace it with a new one
Redemptive social movements
seek to create a more dramatic change, but only in specific individual's lives
The three explanations that address how social movements originate are
individual explanations, micro social explanations, macrostructural explanations
The Individual explanation of social movements
irrationality and crowds and rational choice
The Microsocial explanation of social movements
relative deprivation and status strains
The Macrostructural explanation of social movements
broad societal conditions that cause collective behavior; value-added theory
Value-added theory
there are six conditions which operate to predict people's mobilization to act collectively: structural conduciveness, structural strain, growth and spread of generalized beliefs, precipitating factors, mobilization of participants for action, weakening of social control
Structural conduciveness
the permissiveness of an existing social order to generate collective behavior and social movements
Structural strain
refers to various social problems which may exist
Growth and spread of generalized beliefs
the more beliefs in a society that identify the source of strain or suggest solutions to problems, the more likely collective behavior will emerge
Precipitating factors
specific events that sharpen the focus of strain will cause people to mobilize together
Mobilization of participate for action
without some sort of organizing force which focuses efforts and defines responsibilities of those aligned with a cause, people are not likely to mobilize effectively
Weakening of social control
ineffectiveness of the mechanism of constraint in society can lead to collective behavior