C954 - MIS Infrastructure/Information Security - Section 5 with expert curated questions and answers
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
ransomeware
This is a form of malware designed to encrypt files, rendering them unusable. The ransomware creators demand a ransom in exchange for decryption.
spyware
A special class of adware that collects data about the user and transmits it over the internet without the user's knowledge or permission
adware
Software that claims to serve some useful function and often fulfils that function but also allows internet advertisers to display advertisements without the user's consent
worm
Software that spreads itself not only from file to file but also from computer to computer
virus
Software written with malicious intent to cause annoyance or damage
drive-by hacking
A hacking attempt made from outside your home or facility using wireless transmissions
agile MIS infrastructure
Includes the hardware, software, and telecommunications equipment that, when combined, provide the underlining foundation to support the organizational goals
sustainable MIS infrastructure
Identifies ways that a company can grow in terms of computing resources while simultaneously becoming less dependent on hardware and energy consumption
fault tolerance
The ability for a system to respond to unexpected failures or system crashes as the backup system immediately and automatically takes over with no loss of service
failover
This occurs when a redundant storage server offers an exact replica of the real-time data; if the primary server crashes, the users are automatically directed to the secondary server or backup server
disaster recovery plan
A corporate plan that specifies which employees will participate in business recovery and their duties, as well as what hardware, software, and facilities will be used; includes a detailed process for recovering information or a system in the event of catastrophic disaster and should be based on general conditions, not specific scenarios
hot site
A separate and fully equipped facility where the company can move immediately after a disaster and resume business
cold site
A backup facility with the needed electrical and physical infrastructure of a computer facility, without computer equipment operating
warm site
A separate facility with computer equipment that requires installation and configuration
disaster recovery cost curve
Charts (1) the cost to the organization of the unavailability of information and technology and (2) the cost to the organization of recovering from a disaster over time
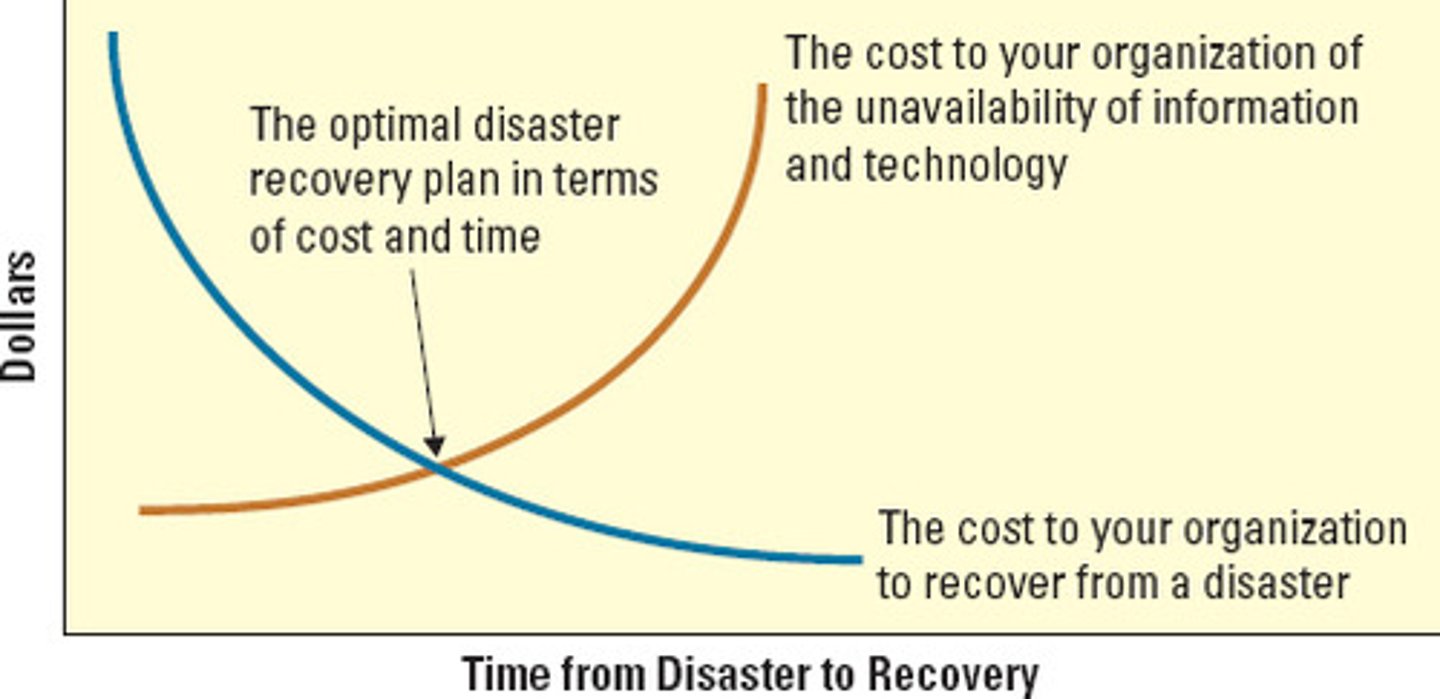
business continuity planning (BCP)
Details how a company recovers and restores critical business operations and systems after a disaster or extended disruption
technology recovery strategy
Focus specifically on prioritizing the order for restoring hardware, software, and data that best meets business recovery requirements
web accessibility initiative (WAI)
Brings together people from industries, disability organizations, government, and research labs from around the world to develop guidelines and resources to make the web accessible to people with disabilities, including auditory, cognitive, neurological, physical, speech, and visual disabilities
portability
Refers to the ability of an application to operate on different devices or software platforms, such as a different operating system
pretexting
A form of social engineering in which one individual lies to obtain confidential data about another individual
vulnerability
System weaknesses that can be exploited by a threat—for example, a password that is never changed or a system that is left on while an employee goes to lunch
scalability
Describes how well a system can scale up or adapt to increased demand of growth
capacity planning
Determines future environmental infrastructure requirements to ensure high-quality system performance
serviceability
How quickly a third-party vendor can change a system to ensure it meets users' needs in terms of agreed levels of reliability, maintainability, or availability
individual information security
Details how an organization will implement an information security policy plan
pharming attack
A group of computers on which a hacker has planted zombie programs
zombie farm
Used often by an organized crime association to launch a massive phishing attack
authentication
A method for confirming users' identities
authorization
The process of providing a user with permissions, including access level, file access, hours of access, and amount of allocated storage space
smart card
A device about the size of a credit card, containing embedded technologies that can store information and a small amount of software to perform limited processing
security token
A peripheral device used to gain access to an electronically restricted resource; used in addition to or in place of a password and acts like an electronic key to gain access
biometrics
The identification of a user based on a physical characteristic such as their fingerprint, iris, face, voice, or handwriting
two-factor (double) authentication
Requires the user to provide two means of authentication
privilege escalation
An attacker gains additional privileges by taking over another account that has additional permissions or by increasing the level of permissions for their account
vertical privilege escalation
Attackers grant themselves a higher access level, allowing the attacker to perform illegal actions, such as running unauthorized code or deleting data.
horizontal privilege escalation
Attackers grant themselves the same access levels they already have but assume the identity of other users.
advanced encryption standard (AES
Introduced by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), ___ ___ ___ is an encryption standard designed to keep government information secure
decryption
Decodes information and is the opposite of encryption
firewall
Hardware or software that guards a private network by analyzing the information leaving and entering the network, thus preventing unauthorized access by an intruder
cyberterrorism
The use of computer and networking technologies against persons or property to intimidate or coerce governments, individuals, or any segment of society to attain political, religious, or ideological goals
phishing expedition
A masquerading attack that combines spam with spoofing
denial of service (DoS)
A software attack that attempts to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users, using a valid request sent in rapid or hyper repetition.
destructive agent
A malicious agent designed by spammers and other internet attackers to farm email addresses of websites or deposit spyware on machines
information secrecy
The category of computer security that addresses the protection of data from unauthorized disclosure and confirmation of data source authenticity
spear phishing
A phishing expedition where the emails are carefully designed to target a particular person or organization
vishing (or voice phishing)
A phone scam that attempts to defraud people by asking them to call a bogus telephone number to confirm their account information
intrusion detection software (IDS)
Features full-time monitoring tools that search for patterns in network traffic to identify intruders ex (Mcaffee)
content filtering
Occurs when organizations use software that filters content to prevent the transmission of unauthorized information