sports med final
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
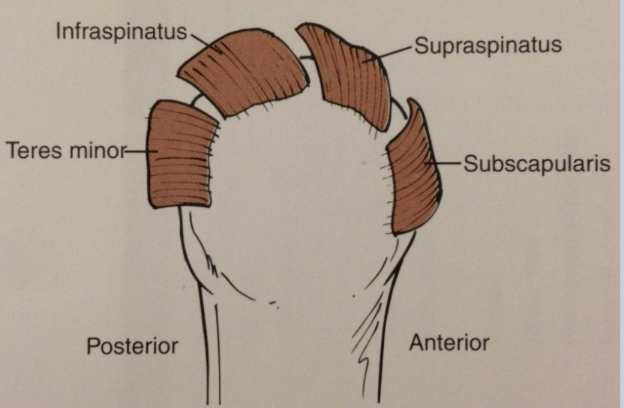
teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis
FOOSH
fall on outstretched hand
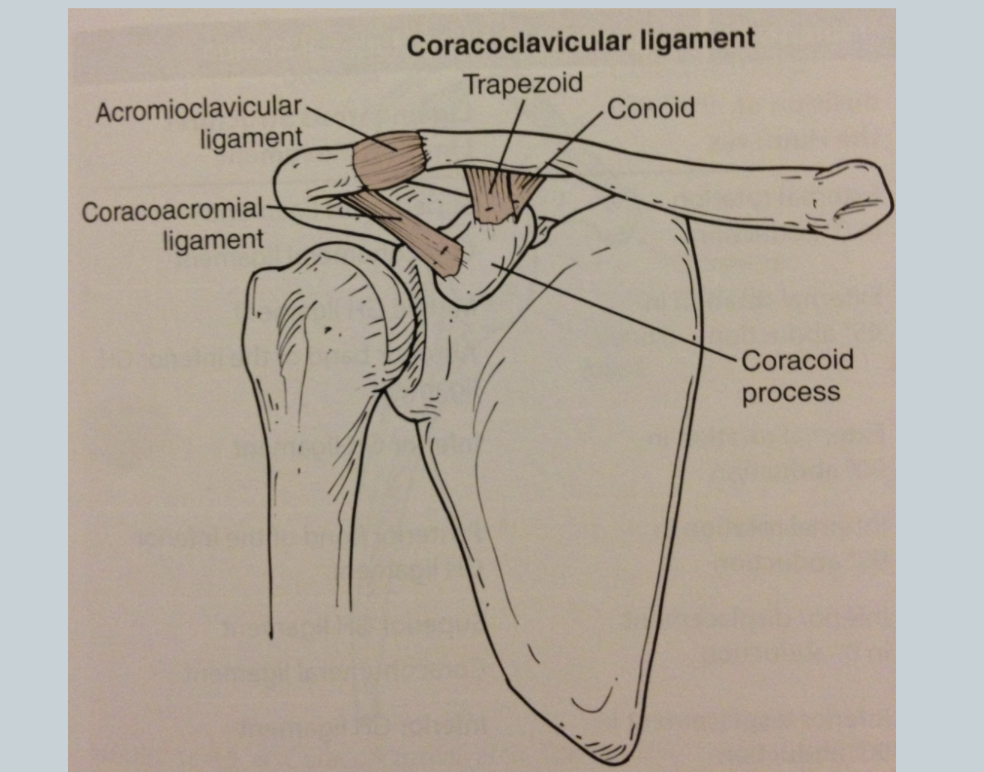
MOI for SC Joint disfunction
FOOSH
AC Joint
acromioclavicular
observations of SC joint dysfunction
edema, ecchymosis
what type of SC joint dysfunction is considered a medical emergency? and why
posteriorly because it is a risk to neurovascular supply
AC joint treatment for grade 1 and 2
conservative
Immobilization/Sling
Cortisone/corticosteroids
PF (pain free) ROM progress to strengthen
AC joint treatment for grade 3
Surgical
Cosmetic vs. function
Long Term outcomes
Immobilization
Progression...
SLAP
superior labrum anterior to posterior lesion
type 1 SLAP
fraying of labrum
type 2 slap
avulsion of labrum
most common fracture in elbow forearm and why
olecranon because it is predisposed to a direct blow
radial head fracture MOI, common injury with, what happens if displaced
MOI: FOOSH
occurs with elbow dislocation
displacement= surgery
forearm fracture described by:
open or closed, simple or compound
what is key to note when dealing with forearm fracture?
capillary refill, distal pulse, check near
does Molly reduce elbow dislocations? why or why not
NO, too risky, compression of nerves+ blood vessels: Molly only does patellas or phalanges
ulcer collateral ligament sprain MOI
secondary to valgus load
RCL
radial collateral ligament
is RCL sprain common or not? why
less common because the body is a natural shield to varus movement
medial epicondylitis, what activities cause
swift snapping of wrist & pronation of forearm; ex. volleyball, pitching, tennis
little leagues elbow
medial epicondylitis apophysitis ; avulsion of the common tendon
entrapment of nerves, 3 ways
anatomical tissues, scar tissue, muscular
nerve pathology
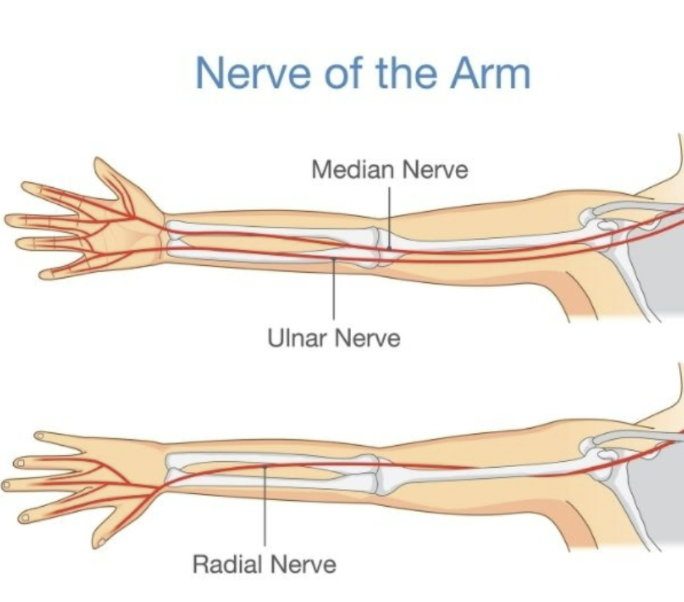
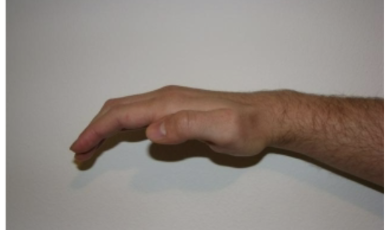
ape hand
causes of ape hand
median nerve neuropathy
cause of bishop’s deformity
inhibition of ulnar nerve

bishop’s deformity
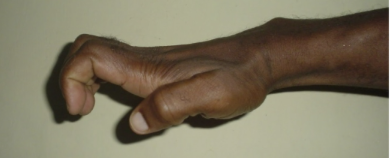
claw hand
cause of claw hand
ulnar and median nerve involvement
trigger finger impairment
stenosing tenosynovitis that forms a nodule in a flexor tendon, not allowing full extension
colle’s fracture
describes any distal radial fracture
what percentage of carpal fractures are scaphoid?
70% because it’s a bony block to wristt extension
scaphoid blood supplly
only has blood supply coming from the distal end
MOI of scaphoid fracture
FOOSH, forceful hyperextension
TFCC
triangular fibrocartilage complex
carpal tunnel results from
median nerve compression
MOI of carpal tunnel
insidious onset, typing, any repetitive hand motions
DeQuervain’s syndrome
Stenosing Tenosynovitis of the
muscles: extensor
pollicis brevis /abductor
pollicis longus
ringworm
dermatophytes, aka ringworm fungi
most common ribs fractured
5-9
pnuemothorax
accumulation of air in the plural cavity
spontaneous pnuemothorax
occurs when a bleb (large sac filled w/air or fluid with potential to rupture) ruptures and allow air leak into pleural cavity
tension pneumothorax
spontaneous pneumothorax doesn’t close or due to a blunt or penetrating trauma; air enters the pleural cavity but cant exit
if unchecked = death (pressure on opp lung, heart and major arteries)
hemothorax
blood in pleural cavity
what organ is at risk if hit and the person has mono
SPLEEN
3 signs of shock
rapid weak pulse
decreased blood pressure
rapid, shallow breathing
excessive thirst
nausea and vomiting
pale, bluish skin
restlessness or irritability
drowsiness or loss of consciousness
kidney is protected by
lower ribs
hematuria
blood in peeb
blood in vomit
looks like coffee grounds
kidney stones first signs
pain in left or right abdomen, feels like period cramps
can mimic S&S of appendicitis, if in lower right quadranta
appendicitis is more common in which gender
males3
3 outwards symptoms of appendicitis
fever
lower ab tenderness
naseau
vomiting
is testicular contusion a medical emergency
yes
female athlete triad
osteoporosis
disordered eating
amenorrhea
commotio cordis
cardiac concussion,
getting hit in the heart by projectile, stops electrical circuit, AED is keyh
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
enlargement of heart muscles without an increase in the size of heart’s chambers
myocardial infarction
heart attackho
how to increase survival rate with myocardia infarction
aspirin
AED/CPR
getting to hospital / ER
degenerative disk/jt disease caused by
aging
collapse of disk occurs first, osteophytes develop and ultimately leads to pressure on spinal cord
brachial plexus trauma MOIs
stretching vs compression
thoracic outlet syndrome
group of conditions caused by compression of nerves or blood vessels in the area between the neck and shoulder
what is in the neurovascular bundle
brachia plexus (nerve)3 t
subclavian artery
subclavian vein
3 types of thoracic outlet syndrome
vascular (arterial / veinous) - least common
neurogenic (born that way)
non-specific
causes of TOS
presence of extra cervicular rib
compression of NVM between clavicle + first rib
compression between pec minor + ribcage
tightness of anterior/middle scalene (molly’s fav muscles) muscles