Edexcel IGCSE Physics Full Course
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
251 Terms
How do you calculate the speed from a distance-time graph ?
the speed/velocity is the gradient
State the equation for average speed
average speed = distance travelled /time taken
v[m/s]=s[m]/t[s]
Practical: investigate the motion of everyday objects such as toy cars or tennis balls
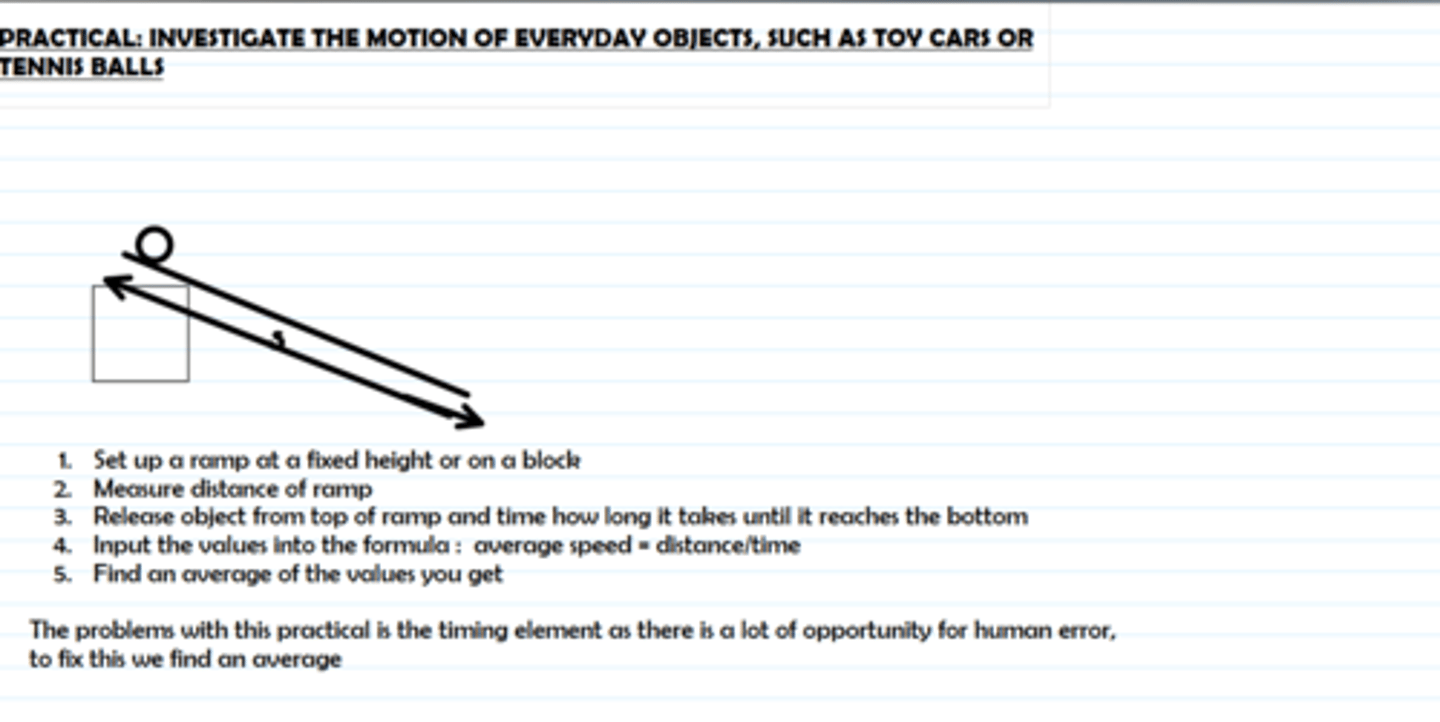
state the equation for acceleration ( using velocity and time)
acceleration = change in velocity / time taken
a[m/s/s] = (v-u)[m/s]/t[s]
How do you calculate the distance from a velocity time graph?
The distance is the area under the graph
How do you calculate the acceleration from a velocity time graph?
The acceleration is the gradient of the graph
State the equation for final speed
final speed squared [m/s] = initial speed squared [m/s] + 2 x acceleration[m/s/s] x speed [m/s]
What are the effects of a force?
1. can change the speed of an object
2. can change direction an object is travelling in/ can rotate an object
3. can change shape of an object
List the different types of forces:
1. Gravity/Weight
2. Reaction Force
3. Electrostatic Force
4. Thrust
5. Drag/Air Resistance
6. Friction
7. Lift
8. Tension
9. Magnetic
10. Nuclear
What is the difference between a vector quantity and a scalar quantity?
a scalar quantity only has magnitude (size) whereas a vector quantity has magnitude(size) and direction
How do you calculate the resultant force of forces acting on a line ?
you add up the forces in each direction
You subtract the larger force from the smaller force, to get the resultant force
The resultant force acts in the direction of the larger force
What is friction ?
a force that opposes motion
State the equation for force (using mass and acceleration)
force = mass x acceleration
F[N] = m[Kg] x a[m/s/s]
State the equation for weight
Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg)
W[N]=m[Kg] x g[m/s/s]
What is stopping distance and how do you calculate it ?
the distance a vehicle travels from the second a hazard is detected till the car stops
stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
What factors affect stopping distance?
speed
mass
road condition
reaction time
Describe the forces acting on a falling object
*CHECK
1. initially v=0 and drag=0 , only weight acting on it
2. Then as it falls it will experience drag , however initially the weight force is higher
3. the object will begin to move faster towards the ground, simultaneously the force of drag increases
4. the weight and drag forces balance out so there is no resultant force on the object and it reaches(constant) terminal velocity
Practical: Investigate how extension varies with applied force for helical springs, metal wires and rubber bands
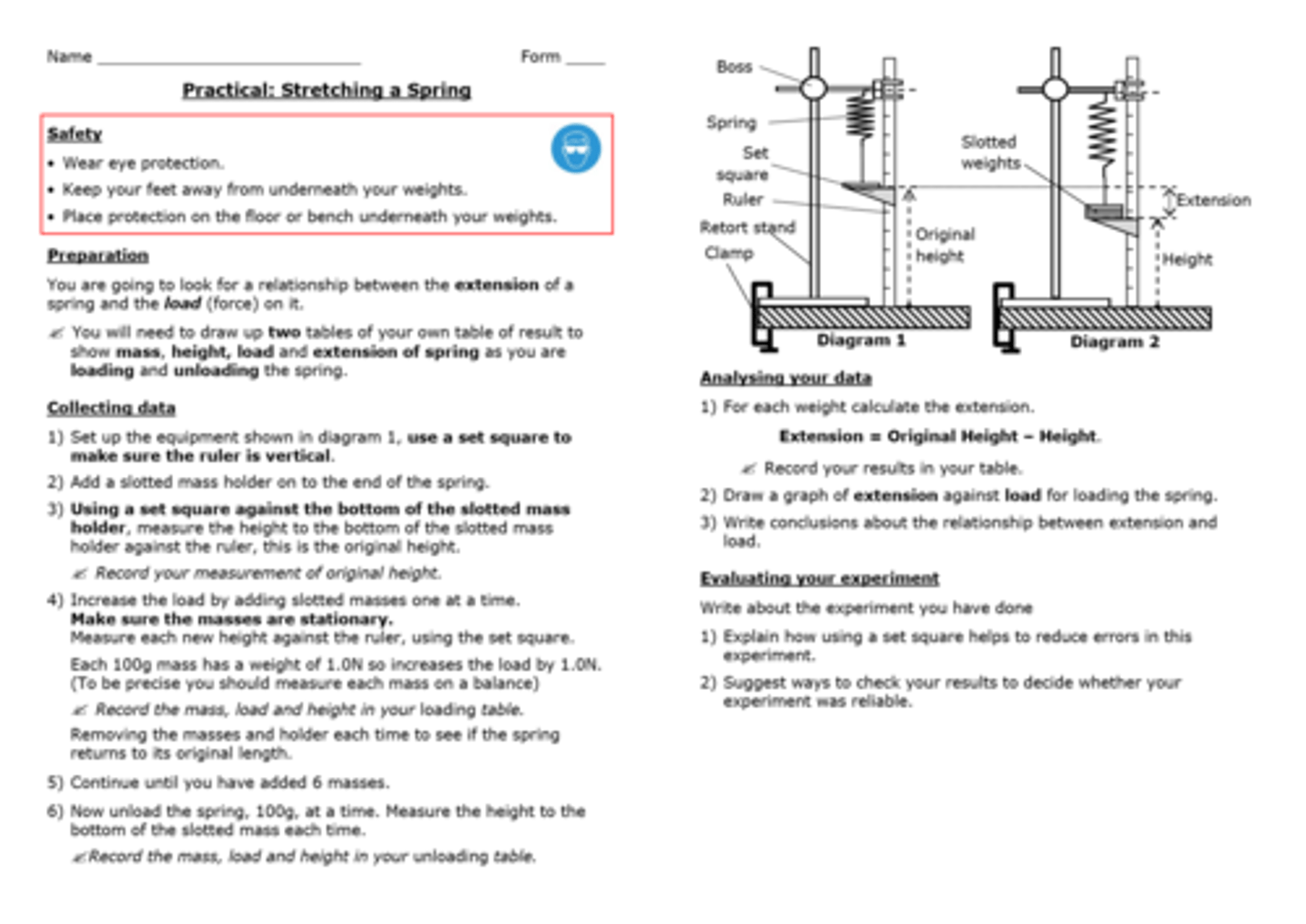
What is Hooke's law?
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied up until the limit of proportionality
Define the term elastic behaviour
the ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed
State the equation for momentum
momentum = mass x velocity
p[kgm/s]=m[kg] x v[m/s]
Explain how safety features in a car work , with respect to momentum
Airbags&Seatbelts
1. Absorbs energy from the impact, 2.increases time taken for the force to act on the passenger
3. Since force = change in momentum/ time taken , and time increases = the force decreases
Crumple Zones
1. part of the car which collapses during a collision
2. Increases time during which the car is decelerating
3. And since force = change in momentum / time , and if time increases force felt on the passenger decreases
State the principle of conservation of momentum
momentum before collision = momentum after collision
total initial momentum = total final momentum in an elastic reaction
elastic reaction , a reaction where initial KE = final KE
State the relationship between force and momentum
force = change in momentum / time taken
F[N] = (mv-mu)[kgm/s]/t[s]
Explain Newton's third law
if object A exerts a force on object B then object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A
State the equation for a moment
moment = force x perpendicular distance
m[Nm] = F[N] x d [m]
Where does weight act on a body?
through the centre of gravity (the centre of the object)
How do you calculate the moment for parallel forces acting in one plane?
you use the moment formula and calculate the distance from the pivot of both of the forces
You then subtract the smaller moment from the larger moment to give the total moment which is in the direction of the larger moment
You may use:
F1 x d1 = F2 x d2
Then rearrange if asked to find a particular force or distance
Describe how the upward forces on a light beam supported at its ends vary with position of a heavy object placed on the beam
If a beam is supported at ends A and B
(take centre as pivot )
As the mass moves towards A :
Upwards Force on A increases
Upwards force on B decreases
As the mass moves towards B:
Upwards force on A decreases
Upwards force on B increases
This is because the CW moment must equal the ACW moment to secure the beam
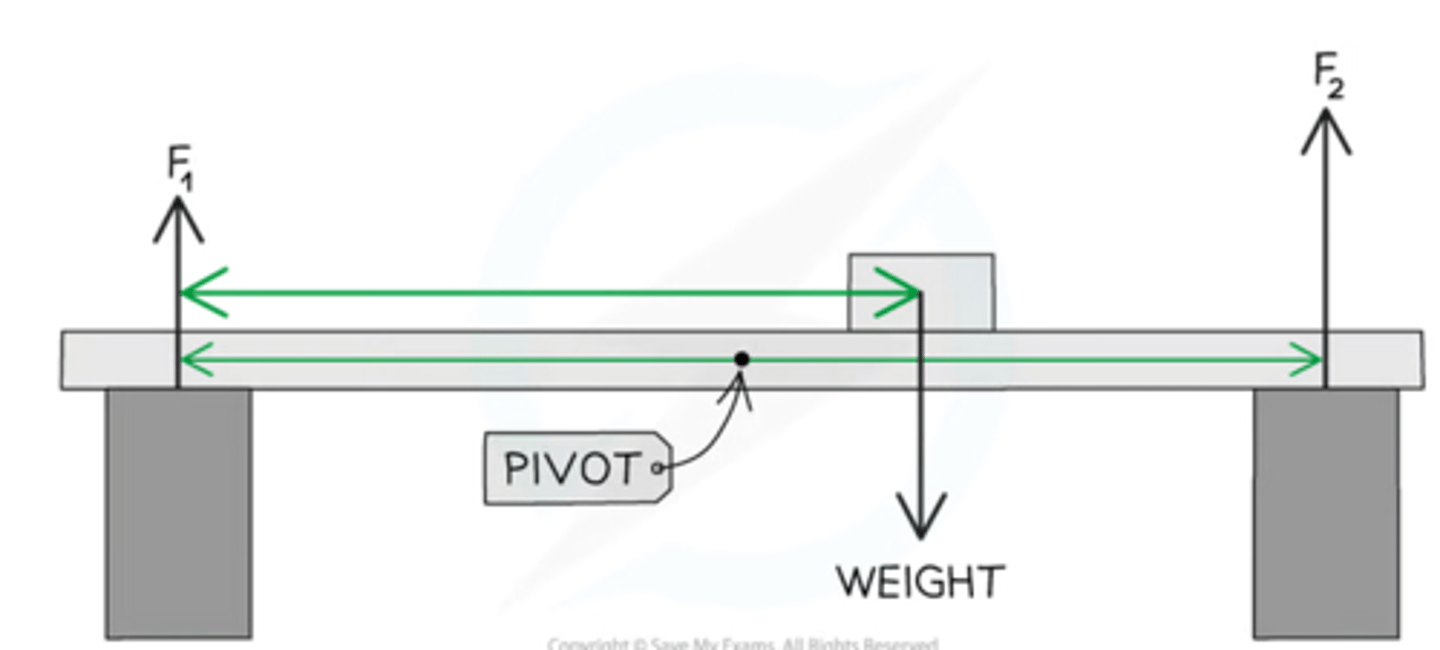
What is insulation in domestic appliances ?
1. insulation in a plug is when the live, neutral and earth wires are covered with a plastic layer
2. plastic is a good insulator
3. this prevents contact with the live wire when handling the plug and prevents the person receiving a large current
What is double insulation in domestic appliances?
1. double insulation is when the casing of the plug is made of plastic and wires are covered in plastic casing
2. this means that even if the live wire breaks and touches the outer casing a charge cannot go through
3. as plastic is a good insulator
4. preventing any risk of electric shock as well as reducing the need for an earth wire
What is earthing in domestic appliances?
1. earth connected to (metal) casing;
2. If casing becomes live/ live wire touches case;
2b. absorbs electrons
3. Provides low resistance path (to earth);
4. (So) large/surge current in earth wire;
5. (hence) fuse breaks/melts/blows;
6. (so) circuit switches off
What are fuses ?
1. a thin piece of metal with a low melting point
2. if there is a current which is too large, the fuse heats up and becomes very hot and melts/breaks
3. breaking the circuit and preventing the large current from flowing
4. preventing the risk of electrical fire and severe electrical shock
What are circuit breakers?
1. A circuit breaker has a coil or a metallic strip which detects the amount of current lowing through a circuit
2. When the current goes above the acceptable range the current sensing system detects it and causes the circuit breaker contacts to open
3.Breaking the circuit preventing the large current from flowing , preventing electrical fires and risk of electrical shock
4.After the fault is checked the circuit breaker can be reset and some do this on their own, meaning a circuit breaker can be re-used
5.This makes it better to use than a fuse, however they are more expensive than fuses
How do resistors heat up and how can this be used in domestic appliances?
1. when resistors are applied current is reduced and the rate of flow of electrons slows down
2. this means that there is more collision of electrons and ions in the resistor
3. this means there are more transfers of electrical energy into heat energy in the resistor
P= I x I x R so higher R is more power dissipated as heat
State the relationship between power , current and voltage
Power[W] = current [A] x voltage [v]
P = I x V
State the relationship between energy transferred, current, voltage and time
Energy Transferred [J] = Current [A] x Voltage [v] x Time [s]
E = I x V x t
What is the difference between alternating current and direct current ?
1. Alternating current is supplied by mains electricity
Direct current is supplied by a cell or battery
2. Alternating current changes direction , Direct current travels in one direction
3. Alternating current can vary in size , Direct current remains at one size
Which is better suited for domestic lighting series or parallel circuits , and why ?
1. A parallel circuit is better suited
2. because if there is a fault in one of the branches it will not effect the others
3. whereas in a series circuit if there is a fault in any part the whole circuit stops working
What factors affect current in a series circuit ?
Voltage:
the higher the voltage the higher the current (I=V/R)
Number of components :
The higher the number of components the lower the current as the overall resistance increases and voltage has to be split up further resulting in a lower current
Nature of components:
components with a higher resistance will reduce current as I=V/R
Describe the IV characteristics of a. wire
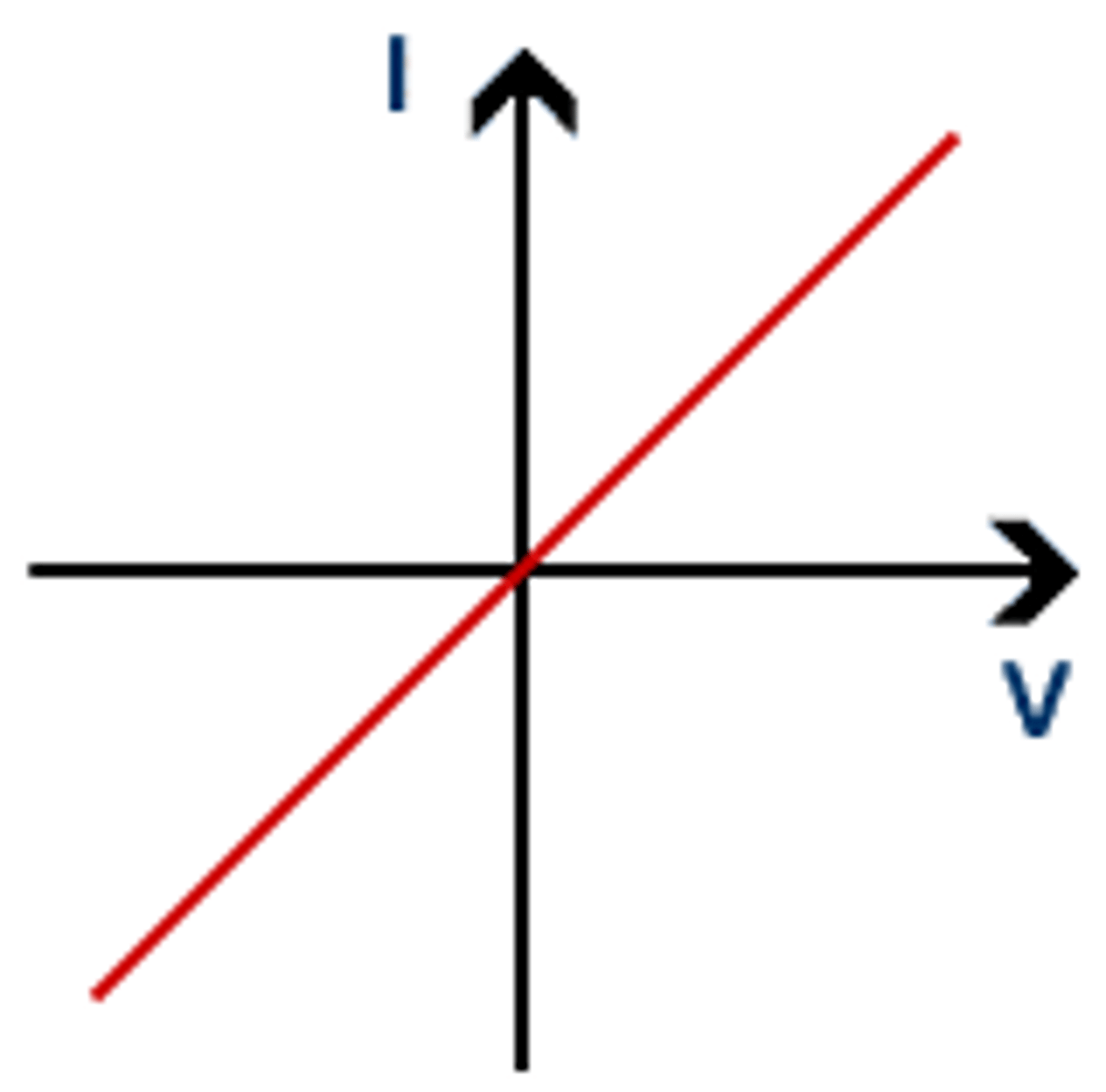
Describe the IV characteristics of a resistor
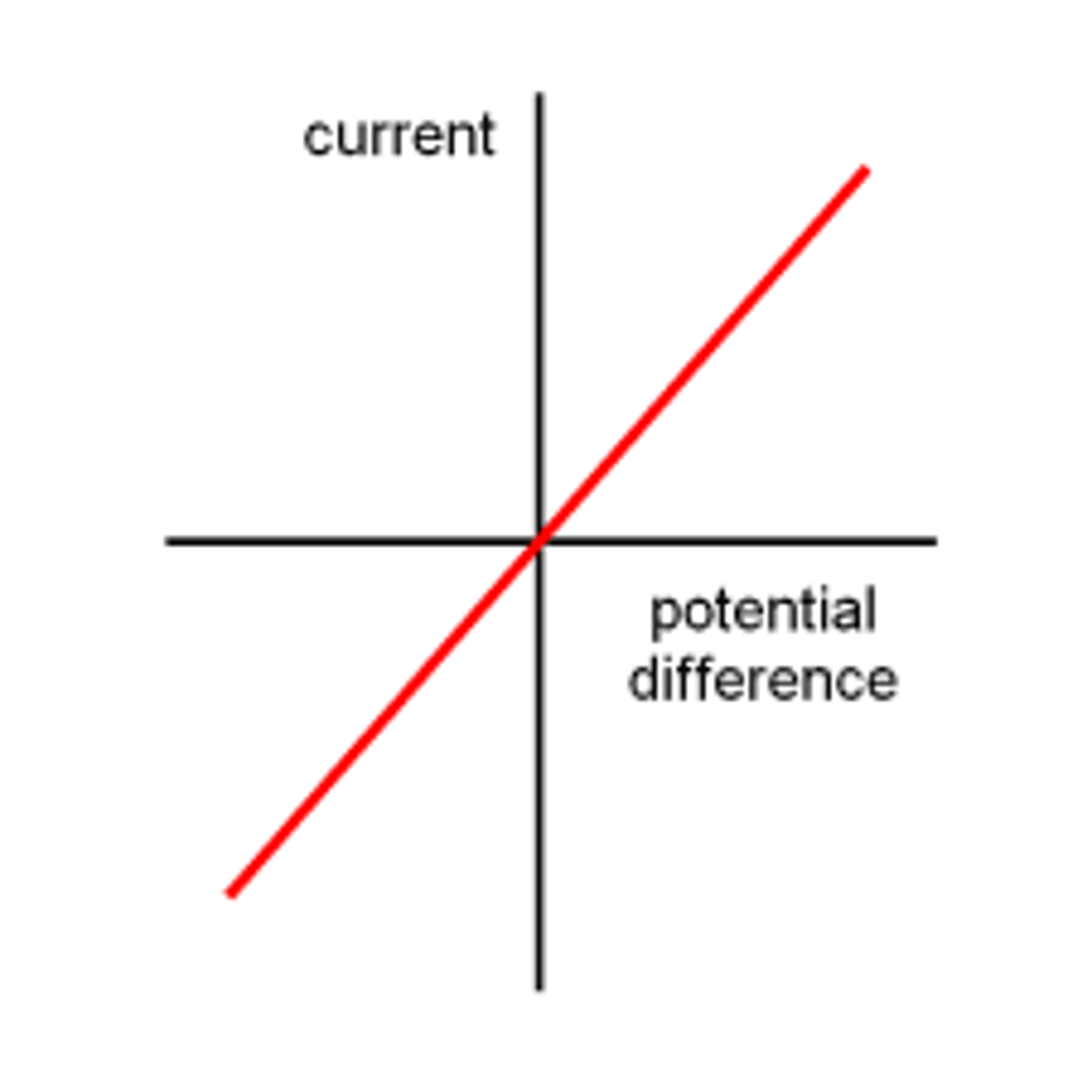
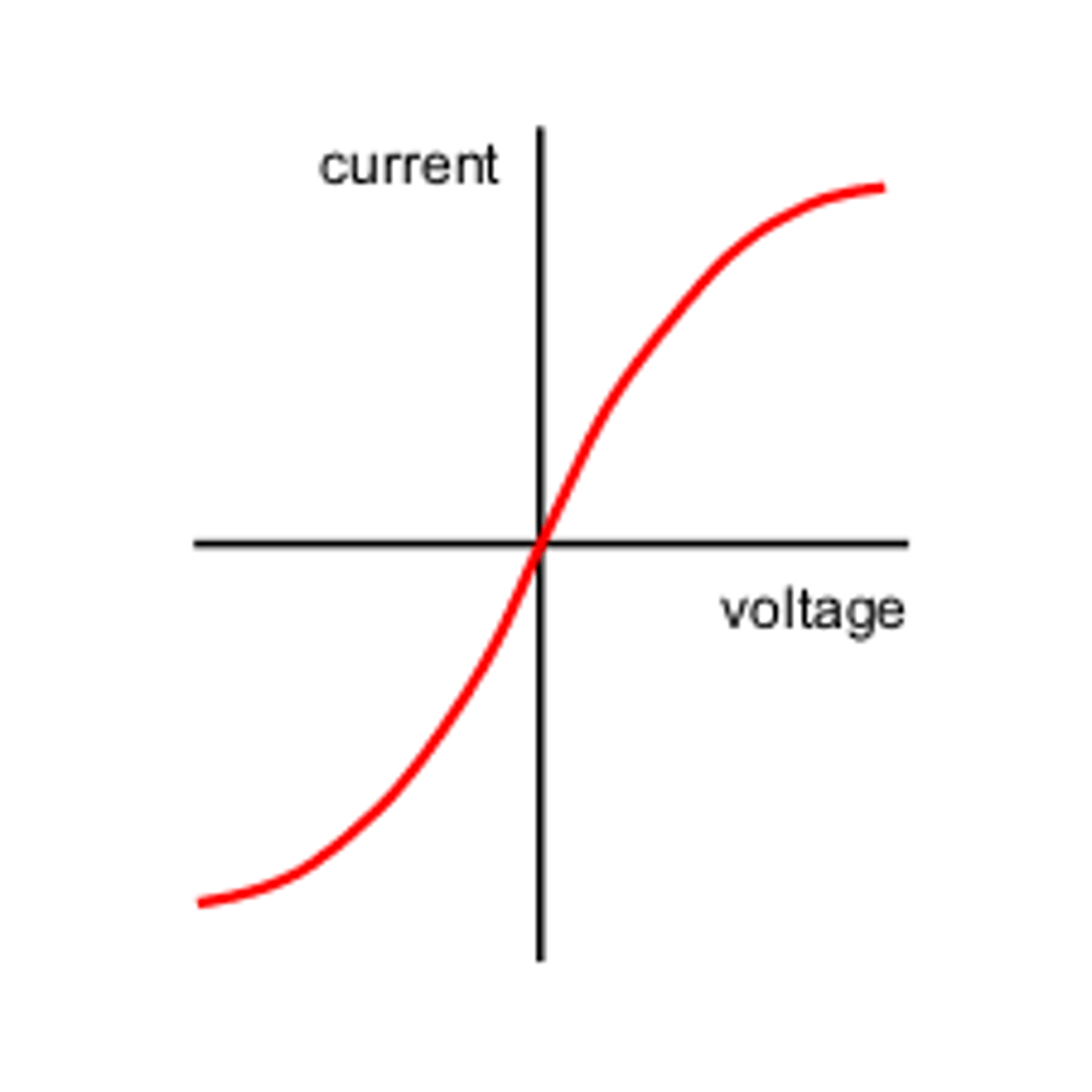
Describe the IV characteristics of a filament lamp
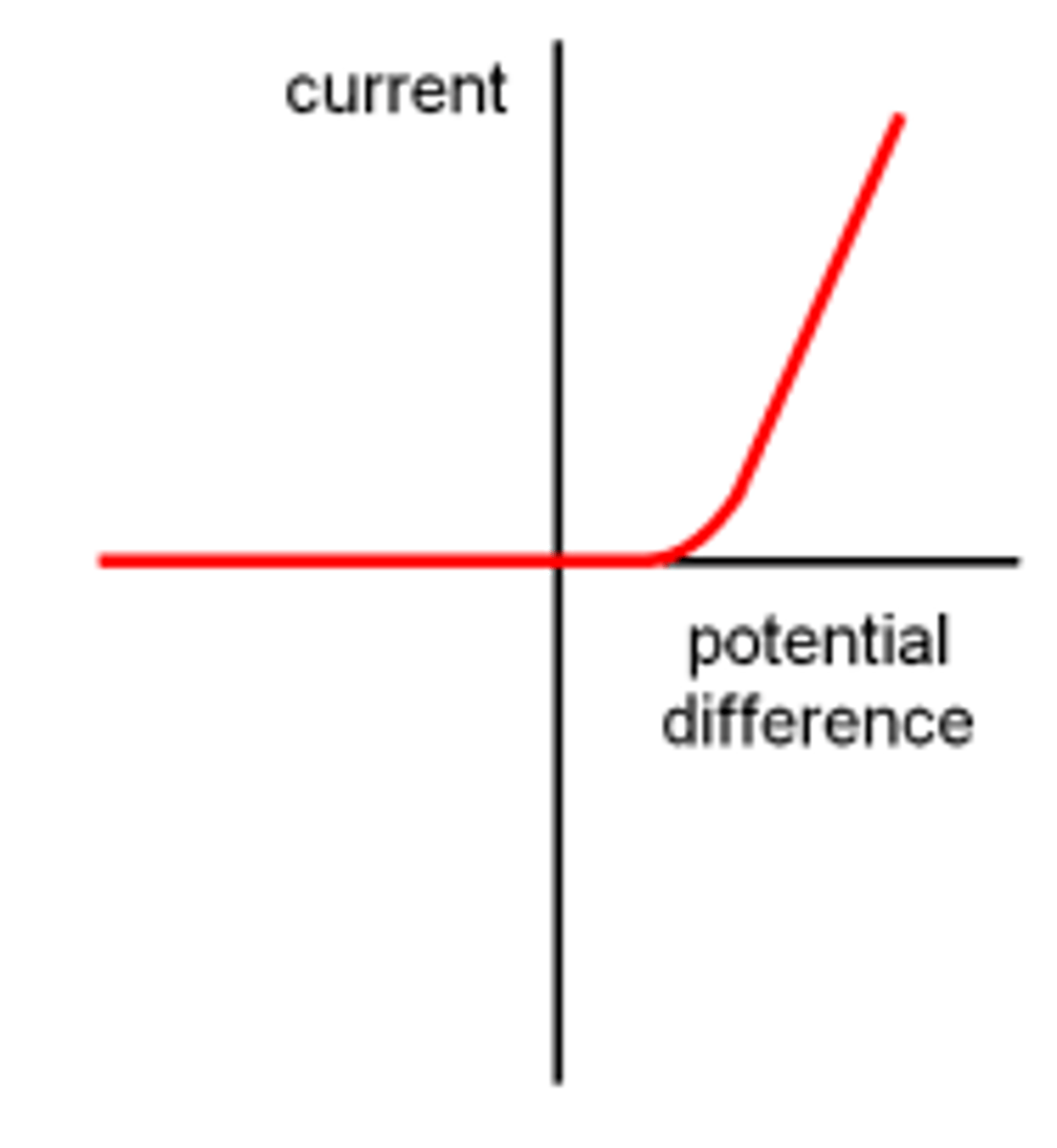
Describe the IV characteristics of a diode
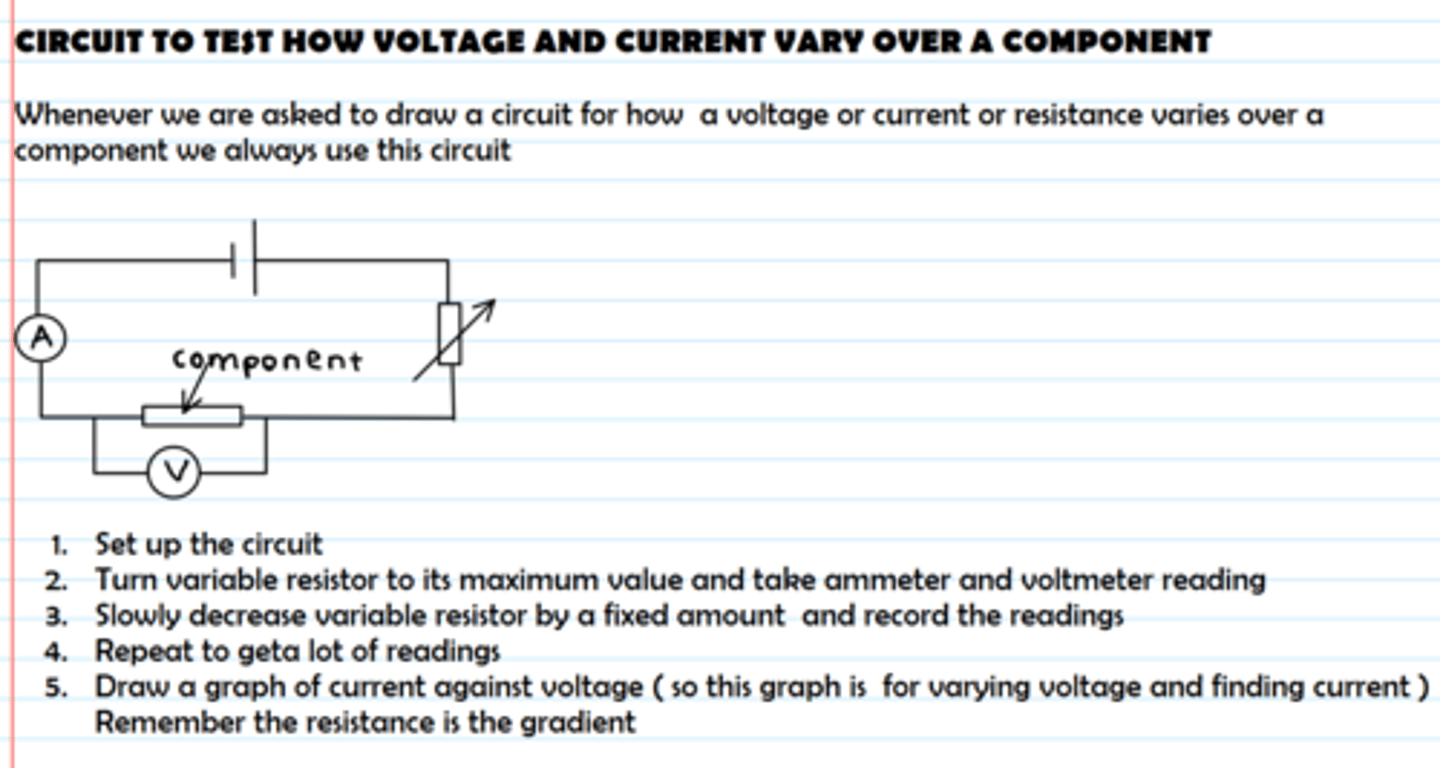
How do you test the IV characteristics of a component?
What is the effect of changing resistance on the current in a circuit?
increasing the resistance in a circuit reduces the amount of current which flows through the circuit
(so we use resistors to limit current, e.g. before lamps)
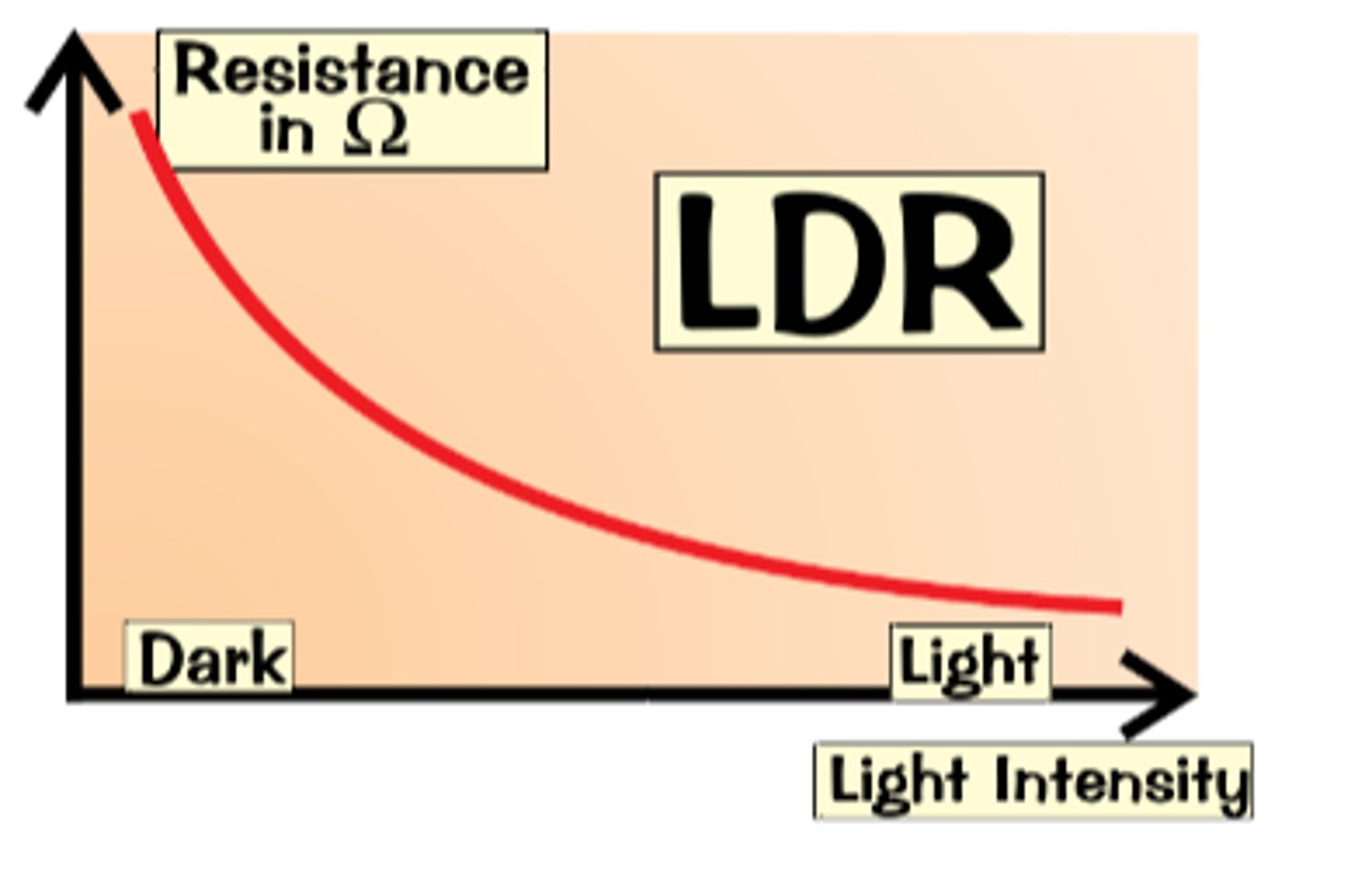
How does a LDR work ?
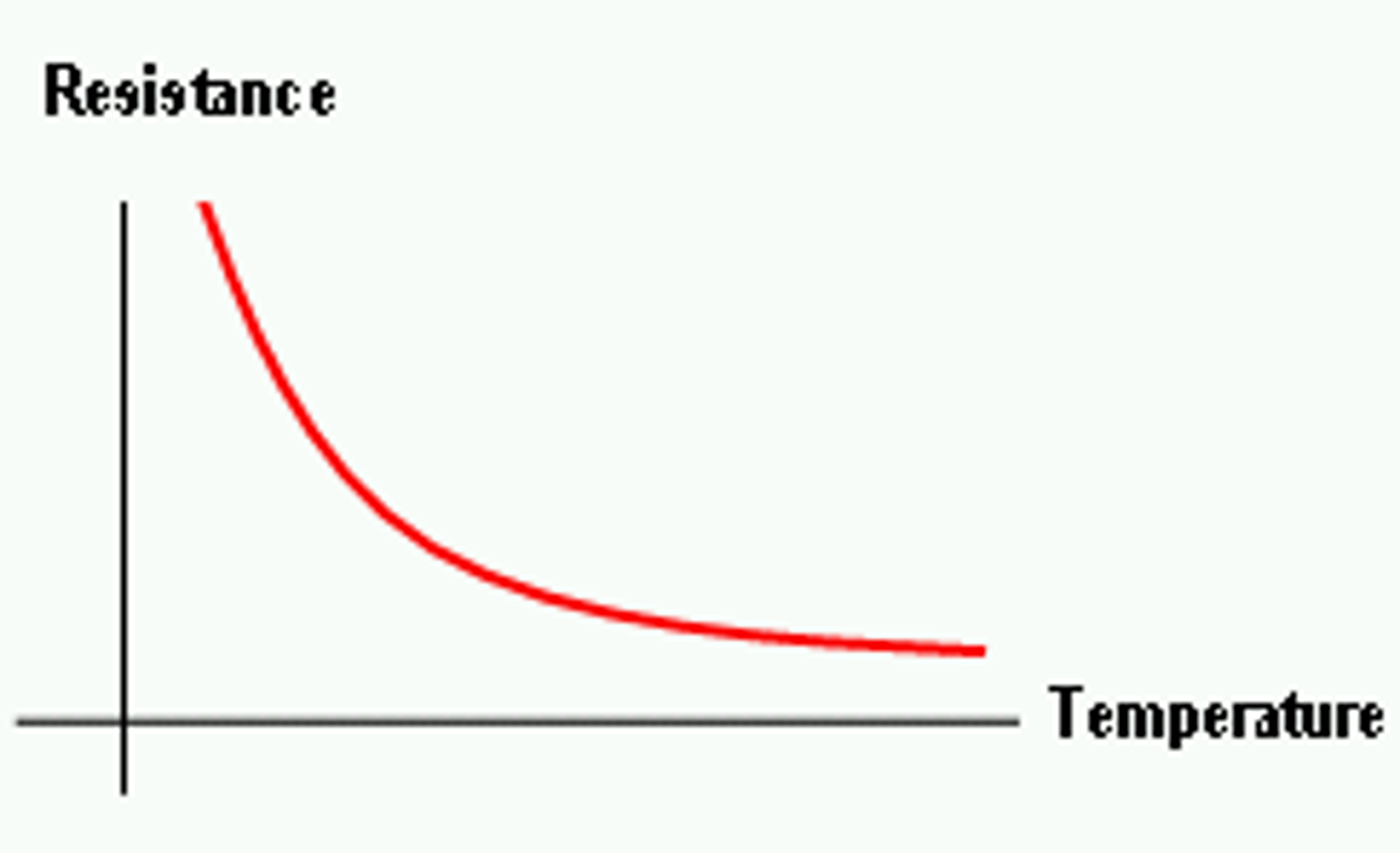
How does a thermistor work ?
State the formula for voltage , current and resistance
Voltage [V] = Current [A] x Resistance [Ohms]
V=I x R
Define the term current
current is the rate of flow of charge(/electrons)
State the formula for charge, current and time
Charge [C] = Current [A] x time [s]
Q = I x t
Define the term electric current
electric current in solid metallic conductors is the flow of negatively charged electrons
Why is current conserved at a junction in a circuit ?
this is because the current entering a junction = the current exiting a junction
Describe the voltage in a parallel circuit ?
The voltage across two components connected in parallel is the same
How do you calculate the current, voltage and resistance of two components connected in series ?
the current through both components is the same
To calculate voltage :
1. use V=IR to find voltage over one component
2. subtract voltage from power supply to find voltage over other component
To calculate resistance:
1. use V=IR to find voltage over one component
2. subtract voltage from power supply to find voltage over other component
3. Use R = V/I to find resistance of second component
Define the term voltage
voltage is energy transferred per unit charge passed
What is a volt
a volt is a measure of joule transferred per coulomb
State the relationship between energy transferred, charge and voltage
Energy transferred [J] = Charge [C] x Voltage [V]
E = Q x V
Which common materials are electrical insulators ?
a material that doesn't allow electricity to flow through easily
examples :
plastic
rubber
glass
wood
Which common materials are electrical conductors?
A conductor is a material that allows electricity to flow through it easily
Examples:
Graphite
Copper
Tin
Gold
Practical: Investigate how insulating materials can be charged by friction
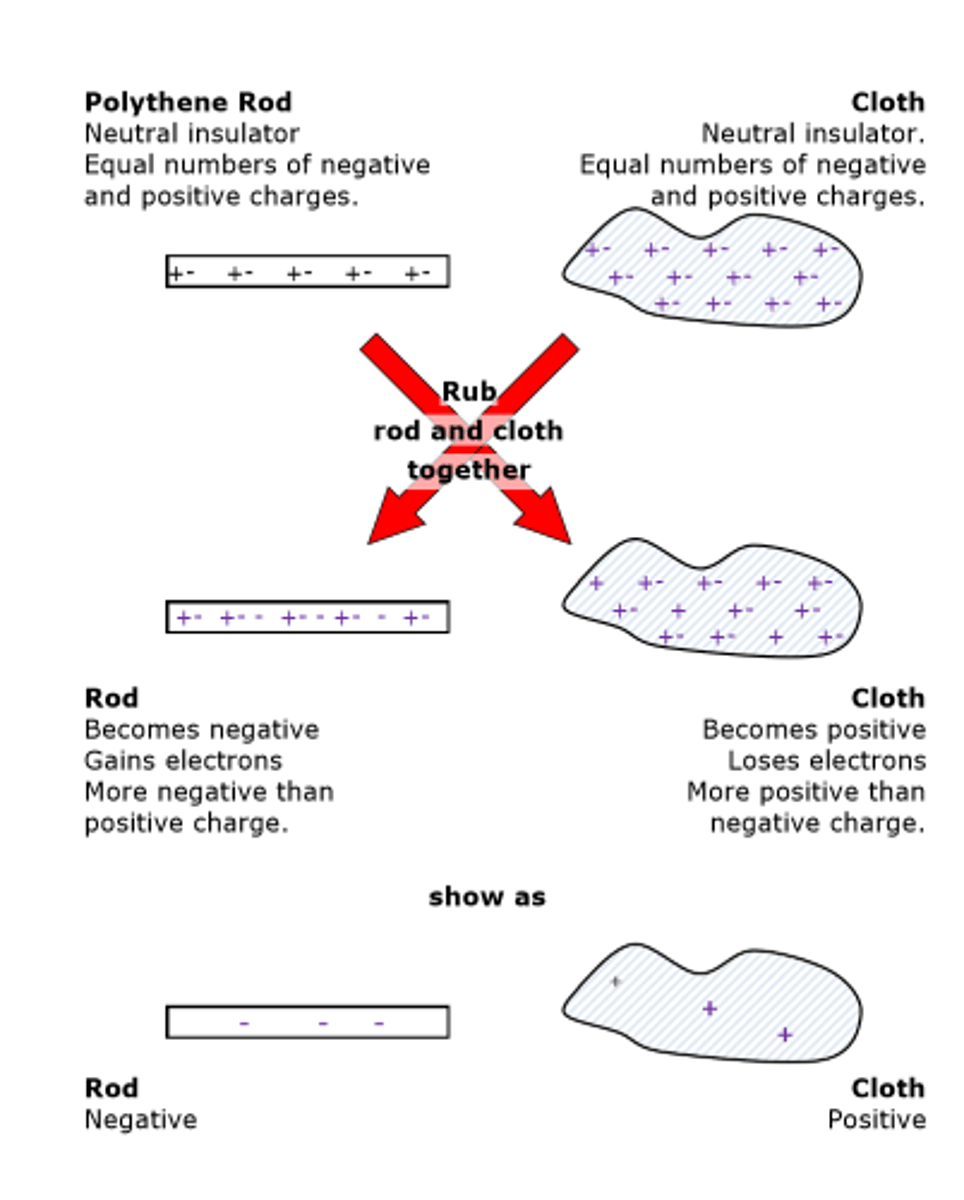
How are positive and negative electrostatic charges produced on materials ?
1. when you rub two neutral insulators together
2. the friction causes one of the materials to take electrons from the other
3. the material which loses electrons becomes positively charged
4. the material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged
State the law of electrostatics
Like charges repel and unlike charges attract
Explain an electrostatic phenomena?
Lightning:
1. rubbing of air and dust particles causes some negatively charged particles at the bottom of clouds
2. these negative charges repel electrons in the ground leaving a positive charge near the top of the ground
3. the difference in charge becomes too large and a potential difference which drives a current between the cloud and the ground is created
4. current heats the air till it begins to glow as a flash of lightning
5. (due to the quick heating ) the air also expands rapidly creating the sound of thunder
What are the dangers of electrostatic charges when fuelling aircrafts and tankers ?
1. Planes travel through air and clouds
2. friction between the plane, air and dust particles causes the plane to become charged with static electricity
3. when the plane lands the charge could escape to earth as a spark or flash
4. however if someone is trying to refuel the plane during this a spark could occur and cause an explosion
How can electrostatic charges be used in photocopiers ?

How can electrostatic charges be used in inkjet printers?

What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves ?
longitudinal waves vibrate parallel to the direction the wave travels
Transverse waves vibrate perpendicular to the direction the wave travels
Define the term amplitude
the maximum distance moved by a vibrating object from its equilibrium position
Define the term wavefront
an imaginary surface which shows the position of particles at different phases of the wave, it is made by overlapping lots of different waves
a wavefront is a line where all the vibrations are in phase and the same distance from the source
Define the term frequency
the number of waves passing a point per second
Define the term wavelength
the distance from one point on a wave to the corresponding point on the next wave
Define the term time period
the time needed to make one complete wave or vibration, measured in seconds
What is a wave?
(a disturbance) that transfers energy and information without transferring matter
State the relationship between speed, frequency and wavelength
Wave Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
v = f × λ
State the relationship between frequency and time period
Frequency = 1 / Time Period
f = 1/T
What is the doppler effect ?
the change in frequency caused by the relative movement of the source of the waves or the observer
( wavefronts squash or stretch, changing wavelength and frequency )
What are some similarities between all waves ?
all waves can be reflected and refracted
all waves transfer energy and information without transferring matter
What spectrum is light in ?
Electromagnetic Spectrum
What properties are shared by EM waves?
all EM waves travel at the same speed in free space
State the order of the EM spectrum in terms of decreasing wavelength ?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
State the order of the EM spectrum in terms of increasing frequency ?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
What are the uses of radio waves?
broadcasting and communications
What are the uses of microwaves?
cooking and satellite transmissions
What are the uses of infrared waves?
heaters and night-vision equipment
What are the uses of visible light ?
optical fibres and photography
What are the uses of ultraviolet ?
fluorescent lamps
What are the uses of x-rays ?
Observing the internal structure of objects and materials and medical applications (medical imaging and treatments)
What are the uses of gamma rays?
Sterilising food and medical equipment
What are the dangers of microwaves and how can we prevent this?
internal heating of body tissue
Microwave ovens have a metal grill over the door which reflects back microwaves into the oven to protect users
What are the dangers of infrared waves and how can we prevent this?
skin burns
take care when using sources of infrared waves, e.g. move heater away from body
What are the dangers of ultraviolet waves and how can we prevent this?
damage to surface cells ( sunburn) blindness
wear sun-cream, stay in shade
wear UV absorbing sunglasses
don't use tanning beds for too long
What are the dangers of gamma rays and how can we prevent this?
can cause cancer and cell mutations
wear photographic film badges , if they turn dark when developed a person has too much radiation and must stop working/ being around them
What are the properties of light waves?
transverse waves that can be reflected and refracted
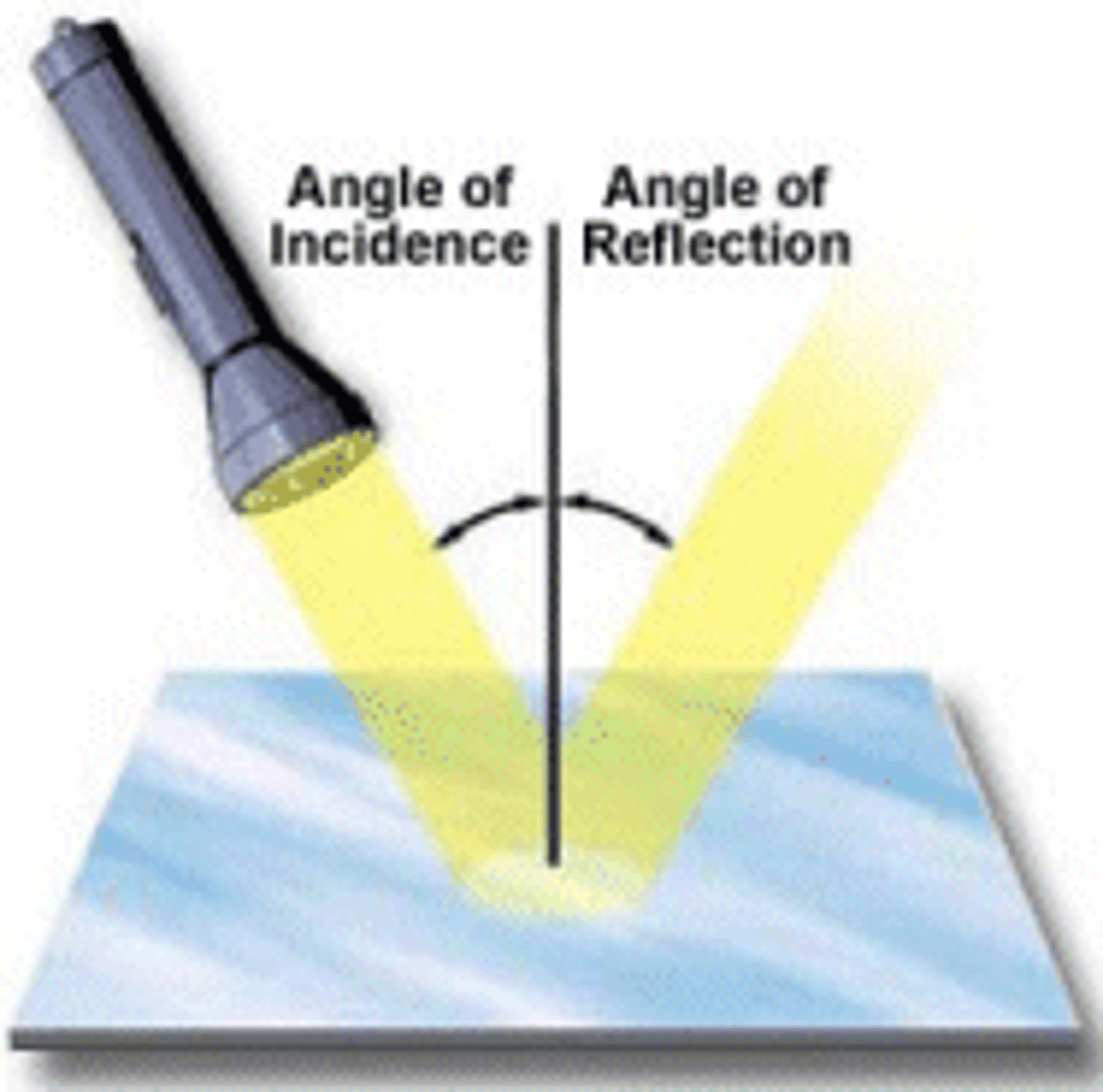
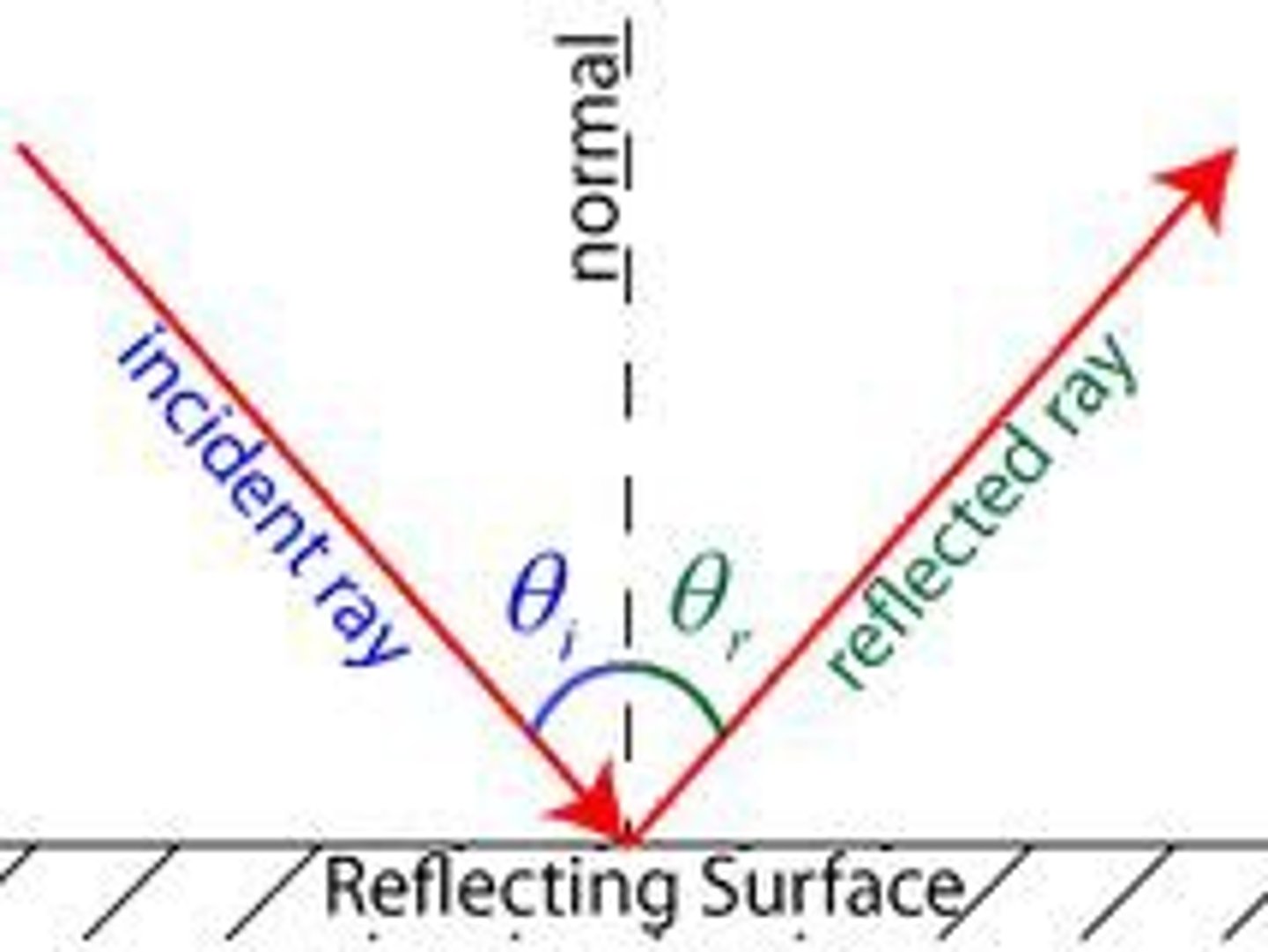
How do you use the law of reflection ?
the law of reflection states that the angle of incidence = the angle of reflection
so when given one of these angles you can find the other
How do you draw ray diagrams of reflection and refraction ?
you draw arrows in the direction which light travels
whenever light changes direction/ goes through a material draw a normal at 90 degrees
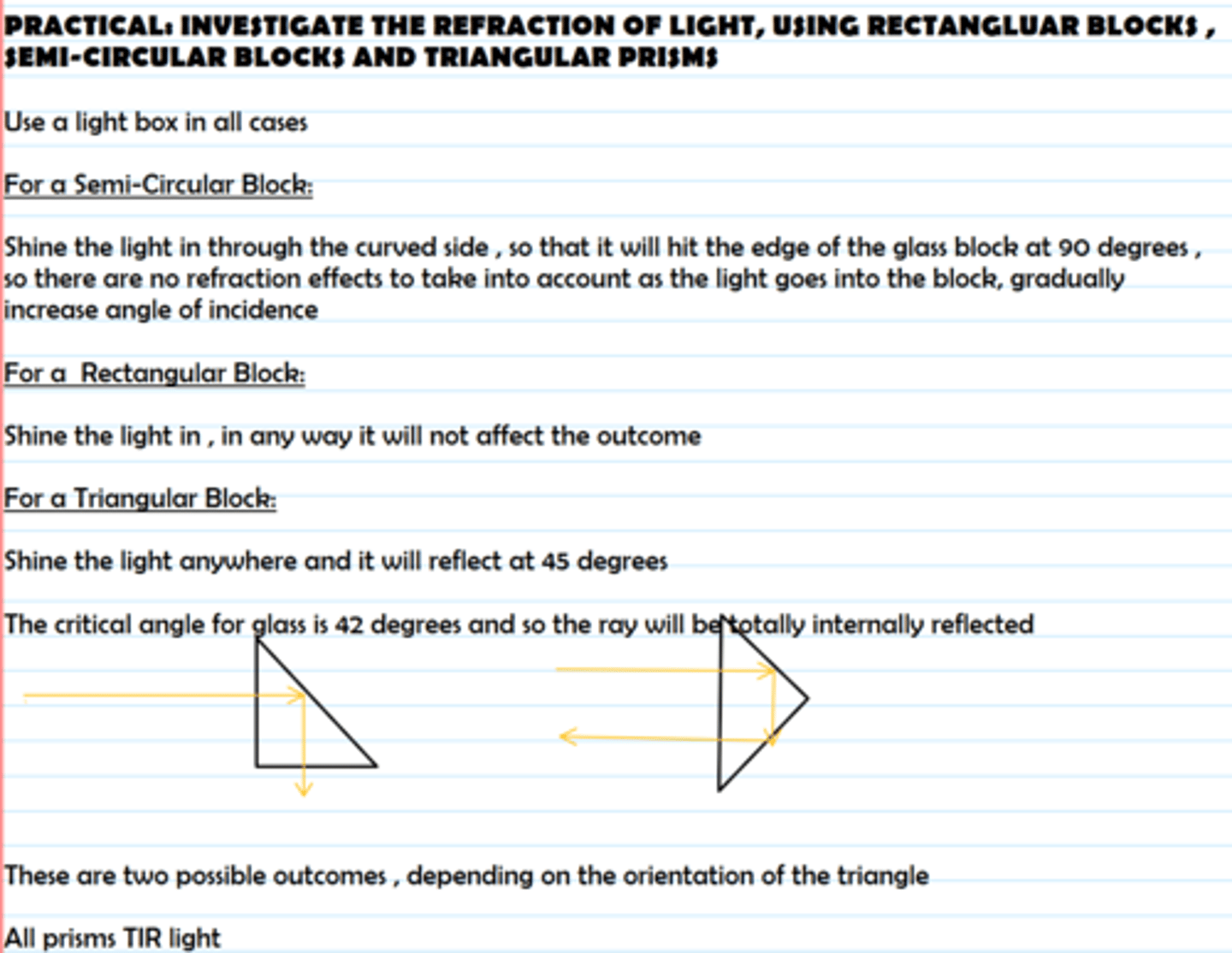
Practical: investigate the refraction of light, using rectangular blocks, semi-circular blocks and triangular prisms
state the relationship between , refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction
refractive index = (sin angle of incidence ) / (sin angle of refraction)
Practical: investigate the refractive index of glass, using a glass block

How can total internal reflection be used to transmit information in optical fibres and prisms ?
thin glass fibres are bent so that the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
so when light his the fibre TIR will occur and no light will be refracted until it reaches the end of the optical fibre