genetics
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Gene
Short segment of DNA that controls expression of trait
Hormones
Proteins critical for transportation
What makes organism uniques
Order of nitrogen base in DNA
Double helix
Shape of DNA
Chromosomes
Coiled DNA inside nucleus carries genetic information for specific set of traits in genes
DNA stands for
déoxyribonucléic acid
Somatic cells
Body cells have 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs, diploid have two replicates, made by mitosis
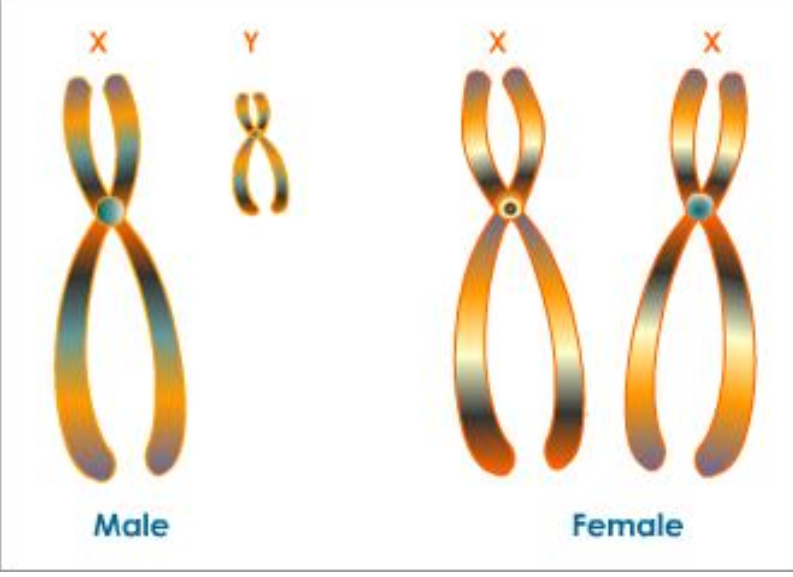
X and Y chromosomes
Somatic cells 23rd pair but can have different number of x or y détermine sex
Gamete
Sex cells only found in ovaries or testes, 23 chromosomes haploid means only single copy, meiosis,
Interphase stages
Growth 1 phase, Synthesis phase, growth 2 phase
Growth 1 phase
Cell makes new molecules + grows larger, duration of growth varies depending on type + health of cell
Synthesis stage
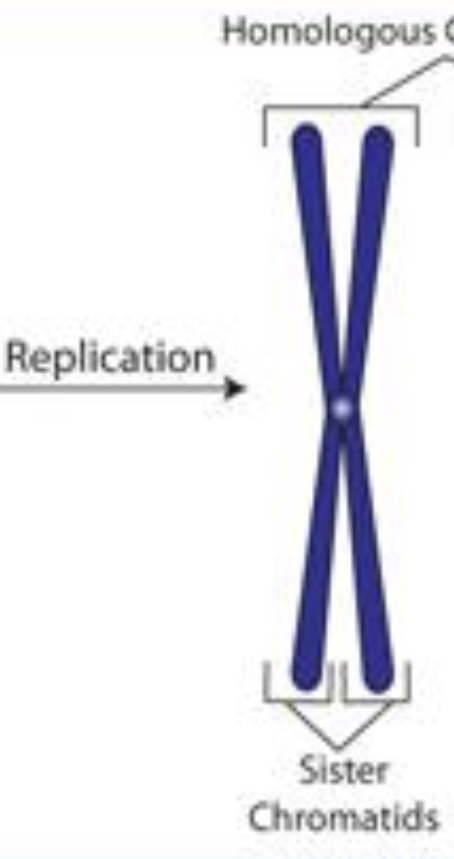
Chromatin (uncoiled chromosomes) are duplicated form sister chromatids held together by centromere
Growth 2 phase
Synthesize more molecules grows larger
Contact inhibition
‘Normal’ cells stop dividing when coming into contact with like cells
Chemotherapy
Halt cell division
Cancer drugs
Damage RNA or DNA induce cell suicide (apoptosis)
Cell-cycle specific drugs
Kill when dying
Cell-cycle non-specific drugs
Kill cancer cells resting
Normal cells affected by chemotherapy
Blood cells, mouth cells, stomach + bowel, hair
Side effects of chemotherapy
low blood counts, mouth sores, nausea, diarrhea, hair loss
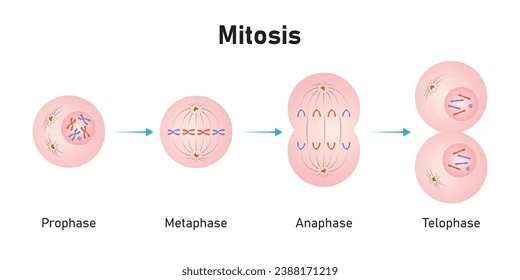
Mitosis
P: sister chromatids are visible M: line up A: pulled apart T: new nucleus
DNA
molecules in cell has instructions make other cell parts
Who made double helix model and when and what was their first mistake and how did they fix it
James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 thought paired like with like (A with A) but then didnt result in uniform width of DNA molecule, found needed specific pairing
What does DNA look like
Anti parallel strands that twist around each other
What unit is DNA made of
Nucleotides, basic unit of nucleic acid
What are nucleotides made of
Sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate group, one of four nitrogen bases
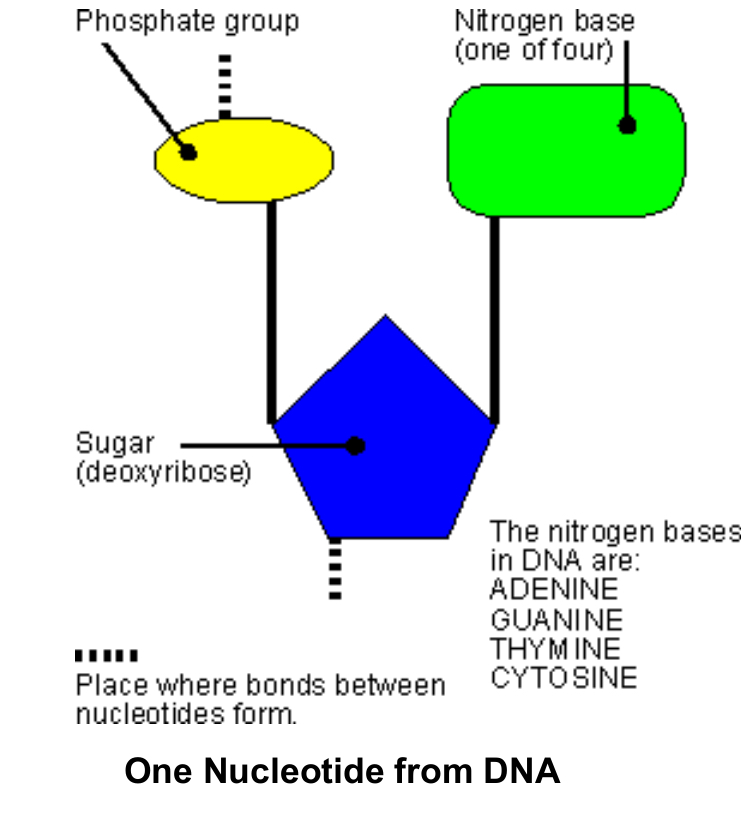
4 nitrogen bases
Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T)
Nitrogen base pairs
Apples in the tree (A to T), Car in the garage (C to G)
What are the nitrogenous base pairs held together by
Hydrogen bonds, AT have two, CG have three
Rosalind Franklin DNA discovery
X-ray crystallography found two antiparallel sugar phosphate backbones paired in DNA’s molecule interior
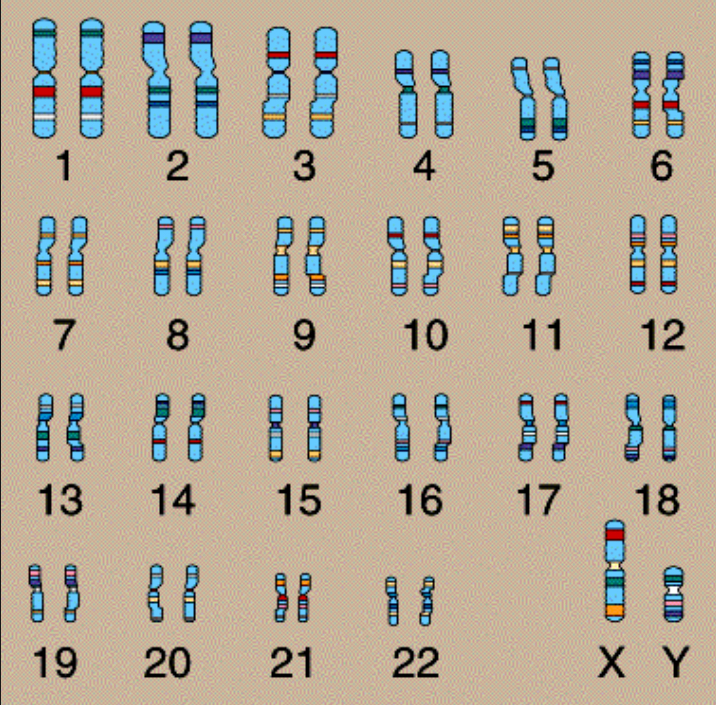
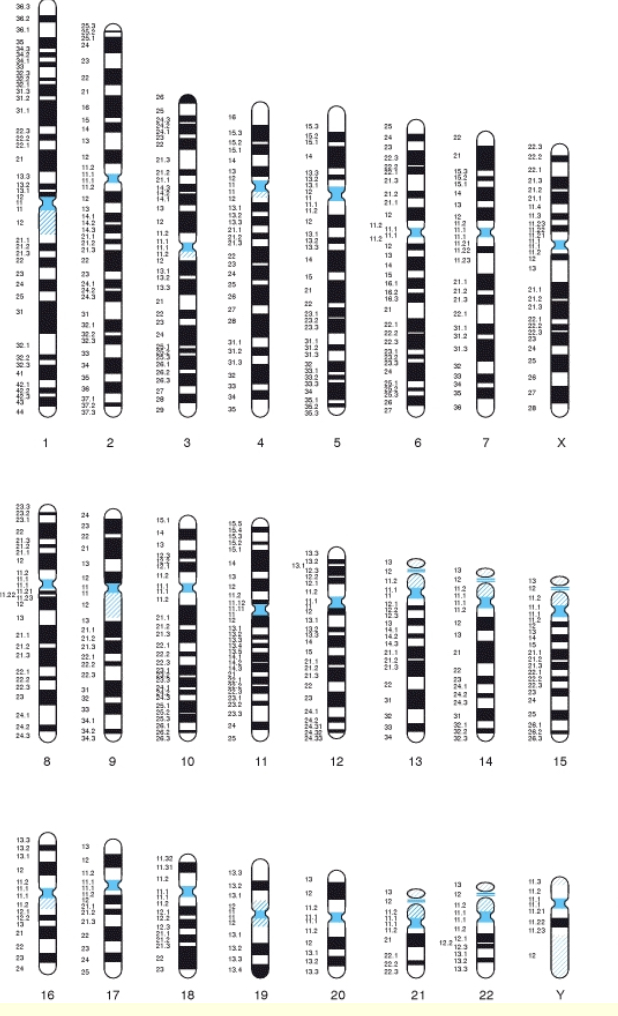
Karyotype and use
Taken picture of chromosomes used to diagnose disorders
Allele
Variations on gene
Homologous chromosomes
Identical chromosomes in length, centromere location and banding pattern, one from each parent, alleles found on same gene of these chromosomes
How many alleles for hair color gene
4
double single blue stick from each parent with brown background image from slides
diploid and unreplicated (single stranded), autosomes and sex chromosomes
Beginning interphase somatic cells
When are sex chromosomes homologous
Only in females, x chromosome
Autosomes
First 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Transparent background realistic ish chromosomes grainy pinched in middle
Double replicated chromosomes, look like x with sister chromatid connected by centromere, somatic cells visible in prophase also starting cells make gametes in ovaries + testes
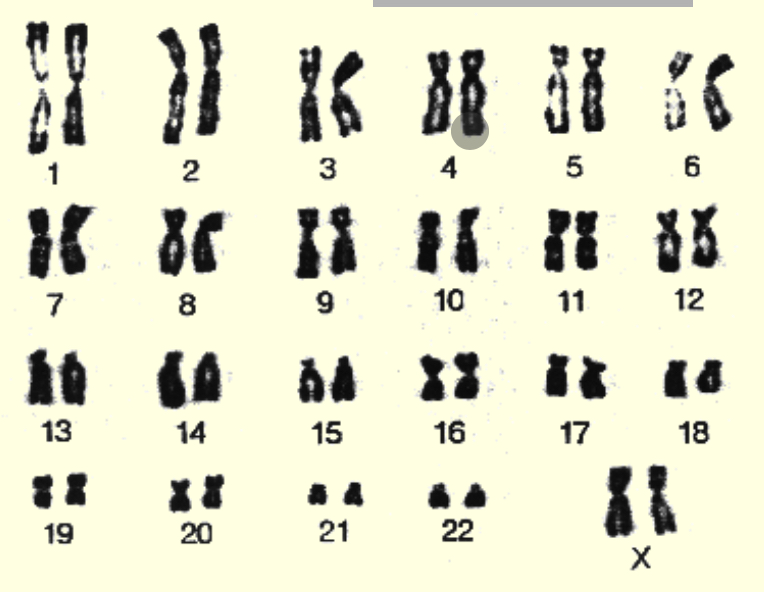
White background single sticks from which karyotype is it with black lines in single sticks
Gamete haploid and unreplicated, 23 chromosomes, after fertilization zygote get diploid unreplicated
What is n
Indicate # chromosome copies in species ie humans n = 23
How are chromosomes arranged in karyotype
Largest to smallest by size
gametogenesis
meiosis
What is the starting and ending cell type in meiosis?
Starts with 1 diploid cell (2n) from either ovaries or testes and ends with 4 haploid daughter cells (n)
Reduction division
Homologous chromosomes separated make haploid cells
What happens in Meiosis I
Nuclear membrane dissolves, centrioles, P1: chromosome pairs w/ homologous form tetrad, crossing over happens, M1: still forming tetrad homologous pair chromosome line up tetrad double line A1: pull pair apart reduction division T: nuclear membranes MIGHT cytoplasm divides
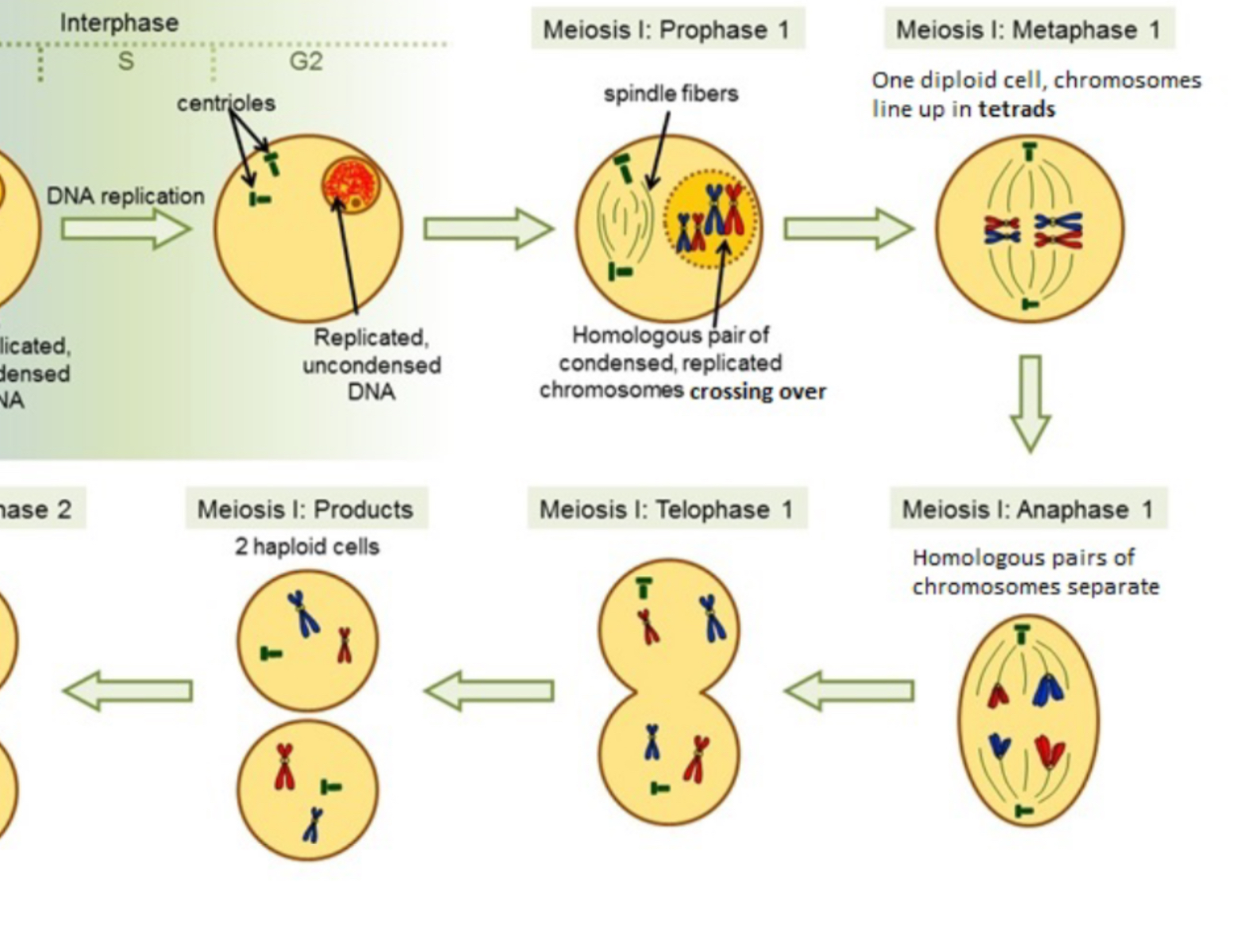
Meiosis II
Mitosis but two haploid cells are coordinated nuclear membrane reforms
Tetrad
homologous chromosomes pair up
Crossing over
the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I of meiosis like switching shoes
Is meiosis a cycle
No
Spermatogenesis
Meiosis form 4 sperm cells
Oogenesis
Meiosis 1 egg cell 3 polar bodies contribute cytoplasm make one large egg cell
which one have haploid ending cell which one diploid in mitosis vs meiosis
Haploid meiosis cells, diploid mitosis
what occurs in zygotes and most body cells
Mitosis
Part of cell division that produces growth
Mitosis
Promotes variation among offspring
Meiosis
Ensures same number of chromosomes between generations
Mitosis
Sister chromatid
two identical newly replicated chromosomes joined by centromere
Trisonomy
person has three copies of chromosomes (weird)
genetic variation methods
Independent Assortment, Crossing Over, Non-disjunction Chromosomal Mutations, Structural Chromosomal Mutations, Nucleotide Point Mutations
Law of Independent Assortment
when different traits don’t depend on each other to show up
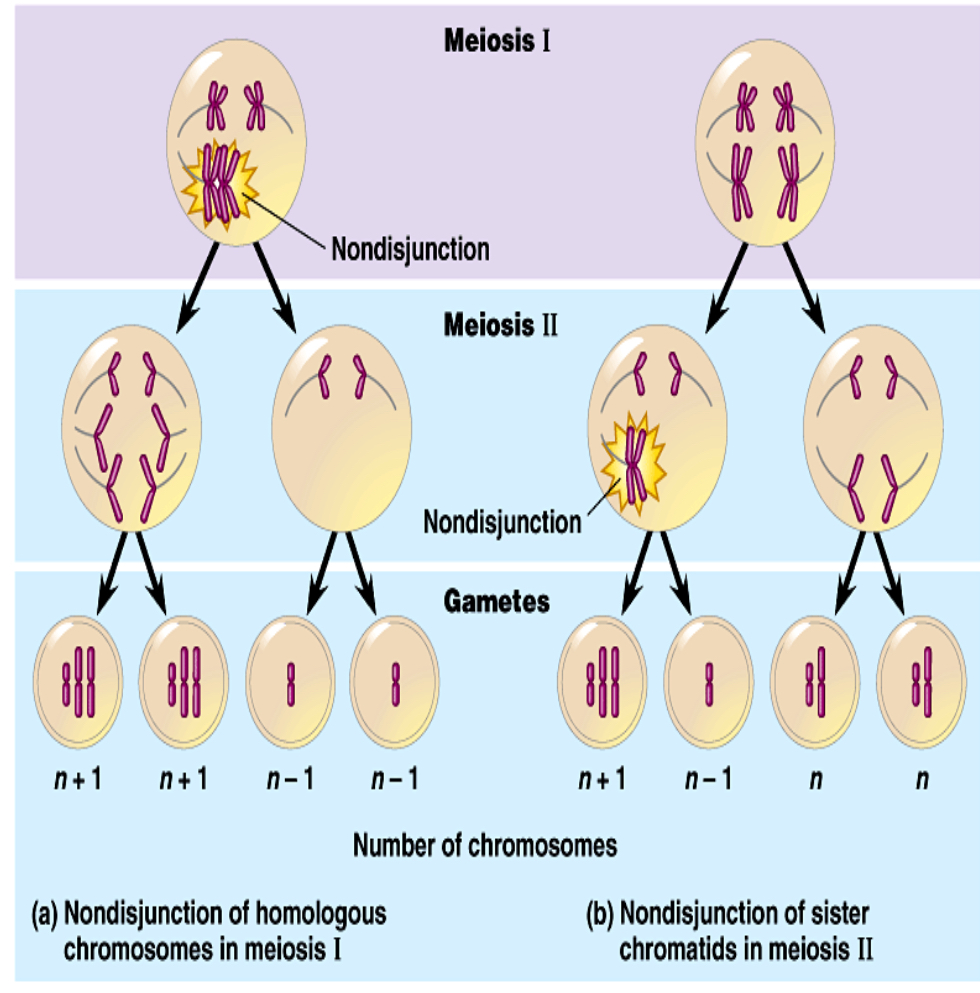
Non-disjunction chromosomal mutation
Sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes refuse to seperate resulting in n + 1 or n - 1
Polyploidy
Extra sets of chromosomes
Structural chromosomal mutation, four main types
Mutation in chromosome structure, deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation
Nucleotide point mutations
Mistake in DNA replication cause addition, substituition or deletion of nitrogen base pair
Purebred
Homozygous dominant
F1
First fillial generation (kids)
genotype vs phenotype
genetic makeup vs appearance
test cross
Determine genotype of individual showing dominant trait by making them have babies with a homozygous recessive
Incomplete dominance
When dominant allele doesn’t commit and red and white flower make pink flower, but also two alleles are equally dominant
Codominance
Both alleles dominant shows up at the same time (red and white cow)
Why focus on x linked genes
Because x chromosome bigger than y has more alleles
Mendel’s laws of inheritance
Law of segregation, law of independent assortment, genes located on chromosomes
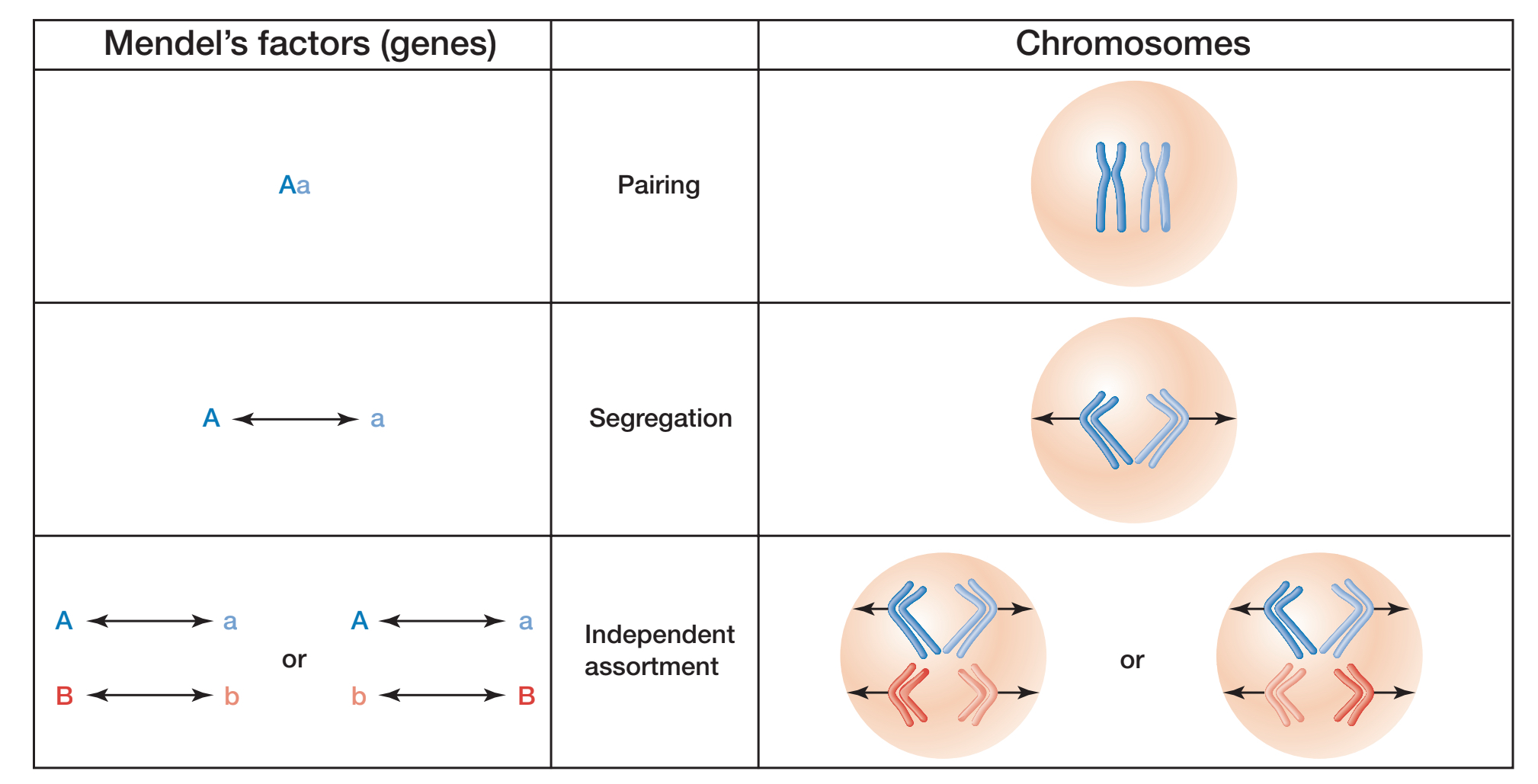
Law of segregation
Ability of chromosomes in meiosis to be pulled apart randomly
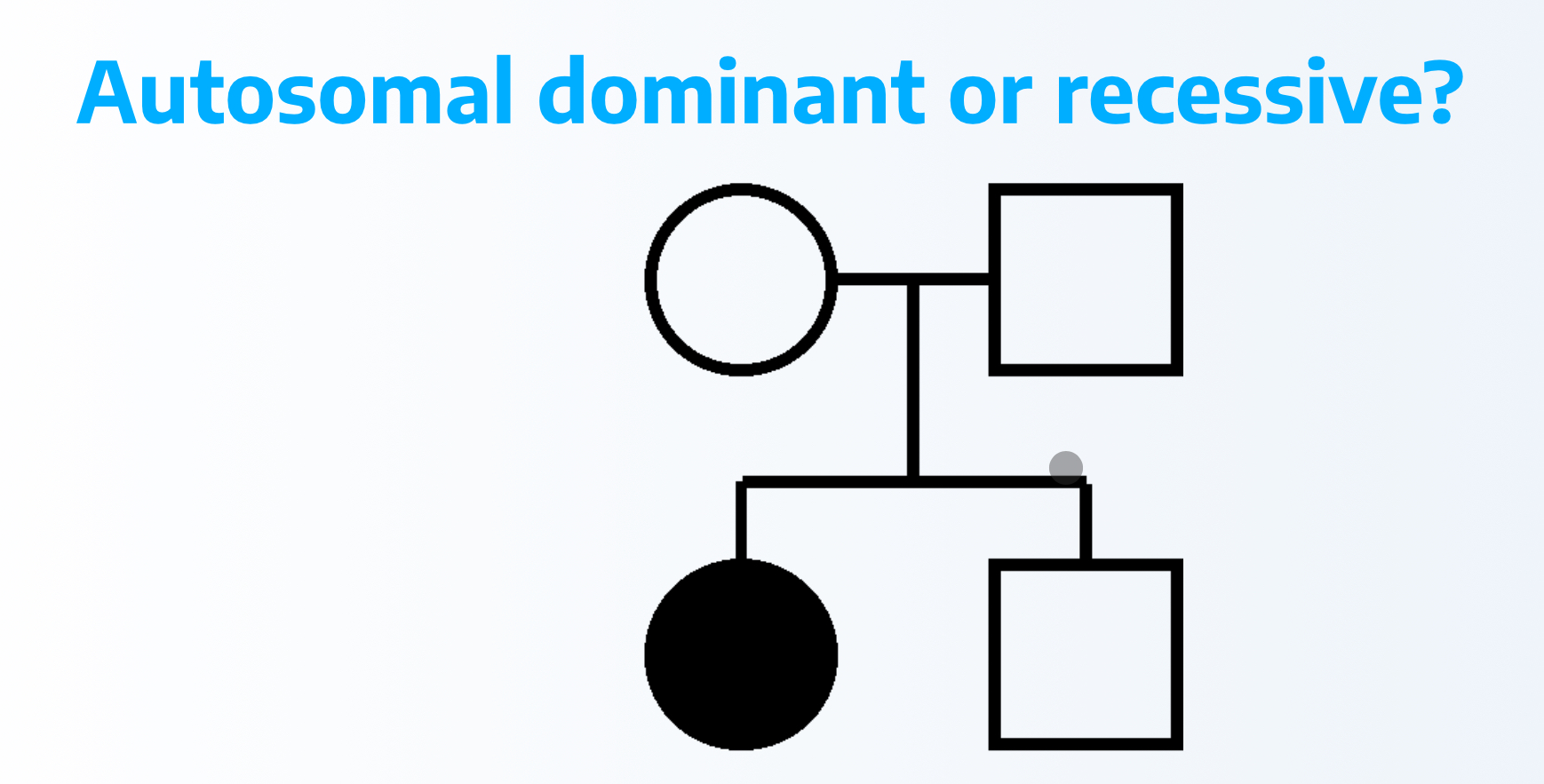
Must be autosomal recessive because two unaffected parents have affected child
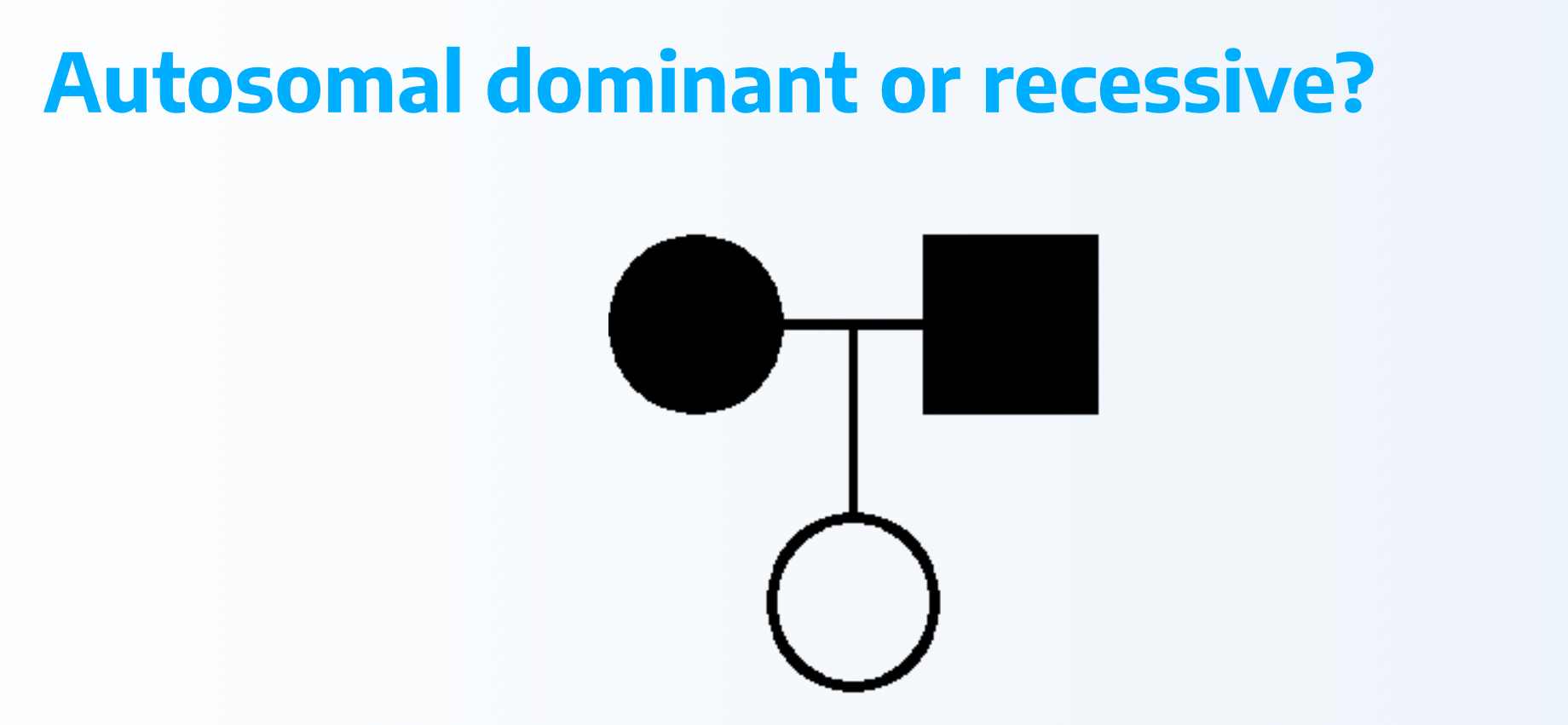
Dominant because two affected have unaffected
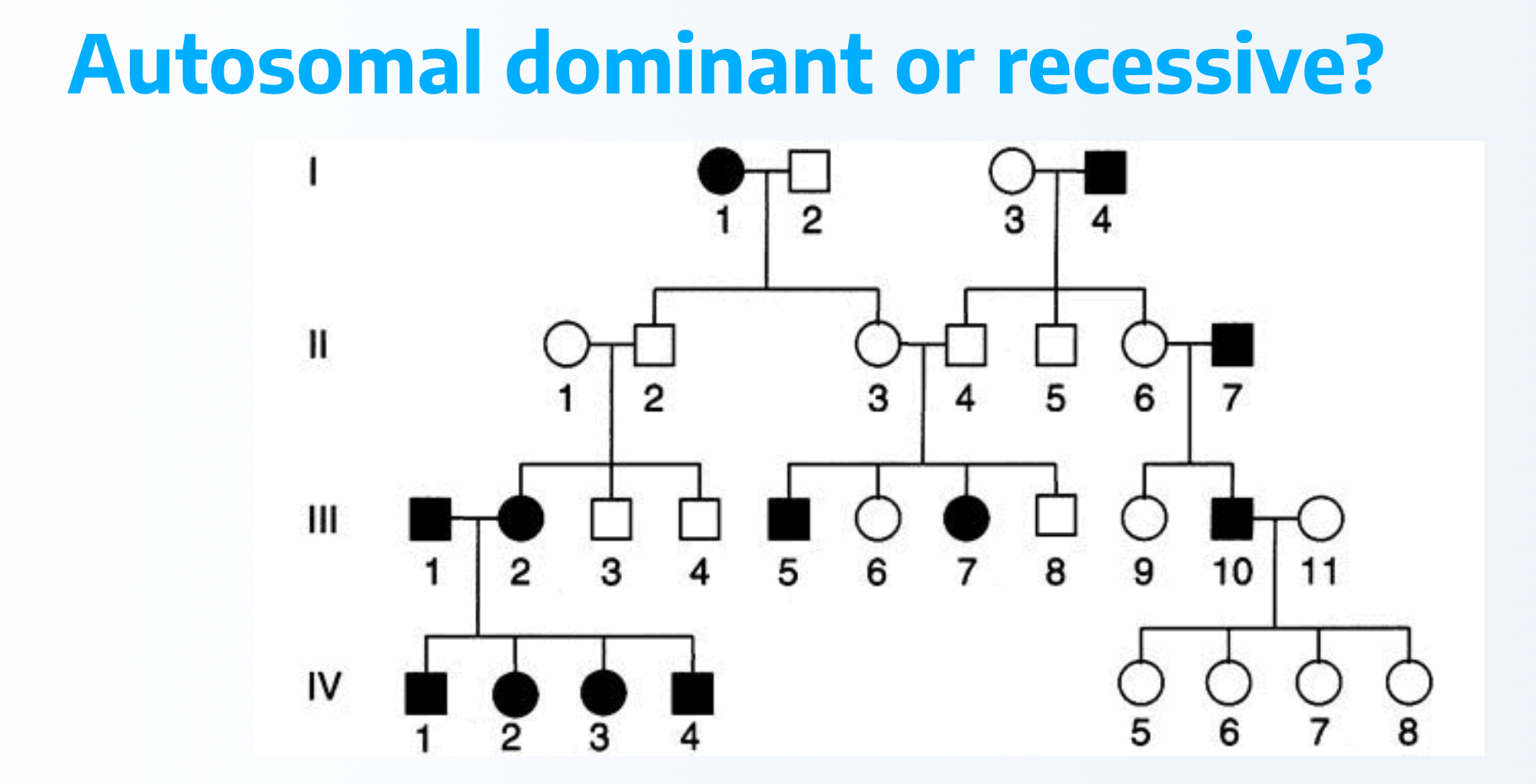
recessive because two unaffected have affected kid then all kids get it
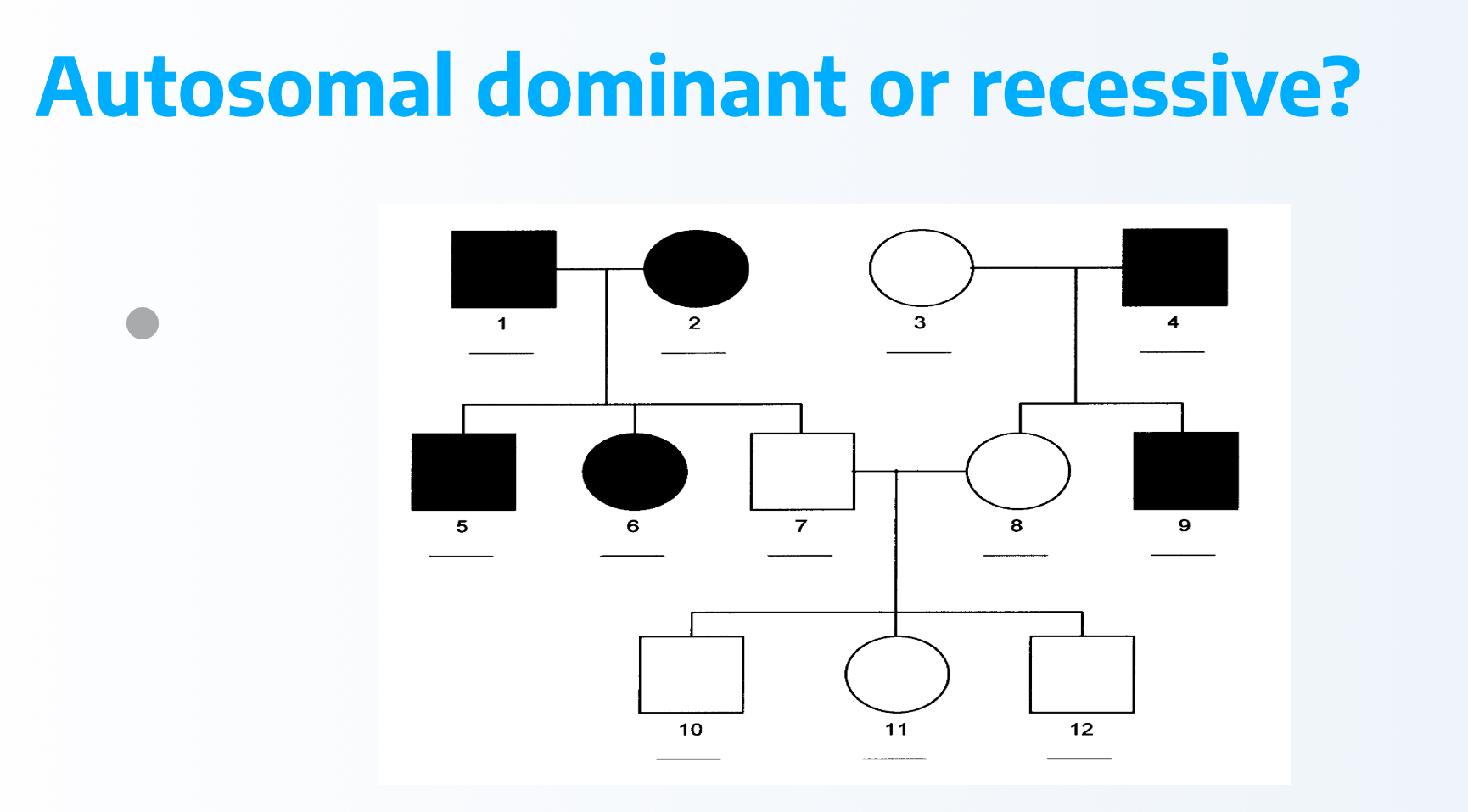
dominant because two affected parents have unaffected child
example of trisonomy
Down syndrome
synthesis of new DNA
another way to just say DNA replication
precipitate
Two chemicals mix together to form a solid
translocation
when one homologous chromosome pair’s chromosome does crossing over with another homologous chromosome pair (ex. Chromosome 1 pair crossing over with chromosome 15 pair)
difference between point mutations and missense mutations
point have no effect on protein making but missense make non-working protein
what number start out in interphase end in mitosis and meiosis
start 4n end mitosis 2n and meiosis n
Replication
Occurs before mitosis, meisosis, forms sister chromatids, requires synthesis of new DNA, does not make haploid diploid
Haploid
One pair of chromosome (one person)
Diploid
Two pairs of chromosomes (2n) (one mom one dad)