APUSH Unit 1.1-1.2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms

First Americans
Earliest inhabitants of North America, arriving via the Bering Strait at a time where temperatures were colder, creating an ice bridge. They established diverse cultures and societies long before the Europeans.
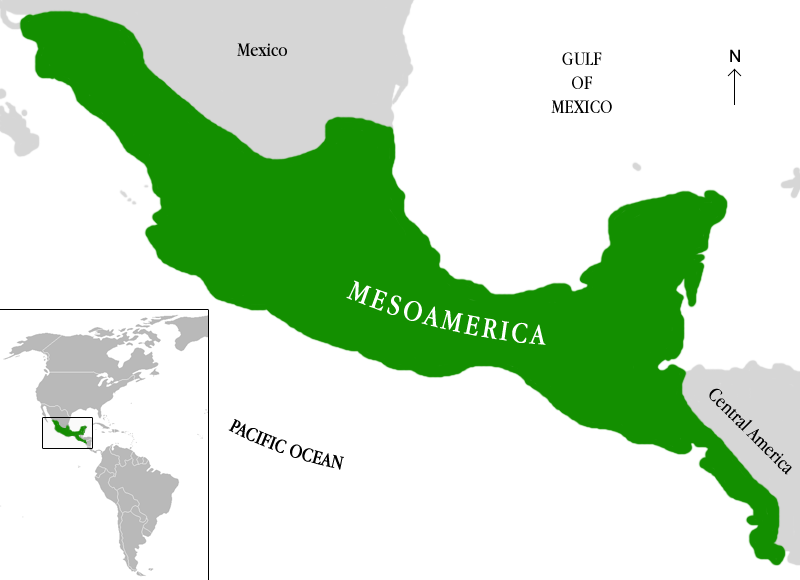
Meso-American Tribes
(Aztecs, Incas, Mayas) Advanced civilizations in Central and South America known for their intricate societies, pyramids, and significant contributions to agriculture and mathematics before European contact.
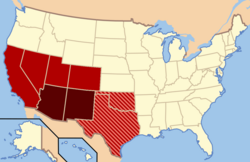
Southwest Natives
(Pueblos, Navajo, Hopi) Used irrigation canals to grow crops (maize & beans) and they were known for cliff dwellings and pottery.
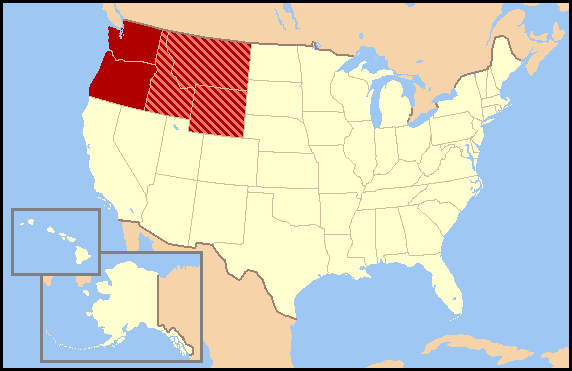
Pacific Northwest
(Chinook) Known for hunting, fishing, and foraging. They built canoes, plank houses, and totem poles. They followed a matrilineal (relationships traced through mother’s history) kinship system.

Northeast Indians (aka Eastern Woodlands)
(Iroquois, Algonquin) Small, organized groups ruled by a chief. Known for their hunting and farming practices, they formed political alliances such as the Iroquois Confederacy.

Plains Indians
(Lakota Sioux) Known for their nomadic lifestyle, they hunted buffalo for food and clothing. They also traveled in teepees.
Negative Effects of European Conquest on America
Natives were eradicated by disease like smallpox, some were pressured to adapt to European settlers, and they were also used for slavery.
Positive Effects of European Conquest for the Natives
Introduction of new crops (coffee, beans, bananas) and animals such as horses.
Similarities between Native Americans & European Settlers
Strong sense of spirituality, divided labor by gender, depended on agriculture, and lived in village communities.
Columbian Exchange (1500s)
An exchange of ideas, crops, plants, animals, people, and disease.
Natives were decimated by smallpox; livestock (horses) and guns changed warfare.
Europeans gained new crops (potatoes & maize) along with increase of capitalism and decline of feudalism
Motivations of European Exploration
“God, Glory, and Gold!”
Europeans wanted to spread Christianity, elevate their status, and gain wealth (primarily motivated by mercantilism).
Portugal, Spain, England, and the Netherlands
Improvements on Technology for Exploration
Compasses, improved map-making, ship building, and gunpowder.
Encomienda System
A royal grant towards Spanish settlers which granted the right to extract labor from the natives in exchange for the settler’s protection and religious conversion.
Spanish Colonial Societies
Converted many natives to Christianity; most settlers were men.
Mestizo
Mixed Spanish and Native ancestry.
Mulattos
Mixed Spanish and African ancestry.
Bartolome de Las Casas
A Spanish priest that advocated for better treatment of the Natives.
Juan de Sepulveda
Argued that harsh treatment of the Natives was justified.
Pueblo’s Revolt (1860)
Pueblo Indians successfully rid of the Spanish for 10 years. Eventually, the Spanish regained control, but accommodated to the Native’s needs.
First Permanent English Settlement
The colony of Jamestown (1607) under the joint-stock company Virginia Company.
Virginia House of Burgesses
First representative government in the North American colonies
Pilgrims
Puritans who sought religious freedom and wanted a separation of church and state. They arrived in 1620 on the Mayflower.
Massachusetts Bay
“City upon a hill”, focused on agriculture and commerce.
John Winthrop was the first governor of the colony.
Roanoke Colony
Earliest English attempt at colonization in 1587. John Smith found the place to be mysteriously abandoned with the words “CROATOAN” carved on a tree.
Rhode Island
Founded by Roger Williams and Anne Hutchison after they were banned from Massachusetts Bay. The colony became a safe haven for religious freedom.
Dissidents
Those that weren’t “like-minded” believers.
Middle Colonies (Breadbasket Colonies)
(New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware) Most diverse religiously, ethnically, and demographically of the English colonies. They largely produced grain such as wheat.
Pennsylvania
A liberal colony, also known as “Penn’s Holy Experiment”, it was founded by William Penn as a refuge for Quakers and committed to religious tolerance.
Chesapeake / Southern Colonies
Virginia and Maryland; focused on tobacco and initially used indentured servants (prior to Bacon’s Rebellion).
Carolinas and Georgia
Focused on rice and sugar; slaves made up most of the population. North Carolina had tobacco farms, while Georgia was used as a buffer colony against outside threats.
Navigation Acts
Forced colonies to trade only with England, promoting mercantilism and encouraged colonists to smuggle goods with other nations.
Effects of Navigation Acts
New England prospered due to large scale ship building businesses. Chesapeake colonies forced to receive lower prices for tobacco and other crops which hurt them financially.
Dominion of New England
Established by King James II. He sought to control the colonies by combining them into one. He levied taxes and revoked town halls, asserting control over New England.
Pequot War (1630s)
New England colonists wipe out the Pequot tribe.
King Phillip’s / Metacom’s War (1675-76)
Leader of the Wampanoags defeated by the colonists, ended major Native resistance to the New England colonists.
Bacon’s Rebellion (1676)
Small farmers were frustrated by a lack of land and political power along with attacks from the Natives. Nathaniel Bacon leads a rebellion against the Indians and burned Jamestown. This led to the transition towards African slave labor.