APBio Unit 6 Gene Expression and Regulation
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
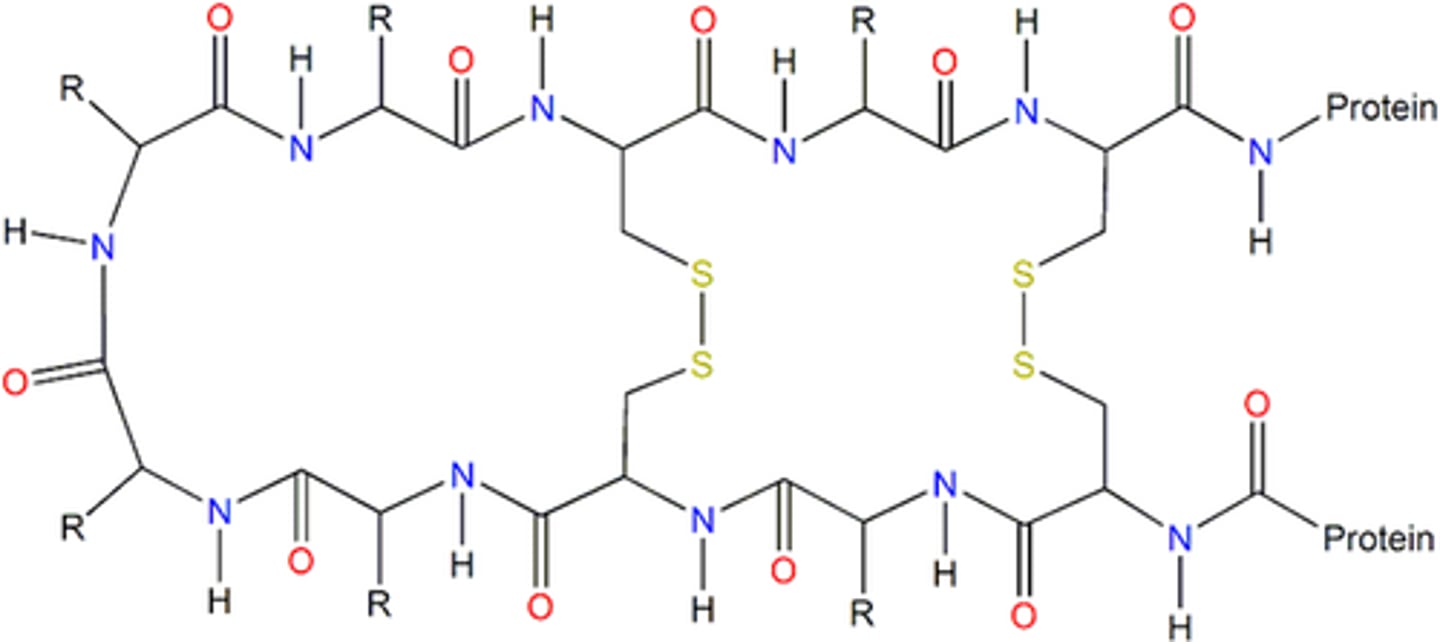
disulphide bridges
Reinforce tertiary structure.
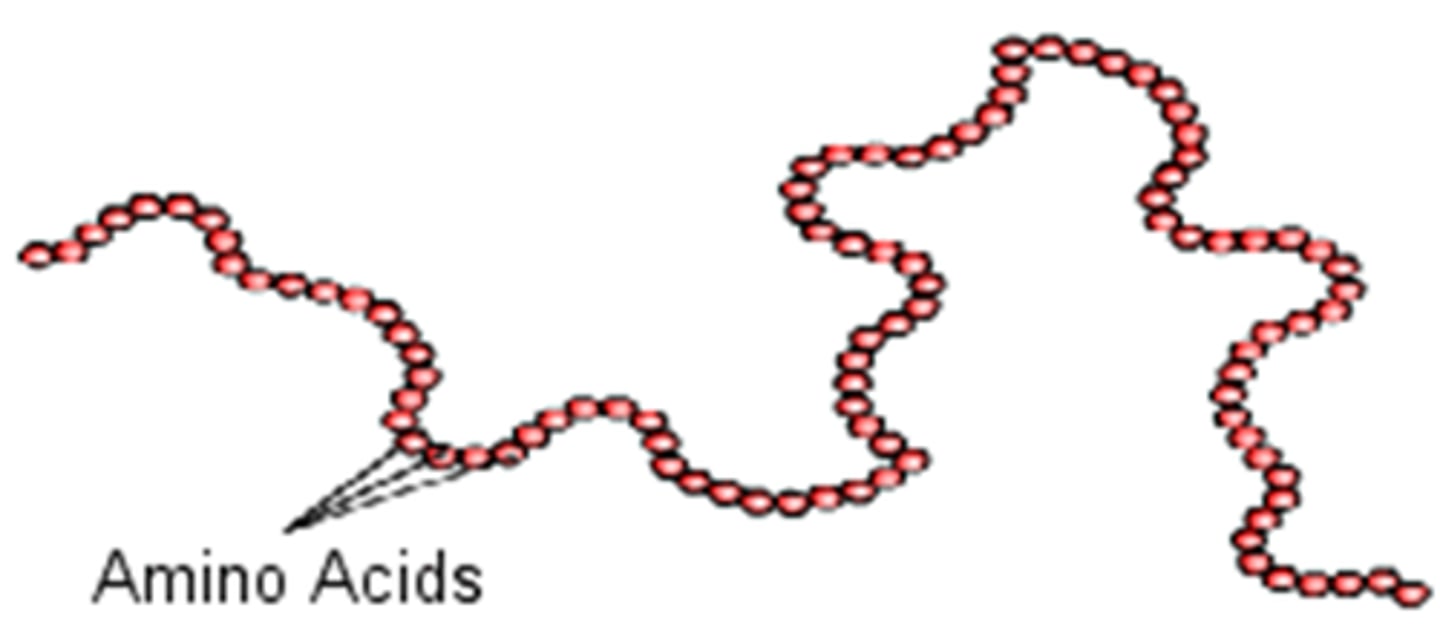
primary structure
Chain of amino acids.

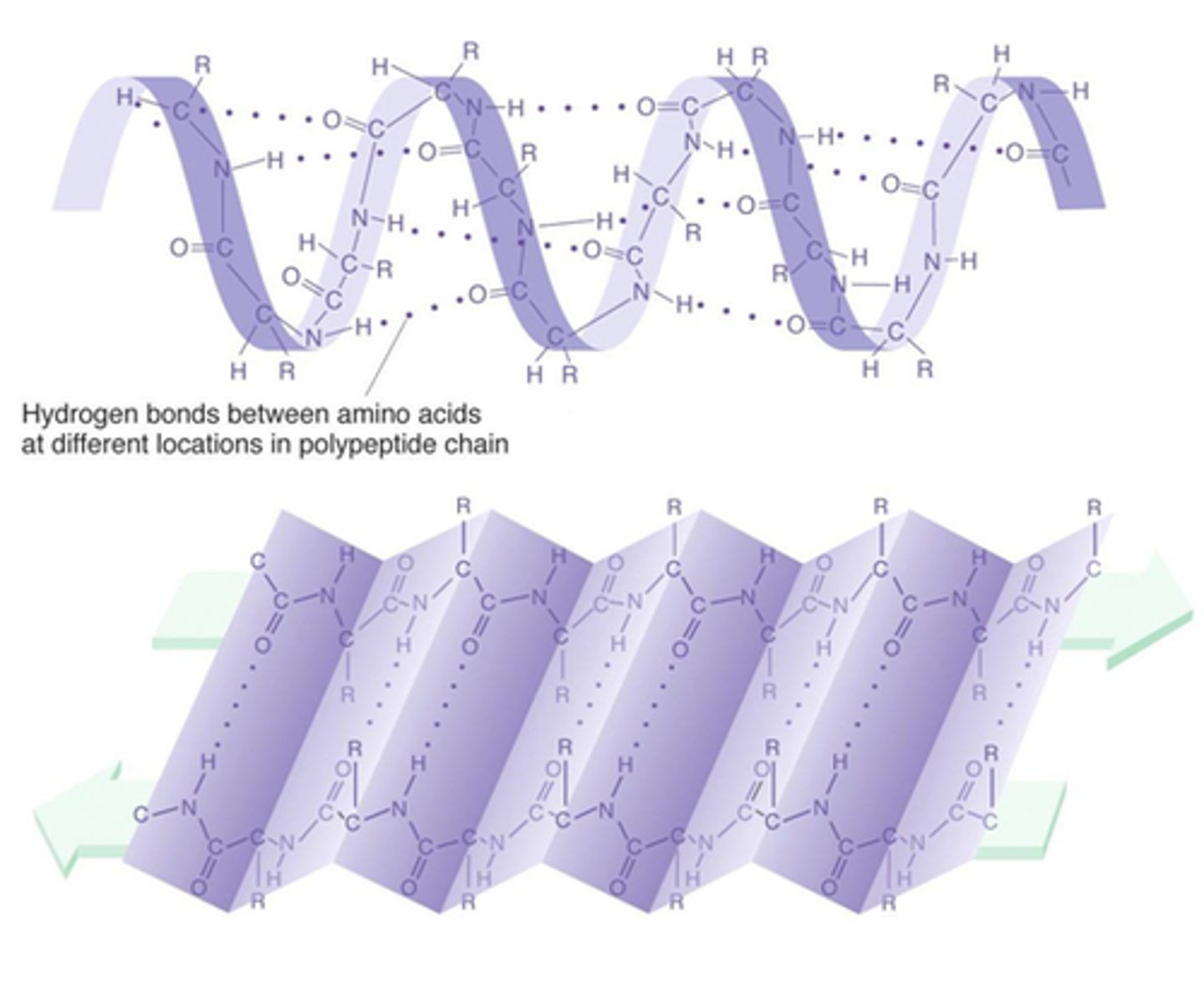
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
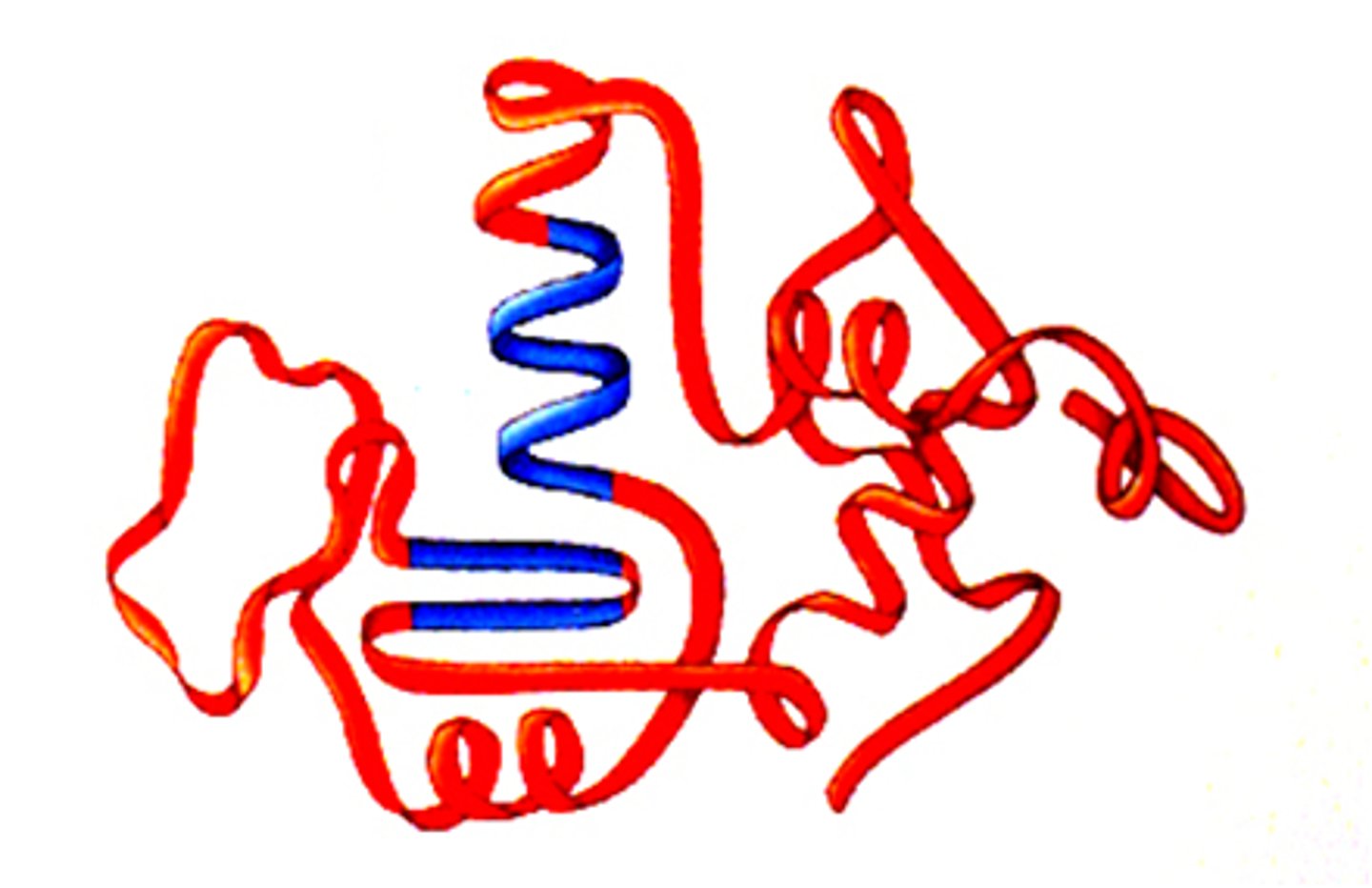
tertiary structure
Results from interactions between side chains.
quaternary structure
Results from two or more polypeptide subunits.
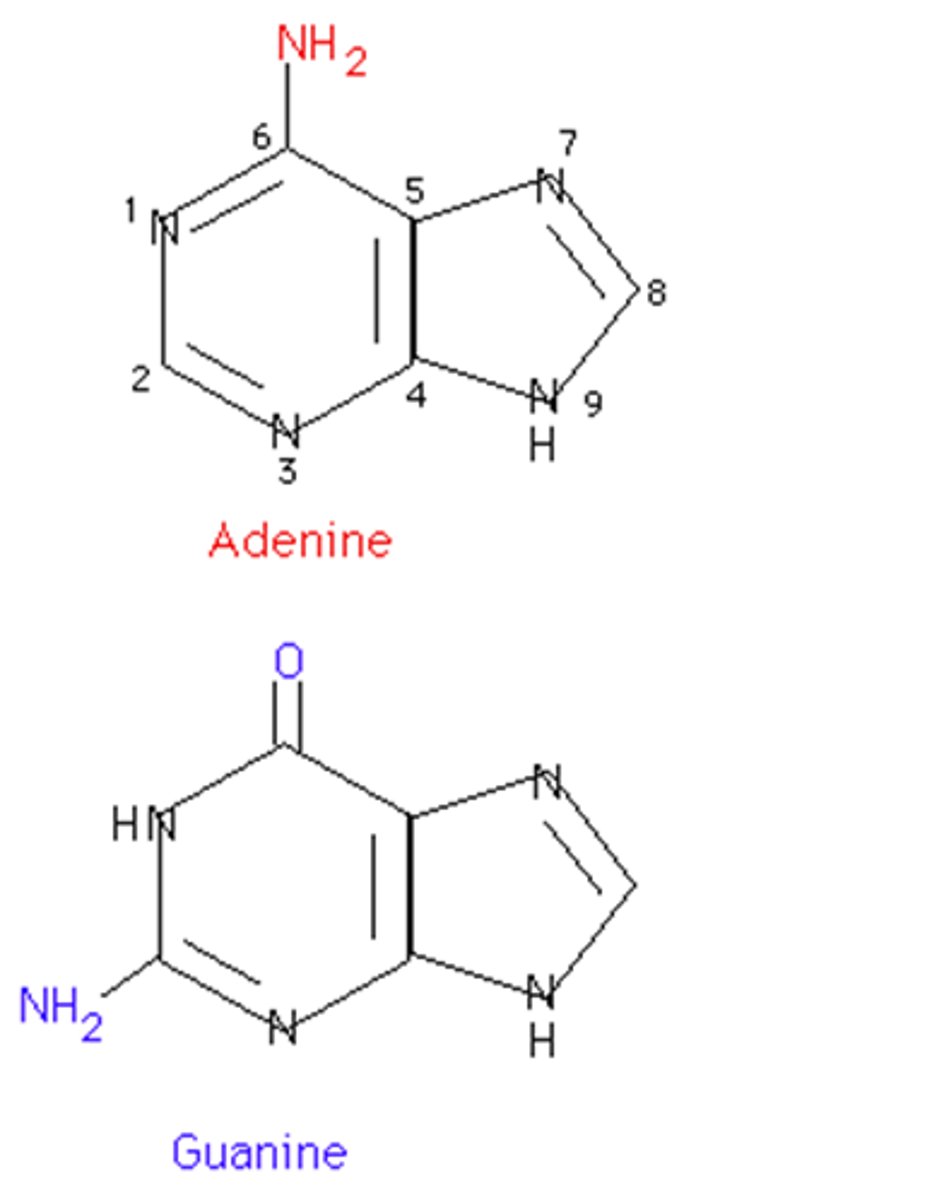
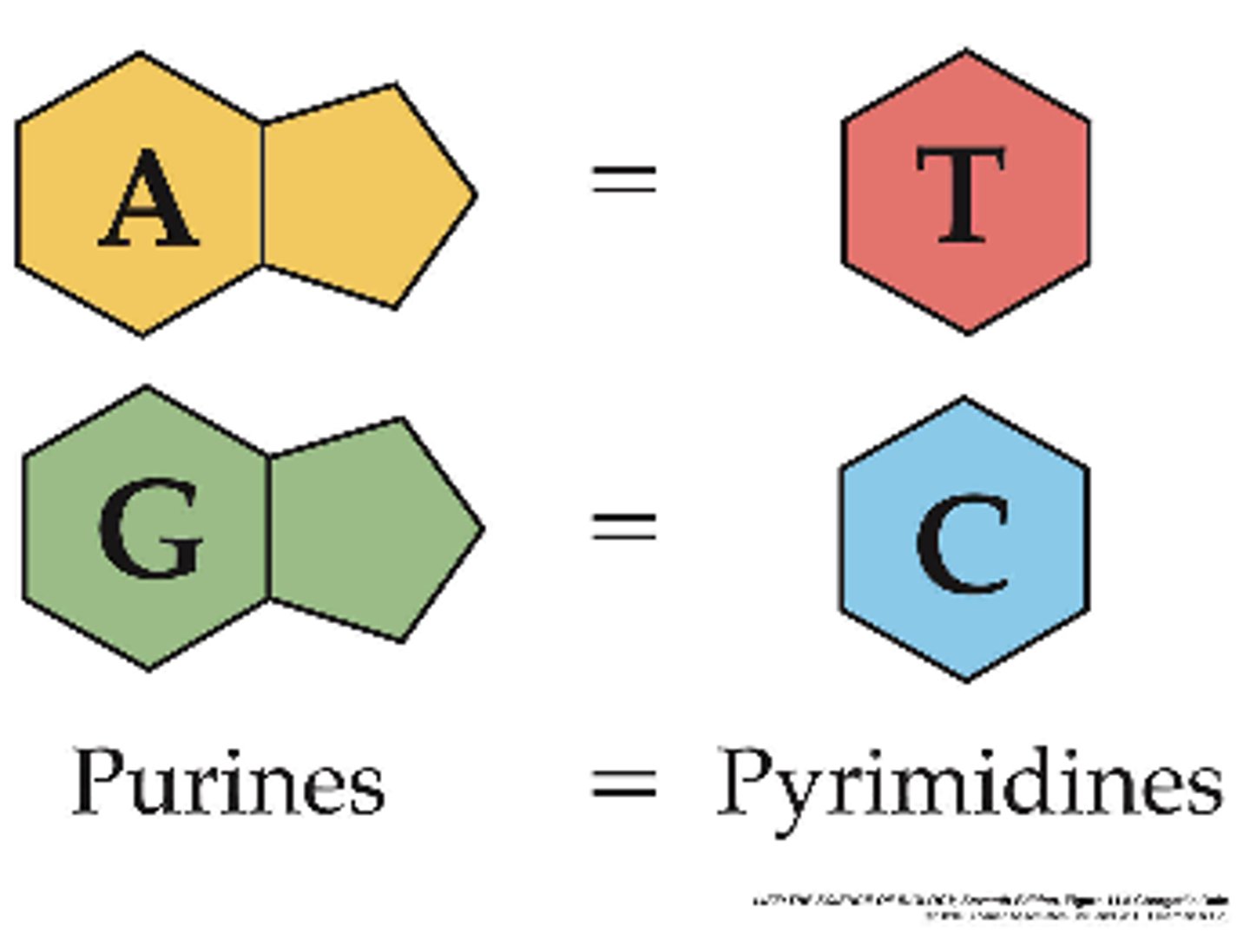
purines
Bases with a double-ring structure.
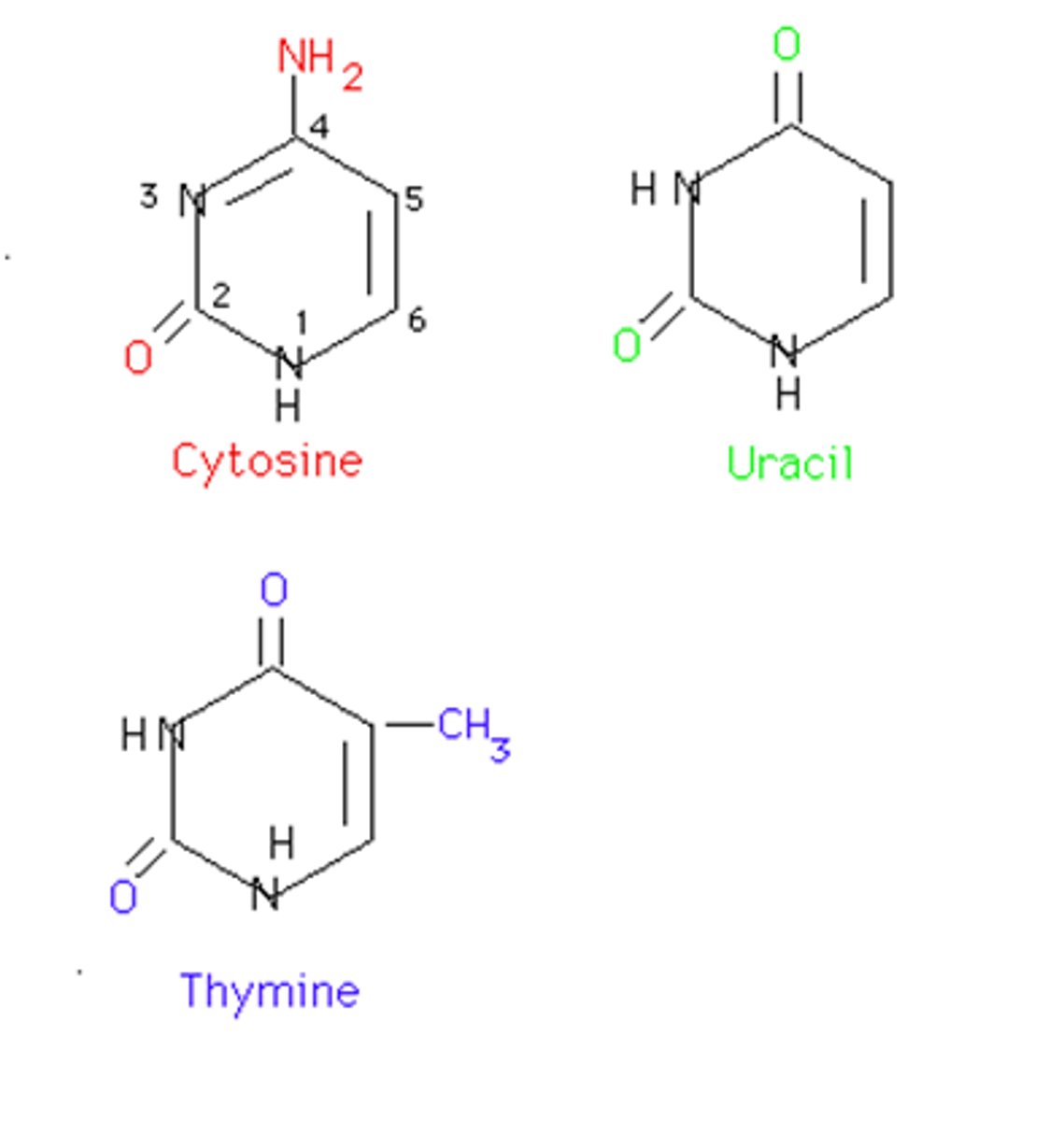
pyrimidines
Bases with a single-ring structure.
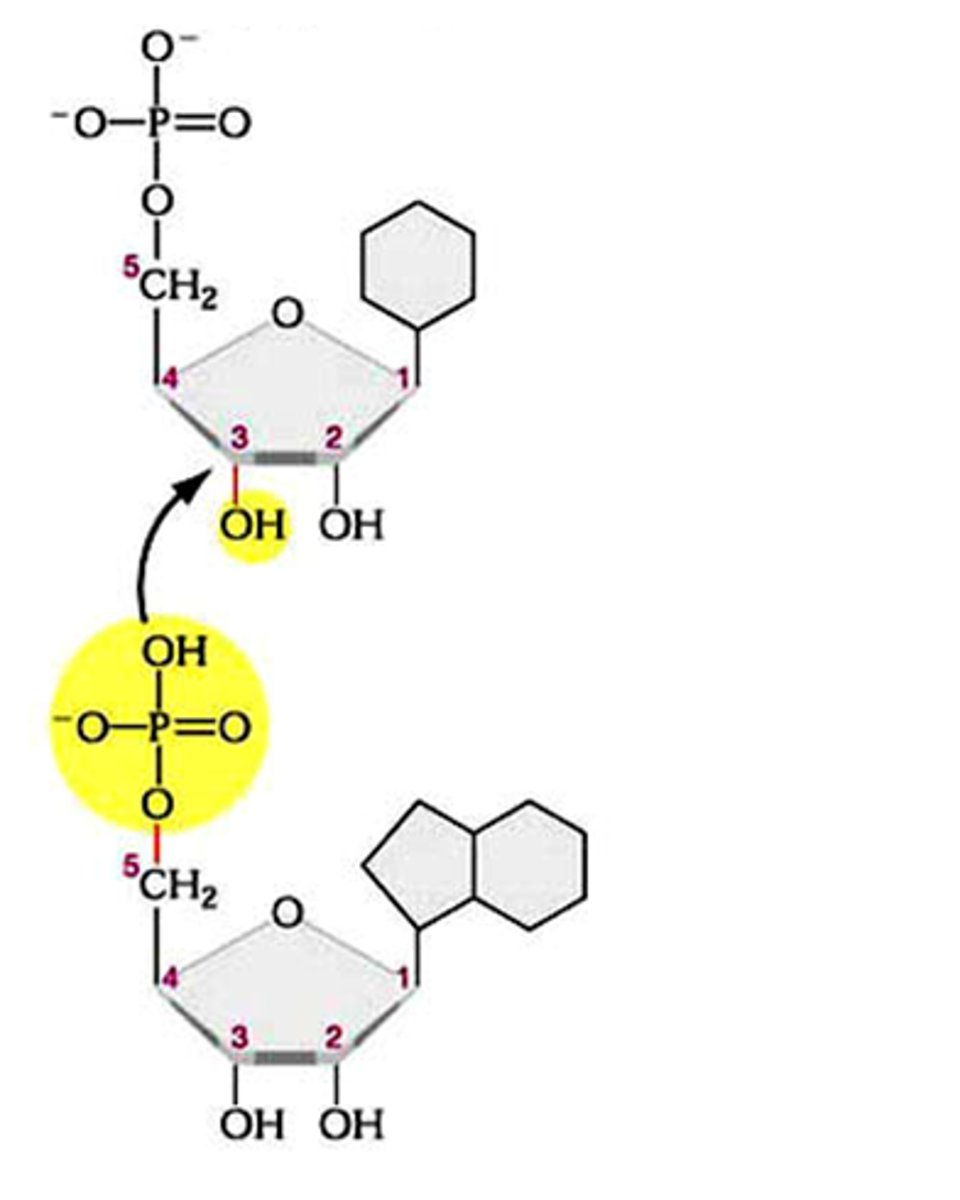
phosphodiester bonds
Bonds between phosphate group and pentose sugar in nucleic acids.
genes
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait/protein
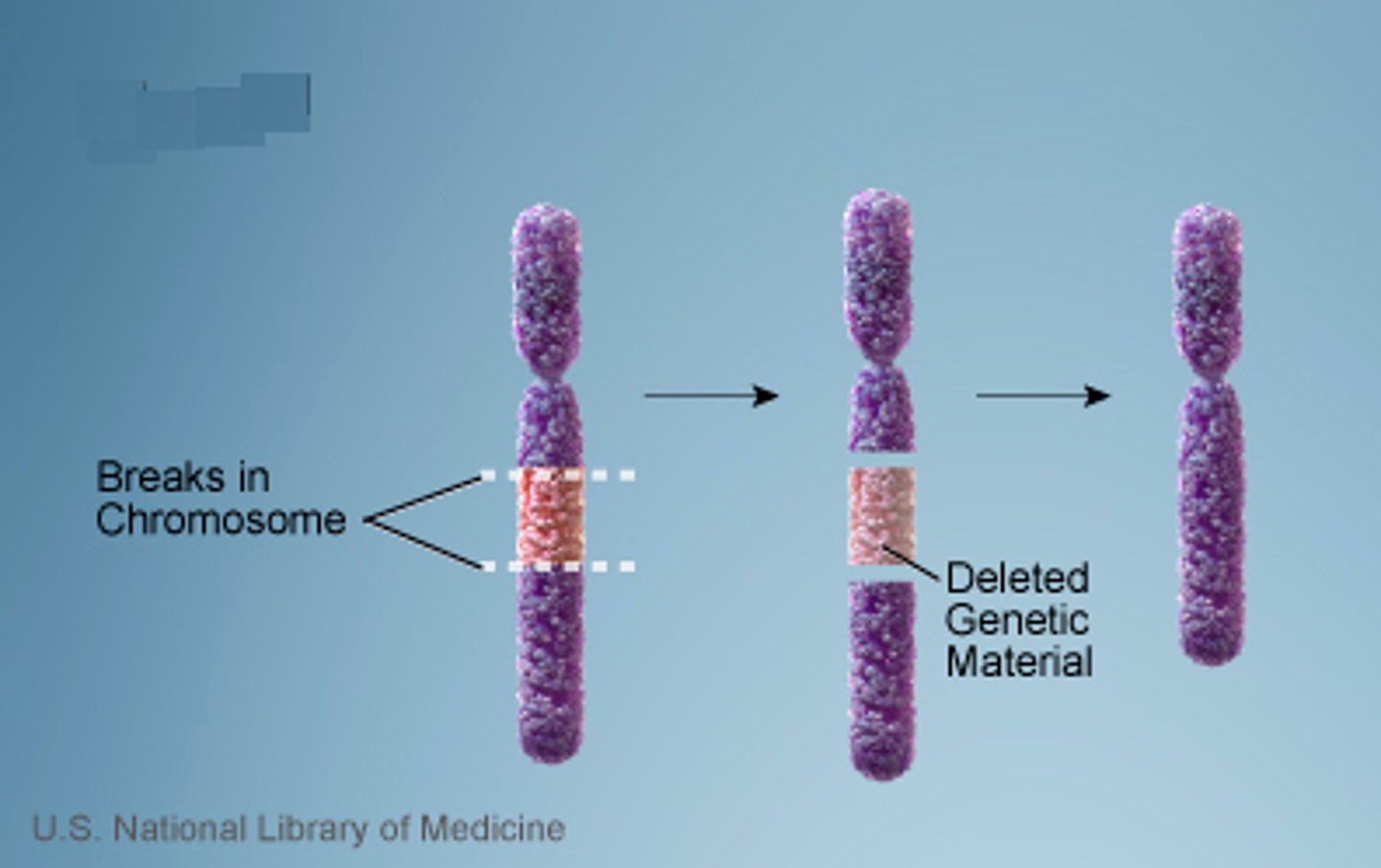
deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.
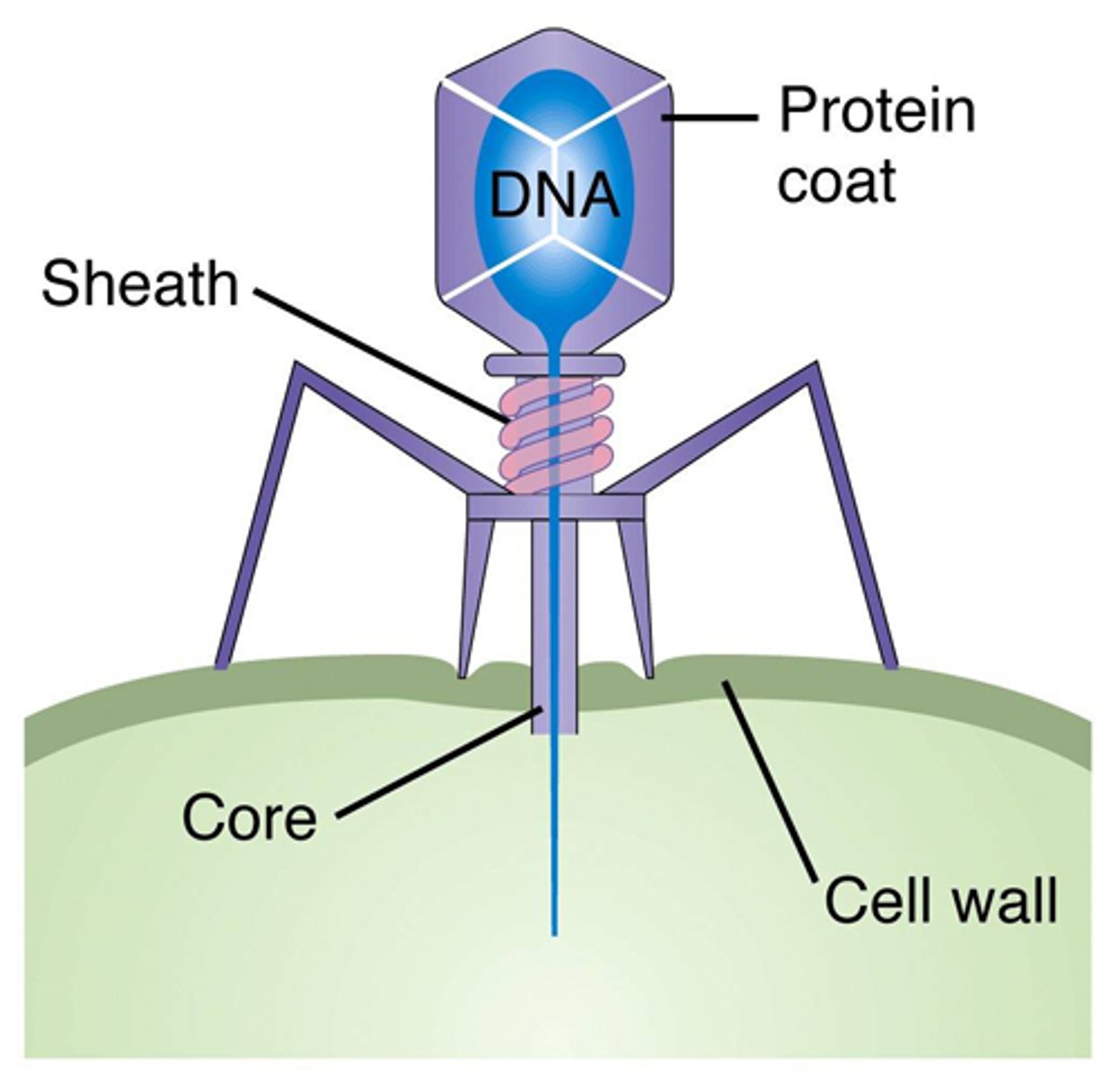
bacteriophages
A virus that infects bacteria; also called a phage.
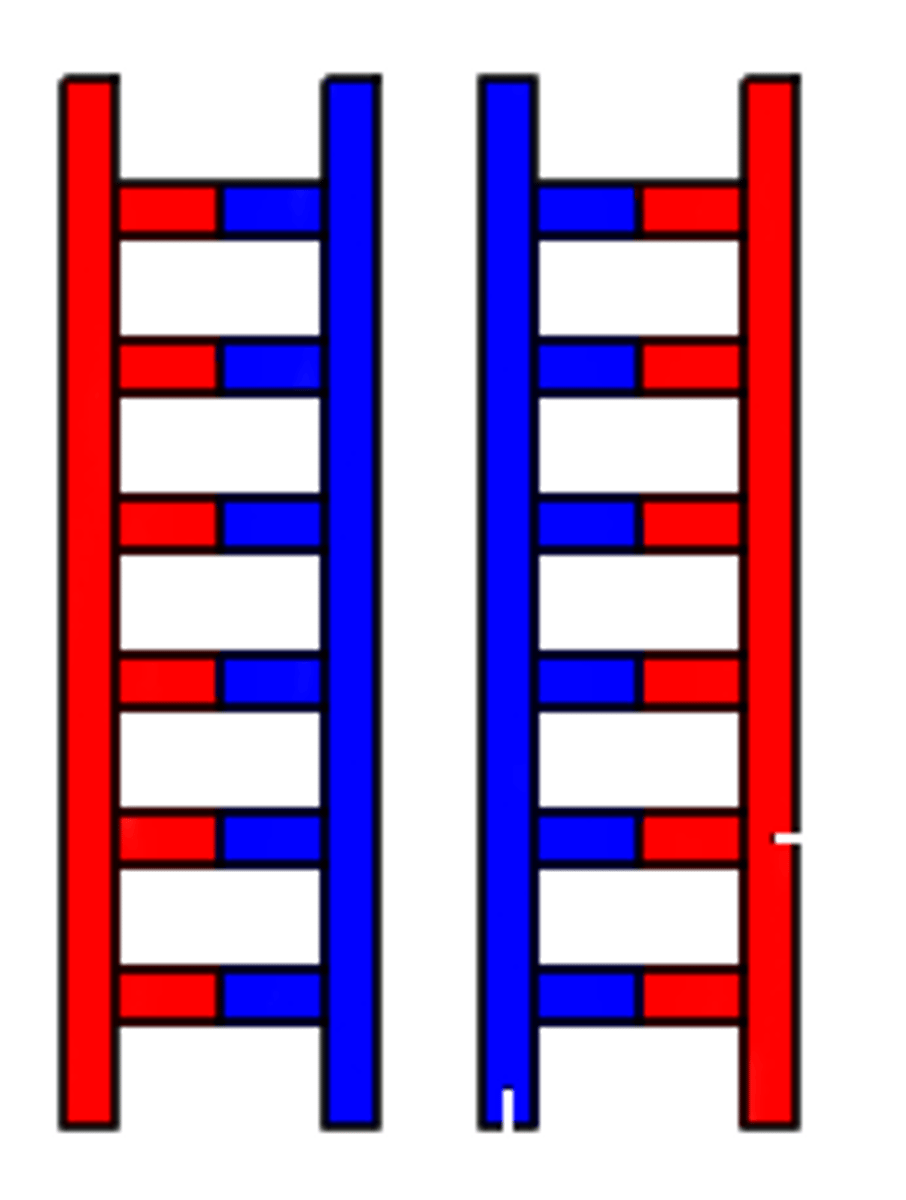
semiconservative model
Type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from the old molecule, and one newly made strand.
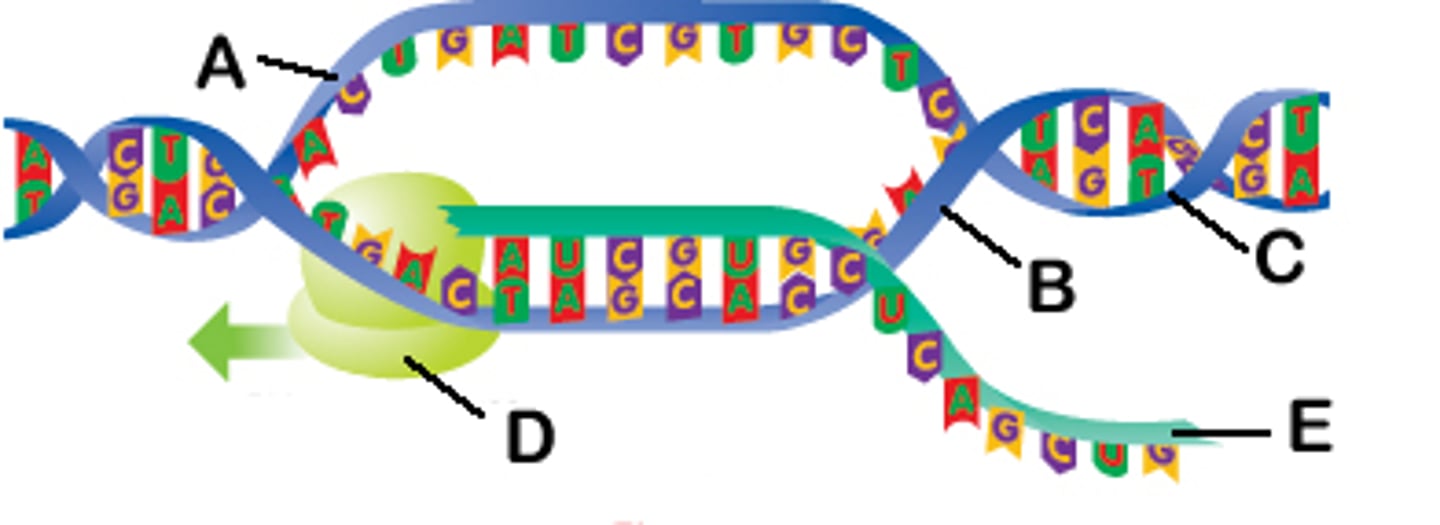
replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
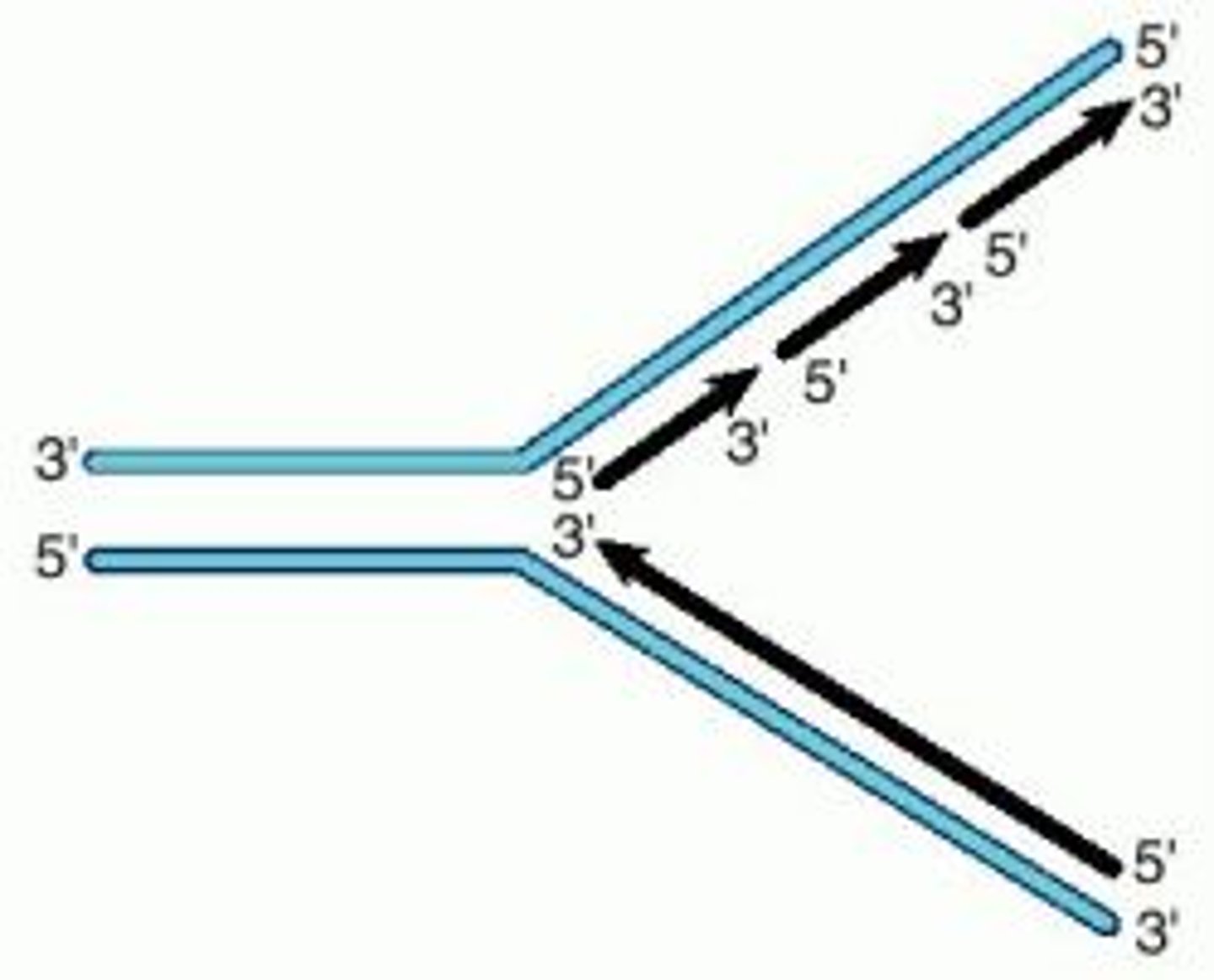
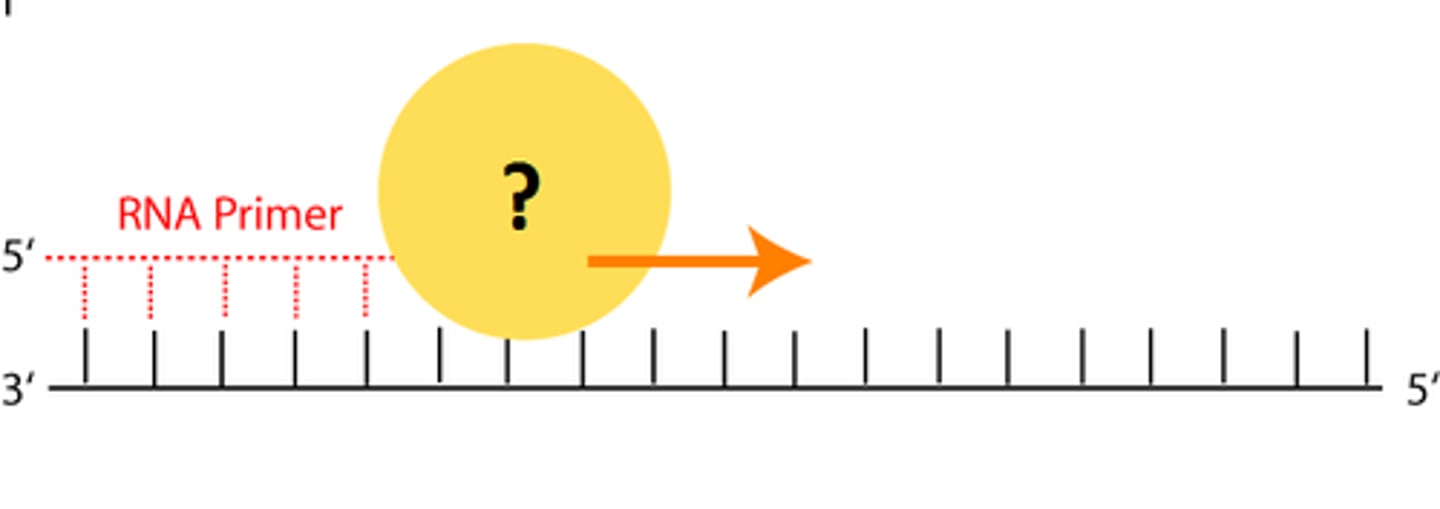
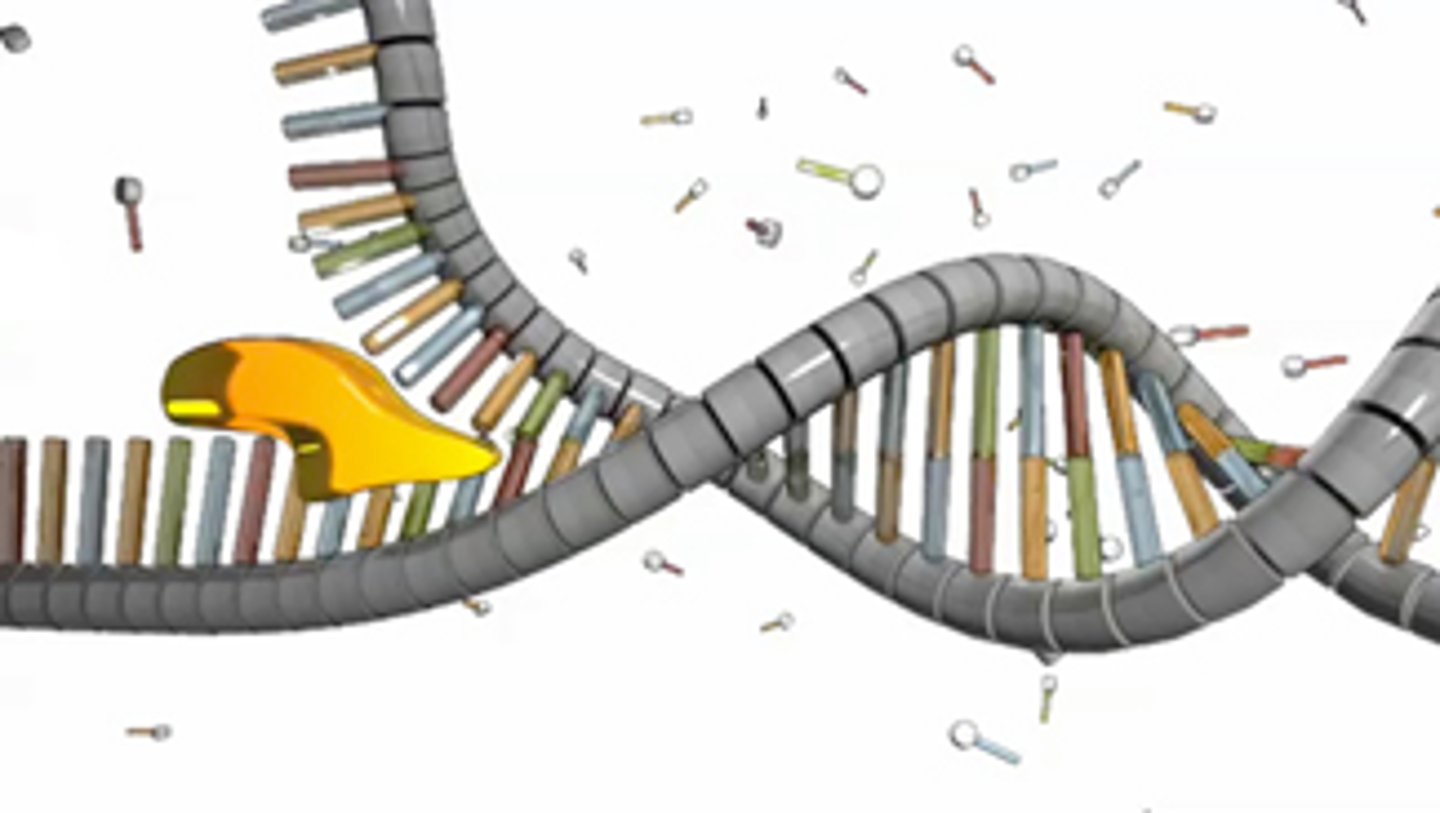
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the DNA molecule. Facilitates the addition of nucleotides in the 5'-3' direction.
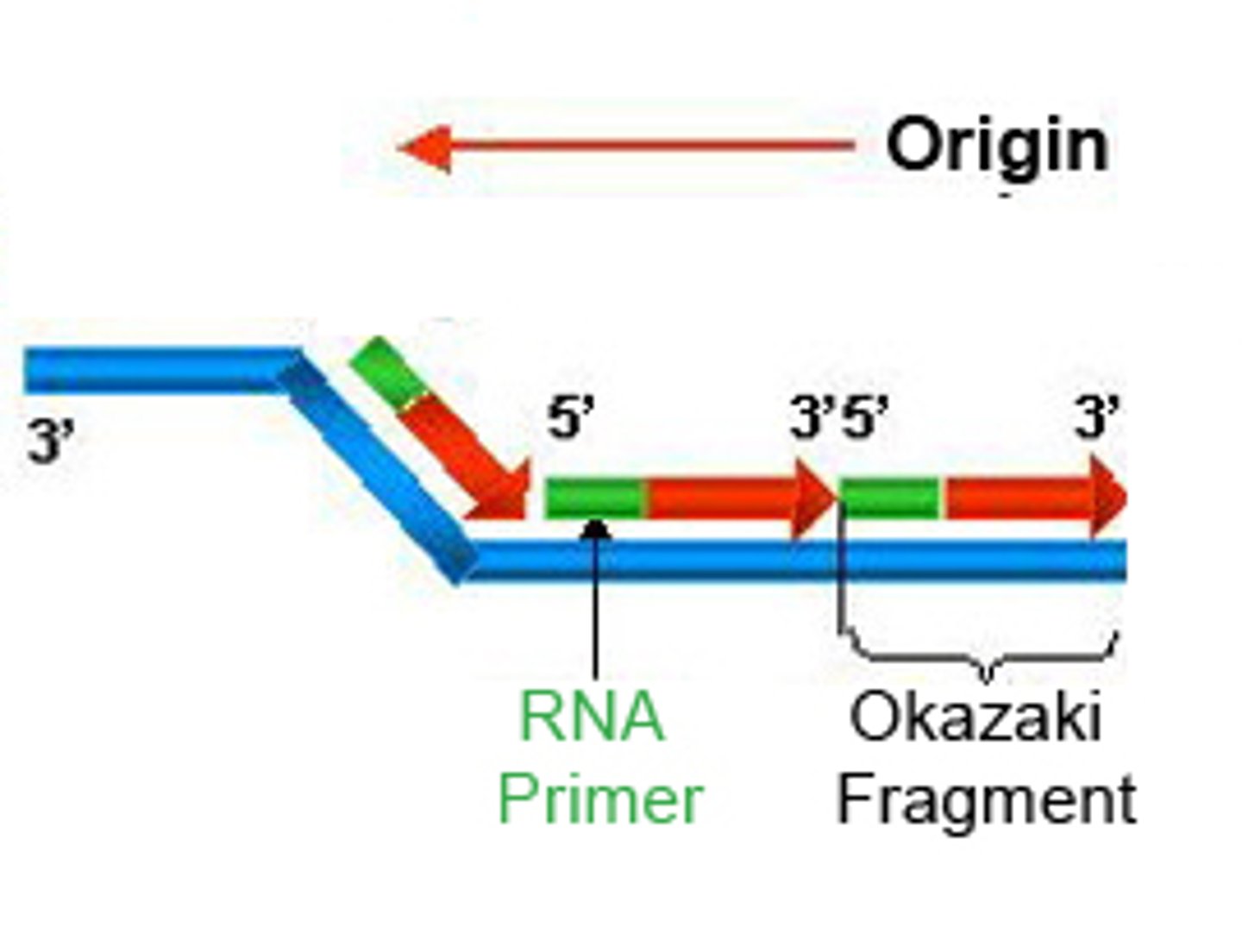
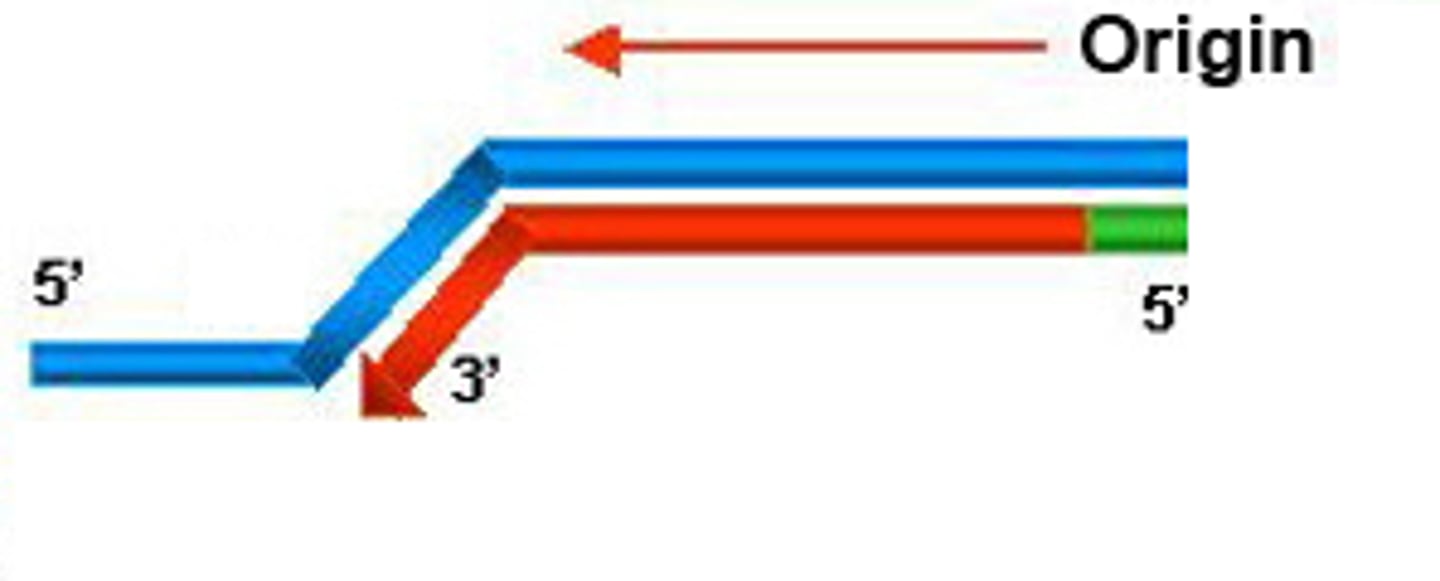
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
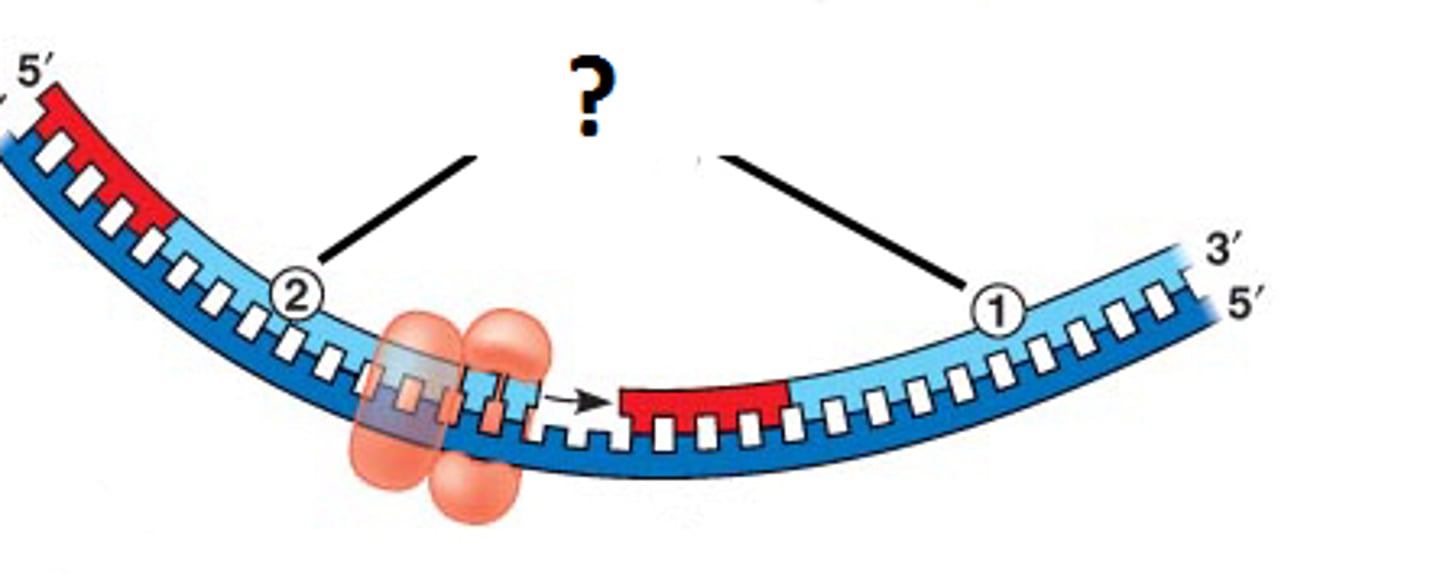
primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
helicase
An enzyme that separates the double helix at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands and making them available as template strands.
telomeres
Repeated DNA sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
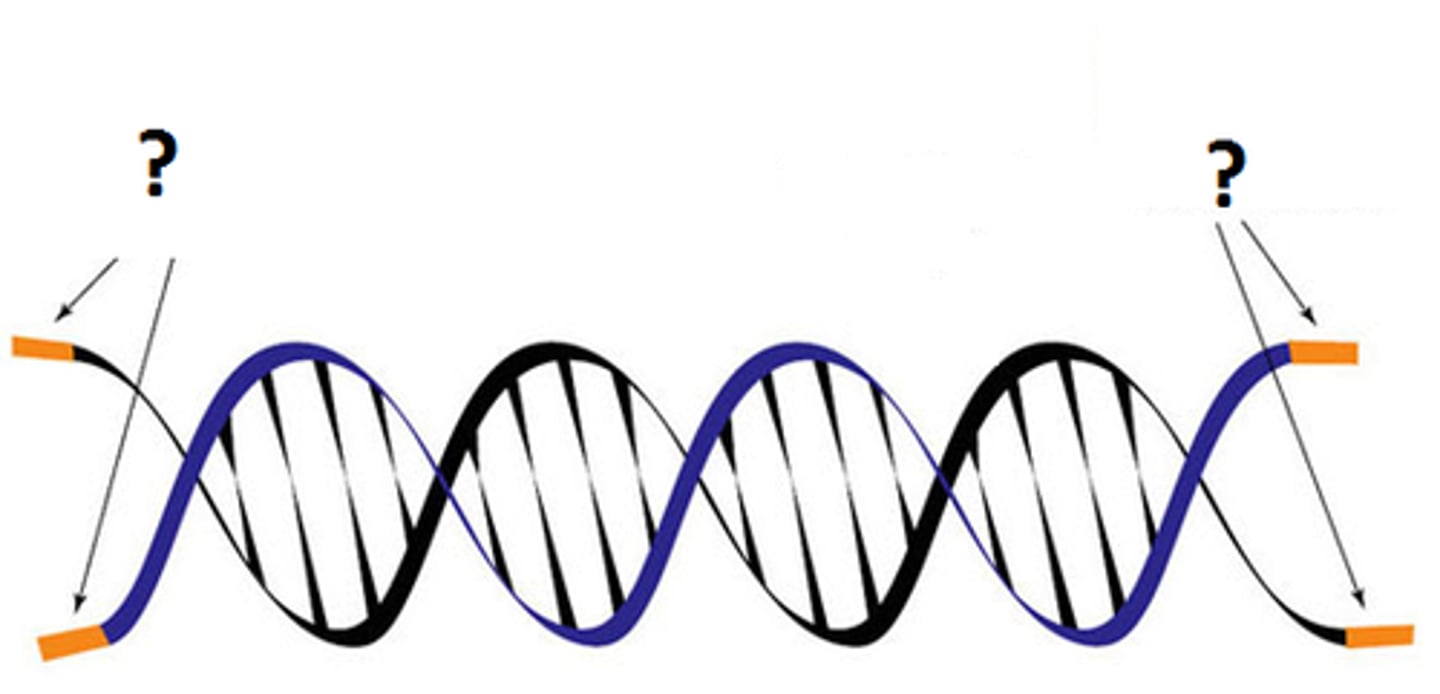
telomerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells.
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.
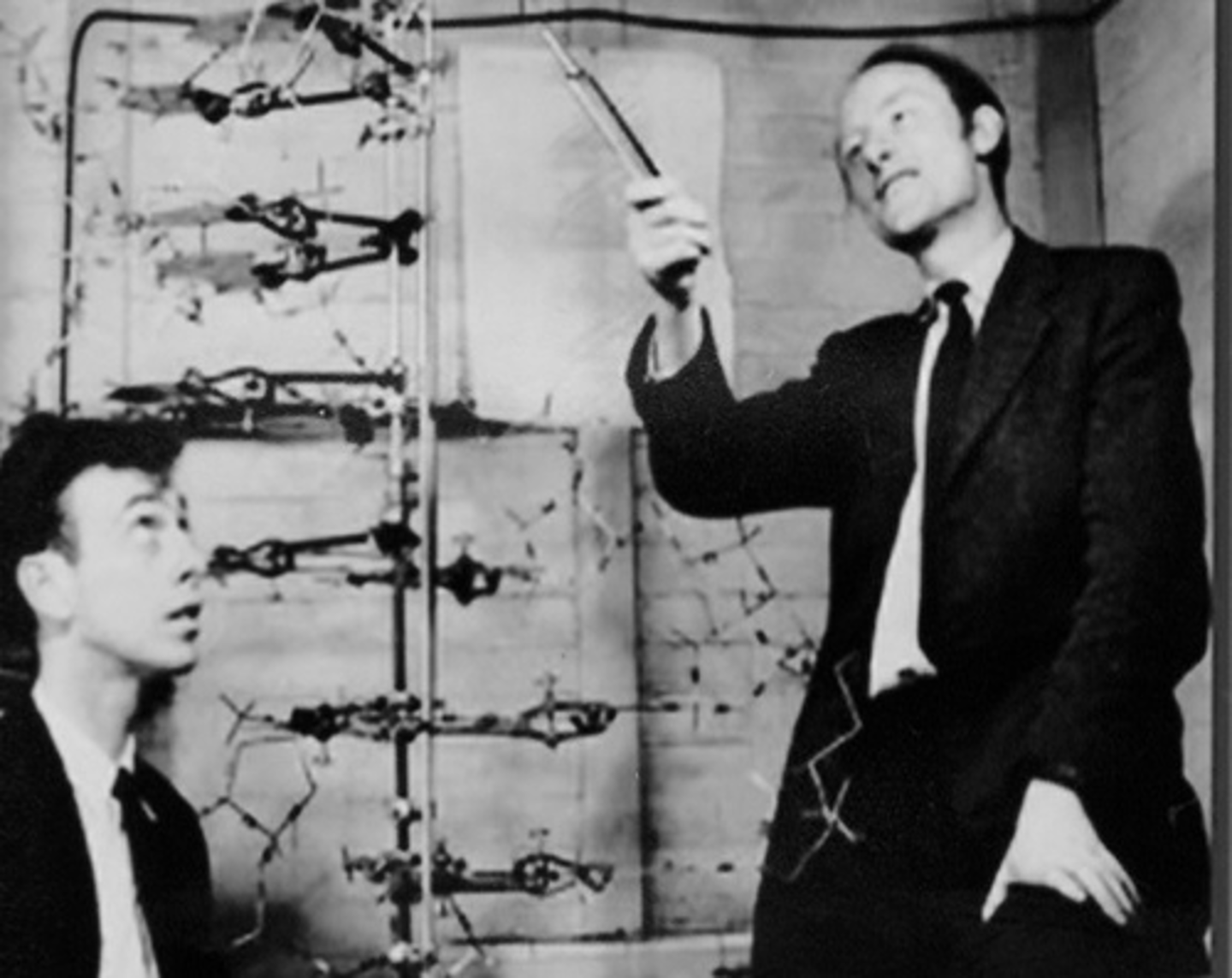

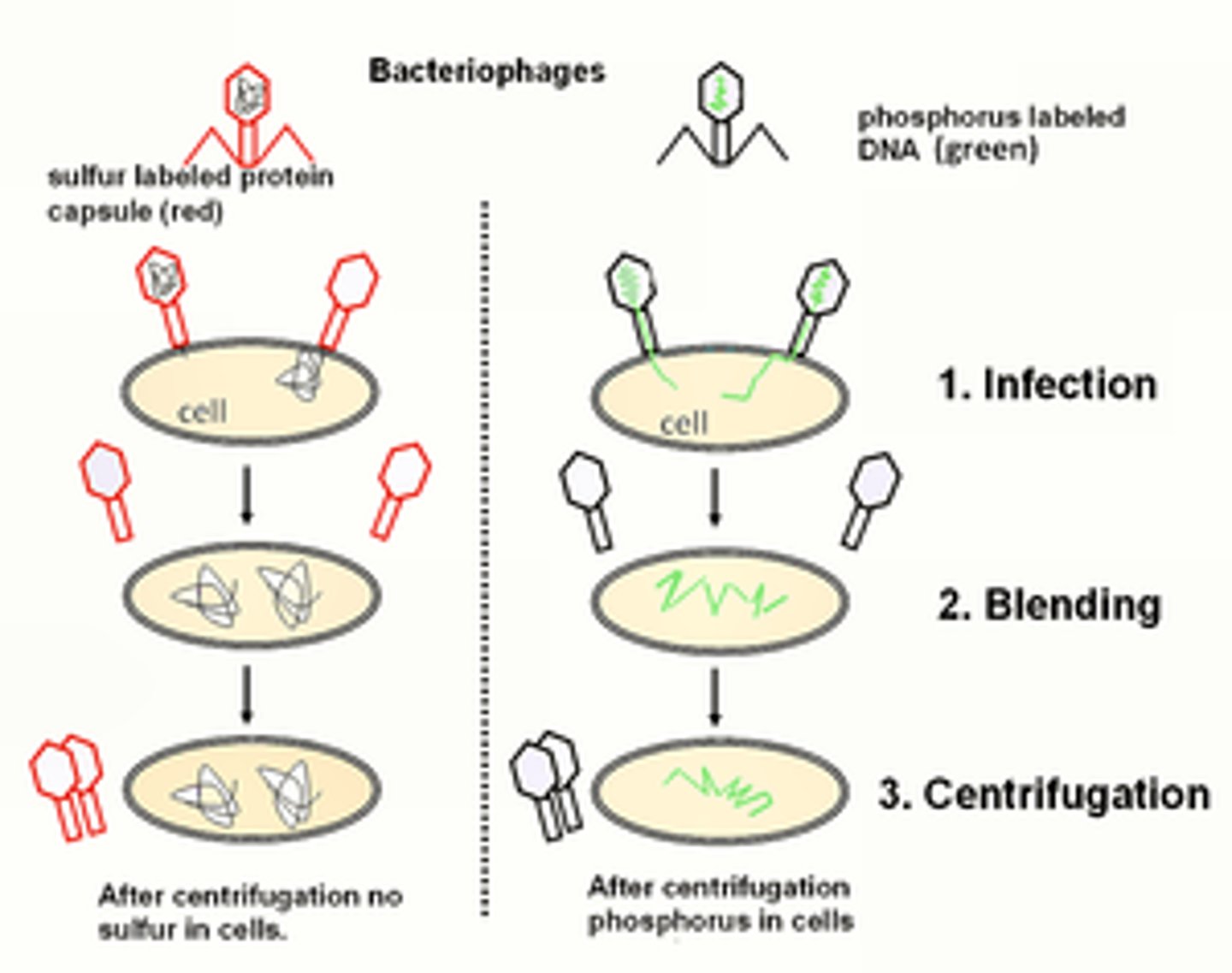
Hersey-Chase Experiment
Devised an experiment that showed that only the DNA of T2 phages enters a bacterial cell during infection.
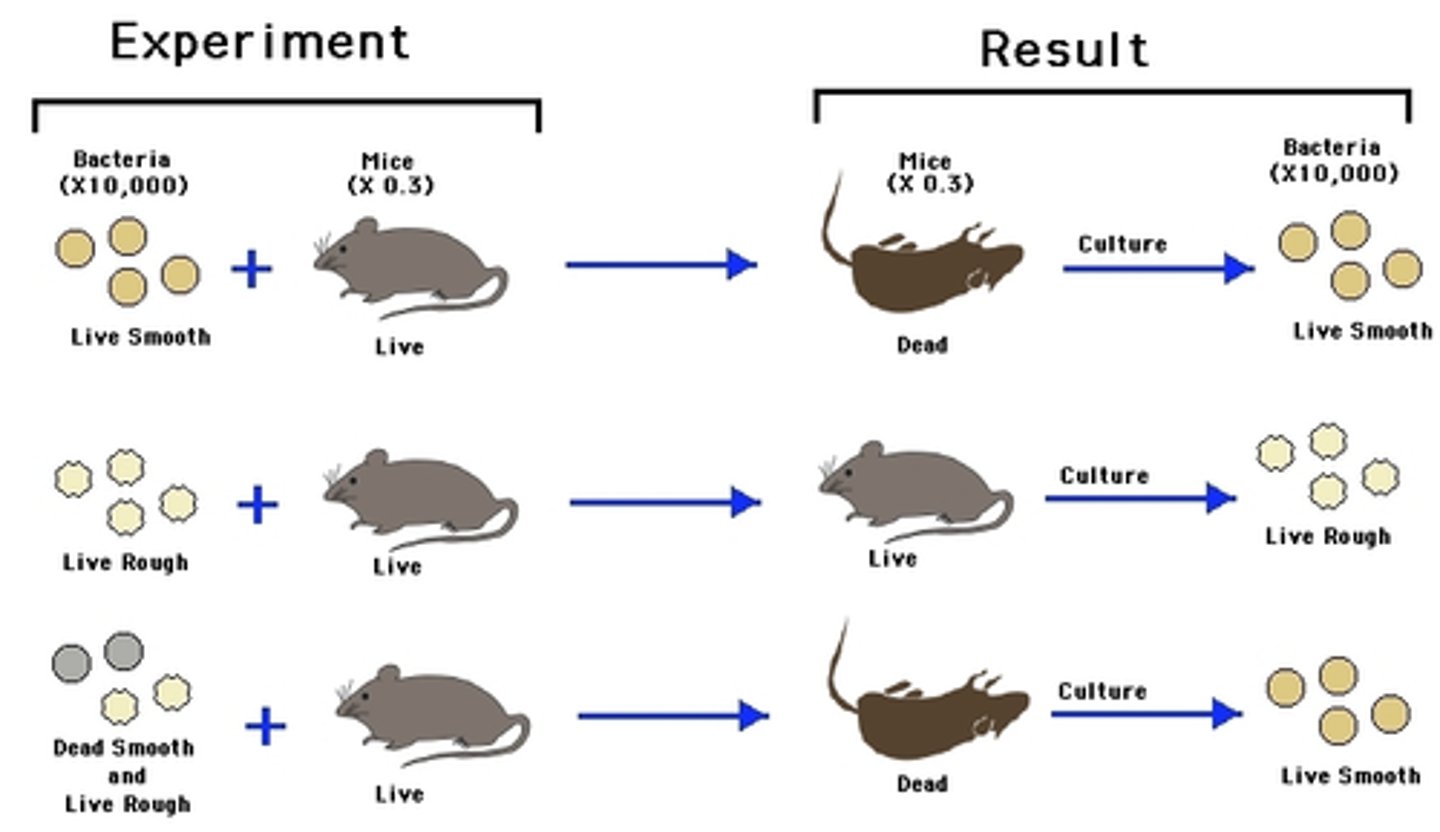
Frederick Griffith
Discovered transformation during an experiment that involved injecting mice with smooth (S) cells, rough (R) cells, heat-killed S cells, and heat-killed S cells with living R cells.
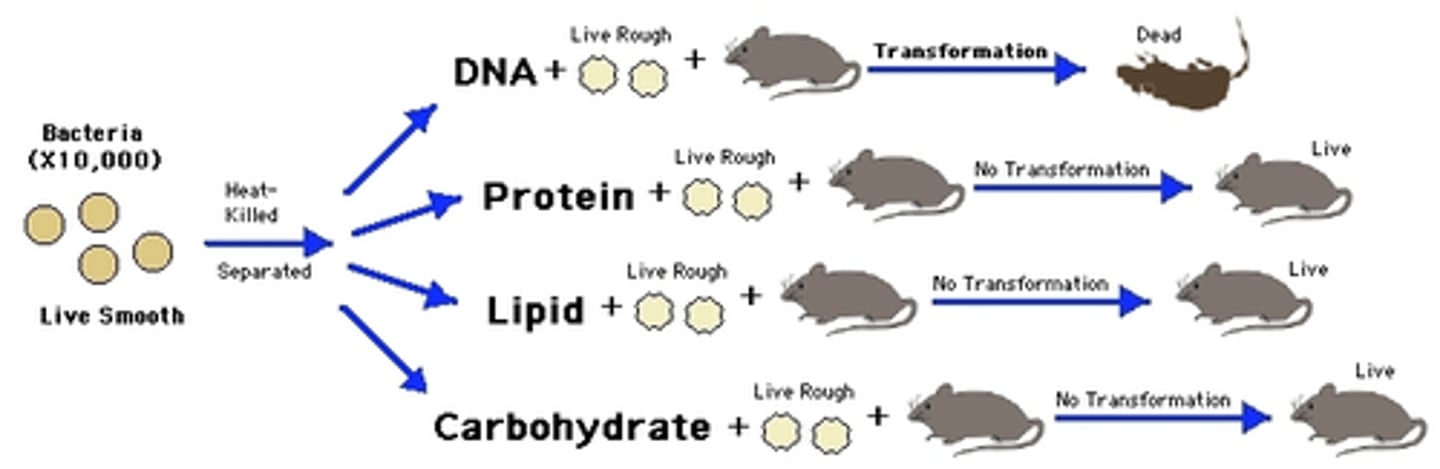
McCarty, Avery, & MacLeod
Confirmed that the transforming agent in Griffith's experiment was DNA.
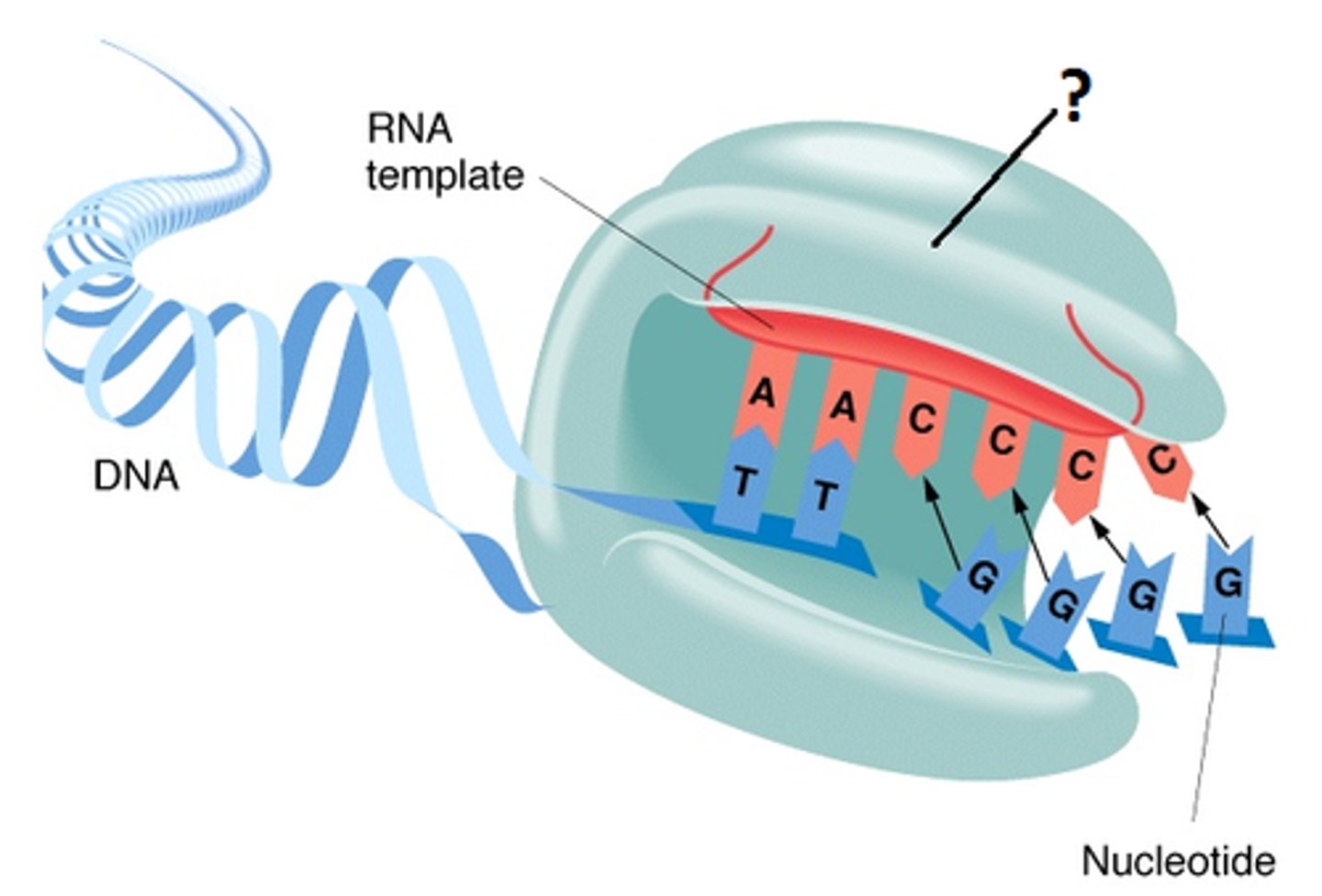
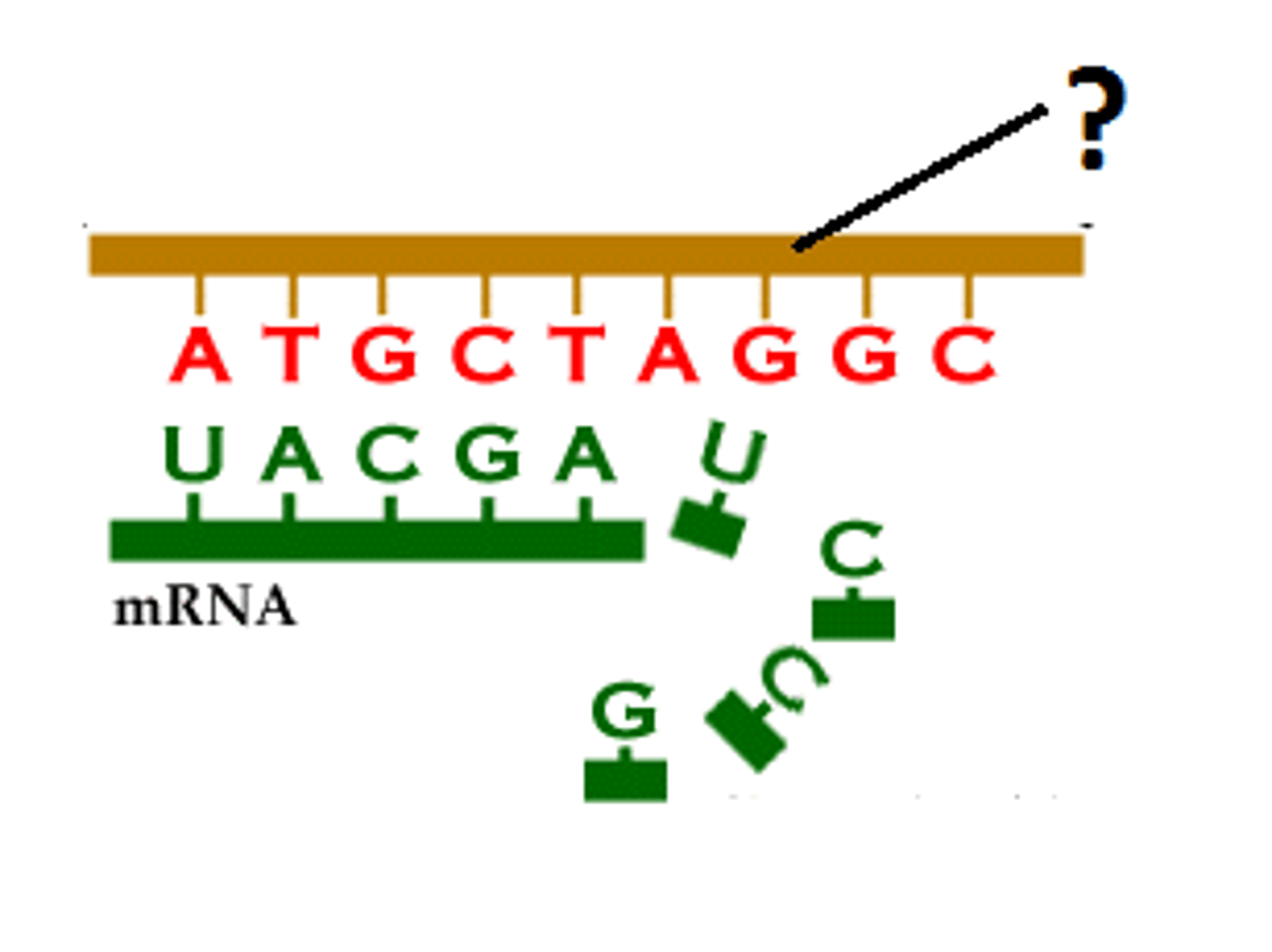
transcription
Synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template.
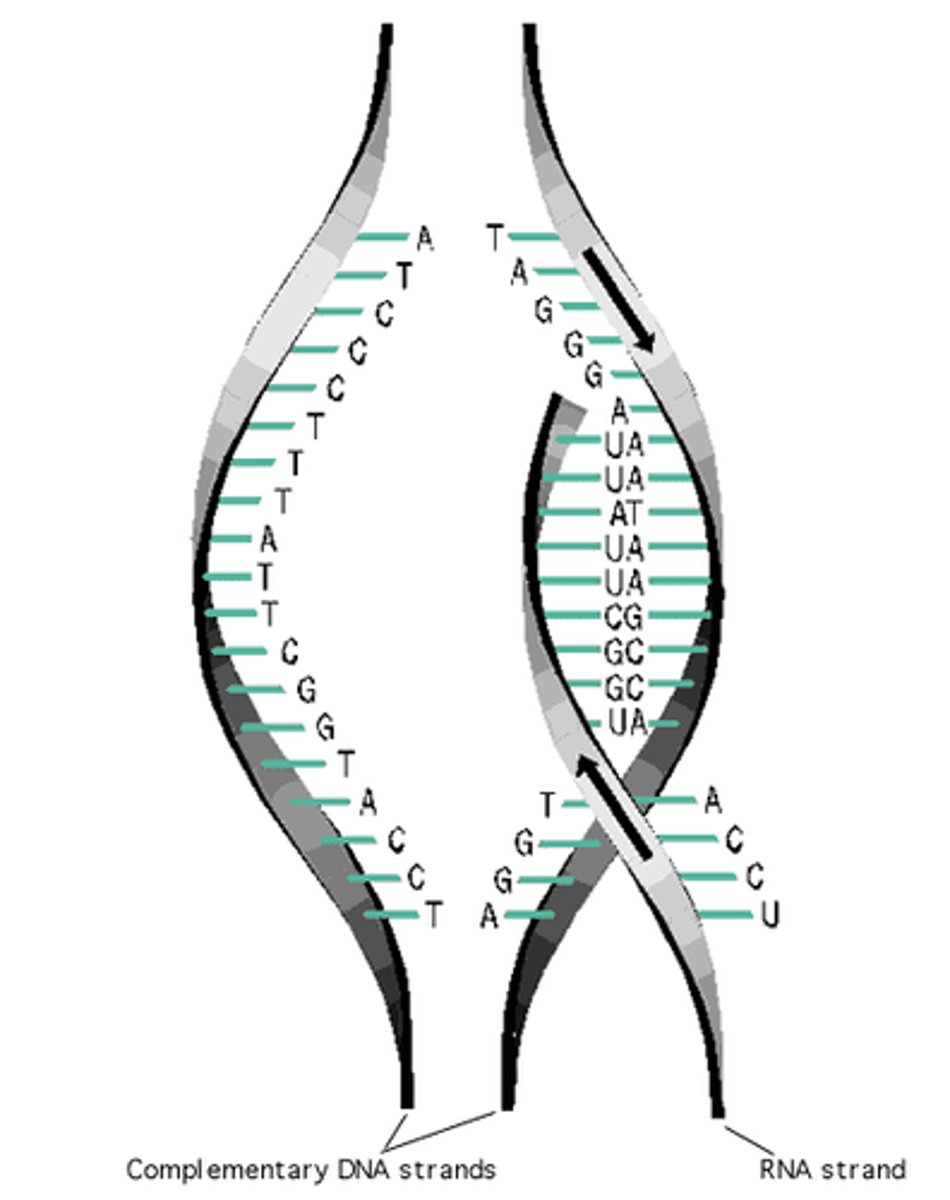
messenger RNA (mRNA)
Carries genetic message from the DNA to he protein-synthesizing machinery of the cell.

Erwin Chargaff
Discovered that DNA composition varies, but the amount of adenine is always the same as thymine and the amount of cytosine is always the same as guanine.
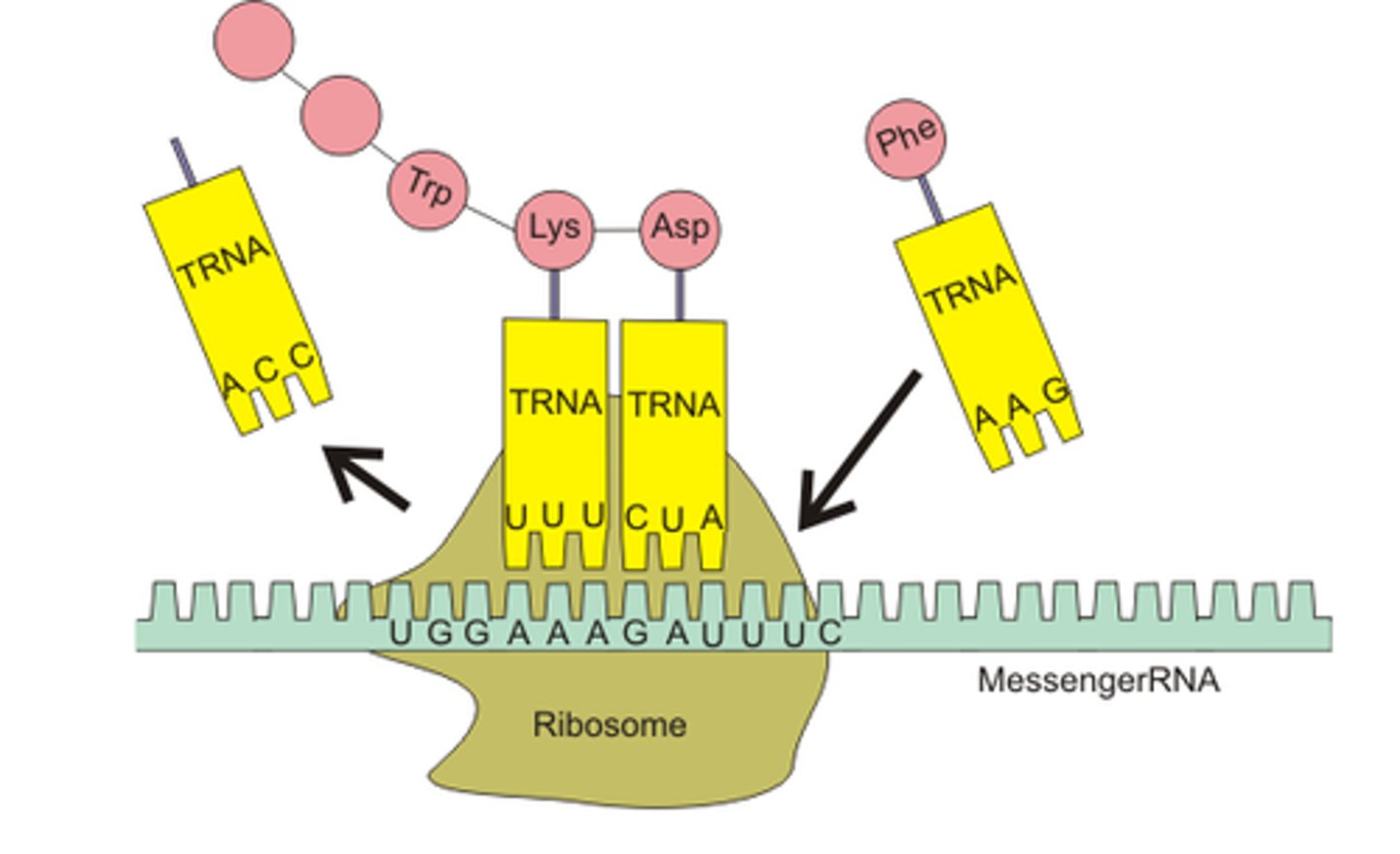
translation
The synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA.
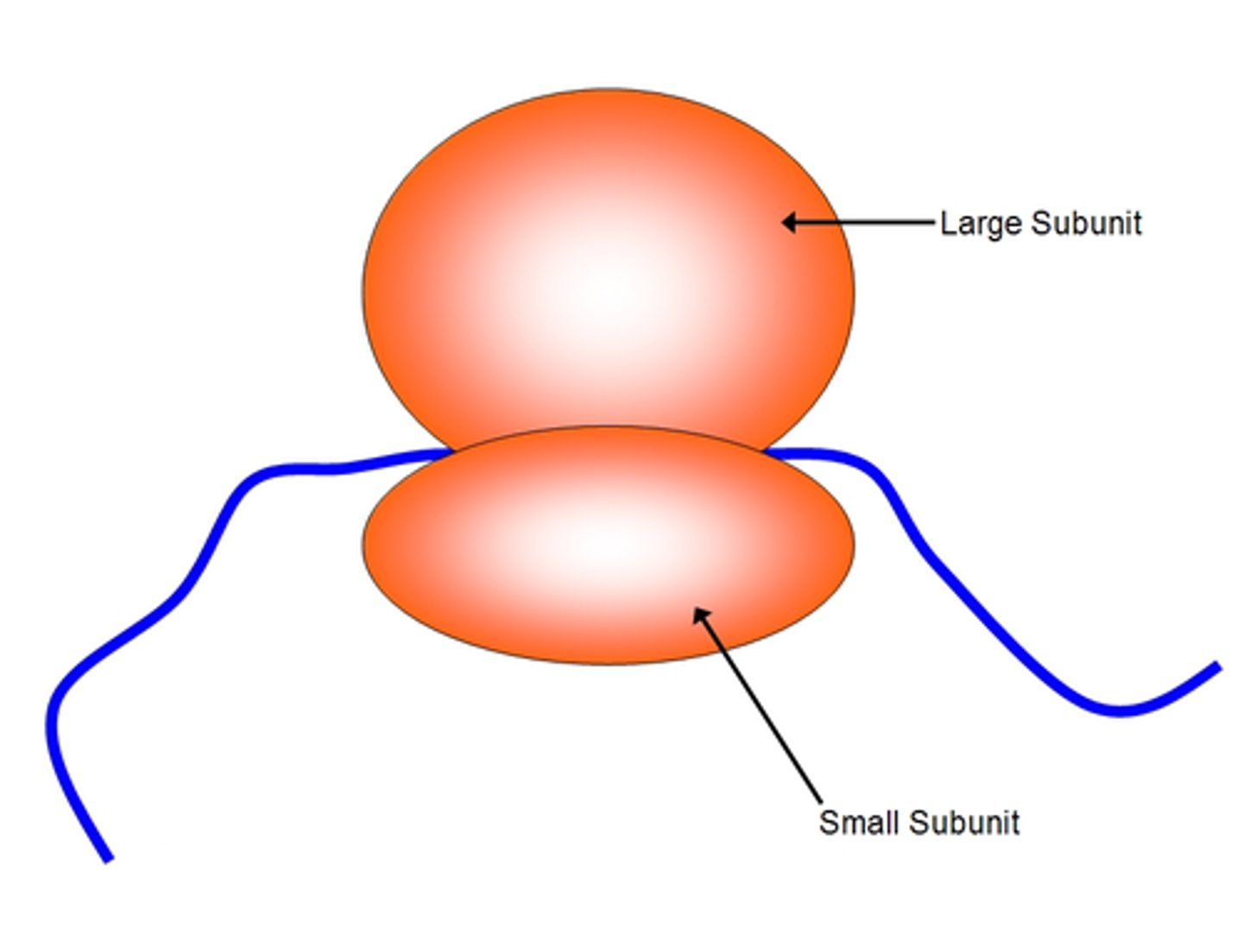
ribosomes
Complex particles that facilitate the orderly linking of amino acids into polypeptide chains.
RNA processing
The modification of mRNA before it leaves the nucleus that is unique to eukaryotes.
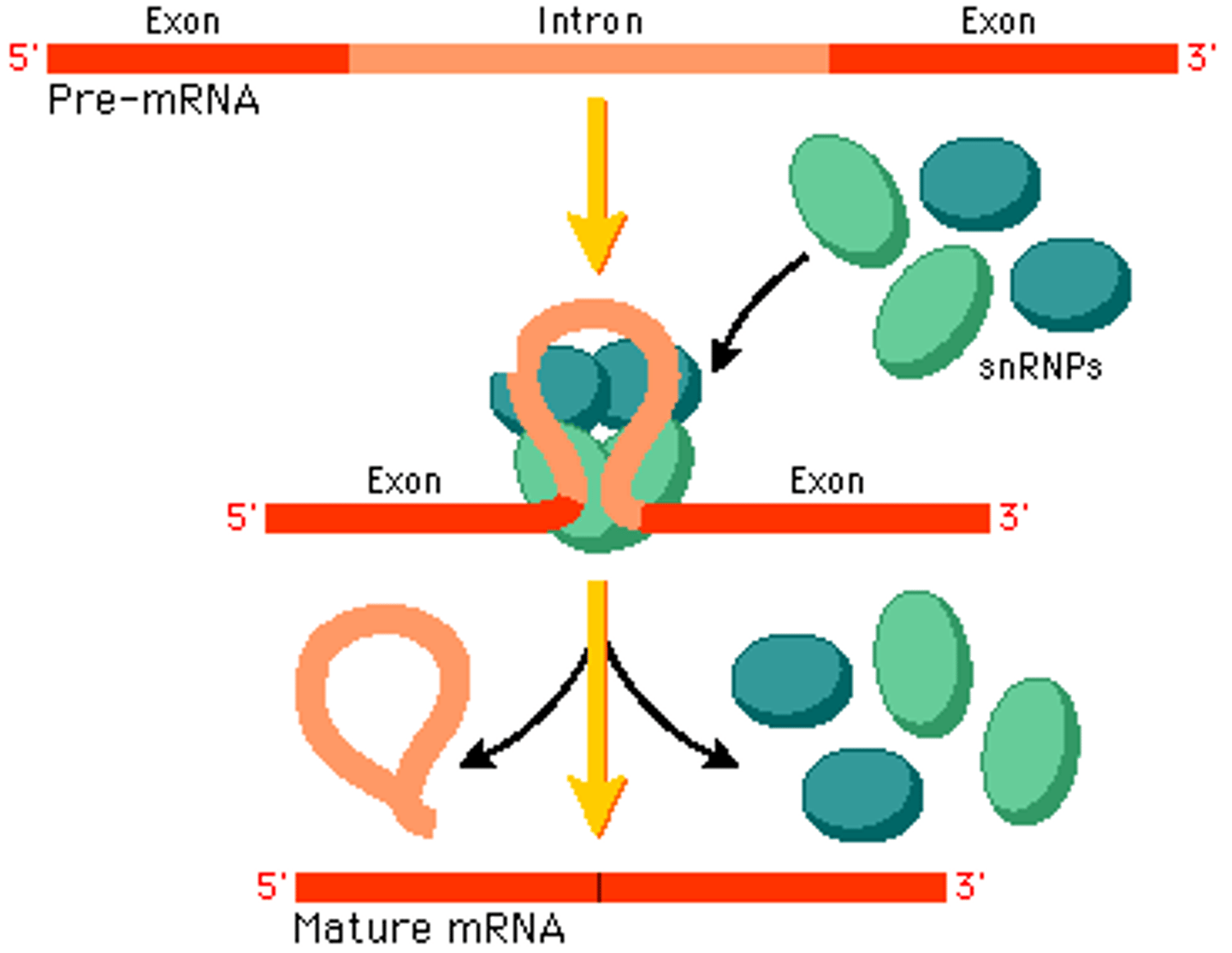
pre-mRNA
In a eukaryote, the initial mRNA transcript that is transcribed from a protein coding gene.

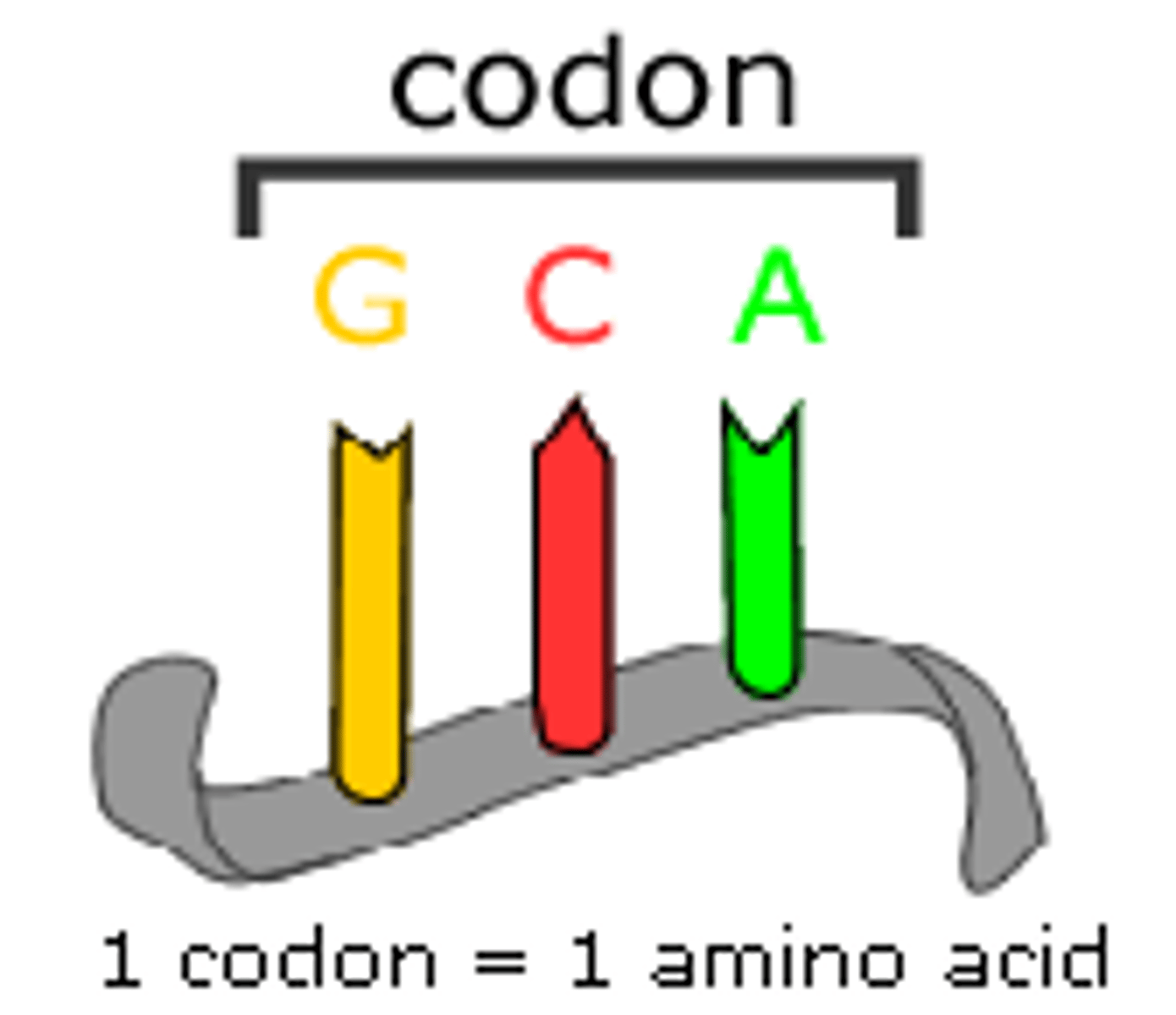
triplet code
Three-nucleotide long set that specifies a specific amino acid for a polypeptide chain.
template strand
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an mRNA transcript.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
poly-A tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides.
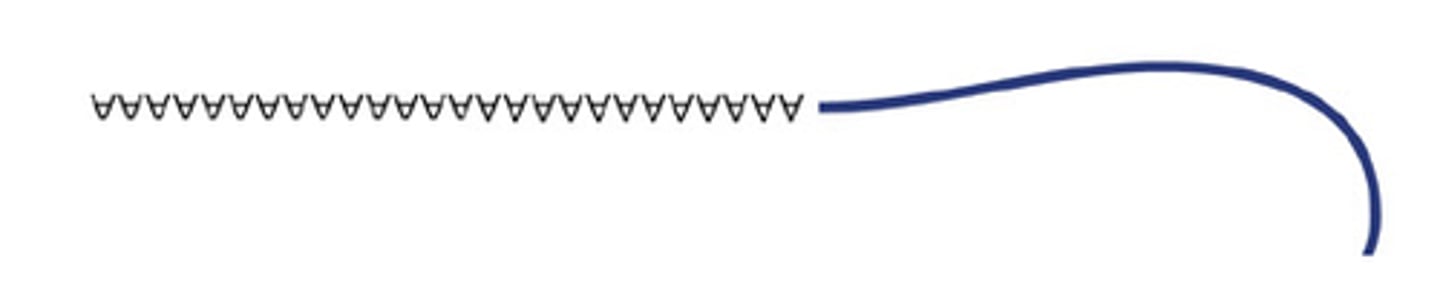
5' cap
The 5' end of a pre-mRNA molecule modified by the addition of a cap of guanine nucleotide.

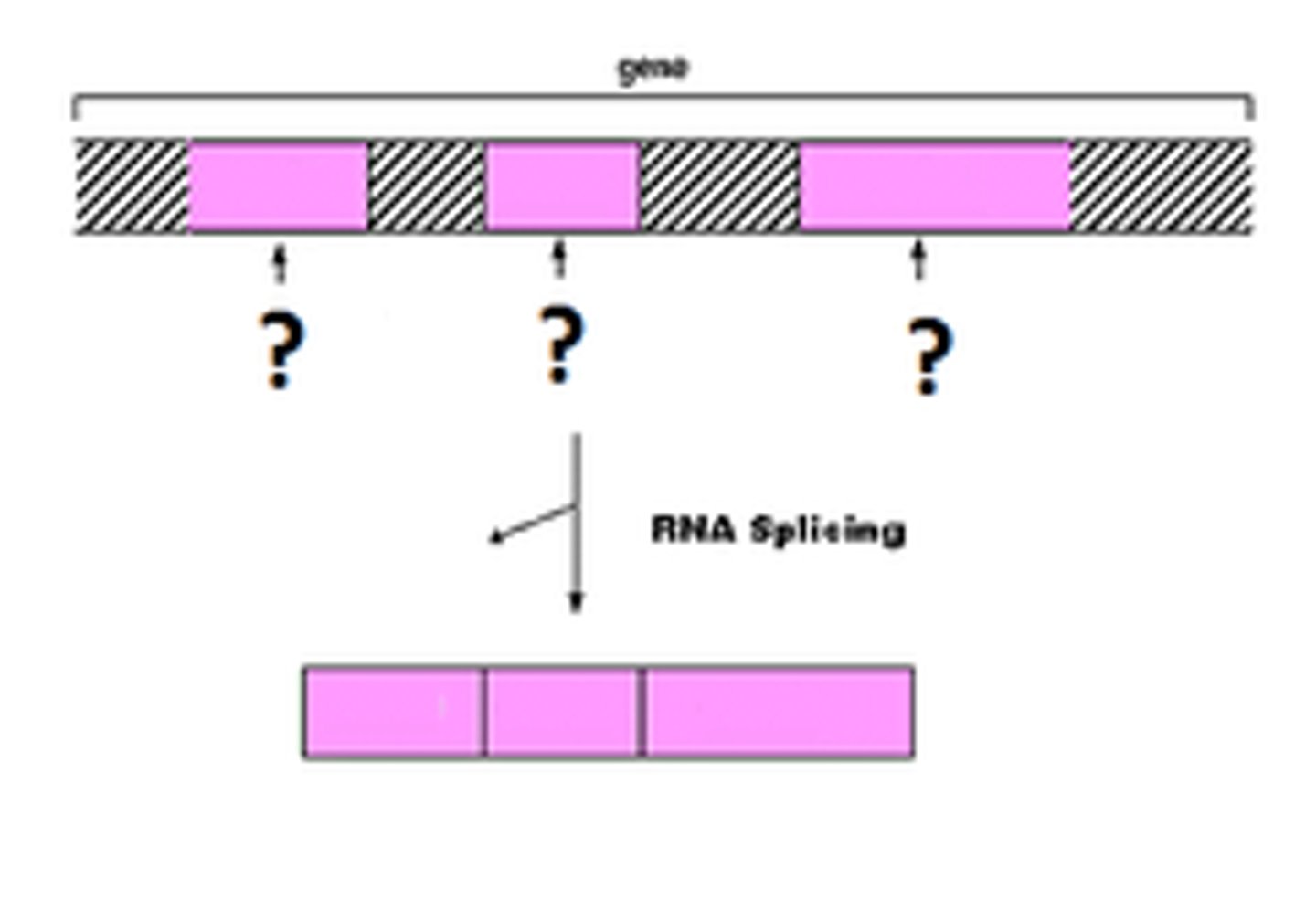
exons
Coding segments of eukaryotic DNA.
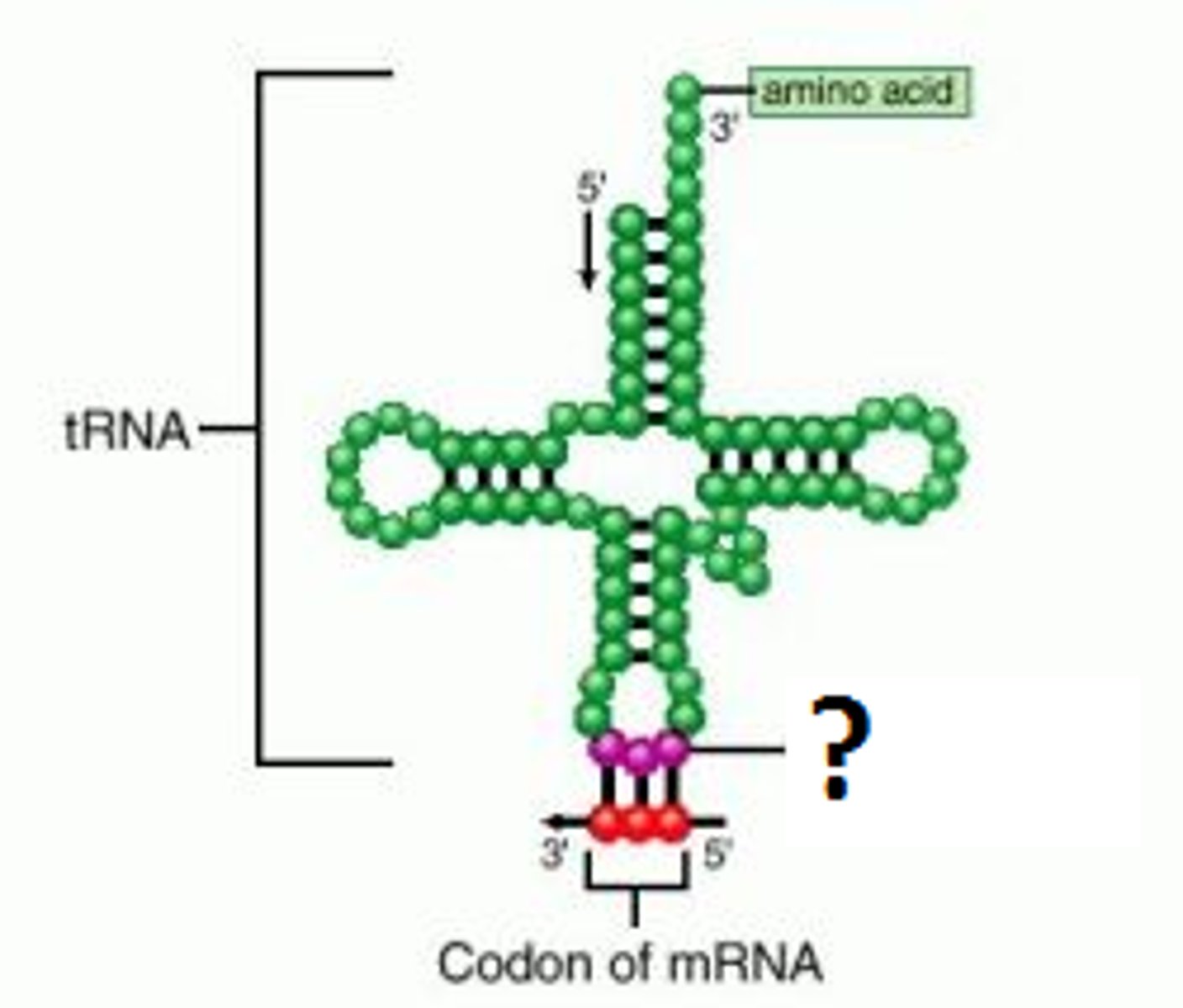
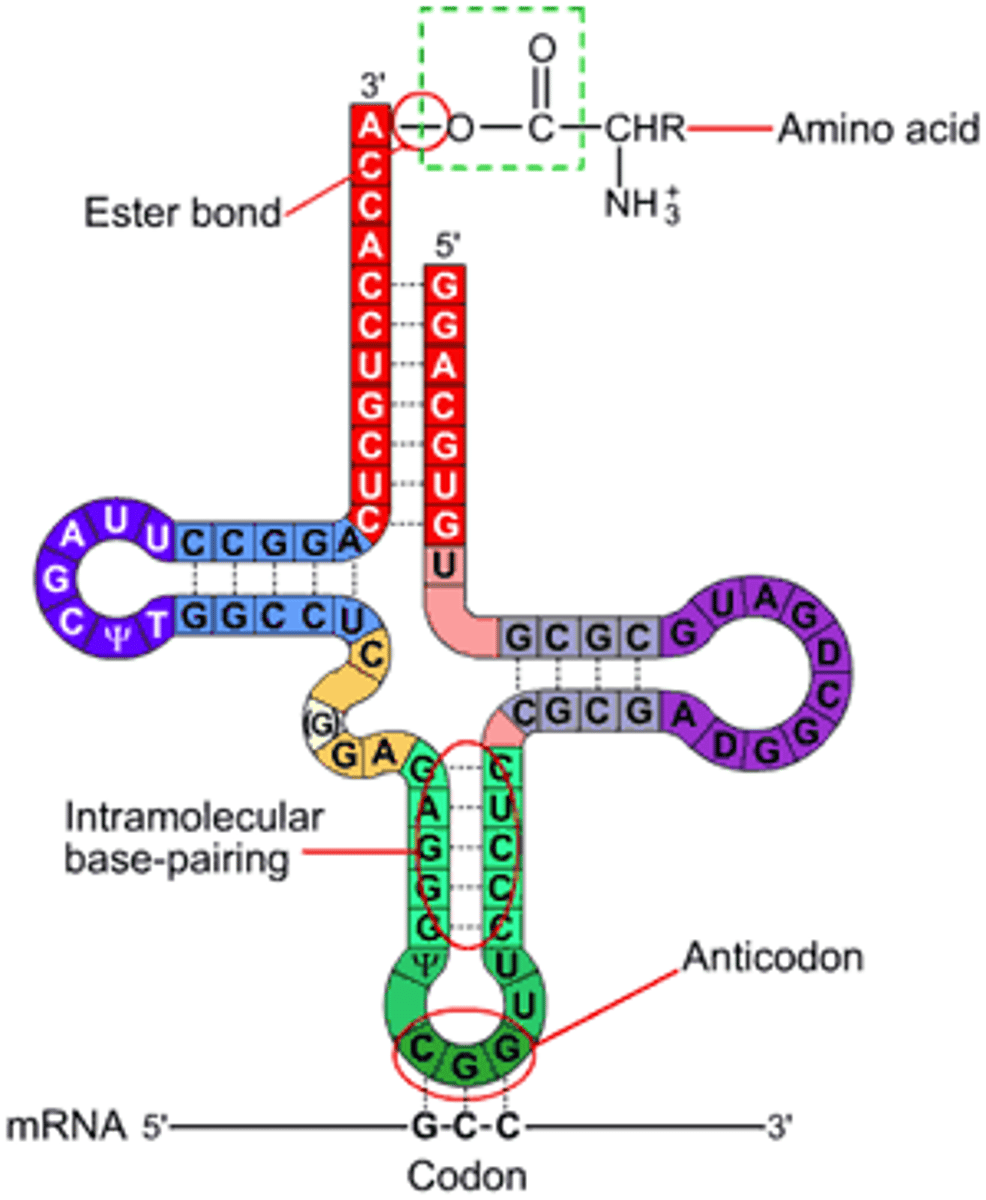
anticodon
Specialized base triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule.
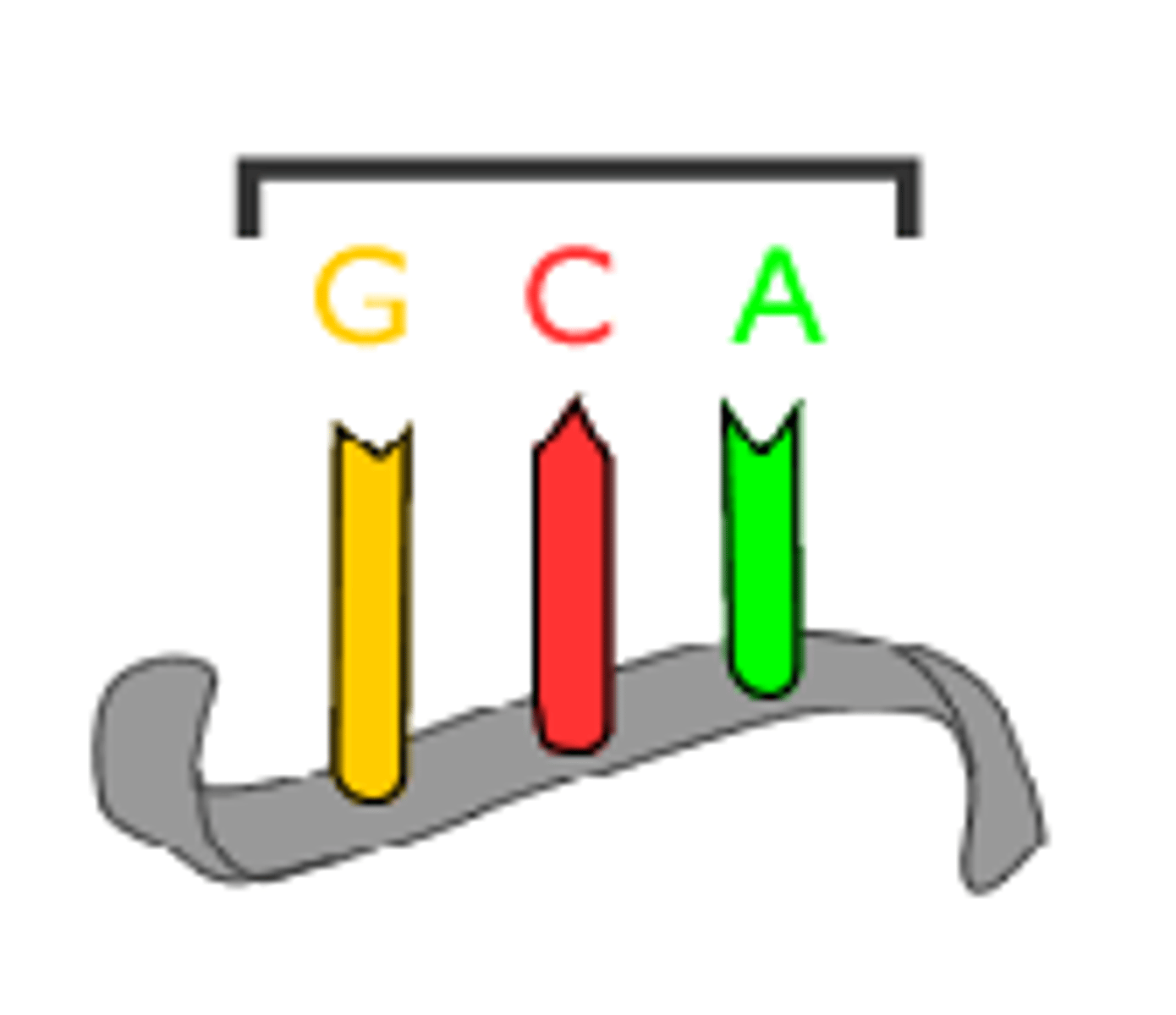
codons
mRNA base triplets.
RNA splicing
Process by which the introns are removed from RNA transcripts and the remaining exons are joined together.
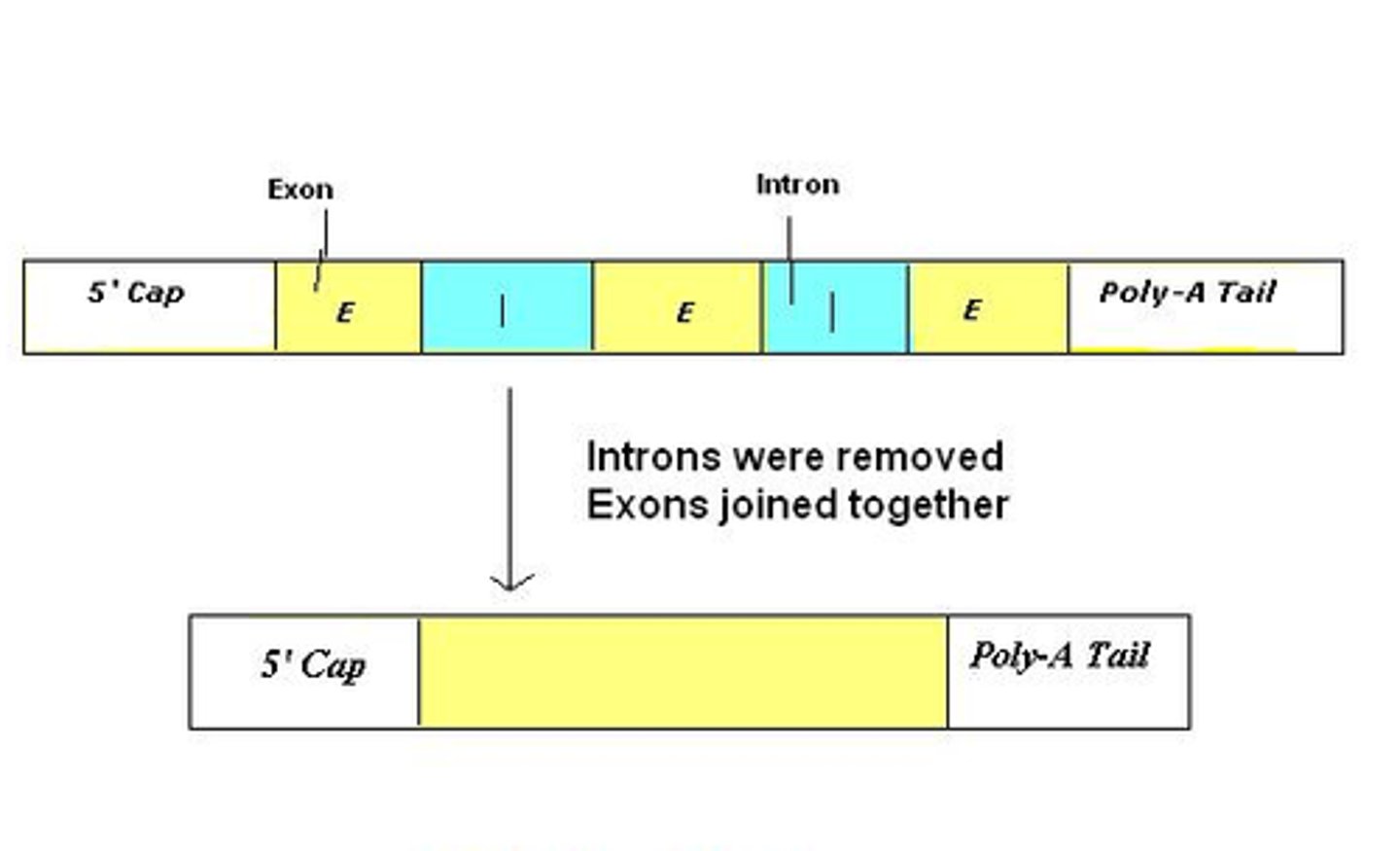
introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
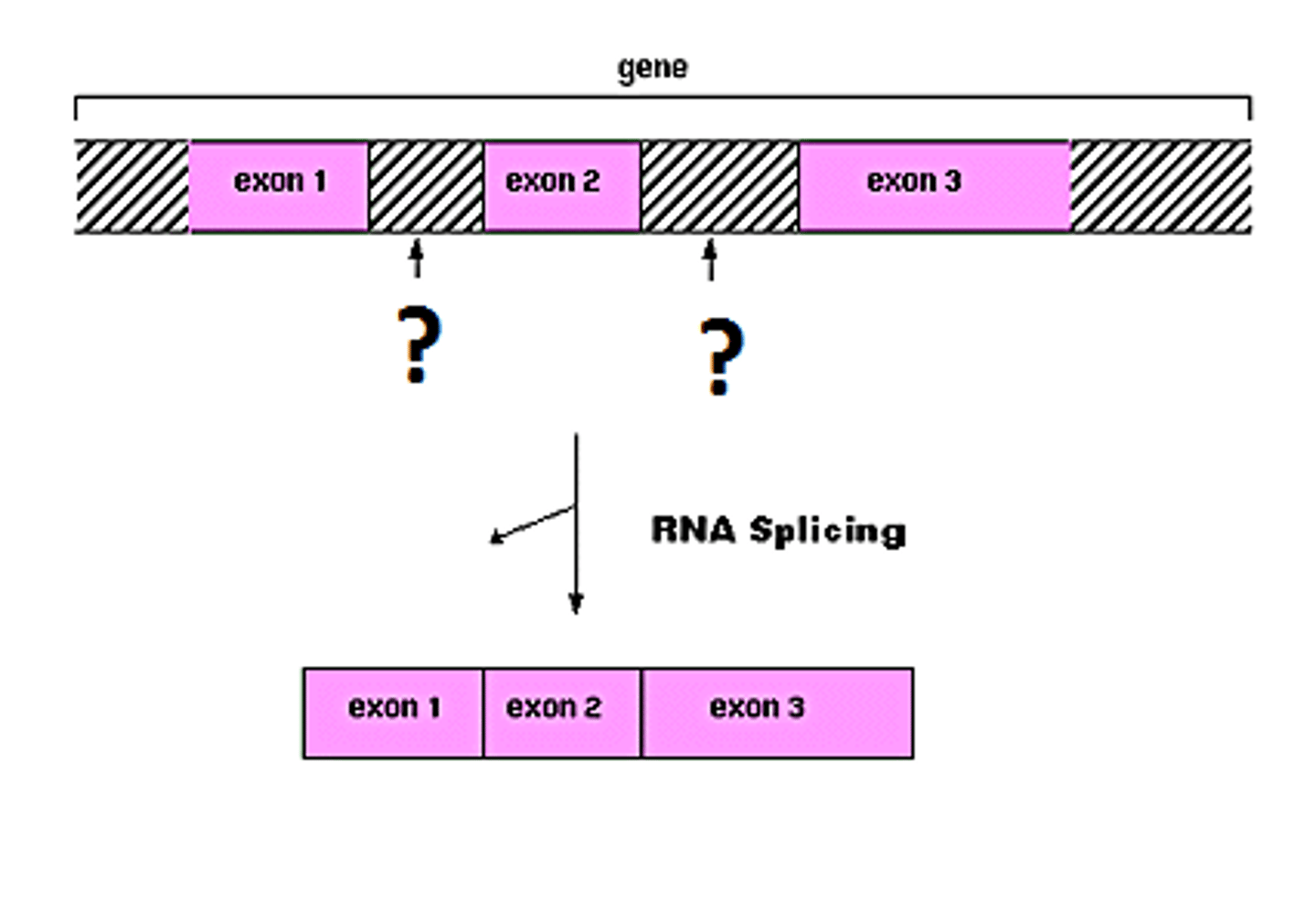
splicosome
Different particles that recognize splice sites are compiled in a large assembly. A complex of RNA and protein subunits. Removes introns from a transcribed pre-RNA segments.
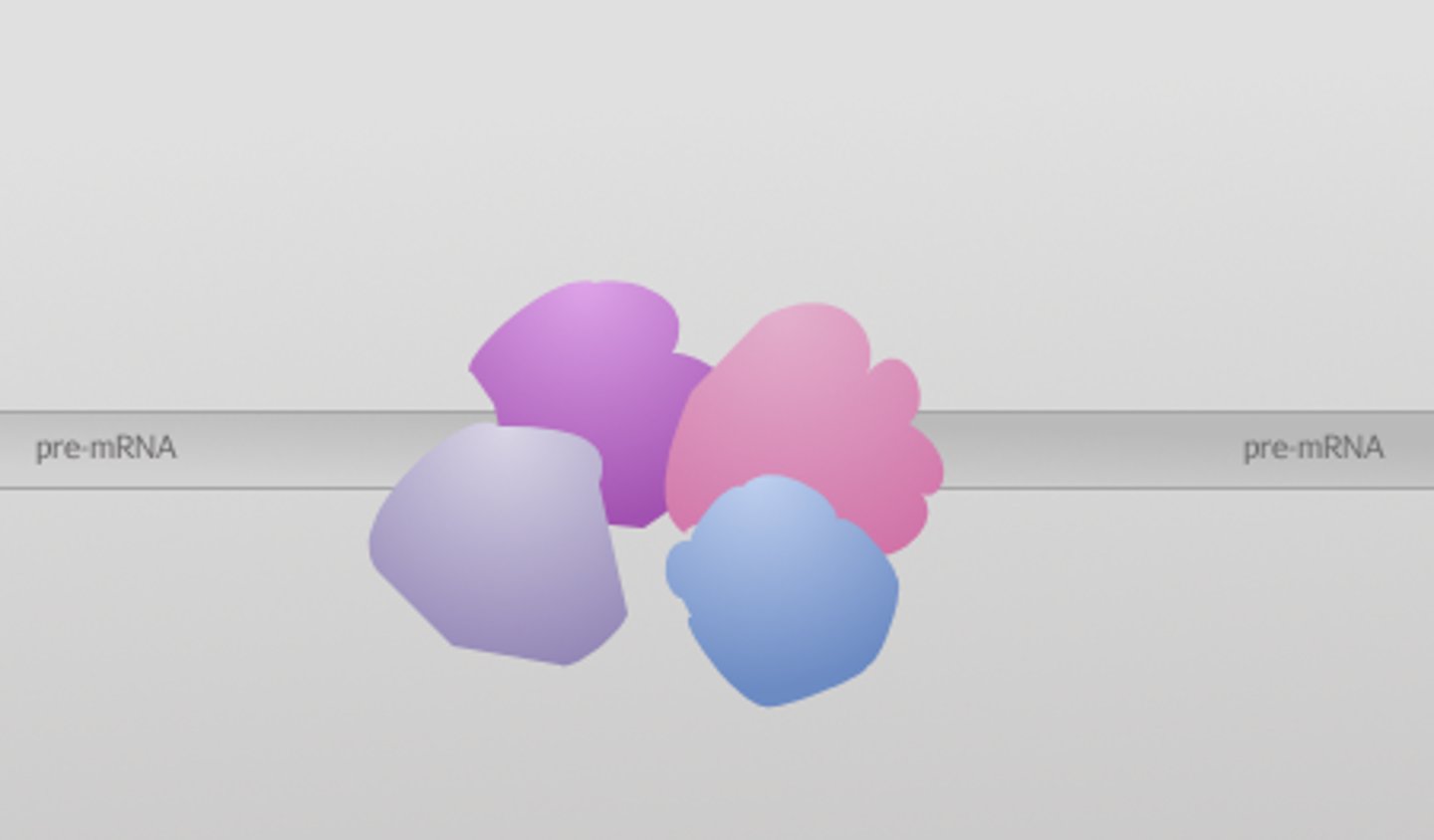

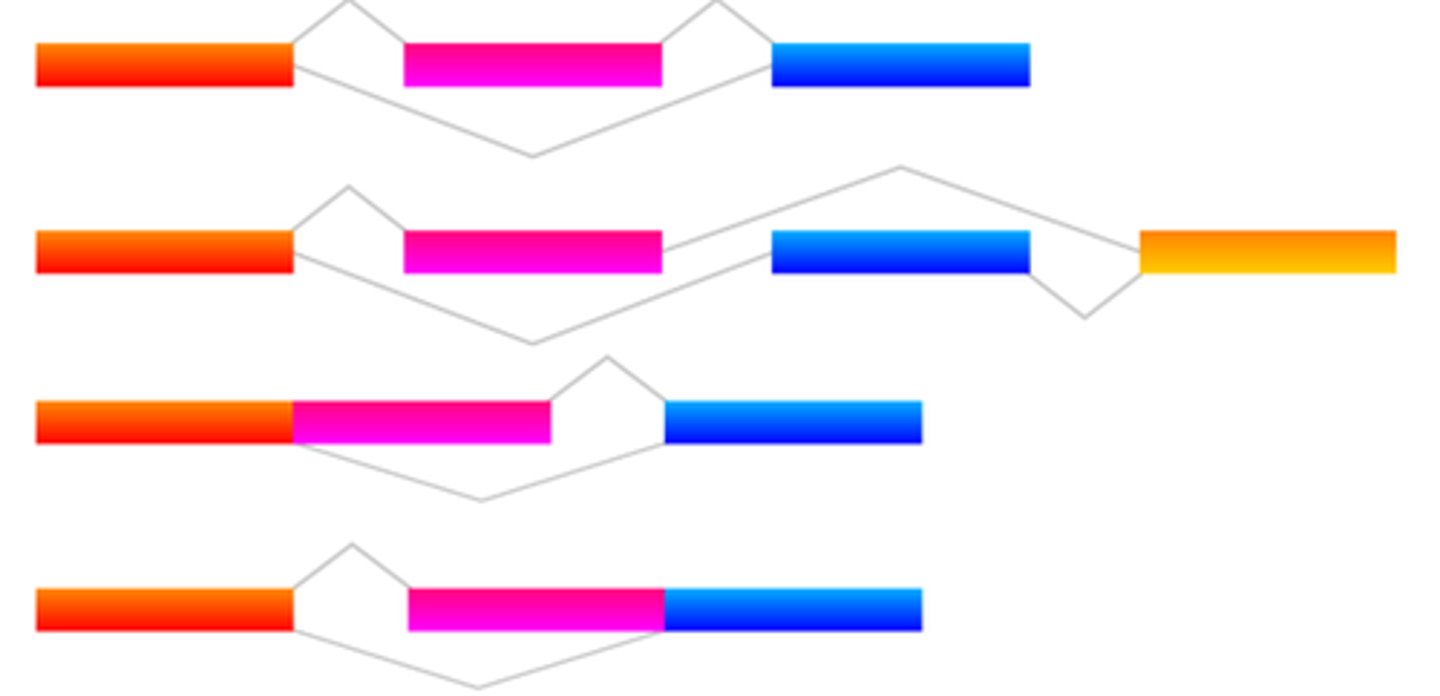
alternative RNA splicing
Genes giving rise to two or more different polypeptides depending upon which segments are treated as exons.
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Interpreter of a series of codons along a mRNA molecule.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA molecules that construct ribosomal subunits.
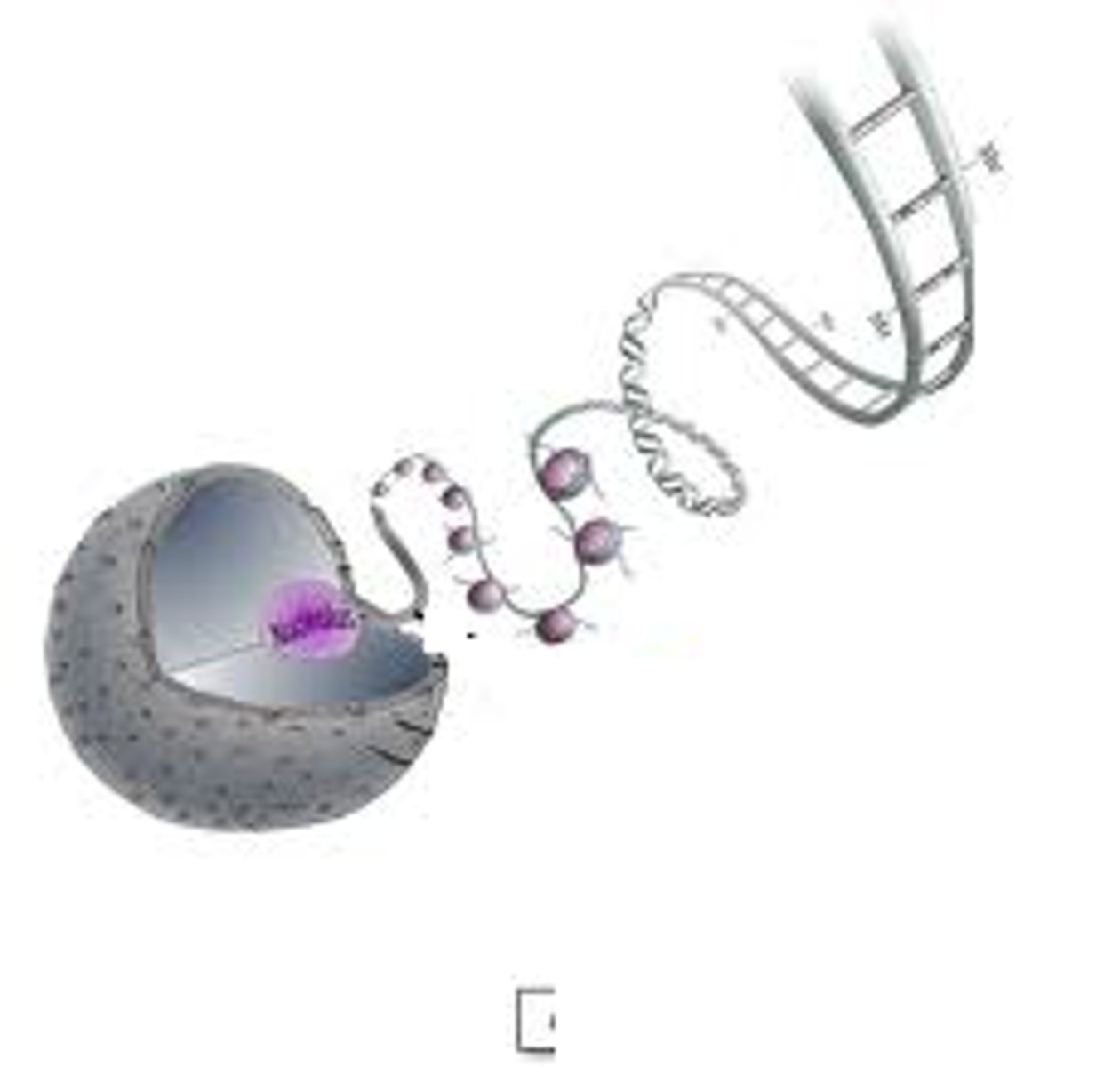
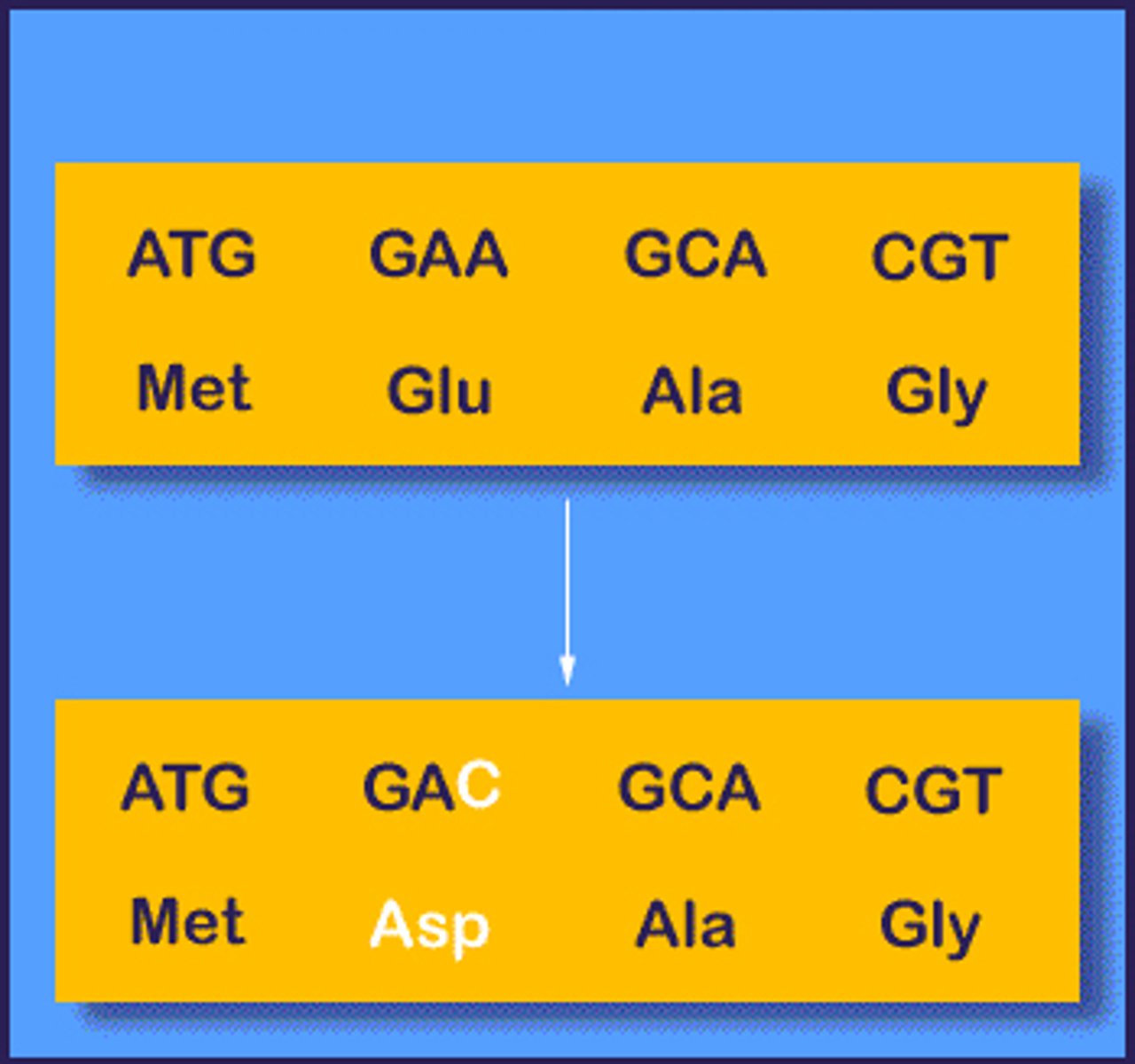
mutations
Random errors in gene replication that lead to a change in the sequence of nucleotides. The source of all genetic diversity.
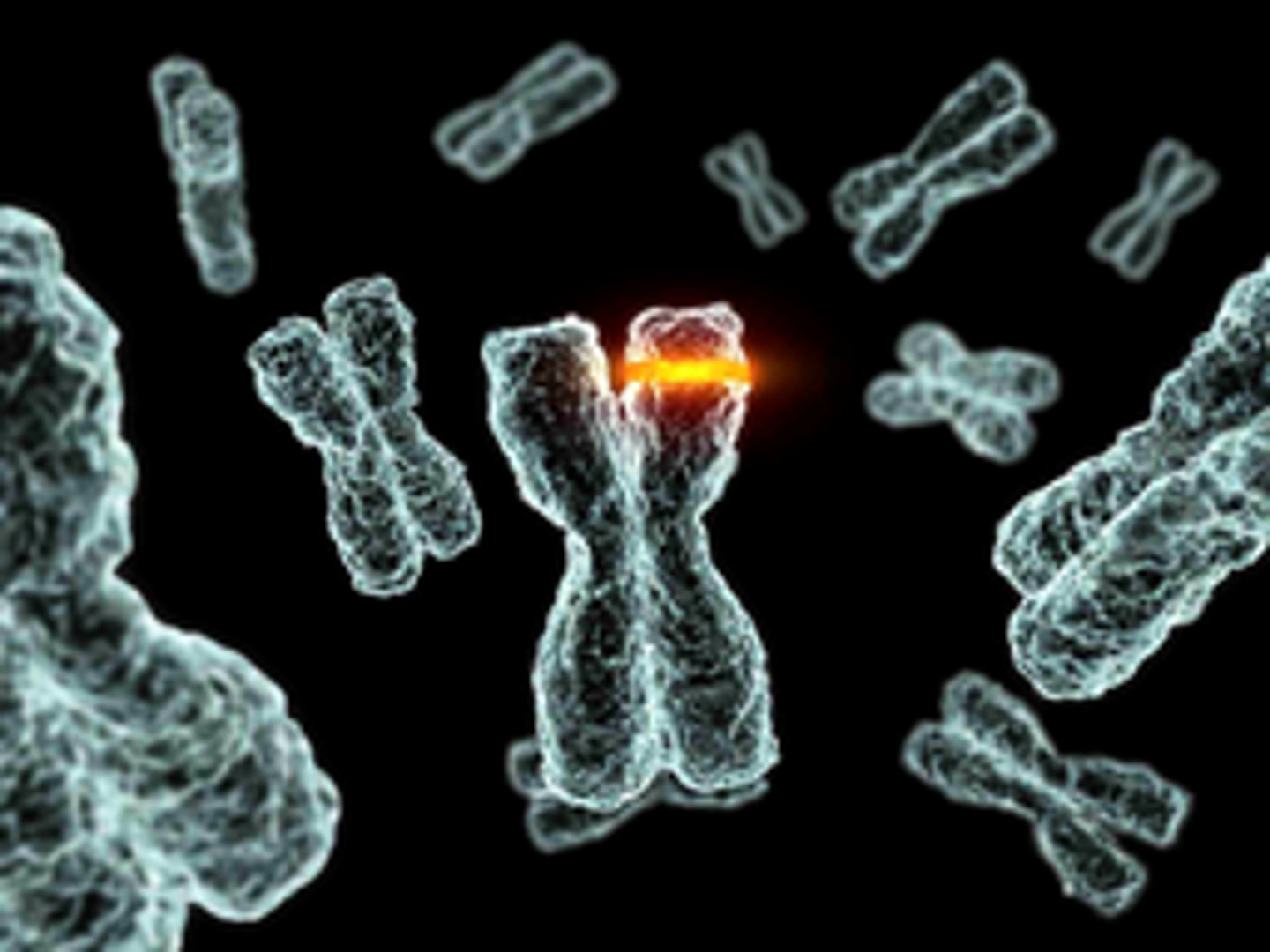
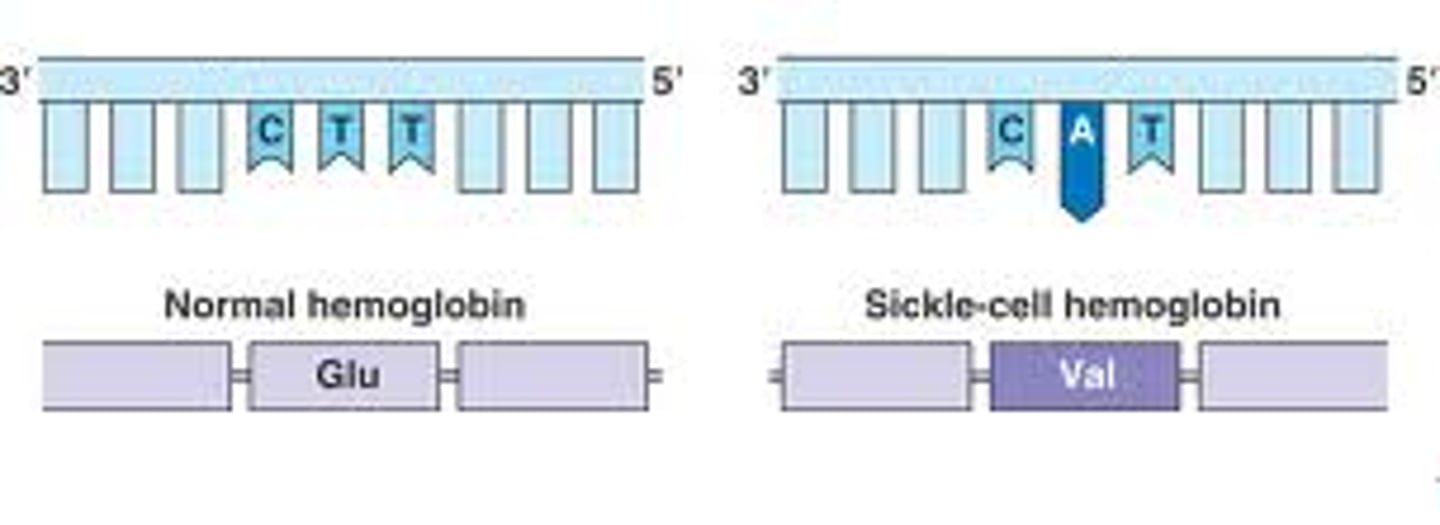
point mutations
chemical changes in just one base pair of a gene
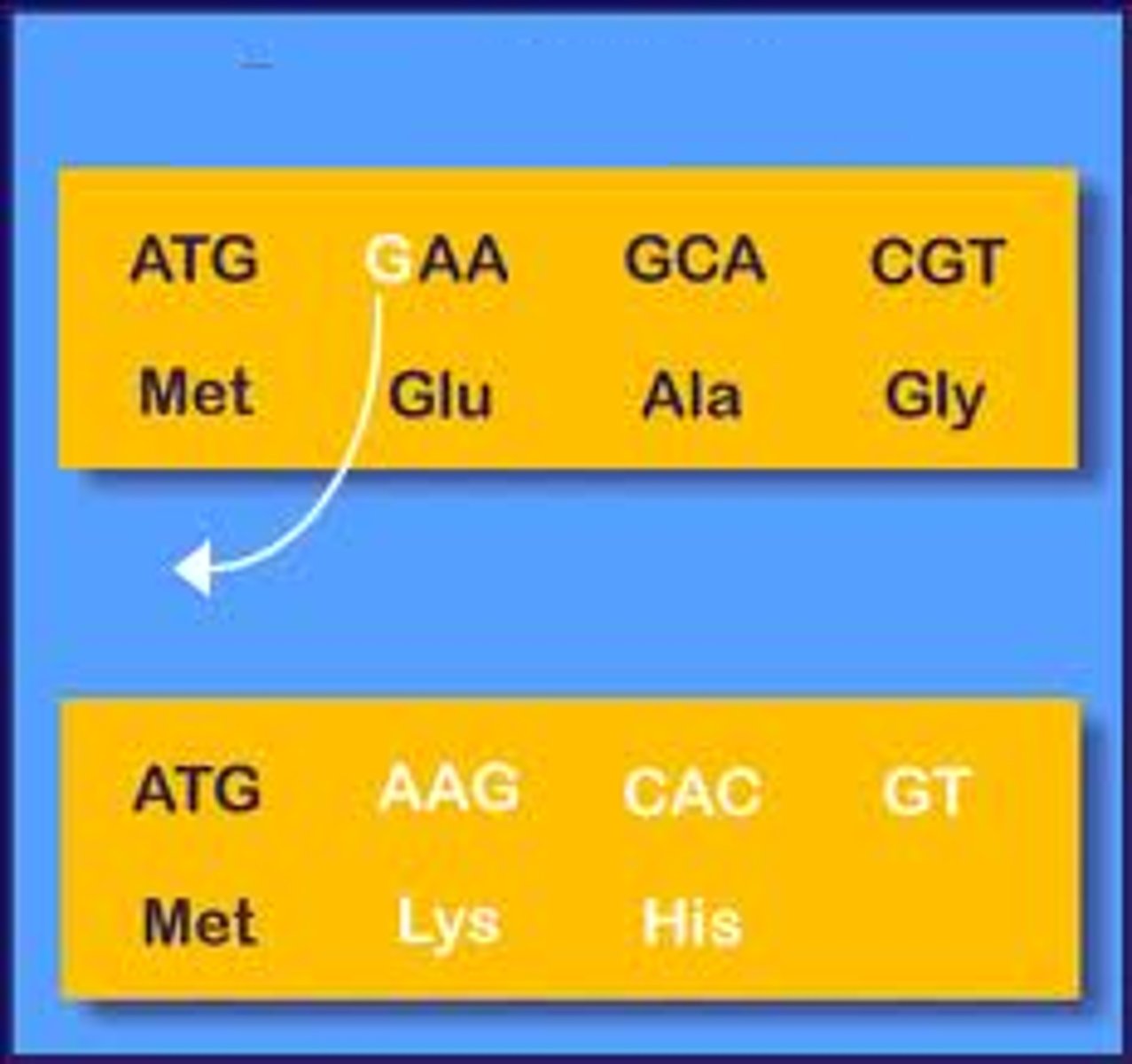
frameshift mutation
Mutation occurring when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three, resulting in improper grouping of nucleotides into codons.
mutagens
physical and chemical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations

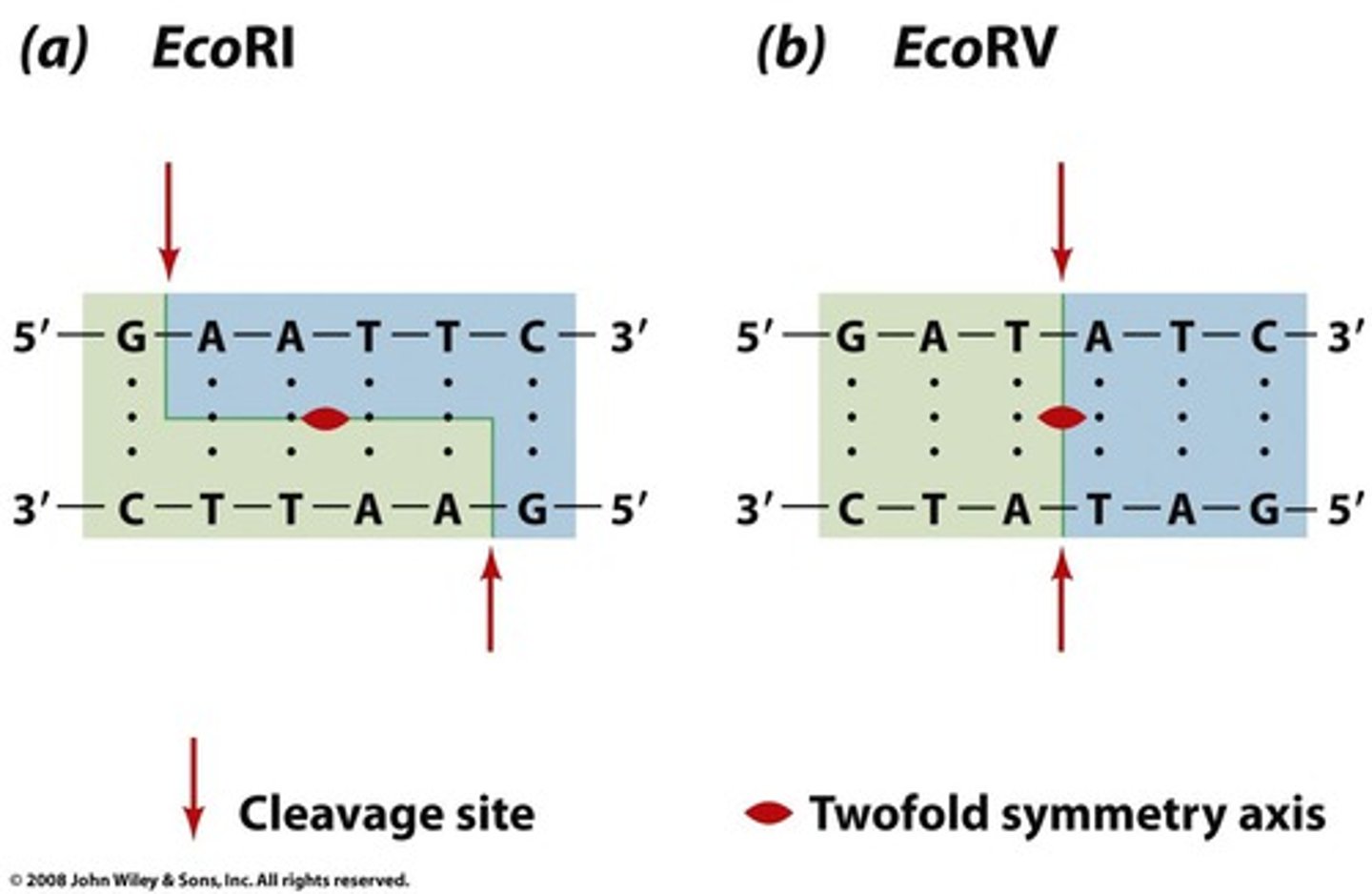
Blunt Ends
the result when restriction enzymes cut DNA straight across both strands, no overlapping ('sticky') ends
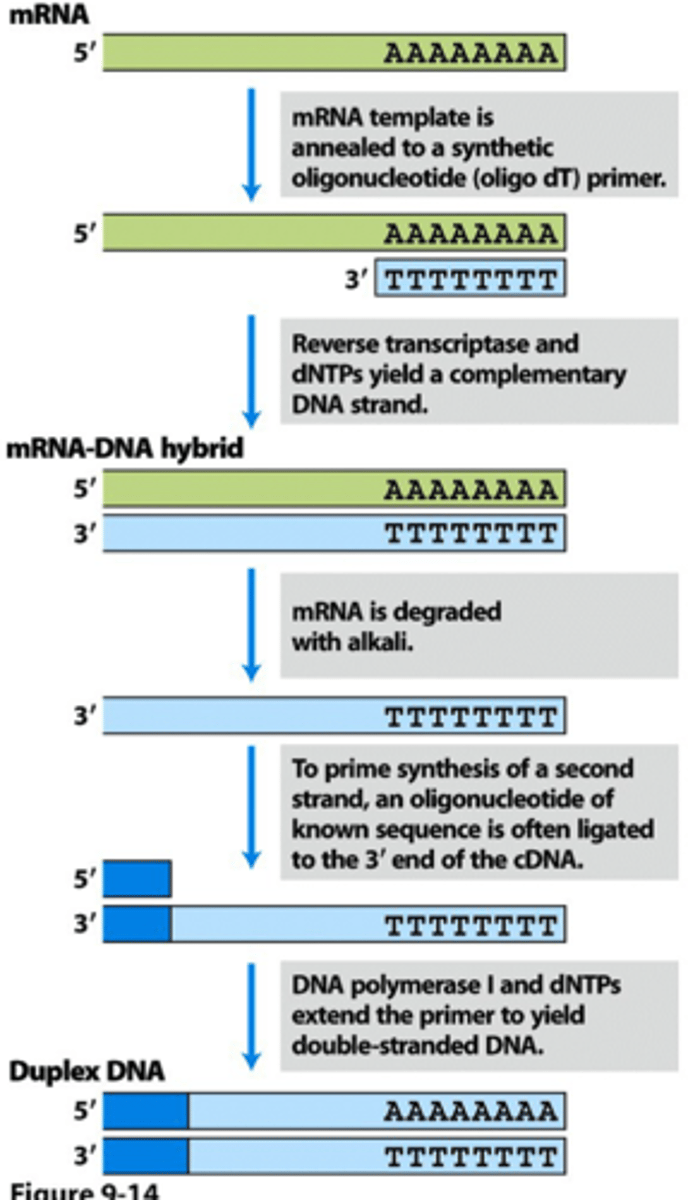
cDNA
DNA produced synthetically by reverse transcribing mRNA, (with the enzyme reverse transcriptase) contains no introns.
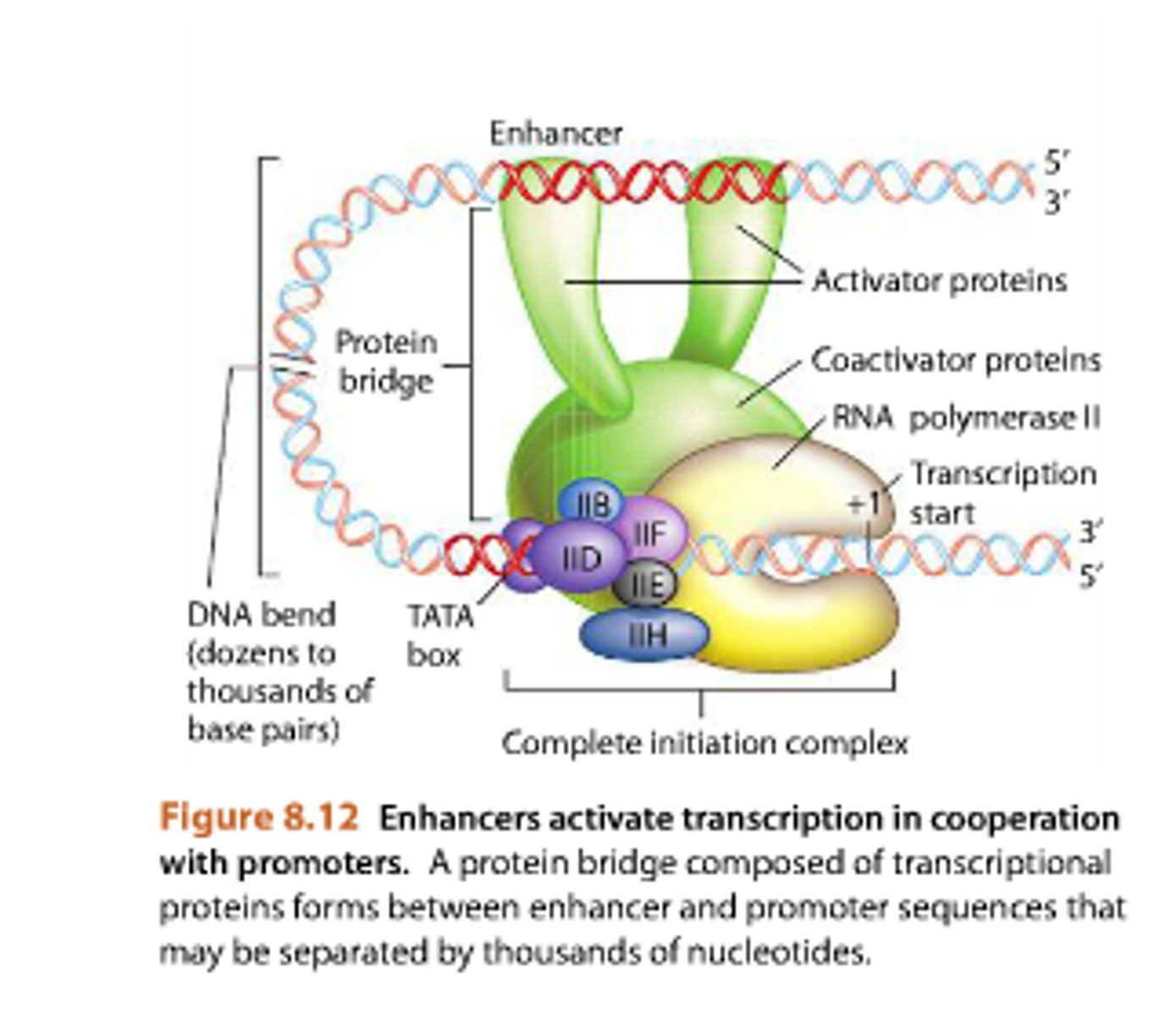
Enhancer sequences
DNA sequences that bind to specific transcriptional proteins that help stimulate transcription of eukaryotic genes and are usually quite far from the promoter regions. (can be upstream or downstream from the promoter regions)
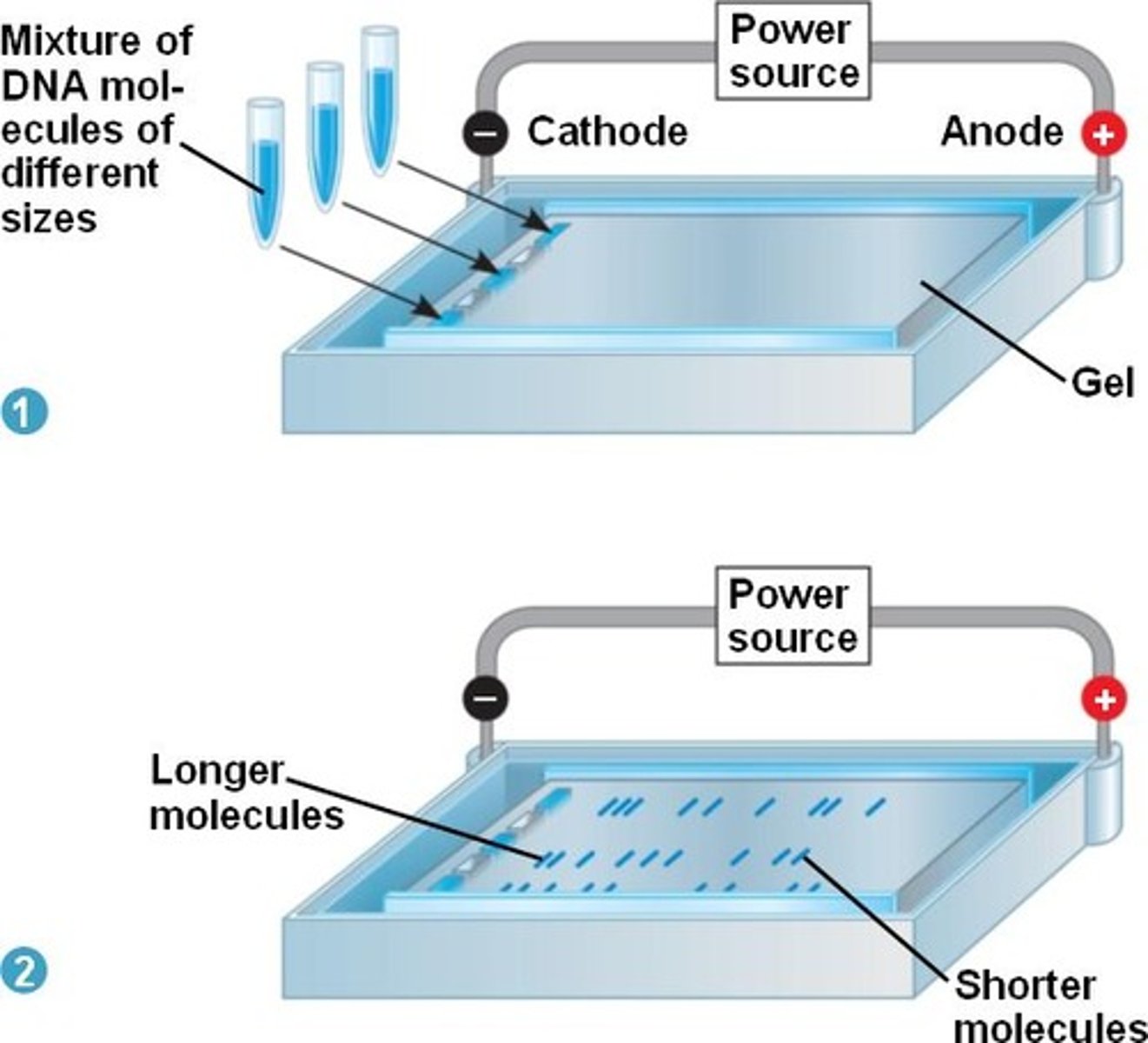
Gel Electrophoresis
The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electrical field in a gel.
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for the production of a protein or a portion of protein, thereby causing a trait
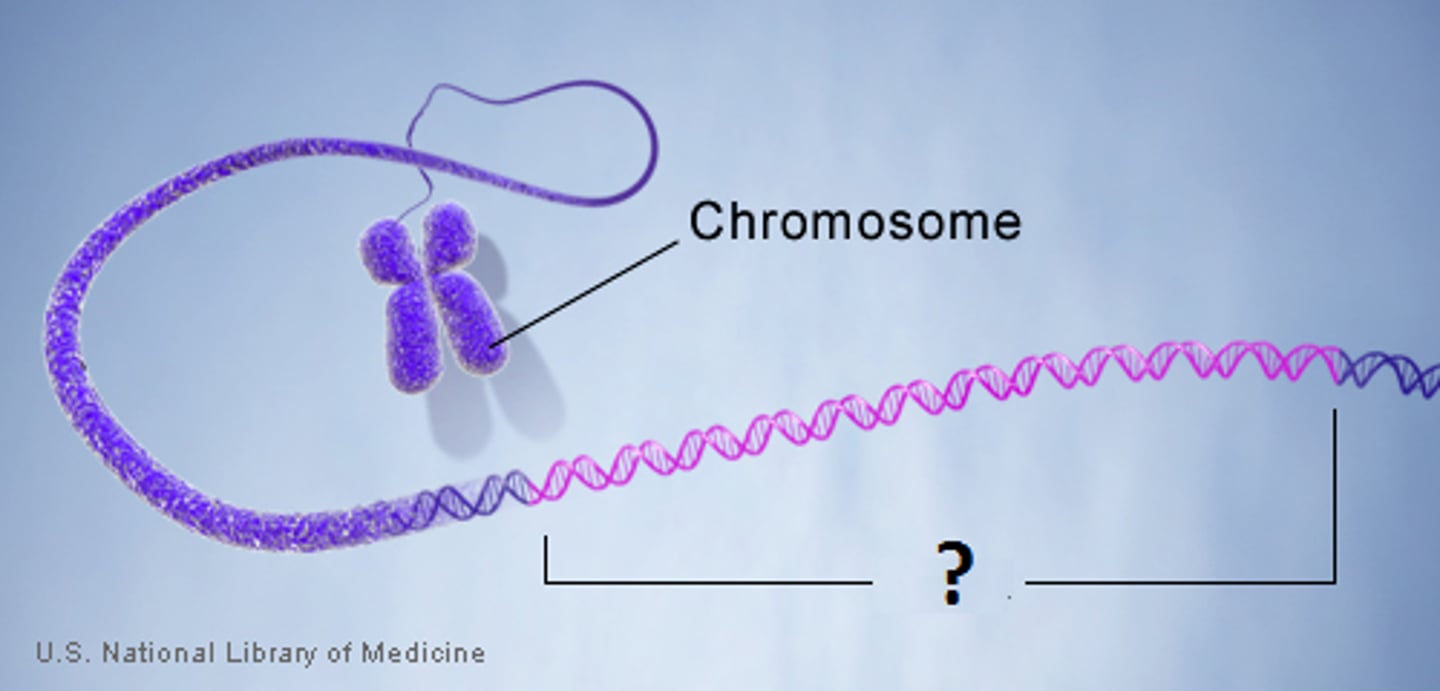
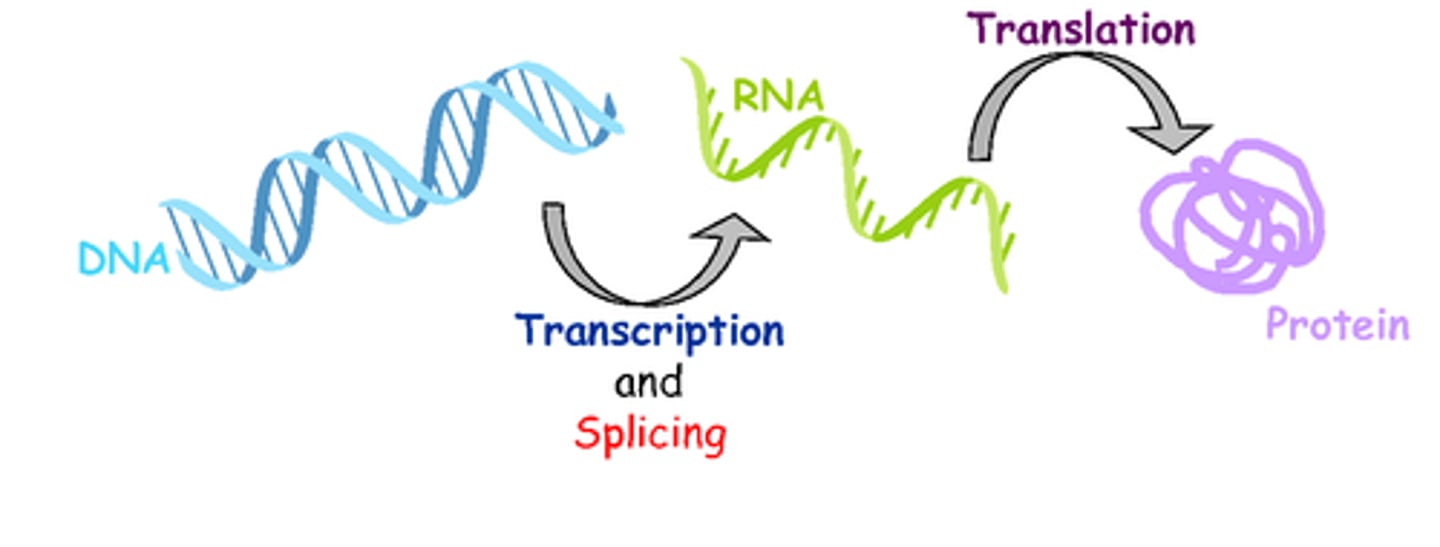
Gene Expression
Conversion of the information encoded in a gene first into messenger RNA and then to a protein.
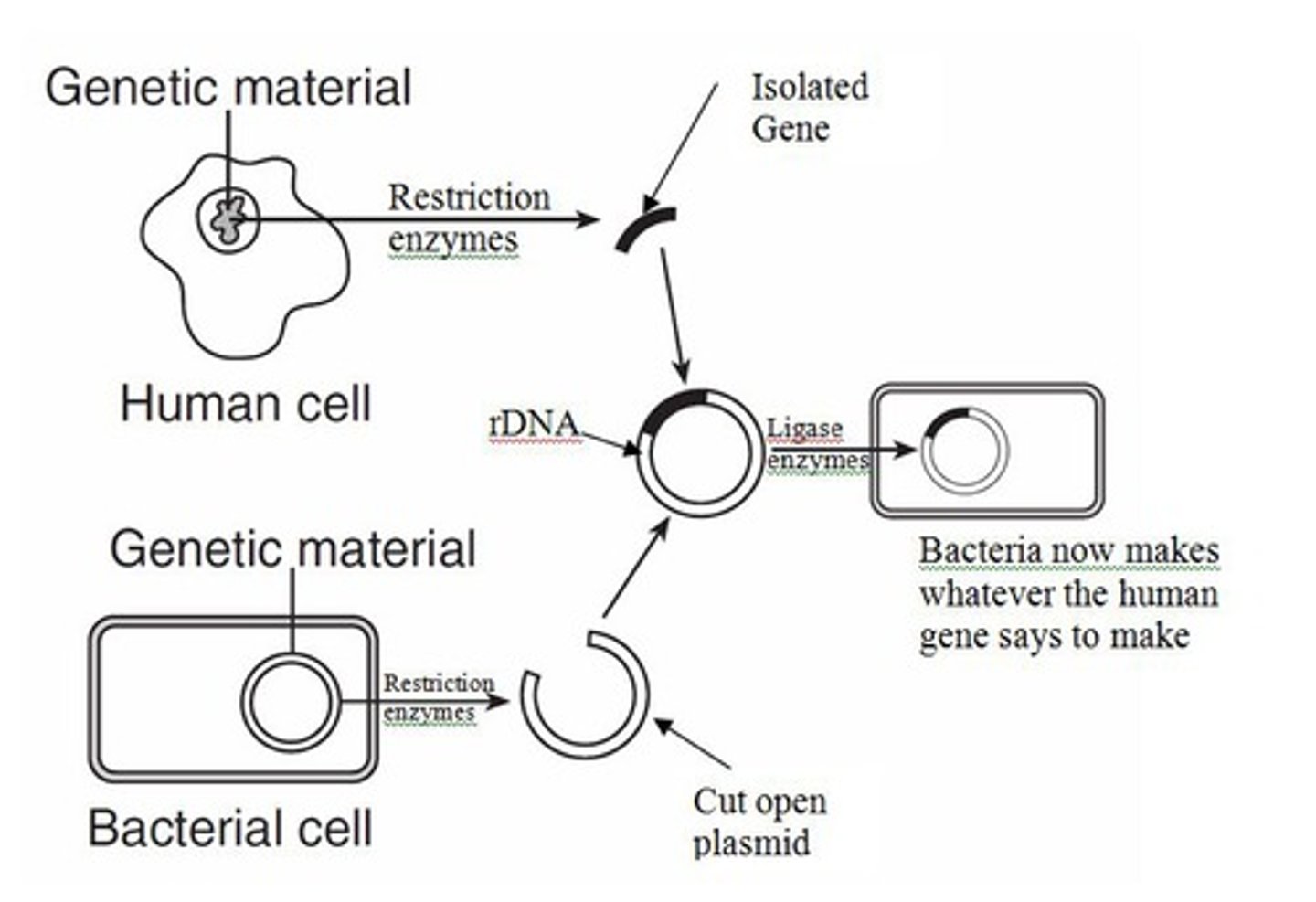
Genetic Engineering
Manipulating/altering genetic material to produce desirable functions/outcomes
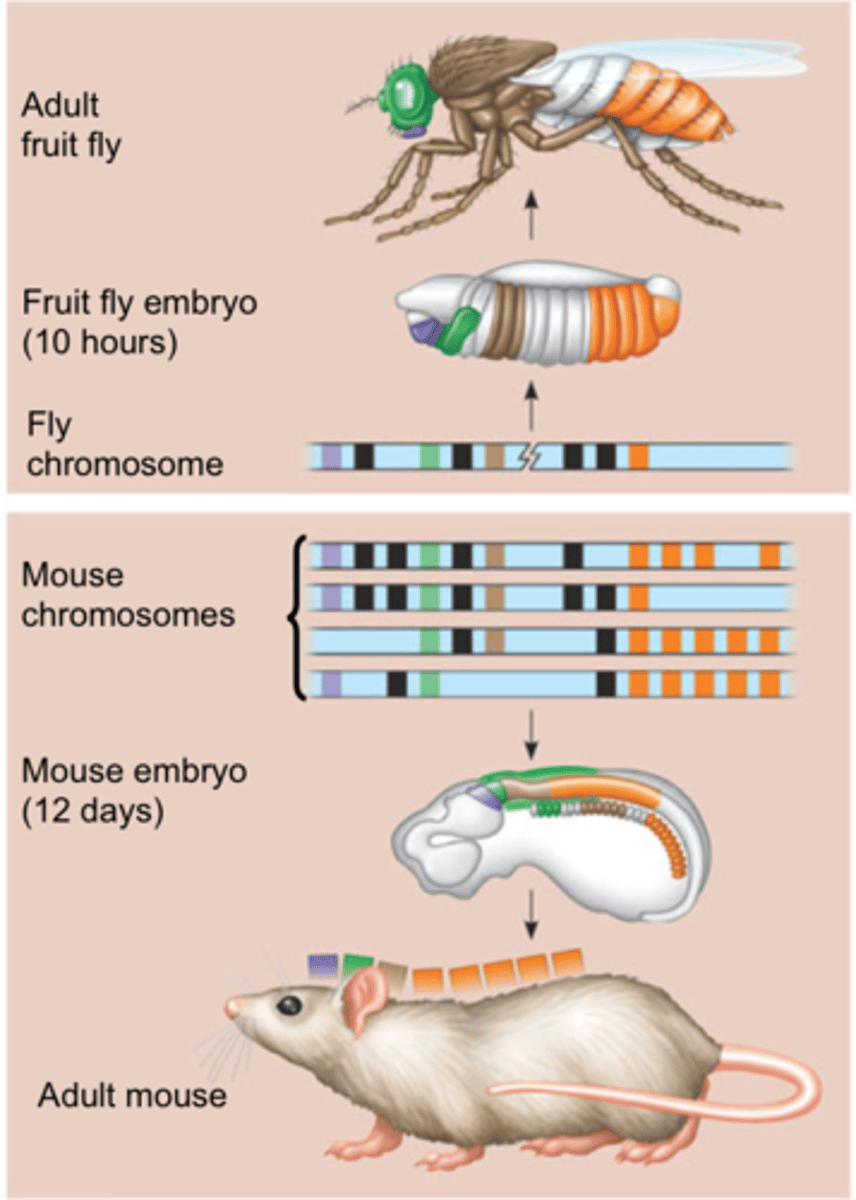
Hox Genes
a group of related genes that control the body plan of an embryo along the anterior-posterior (head-tail) axis
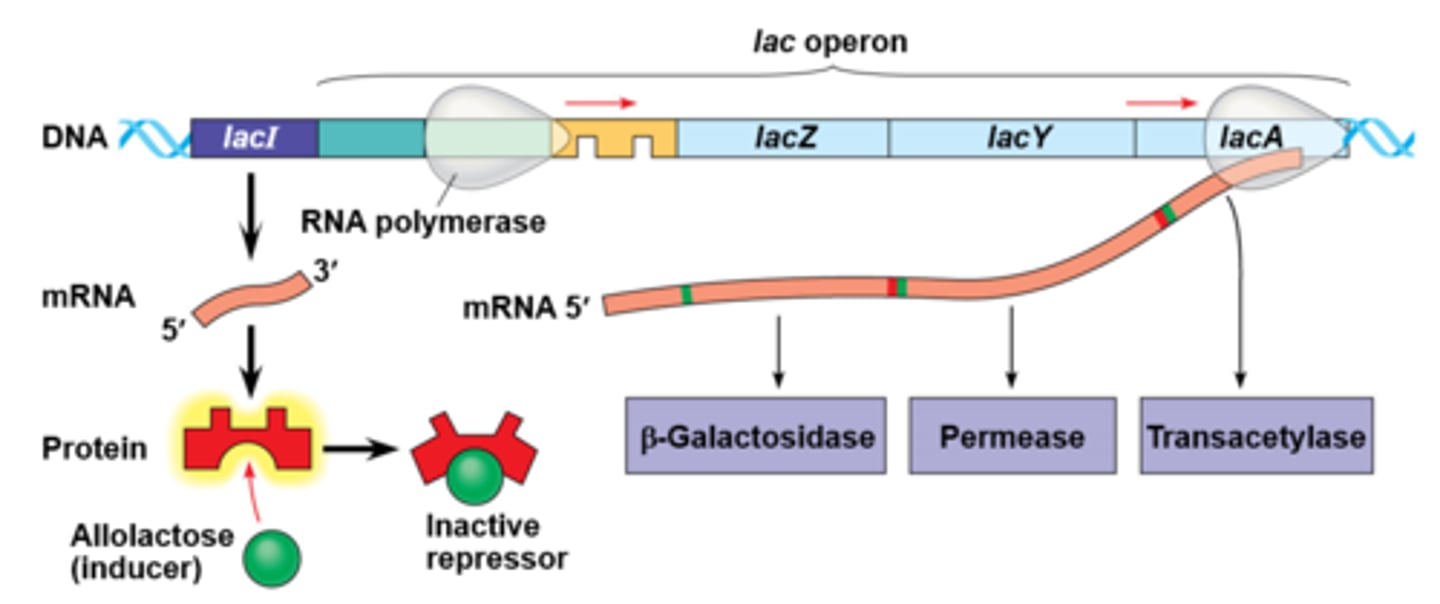
Inducible Operon
usually off, but can be stimulated when a specific small molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (example lac operon)
Mutation
A change in the nucleotide-base sequence of a DNA molecule
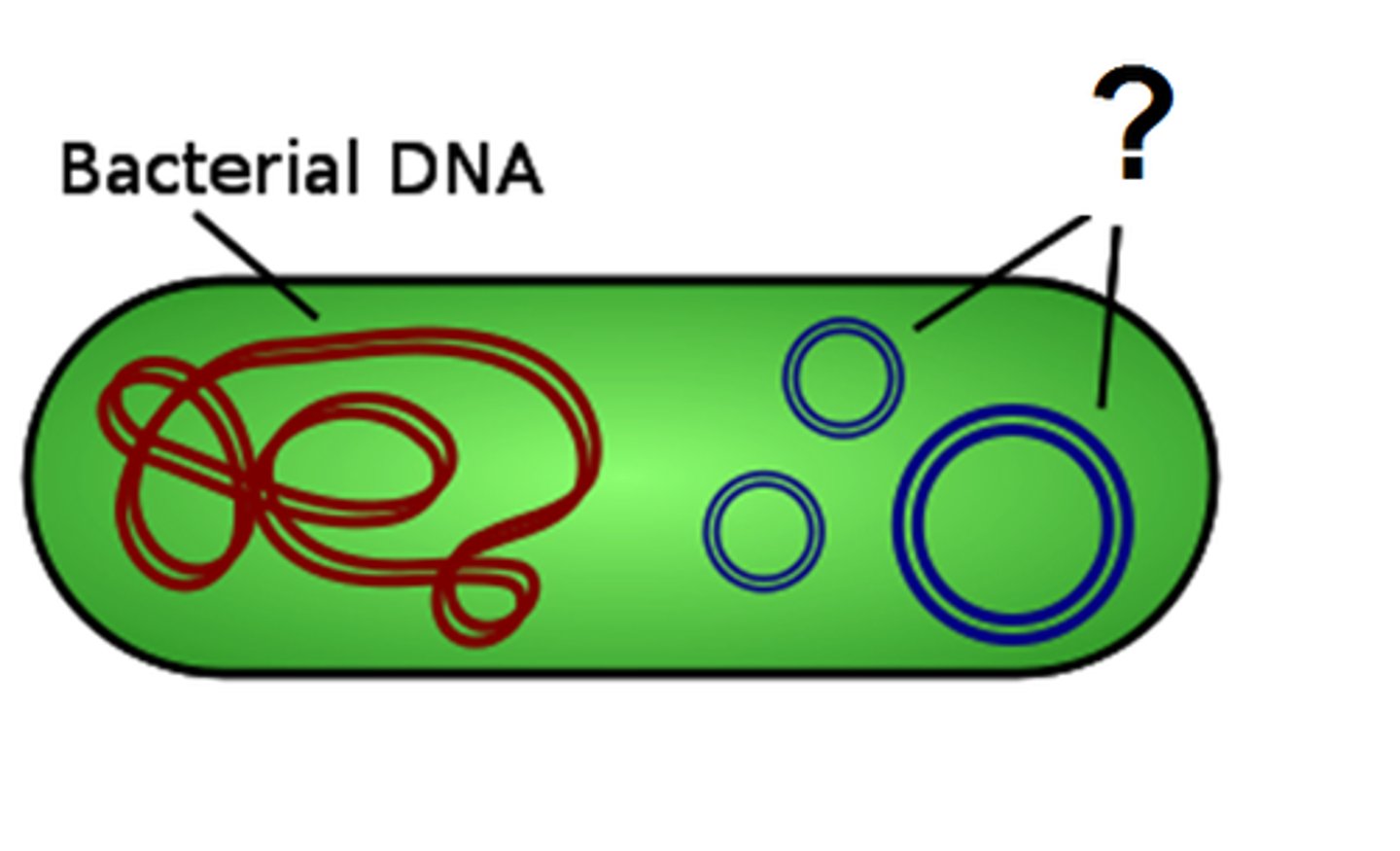
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
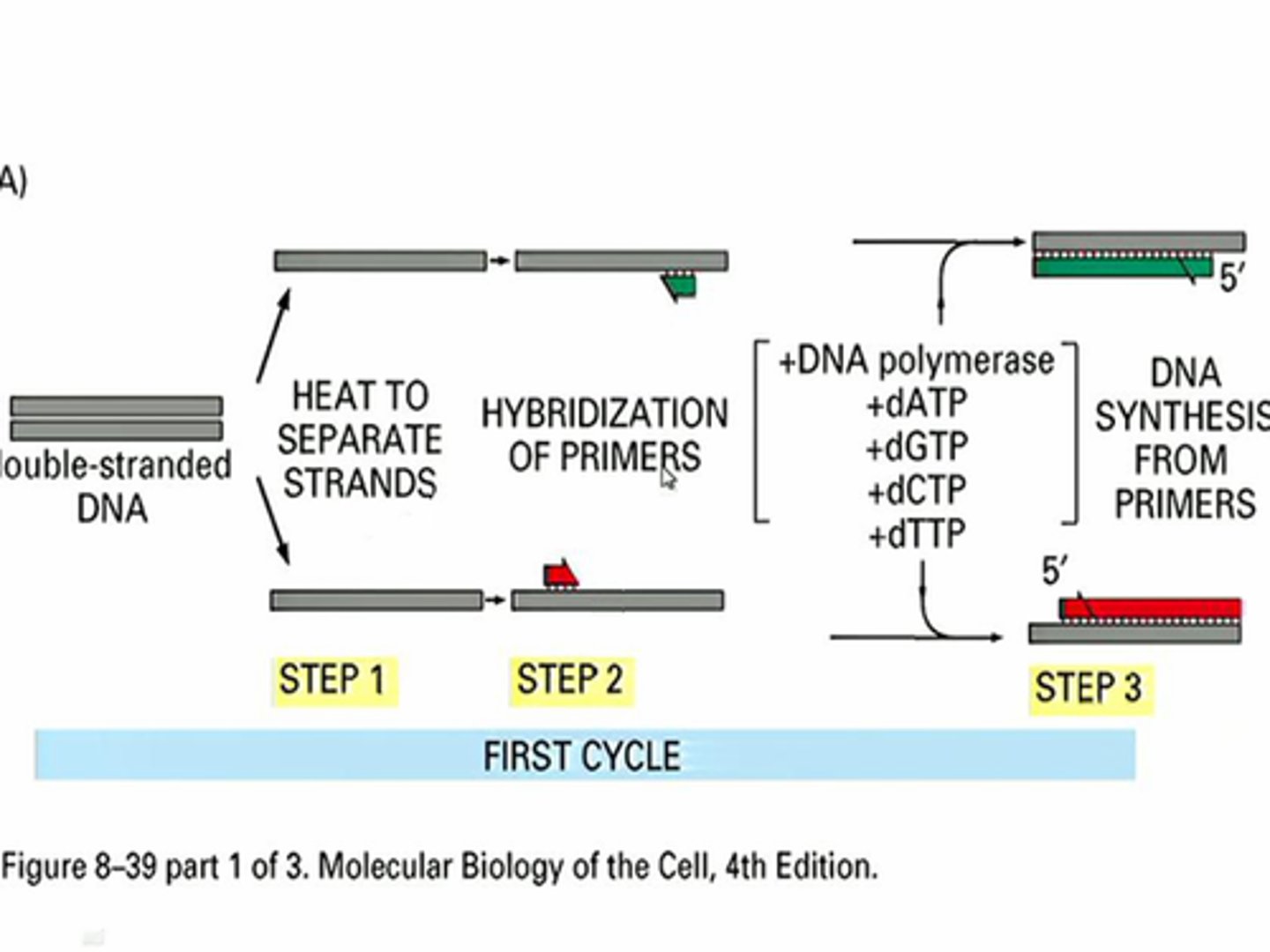
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A cell-free, automated technique by which a piece of DNA can be rapidly copied or amplified. Useful in genetic engineering.
Promoter
A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing mRNA.
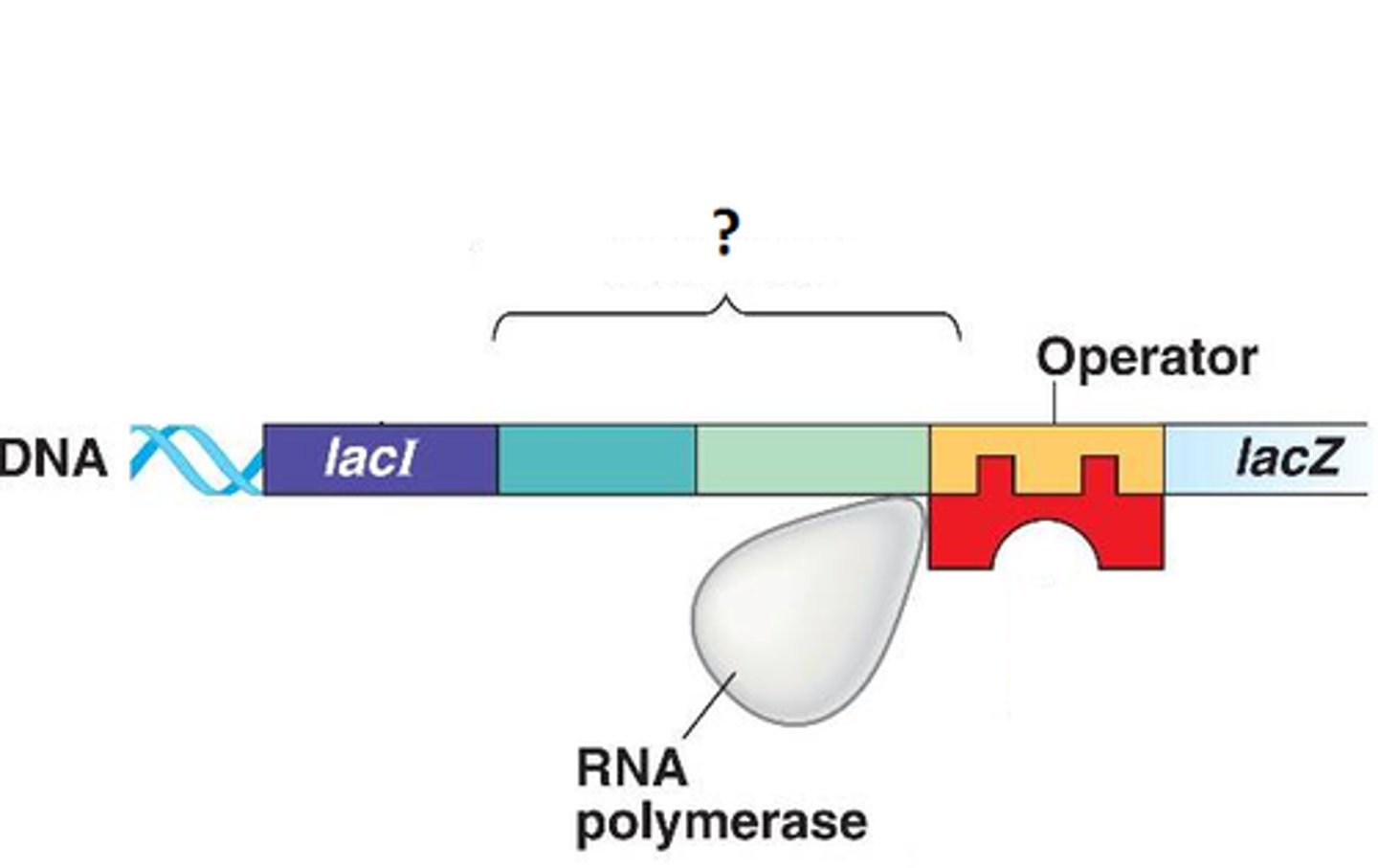
Recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
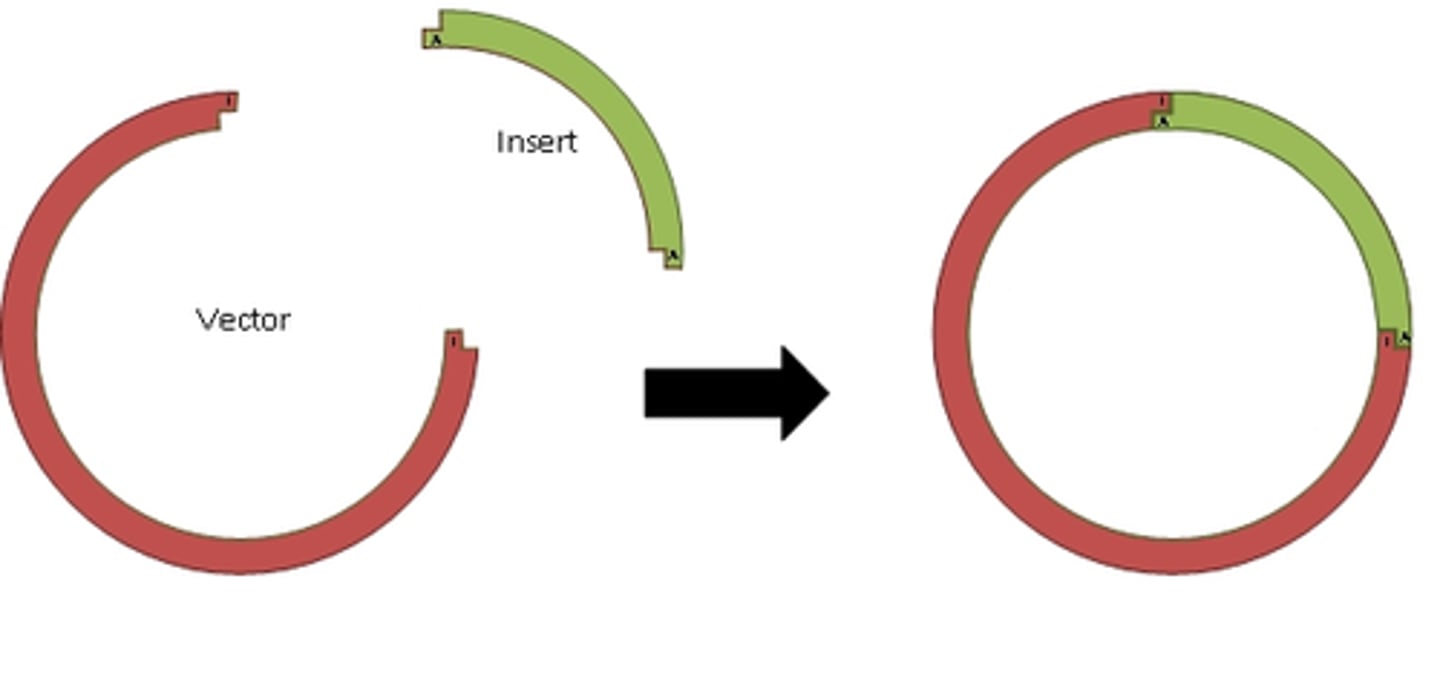
Repressible Operon
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited when a specific small molecule binds allosterically to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan)
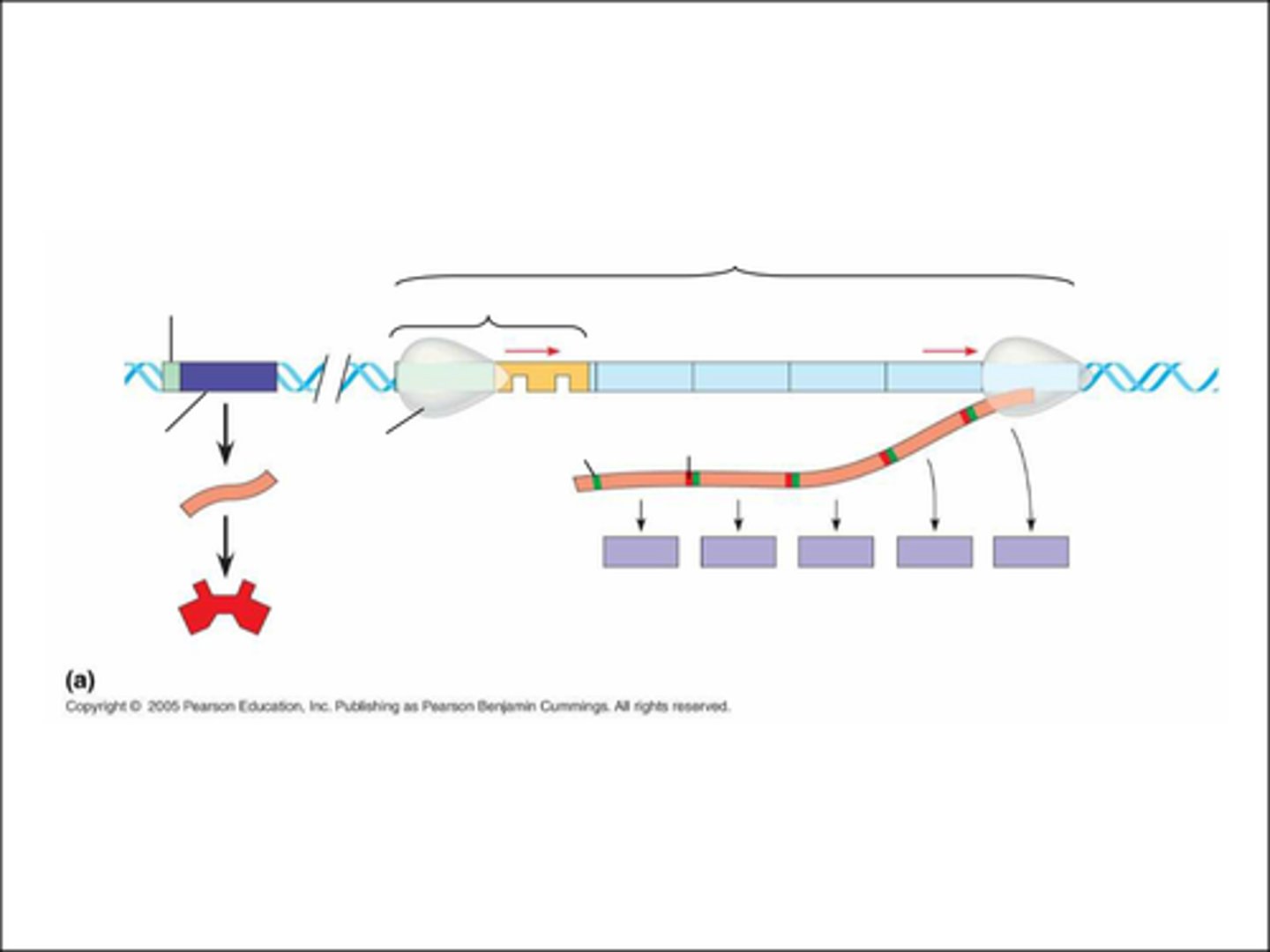
Restriction Enzyme
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides
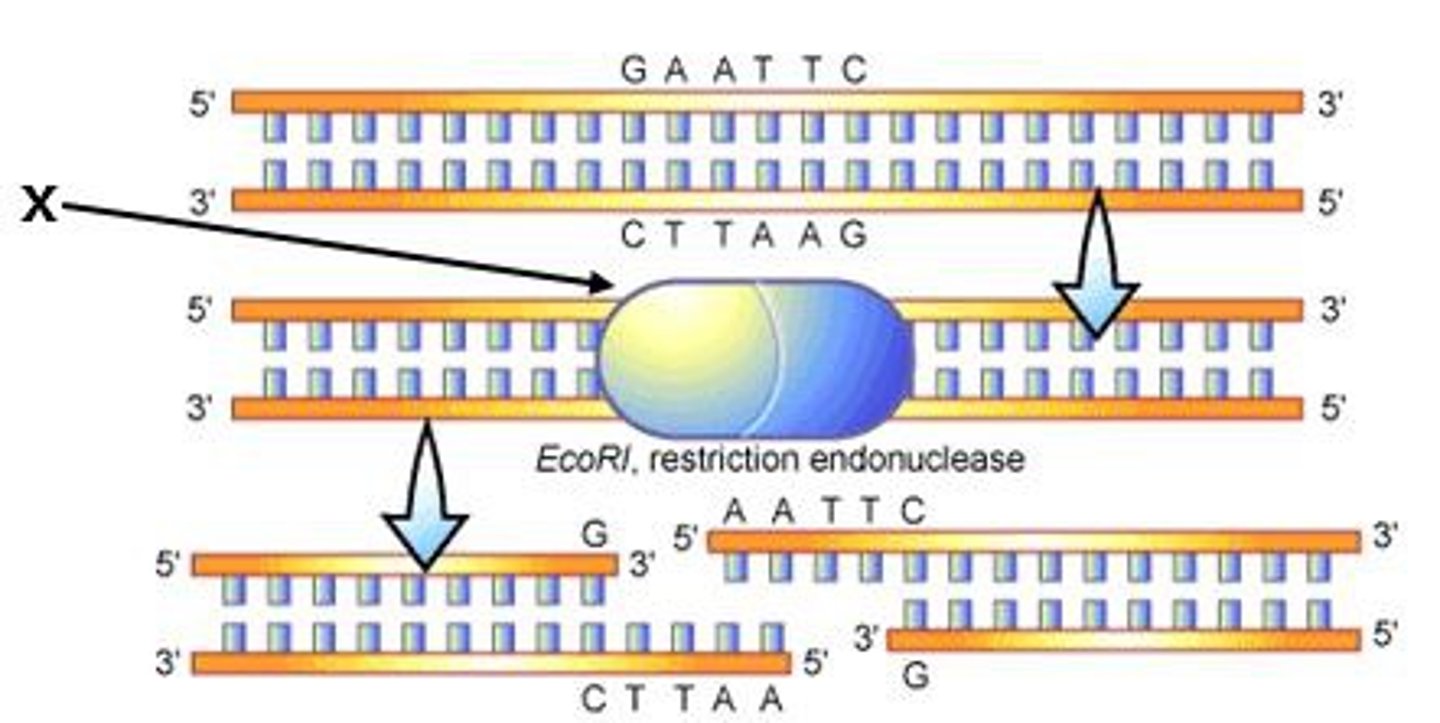
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis
A common method of DNA fingerprinting, the comparison set of restriction fragments produced by DNA from individuals
RNAi
biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules
Sticky Ends
the uneven ends of a double-stranded DNA molecule that has been cut with a restriction enzyme
Transcription Factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
Transgenic Organism
An organism that contains DNA from another species
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria

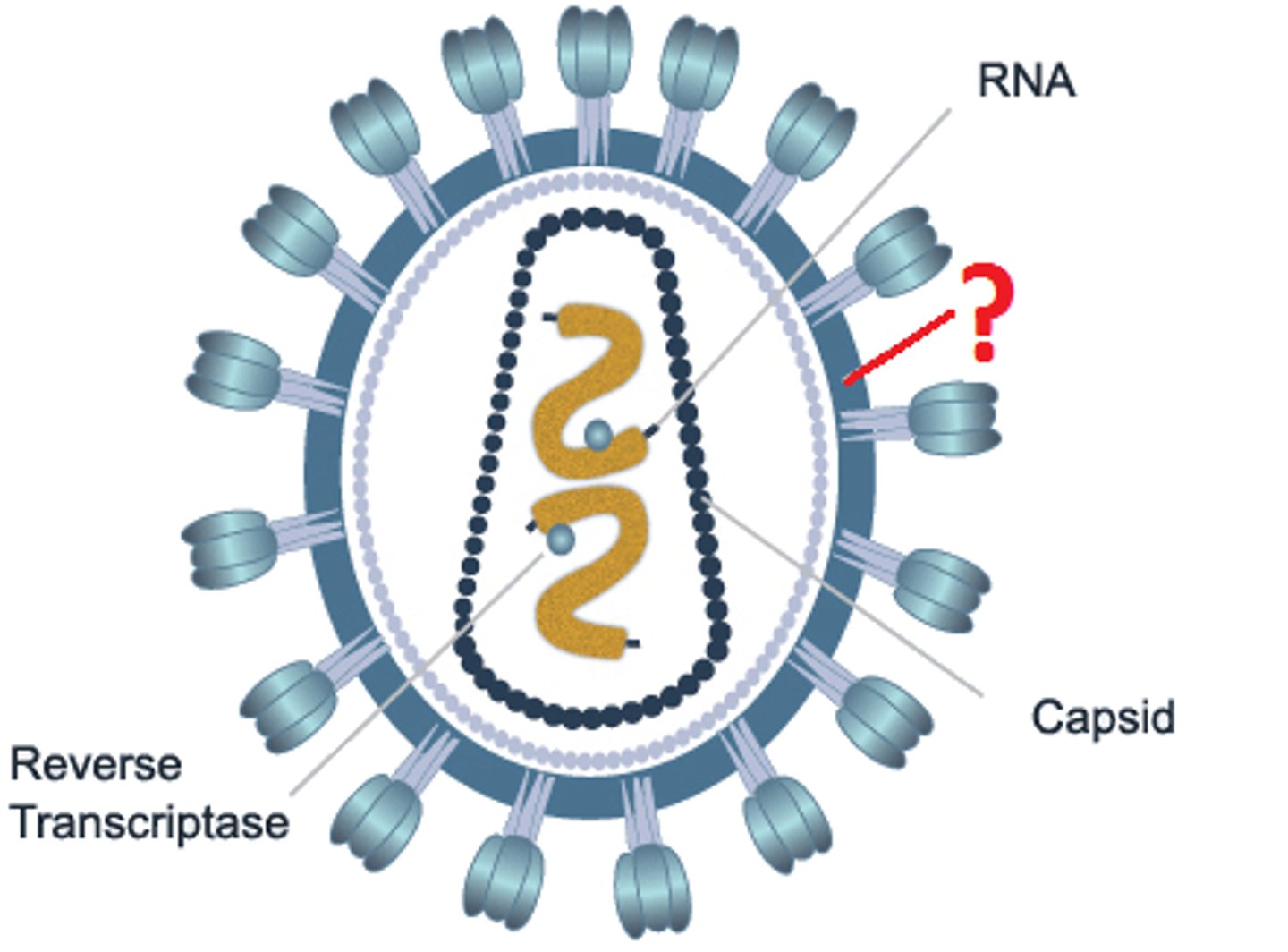
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
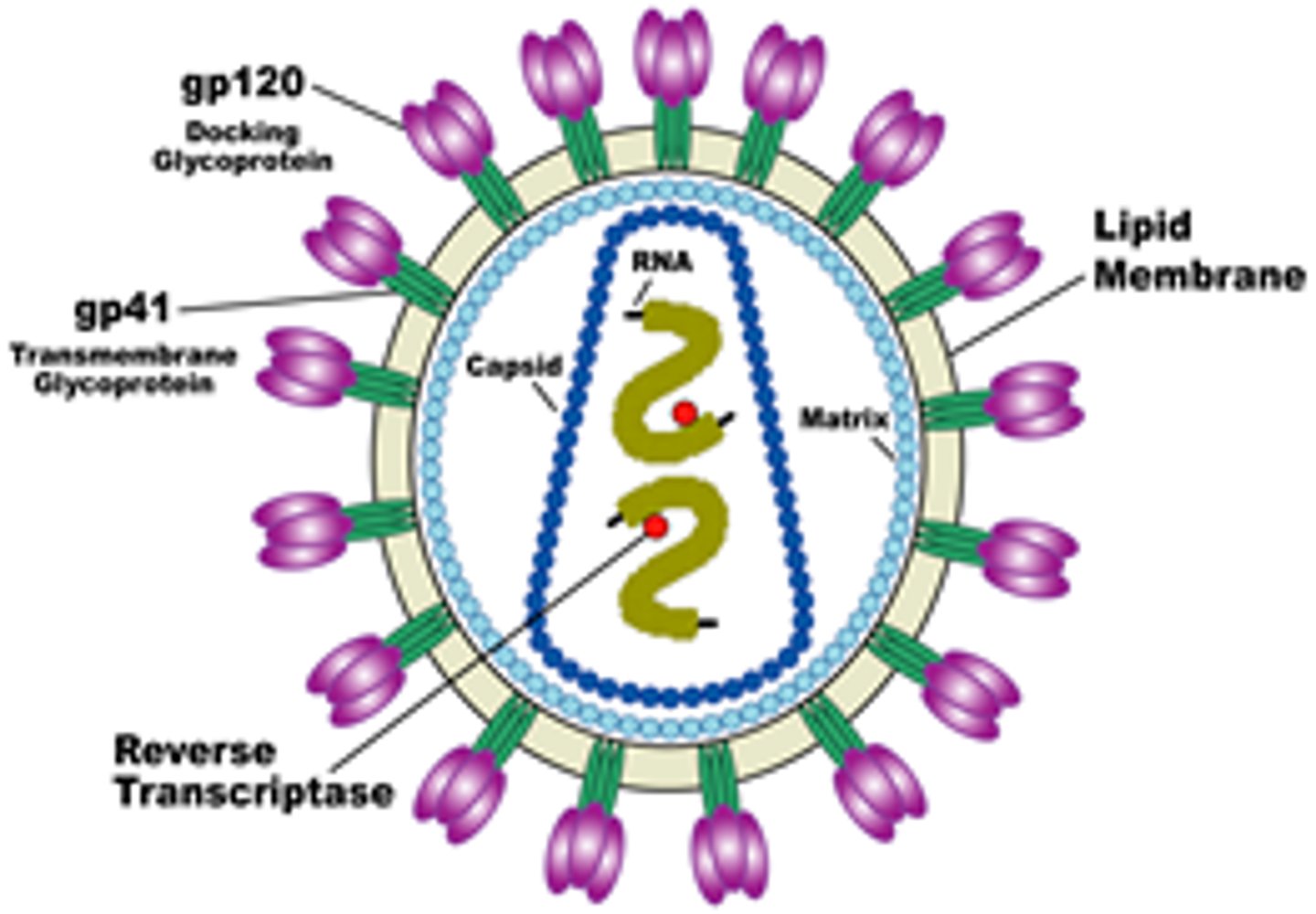
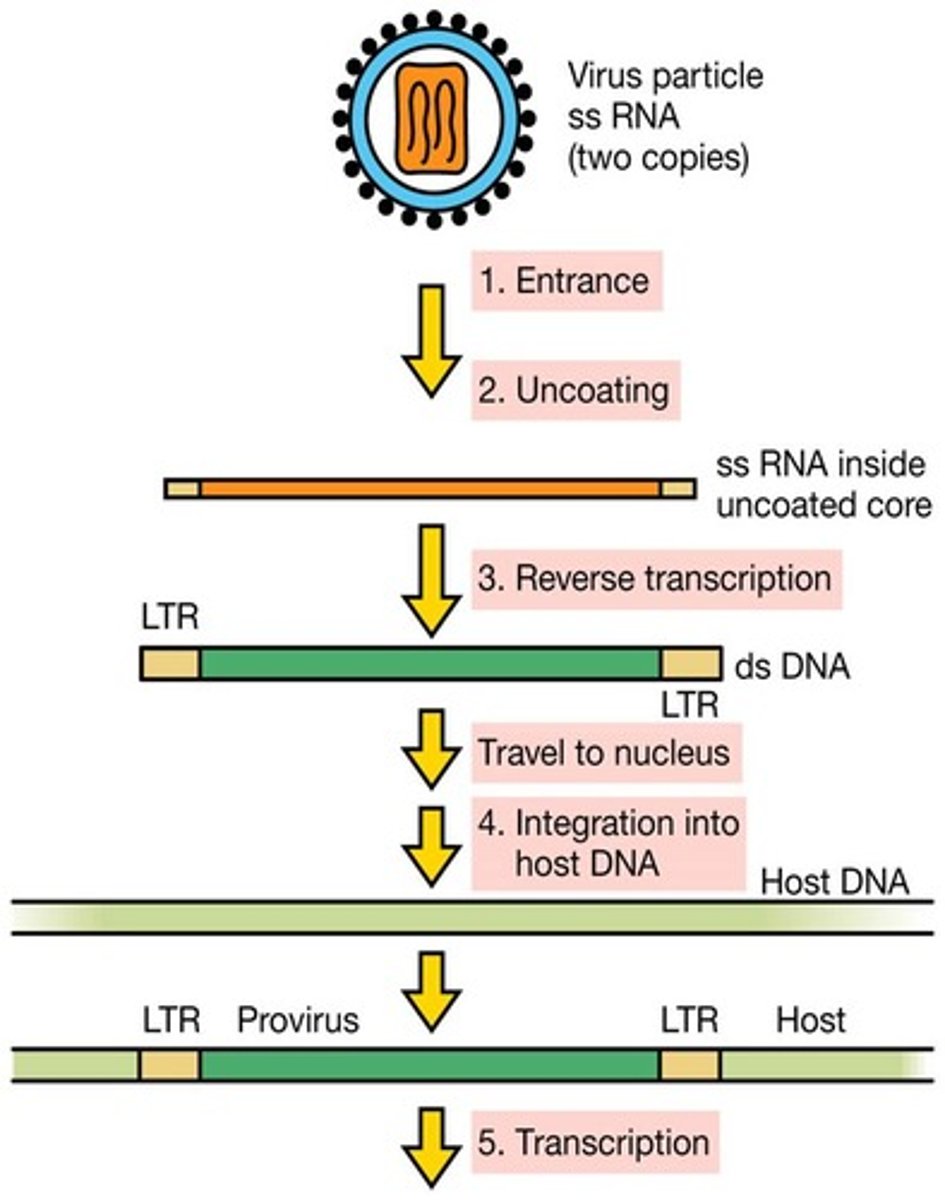
Retrovirus
An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome; an important class of cancer-causing viruses.
F factor
A fertility factor in bacteria; a DNA segment that confers the ability to form pili for conjugation and associated functions required for the transfer of DNA from donor to recipient. It may exist as a plasmid or be integrated into the bacterial chromosome.
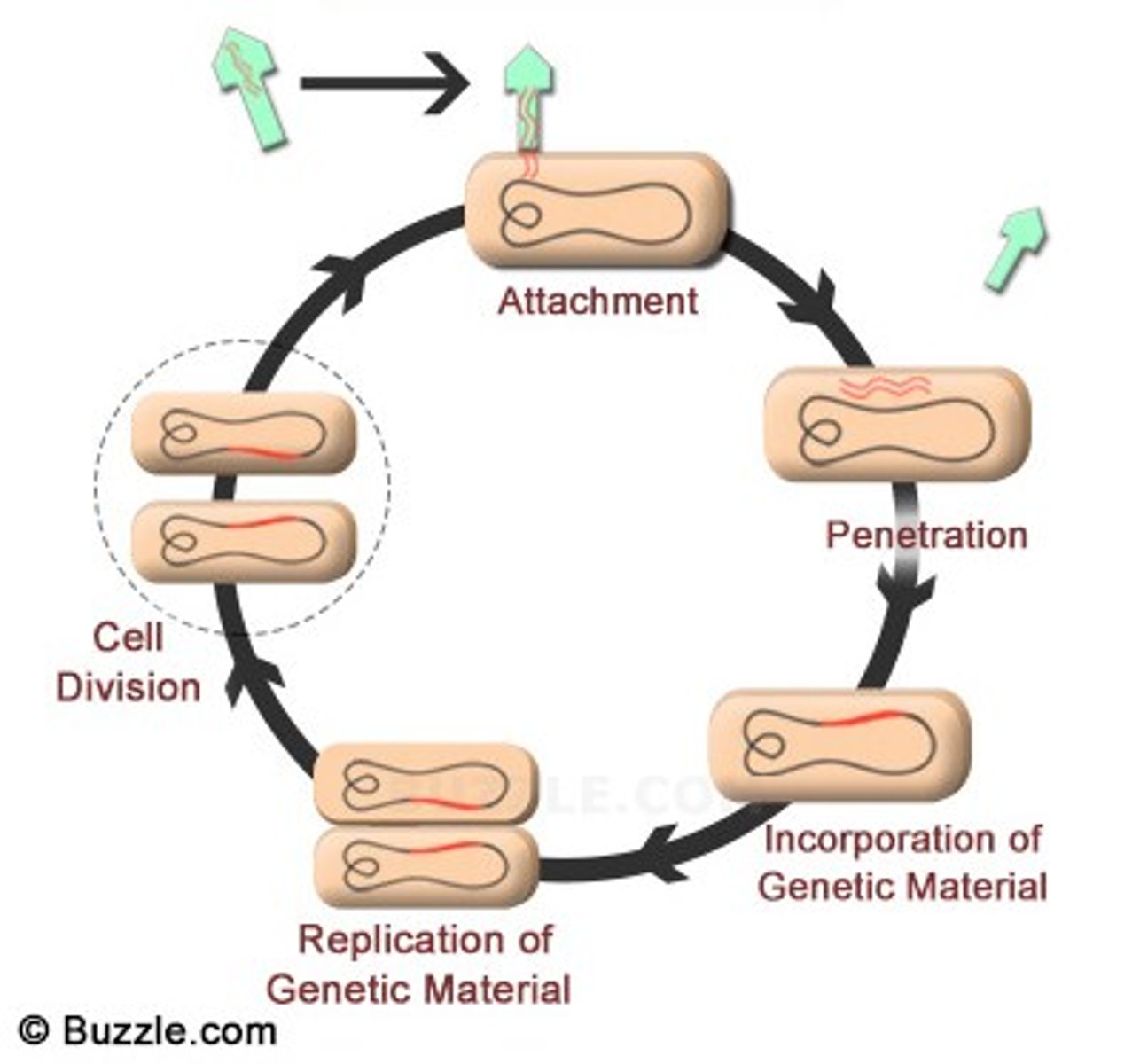
Lytic Cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses

Lysogenic Cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
Reverse Transcriptase
An enzyme found in retroviruses that facilitates the production of DNA from RNA
Vaccine
A weakened or inactive version of a pathogen that stimulates the body's production of antibodies which can aid in destroying the pathogen

Viral Envelope
a membrane, derived from membranes of the host cell, that cloaks the capsid, which in turn encloses a viral genome