Unit 7 - Ionic Compounds
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WOMENS HISTORY MONTH
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Cations
Elements that lose electrons form positive (+) ions
cations
Transition metals tend to form ___, but are difficult to predict because of d and f orbitals
Anions
Elements that gain electrons form negative (-) ions
releases; requires/absorbs
When an atom picks up an electron, it ___ energy; when it releases an electron it ___ energy.
Explanation: Gaining an electron often results in a more stable configuration, releasing energy in the process. Losing an electron, on the other hand, requires energy to overcome the attraction between the electron and the nucleus.
Ionic Bond
Electrostatic force that holds oppositely charged particles together
cations (+); anions (-)
Ionic bonds form when ___ and ___ combine
Ionic Crystal
Regular and repeating patterns formed when Ionic compounds push positive and negative ions together
Monoatomic; valence electrons
___ ions form from a single atom: Li+, Ca2+, Br-. Charge is based off ___.
space out
Positive and negative ions ___ to reduce repulsive forces
Oxidation Number
The charge of the ion
oxygen
Oxidation number is a reference to ___
Roman Numerals
Use ___ in the name of transition metals to represent its charge
Polyatomic Ions
ions made up of more than one atom
entire group
Charge of the polyatomic ion applies to the ___ of atoms.
crystal lattices
Ions are arranged in large ___.
Crystal Lattice
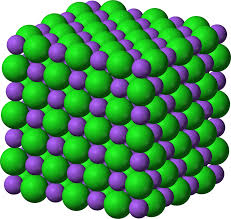
Formula Unit
Simplest ratio to represent Ionic compounds
zero
Positive and negatives charges must add up to net charge ___.
Chemical Nomenclature
Rules for naming compounds
first
Cations are named ___.
original element name
Cations use their ___
roots; -ide
Anions use ___ of the anion name plus ___ suffix.
roman numerals; oxidation numbers
Transition metals use ___ to define their oxidation numbers because they have can multiple ___.
crystal lattices
Strong attraction of ions results in 3D geometric arrangements of particles called ___.
strong; high melting, high boiling points, and significant hardness
Crystal lattices create ___ bonds in ionic compounds. They have ___ properties.
Endothermic
Reactions that absorb energy and make the temperature go down.
Exothermic
Reactions that release energy and make the temperature go up.
exothermic
Energy of Ionic compounds will always be ___.
Lattice Energy
Energy needed to separate ions of an Ionic compound
similar
Metals form bonds ___ to Ionic bonds
sea of electrons; valence electrons; act; cations
Metals create a ___ where they contribute their ___, and that bond makes those metals atoms ___ like ___.
delocalized electrons
Valence electrons that are in the “sea of electrons”, or electrons that are free to move.
Metallic bond
The attraction of a metallic cation for delocalized electrons.
melting points; boiling points; seperate
High ___ of metals can be explained by: atoms are easily able to slide past each other, but even higher ___ because they are hard to ___.
malleable; ductile
Metals are ___ and ___ because their atoms can be easily pushed and pulled around
conductors; delocalized electrons
Metals are excellent ___ because ___ can move heat around from place to place easily.
high; d-orbitals
Transition metals have ___ conductivity (better than normal metals) because of their loose ___.
Alloy
A mixture of elements that have metallic properties
Mixture
A material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method
Sea of electrons surrounding lattice of positively charged metal ions, valence electrons in metals are delocalized and able to move throughout the crystal lattice structure
What do metallic bonds look like?
High electrical & thermal conductivity, malleability & ductility, high melting & boiling points, strong & hard
List some properties of metals that are due to the way metallic bonds form.