R&EGOV final study guide
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
•Testamentary trust
A trust that is created by will and therefore does not take effect until the death of the testator.
•Charitable trust

A trust in which the property held by the trustee must be used for a charitable purpose, such as the advancement of health, education, or religion.
Durable power of attorney

•A document that authorizes a person to act on behalf of another person—write checks, collect insurance proceeds, and otherwise manage the disabled person’s affairs, including health care—when that person becomes incapacitated.
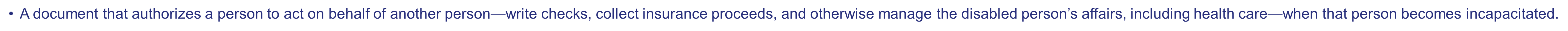
Healthcare power of attorney

•A document that designates a person who will have the power to choose what type of and how much medical treatment a person who is unable to make such a choice will receive.

Constructive trust

An equitable trust that is imposed in the interests of fairness and justice when someone wrongfully holds legal title to property

What event led black americans to support the republican party en masse in the 1800s?
Post civil war, post 1865 because of Abe Lincoln
What events began to shift blacks’ support from the republican party to the democratic party?
The end of the Reconstruction period/ Rutherford B. Hayes assumes presidency on a “deal”
What pieces of legislation solidified African Americans support for the democratic party?
Civil Rights Act of 1964 & Voting rights act of 1965
What is public opinion?
the attitudes or views of a large communities have about politics
What is political socialization?
The process through which people establish their beliefs
What is political ideology?
The attitudes and beliefs that help shape our opinions on political theory and policy
what is primacy principle?
what is learned first tends to leave a lasting impression and stays with that person for the majority of their lives
what is linked fate?
The notion that what happens to one person impacts the group as a whole.
what is racial threat hypothesis?
the larger population of minoritized group, the more the majority group aims to exert control.
what is collective racial memory?
Historical events not only impact the people that experienced it/ancestors but also the generations to come.
ex. systemic racism, slavery, segregation
what is the southern strategy?
the political strategy to use racial symbols + coded language to paint a negative picture of a black archetype and draw support from prejudice voters
what is an example of the southern strategy?
the welfare queen scandal suggested black people will misuse governmental funds and will commit fraud and exploit funds
How did the welfare queen stereotype emerge? How was it used?
Raegan’s campaign to Philly & Miss. in 1964. The slogan was used to exaggerate and spread rumors.
what are racial covenants?
A promise made between property owners and white people to never sell the home to a black family
what us racial steering? identify some examples
when realtors or mortgage companies steer certain families that are all black or all white towards certain neighborhoods based on race.
what is blockbusting?
when a black family is scammed/encouraged by white realtors to sell their homes at a low price
what is redlining?
a map that restricts certain areas from resources primarily negatively effecting black and latino communities
what was the goverment’s tole in redlining and housing segregation?
FHA home loan program ( FHA encouraged restrictive covenants) & the G.I bill (provided stipends covering college tuition, ( primarily for white students ). College enrollment went up considerably
what are sundown towns?
towns that are unsafe for black people to be in, or travel through after sundown. These towns commit hate crimes like lynchings, beatings and murders
what is environmental racism?
any policy or practice that differentially affects a group based on race or color, shifting industry cots onto communities of color
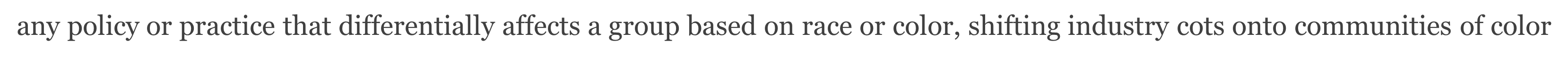
what are food deserts?
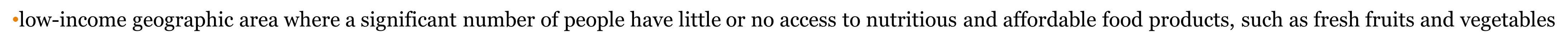
•low-income geographic area where a significant number of people have little or no access to nutritious and affordable food products, such as fresh fruits and vegetables
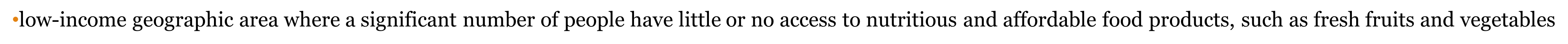
what are the health impacts of food deserts?
•Obesity
•High blood pressure
•Childhood hunger
•Poor diets
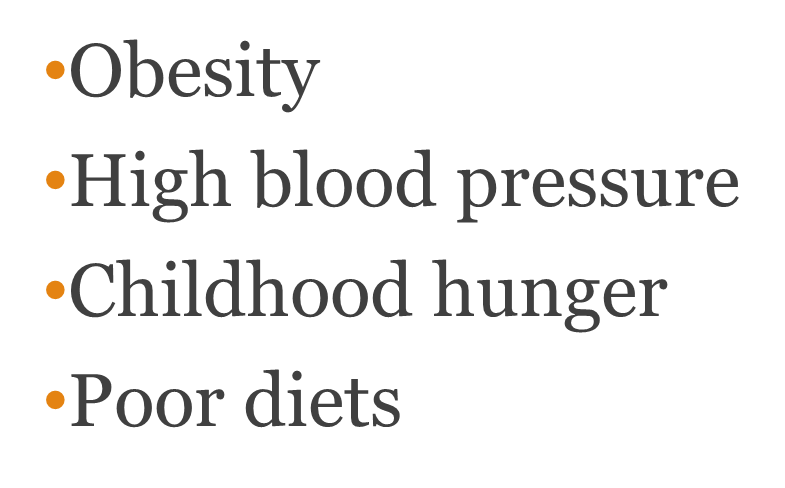
The Flint water crisis
lead poisoning from the flint river after changing the water supply. ◦To cut costs, the city decided they were going to find ways to shrink the budget, and one of them was changing the city’s water supply
◦They had been getting their water from the city of Detroit, another city that was bankrupt and charging them alot of money for access to the water supply
◦The city of flint decided to get their water from the flint river instead
◦The flint river had long been known as a site for industrial waste
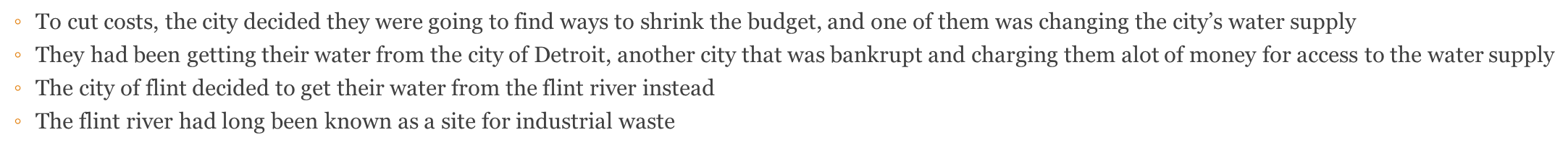
how does environmental racism impact indigenous communities?
The federal government produces most of their nuclear weapons on tribal lands and reservations. The government pays the tribes to keep radioactive nuclear waste on the tribal lands.
How does redlining impact modern day food deserts?
There becomes a increase in convenience stores and a lack of fresh produce and healthy food options which leads to a lack of nutrition within minoritized communities
what are the health impacts of environmental racism?
higher rates of chronic illnesses, asthma, lead poisoning, reproductive disorders, lung cancer,
how does redlining impact modern day issues of climate change?
historically relined neighborhoods are 5 degrees warmer compared to non redlined neighborhoods.
what is affirmative action?
a system that is aimed to increase representation of women & people of color in higher education
what year did Alverez v. Lemon Grove happen? And what was it over?
1931: there was a South California small community w/o segregated schools, they put all the Mexican students in one room. Parents sued for equal education and won the case because Mexicans were considered white
Gaines v Canada 1938
•Lloyd Gaines sued the University of Missouri Law School because he was denied admission due to his race.

Court ruled that states that don’t have educational institutions for African Americans must admit Black students.
Sweatt v. Painter 1950
•Heman Sweatt denied entry into UT Law School because of race
•To avoid integrating the UT law school, the State of Texas established the Texas State University for Negroes in Houston.
•Supreme Court ruled separate law school did not meet “equal standard” established in Plessy v. Ferguson
•University of Texas was forced to admit Sweatt to the law school

Brown V. Board of Education 1954
•Racial segregation of students in public education violates the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment
•Overturned the Plessy v Ferguson (1896) precedent that “separate but equal” was constitutional
•Met with massive widespread resistance in the South

Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education 1971
Led to court ordered desegregation of schools through busing ( meaning they would bus a group of black kids and then white kids to opposite schools )
What us forced busing?
Forced busing is a policy used to achieve school desegregation by transporting students to schools outside their local districts, often to balance racial demographics.
What are segregation academics?
Segregation academics refer to educational systems or practices that separate students based on race or ethnicity, often resulting in unequal resources and opportunities.
why do white women not support affirmative action programs?
an example of why would be: Grutter v. Bollinger. White women/white people feel like women of color or minoritzed students in general are given “special treatment” it dates back to black. latinos, and asians taking “ white jobs”
Who are the primary beneficiaries of affirmative action programs?
legacy students, diversity admins, Asian students
why were legacy admissions first created in the early in the early 1900s?
•Legacy admissions have their roots in elite institutions wanting to limit the number of Jews that could come to their university.
•Schools want legacy admits because of the thought that these students are more likely to become donors when they become alums

who are the primary beneficiaries of legacy admissions?
•Legacy admits tend to be less qualified and less racially and ethnically diverse
•Currently almost 70% of Harvard legacy applicants were white.
•Many colleges coach legacies through the admissions process and advise them about strategies for constructing successful applications
•Some universities employ admissions counselors dedicated solely to legacy applicants
In cases where legacies are rejected, some universities offer legacy admissions counseling and help with placement at other colleges
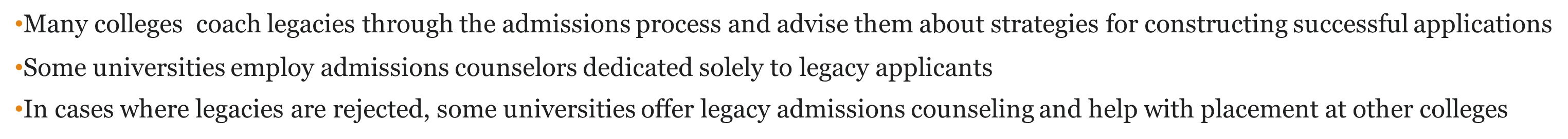

what is the University of California v. Bakke Supreme Court Decision
Allan Bakke sued UC Davis medical school after being rejected
At the time, UC Davis guaranteed 16/100 of their admission slots to people of color
Supreme court ruled such a quota system as unconstitutional and a violation of the equal protection clause of the 14th amendment
Due to Bakke, race could still be considered in college admissions, but as one factor among many others
What is critical race theory?
•Critical race theory is an academic framework that examines the relationship between race, racism and institutional power.
•Critical race theory argues racism is fundamentally built into U.S. laws and institutions.
•Critical race theory emerges in the 1970s after the civil rights movement's victories.

what is the focus of critical theory?
examines power structures and institutions
what are some core tenets of critical race theory?
Interest Convergence, intersectionality, race is a social construct, critiquing colorblindness
what is interest convergence
•Anytime there are advancements or progress made on race relations it is not done out of altruistic reasons
•It is done because the dominant white ruling class has an interest that would be served
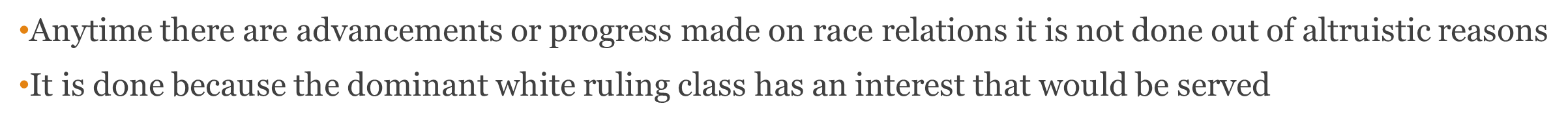
what are examples of interest convergence shown in the slides
•Emacipation Proclimation
•School Desegregation in the 1950s
•Efforts to end mass incarceration
•Death penalty

What is intersectionality?
•Citizens can have multiple marginalized identities
•Race, gender, LGBTQ status,
•One can have both privileged and marginalized identities
what are critical legal studies?
•Examines how the law creates and reinforces systematic inequality
• The law supports the interests of those who create the law.
•Law inherently creates power dynamics

How does critical race theory critique colorblindness?
Critical race theory critiques colorblindness by arguing that it ignores the systemic inequalities and racism that continue to affect marginalized communities. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing race in understanding social justice and advocating for equity.
What is the Black-white binary?
•Racial history is presented as a linear story between White and Black Americans.
•Theorizes society views Black and White people as the two primary racial groups,
o All racism experienced by other groups is compared to anti-blackness, and the Black–White relations as central to racial analysis.

What are some common misconceptions of critical race theory?
•Critical Race theory teaches that white people are inherently evil because they are White
•That CRT teaches an individual is inherently racist or oppressive because of their own race
• White people should be ashamed or guilty because of their race

According to the core tenets of critical race theory, is racism systemic or an individual level phenomenon?
Racism is viewed as a systemic phenomenon that is embedded in societal structures and institutions, rather than merely an individual level issue.
what was the first form of policing in America?
Slave codes
What are black codes?
•Selling produce from your farm after dark
•Loitering
•Quitting 1 job and going to work at another job without permission from job 1
•Entering town without the written permission of the city government
•It required Blacks to present, each January, written proof of employment

What are the Rockefeller drug laws?
o Possession of 2 ounces or more of a schedule I or II drugs results in a mandatory minimum sentence of 15 to life in New York State
• During this period outward appeals to racism and racists were no longer politically viable
o So begins the phraseology such as “law and order,” “war on crime”, “tough on crime”.

What is Anti-drug abuse Act of 1986 and what did it do?
◦ If you were found with 1 gram of rock cocaine you were sentenced as if you had 100 grams (about 3.53 oz) of powder cocaine
◦ This act mandated a minimum sentence of 5 years without parole for possession of 5 grams of crack cocaine while it mandated the same for possession of 500 grams of powder cocaine.
◦ Makes crack cocaine the only drug with a mandatory minimum penalty for a first offense of simple possession
◦ Reinstates the death penalty at the federal level

What is the 1994 crime bill and what did it do?
•Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act of 1994
o eliminated the ability of lower-income prison inmates to receive college educations during their term of imprisonment
o Truth In Sentencing Provision
o More policemen and women on the streets
o Three Strikes Law

What is broken windows policing? what types of crimes does this crime fighting strategy focus on on preventing?
• low-level crime and disorder creates an environment that encourages more serious crimes.
o Focus on quality-of-life offenses: fare beating, selling loosies, public intoxication

who are the primary groups who are disproportionately impacted by stop and frisk and broken windows strategy?
Black and Latinos
What are core tenets of defunding the police?
After school programs, expanded social services, dispute resolution
pre-contextual traffic stop
when a police officer stops a vehicle to conduct a speculative criminal investigation unrelated to the reason for enforcing a traffic code
what is the core idea behind the idea of police abolition
•This is the idea that policing is fundamentally rooted in systems of oppression.
•Systems built on these structures of inequality cannot be reformed. These systems must slowly be re-oriented and eventually replaced by systems that are built to support citizens
•Looks a lot of different ways
