motor units, muscle fiber types, and muscle knowledge
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
motor units
a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
small motor units
recruit few neurons and recruit few muscle fibers
-for lifting light loads, like a pencil
large motor units
recruit many neurons and many muscle fibers
-for moving heavy loads, like a bowling ball
slow fibers
fibers that contract slowly and are resistant to fatigue. They are primarily used for endurance activities.
fast fibers
fibers that contract quickly and are prone to fatigue. They are primarily used for short bursts of strength or speed.
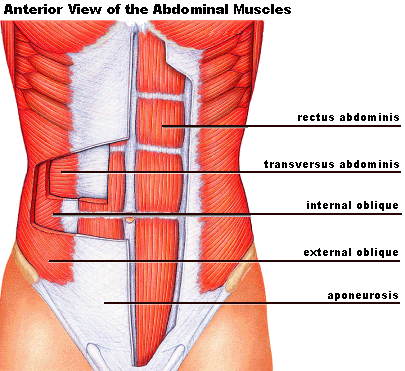
parallel muscles
Fibers run parallel to each other, allowing long-range motion but less force.
Example: rectus abdominis.
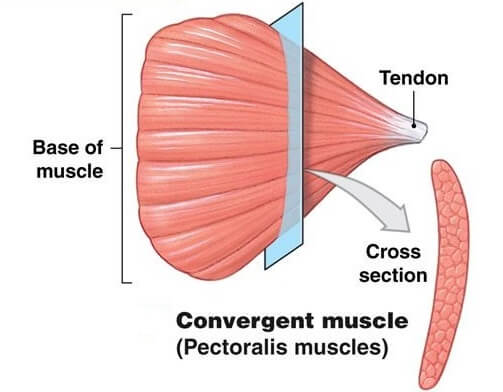
convergent muscles
Fibers spread out and converge at a common attachment site. This allows for versatile movement.
Example: pectoralis major.
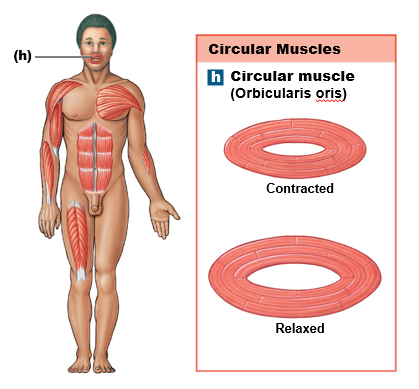
circular muscles
Fibers arranged in a ring, controlling openings in the body. Example: orbicularis oris (mouth) and orbicularis oculi (eye).
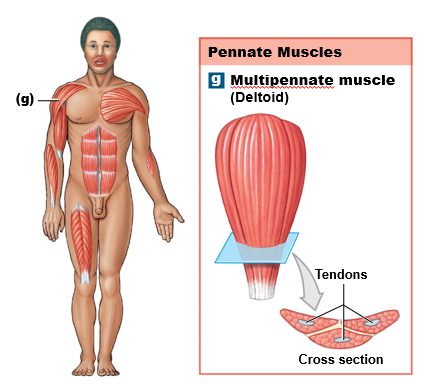
pennate muscles
Fibers attach at an angle to a central tendon, producing more force but less movement.
origin
the part of the muscle that stays fixed during contraction, serving as the attachment point for the muscle.
insertion
the part of the muscle that moves during contraction, allowing for movement at the joint.
origin movement
The proximal end of attachment of a muscle to a bone that will not be moved by the action of that muscle.
insertion movement
The distal end of attachment of a muscle to a bone that will be moved by the muscle when it contracts.
Intermediate FIbers
a faster contraction speed than slow fibers and a moderate fatigue resistance compared to both
ex. light jogging