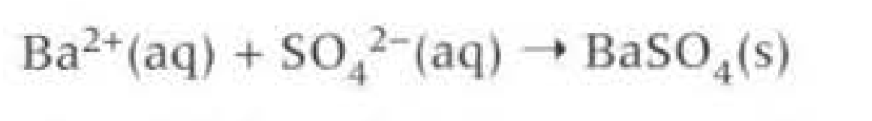Section 2 9 Group 2 alkaline earth metals
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Properties of group2 (atomic radius, BP, Ionisation energies)
The atomic radius increases going down the group, because regardless of increased proton number the number of shells increases.
Going down the group the melting point decreases because when metal ions in metallic structure is formed the sea of delocalised electrons are further away from the positive ions so less attraction so lower BP.
Going down the group ionisation energy decreases as the atomic radius increases less energy required to remove one electron from outermost shell.
Group 2 metals and their reaction to water LIQUID and GAS
Group 2 metals reacting with water increases going down the group, because the atomic radius increases the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative electron decreases so easier attraction to water. Reaction with steam is rapid.
Liquid:
Mg(s) + 2H2O(l) —> Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Gas:
Mg(s) + H2O(g) —>MgO(s) + H2(g)
The solubility of group 2 hydroxides:
From Magnesium hydroxide to Barium hydroxide - they become more soluble.
The solubility of group 2 sulfates:
Going down the group the group 2 sulfates become insoluble.
This is important for:
Barium sulfate (insoluble) can be eaten and can be detected outside the body to detect the gut, regardless of being highly toxic it is insoluble.
Acidified (Nitric or HCl) barium chloride to test for sulfate ions (cloudy precipitate as insoluble)