sleep as a psychological construct
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is consciousness
the level of awareness an individual has over their thoughts, feelings, perceptions, and existence
How is consciousness described in psychology
a psychological construct that is continuous, ever-changing, and a highly personal experience
What is a psychological construct
an agreed upon description and understanding of psychological phenomena that cannot be directly measured or observed
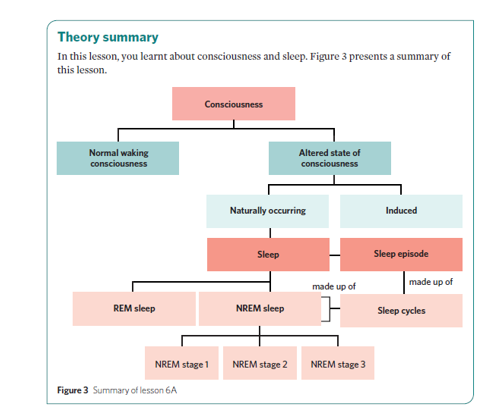
What are the two main types of consciousness
normal waking consciousness (NWC)
altered states of consciousness (ASC)
What is normal waking consciousness (NWC)
a state of consciousness in which an individual is awake and aware
What is an altered state of consciousness (ASC)
a state of consciousness that is distinctly different from normal waking consciousness in terms of quality of experience and levels of awareness
What are the two categories of altered states of consciousness
Naturally occurring
Induced altered states of consciousness
What is a naturally occurring altered state of consciousness
a type of ASC that occurs without intervention
What is an induced altered state of consciousness
a type of ASC that occurs due to a purposeful action or aid
Give examples of naturally occurring altered states of consciousness
Sleep
Daydreaming
Give examples of induced altered states of consciousness
Meditation
Hypnosis
The influence of alcohol and/or drugs
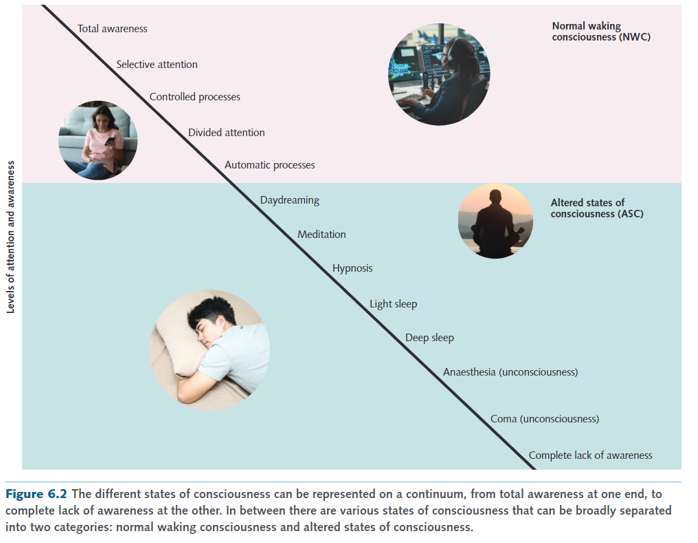
What does the consciousness continuum represent
It is a visual representation of the different states of consciousness that progress from lower levels of awareness to higher levels of awareness
How can consciousness be reflected
Consciousness can be reflected by a continuum
draw consciousness as a continuum
What is sleep
a regular and naturally occurring altered state of consciousness that involves a loss of awareness and disengagement from internal and external stimuli
Why is sleep considered a psychological construct
Because the subjective experience of sleep cannot be directly measured, yet it is widely understood and acknowledged to exist
Name one characteristic of sleep related to behaviour
A reduced ability to control behaviour
What happens to our control over thoughts during sleep
There is a reduction in control, such as lacking control over what we dream about
How is our sense of time affected during sleep
We have a less accurate understanding of the passage of time
What types of distortions can occur during sleep
Perceptual and cognitive distortions
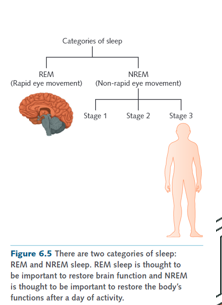
What are the two different types of sleep
REM (rapid eye movement) sleep
NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep
What characterises REM sleep
Rapid eye movement, high levels of brain activity, and low levels of physical activity
What is somatic nervous system activity like during REM sleep
It is low, meaning there are low levels of physical movement
What characterises NREM sleep
A lack of rapid eye movement and lower levels of brain activity compared to REM sleep
How many stages does NREM sleep have
Three stages:
NREM stage 1
NREM stage 2
NREM stage 3
How is the brain and body activity described during REM sleep
The brain is highly active and the body is less active
What happens to muscle movement during REM sleep
The sleeper is virtually paralysed; most muscle movement is not possible
Is REM sleep light or deep
REM is a relatively light stage of sleep; sleepers can be woken fairly easily
When do vivid dreams typically occur
During REM sleep
How much of a sleep episode is typically spent in REM sleep
Approximately 20–25%
How does the amount of REM sleep change throughout the night
It increases as the night progresses, with the longest REM periods occurring before waking
How is brain activity during NREM sleep compared to waking consciousness
The brain is less active than during normal waking consciousness
Is physical movement possible during NREM sleep
Yes, physical movement is possible and the body is more active than in REM sleep
What happens to movement as NREM stages progress
Movement tends to decrease
Can dreams occur during NREM sleep
Yes, but they are often non-vivid and less frequently recalled
When is the most NREM sleep experienced during the night
During the first half of a sleep episode
How much of a sleep episode is typically spent in NREM sleep
Approximately 75–80%
How does the length of NREM sleep change through the night
It tends to become shorter with each sleep cycle
How many stages is NREM sleep divided into
Three stages:
NREM Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3
What is a sleep episode
A sleep episode is the full duration of time spent asleep
What is a sleep cycle
A sleep cycle is an approximately 90-minute period that repeats during a sleep episode, in which an individual progresses through stages of REM and NREM sleep
What makes up a sleep episode
Multiple repeated cycles of REM and NREM sleep, called sleep cycles
Draw a diagram of a sleep cycle
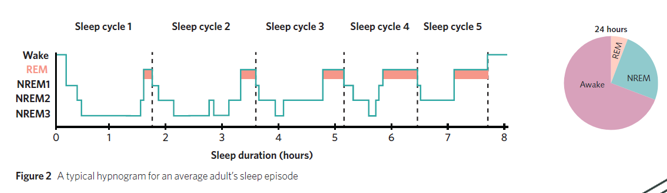
What is the first stage of a sleep cycle
Stage 1 NREM sleep
How often does the sleeper enter stage 1 NREM sleep during a sleep cycle
Usually only at the beginning of the sleep episode
What is the order of progression through the NREM stages during a sleep cycle
Stage 1 → Stage 2 → Stage 3 → back to Stage 2 → REM sleep
What is the hypnagogic state
A transitional state between wakefulness and sleep, often involving sensations like floating, falling, or a sudden jerk (hypnic jerk)
What characterises NREM Stage 1 sleep
Light sleep, loss of awareness of self and surroundings, but awareness of faint sounds; easy to wake
How long does NREM Stage 1 typically last
Approximately 2–10 minutes
What characterises NREM Stage 2 sleep
Light sleep, considered the stage of 'true' sleep due to specific brain wave patterns
In which stage do people spend most of their sleep time
NREM Stage 2
How long does NREM Stage 2 typically last
20–30 minutes
What characterises NREM Stage 3 sleep
deep sleep, difficult to wake from, with possible occurrences of sleepwalking and sleep talking
How does a person typically feel if woken during NREM Stage 3
Drowsy and disoriented
How long does NREM Stage 3 typically last
20–40 minutes
Theory summary