Body Systems Semester 1 Final
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
anterior
towards the front
posterior
towards the back
inferior
below another body part
superior
above another body part
proximal
close to attachment point
distal
far from attachment point
medial
towards the midline
lateral
towards the sides from the midline
cephalic
anything related to the head
caudel
anything towards the tail/ behind & away from the head
superficial
towards the surface
deep
towards the inside
Two major cavity divisions
Anterior & Posterior Cavities
Anterior Cavity
Thoracic & Abdominopelvic Cavities
Posterior Cavity
Cranial & Spinal Cavities
Thoracic Cavity
Mediastinum, Pericardial, and Pleural Cavities
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Pelvic & Abdominal Cavities
How is epithelial tissue classified
number of layers & shapes
How is connective tissue classified
Smooth Muscle movement type
involuntary
Smooth Muscle Location
walls of tubular organs & blood vessels
Smooth Muscle Cell Appearance
cells are non-striated, short, and spindle-shaped uninucleates
Skeletal Muscle movement type
voluntary
Skeletal Muscle Location
Attached to skeleton
Skeletal Muscle Appearance
cells are striated, long, cylindrical, and multi-nucleated
Cardiac Muscle Movement Type
Involuntary contraction
Cardiac Muscle Location
Heart Walls
Cardiac Muscle Appearance
cells are striated, short, branched, cylindrical, and uninucleated.
Connective Tissue
Tissue that holds your body together
Epithelial Tissue
The covering on al internal & external surfaced of the body, they help w/ protection, secretion, and absorption.
Muscle Tissue
Help w/ movement
Nervous Tissue
sends signals between the brain & all the other parts of the body
Loose Fibrous Areolar Connective Tissue Location
Muscle & Matrix
Loose Fibrous Areolar Connective Tissue Function
wraps & binds muscles to each other & skin
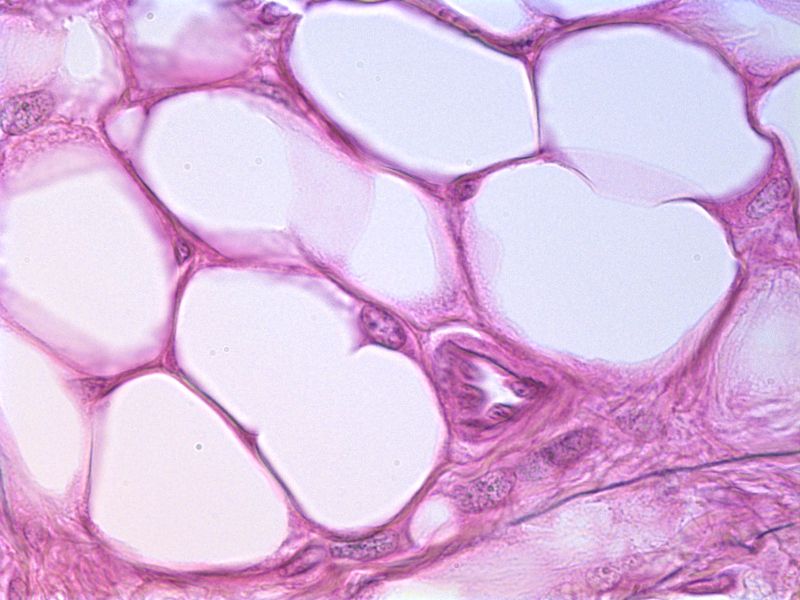
Loose Fibrous Adipose Connective Tissue Location
Beneath the skin
Loose Fibrous Adipose Connective Tissue Function
stores fat
Loose Fibrous Areolar Connective Tissue
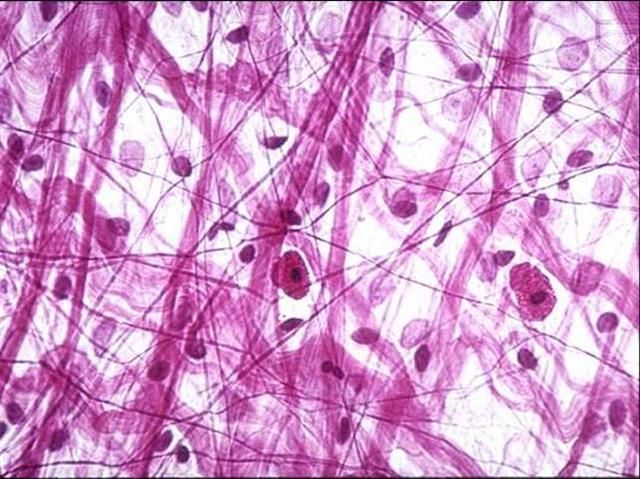
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Loose Fibrous Adipose Connective
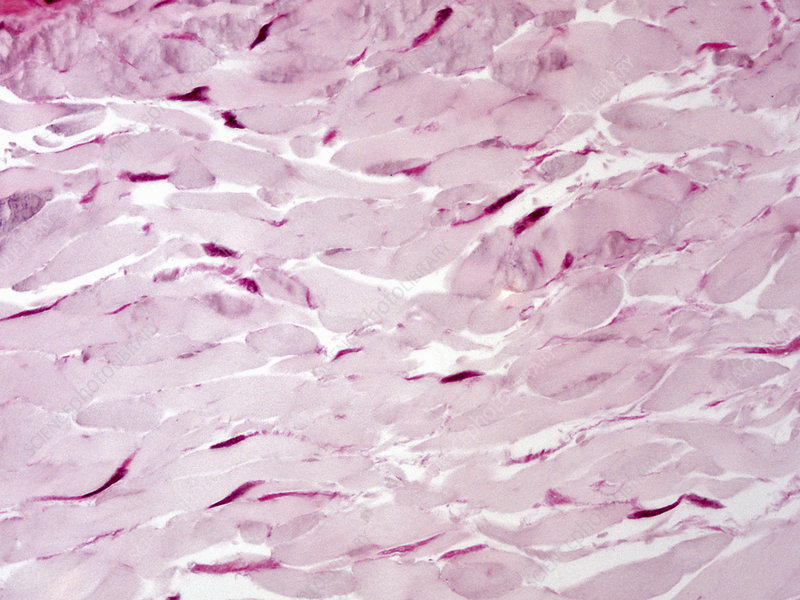
Dense Regular Connective
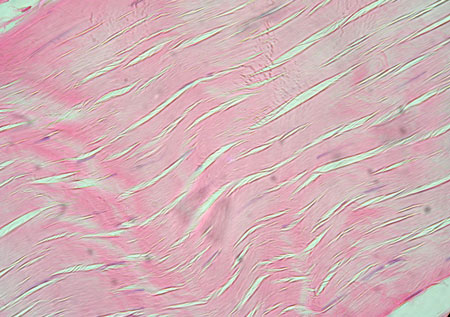
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue location
Dermis
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Function
Binds & resists tension
Dense Regular Connective Tissue Location
Tendons & Ligaments
Dense Regular Connective Function
Binds tendons & ligaments
Plasma Membrane
a semi-permeable phospholipid bilayer w/ embedded proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Appearance
smooth surface w/ no ribosomes
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Involved with the production & metabolism of lipids
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
associated w/ protein synthesis, modifications & delivery
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Appearance
surface is dotted w/ ribosomes w/ a rough look
Mitochondria
generates energy, ATP, stores calcium, cell-signaling activities, regulates metabolism, and undergoes apoptosis
Ribosomes
an intercellular structure made of RNA & protein, and is the site of protein synthesis
Langerhans Cells
white blood cells that ingest microbes, essential components of the skins immunologic barrier & serve as a first line of defense
Skin cancer that doesn’t spread
basal cell carcinoma
osteoblasts
bone-building cells that form & secrete collagen & deposit minerals into the bone matrix
osteoclasts
bone-destroying cells that break down bone matrix & releases its calcium
Intramembranous Ossification
occurs as bone is formed between 2 sheets of fibrous connective tissue, responsible for flat bones
Endochondral Ossification
occurs as hyaline cartilage is replaced by bones