chapter 13: nicotine, caffeine, and kratom
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Vaping: What's the deal?
- originally developed to help smokers quit
- Main difference between smoking and vaping>>>how the nicotine is delivered
- Burning end of a cigarette reaches temps of up to 9000C (which creates tobacco smoke)
- Process of combustion generates carcinogenic chemicals
- Vaping does not involve combustion
- heats the ingredients into an aerosol (aka vapor) >>>>dramatically reduces the release of harmful chemicals (at least that is the thought)
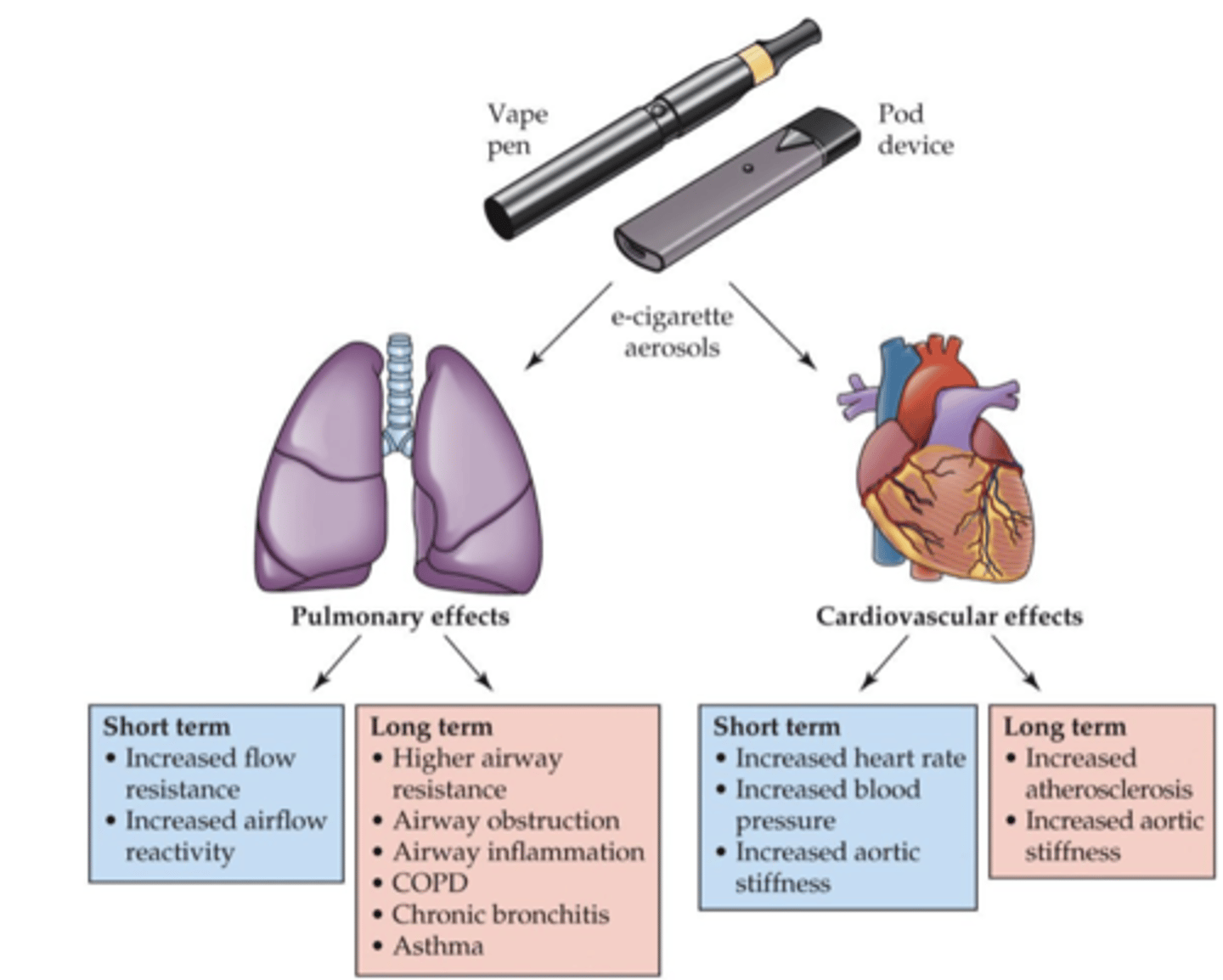
effects of vaping on the lung and heart
Evidence for Mayan use of tobacco in 700 A.D.
- Mid 16th century, Jean Nicot de Villemain, French ambassador to Portugal, brought back tobacco plants to France
- King James I of England: “A custom loathsome to the eye, hateful to the nose, harmful to the brain, dangerous to the lungs, and in the black stinking fumes thereof, nearest resembling the horrible Stygian Smoke of the Pit that is bottomless”
- Ben, collateral for a loan from France, and the Revolutionary War
Cigarette smoking: linked to...
Spanish troops returning from the Crimean War
- Tobacco use limited to pipes, cigars, and chewing… until the invention of automatic cigarette roller
- Duke family of Durham, NC perfected the machine in early 1880’s
Nicotine
alkaloid produced in the roots and concentrated in the leaves as a potent antiherbivore
typical cigarette
~10 mg of nicotine
- no more than 1 to 3 mg
reaches bloodstream
- CNS stimulant effects are felt w/I 7-10 seconds
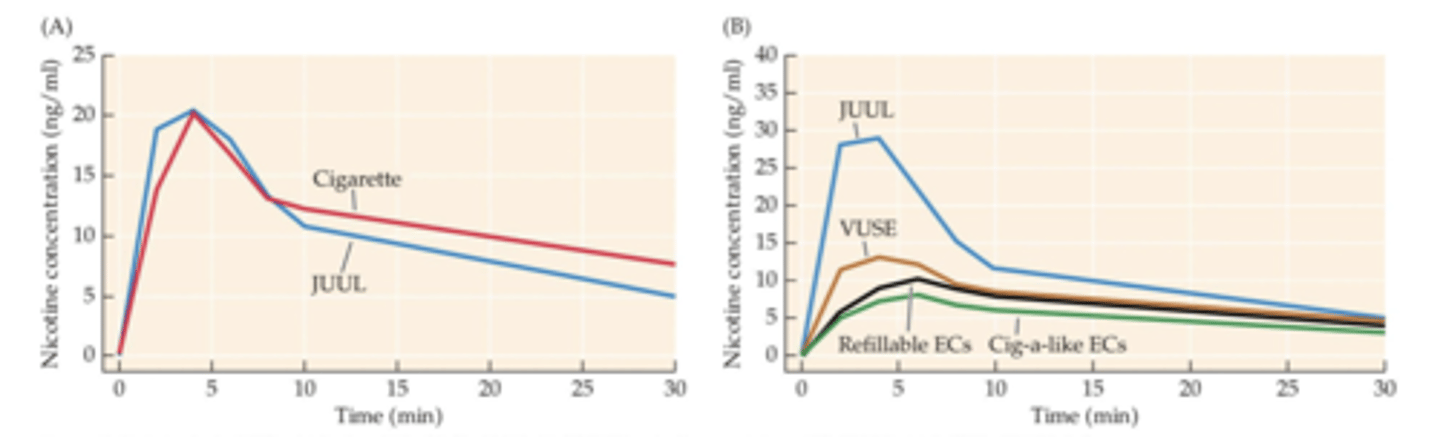
Regular e-cigarettes users
Average time course of plasma nicotine concentrations after smoking tobacco cigarettes or vaping JUULs or other brands of e-cigarettes
Most nicotine (~75%) is metabolized to...
cotinine by CYP2A6
- Basis for urine drug screens (biomarker for nicotine exposure)
- Half-life of nicotine: ~ two hours
- Cotinine half-life of ~20 hours
CYP2A6 expression is increased by...
estrogen
- faster nicotine metabolism in women than in men
- Menthol inhibits CYP2A6 activity
- slower nicotine conversion to cotinine when smoking mentholated vs non-mentholated cigarettes
Individual variability in CYP2A6 function
- low CYP2A6 activity>>>reduced nicotine metabolism
- less likely to become smokers
- Slow breakdown of nicotine is protective against smoking
nicotine activates...
nicotinic cholinergic receptors (nAChRs)
• α4β2 receptors are relatively rare>>> highly
- expressed on DA neurons in the VTA
- KO mice lacking α4 or
β2 subunit do not self-administer nicotine
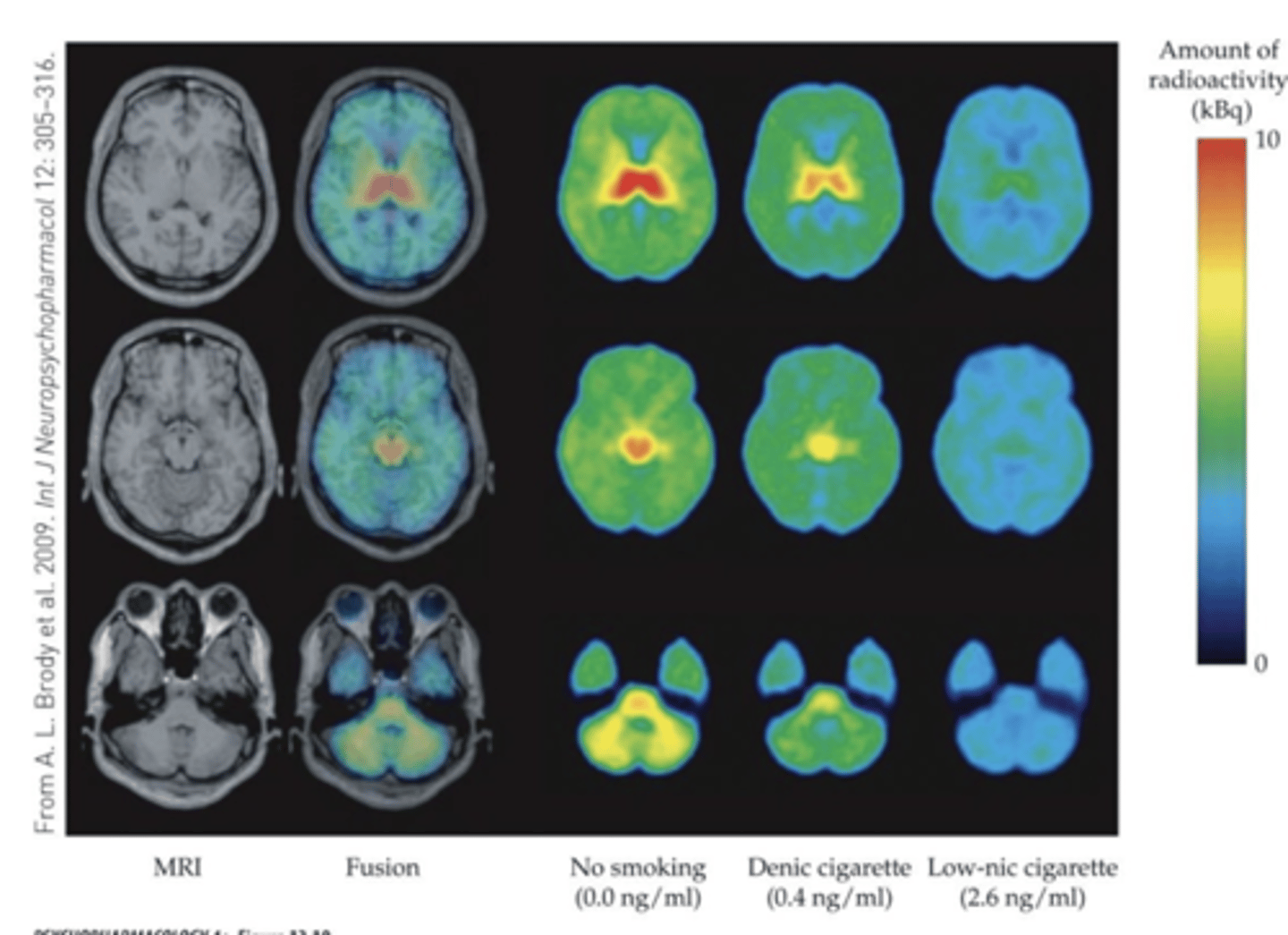
Dose-dependent occupancy
α4β2 nAChRs
- PET imaging of Tobacco- dependent cigarette smokers with a radiolabeled drug that binds selectively to α4β2 subunit–containing nAChRs in the brain
- even low levels of nicotine cause significant occupancy of high-affinity nAChRs in multiple brain areas
- Radiotracer is displaced by nicotine!
high doses of nicotine leads to...
- persistent activation of
nicotinic receptors
- continuous depolarization of the postsynaptic
- cell—depolarization block
- cell cannot fire again until the nicotine is
removed
biphasic effect
begins with stimulation>>>turns to blockade
- A mechanism of toxicity at high levels of
nicotine
nicotine effects on smokers
- produces a calm or relaxed state
- partly as relief from nicotine withdrawal symptoms
- Nicotine withdrawal:
- Restlessness, irritability, increased appetite, insomnia, difficulty concentrating
nicotine effects on non-smokers
- heightened tension or arousal, light-headedness,
dizziness, and nausea
- Tolerance develops with repeated use
- Receptor desensitization?
Animal studies
- Nicotine enhances working memory and attention
- Rats given nicotine show improvement on the 5-CSRTT of attention
- improved performance with acute or chronic nicotine administration
- poorer performance during withdrawal from chronic nicotine
- Non-smokers given nicotine show enhanced performance on many kinds of cognitive and motor tasks
Do nAChRs have a role in
attentional performance?
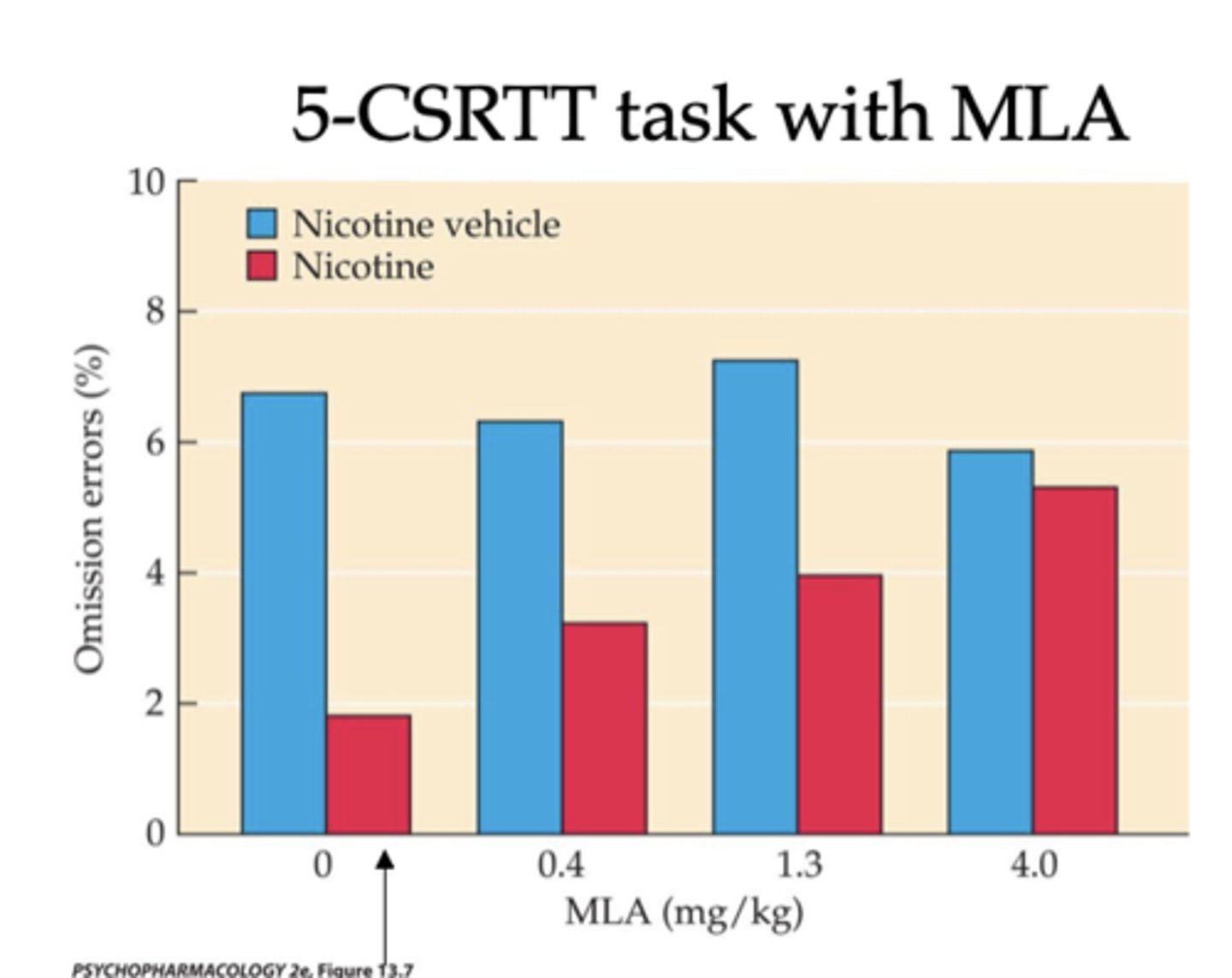
- α7-subunit antagonist (MLA) dose-dependently blocks the influence of nicotine on omission errors
- α7-containing nicotinic receptors mediate the ability of nicotine to enhance attentional function
- α7 agonists to improve cognitive performance?
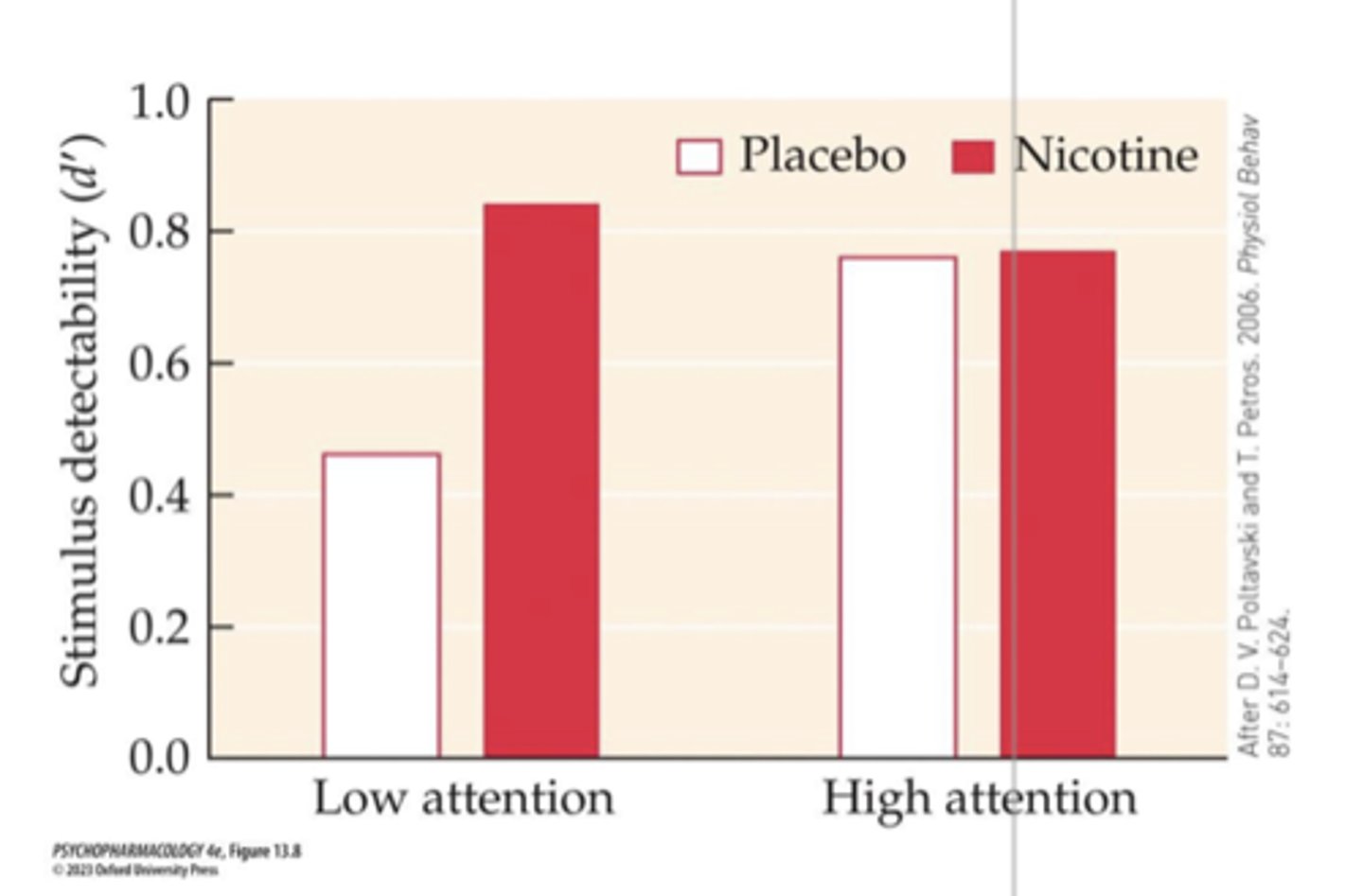
Nicotine enhancement of attention in “low-attention” participants
- Subjects divided into two groups base on baseline attentional performance: Low and High
- tested for their ability to detect and correctly identify a brief visual stimulus
- Subjects who received a transdermal nicotine patch (7 mg) prior to testing showed enhanced stimulus detectability only if they were in the low-baseline- attention
Mesolimbic DA pathway plays a key role in...
reinforcement
- 6-OHDA lesions in NAcc block nicotine self-admin
- nAChR antagonists in VTA block self-admin
- DA receptor antagonists in NAcc block self-admin
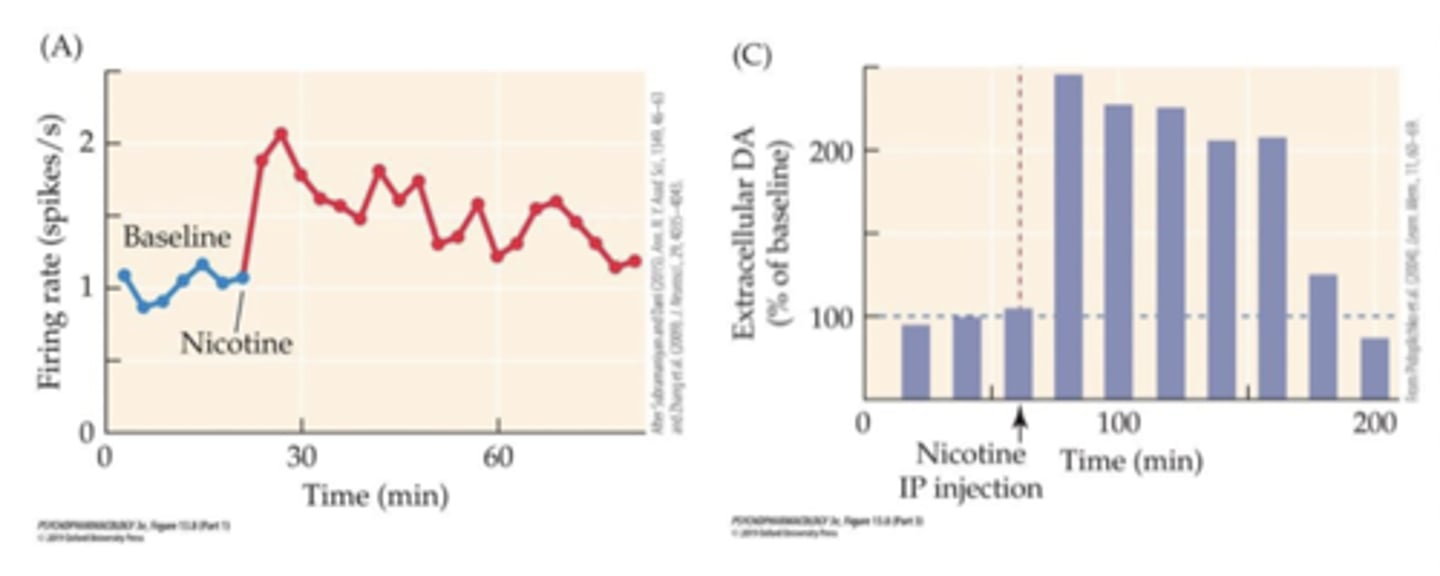
Nicotine results in...
doubling of firing rate of VTA DA neurons and enhanced DA release in NAcc
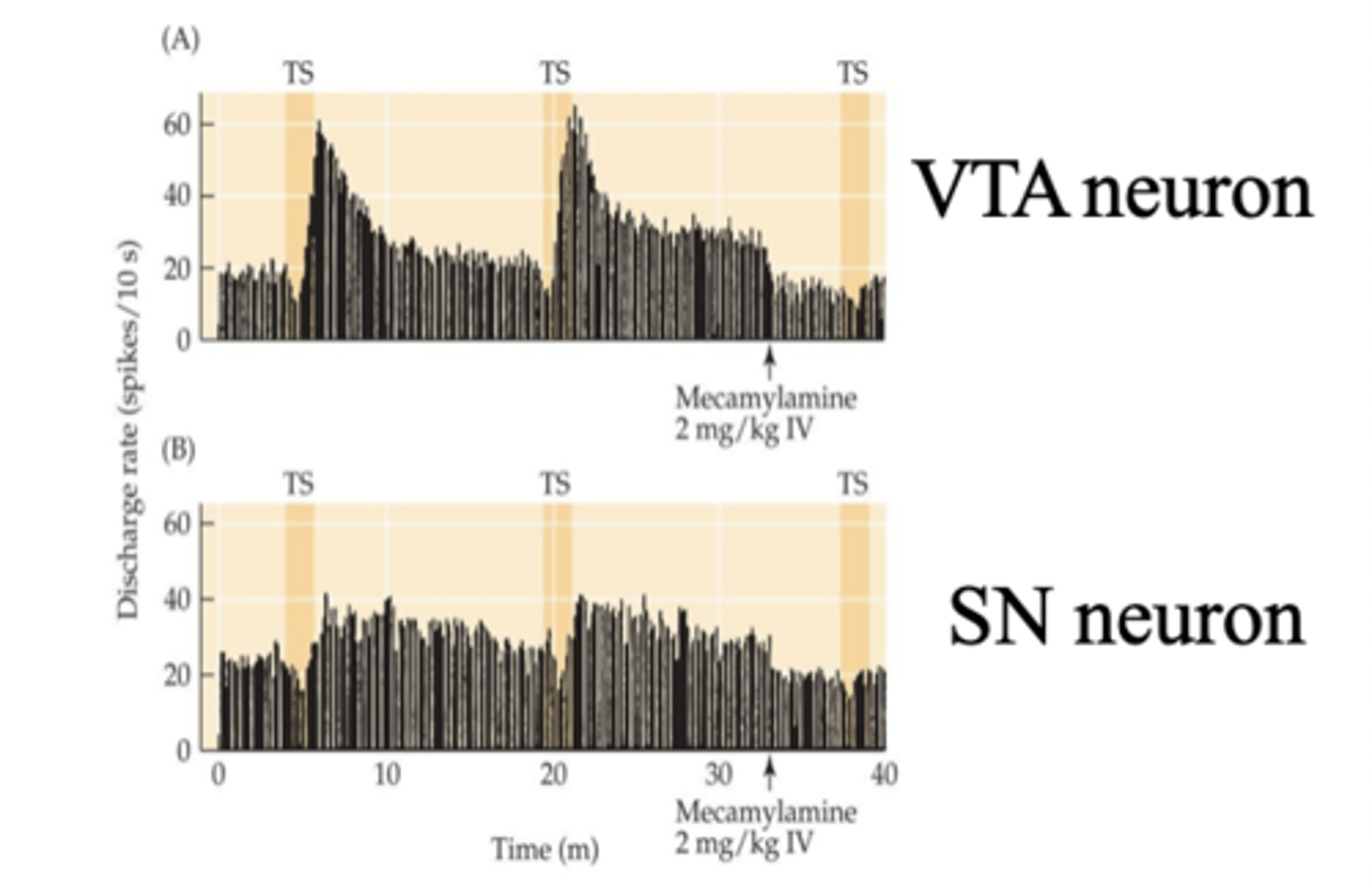
Rats inhaling tobacco smoke (TS):
- TS stimulates DA neurons
- Mecamylamine (nAChR antagonist) blocks effects of tobacco smoke
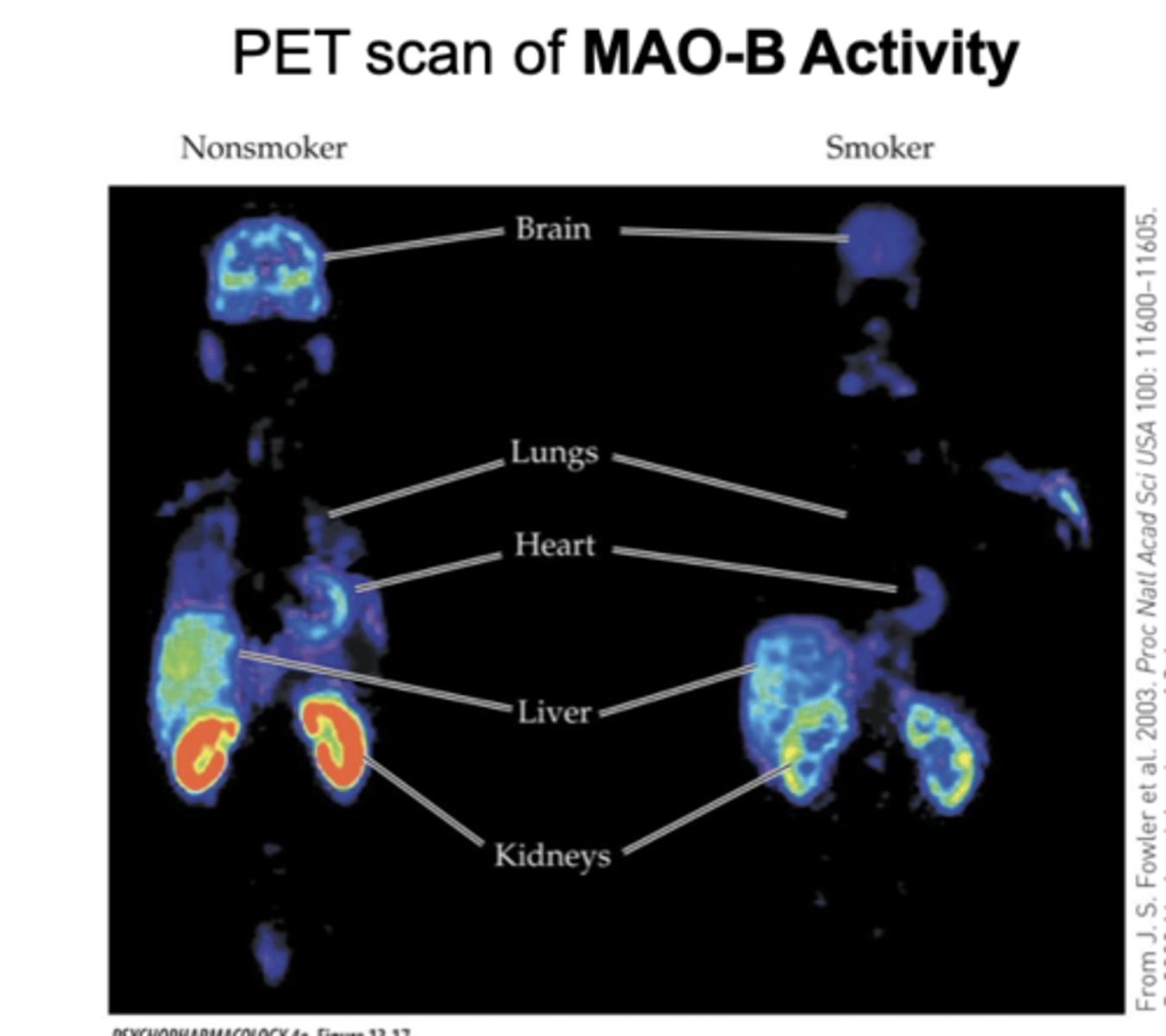
Tobacco smoke: contains other compounds that...
inhibit MAO-A and MAO-B in brain and other organs
Does MAO inhibition might contribute to reinforcing effects of smoking?
- inhibition in several organs
Nicotinic receptors are...
abundant in ANS (on autonomic ganglia) and adrenal medulla
- Smoking activates both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems and adrenal medulla
- Parasympathetic activation:
- most pronounced effects in stomach>>> increases HCL secretion and increased bowel contractility
- Sympathetic activation:
- Tachycardia, elevated blood pressure
- Adrenal medulla
- Catecholamine secretion
Accidental nicotine poisoning
- swallowing (involving children and packs of cigarettes)
- farmworkers in contact with tobacco in the field
- insecticides that contain nicotine
Accidental nicotine poisoning
nausea, excessive salivation, vomiting, diarrhea, mental confusion, cold sweat
- Untreated fatal dose: respiratory failure due to
depolarization block of diaphragm
Difficulties with nicotine self-administration—not resolved until 1981
- Nicotine on its own is reinforcing at the
right dose
- high doses are aversive because of side effects
- Self-admin is not as strong as opioids or psychomotor stimulants
- Reinforcement by smoking is more than
just the delivery of nicotine
Aversive effects of nicotine
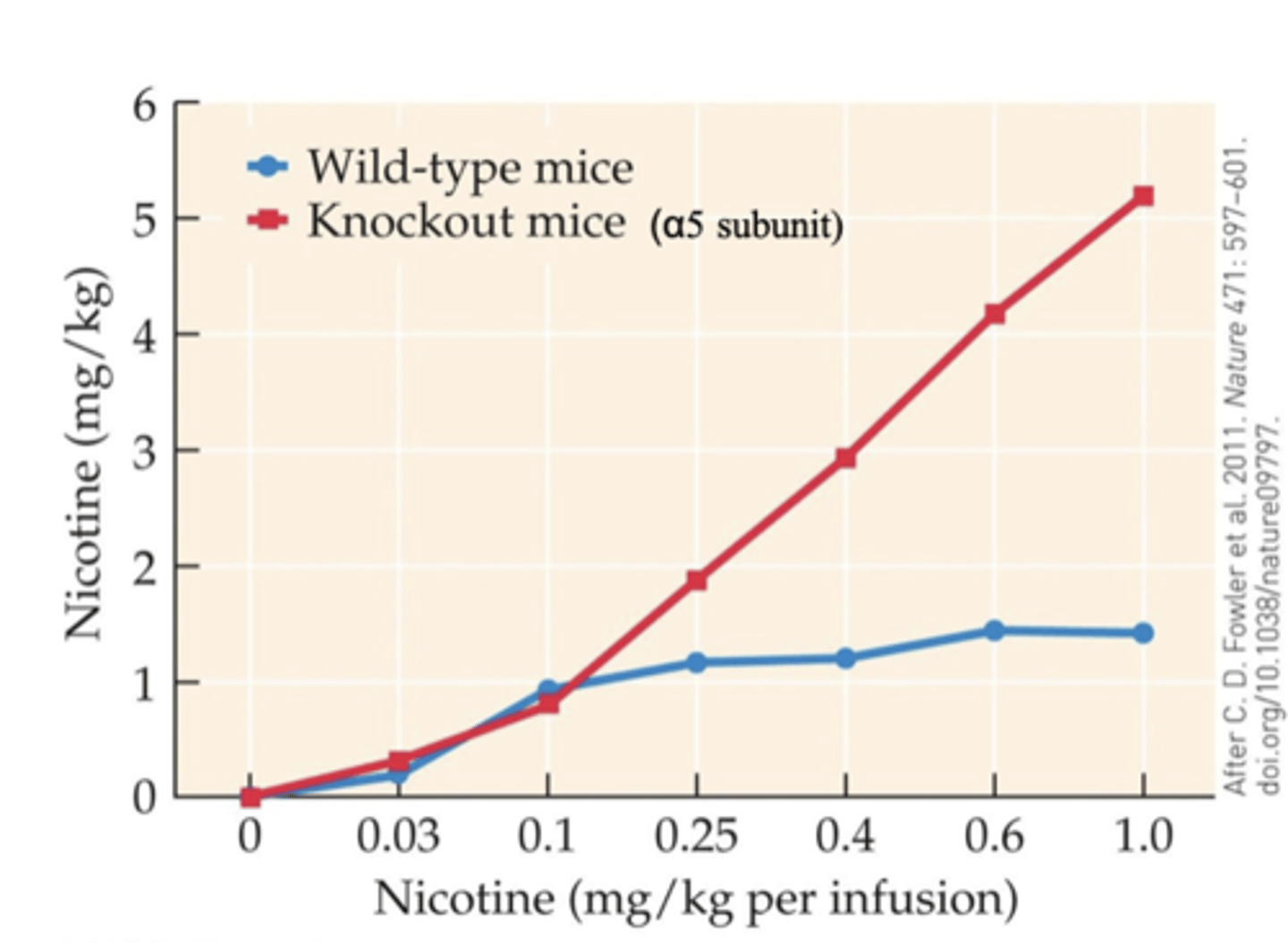
- mediated by α5-nAChR subunit
- α5-nAChRs are highly expressed in the interpeduncular nucleus, where they are activated by cholinergic input from the medial habenula
- KO mice administer successively greater amounts of nicotine as the dose per infusion increases
- WT mice plateau at a relatively low level of intake because of the aversive effects of nicotine at higher doses
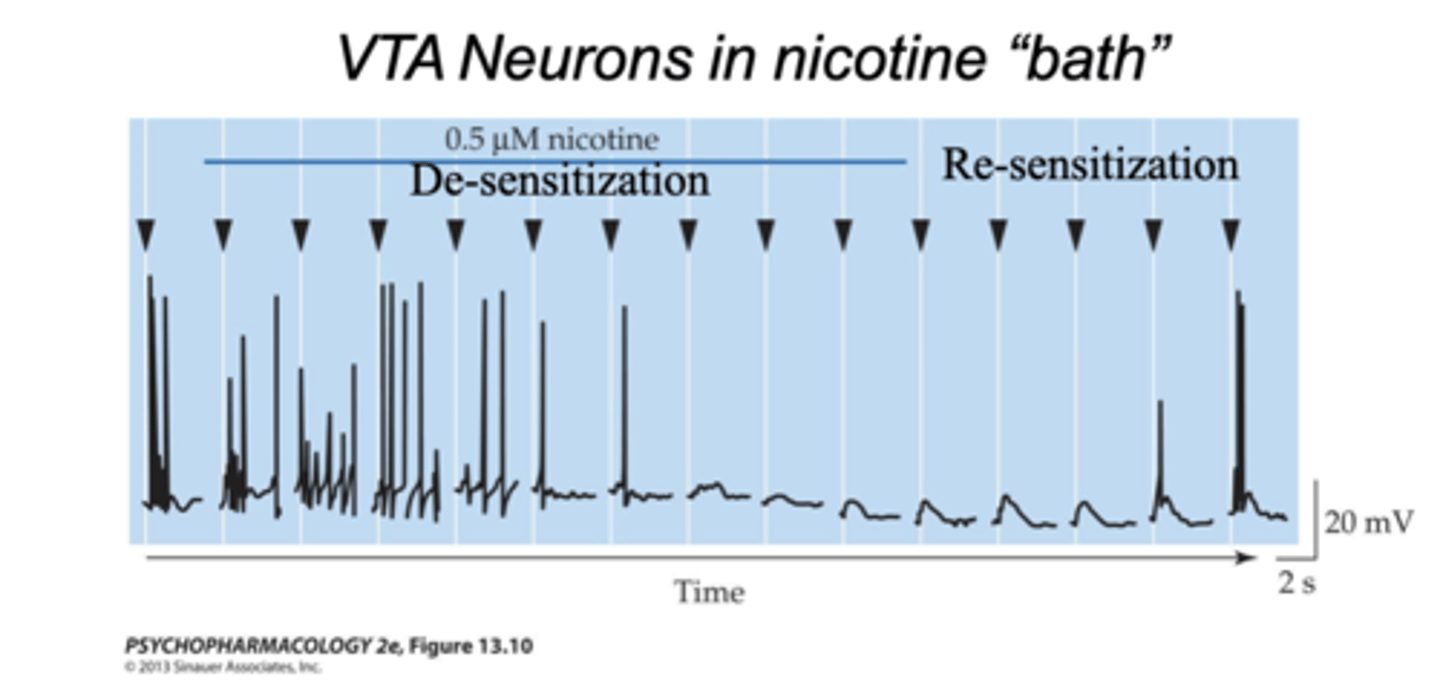
Acute tolerance to nicotine
- Cigarette smokers undergo acute tolerance over the
course of the day
- related to desensitization of nicotinic receptors
- Spikes induced by ACh application (arrowheads)
- Desensitization of DA neurons to continuous nicotine exposure
24-hour period
- a regular smoker undergoes repeated
elevations and drops in plasma nicotine levels
- Early in the day, mood may be elevated above baseline level
- later peaks in nicotine may be only enough to maintain neutral mood (avoid withdrawal symptoms)
what happen's to nAChRs overnight?
re-sensitize significantly overnight>>>allows cycle to repeat everyday
Tolerance and dependence in animals
•Withdrawal symptoms occur when the pump runs out of nicotine or if a nicotinic receptor antagonist (mecamylamine) is given
Brain reward function is...
reduced during
withdrawal from chronic nicotine
- increased threshold for ICSS
- Withdrawal symptoms are mediated by reduced DA activity in NAcc and increased CRF in amygdala
"wanting," "craving," and "needing": each successive stage being more powerful than the one before
- Wanting is mild, short-lived and easily ignored
- Craving is a desire to smoke that is more intense and compelling than wanting
- Wanting will go away if ignored, but craving is more
persistent.
- Needing to smoke when withdrawal symptoms are so troublesome that they cannot function normally
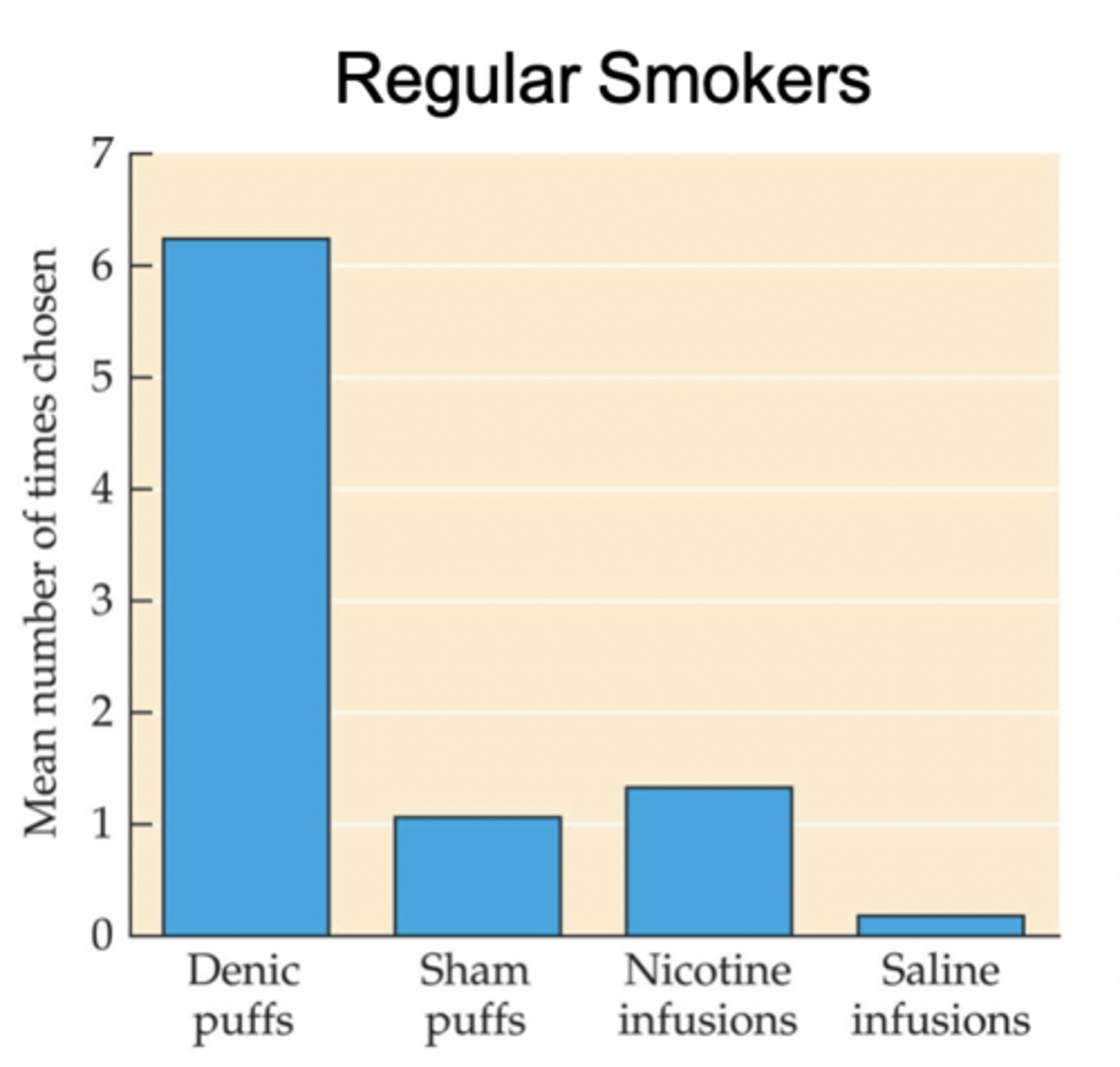
Cigarette Smoking and
Secondary Reinforcers
▪Sensory stimuli associated with the act of smoking become conditioned to the reinforcing effects of nicotine
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
- relieves withdrawal symptoms
- delivered in safer ways than smoking
- use of NRT (regardless of vehicle) increases the likelihood of quitting smoking by 50% to 60% compared to controls given either a placebo or no intervention
Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban): initially developed as an...
antidepressant
- a dopamine and NE reuptake inhibitor (NDRI)
- similar in structure to stimulants
- Reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms
Varenicline (Chantix)
- partial agonist of α4β2 nicotinic receptors
- produces a moderate amount of receptor activation
- reduces nicotine cravings and adverse withdrawal symptoms
- More effective than buproprion
Major source of caffeine is...
coffee beans>>>seeds of Coffea arabica
normally consumed...
- orally in beverages
- completely absorbed from the GI tract in 30 to 60 minutes
caffeine is converted to..
metabolites in the liver via
(CYP1A2)
- first to paraxanthine, a CNS stimulant
- Further breakdown of paraxanthine leads to metabolites that are mostly excreted in the urine
- 95% are eliminated through the urine
Average plasma half-life of caffeine is about
four hours (highly variable)
In laboratory animals...
biphasic effects
- low doses of caffeine >>>stimulant effects
- at high doses animals show reduced activity
Low doses in humans...
positive subjective effects
- feeling of well-being, increased energy, increased alertness, enhanced sociability
high doses in humans (>400mg)...
anxiogenic
- People with panic disorder are hypersensitive
to caffeine’s anxiogenic effects
Cognitive effects of caffeine
good, enhances cognitive performance
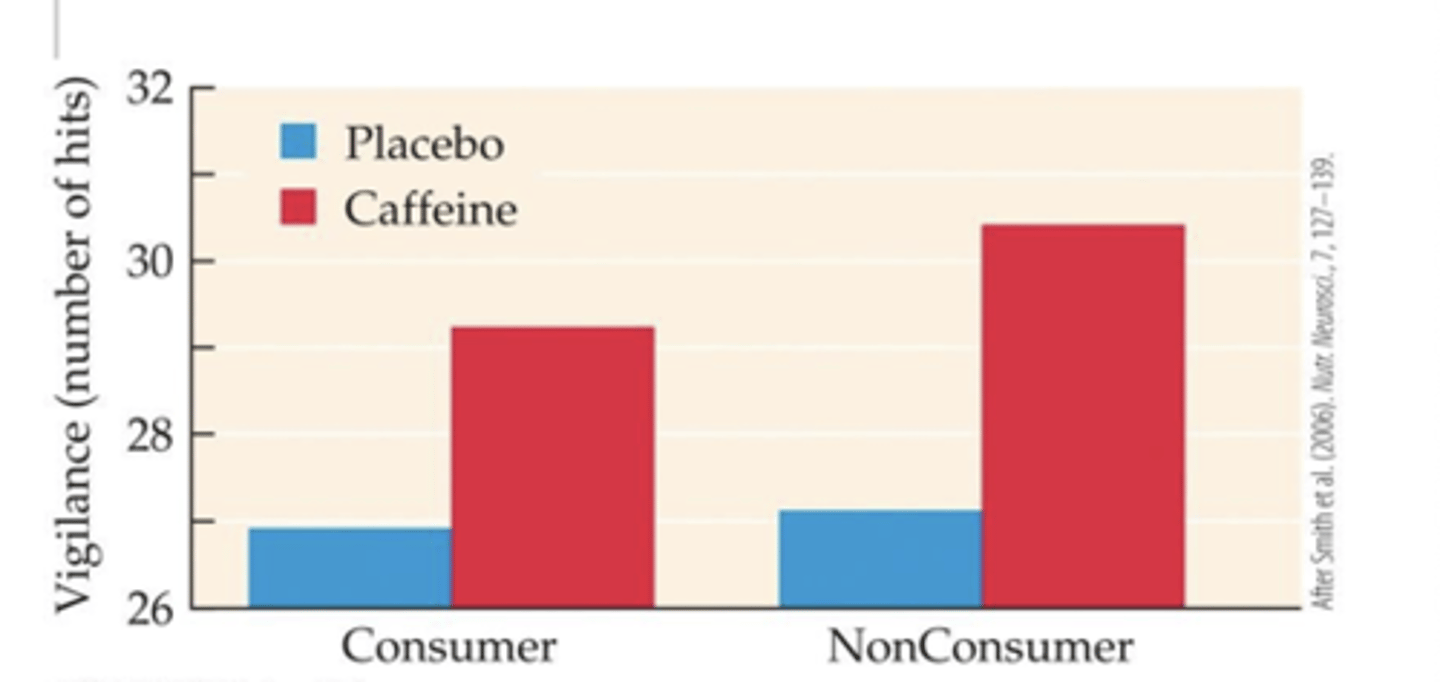
Autonomic effects caffeine
increased blood pressure and heart rate, and increased urine output
- Chronic caffeine use leads to tolerance
- Can produce a mild form of dependence
Caffeine Withdrawal
- sleepiness, headache, and irritability
- intense craving
- Relief from withdrawal>>>a major factor in chronic coffee drinking
Acute caffeine intake leads to several physiological effects
- increased blood pressure and respiration rate
- enhanced water excretion (diuresis)
- Most evident in non-regular caffeine drinkers
Consumption of high doses associated with two psychiatric disorders
- Caffeine intoxication – restlessness, nervousness, insomnia, tachycardia, muscle twitching, GI upset
- difficult to distinguish from a primary anxiety
disorder
- Extremely high doses (3 to 5 g or more) can
produce severe toxicity and even death
- Caffeine use disorder – 3 criteria: difficulty in reducing caffeine use, continued caffeine use despite knowledge of effects, and withdrawal symptoms upon abstinence
Therapeutic uses of caffeine
- potentiates analgesic properties of aspirin and
acetaminophen
- included in some OTC pain medications (Anacin and Excedrin)
- effective in treatment of apnea in premature newborns
- regularizes breathing
Epidemiological studies
3 to 5 cups of coffee/day reduces vulnerability to obesity, type 2 diabetes, liver cirrhosis, several kinds of cancer, Parkinson's disease and age-related dementia
- attributed mainly to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
substances in coffee
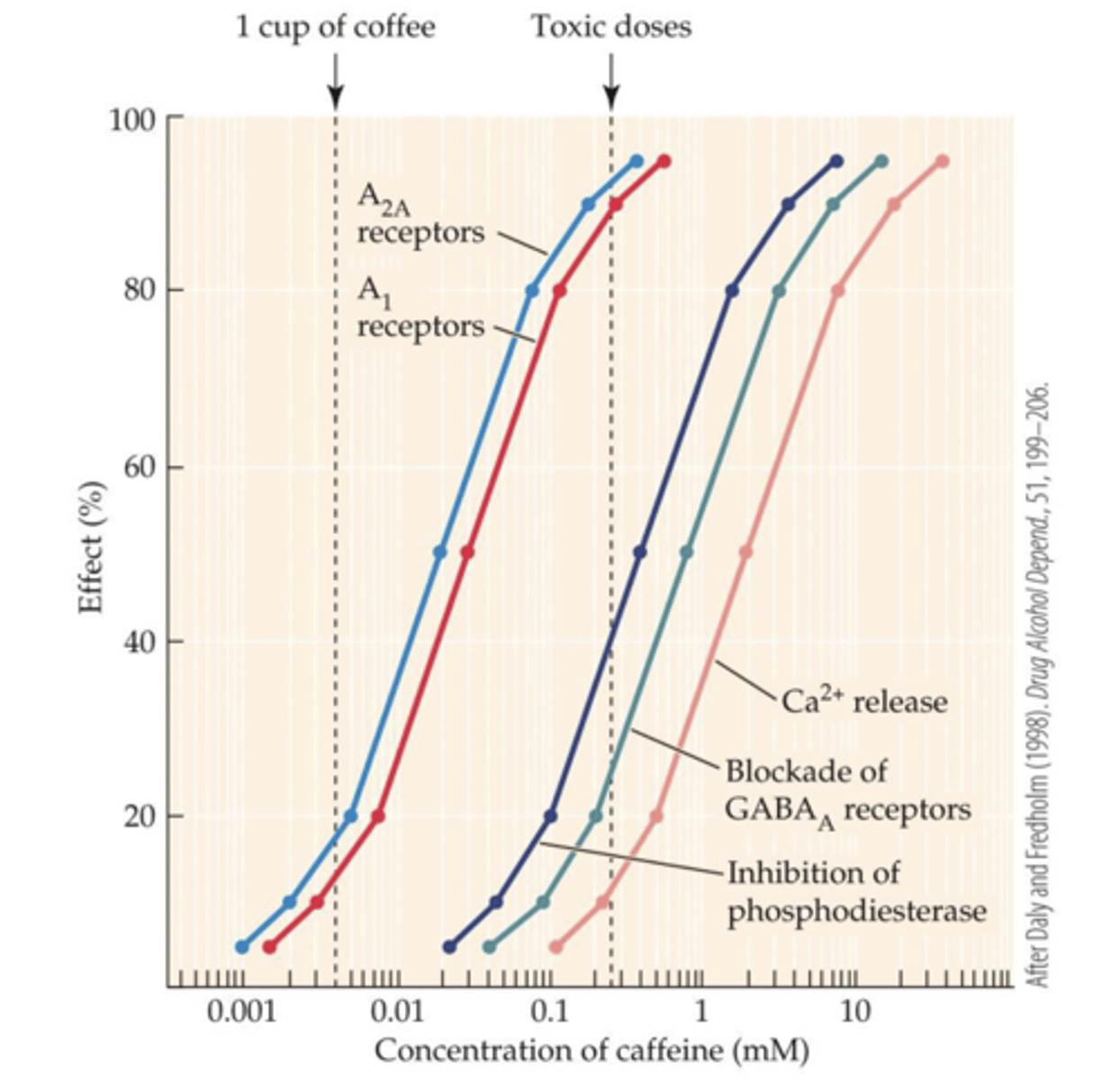
Caffeine’s biochemical effects
- Inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE)
- Blocks GABAA receptors
- Stimulates Ca2+ release within cells
- Blockade of A1 and A2A adenosine receptors
why does caffeine do at a physiological relevant dose?
- Dose-dependent inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase, blockade of GABAA receptors, stimulation of Ca2+ release in cells, and blockade of adenosine receptors
- only partial blockade of A1 and A2A adenosine receptors has effects that operate at doses found in a cup of coffee
Adenosine
- in the brain, has NT-like function
- a modulator in inducing drowsiness and sleep?
- stimulant properties of caffeine depend on antagonism of adenosine receptors in the brain, especially the striatum
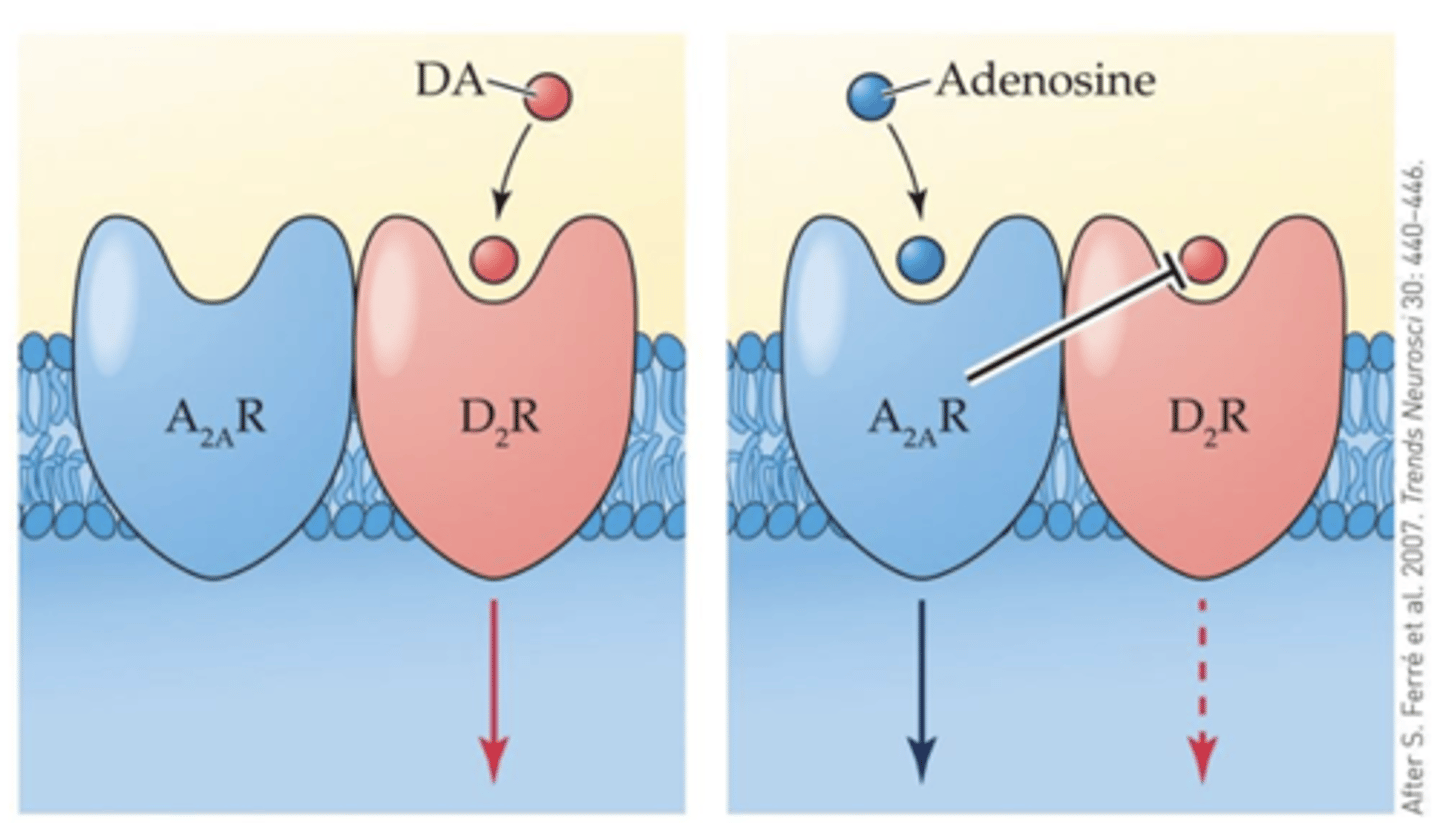
Caffeine and DA
Caffeine may remove the “brake” on DA signaling that is normally mediated by adenosine
Striatum expresses high levels of A2AR
- co-expressed with postsynaptic
D2 receptors (D2R)>>>form A2AR-D2R hetero-tetramers
- adenosine allosterically inhibits D2R signaling (NAM)
- In striatal neurons, A2AR agonists decrease D2R agonist binding>>decrease affinity of DA for its receptor
- caffeine-induced increases in locomotor activity and arousal are absent in A2AR KO mice
Caffeine enhances...
DA signaling in the striatum by antagonizing A2A receptors
Kratom
•(Mitragyna speciosa) : a tree in the coffee family found in Thailand and neighboring countries
- two main chemical components: mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine (7- OH-mitragynine)
- leaves are steeped into a tea or chewed
- At low doses (chewing leaves), kratom acts as a stimulant
- At higher doses (concentrated paste), has a sedative or narcotic effect
- often used to self-treat conditions such as pain, coughing, diarrhea, anxiety and depression, opioid use disorder, and opioid withdrawal
why is kratom known as Nature's atypical opiods
- active ingredients bind to mu-opioid receptors
- structures of mitragynine do not resemble a typical opioid like morphine
- Mitragynine and/or 7-OH-mitragynine have additional mechanisms of action on other NTs, including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and kappa opioid receptors
- Kratom is not scheduled under the Controlled Substances Act
- There are some state regulations or prohibitions against the possession and use of kratom
- DEA has listed kratom as a Drug and Chemical
of Concern
- Not listed in DSM-V